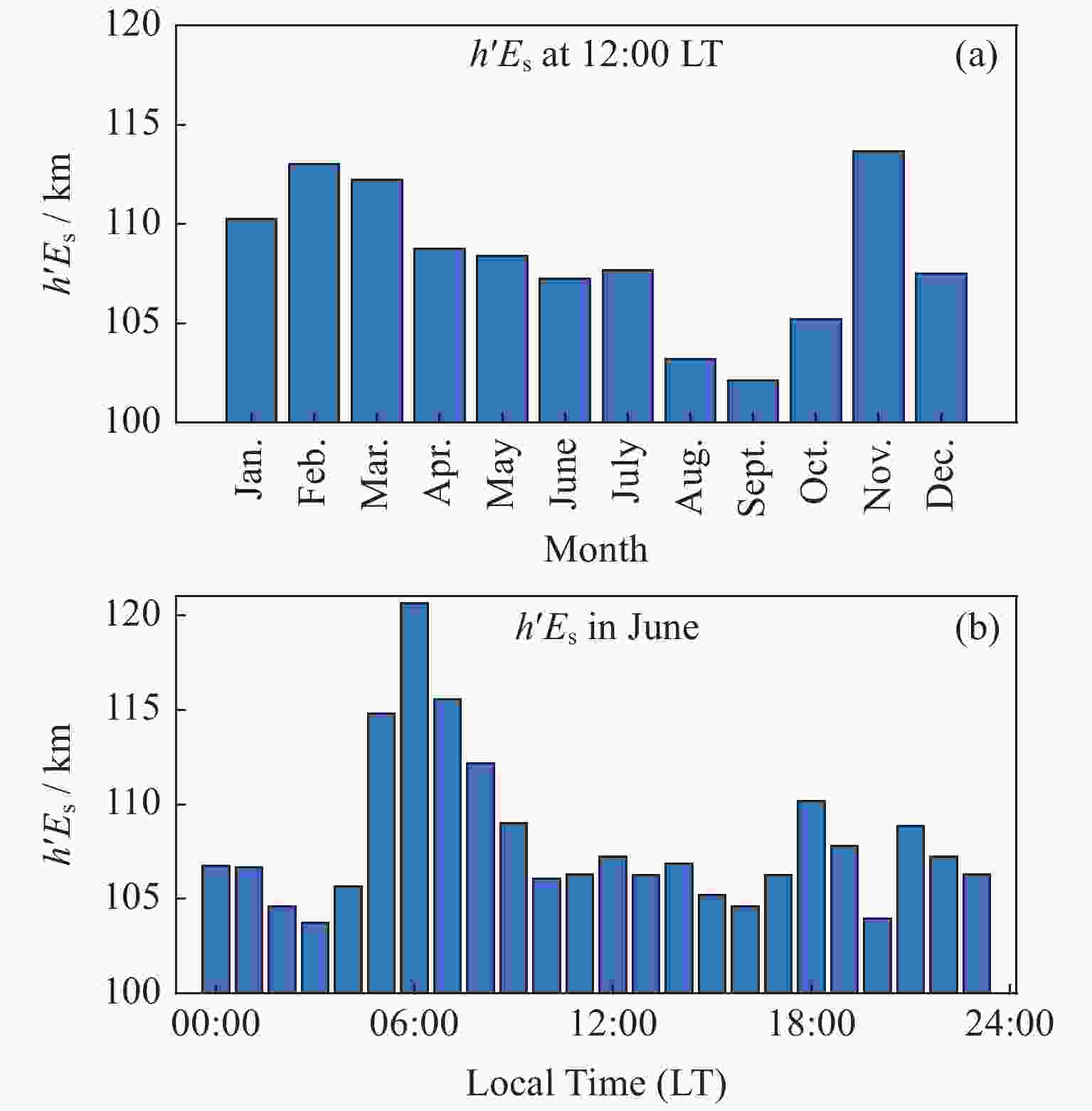
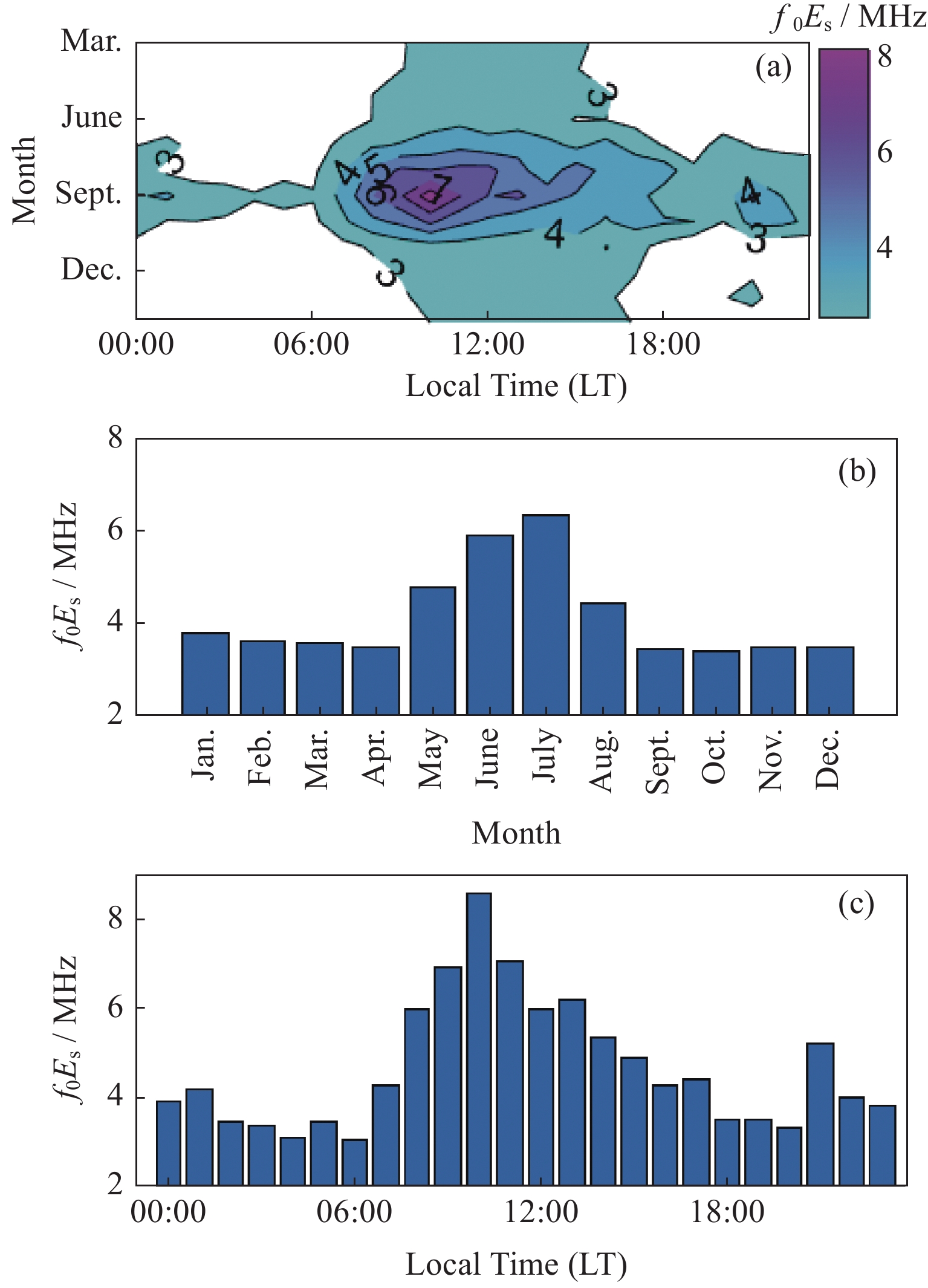
| [1] |
SMITH E K. Worldwide Occurrence of Sporadic E[M]. United States: National Bureau of Standards, 1957
|
| [2] |
HOCKING W K, FULLER B, VANDEPEER B. Real-time determination of meteor-related parameters utilizing modern digital technology[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2001, 63(2/3): 155-169
|
| [3] |
DUNGEY J W. Cosmic Electrodynamics[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1958: 167-168
|
| [4] |
WHITEHEAD J D. Recent work on mid-latitude and equatorial sporadic-E[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, 1989, 51(5): 401-424 doi: 10.1016/0021-9169(89)90122-0
|
| [5] |
AXFORD W I. The formation and vertical movement of dense ionized layers in the ionosphere due to neutral wind shears[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1963, 68(3): 769-779 doi: 10.1029/JZ068i003p00769
|
| [6] |
JACOBI C, ARRAS C. Tidal wind shear observed by meteor radar and comparison with sporadic E occurrence rates based on GPS radio occultation observations[J]. Advances in Radio Science, 2019, 17: 213-224 doi: 10.5194/ars-17-213-2019
|
| [7] |
LIU Y, ZHOU C, TANG Q, et al. The seasonal distribution of sporadic E layers observed from radio occultation measurements and its relation with wind shear measured by TIMED/TIDI[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2018, 62(2): 426-439 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2018.04.026
|
| [8] |
WU Jinnan. Simulation and Observation of the Low and Middle Latitude Ionospheric E Region Irregularity[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2019
|
| [9] |
牛晓娟, 熊建刚, 万卫星, 等. 武汉上空偶发E层与流星雨的联系[J]. 空间科学学报, 2004, 24(2): 105-111 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2004.02.004NIU Xiaojuan, XIONG Jiangang, WAN Weixing, et al. Relationship between the meteor showers and the occurrence of sporadic E over Wuhan[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2004, 24(2): 105-111 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2004.02.004
|
| [10] |
ZHOU C, TANG Q, SONG X X, et al. A statistical analysis of sporadic E layer occurrence in the midlatitude China region[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2017, 122(3): 3617-3631 doi: 10.1002/2016JA023135
|
| [11] |
邱世灿, 王兴金. 大气电场倒转与突发钠层及突发E层的相关性[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2021, 43(2): 356-365QIU Shican, WANG Xingjin. Correlation between atmospheric electric fields overturning and mesospheric sporadic thin layers[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2021, 43(2): 356-365
|
| [12] |
LIU Y, ZHOU C, TANG Q, et al. Evidence of mid- and low-latitude nighttime ionospheric E–F coupling: coordinated observations of sporadic E layers, F -region field-aligned irregularities, and medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(10): 7547-7557 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2914059
|
| [13] |
王晓宾, 马征征, 张雅彬. 青岛地区电离层Es特征统计分析[J]. 电波科学学报, 2014, 29(5): 969-972,993WANG Xiaobin, MA Zhengzheng, ZHANG Yabin. Statistical analysis on characteristics of Es in Qingdao region[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2014, 29(5): 969-972,993
|
| [14] |
张雅彬, 吴健, 许正文, 等. 电离层Es电波传播模型研究[J]. 空间科学学报, 2019, 39(1): 55-61 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.01.055ZHANG Yabin, WU Jian, XU Zhengwen, et al. Radio propagation model of ionospheric sporadic E[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2019, 39(1): 55-61 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.01.055
|
| [15] |
陈春, 杨戈, 林惠娇. 夏季短波Es场强计算方法研究[J]. 电波科学学报, 2021, 36(2): 285-295CHEN Chun, YANG Ge, LIN Huijiao. Method for calculating Es field strength of HF bands in summer[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2021, 36(2): 285-295
|
| [16] |
王胜, 周晨, 姜春华, 等. 频高图Es层回波的自动识别[J]. 空间科学学报, 2019, 39(4): 432-441 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.04.432WANG Sheng, ZHOU Chen, JIANG Chunhua, et al. Automatical scaling of Es layer echoes on ionograms[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2019, 39(4): 432-441 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.04.432
|
| [17] |
王国军, 史建魁, 王霄. 低纬(海南)地区电离层偶发E层的潮汐类周期研究[J]. 空间科学学报, 2013, 33(5): 501-508 doi: 10.11728/cjss2013.05.501WANG Guojun, SHI Jiankui, WANG Xiao. Tidelike periodicities of ionospheric sporadic E observed at low latitude Hainan station[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2013, 33(5): 501-508 doi: 10.11728/cjss2013.05.501
|
| [18] |
SASSI F, LIU H L, MA J, et al. The lower thermosphere during the northern hemisphere winter of 2009: A modeling study using high-altitude data assimilation products in WACCM-X[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2013, 118(16): 8954-8968 doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50632
|
| [19] |
WANG Shengguo, SHI Jiankui, WANG Guojun, et al. Variation of E layer over Hainan station[C]//National Security Geophysics Series (XIV) -- Resources, Environment and Geophysics. 2018
|
| [20] |
左小敏, 万卫星, 谭辉. 大气潮汐风场诱导中纬突发E层的观测证据及理论模拟分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2006, 26(5): 346-351 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2006.05.005ZUO Xiaomin, WAN Weixing, TAN Hui. Observational evidences and simulation of tide wind induced mid-latitude sporadic E-layers[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2006, 26(5): 346-351 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2006.05.005
|






 下载:
下载: