基于因果卷积与LSTM网络的电离层总电子含量预报
doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210401042 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2022.03.210401042
Prediction of Ionospheric Total Electron Content Based on Causal Convolutional and LSTM Network
-
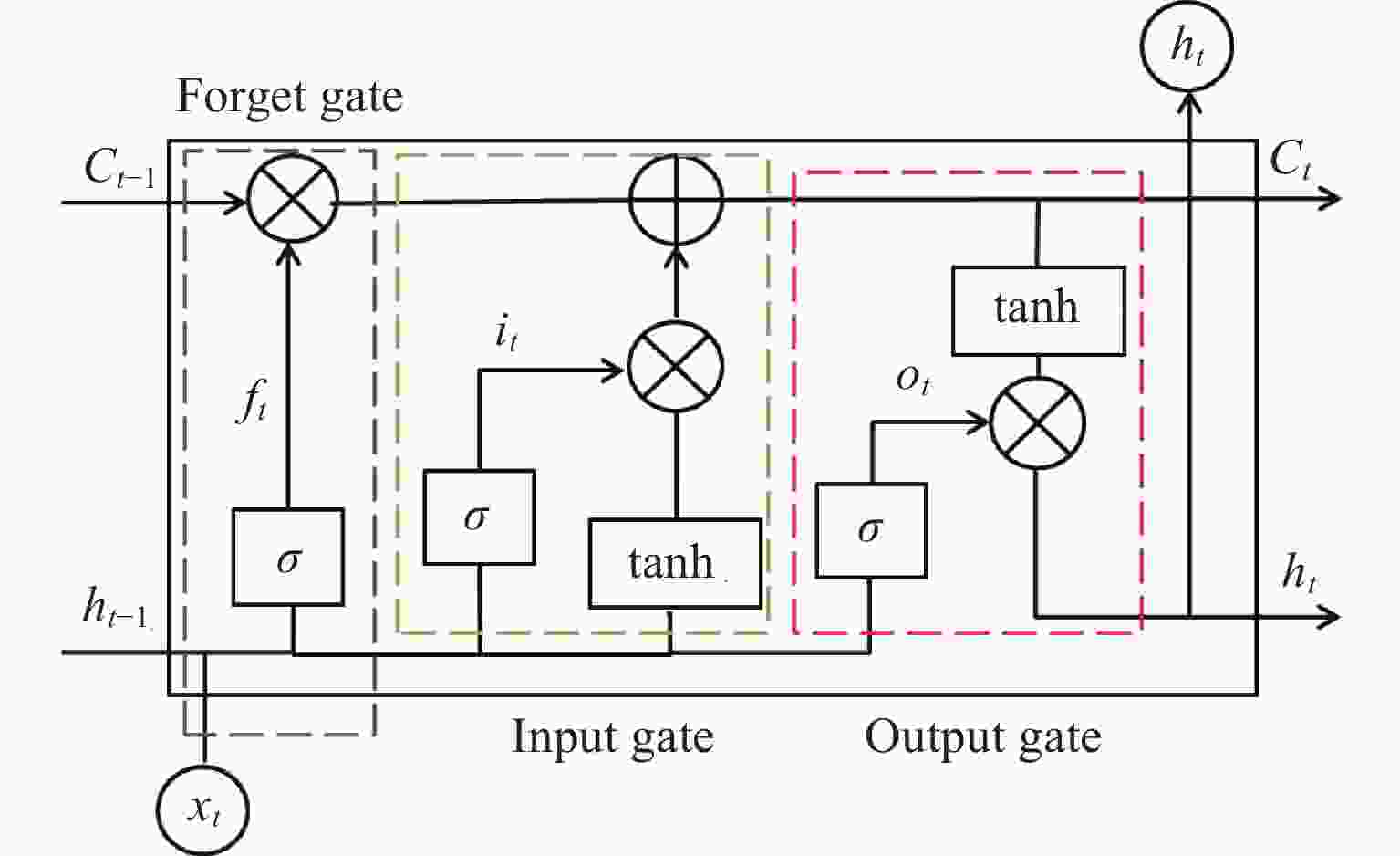
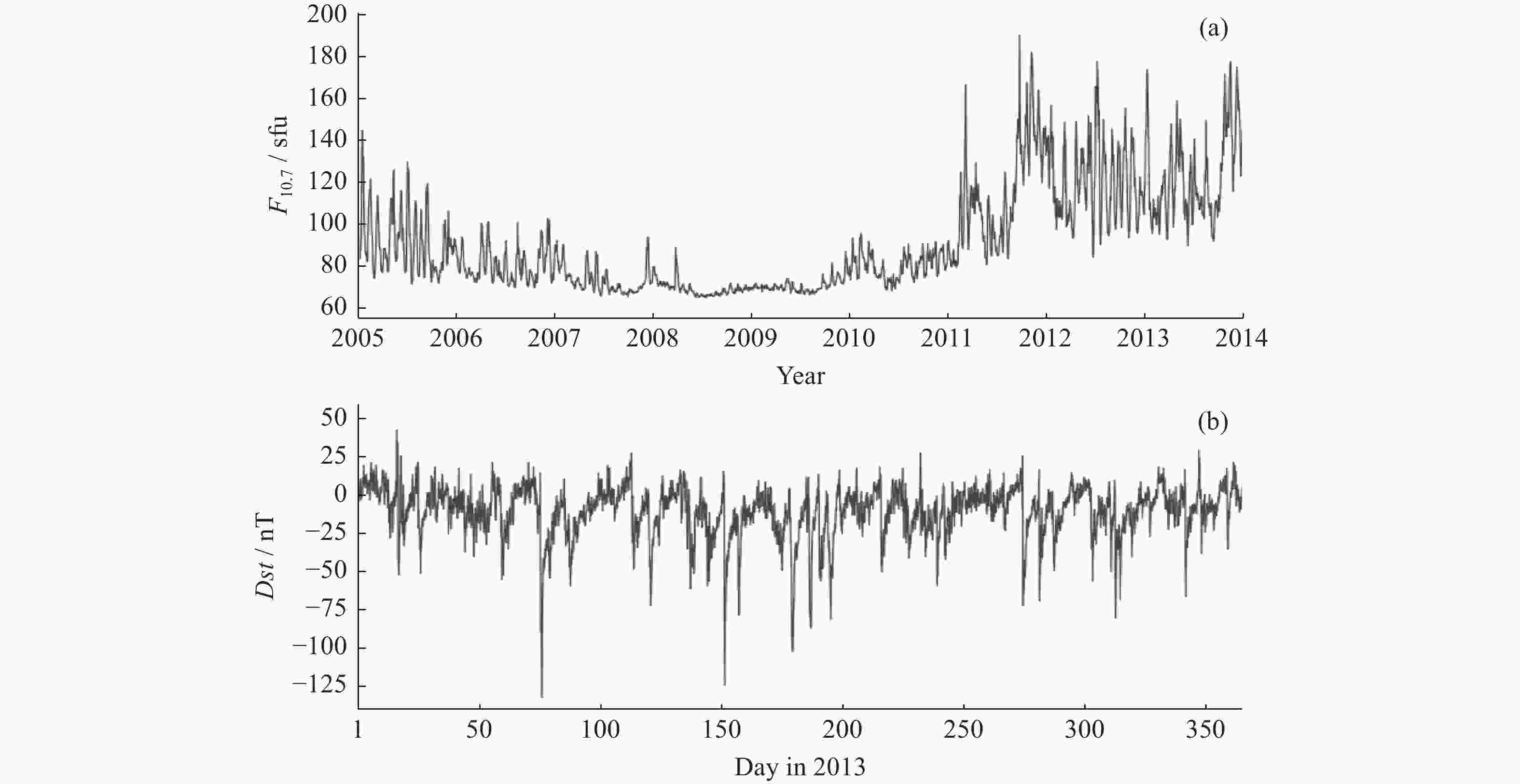
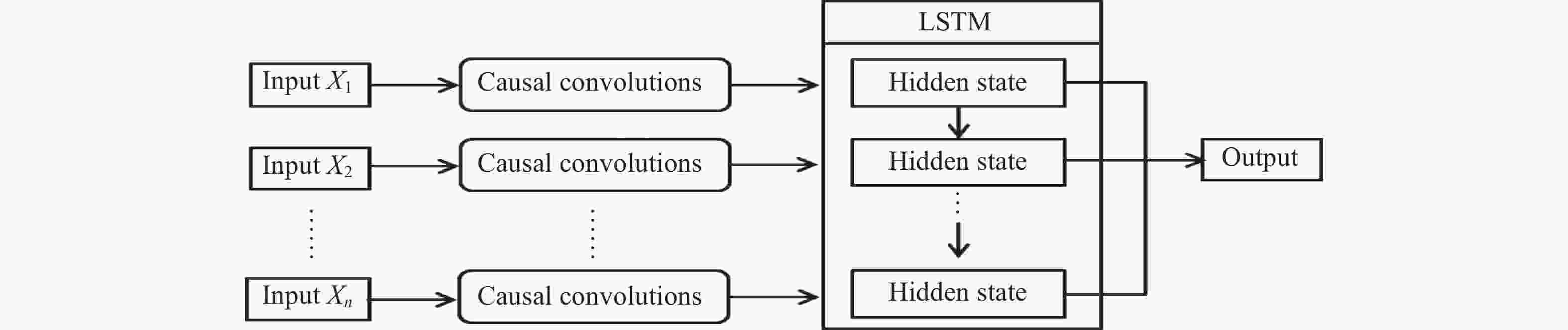
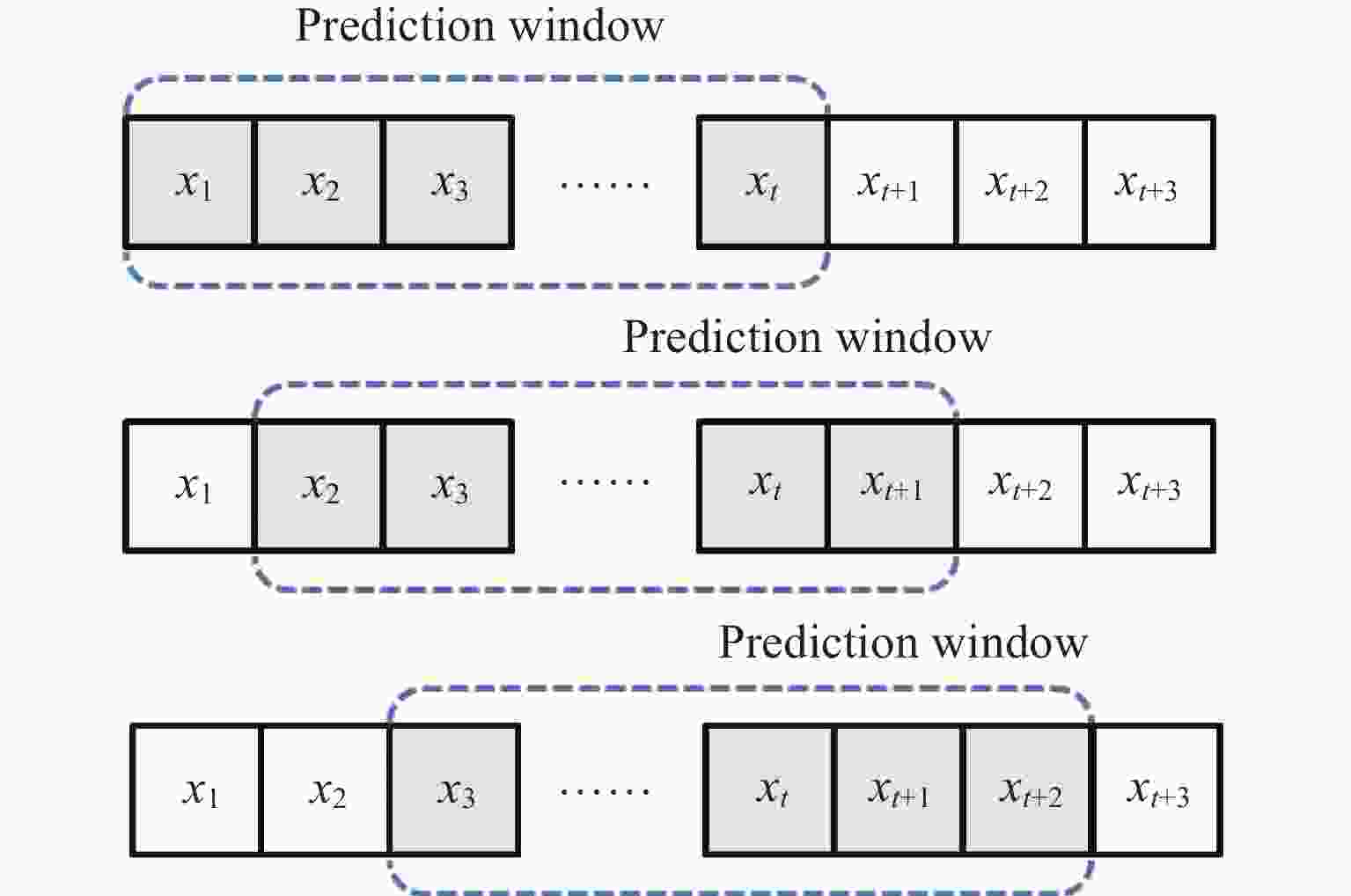
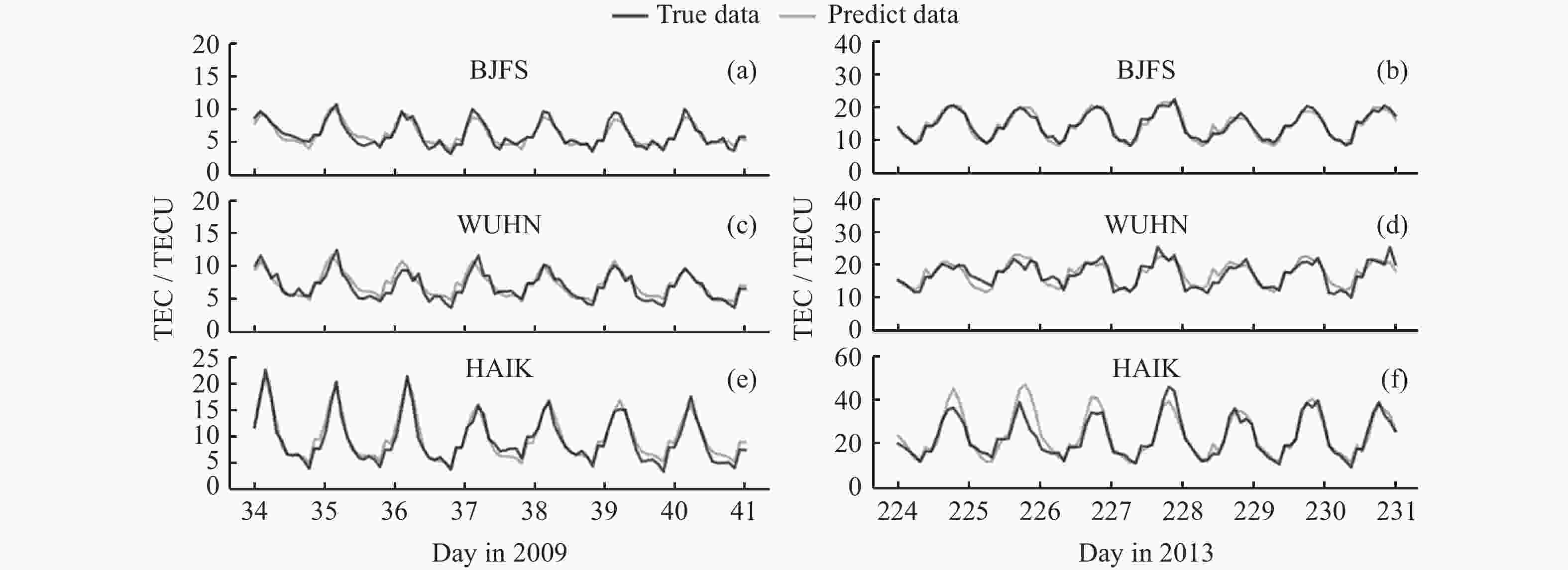
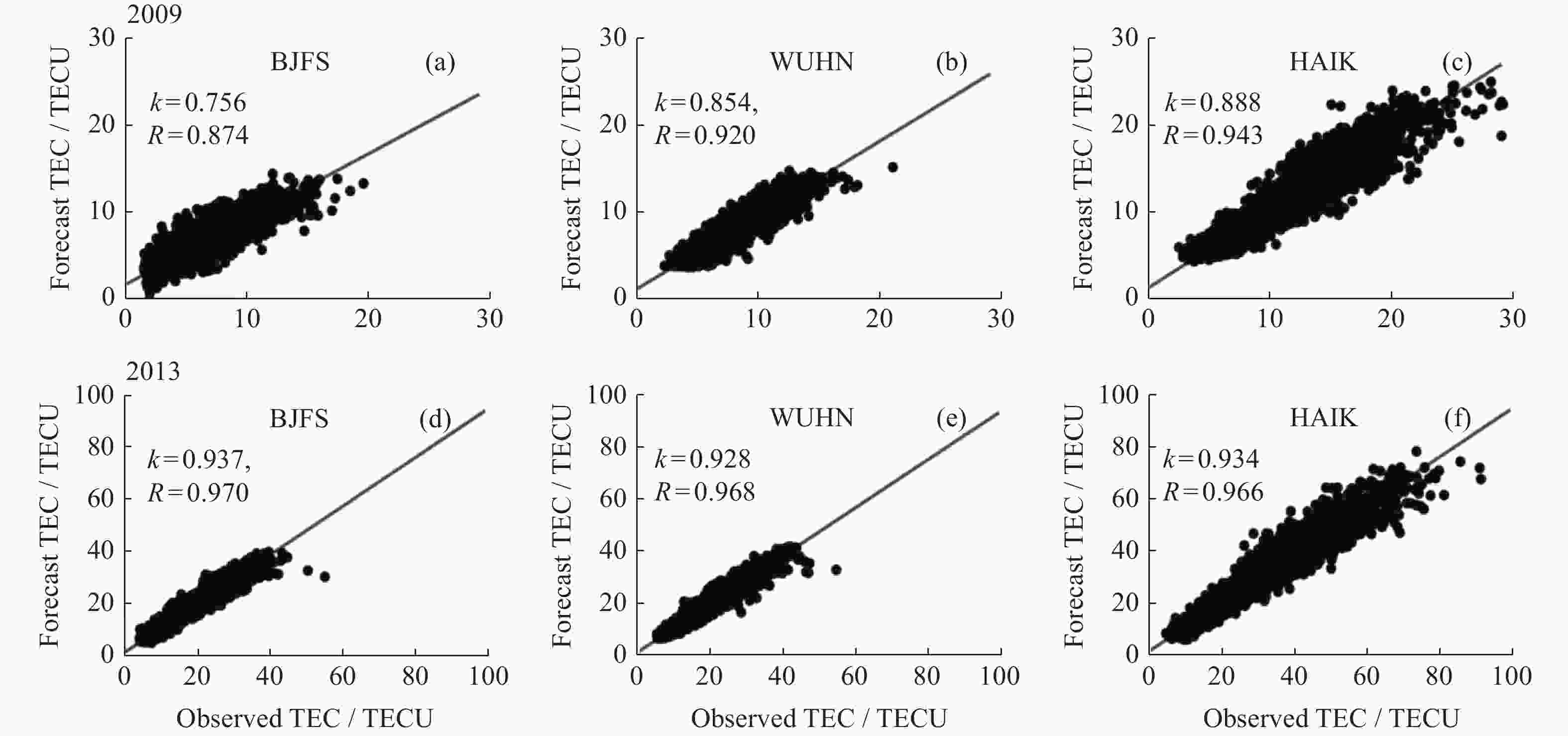
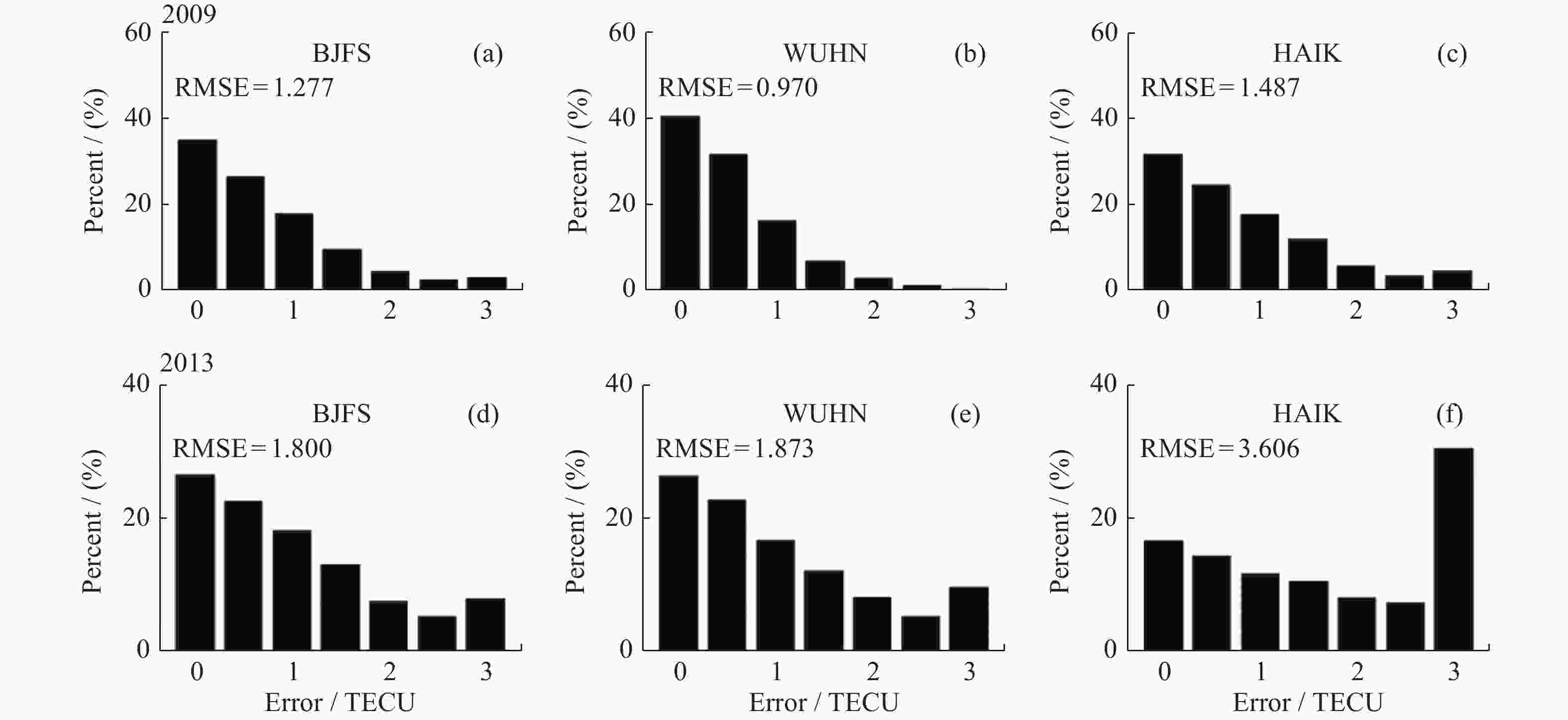
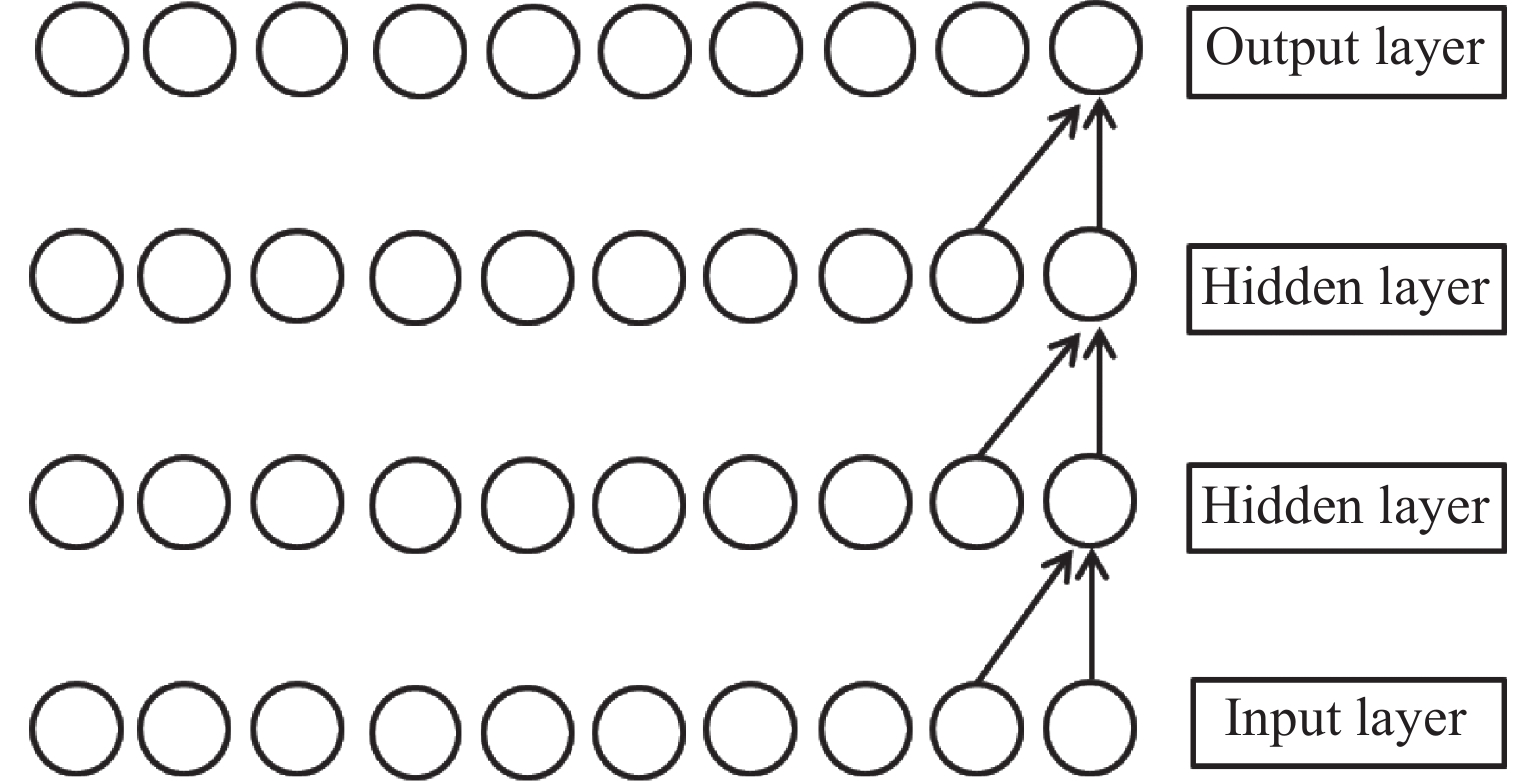
摘要: 电离层总电子含量(TEC)不仅是分析电离层形态的关键参数之一,同时为导航及定位等空间应用系统消除电离层附加时延提供重要支撑。由于电离层TEC的时空变化特征,本文融合因果卷积和长短时记忆网络,以太阳活动指数F10.7、地磁活动指数Dst和电离层TEC历史数据作为特征输入,构建深度学习模型,实现提前24 h预报电离层TEC。进一步利用2005-2013年连续9年的CODE TEC数据,全面评估了模型在北京站(40°N,115°E)、武汉站(30.53°N,114.36°E)和海口站(20.02°N,110.38°E)的预报性能。结果显示不同太阳活动条件下三个站的TEC值与真实测量值的相关系数都大于0.87,均方根误差大都集中在0~1 TECU以内,且模型预报精度与纬度、太阳、地磁活动程度、季节变化相关。与仅由长短时记忆网络构成的预报模型相比,本实验模型均方根误差降低了15%,为电离层TEC预报模型的实际应用提供了参考。Abstract: The Total Electron Content (TEC) of the ionosphere is not only one of the key parameters to analyze the shape of the ionosphere, but also provides an important support for the navigation, positioning and other space applications to eliminate the additional ionospheric delay. Due to the temporal and spatial variation characteristics of ionospheric TEC, an ionospheric TEC hybrid deep learning model based on Causal convolution and Long Short-Term Memory network is proposed in this paper. The solar activity index F10.7, the geomagnetic activity index Dst and the historical ionospheric TEC data are used as feature inputs to predict the TEC 24 hours in advance. Using CODE TEC data covering the low and high solar activities during 2005-2013, the performance of the model is comprehensively evaluated at Beijing station (40°N, 115°E), Wuhan station (30.53°N, 114.36°E) and Haikou station (20.02°N, 110.38°E). The results show the correlation coefficients between the predicted TEC values of the three stations and the actual values under different solar activity conditions are greater than 0.87, and most root mean square errors concentrated within 1 TECU. The prediction accuracy of the model is related to latitude, solar activity, geomagnetic activity and seasonal variation. Compared with the prediction model composed of LSTM network, the root mean square error of the proposed model is reduced by 15%, which provides a valuable reference for the practical application of the ionospheric TEC prediction.
-
Key words:
- TEC /
- Forecast /
- Causal convolution /
- LSTM
-
表 1 GPS观测站位置
Table 1. Location of GPS stations
站点 纬度/(°)N 经度/(°)E 北京站(BJFS) 39.61 115.89 武汉站(WUHN) 30.53 114.36 海口站(HAIK) 20.02 110.38 表 2 2009年和2013年不同站点在不同季节的预报误差RMSE(TECU)
Table 2. Forecast RMSEs at different stations in different seasons in 2009 and 2013
站名 年份 春季 夏季 秋季 冬季 北京 2009 0.92 2.0 1.63 1.31 2013 1.95 3.30 1.74 1.80 武汉 2009 0.96 1.76 1.04 0.95 2013 1.75 2.24 1.87 2.67 海口 2009 1.57 2.95 1.50 1.54 2013 3.73 3.71 3.52 5.00 表 3 混合神经网络模型与LSTM预报均方根误差对比结果(TECU)
Table 3. Comparison of the RMSE between the mixed neural network model and LSTM network
模型 RMSE 北京 武汉 海口 LSTM 1.50/2.09 1.14/2.29 1.68/4.05 CC-LSTM 1.27/1.80 0.97/1.87 1.48/3.60 注 斜线前为2009年均方根误差,斜线后为2013年均方根误差。 -
[1] KERSLEY L, MALAN D, PRYSE S E, et al. Total electron content-A key parameter in propagation: measurement and use in ionospheric imaging[J]. Annals of Geophysics, 2004, 47(2/3): 1067-1091 [2] WINGLEE R M, CHUA D, BRITTNACHER M, et al. Global impact of ionospheric outflows on the dynamics of the magnetosphere and cross-polar cap potential[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2002, 107(A9): 1237 doi: 10.1029/2001JA000214 [3] ACHARYA R, ROY B, SIVARAMAN M R, et al. Prediction of ionospheric total electron content using adaptive neural network with in-situ learning algorithm[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2011, 47(1): 115-123 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2010.08.016 [4] BILITZA D, ALTADILL D, ZHANG Y L, et al. The International Reference Ionosphere 2012-a model of international collaboration[J]. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2014, 4: A07 doi: 10.1051/swsc/2014004 [5] 张小红, 任晓东, 吴风波, 等. 自回归移动平均模型的电离层总电子含量短期预报[J]. 测绘学报, 2014, 43(2): 118-124ZHANG Xiaohong, REN Xiaodong, WU Fengbo, et al. Short-term TEC prediction of ionosphere based on ARIMA model[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2014, 43(2): 118-124 [6] 李淑慧, 彭军还, 徐伟超, 等. 利用神经网络预报短期电离层TEC变化[J]. 测绘科学, 2013, 38(1): 8-9,12LI Shuhui, PENG Junhuai, XU Weichao, et al. Short-term ionospheric TEC change prediction by neural network[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2013, 38(1): 8-9,12 [7] HUANG Z, YUAN H. Ionospheric single-station TEC short-term forecast using RBF neural network[J]. Radio Science, 2014, 49(4): 283-292 doi: 10.1002/2013RS005247 [8] 汤俊, 高鑫. 贝叶斯正则化的Elman神经网络电离层TEC预报模型[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2020, 40(8): 799-805TANG Jun, GAO Xin. Prediction models of ionospheric TEC by Elman neural network with Bayesian regularization[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2020, 40(8): 799-805 [9] 袁天娇, 陈艳红, 刘四清, 等. 基于深度学习递归神经网络的电离层总电子含量经验预报模型[J]. 空间科学学报, 2018, 38(1): 48-57 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.048YUAN Tianjiao, CHEN Yanhong, LIU Siqing, et al. Prediction model for ionospheric total electron content based on deep learning recurrent neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(1): 48-57 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.048 [10] WEN Z C, LI S H, LI L H, et al. Ionospheric TEC prediction using Long Short-Term Memory deep learning network[J]. Astrophysics and Space Science, 2021, 366(1): 3 doi: 10.1007/s10509-020-03907-1 [11] SUN W Q, XU L, HUANG X, et al. Bidirectional LSTM for ionospheric vertical Total Electron Content (TEC) forecasting[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP). St. Petersburg: IEEE, 2017: 1-4 [12] 张群, 唐振浩, 王恭, 等. 基于长短时记忆网络的超短期风功率预测模型[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(10): 275-281ZHANG Qun, TANG Zhenhao, WANG Gong, et al. Ultra-short-term wind power prediction model based on long and short term memory network[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42(10): 275-281 [13] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324 doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [14] 贵向泉, 高祯, 李立. 融合TCN与BiLSTM+Attention模型的疫情期间文本情感分析[J]. 西安理工大学学报, 2021, 37(1): 113-121GUI Xiangquan, GAO Zhen, LI Li. Text sentiment analysis during the epidemic based on TCN and BiLSTM+Attention fusion model[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Technology, 2021, 37(1): 113-121 [15] 杨旭, 朱亚光, 杨升高, 等. LSTM神经网络在太阳F10.7射电流量中期预报中的应用[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(2): 176-185 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.02.176YANG Xu, ZHU Yaguang, YANG Shenggao, et al. Application of LSTM neural network in F10.7 solar radio flux mid-term forecast[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(2): 176-185 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.02.176 [16] SUN W Q, XU L, HUANG X, et al. Forecasting of ionospheric vertical total electron content (TEC) using LSTM networks[C]//Proceedings of 2017 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (ICMLC). Ningbo: IEEE, 2017: 340-344 [17] 汤俊, 李垠健, 钟正宇, 等. EOF-LSTM神经网络的电离层TEC预报模型[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2021, 41(9): 911-915,944TANG Jun, LI Yinjian, ZHONG Zhengyu, et al. Prediction model of ionospheric TEC by EOF and LSTM neural network[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2021, 41(9): 911-915,944 [18] 殷梦婷, 邹自明, 钟佳. 一种电离层TEC格点预测模型[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(4): 568-579 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.04.568YIN Mengting, ZOU Ziming, ZHONG Jia. A Prediction model of the grid point ionospheric TEC[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(4): 568-579 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.04.568 -
-






 下载:
下载: