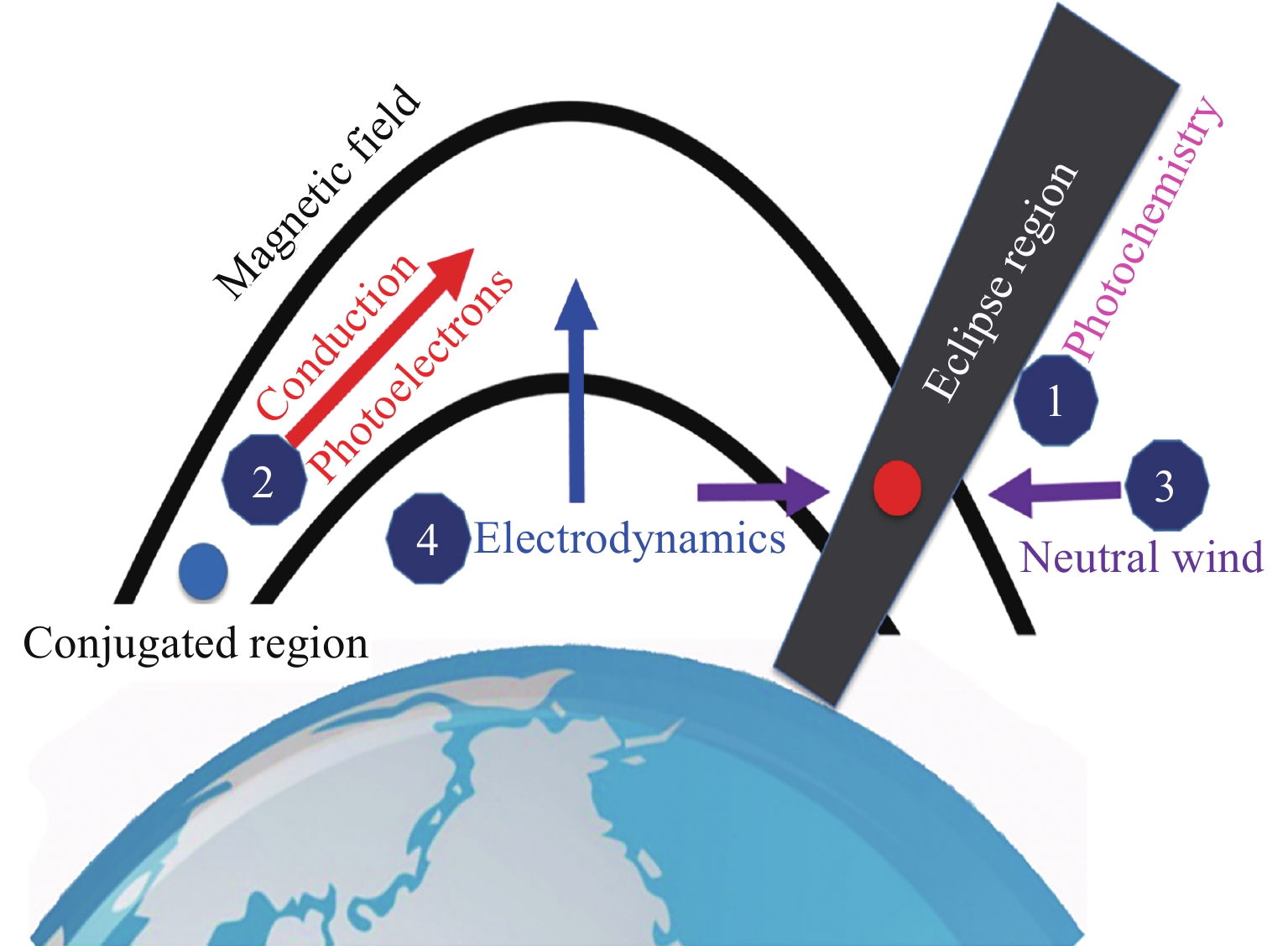
Ionospheric Investigations Conducted by Chinese Mainland Scientists in 2020–2021
doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.04.yg13 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2022.04.yg13
-
Abstract: In this report, we outline works done by scientists from the Mainland of China on various ionospheric topics after the release of the National Report of China in 2020 on ionospheric research[
1 ] to the Committee on Space Research (COSPAR). More than 170 papers were published in 2020–2021. The current report covers the following topics: ionospheric space weather, ionospheric structures and climatology, ionospheric dynamics and couplings, ionospheric irregularity and scintillation, modeling and data assimilation, and ionosphere and sounding techniques. Planetary ionospheres are included for the first time.-
Key words:
- Ionospheric /
- Space weather /
- Planetary ionospheres
-
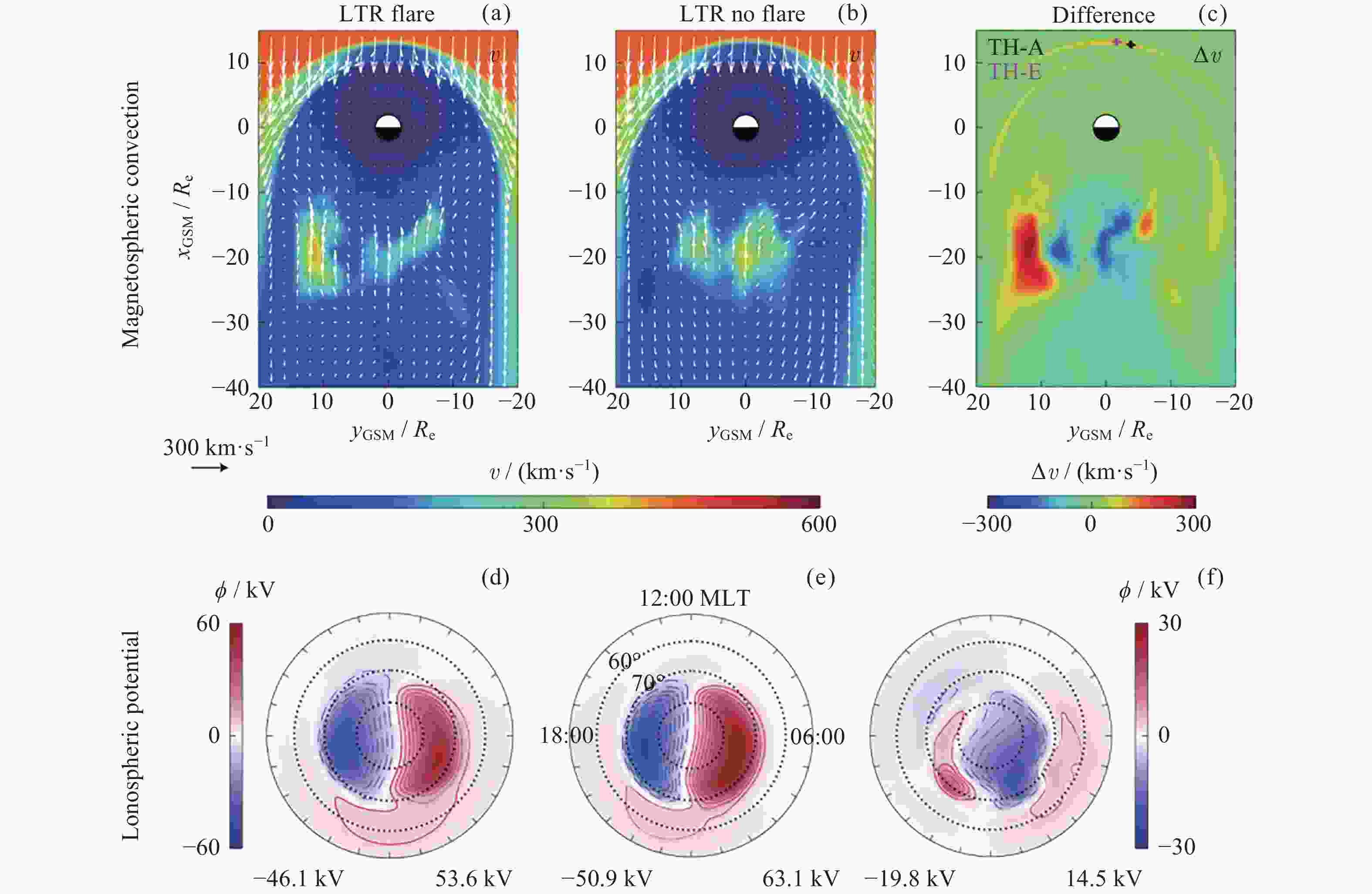
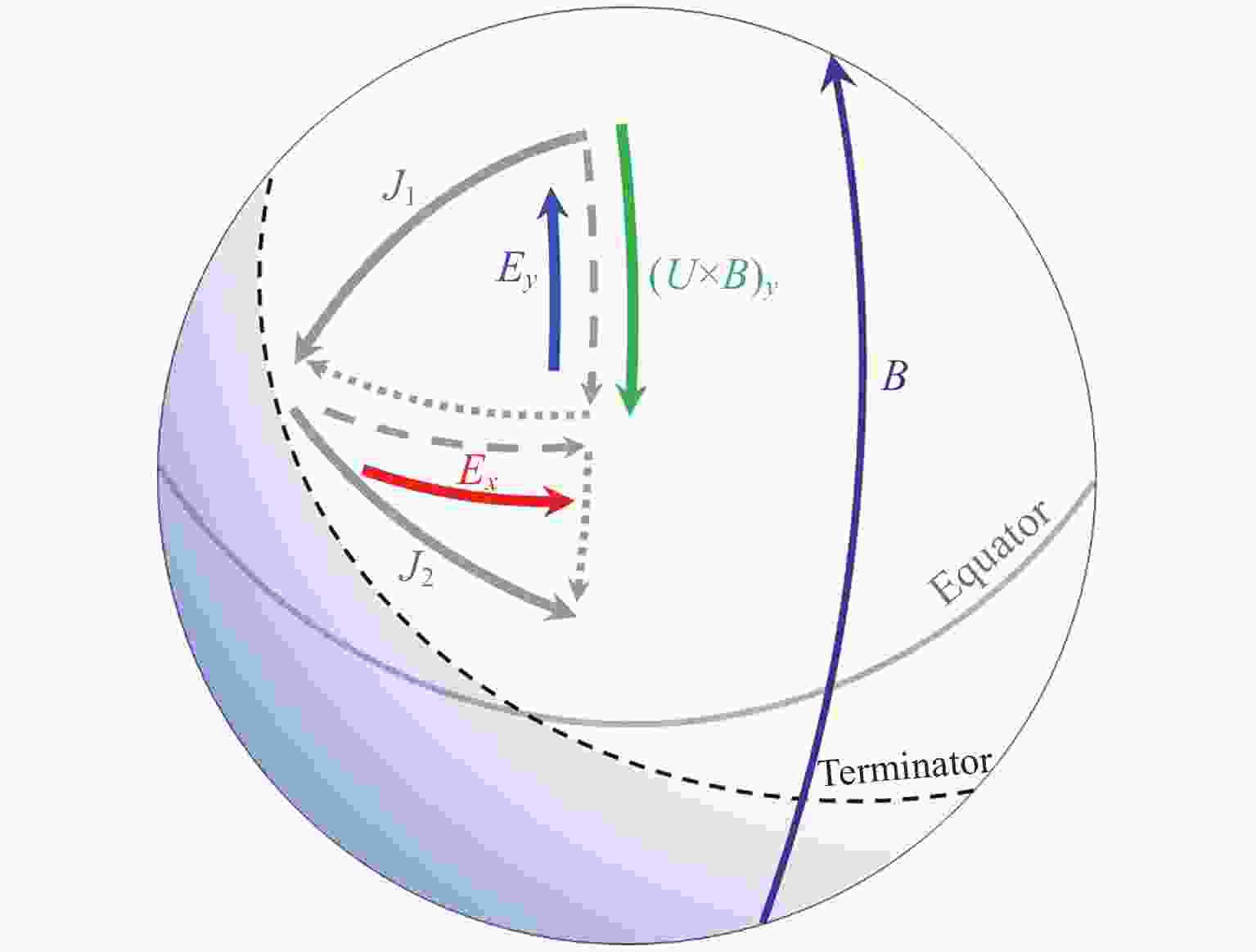
Figure 2. Comparison of 50 min averages from the coupled geospase model simulations of magnetospheric and ionospheric states with and without the solar flare effects. Projections in GSM coordinates of the simulated magnetospheric convection velocity in the equatorial plane with (a) and without (b) the solar flare effects and their difference (c). High-latitude electric potential in the ionosphere with (d) and without (e) solar flare effects and their difference (f)
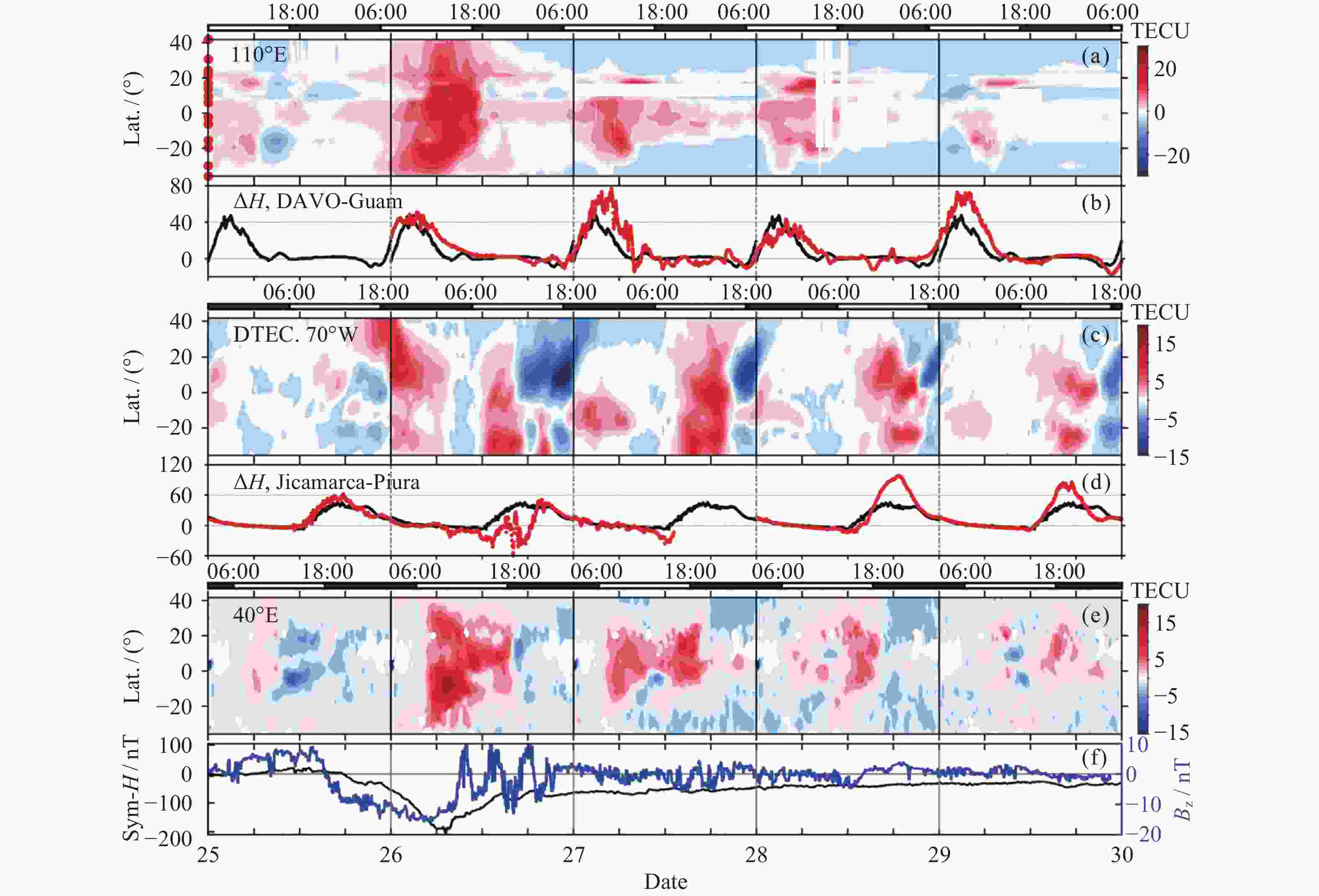
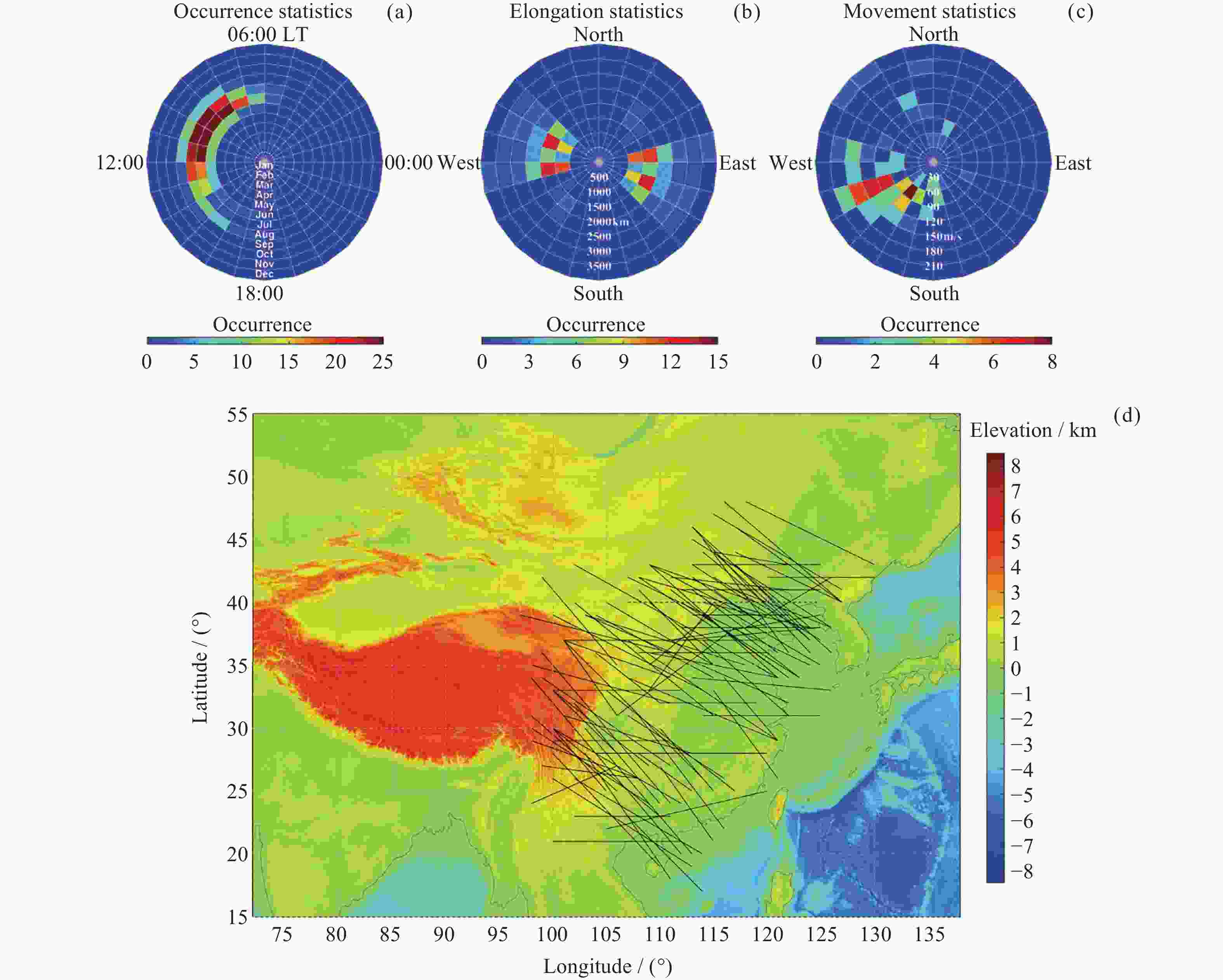
Figure 9. Occurrence of large-scale strong Es structures during 2017–2019 binned into (a) local time and month, (b) the elongation azimuth and dimension, and (c) the horizontal drifting direction and average velocity. (d) The onset locations of all the cases of large-scale Es structures observed during 2017–2019 on a map of topography elevation height. Each black solid line illustrates the location, dimension and elongating direction at the onset of each large-scale Es case
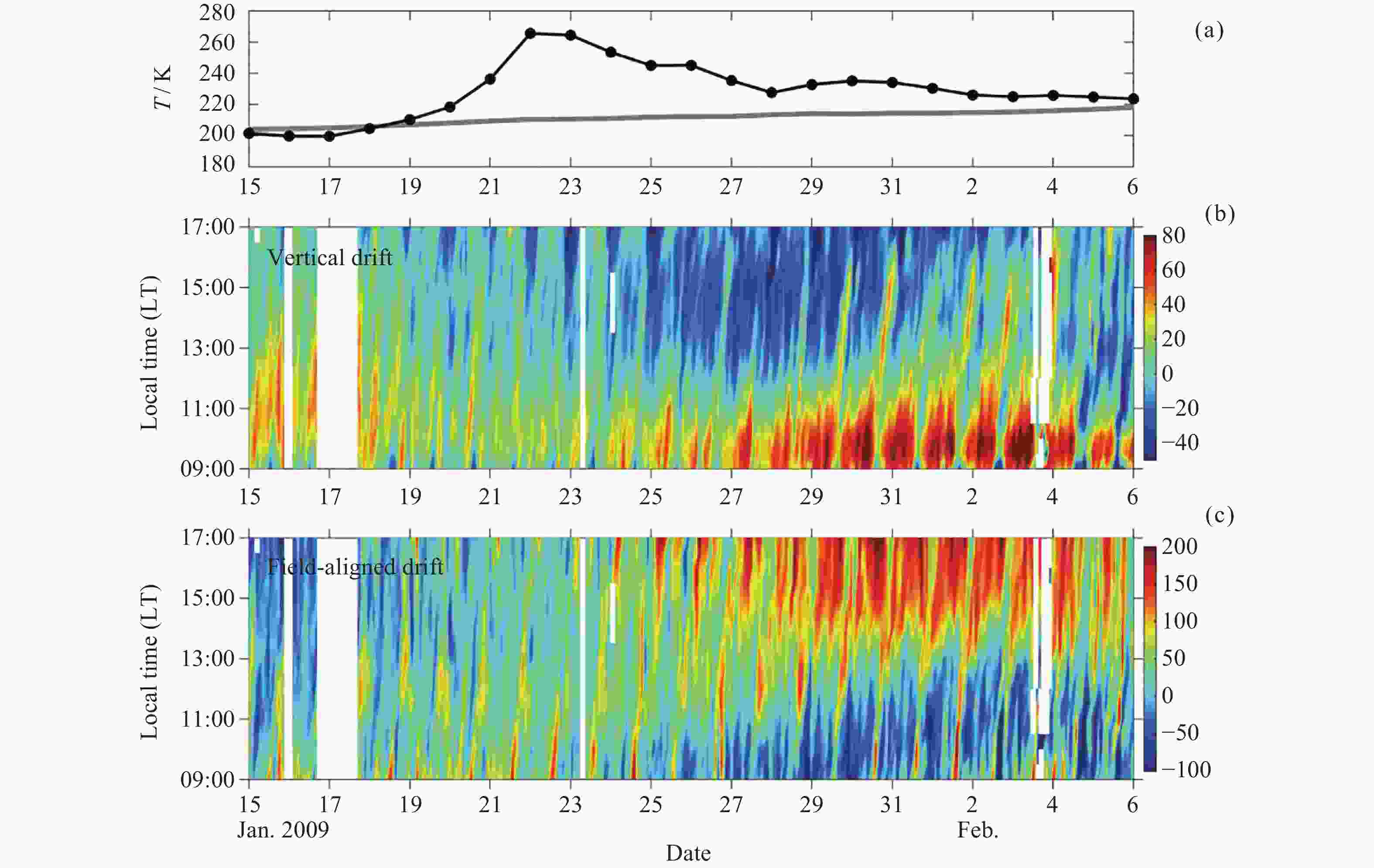
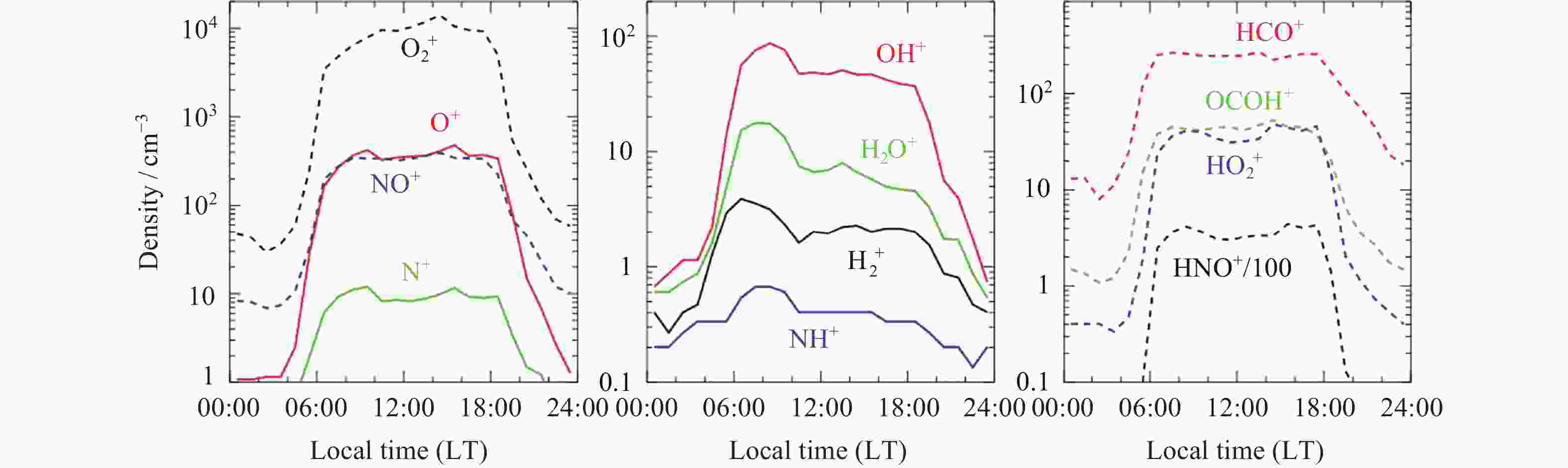
Figure 14. Density variations of the same species as a function of local time and at fixed altitudes, either 300 km (solid) or 180 km (dashed) depending on whether a distinctive layer structure is observable over the altitude range examined in this study. A strong dawn enhancement is observed for each species in the middle panel. Note that the HNO+ density has been everywhere divided by 100 to improve visibility
-
[1] LIU L B, WAN W X. Recent ionospheric investigations in China (2018–2019)[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2020, 4(3): 179-205 doi: 10.26464/epp2020028 [2] ZHANG R L, LE H J, LI W B, et al. Multiple technique observations of the ionospheric responses to the 21 June 2020 solar eclipse[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(12): e2020JA028450 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028450 [3] LE H J, LIU L B, REN Z P, et al. Effects of the 21 June 2020 solar eclipse on conjugate hemispheres: a modeling study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(11): e2020JA028344 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028344 [4] DANG T, LEI J H, WANG W B, et al. Prediction of the thermospheric and ionospheric responses to the 21 June 2020 annular solar eclipse[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2020, 4(3): 231-237 doi: 10.26464/epp2020032 [5] HUANG F Q, LI Q L, SHEN X H, et al. Ionospheric responses at low latitudes to the annular solar eclipse on 21 June 2020[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(10): 2020JA028483 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028483 [6] SUN Y Y, CHEN C H, QING H, et al. Nighttime ionosphere perturbed by the annular solar eclipse on June 21, 2020[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(9): e2021JA029419 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029419 [7] SUN Y Y, SHEN M M, TSAI Y L, et al. Wave steepening in ionospheric total electron density due to the 21 August 2017 total solar eclipse[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(3): e2020JA028931 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028931 [8] YAN M D, DANG T, LEI J H, et al. From bow waves to traveling atmospheric disturbances: thermospheric perturbations along solar eclipse trajectory[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(4): e2020JA028523 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028523 [9] LIU J, WANG W B, QIAN L Y, et al. Solar flare effects in the Earths magnetosphere[J]. Nature Physics, 2021, 17(7): 807-812 doi: 10.1038/s41567-021-01203-5 [10] CHEN J J, LEI J H, WANG W B, et al. Ionospheric electrodynamic response to solar flares in September 2017[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(11): e2021JA029745 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029745 [11] LIU J, QIAN L Y, MAUTE A, et al. Electrodynamical coupling of the geospace system during solar flares[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(1): e2020JA028569 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028569 [12] CHEN X T, DANG T, ZHANG B Z, et al. Global effects of a polar solar eclipse on the coupled magnetosphere-ionosphere system[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(23): e2021GL096471 doi: 10.1029/2021GL096471 [13] REN D X, LEI J H, ZHOU S, et al. High-speed solar wind imprints on the ionosphere during the recovery phase of the august 2018 geomagnetic storm[J]. Space Weather, 2020, 18(7): e2020SW002480 doi: 10.1029/2020SW002480 [14] LI Q L, HUANG F Q, ZHONG J H, et al. Persistence of the long-duration daytime TEC enhancements at different longitudinal sectors during the August 2018 geomagnetic storm[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(11): e2020JA028238 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028238 [15] JIN Y Y, ZHAO B Q, LI G Z, et al. Inhibition of F3 layer at low latitude station Sanya during recovery phase of geomagnetic storms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(12): e2021JA029850 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029850 [16] WAN X, ZHONG J H, XIONG C, et al. Persistent occurrence of strip-like plasma density bulges at conjugate lower-mid latitudes during the September 8–9, 2017 geomagnetic storm[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(5): e2020JA029020 doi: 10.1029/2020JA029020 [17] JIANG C H, WEI L H, YANG G B, et al. Large-scale ionospheric irregularities detected by ionosonde and GNSS receiver network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(6): 940-943 doi: 10.1109/Lgrs.2020.2990940 [18] WEI L H, JIANG C H, HU Y G, et al. Ionosonde observations of spread F and Spread Es at low and middle latitudes during the recovery phase of the 7–9 September 2017 geomagnetic storm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(5): 1010 doi: 10.3390/rs13051010 [19] ZHAI C Z, SHI X L, WANG W B, et al. Characterization of High-m ULF wave signatures in GPS TEC data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(14): e2021GL094282 doi: 10.1029/2021GL094282 [20] WANG H, HE Y F, LÜHR H, et al. Local time and longitudinal differences in the occurrence frequency of ionospheric EMIC waves during magnetic storm periods[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(2): e2020JA028878 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028878 [21] HE Shichuang, ZHANG Donghe, HAO Yongqiang, et al. Statistical study on the occurrence of the ionospheric mid-latitude trough and the variation of trough minimum location over northern hemisphere[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(1): 31-46 doi: 10.6038/cjg2020M0564 [22] LIU J, ZHANG D H, HAO Y Q, et al. The time delay between the equatorial ionization anomaly and the equatorial electrojet in the eastern Asian and American sectors[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 69(1): 187-196 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.10.004 [23] LIU J, ZHANG D H, MO X H, et al. Morphological differences of the northern equatorial ionization anomaly between the eastern Asian and American sectors[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(3): e2019JA027506 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027506 [24] MO X H, ZHANG D H. A comparative study of the northern and southern equatorial ionization anomaly crests in the East-Asian sector during 2006–2015[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 68(3): 1461-1472 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.04.003 [25] MO X H, ZHANG D H, LIU J, et al. Lunar tidal effect on equatorial ionization anomaly region in China low latitude[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(11): e2021JA029845 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029845 [26] MA H, LIU L B, CHEN Y D, et al. Longitudinal differences in electron temperature on both sides of zero declination line in the mid-latitude topside ionosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(2): e2020JA028471 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028471 [27] LI J C, CHEN Y D, LIU L B, et al. Occurrence of Ionospheric Equatorial Ionization Anomaly at 840 km height observed by the DMSP satellites at solar maximum dusk[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(5): e2020SW002690 doi: 10.1029/2020SW002690 [28] TIAN Y Y, HAO Y Q, LI Q H, et al. The role of strong meridional neutral winds in the formation of deep equatorial ionization trough in CHAMP observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(8): e2021JA029319 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029319 [29] ZHOU Y L, LÜHR H, ALKEN P. Average ionospheric middle and low latitudes nighttime zonal currents deduced from CHAMP[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(8): e2019JA027702 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027702 [30] XIONG C, STOLLE C, ALKEN P, et al. Relationship between large-scale ionospheric field-aligned currents and electron/ion precipitations: DMSP observations[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2020, 72(1): 147 doi: 10.1186/s40623-020-01286-z [31] XIONG C, STOLLE C, MICHAELIS I, et al. Correlation analysis of field-aligned currents from the magnetic measurements of GRACE follow-on mission[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2021, 73(1): 206 doi: 10.1186/s40623-021-01540-y [32] CHEN Y D, LIU L B, LE H J, et al. Equatorial north-south difference of noontime electron density bite-out in the F2 layer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(8): e2020JA028124 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028124 [33] CHEN Y D, LIU L B, LE H J, et al. Latitudinal dependence of daytime electron density bite-out in the ionospheric F2-Layer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(1): e2020JA028277 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028277 [34] LIU M M, YUAN Y B, HUO X L, et al. Simultaneous estimation of GPS P1-P2 differential code biases using low earth orbit satellites data from two different orbit heights[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2020, 94(12): 121 doi: 10.1007/s00190-020-01458-5 [35] LIU L B, DING Z H, ZHANG R L, et al. A case study of the enhancements in ionospheric electron density and its longitudinal gradient at Chinese low latitudes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(5): e2019JA027751 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027751 [36] KUAI J W, LI Q L, ZHONG J H, et al. The ionosphere at middle and low latitudes under geomagnetic quiet time of December 2019[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(6): e2020JA028964 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028964 [37] CHEN J J, WANG W B, LEI J H, et al. The physical mechanisms for the sunrise enhancement of equatorial ionospheric upward vertical drifts[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(8): e2020JA028161 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028161 [38] CHEN J J, WANG W B, LEI J H. Longitudinal variations of equatorial ionospheric electric fields near sunrise[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(5): e2020JA028977 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028977 [39] WANG Y H, HUANG F Q, LEI J H, et al. Ionospheric diurnal double-maxima patterns observed by the TEC from Beidou geostationary satellites in the Asian-Australian sector during 2016–2018[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(1): e2020JA028578 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028578 [40] ZHANG R L, LIU L B, LIU H X, et al. Interhemispheric transport of the ionospheric F region plasma during the 2009 sudden stratosphere warming[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(6): e2020GL087078 doi: 10.1029/2020GL087078 [41] HUANG F Q, LEI J H, ZHANG R L, et al. Prominent daytime TEC enhancements under the quiescent condition of January 2017[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(14): e2020GL088398 doi: 10.1029/2020GL088398 [42] LIU J, ZHANG D H, HAO Y Q, et al. Multi-instrumental observations of the quasi-16-day variations from the lower thermosphere to the topside ionosphere in the low-latitude eastern Asian sector during the 2017 sudden stratospheric warming event[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(3): e2019JA027505 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027505 [43] LIU J, ZHANG D H, GONCHARENKO L P, et al. The latitudinal variation and hemispheric asymmetry of the ionospheric lunitidal signatures in the American sector during major sudden stratospheric warming events[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(5): 2020JA028859 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028859 [44] MO X H, ZHANG D H. Quasi-10 d wave modulation of an equatorial ionization anomaly during the Southern Hemisphere stratospheric warming of 2002[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2020, 38(1): 9-16 doi: 10.5194/angeo-38-9-2020 [45] MO X H, ZHANG D H. Six-day periodic variation in equatorial ionization anomaly region[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(11): e2020JA028225 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028225 [46] TANG Q, ZHOU C, LIU Y, et al. Response of sporadic e layer to sudden stratospheric warming events observed at low and middle latitudes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(2): e2019JA027283 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027283 [47] LI N, LUAN X L, LEI J H, et al. Variations of mesospheric neutral winds and tides observed by a meteor radar chain over China during the 2013 sudden stratospheric warming[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(5): e2019JA027443 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027443 [48] LI N, LEI J H, HUANG F Q, et al. Responses of the ionosphere and neutral winds in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere in the Asian-Australian sector to the 2019 southern hemisphere sudden stratospheric warming[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(10): e2020JA028653 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028653 [49] TANG Q, ZHOU C, LI Z S, et al. Semi-monthly lunar tide oscillation of f0F2 in Equatorial Ionization Anomaly (EIA) crests during 2014–2015 SSW[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(2): e2020JA028708 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028708 [50] YU T, YE H L, LIU H X, et al. Ionospheric F layer scintillation weakening as observed by COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 during the major sudden stratospheric warming in January 2013[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(9): e2019JA027721 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027721 [51] YE H L, XUE X H, YU T, et al. Ionospheric F-layer scintillation variabilities over the American sector during sudden stratospheric warming events[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(8): e2020SW002703 doi: 10.1029/2020SW002703 [52] LIU Y, TANG Q, CHEN G Y, et al. Quasi-6-day wave effects in ionospheric E and F region during the recent solar maximum 2014–2015[J]. Earth Planets and Space, 2020, 72(1): 190 doi: 10.1186/s40623-020-01319-7 [53] ZHOU X, YUE X A, LIU H L, et al. Response of atmospheric carbon dioxide to the secular variation of weakening geomagnetic field in whole atmosphere simulations[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2021, 5(4): 327-336 doi: 10.26464/epp2021040 [54] LIU J, WANG W B, ZHANG X M. The characteristics of terdiurnal tides in the ionosphere[J]. Astrophysics and Space Science, 2020, 365(9): 155 doi: 10.1007/s10509-020-03874-7 [55] ZHANG R L, LIU L B, YU Y, et al. Westward electric fields in the afternoon equatorial ionosphere during geomagnetically quiet times[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(12): e2020JA028532 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028532 [56] WANG H, ZHENG Z, ZHANG K, et al. Influence of nonmigrating tides and geomagnetic field geometry on the diurnal and longitudinal variations of the equatorial electrojet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(6): e2019JA027631 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027631 [57] LIU J, GUAN Y B, ZHANG X M, et al. The data comparison of electron density between CSES and DEMETER satellite, Swarm constellation and IRI model[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2021, 8(2): e2020EA001475 doi: 10.1029/2020EA001475 [58] CHEN J J, LEI J H, ZHANG S R, et al. A simulation study on the relationship between field-aligned and field-perpendicular plasma velocities in the ionospheric F region[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(1): e2019JA027350 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027350 [59] JIANG C H, WANG W B, YANG G B, et al. An investigation of mid-latitude ionospheric peak in TEC using the TIEGCM[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar: Terrestrial Physics, 2020, 211: 105480 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2020.105480 [60] CAI Y H, WANG W B, ZHANG S R, et al. Climatology analysis of the daytime topside ionospheric diffusive O+ flux based on incoherent scatter radar observations at millstone hill[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(10): e2021JA029222 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029222 [61] ZHOU X, LIU H L, LU X, et al. Quiet‐time day‐to‐day variability of equatorial vertical E×B drift from atmosphere perturbations at dawn[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(4): e2020JA027824 doi: 10.1029/2020JA027824 [62] ZHOU X, YUE X A, LIU H L, et al. A comparative study of ionospheric day-to-day variability over Wuhan based on ionosonde measurements and model simulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(3): e2020JA028589 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028589 [63] WANG H, LÜHR H. Effects of solar illumination and substorms on auroral electrojets based on CHAMP observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(2): e2020JA028905 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028905 [64] WANG H, LÜHR H, ZHANG K D. Longitudinal variation in the thermospheric superrotation: CHAMP observation and TIE-GCM simulation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(18): e2021GL095439 doi: 10.1029/2021GL095439 [65] ZHAO S F, SHEN X H, ZHOU C, et al. The influence of the ionospheric disturbance on the ground based VLF transmitter signal recorded by LEO satellite-Insight from full wave simulation[J]. Results in Physics, 2020, 19: 103391 doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103391 [66] CHEN C H, SUN Y Y, LIN K, et al. A new instrumental array in Sichuan, China, to monitor vibrations and perturbations of the lithosphere, atmosphere, and ionosphere[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2021, 42(6): 1425-1442 doi: 10.1007/s10712-021-09665-1 [67] HAO Yongqiang, LI Quanhan, GUO Jianguang, et al. Imaging of the large-scale ionospheric disturbances induced by seismic waves using GPS network in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(11): 3925-3932 doi: 10.6038/cjg2021P0088 [68] TARIQ M A, SHAH M, LI Z S, et al. Lithosphere ionosphere coupling associated with three earthquakes in Pakistan from GPS and GIM TEC[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2021, 147: 101860 doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2021.101860 [69] ZHAO S F, SHEN X H, LIAO L, et al. Investigation of precursors in VLF subionospheric signals related to strong earthquakes (M>7) in Western China and possible explanations[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(21): 3563 doi: 10.3390/rs12213563 [70] XIONG P, LONG C, ZHOU H Y, et al. Identification of electromagnetic pre-earthquake perturbations from the DEMETER data by machine learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(21): 3643 doi: 10.3390/rs12213643 [71] XIONG P, MARCHETTI D, DE SANTIS A, et al. SafeNet: SwArm for earthquake perturbations identification using deep learning networks[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(24): 5033 doi: 10.3390/rs13245033 [72] XIONG P, LONG C, ZHOU H Y, et al. Pre-earthquake ionospheric perturbation identification using CSES data via transfer learning[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2021, 9: 779255 doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2021.779255 [73] ZHAO S F, SHEN X H, ZHIMA Z, et al. The very low-frequency transmitter radio wave anomalies related to the 2010 Ms7.1 Yushu earthquake observed by the DEMETER satellite and the possible mechanism[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2020, 38(5): 969-981 doi: 10.5194/angeo-38-969-2020 [74] OUYANG X Y, PARROT M, BORTNIK J. ULF wave activity observed in the nighttime ionosphere above and some hours before strong earthquakes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(9): e2020JA028396 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028396 [75] ZHANG X M, WANG Y L, BOUDJADA M Y, et al. Multi-experiment observations of ionospheric disturbances as precursory effects of the Indonesian Ms6.9 earthquake on August 05, 2018[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(24): 4050 doi: 10.3390/rs12244050 [76] ZHIMA Z M, HU Y P, SHEN X H, et al. Storm-time features of the ionospheric ELF/VLF waves and energetic electron fluxes revealed by the China Seismo-electromagnetic satellite[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(6): 2617 doi: 10.3390/app11062617 [77] ZHANG Q H, ZHANG Y L, WANG C, et al. A space hurricane over the Earths polar ionosphere[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1207 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21459-y [78] ZHANG Q H, ZHANG Y L, WANG C, et al. Multiple transpolar auroral arcs reveal insight about coupling processes in the Earth’s magnetotail[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 2020, 117(28): 16193-16198 doi: 10.1073/pnas.2000614117 [79] LIU Yingyu, XING Zanyang, FENG Huiting, et al. Comparative analysis of optical observation characteristics between PMAFs and throat aurora[J]. Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(5): 737-745 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.05.737 [80] YANG Z Y, ZHANG B Z, LEI J H, et al. Nonlinear response of the cross polar cap potential to solar wind density under northward interplanetary magnetic field[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(8): e2020GL087559 doi: 10.1029/2020GL087559 [81] MA Y Z, ZHANG Q H, LYONS L R, et al. Is westward travelling surge driven by the polar cap flow channels?[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(8): e2020JA028498 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028498 [82] MA Y Z, ZHANG Q H, JAYACHANDRAN P T, et al. Statistical study of the relationship between ion upflow and field-aligned current in the topside ionosphere for both hemispheres during geomagnetic disturbed and quiet time[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(9): e2019JA027538 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027538 [83] WANG Z W, HU H Q, LU J Y, et al. Observational evidence of transient lobe reconnection triggered by sudden northern enhancement of IMF Bz[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(9): e2021JA029410 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029410 [84] YUAN Y B, WANG N B, LI Z S, et al. The BeiDou global broadcast ionospheric delay correction model (BDGIM) and its preliminary performance evaluation results[J]. Navigation, 2019, 66(1): 55-69 doi: 10.1002/navi.292 [85] ZHANG K D, WANG H, WANG W B, et al. Nighttime meridional neutral wind responses to SAPS simulated by the TIEGCM: a universal time effect[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2021, 5(1): 52-62 doi: 10.26464/epp2021004 [86] ZHANG K D, WANG H, YAMAZAKI Y, et al. Effects of subauroral polarization streams on the equatorial electrojet during the geomagnetic storm on June 1, 2013[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(10): e2021JA029681 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029681 [87] SUN W J, NING B Q, HU L H, et al. The evolution of complex Es observed by multi instruments over low‐latitude China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(8): e2019JA027656 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027656 [88] SUN W J, ZHAO X, HU L, et al. Morphological characteristics of thousand-kilometer-scale Es structures over China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(2): e2020JA028712 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028712 [89] SUN W J, HU L H, YANG Y Y, et al. Occurrences of regional strong Es irregularities and corresponding scintillations characterized using a high-temporal-resolution GNSS network[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(11): e2021JA029460 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029460 [90] TANG Q, ZHAO J Q, YU Z B, et al. Occurrence and variations of middle and low latitude sporadic E layer investigated with longitudinal and latitudinal chains of ionosondes[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(12): e2021SW002942 doi: 10.1029/2021SW002942 [91] TANG Q, ZHOU C, LIU H X, et al. The possible role of turbopause on sporadic-E layer formation at middle and low latitudes[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(12): e2021SW002883 doi: 10.1029/2021SW002883 [92] XU T, HU Y L, DENG Z X, et al. Revisit to sporadic E layer response to presumably seismogenic electrostatic fields at middle latitudes by model simulation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(3): e2019JA026843 doi: 10.1029/2019JA026843 [93] QIU L H, YU T, YAN X X, et al. Altitudinal and latitudinal variations in ionospheric sporadic-E layer obtained from FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC radio occultation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(9): e2021JA029454 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029454 [94] QIU L H, ZUO X M, YU T, et al. The characteristics of summer descending sporadic E layer observed with the ionosondes in the China region[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(3): e2020JA028729 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028729 [95] CHEN X C, HUANG W T, BAN C, et al. Dynamic properties of a sporadic sodium layer revealed by observations over Zhongshan, Antarctica: a case study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(11): e2021JA029787 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029787 [96] WANG J, ZUO X M, SUN Y Y, et al. Multilayered sporadic-E response to the annular solar eclipse on June 21, 2020[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(3): e2020SW002643 doi: 10.1029/2020SW002643 [97] WANG Y, JAYACHANDRAN P T, THEMENS D R, et al. A case study of polar cap sporadic-E layer associated with TEC Variations[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(7): 1324 doi: 10.3390/rs13071324 [98] WANG J, CHEN G, YU T, et al. Middle-scale ionospheric disturbances observed by the oblique-incidence ionosonde detection network in north China after the 2011 Tohoku Tsunamigenic earthquake[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(3): 1000 doi: 10.3390/s21031000 [99] DENG Z X, WANG R, LIU Y, et al. Investigation of low latitude spread-F triggered by nighttime medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbance[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(5): 945 doi: 10.3390/rs13050945 [100] HUANG F Q, LEI J H, OTSUKA Y, et al. Characteristics of medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances and ionospheric irregularities at mid-latitudes revealed by the total electron content associated with the Beidou geostationary satellite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6424-6430 doi: 10.1109/Tgrs.2020.3032741 [101] HU L H, LEI J H, SUN W J, et al. Latitudinal variations of daytime periodic ionospheric disturbances from Beidou GEO TEC observations over China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(3): e2020JA028809 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028809 [102] CHEN G, DING F, WAN W X, et al. Structures of multiple large-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances observed by dense Global Navigation Satellite System networks in China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(2): e2019JA027032 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027032 [103] XIE H Y, LI G Z, ZHAO X K, et al. Coupling between E region quasi‐periodic echoes and F region medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances at low latitudes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(5): e2019JA027720 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027720 [104] LI G Z, NING B Q, OTSUKA Y, et al. Challenges to equatorial plasma bubble and ionospheric scintillation short-term forecasting and future aspects in East and Southeast Asia[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2021, 42(1): 201-238 doi: 10.1007/s10712-020-09613-5 [105] ZHAO X K, XIE H Y, HU L H, et al. Climatology of equatorial and low-latitude F region kilometer-scale irregularities over the meridian circle around 120°E/60°W[J]. GPS Solutions, 2021, 25(1): 20 doi: 10.1007/s10291-020-01054-2 [106] XIE H Y, YANG S P, ZHAO X K, et al. Unexpected high occurrence of daytime F‐region backscatter plume structures over low latitude Sanya and their possible origin[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(22): e2020GL090517 doi: 10.1029/2020GL090517 [107] AJITH K K, LI G Z, TULASI RAM S, et al. On the seeding of periodic equatorial plasma bubbles by gravity waves associated with tropical cyclone: a case study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(10): e2020JA028003 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028003 [108] HUANG F Q, LEI J H, XIONG C, et al. Observations of equatorial plasma bubbles during the geomagnetic storm of October 2016[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2021, 5(5): 416-426 doi: 10.26464/epp2021043 [109] LIU Y, ZHOU C, XU T, et al. Investigation of midlatitude nighttime ionospheric E-F coupling and interhemispheric coupling by using COSMIC GPS radio occultation measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(3): e2019JA027625 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027625 [110] ZHANG Q H, XING Z Y, WANG Y, et al. Formation and evolution of polar cap ionospheric patches and their associated upflows and scintillations[M]//ZONG Q G. ESCOUBET P, SIBECK D, et al. Dayside Magnetosphere Interactions. Wiley, 2020. DOI: 10.1002/9781119509592.ch16 [111] ZHANG D, ZHANG Q H, MA Y Z, et al. Solar and geomagnetic activity impact on occurrence and spatial size of cold and hot polar cap patches[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(18): e2021GL094526 doi: 10.1029/2021GL094526 [112] WANG Y, ZHANG Q H, MA Y Z, et al. Polar ionospheric large-scale structures and dynamics revealed by TEC Keogram extracted from TEC maps[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(1): e2019JA027020 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027020 [113] WANG Y, CAO Z, XING Z Y, et al. GPS scintillations and TEC variations in association with a polar cap arc[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(3): e2020JA028968 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028968 [114] GENG W, HUANG W G, LIU G Q, et al. Generation of ionospheric scintillation maps over southern China based on kriging method[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2020, 65(12): 2808-2820 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2020.03.035 [115] GENG W, HUANG W G, LIU G Q, et al. The distribution characteristics of GPS cycle slip over the China mainland and adjacent region during the declining solar activity (2015-2018) period of solar cycle 24[J]. Radio Science, 2021, 56(5): e2020RS007196 doi: 10.1029/2020RS007196 [116] XIONG C, XU J S, STOLLE C, et al. On the occurrence of GPS signal amplitude degradation for receivers on board LEO satellites[J]. Space Weather, 2020, 18(2): e2019SW002398 doi: 10.1029/2019SW002398 [117] ZHAO Weihua, ZHANG Qinghe, WANG Cheng, et al. Preliminary study on loss of lock of satellite signal at the mid-latitude region in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2022, 37(3): 1-8 doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2021076 [118] JIANG C H, WEI L H, YANG G B, et al. Numerical simulation of the propagation of electromagnetic waves in ionospheric irregularities[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2020, 4(6): 565-570 doi: 10.26464/epp2020059 [119] GAO J F, GUO L X, XU Z W, et al. Simulation of plasma instabilities artificially induced in the equatorial ionosphere[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2020, 27(9): 092902 doi: 10.1063/5.0013329 [120] ZHAO H S, XU Z W, TANG W, et al. Electromagnetic scattering by artificial plasma clouds in the ionosphere[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(6): 4810-4819 doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.2972608 [121] DANG T, ZHANG B Z, LEI J H, et al. Azimuthal averaging-reconstruction filtering techniques for finite-difference general circulation models in spherical geometry[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2021, 14(2): 859-873 doi: 10.5194/gmd-14-859-2021 [122] LI W B, CHEN Y D, LIU L B, et al. Variations of thermospheric winds observed by a Fabry-Perot interferometer at Mohe, China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(2): e2020JA028655 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028655 [123] LI Q L, LIU L B, HE M S, et al. A global empirical model of electron density profile in the F region ionosphere basing on COSMIC measurements[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(4): e2020SW002642 doi: 10.1029/2020SW002642 [124] HUANG H, MOSES M, VOLK A E, et al. Assessment of IRI-2016 hmF2 model options with digisonde, COSMIC and ISR observations for low and high solar flux conditions[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 68(5): 2093-2103 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.01.033 [125] ZHAO X K, LI G Z, XIE H Y, et al. The prediction of day-to-day occurrence of low latitude ionospheric strong scintillation using gradient boosting algorithm[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(12): e2021SW002884 doi: 10.1029/2021SW002884 [126] HE J H, YUE X A, HU L H, et al. Observing system impact on ionospheric specification over China using EnKF assimilation[J]. Space Weather, 2020, 18(10): e2020SW002527 doi: 10.1029/2020SW002527 [127] HE J H, YUE X A, REN Z P. The impact of assimilating ionosphere and thermosphere observations on neutral temperature improvement: Observing system simulation experiments using EnKF[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(10): e2021SW002844 doi: 10.1029/2021SW002844 [128] HE J H, YUE X A. The impact of perturbing eddy diffusion and upper boundary on the ionosphere EnKF assimilation system[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(8): e2021JA029366 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029366 [129] HU Z J, HAN B, ZHANG Y S, et al. Modeling of ultraviolet aurora intensity associated with interplanetary and geomagnetic parameters based on neural networks[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(11): e2021SW002751 doi: 10.1029/2021SW002751 [130] HU Zejun, HAN Bing, LIAN Huifang, et al. Modeling of ultraviolet auroral intensity based on generalized regression neural network associated with IMF/solar wind and geomagnetic parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(5): 1738-1750 doi: 10.6038/cjg2020N0151 [131] ZHANG W, HUO X L, YUAN Y B, et al. Algorithm research using GNSS-TEC data to calibrate TEC calculated by the IRI-2016 Model over China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(19): 4002 doi: 10.3390/rs13194002 [132] LI M, YUAN Y B, ZHANG X, et al. A multi-frequency and multi-GNSS method for the retrieval of the ionospheric TEC and intraday variability of receiver DCBs[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2020, 94(10): 102 doi: 10.1007/s00190-020-01437-w [133] SHE C L, YUE X A, HU L H, et al. Estimation of ionospheric total electron content from a multi-GNSS station in China[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(2): 852-860 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2941049 [134] ZHONG J H, LEI J H, YUE X A, et al. Correlation between ionospheric TEC and the DCB stability of GNSS receivers from 2014 to 2016. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2657[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(21): 3496 doi: 10.3390/rs12213496 [135] XIONG P, ZHAI D L, LONG C, et al. Long short‐term memory neural network for ionospheric total electron content forecasting over China[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(4): e2020SW002706 [136] LING Y M, LIU Y, LEI J H, et al. Laboratory evidence of a pre-existing instability that can enhance the ionospheric heating efficiency[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(9): e2021GL092560 doi: 10.1029/2021GL092560 [137] SUN W J, WU B Y, WU Z, et al. IONISE: an ionospheric observational network for irregularity and scintillation in East and Southeast Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(8): e2020JA028055 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028055 [138] YANG S P, WU Z, DUBS M, et al. MIOS optical subsystem for determining physical and chemical properties of meteors producing plasma irregularities[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 68(3): 1556-1567 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.03.031 [139] YUE X A, WAN W X, XIAO H, et al. Preliminary experimental results by the prototype of Sanya Incoherent Scatter Radar[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2020, 4(6): 579-587 doi: 10.26464/epp2020063 [140] LI Y, YUAN K, YAO M, et al. The prototype incoherent scatter radar system of Nanchang university[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(7): 1184-1188 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2994082 [141] JIANG C H, WEI L H, LAN T, et al. A statistical study of autoscaled data at the northern equatorial ionization anomaly during the year 2016[J]. Radio Science, 2020, 55(2): e2019RS006898 doi: 10.1029/2019RS006898 [142] FENG T, LIU M R, XU B, et al. Auroral-enhanced plasma lines by suprathermal electrons observed by EISCAT[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(3): e2020JA028495 doi: 10.1029/2020JA028495 [143] WU J, BLAGOVESHCHENSKAYA N F, WU J, et al. Altitude descents in high-frequency enhanced plasma and ion lines during ionospheric heating at EISCAT[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2021, 212: 105425 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2020.105425 [144] YANG J T, LI Q L, LU H, et al. CSES observations of ELF wave radiation excited by the EISCAT heater[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2020, 27(12): 122903 doi: 10.1063/5.0022474 [145] LU H, YANG J T, LI Q L, et al. ELF/VLF communication experiment by modulated heating of ionospheric auroral electrojet at EISCAT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(4): 2267-2273 doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3026872 [146] YAN R, ZHIMA Z, XIONG C, et al. Comparison of electron density and temperature from the CSES satellite with other space-borne and ground-based observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(10): e2019JA027747 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027747 [147] ZHANG X M, FROLOV V, SHEN X H, et al. The electromagnetic emissions and plasma modulations at middle latitudes related to SURA-CSES experiments in 2018[J]. Radio Science, 2020, 55(8): e2019RS007040 doi: 10.1029/2019RS007040 [148] LIU D P, ZEREN Z, SHEN X H, et al. Typical ionospheric disturbances revealed by the plasma analyzer package onboard the China seismo-electromagnetic satellite[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 68(9): 3796-3805 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.08.009 [149] YANG Y Y, ZHIMA Z R, SHEN X H, et al. The first intense geomagnetic storm event recorded by the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite[J]. Space Weather, 2020, 18(1): e2019SW002243 doi: 10.1029/2019SW002243 [150] YANG N, XIA C L, YU T, et al. Measurement of Martian atmospheric winds by the O2 1.27 μm airglow observations using Doppler Michelson interferometry: a concept study[J]. Science China-Earth Sciences, 2021, 64(11): 2027-2042 doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9814-7 [151] CAO Y T, CUI J, NI B B, et al. Bidirectional electron conic observations for photoelectrons in the Martian ionosphere[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2020, 4(4): 403-407 doi: 10.26464/epp2020037 [152] CAO Y T, CUI J, WU X S, et al. A survey of photoelectrons on the nightside of mars[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(2): e2020GL089998 doi: 10.1029/2020GL089998 [153] CAO Y, CUI J, WU X, et al. Photoelectron pitch angle distribution near Mars and implications on cross terminator magnetic field connectivity[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2020, 4(1): 17-22 doi: 10.26464/epp2020008 [154] WU X S, CUI J, CAO Y T, et al. Response of photoelectron peaks in the Martian ionosphere to solar EUV/X-ray irradiance[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2020, 4(4): 390-395 doi: 10.26464/epp2020035 [155] WU X S, CUI J, YELLE R V, et al. Photoelectrons as a tracer of planetary atmospheric composition: application to CO on mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets, 2020, 125(7): e2020JE006441 doi: 10.1029/2020JE006441 [156] NIU D D, CUI J, GU H, et al. Energetic electron depletions in the Nightside Martian upper atmosphere revisited[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(4): e2019JA027670 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027670 [157] NIU D D, CUI J, GU H, et al. In situ heating of the Nightside Martian upper atmosphere and ionosphere: the role of solar wind electron precipitation[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2021, 909(2): 108 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/abdbb0 [158] CAO Y T, WELLBROCK A, COATES A J, et al. Field-aligned photoelectron energy peaks at high altitude and on the nightside of titan[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets, 2020, 125(1): e2019JE006252 doi: 10.1029/2019je006252 [159] GU H, CUI J, HE Z G, et al. A MAVEN investigation of O++ in the dayside Martian ionosphere[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2020, 4(1): 11-16 doi: 10.26464/epp2020009 [160] GU H, CUI J, NIU D D, et al. Observation of CO2++ dication in the dayside Martian upper atmosphere[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2020, 4(4): 396-402 doi: 10.26464/epp2020036 [161] WU X S, CUI J, NIU D D, et al. Compositional variation of the dayside Martian ionosphere: inference from photochemical equilibrium computations[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2021, 923(1): 29 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ac24fe [162] NIU D D, CUI J, WU S Q, et al. Species-dependent response of the Martian ionosphere to the 2018 global dust event[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets, 2021, 126(2): e2020JE006679 doi: 10.1029/2020JE006679 [163] CUI J, REN Z P, WU Z P, et al. Abnormal dawn-dusk asymmetry of protonated ions in the Martian ionosphere[J]. Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2020, 895(2): L43 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ab930c [164] JIANG C H, YOKOYAMA T, WEI L H, et al. Nonlinear simulation of ionospheric irregularities at mars[J]. Astrophysical Journal, 2021, 909(1): 47 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/abdc1d -
-






 下载:
下载: