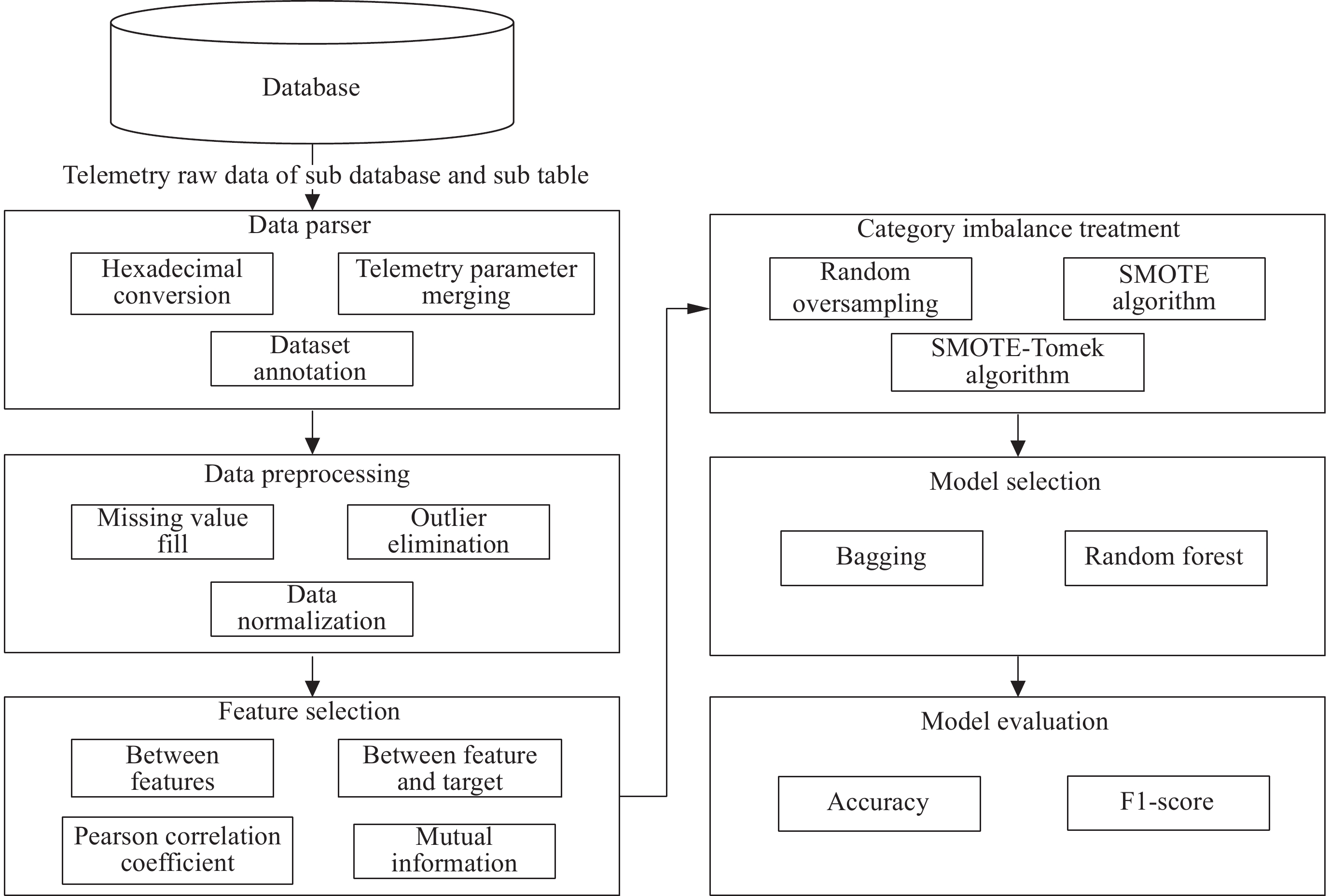
基于集成学习的空间科学卫星工作模式识别
doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.04.20220301022 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2023.04.20220301022
Recognition of Working Pattern of Space Science Satellite Based on Ensemble Learning
-
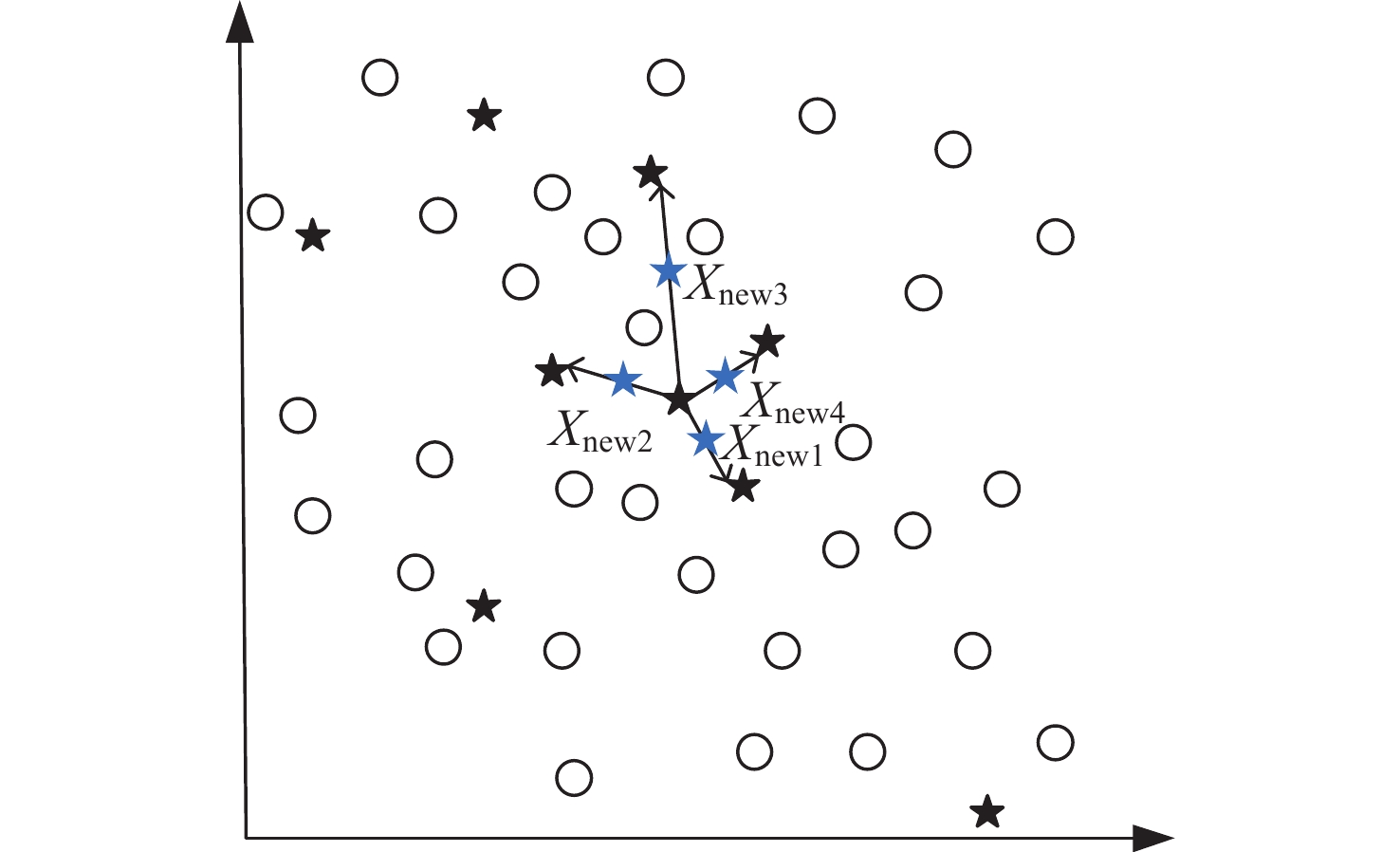
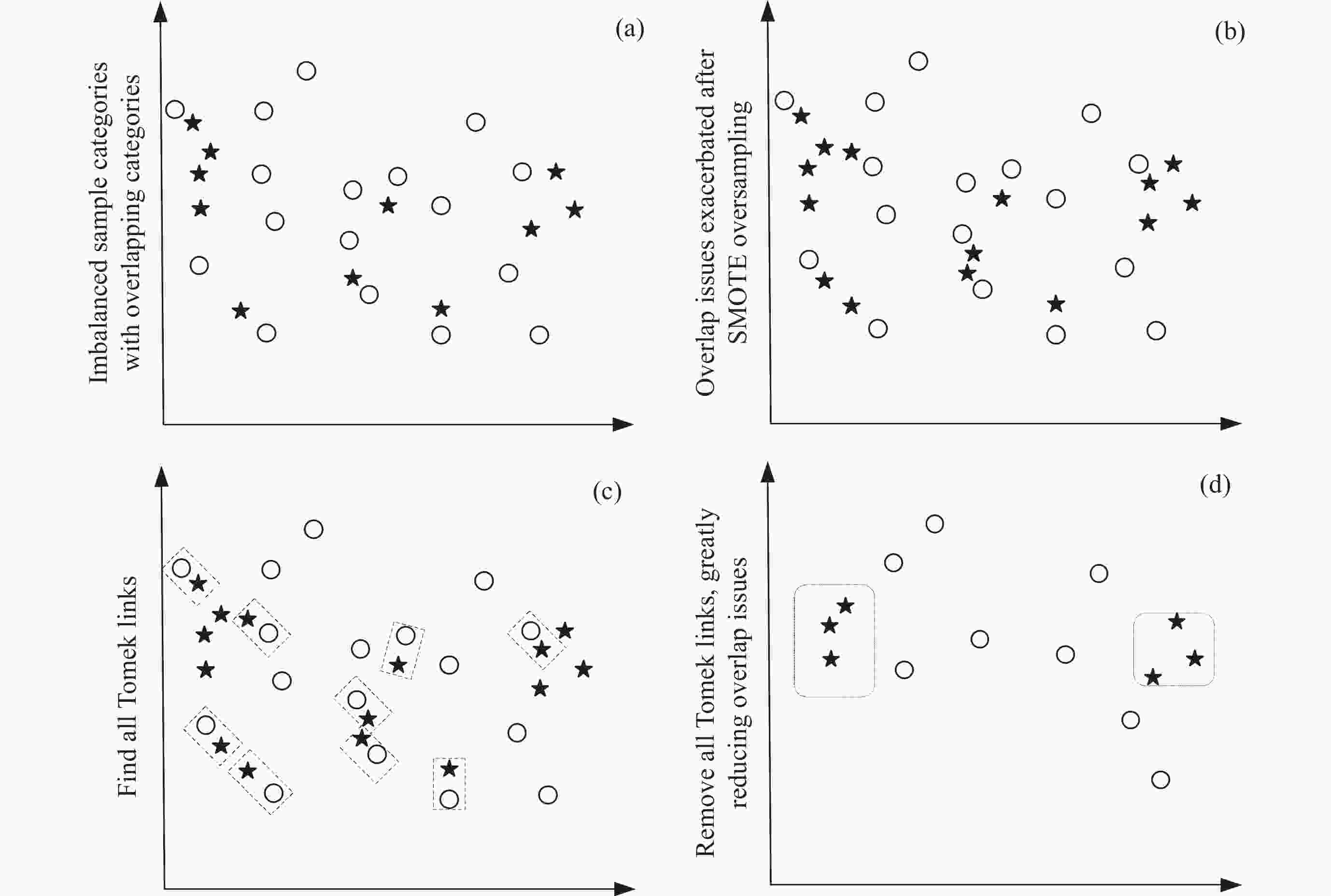
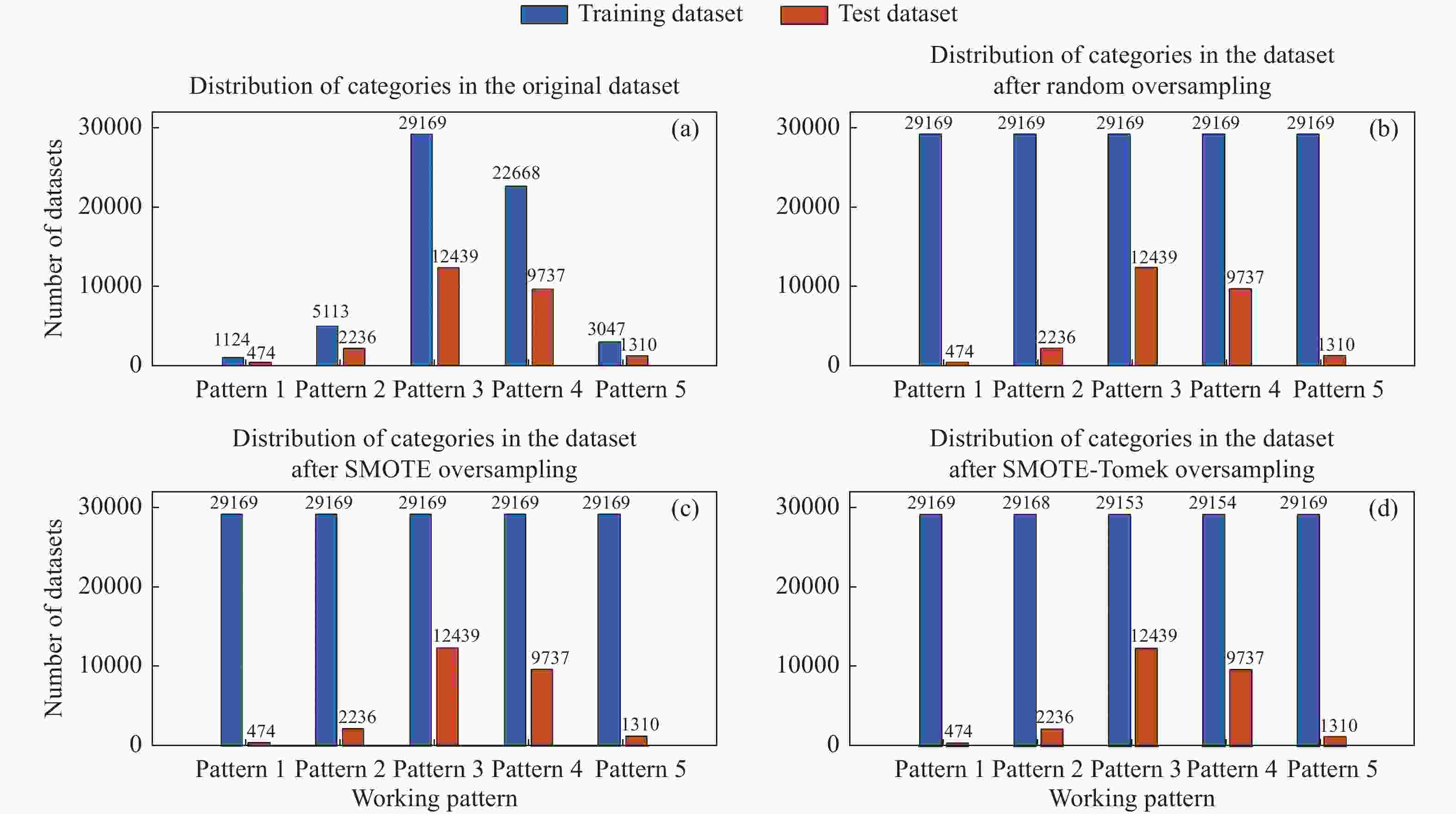
摘要: 针对空间科学卫星遥测参数数据量大且特征维度高、需要消耗大量人力资源预先设置海量阈值、预先设置的阈值可能不再适用、现有监测手段可扩展性低等问题,提出了一种基于集成学习的空间科学卫星工作模式识别方法。该方法采用相关系数统计特性和互信息理论对遥测参数数据进行筛选降维,使用数据重采样技术解决数据集中存在的类别不平衡问题,构建集成学习模型,实现空间科学卫星工作模式的识别。借助某型号科学卫星真实遥测参数数据对该方法进行验证,在短时内便可构建完成算法模型,模型对整体类别的识别正确率高达99.67%,可正确识别多数类样本和少数类样本,为地面运控人员判断空间科学卫星工作模式提供了决策依据。Abstract: Aiming at the issues of space science satellite telemetry parameters, such as large amount of data, high dimension, the need of numerous artificial resource consumption for preset massive thresholds, the preset thresholds that may not be applicable, and the current monitoring methods with low scalability, a working pattern recognition method is proposed for scientific satellite based on ensemble learning. Correlation coefficient statistical characteristics and mutual information theory are used to screen and reduce the dimension of telemetry parameter data. Data resampling technology is used to solve the problem of category imbalance for the dataset. An integrated learning model is used to identify the working mode of space science satellite. The method is verified with the real telemetry parameter data of quantum science satellites. And the algorithm model can be constructed in a short time, and the overall recognition accuracy rate reaches 99.67%, which can correctly identify the majority and minority class samples. The method can provide decision-making basis for ground personnel to judge the working mode of space science satellites.
-
表 1 皮尔逊系数与相关程度的关系
Table 1. Relationship between Pearson coefficient and correlation degree
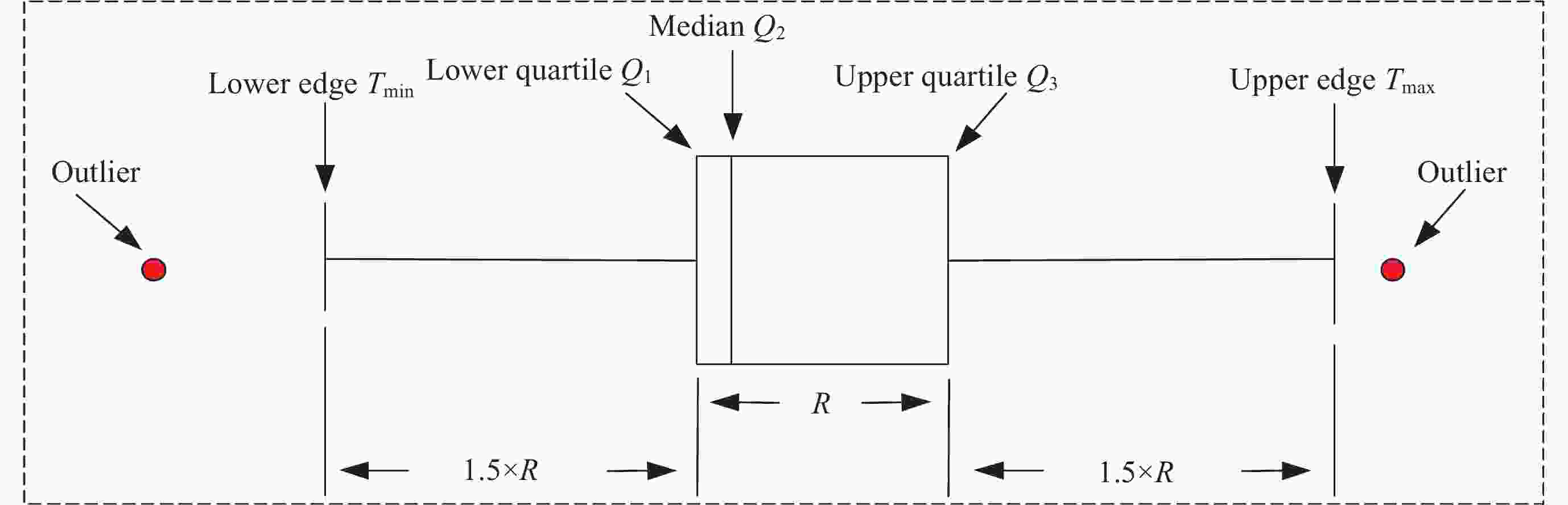
皮尔逊相关系数绝对值$ |\rho | $取值 相关程度 $ 0 \leqslant |\rho | < 0.3 $ 低相关 $ 0.3 \leqslant |\rho | < 0.8 $ 中相关 $ 0.8 \leqslant |\rho | \leqslant 1 $ 高相关 表 2 实验环境信息
Table 2. Experimental environment information
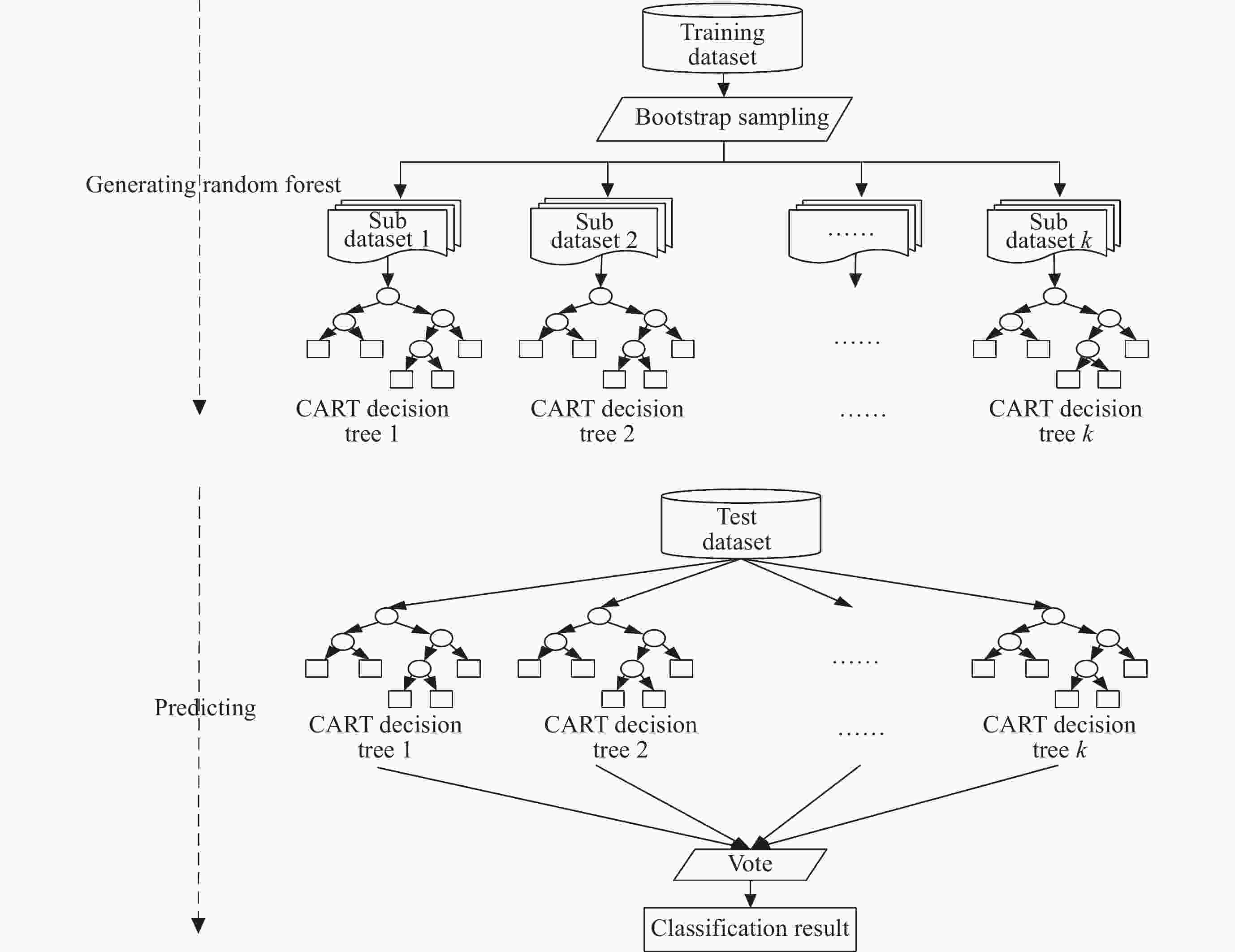
类目 详细信息 CPU 8核i7-1165 G7 2.8 GHz 内存 16 GByte 硬盘 500 GByte 操作系统 Windows 10家庭中文版 编程语言 Python 编程工具 Pycharm Community 2021.3 表 3 随机森林模型(基学习器数19)在不同数据集上的性能表现
Table 3. Performance of random forest model (number of base learners 19) on different datasets
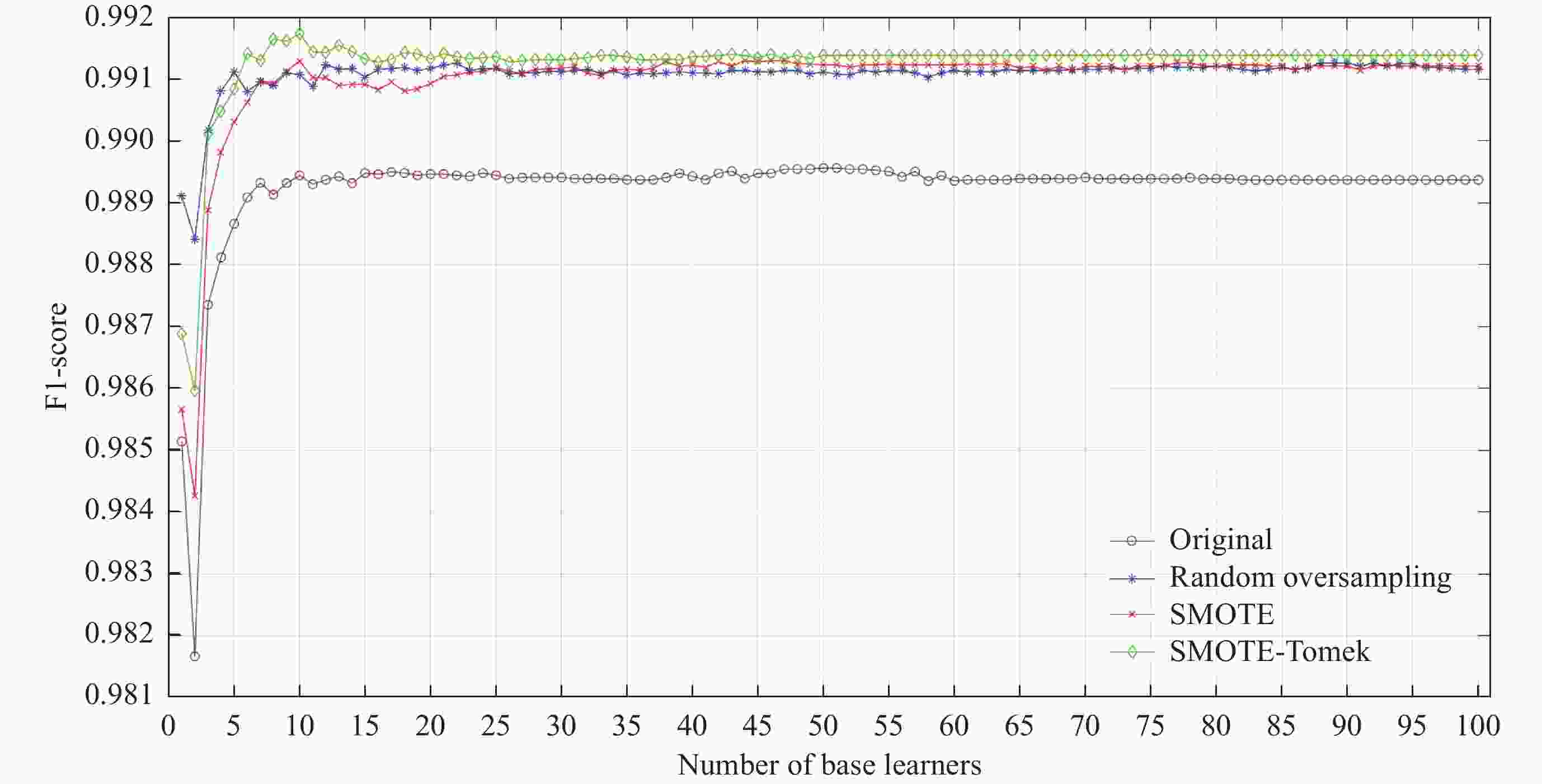
数据集类别 正确率 F1-score 原始数据集 0.9966 0.9894 随机过采样后数据集 0.9967 0.9911 SMOTE过采样后数据集 0.9967 0.9908 SMOTE-Tomek过采样后数据集 0.9967 0.9914 注 黑体数字表示该数据在所列中表现最优。 表 4 不同机器学习模型的性能表现
Table 4. Performance of different machine learning models
机器学习模型类别 正确率 F1-score 训练时间/s 朴素贝叶斯 0.7456 0.6176 0.18 逻辑回归 0.9309 0.8664 6.42 支持向量机 0.9169 0.8483 144.36 CART决策树 0.9959 0.9896 2.88 随机森林(基学习器数19) 0.9967 0.9914 4.36 注 黑体数字表示该数据在所列中表现最优。 -
[1] 彭喜元, 庞景月, 彭宇, 等. 航天器遥测数据异常检测综述[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2016, 37(9): 1929-1945 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2016.09.002PENG Xiyuan, PANG Jingyue, PENG Yu, et al. Review on anomaly detection of spacecraft telemetry data[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 37(9): 1929-1945 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2016.09.002 [2] MARTÍNEZ-HERAS J A, DONATI A, KIRSCH M G F, et al. New Telemetry monitoring paradigm with novelty detection[C]//SpaceOps 2012 Conference. Stockholm, Sweden: AIAA, 2012 [3] TAGAWA T, YAIRI T, TAKATA N, et al. Data monitoring of spacecraft using mixture probabilistic principal component analysis and hidden Semi-Markov models[C]//Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Data Mining and Intelligent Information Technology Applications. Macao, China: IEEE, 2011 [4] 李鑫, 高家智, 崔俊峰, 等. 一种遥测缓变参数自动判读的新方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 39(5): 585-592LI Xin, GAO Jiazhi, CUI Junfeng, et al. A novel method of automatic interpretation for slow-varying telemetry parameters[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2018, 39(5): 585-592 [5] 史欣田, 庞景月, 张新, 等. 基于集成极限学习机的卫星大数据分析[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2018, 39(12): 81-91 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1803770SHI Xintian, PANG Jingyue, ZHANG Xin, et al. Satellite big data analysis based on bagging extreme learning machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2018, 39(12): 81-91 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1803770 [6] 李楠, 张云燕, 李言俊. 一种自旋稳定卫星姿态传感器数据异常的诊断方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2011, 32(6): 1327-1332LI Nan, ZHANG Yunyan, LI Yanjun. A diagnosis algorithm for abnormal data of spin-stabilized satellite attitude sensors[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2011, 32(6): 1327-1332 [7] 徐宇航, 皮德常. 卫星异常模式挖掘方法[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2015, 36(9): 1988-1992XU Yuhang, PI Dechang. Method to mine satellite abnormal patterns[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2015, 36(9): 1988-1992 [8] 王昊天, 厉小润, 赵辽英. 基于箱型图与折点阈值边界的电缆分割方法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2021, 38(9): 244-249WANG Haotian, LI Xiaorun, ZHAO Liaoying. Cable segmentation method based on box-plot and turning point threshold boundary[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2021, 38(9): 244-249 [9] 韩霞, 李秀霞, 史盛楠, 等. 基于Z分数与Sen’s斜率的研究前沿识别方法——以图书馆学领域为例[J]. 情报科学, 2020, 38(1): 93-97,139 doi: 10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2020.01.015HAN Xia, LI Xiuxia, SHI Shengnan, et al. Research fronts identification based on Z-Score and Sen’s Slope method——taking the field of library science as an example[J]. Information Science, 2020, 38(1): 93-97,139 doi: 10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2020.01.015 [10] 纪德洋, 金锋, 冬雷, 等. 基于皮尔逊相关系数的光伏电站数据修复[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(4): 1514-1522 doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.211172JI Deyang, JIN Feng, DONG Lei, et al. Data repairing of photovoltaic power plant based on pearson correlation coefficient[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(4): 1514-1522 doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.211172 [11] 徐遐龄, 胡伟, 王春明, 等. 考虑特征组合效应的电网关键稳定特征筛选方法研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(8): 2232-2238 doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.171734XU Xialing, HU Wei, WANG Chunming, et al. Research on power systems key feature selection based on combination effect considering the stability rule[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(8): 2232-2238 doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.171734 [12] CHAWLA N V, JAPKOWICZ N, KOTCZ A. Editorial: special issue on learning from imbalanced data sets[J]. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 2004, 6(1): 1-3 doi: 10.1145/1007730.1007733 [13] VAN DER PUTTEN P, VAN SOMEREN M. A bias-variance analysis of a real world learning problem: the CoIL challenge 2000[J]. Machine Learning, 2004, 57(1/2): 177-195 doi: 10.1023/B:MACH.0000035476.95130.99 [14] CHAWLA N V, BOWYER K W, HALL L O, et al. SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2002, 16: 321-357 doi: 10.1613/jair.953 [15] BATISTA G E A P A, PRATI R C, MONARD M C. A study of the behavior of several methods for balancing machine learning training data[J]. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 2004, 6(1): 20-29 doi: 10.1145/1007730.1007735 [16] 杨思节. 基于拉曼光谱的海水微塑料快速识别方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. DOI: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2021.004188YANG Sijie. Study on Rapid Recognition of Marine Microplastics Based on Raman Spectroscopy[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021. DOI: 10.27061/d. cnki. ghgdu. 2021.004188 [17] 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2018: 1-415ZHOU Zhihua. Machine Learning[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2018: 1-415 -
-





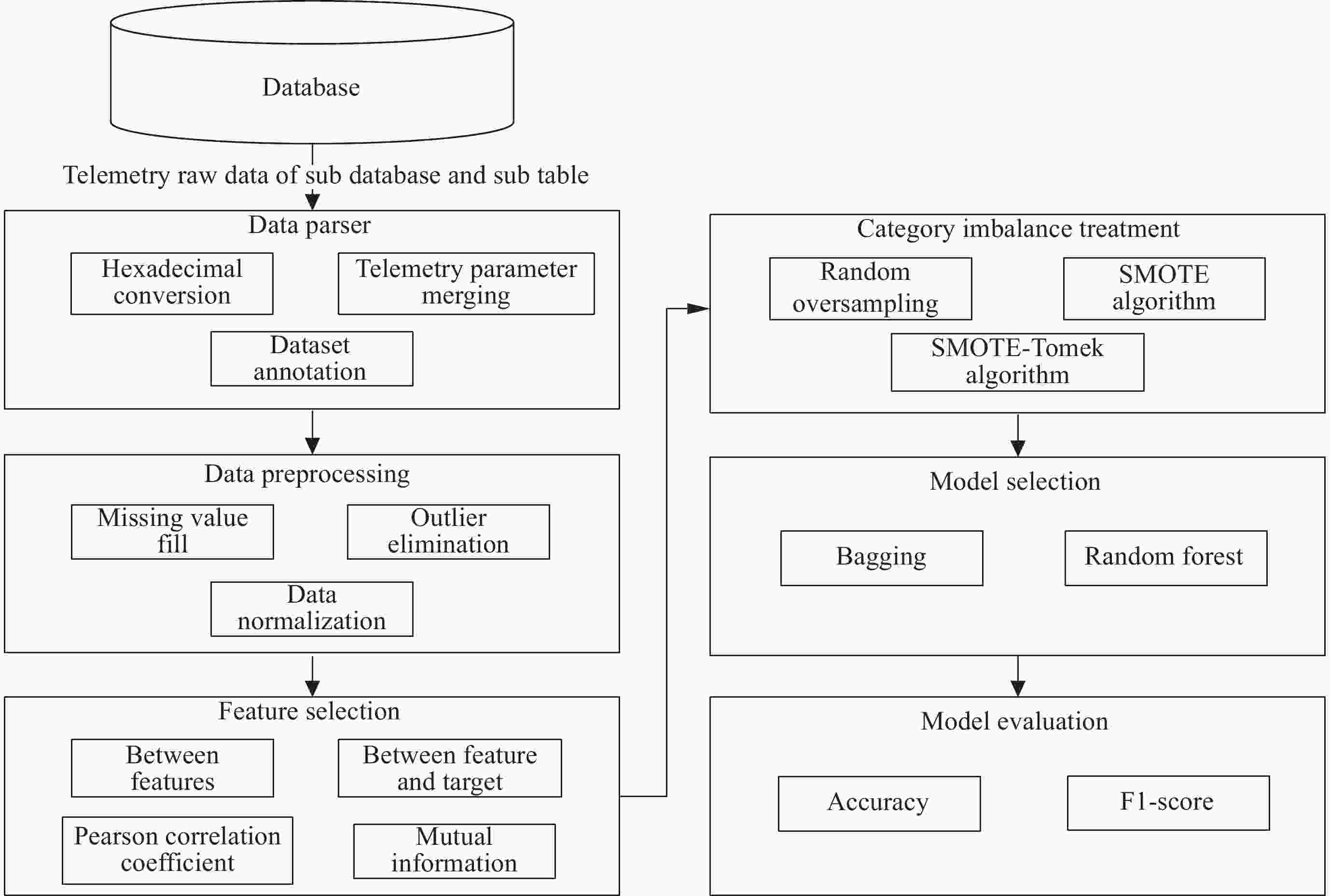
 下载:
下载: