Modeling of Auroral Electrojet Index with Ultraviolet Aurora Image
-
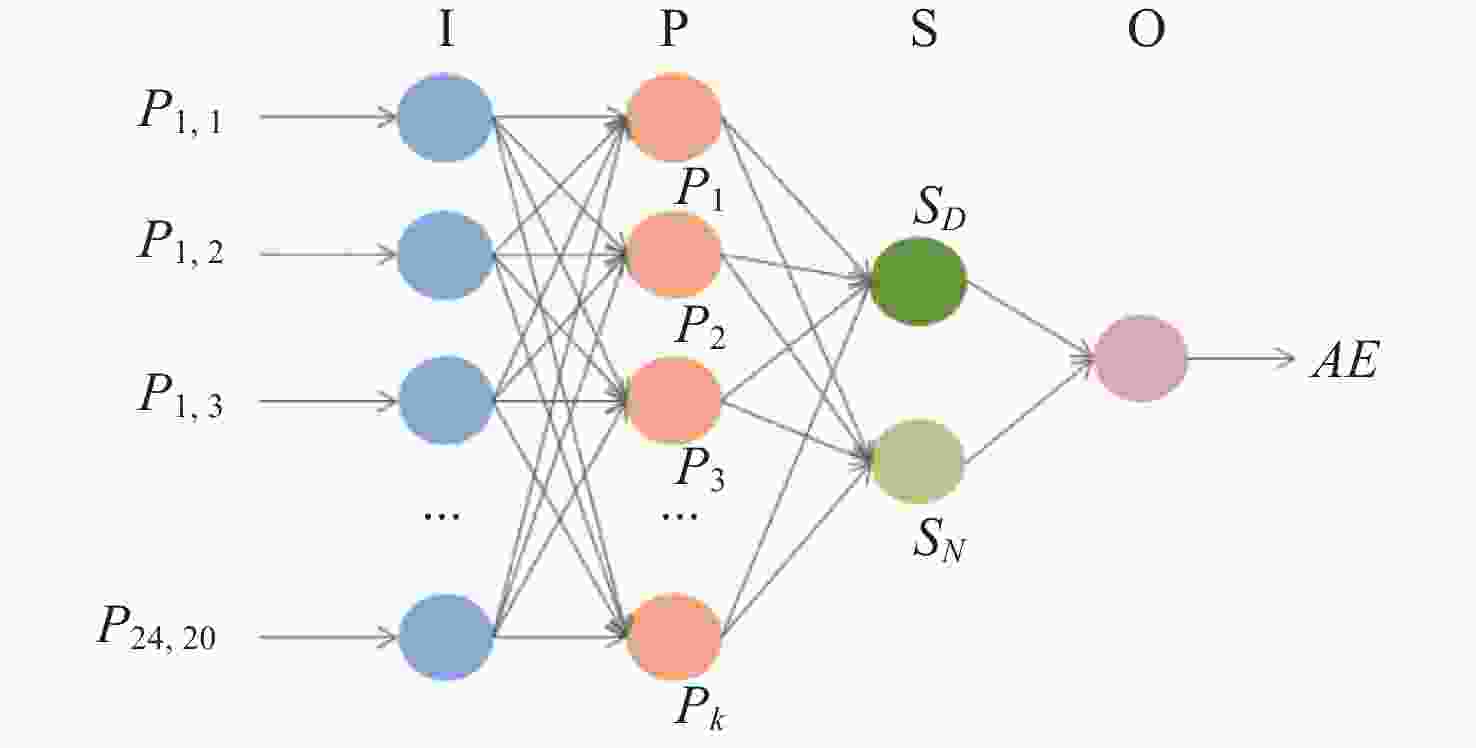
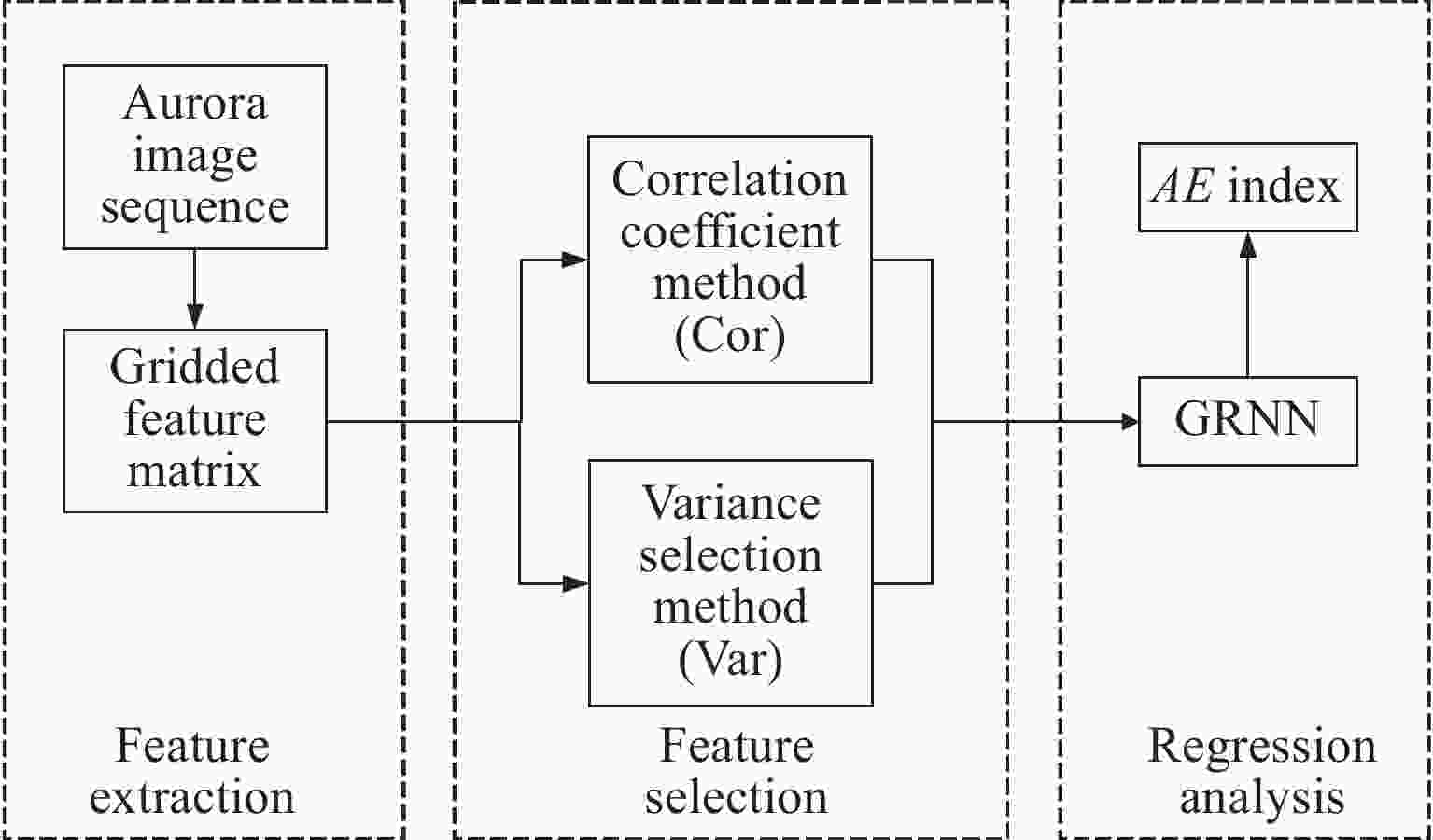
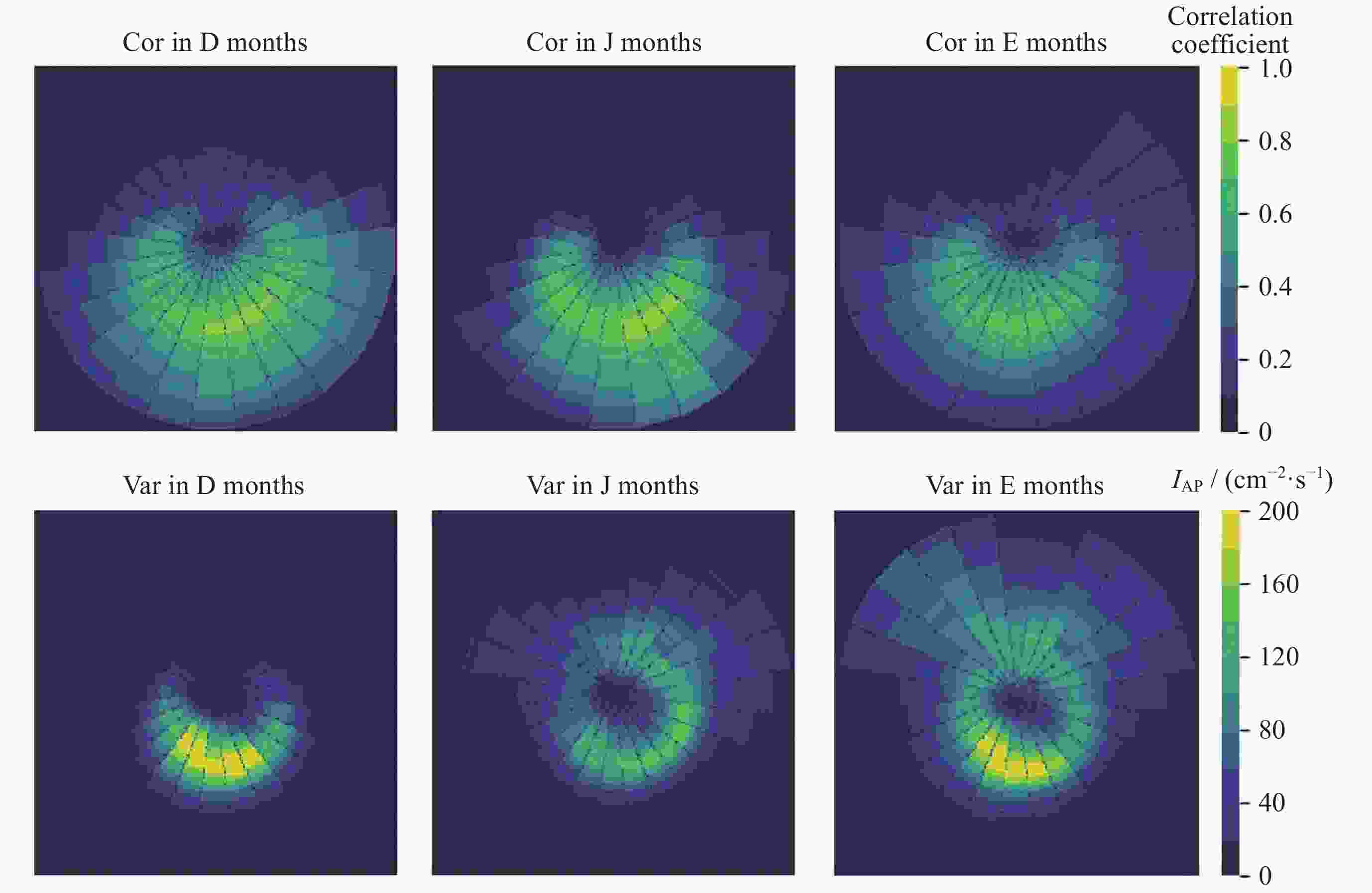
摘要: 极光电集流指数AE是描述地磁亚暴强弱的重要指标,且与极区磁层扰动及极光粒子沉降过程密切相关。因此,建立更加准确的极光电集流指数模型对空间天气的研究具有重要意义。利用1997年POLAR卫星紫外极光图像数据探究了紫外极光图像中极光强度IAP的空间分布与AE指数在不同季节的相关性,并在此基础上提出了基于紫外极光图像的AE指数模型。以网格化方法提取极光强度空间分布特征,采用广义回归神经网络,通过相关系数法和方差选择法构建Cor-GRNN和Var-GRNN两种AE指数模型,并针对冬至月份、夏至月份、分点月份3个季节分别进行训练。研究结果表明,AE指数与IAP具有相似的半年变化趋势,其相关性在不同季节差异较大。相比于太阳风驱动下的AE指数神经网络预测模型,基于极光图像的AE指数模型在ERMS和R2标准上均优于其他模型,其中归一化ERMS小于0.1,模型对于AE指数变化的可解释度提升了10%左右。Abstract: The auroral electrojet index AE is an important indicator to describe the intensity of geomagnetic substorms, and is closely related to the polar magnetosphere disturbance and the precipitation process of auroral particles. Therefore, it is of great significance to establish an accurate prediction model of the electrojet index for the study of space weather. In this paper, the correlation of the spatial distribution of aurora power IAP and AE index in different seasons are studied by using the ultraviolet aurora image data of Polar satellite in 1997, and on this basis, a prediction model of AE index based on the ultraviolet aurora image is proposed. The grid method is used to extract the spatial distribution characteristics of the aurora intensity of the ultraviolet aurora image. The generalized regression neural network GRNN is used to construct two AE index models, Cor-GRNN model and Var-GRNN model, by using the correlation coefficient method and variance selection method, and training is conducted for the three seasons. The results show that AE and IAP have a similar semi-annual change trend, and their correlation varies greatly in different seasons. Compared with the AE index neural network prediction model driven by the solar wind, the model based on aurora images is superior to other models in terms of ERMS and R2 standards. The normalized ERMS is less than 0.1, and the model’s interpretability for AE index changes is increased by about 10%.
-
图 3 1997年D(上)、J(中)、E(下)月份极光强度与AE指数的相关性以及极光强度的累积分布。(a)~(c) 为AE与IAP的散点图和线性关系拟合,(d)~(f) 为极光强度的累积分布(色标表示极光强度,取值0~20 × 104 cm–2·s–1)
Figure 3. Correlation between the total auroral intensity and AE index in D, J and E months in 1997 and the cumulative distribution of auroral intensity. In (a) ~ (c) Scatter plot and linear relationship fitting of AE and IAP. In (d) ~ (f) cumulative distribution of auroral intensity (The color bar represents the aurora power, with values ranging from 0 to 20 × 104 cm–2·s–1)
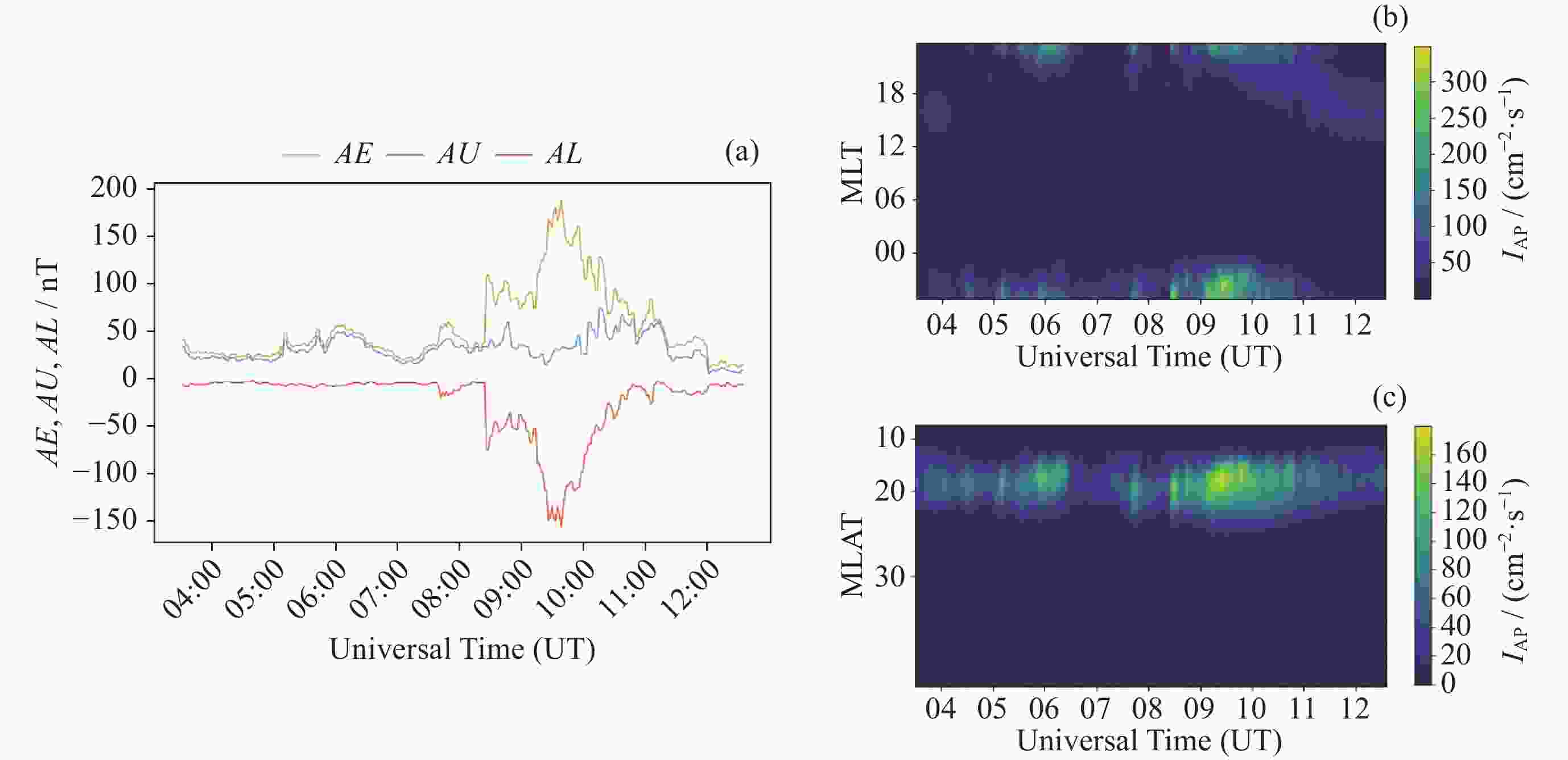
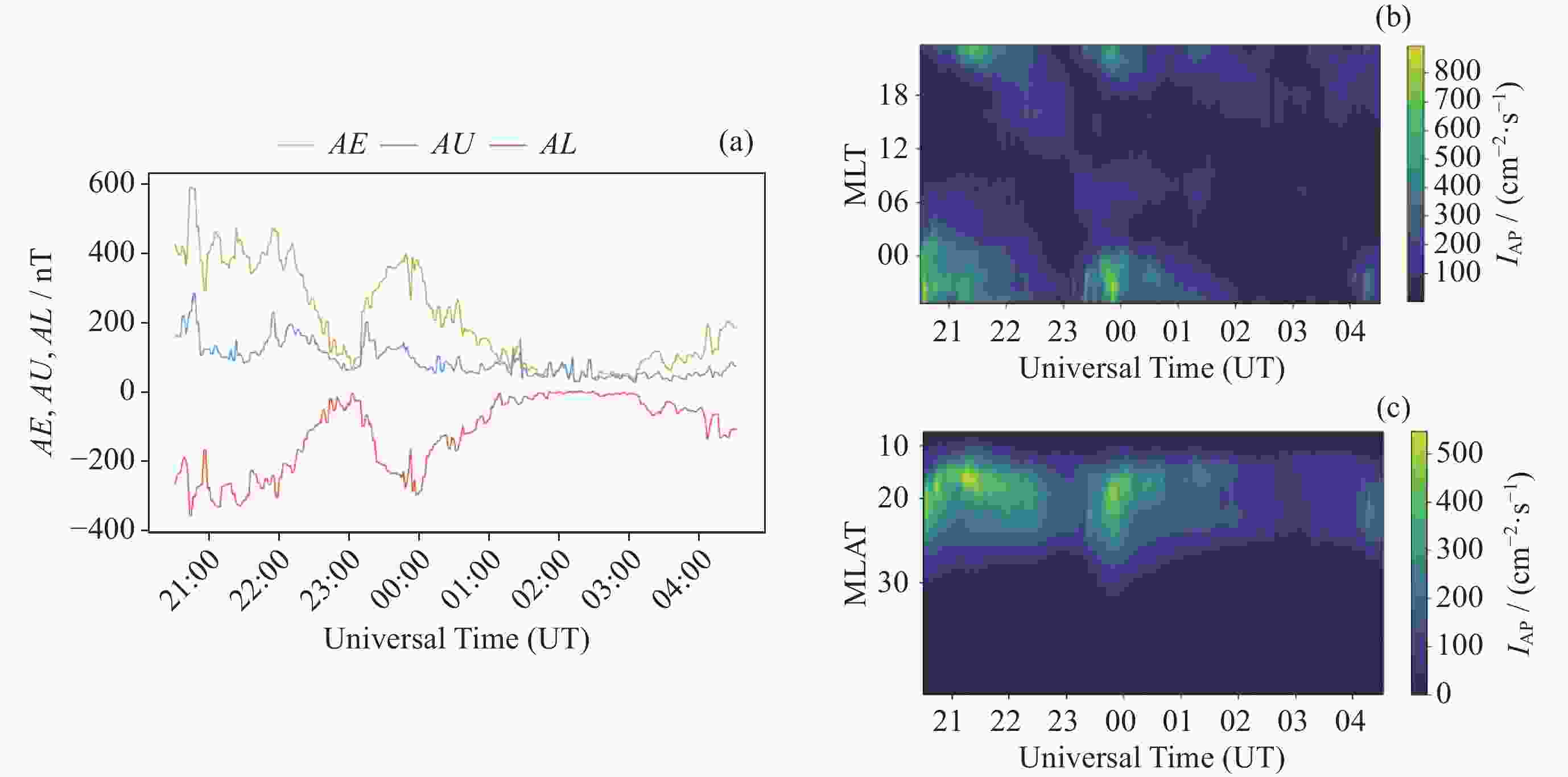
图 5 二级磁扰动期间 AE,AU,AL随UT的变化曲线 (a),极光强度磁经度分布的变化 (b),极光强度经纬度分布的变化 (c)
Figure 5. During second-order disturbance: (a) variation curves of AE, AU, and AL with UT; (b) variation of magnetic longitude distribution of auroral intensity; (c) variation of latitudinal longitude distribution of auroral intensity
表 1 两种预测模型在D,J,E测试集上的预测性能比较
Table 1. Comparison of prediction performance of two prediction models on D, J, E test sets
Dataset Model ERMS(Normalized) VAR $ {R}^{2} $ D Cor-GRNN 0.0805 0.2524 0.9555 Var-GRNN 0.0831 0.2685 0.9526 J Cor-GRNN 0.0989 0.3164 0.9296 Var-GRNN 0.0918 0.3282 0.9420 E Cor-GRNN 0.1019 0.2879 0.9463 Var-GRNN 0.1096 0.3331 0.9378 注 加粗字体表示两种模型中更好的性能数据。 表 2 D月份亚暴发生期间AE指数预测模型性能
Table 2. Performance of AE index prediction model during substorm occurrence in D months
Model ERMS /nT ERMS(Normalized) VAR $ {R}^{2} $ Cor-GRNN 106.6857 0.1034 0.4799 0.9179 Var-GRNN 119.1728 0.1123 0.5666 0.9032 表 3 本文模型与其他AE指数预测模型性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison between this model and other AE index prediction models
Model ERMS(Normalized) VAR $ {R}^{2} $ Cor-GRNN 0.0937 0.2850 0.9438 Var-GRNN 0.0948 0.3104 0.9441 ELM 0.1079 0.2854 0.8351 Random forest 0.1246 0.3808 0.7800 FFBP 0.1105 0.2992 0.8271 SVM 0.1307 0.4184 0.7583 注 加粗数据表示性能最优。 -
[1] DAVIS T N, SUGIURA M. Auroral electrojet activity index AE and its universal time variations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1966, 71(3): 785-801 doi: 10.1029/jz071i003p00785 [2] BARGATZE L F, BAKER D N, MCPHERRON R L, et al. Magnetospheric impulse response for many levels of geomagnetic activity[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1985, 90(A7): 6387-6394 doi: 10.1029/ja090ia07p06387 [3] KLIMAS A J, VASSILIADIS D, BAKER D N. Data-derived analogues of the magnetospheric dynamics[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1997, 102(A12): 26993-27009 doi: 10.1029/97JA02414 [4] WEIGEL R S, HORTON W, TAJIMA T, et al. Forecasting auroral electrojet activity from solar wind input with neural networks[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1999, 26(10): 1353-1356 doi: 10.1029/1999GL900280 [5] 郑志超, 张科灯, 万欣, 等. 基于神经网络的磁平静期赤道电集流预测[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(3): 392-401 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.03.392ZHENG Zhichao, ZHANG Kedeng, WAN Xin, et al. Prediction of equatorial electrojet based on the neural network during quiet time[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(3): 392-401 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.03.392 [6] FERREIRA A A, BORGES R A. Performance analysis of distinct feed-forward neural networks structures on the AE index prediction[C]// IEEE Aerospace Conference. Big Sky: IEEE, 2021: 1-7. DOI: 10.1109/AERO50100.2021.9438504 [7] CAI L, MA S Y, ZHOU Y L. Prediction of SYM-H index during large storms by NARX neural network from IMF and solar wind data[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2010, 28(2): 381-393 doi: 10.5194/angeo-28-381-2010 [8] AMARIUTEI O A, GANUSHKINA N Y. On the prediction of the auroral westward electrojet index[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2012, 30(5): 841-847 doi: 10.5194/angeo-30-841-2012 [9] 邹自明, 曹晋滨, 李毅. 太阳风扰动对极光电急流和环电流指数的影响[J]. 空间科学学报, 2012, 32(1): 14-19 doi: 10.11728/cjss2012.01.014ZOU Ziming, CAO Jinbin, LI Yi. Influence of solar wind disturbance on ring current and auroral electrojet indexes[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2012, 32(1): 14-19 doi: 10.11728/cjss2012.01.014 [10] GOPINATH S, PRINCE P R. A comparison of machine-learning techniques for the prediction of the auroral electrojet index[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2019, 128(7): 172 doi: 10.1007/s12040-019-1194-6 [11] MANSHOUR P, BALASIS G, CONSOLINI G, et al. Causality and information transfer between the solar wind and the magnetosphere–ionosphere system[J]. Entropy, 2021, 23(4): 390 doi: 10.3390/e23040390 [12] NEWELL P T, LIOU K, SOTIRELIS T, et al. Polar ultraviolet imager observations of global auroral power as a function of polar cap size and magnetotail stretching[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2001, 106(A4): 5895-5905 doi: 10.1029/2000ja003034 [13] LIOU K, CARBARY J F, NEWELL P T, et al. Correlation of auroral power with the polar cap index[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2003, 108(A3): 1108 doi: 10.1029/2002JA009556 [14] CHEN A Q, LI J W, YANG G L, et al. Calculating auroral oval pattern by AE index[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2008, 22(1): 91-96 [15] MILAN S E. Both solar wind-magnetosphere coupling and ring current intensity control of the size of the auroral oval[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009, 36(18): L18101 doi: 10.1029/2009GL039997 [16] 杨秋菊, 胡泽骏, 韩德胜, 等. 基于行星际/太阳风和地磁条件的紫外极光卵边界建模和预测[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(2): 426-439 doi: 10.6038/cjg20160203YANG Qiuju, HU Zejun, HAN Desheng, et al. Modeling and prediction of ultraviolet auroral oval boundaries based on IMF/solar wind and geomagnetic parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(2): 426-439 doi: 10.6038/cjg20160203 [17] HAN Y Y, HAN B, HU Z J, et al. Prediction and variation of the auroral oval boundary based on a deep learning model and space physical parameters[J]. Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics, 2020, 27(1): 11-22 doi: 10.5194/npg-27-11-2020 [18] 韩冰, 连慧芳, 胡泽骏. 基于神经网络模型的紫外极光卵边界建模[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2019, 49(5): 531-542 doi: 10.1360/N092018-00227HAN Bing, LIAN Huifang, HU Zejun. Modeling of ultraviolet auroral oval boundaries based on neural network technology[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Technologica, 2019, 49(5): 531-542 doi: 10.1360/N092018-00227 [19] 胡泽骏, 韩冰, 连慧芳. 基于广义回归神经网络的行星际/太阳风参数和地磁指数的紫外极光强度建模[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(5): 1738-1750 doi: 10.6038/cjg2020N0151HU Zejun, HAN Bing, LIAN Huifang. Modeling of ultraviolet auroral intensity based on Generalized Regression Neural Network associated with IMF/solar wind and geomagnetic parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(5): 1738-1750 doi: 10.6038/cjg2020N0151 [20] HU Z J, HAN B, ZHANG Y S, et al. Modeling of ultraviolet aurora intensity associated with interplanetary and geomagnetic parameters based on neural networks[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19(11): e2021SW002751 doi: 10.1029/2021SW002751 [21] NEWELL P T, LIOU K, SOTIRELIS T, et al. Auroral precipitation power during substorms: a Polar UV Imager-based superposed epoch analysis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2001, 106(A12): 28885-28896 doi: 10.1029/2000ja000428 [22] GERMANY G A, TOOR M R, TOOR D G, et al. Use of FUV auroral emissions as diagnostic indicators[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1994, 99(A1): 383-388 doi: 10.1029/93JA02357 [23] CLIVER E W, KAMIDE Y, LING A G. Mountains versus valleys: semiannual variation of geomagnetic activity[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2000, 105(A2): 2413-2424 doi: 10.1029/1999ja900439 [24] SINGH A K, RAWAT R, PATHAN B M. On the UT and seasonal variations of the standard and SuperMAG auroral electrojet indices[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2013, 118(8): 5059-5067 doi: 10.1002/jgra.50488 [25] 万秉东, 李敏, 王源, 等. 极光电集流纬度变化特征初步分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2013, 28(4): 1655-1661 doi: 10.6038/pg20130403WAN Bingdong, LI Min, WANG Yuan, et al. A preliminary analysis of the center latitude distribution of auroral electrojet[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2013, 28(4): 1655-1661 doi: 10.6038/pg20130403 [26] 王秋军, 杜爱民, 赵旭东, 等. 1998年8月6日亚暴期间极光电集流指数AE的特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(12): 2943-2950 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.12.002WANG Qiujun, DU Aimin, ZHAO Xudong, et al. Manifestation of the AE index in substorms on August 6, 1998[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(12): 2943-2950 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.12.002 [27] 徐文耀. 亚暴期间极光电集流带的变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(3): 607-615XU Wenyao. Variations of the auroral electrojet belt during substorms[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(3): 607-615 [28] SPECHT D F. A general regression neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1991, 2(6): 568-576 doi: 10.1109/72.97934 [29] NEWELL P T, GJERLOEV J W. Evaluation of SuperMAG auroral electrojet indices as indicators of substorms and auroral power[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2011, 116(A12): A12211 doi: 10.1029/2011JA016779 [30] NEWELL P T, GJERLOEV J W. Substorm and magnetosphere characteristic scales inferred from the SuperMAG auroral electrojet indices[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2011, 116(A12): A12232 doi: 10.1029/2011JA016936 [31] PALLOCCHIA G, AMATA E, CONSOLINI G, et al. AE index forecast at different time scales through an ANN algorithm based on L1 IMF and plasma measurements[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2008, 70(2/3/4): 663-668 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2007.08.038 -
-






 下载:
下载: