Simulation of Vector Magnetic Field In-orbit Calibration Algorithm for Geomagnetic Survey Satellite
-
摘要: 以SWARM为代表的高精度地磁测量卫星对地球磁场探测精度经过标定之后优于0.5 nT,对于开展地磁科学研究具有重要意义。地磁测量卫星通过安装在伸展杆上的矢量磁通门磁强计、标量磁强计和高精度星敏感器,获取测量方向的惯性空间姿态的地磁信息,其中高精度标量磁强计主要用于对磁通门矢量磁强计进行标定。针对地磁测量卫星,研究了矢量磁强计在轨测量误差的校正方法。考虑到矢量磁强计非正交角、标度因子以及偏差的影响,建立磁场矢量线性输出模型;结合标量磁强计的测量值分别设计基于小量近似的线性校正算法和基于参数辨识更新的非线性校正算法;校验两种算法的标定精度,并通过Tukey权重函数改善算法的鲁棒性。仿真结果表明,两种算法校正结果相似,磁场三轴误差可校正至0.5 nT以内,在标量磁强计存在异常值时仍具有较好的校正效果。Abstract: The precision of geomagnetic survey satellites represented by SWARM is better than 0.5 nT for detection of the Earth’s magnetic field after calibration. The satellites obtain the geomagnetic information of inertial space attitude in measurement direction through the vector fluxgate magnetometer, scalar magnetometer and high-precision star tracker installed on the extension boom. The high-precision scalar magnetometer is mainly used to calibrate the fluxgate vector magnetometer. Calibration methods of in-orbit measurement error of vector magnetometer are proposed for geomagnetic survey satellite. Considering the non-orthogonal angles, scale factors and deviations of vector magnetometer, the linear output model of magnetic field vector is established. The linear correction algorithm based on small approximation and nonlinear correction algorithm based on parameters identification update are designed respectively combined with the measurement values of scalar magnetometer. The calibration accuracy of algorithms is verified, and the robustness of the algorithms is improved by Tukey weight function. Simulation results show that the correction results are similar, the triaxial errors of magnetic field can be corrected to less than 0.5 nT, and the algorithms still have a good correction effect when there is an outlier in scalar measurements.
-
表 1 不同情况下非线性校正算法参数辨识结果与初始参数对比
Table 1. Parameter identification results of the nonlinear correction algorithm in different cases compared with the initial parameters
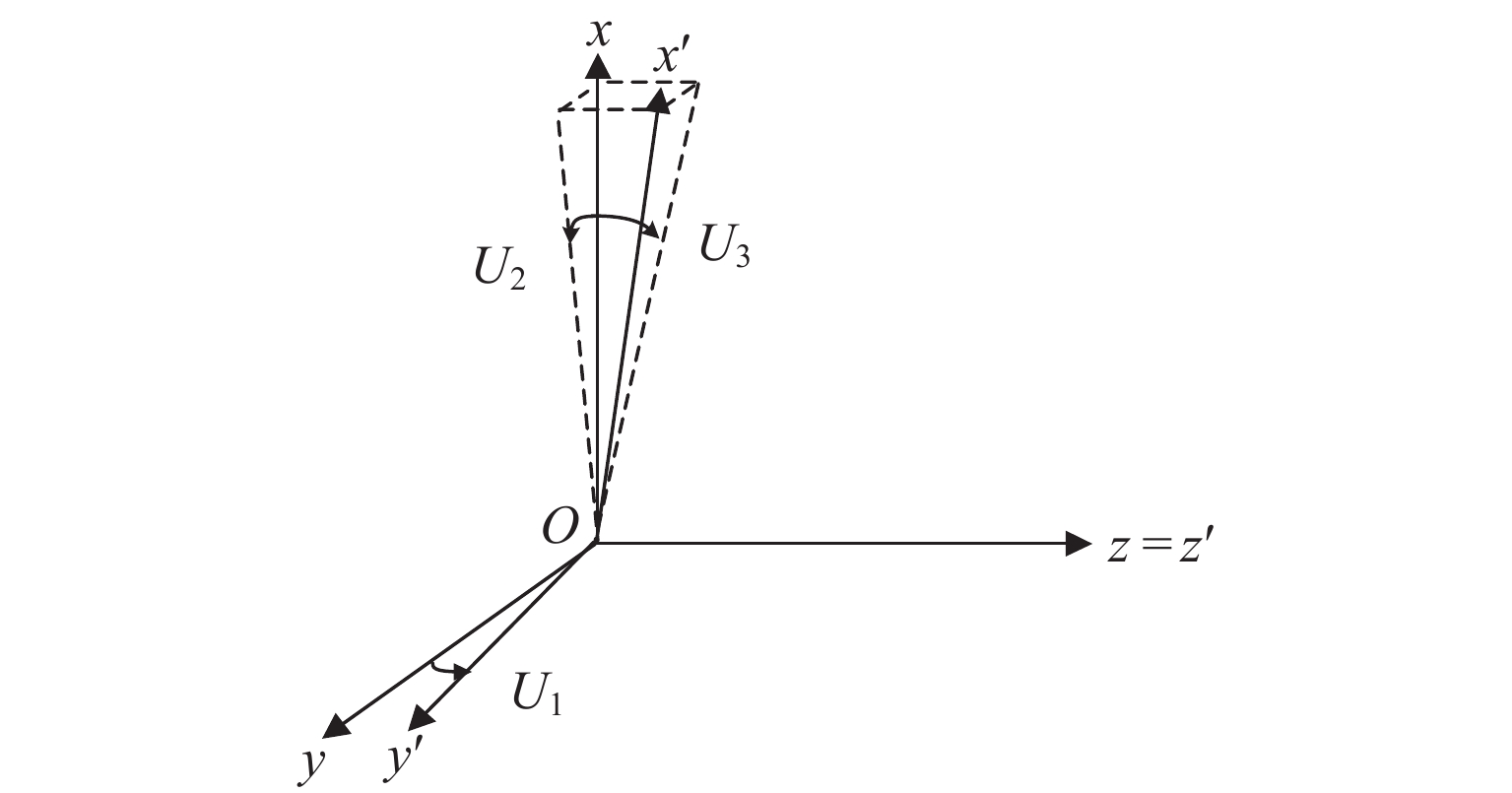
仿真条件 固有偏差/nT 标度因子 非正交角/(°) Sx Sy Sz ${U_1}$ ${U_2}$ ${U_3}$ 初始参数 [10.00,20.00,30.00]T 1.002500 1.002600 1.002400 0.0100 0.0200 0.0300 无干扰 [10.28,20.13,30.29]T 1.002499 1.002594 1.002399 0.0101 0.0204 0.0302 高斯白噪声
(幅值0.15 nT)[11.98,20.91,30.50]T 1.002549 1.002587 1.002404 0.0109 0.0222 0.0304 高斯白噪声
(幅值1 nT)[15.22,19.82,30.94]T 1.002645 1.002615 1.002416 0.0099 0.0243 0.0271 均匀分布噪声
(幅值0.5 nT)[11.93,19.77,30.31]T 1.002547 1.002599 1.002400 0.0097 0.0220 0.0286 周期性噪声
(幅值0.5 nT)[11.50,20.29,30.44]T 1.002535 1.002595 1.002403 0.0103 0.0215 0.0298 标量数据存在
2 nT异常扰动[10.42,19.72,30.23]T 1.002504 1.002598 1.002398 0.0097 0.0205 0.0295 标量数据存在10 nT
异常扰动(应用Tukey
权重函数后)[10.38,20.15,30.30]T 1.002503 1.002594 1.002400 0.0101 0.0204 0.0302 -
[1] 左文辑, 宋福香. 微小卫星磁测自主导航方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2000, 21(2): 100-104ZUO Wenji, SONG Fuxiang. An approach to autonomous navigation using magnetic measurements for small satellites[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2000, 21(2): 100-104 [2] 王淑一, 杨旭, 杨涤, 等. 近地卫星磁测自主导航算法研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2003, 24(6): 634-637,660WANG Shuyi, YANG Xu, YANG Di, et al. Algorithm for autonomous navigation of low earth orbit satellite using magnetic measurements[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2003, 24(6): 634-637,660 [3] ZHOU B, YANG Y Y, ZHANG Y T, et al. Magnetic field data processing methods of the China seismo-electromagnetic satellite[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2018, 2(6): 455-461 doi: 10.26464/epp2018043 [4] 刘逸康, 任顺清, 张高雄, 等. 星敏与磁力仪间安装矩阵的一种地面标定方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2021, 53(6): 34-40LIU Yikang, REN Shunqing, ZHANG Gaoxiong, et al. A calibration method for installation matrix between star sensor and magnetometer on the ground[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021, 53(6): 34-40 [5] 王兰炜, 胡哲, 申旭辉, 等. 电磁监测试验卫星(张衡一号)数据处理方法和流程[J]. 遥感学报, 2018, 22(S1): 39-55WANG Lanwei, HU Zhe, SHEN Xuhui, et al. Data processing methods and procedures of CSES satellite[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 22(S1): 39-55 [6] 于向前, 刘斯, 肖池阶, 等. 基于椭球拟合的三轴磁强计两步校准法[J]. 仪表技术与传感器, 2021(4): 52-56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2021.04.011YU Xiangqian, LIU Si, XIAO Chijie, et al. Two-step calibration of tri-axial magnetometer based on ellipsoid fitting[J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor, 2021(4): 52-56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2021.04.011 [7] 夏琳琳, 耿靖童, 肖建磊, 等. 一种正交三轴磁罗盘的椭球拟合分步优化补偿方法(英文)[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2018, 26(4): 478-483 doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2018.04.010XIA Linlin, GENG Jingtong, XIAO Jianlei, et al. Ellipsoid fitting based two-step optimized correction for orthogonal tri-axis magnetic compass measurements[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2018, 26(4): 478-483 doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2018.04.010 [8] OLSEN N, ALBINI G, BOUFFARD J, et al. Magnetic observations from CryoSat-2: calibration and processing of satellite platform magnetometer data[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2020, 72(1): 48 doi: 10.1186/s40623-020-01171-9 [9] HAMMER M D, FINLAY C C, OLSEN N. Applications for CryoSat-2 satellite magnetic data in studies of Earth's core field variations[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2021, 73(1): 73 doi: 10.1186/s40623-021-01365-9 [10] ALKEN P, OLSEN N, FINLAY C C. Co-estimation of geomagnetic field and in-orbit fluxgate magnetometer calibration parameters[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2020, 72(1): 49 doi: 10.1186/s40623-020-01163-9 [11] HERCEG M, JØRGENSEN P S, JØRGENSEN J L. Characterization and compensation of thermo-elastic instability of SWARM optical bench on Micro Advanced Stellar Compass attitude observations[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2017, 137: 205-213 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2017.04.018 [12] KLOSS C, FINLAY C C, OLSEN N. Co-estimating geomagnetic field and calibration parameters: modeling Earth’s magnetic field with platform magnetometer data[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2021, 73(1): 23 doi: 10.1186/s40623-020-01351-7 [13] 张镇琦, 李磊, 周斌, 等. 基于绝对磁场测量的磁通门磁强计在轨标定方法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2014, 34(2): 235-241 doi: 10.11728/cjss2014.02.235ZHANG Zhenqi, LI Lei, ZHOU Bin, et al. A method of in-orbit calibration of fluxgate magnetometer based on the measurement of absolute scalar magnetometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2014, 34(2): 235-241 doi: 10.11728/cjss2014.02.235 [14] JØRGENSEN J L, JØRGENSEN P S, HERCEG M. Swarm μASC star tracker in-flight status and performance[EB/OL]. (2017-10-14)[2021-12-23]. https://orbit.dtu.dk/en/publications/swarm-%CE%BCasc-star-tracker-in-flight-status-and-performance [15] 秦赓, 管雪元, 李文胜. 基于椭球补偿的三维载体磁场误差补偿方法[J]. 电子测量技术, 2018, 41(2): 37-40QIN Geng, GUAN Xueyuan, LI Wensheng. Compensation method of magnetic field error of three dimensional vector based on ellipsoid compensation[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2018, 41(2): 37-40 [16] YIN F, LÜHR H. Recalibration of the CHAMP satellite magnetic field measurements[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2011, 22(5): 055101 doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/22/5/055101 [17] TøFFNER-CLAUSEN L, LESUR V, OLSEN N, et al. In-flight scalar calibration and characterisation of the Swarm magnetometry package[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2016, 68(1): 129 doi: 10.1186/s40623-016-0501-6 [18] 陈贵芳, 郁丰, 王润. 基于IGRF的地磁基准图技术[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 2020, 41(3): 98-104CHEN Guifang, YU Feng, WANG Run. Geomagnetic reference map technology based on IGRF[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research, 2020, 41(3): 98-104 [19] 胡睿帆. 数字式氦光泵磁力仪的工程样机设计[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017HU Ruifan. Design of Engineering Prototype for Digital Helium Optically Pumped Magnetometer[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017 [20] BLACK M J, RANGARAJAN A. On the unification of line processes, outlier rejection, and robust statistics with applications in early vision[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1996, 19(1): 57-91 doi: 10.1007/BF00131148 -
-






 下载:
下载: