Response of Substorm Onset Location and Expansion Phase Duration to Interplanetary Magnetic Field Bz
-
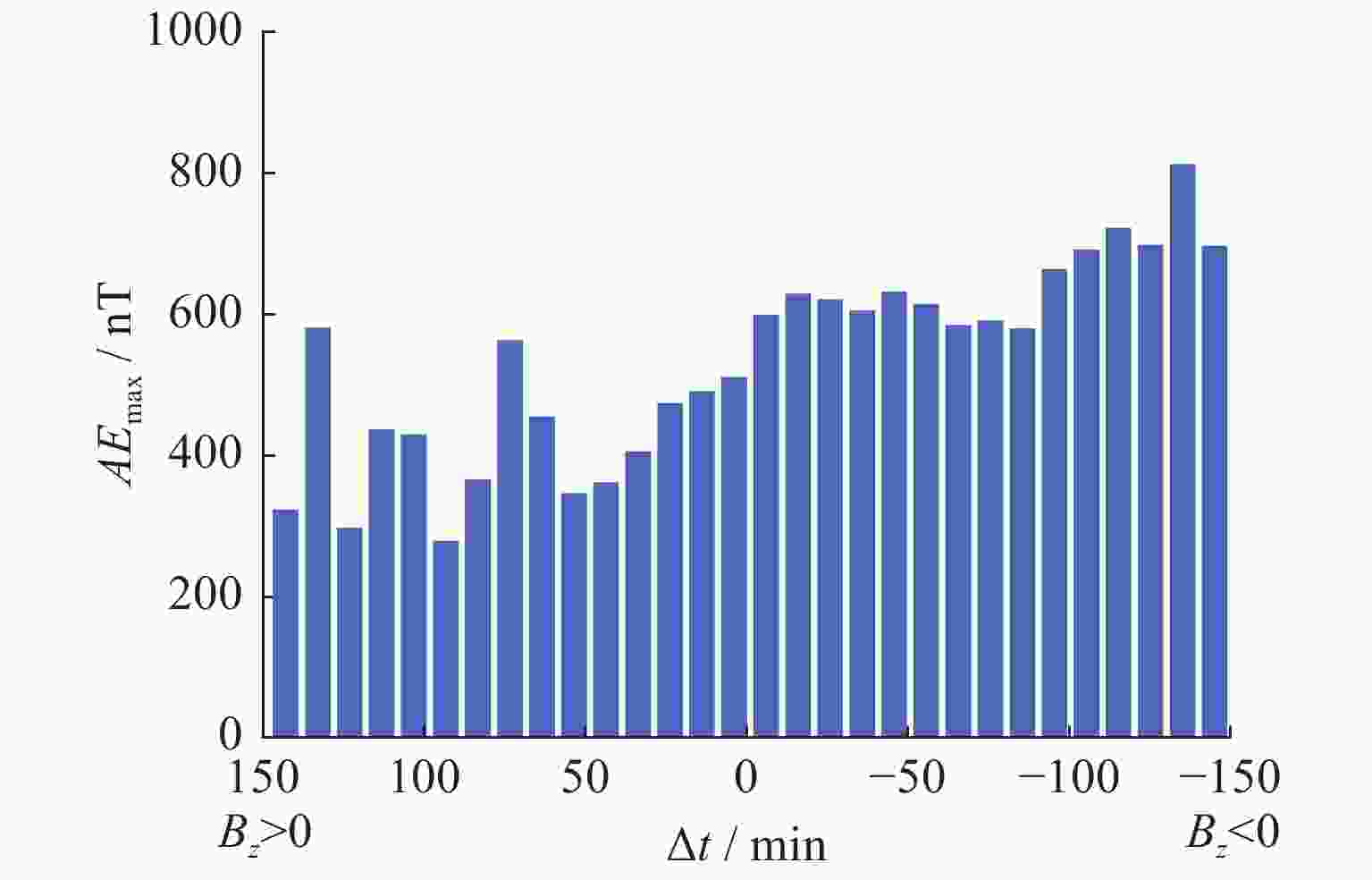
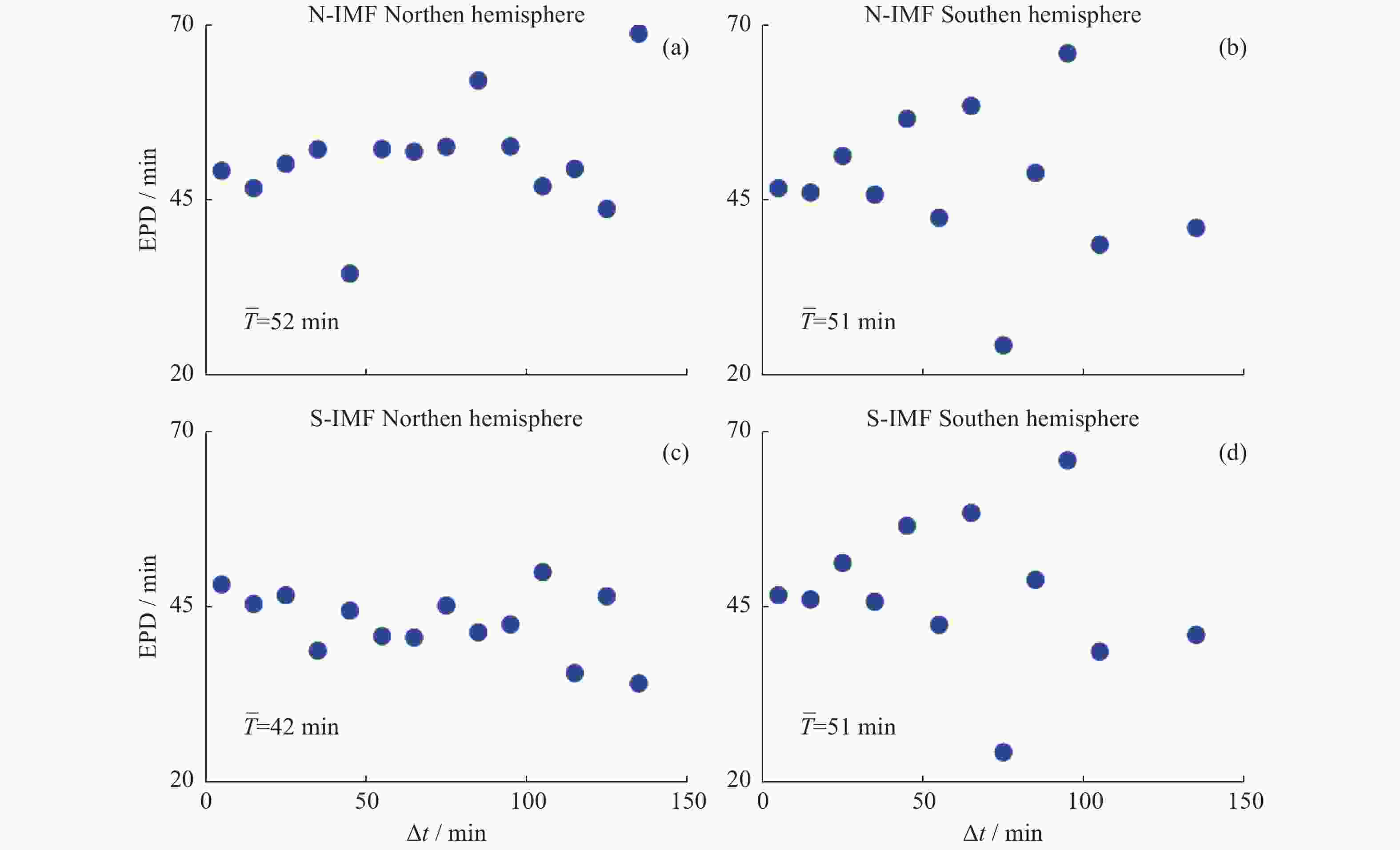
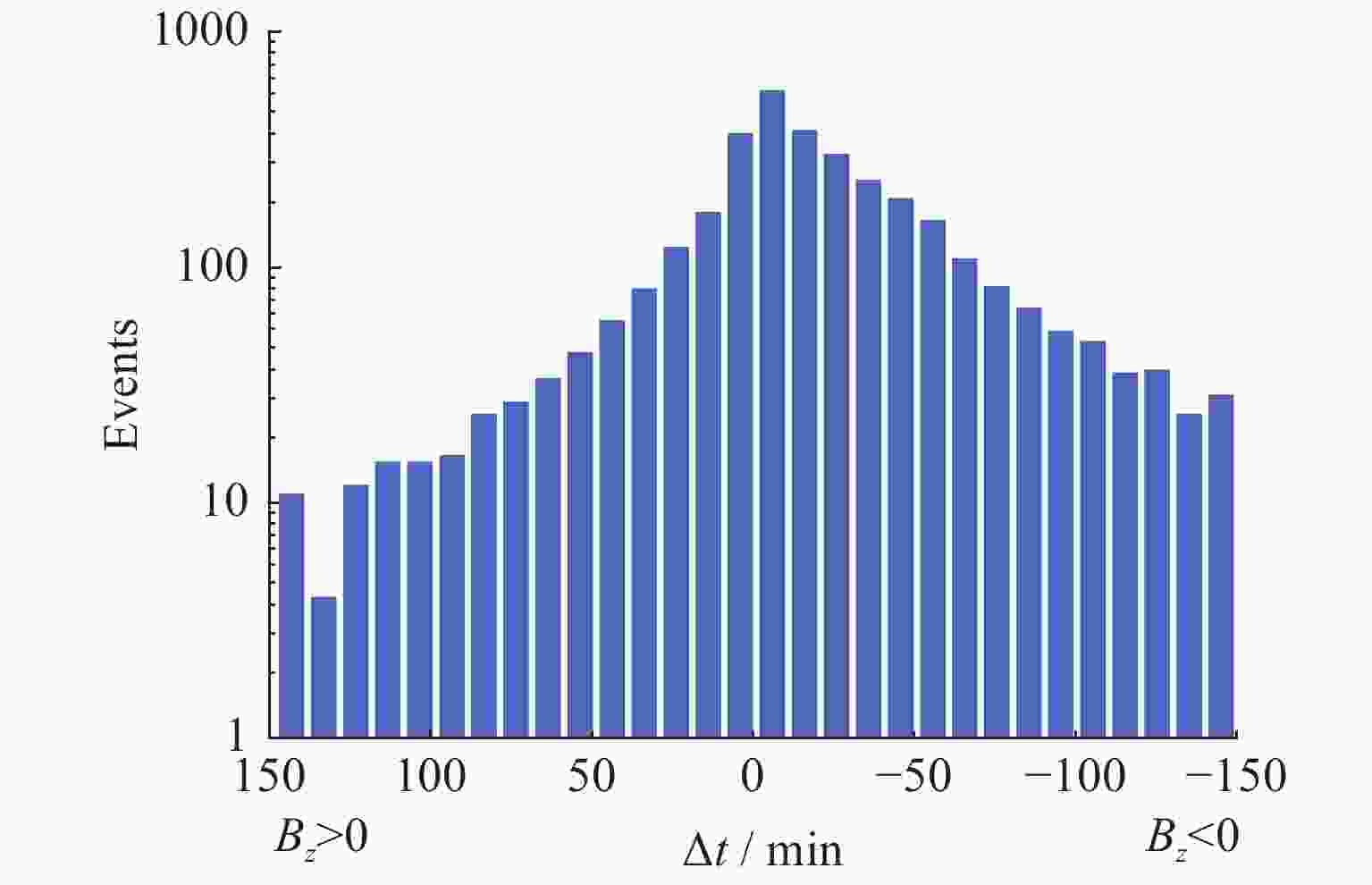
摘要: 磁层亚暴是太阳风–磁层–电离层耦合过程中的重要爆发性事件,其特性受太阳风参数的影响很大。本文利用对IMAGE卫星在2000 - 2005年观测到的4193个亚暴起始事件,统计研究了在不同的行星际磁场(IMF)Bz 条件下亚暴起始位置和膨胀相持续时间。结果表明,南向IMF发生的亚暴比北向IMF下发生的亚暴要多。南向IMF条件下亚暴AE指数最大值的平均值基本上>600 nT,并有随南向IMF持续时间增大而增大的趋势。北向IMF条件下亚暴AE指数最大值的平均值基本上<500 nT,并有随北向IMF持续时间增大而减小的趋势。亚暴的起始磁纬度基本上位于65° - 70°之间。当南向IMF或北向IMF的持续时间增大,超过80 min时,北半球的亚暴起始磁纬度会降低。亚暴起始磁地方时大部分位于22:15 - 23:15 MLT之间。但整体分布比较分散,显示不出特别清晰的随IMF Bz持续时间变化的趋势。相比于南向的IMF,北向IMF期间发生亚暴的平均膨胀相持续时间增大了将近10 min,表明南向IMF期间,亚暴强度虽然较大,但其膨胀相持续时间较短,亚暴能量释放和耗散的速度更快。Abstract: A magnetospheric substorm is a significant process in solar wind-magnetosphere- ionosphere coupling. Substorm onset locations have a great dependence of solar wind parameters. Based on 4193 auroral breakup events identified by Frey et al. from about 5 years IMAGE FUV data, we statistically study the distribution of substorm onset locations and substorm expansion duration time under different Interplanetary Magnetic Field (IMF) conditions in southern and northern hemispheres. It is found that the occurrence rate of a substorm is relatively bigger under southward IMF than northward IMF. The maximum value of substorm AE index is above 600 nT under southward IMF, and increases with the evolution of southward IMF lasting time. While the maximum value of substorm AE index is beneath 500 nT under northward IMF, and decreases with the evolution of northward IMF lasting time. The substorm onset magnetic latitude is around 65°-70°. With the lasting time of northward/southward IMF exceeding 80 minutes, the substorm onset magnetic latitude in the northern hemisphere lower with the evolution of IMF lasting time. The substorm onset is around 22:15-23:15 MLT. It’s irregular under different IMF lasting time. The average expansion time of substorm is about 10 minutes larger under northward IMF than southward IMF. It indicates that the speed of substorm energy release and dissipation is faster under southward IMF with intense substorms.
-
Key words:
- Substorm onset /
- Magnetic local time /
- Magnetic latitude /
- Expansion duration time
-
表 1 不同延迟时间情况下北半球和南半球亚暴起始磁纬度与南向/北向IMF持续时间的相关系数
Table 1. Correlation coefficient of substorm onset magnetic latitude in southern/northern hemisphere and southward/northward IMF duration under different shifted time
Shifted time/min Northward IMF Southward IMF Northern hemisphere Southern hemisphere Northern hemisphere Southern hemisphere 25 –0.53 0.14 –0.77 0.37 30 –0.45 0.07 –0.62 0.42 35 –0.64 –0.11 –0.81 –0.05 40 –0.58 –0.14 –0.68 0.24 45 –0.04 0.28 –0.81 0.03 50 –0.08 0.34 –0.62 0.21 55 0.13 0.34 –0.71 0.01 Average –0.37 0.19 –0.72 0.18 -
[1] AXFORD I W. Magnetospheric convection[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1969, 7 (1/2). DOI: 10.1029/rg007i001p00421 [2] LI H, WANG C, PENG Z, et al. Solar wind impacts on growth phase duration and substorm intensity: a statistical approach[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Space Physics, 2013, 118 doi: 10.1002/jgra.50399 [3] VORONKOV O I. Observations of the phases of the substorm[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(A2). DOI: 10.1029/2002 JA009314 [4] PARTAMIES N, JUUSOLA L, TANSKANEN E, et al. Statistical properties of substorms during different storm and solar cycle phases[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2013, 31(2): 349-358 doi: 10.5194/angeo-31-349-2013 [5] MCPHERRON R L. Growth phase of magnetospheric substorms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1970, 75(28). DOI: 10.1029/JA075 i028 p05592 [6] MCPHERRON R L, RUSSELL C T, AUBRY M P. Satellite studies of magnetospheric substorms on August 15, 1968: 1. State of the magnetosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1973, 78(16): 3044-3053 doi: 10.1029/ja078i016p03131 [7] LIOU K, NEWELL P T, SIBECK D G, et al. Observation of IMF and seasonal effects in the location of auroral substorm onset[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Space Physics, 2001, 106(A4): 5799 doi: 10.1029/2000JA003001 [8] FREY H U, MENDE S B, ANGELOPOULOS V. Substorm onset observations by IMAGE-FUV[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Space Physics, 2004. DOI: 10.1029/2004JA010607 [9] NISHIMURA Y, LYONS L, ZOU S, et al. Substorm triggering by new plasma intrusion: THEMIS all-sky imager observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Space Physics, 2010. DOI: 10.1029/2009 ja015166 [10] NEWELL P T, GJERLOEV J W. Evaluation of SuperMAG auroral electrojet indices as indicators of substorms and auroral power[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Space Physics, 2011, 116(A12). DOI: 10.1029/2011JA016779 [11] CRAVEN J D, FRANK L A. Diagnosis of auroral dynamics using global auroral imaging with emphasis on large-scale evolutions [R]. Iowa: Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa University, 1989 [12] ØSTGAARD N. Interplanetary magnetic field control of the location of substorm onset and auroral features in the conjugate hemispheres[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2004, 109(A7). DOI: 10.1029/2003 JA010370 [13] WANG H, LUEHR H, MA S Y, et al. Interhemispheric comparison of average substorm onset locations: evidence for deviation from conjugacy[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2007, 25(4). DOI: 10.5194/angeo-25-989-2007 [14] ØSTGAARD N, TSYGANENKO N A, MENDE S B, et al. Observations and model predictions of substorm auroral asymmetries in the conjugate hemispheres[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(5): 347-354 doi: 10.1029/2004gl022166 [15] ØSTGAARD N, MENDE S B, FREY H U, et al. Auroral conjugacy studies based on global imaging[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2007, 69(3): 249-255 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2006.05.026 [16] Liou K, Newell P T. On the azimuthal location of auroral breakup: Hemispheric asymmetry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37(23): 817-824 doi: 10.1029/2010GL045537 [17] ØSTGAARD N, LAUNDAL K M, JUUSOLA L, et al. Interhemispherical asymmetry of substorm onset locations and the interplanetary magnetic field[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38 (8). DOI: 10.1029/2011 GL046767 [18] FREY H U, MENDE S B. Substorm onsets as observed by IMAGE-FUV[C]//The 8 th International Conference on Substorms. Calgary: University of Calgary, 2006: 71-76 [19] MENG C I, TSURUTANI B, KAWASAKI K, et al. Cross-correlation analysis of the AE index and the interplanetary magnetic field Bz component[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 1973, 78(4): 617-629 doi: 10.1029/JA078i004p00617 [20] Arnoldy R L. Signature in the interplanetary medium for substorms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1971, 76(22): 5189-5201 doi: 10.1029/JA076i022p05189 [21] ROSTOKER G, LAM H L, HUME W D. Response Time of the Magnetosphere to the Interplanetary Electric Field[J]. Canadian Journal of Physics, 1972, 50(6): 544-547 doi: 10.1139/p72-073 [22] NISHIDA A. Interplanetary origin of electric fields in the magnetosphere[J]. Cosmic Electrodynamics, 1971, 2: 350-74 [23] AKASOFU S I, PERREAULT P D, YASUHARA F, et al. Auroral substorms and the interplanetary magnetic field[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1973, 78(31): 7490-7508 doi: 10.1029/JA078i031p07490 [24] PETRUKOVICH A A, BAUMJOHANN W, NAKAMURA R, et al. Small substorms: Solar wind input and magnetotail dynamics[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Space Physics, 2000, 105(A9): 21109-21117 doi: 10.1029/2000ja900057 [25] LUI A T Y, AKASOFU S I, HONES E W, et al. Observation of the plasma sheet during a contracted oval substorm in a prolonged quiet period[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1976, 81(7): 1415-1419 doi: 10.1029/JA081i007p01415 [26] KAMIDE Y, PERREAULT P D, AKASOFU S I, et al. Dependence of substorm occurrence probability on the interplanetary magnetic field and on the size of the auroral oval[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1977, 82(35): 5521-5528 doi: 10.1029/JA082i035p05521 [27] BAKER D N, PULKKINEN T I, ANGELOPOULOS V, et al. Neutral line model of substorms: Past results and present view[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Space Physics, 1996, 101(A6): 12975-13010 doi: 10.1029/95JA03753 -
-





 下载:
下载: