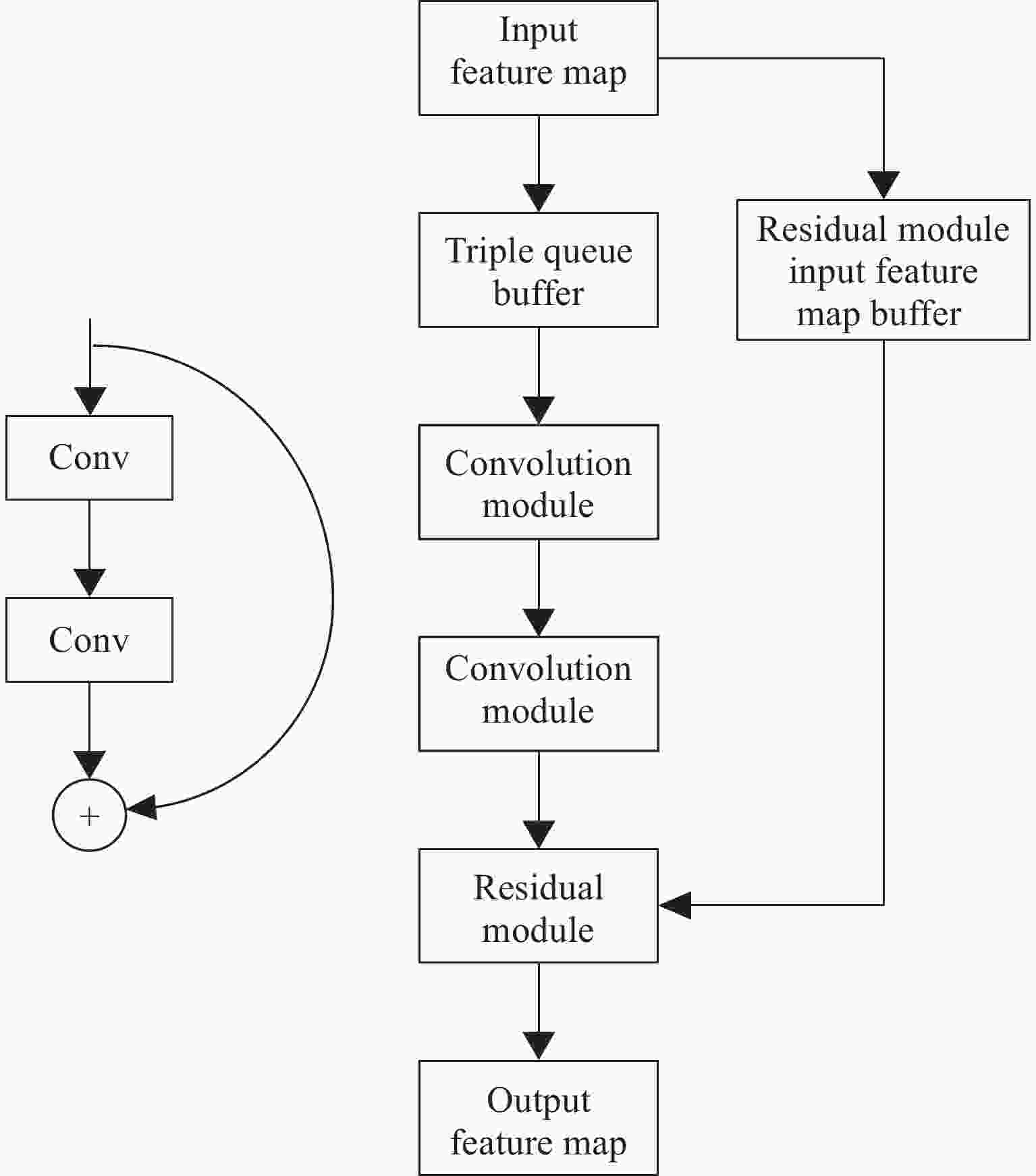
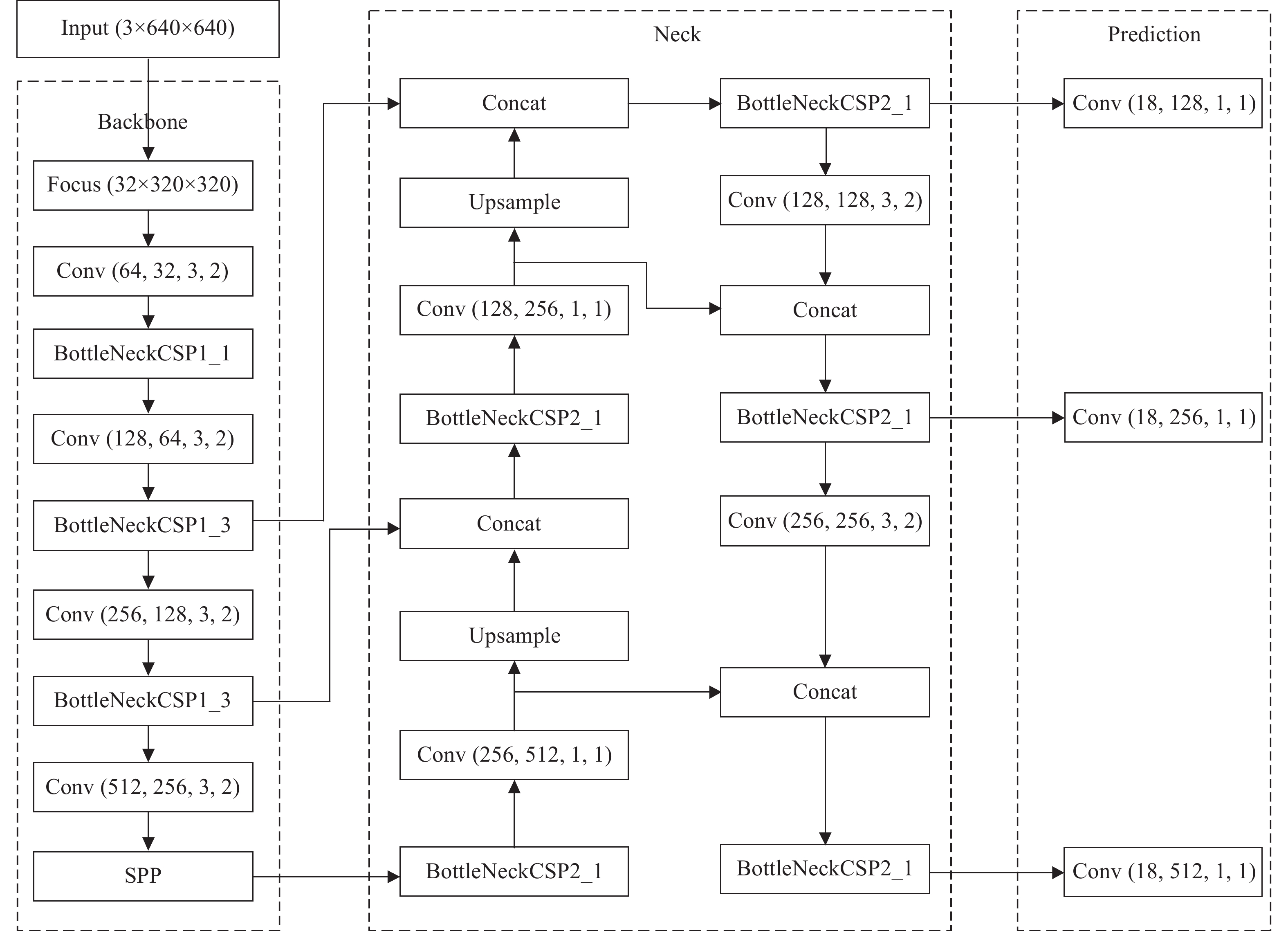
基于宇航级FPGA的YOLOv5s网络模型硬件加速
doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.05.2022-0044 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2023.05.2022-0044
Hardware Acceleration of YOLOv5s Network Model Based on Aerospace-grade FPGA
-
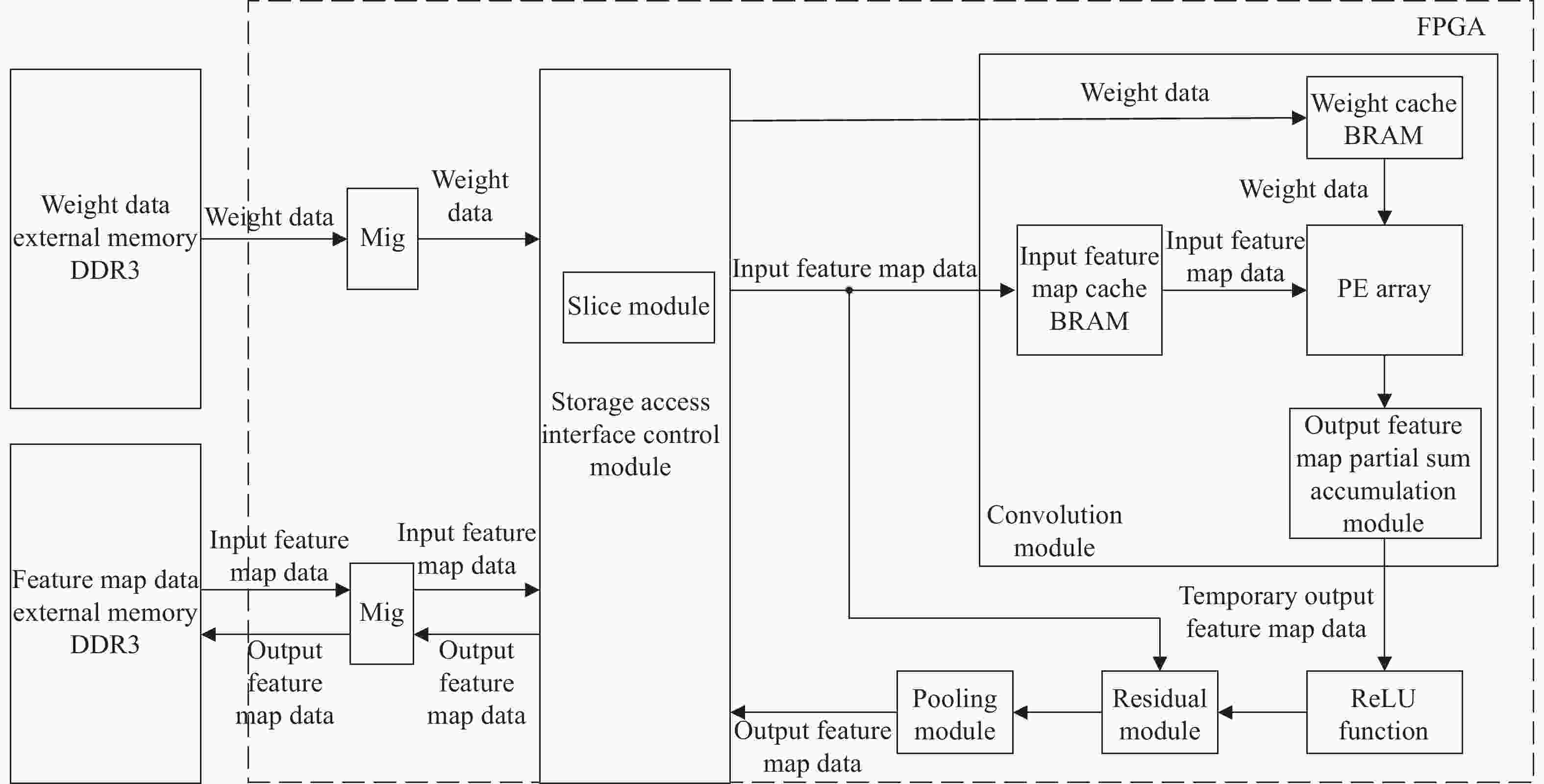
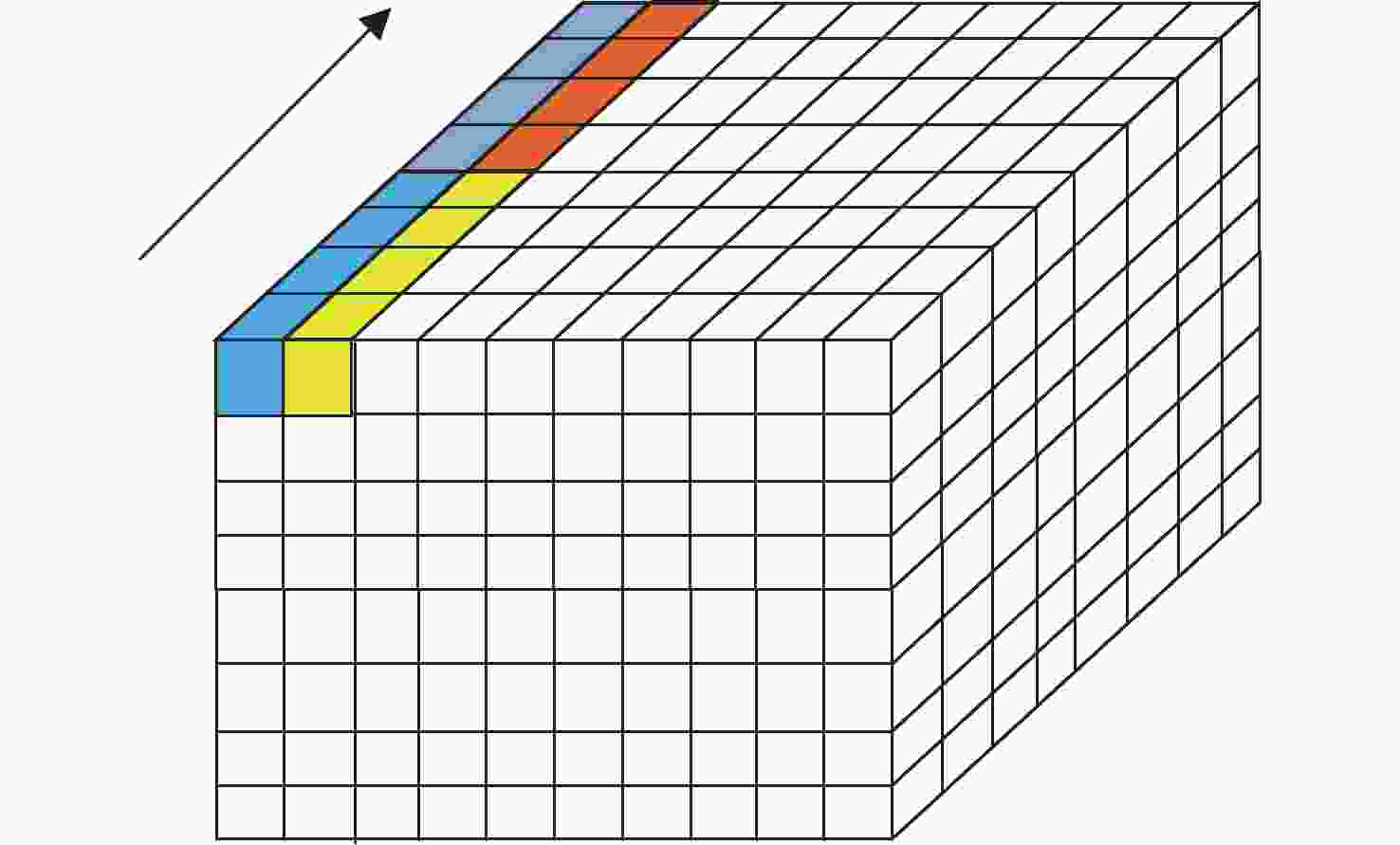
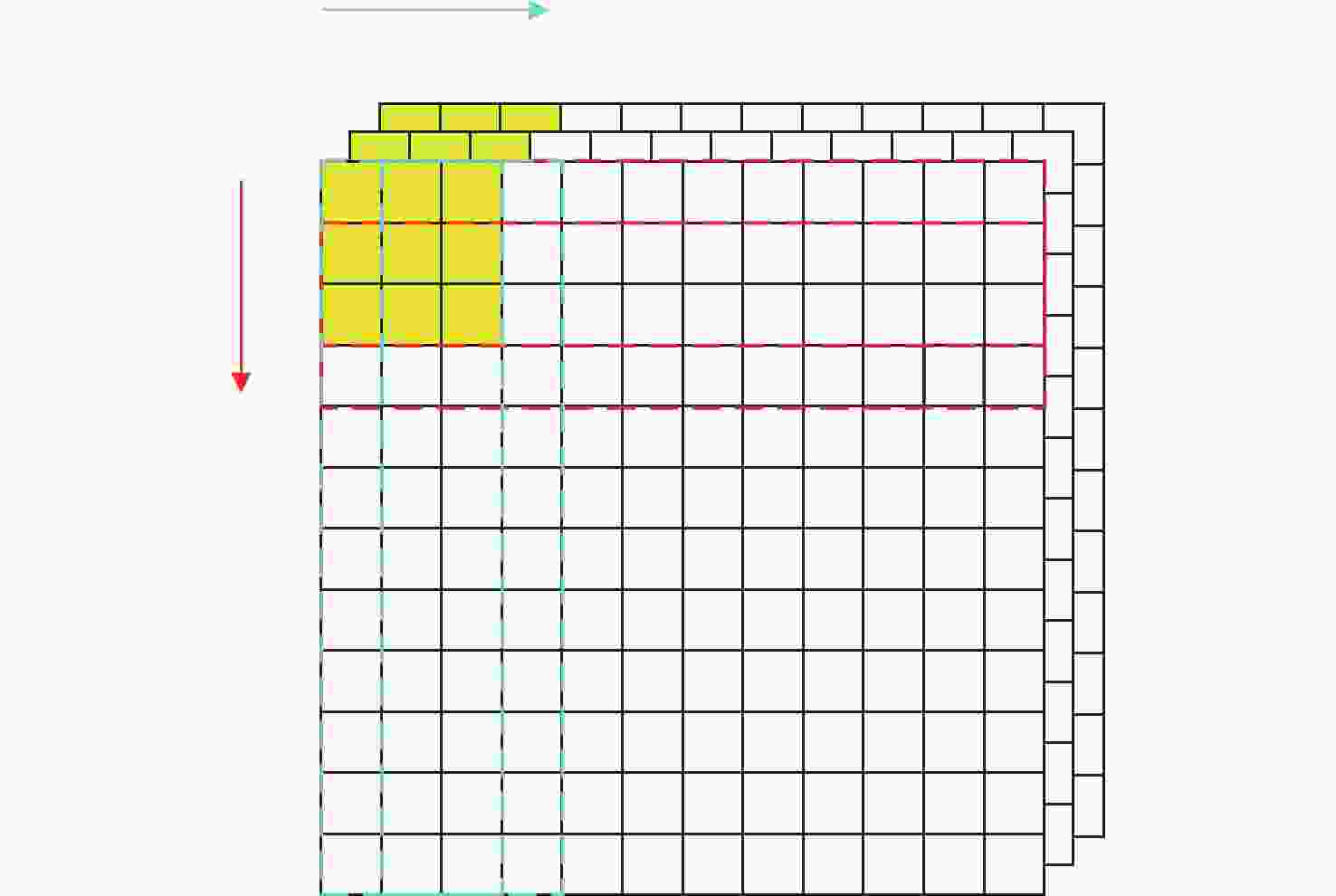
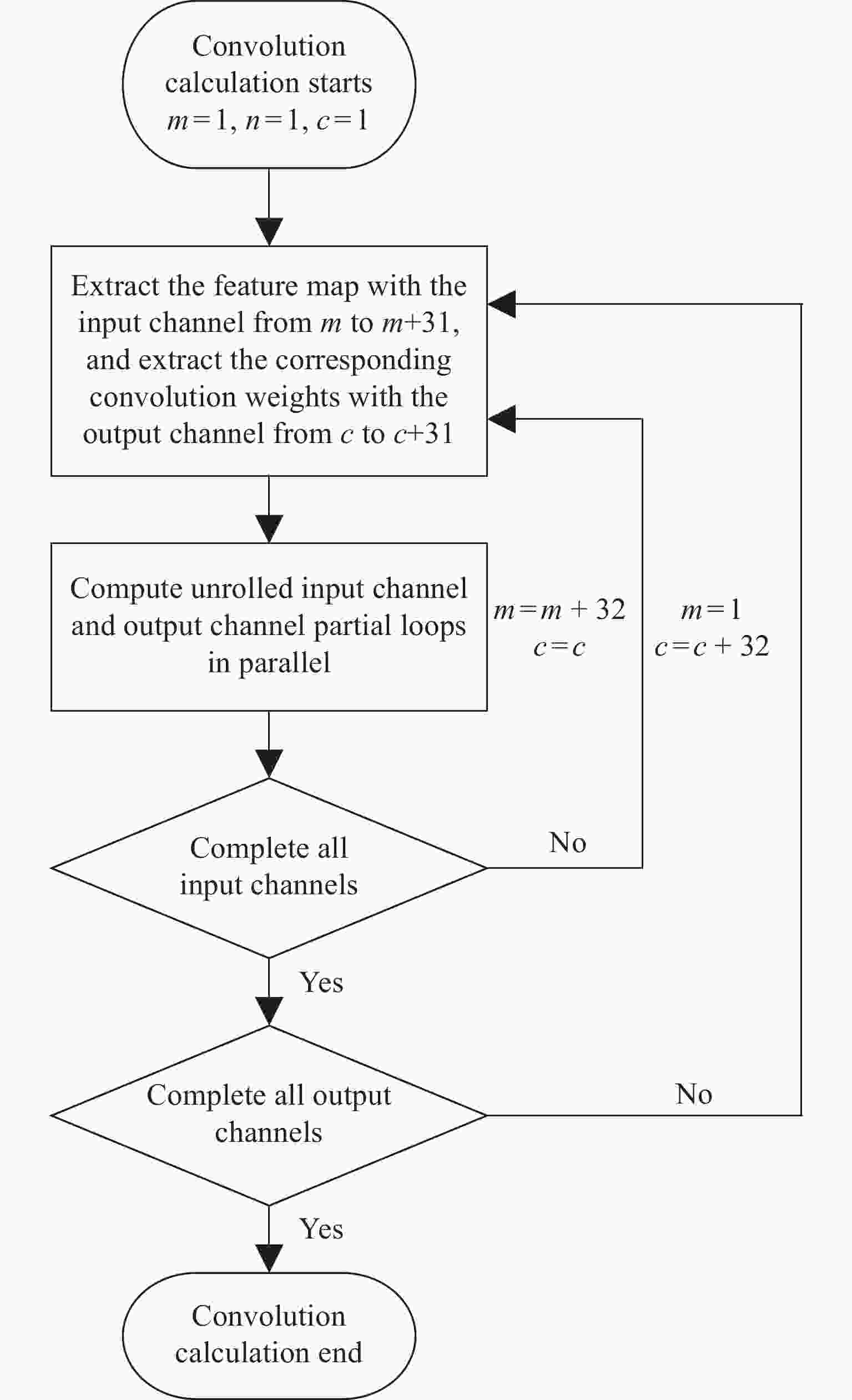
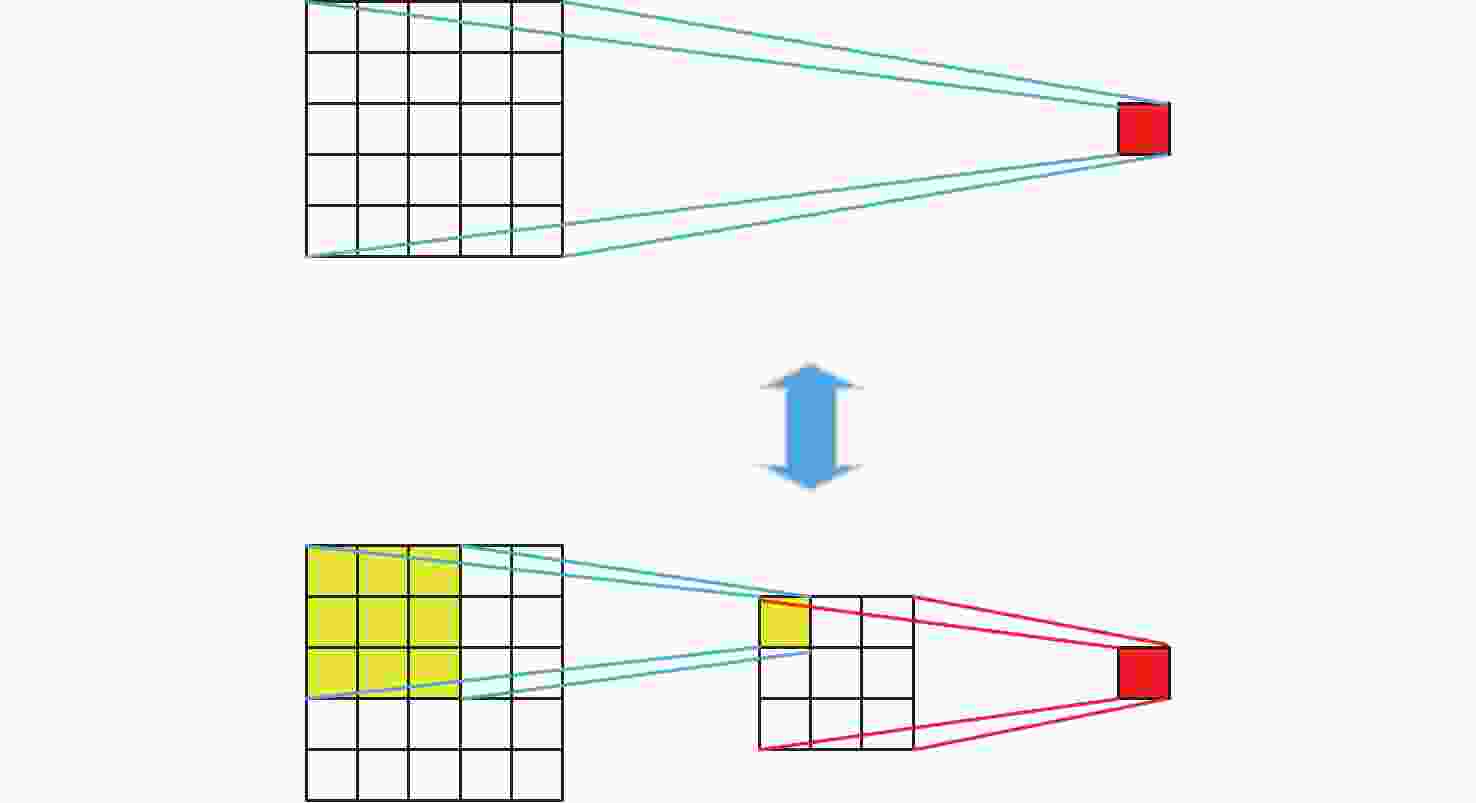
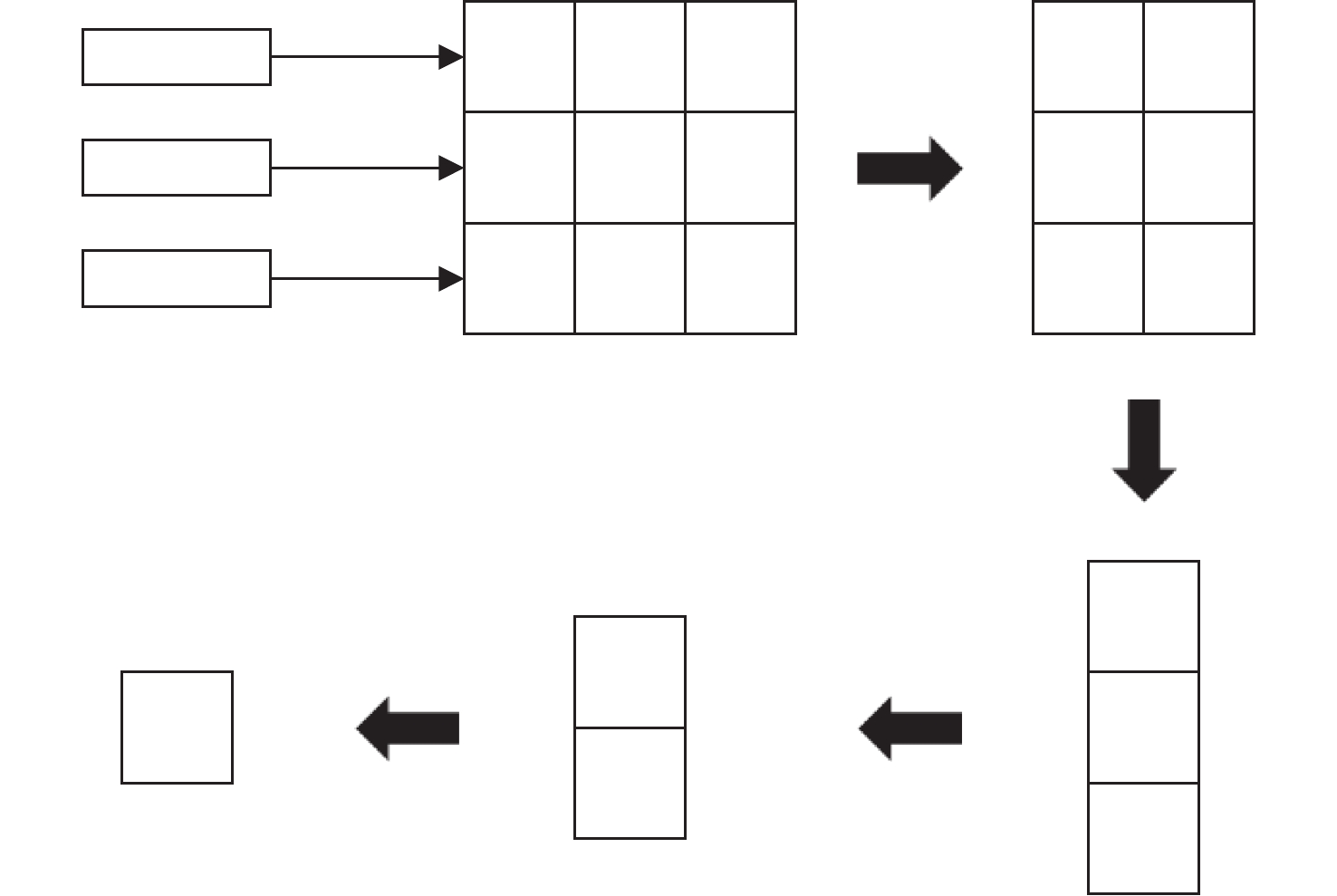
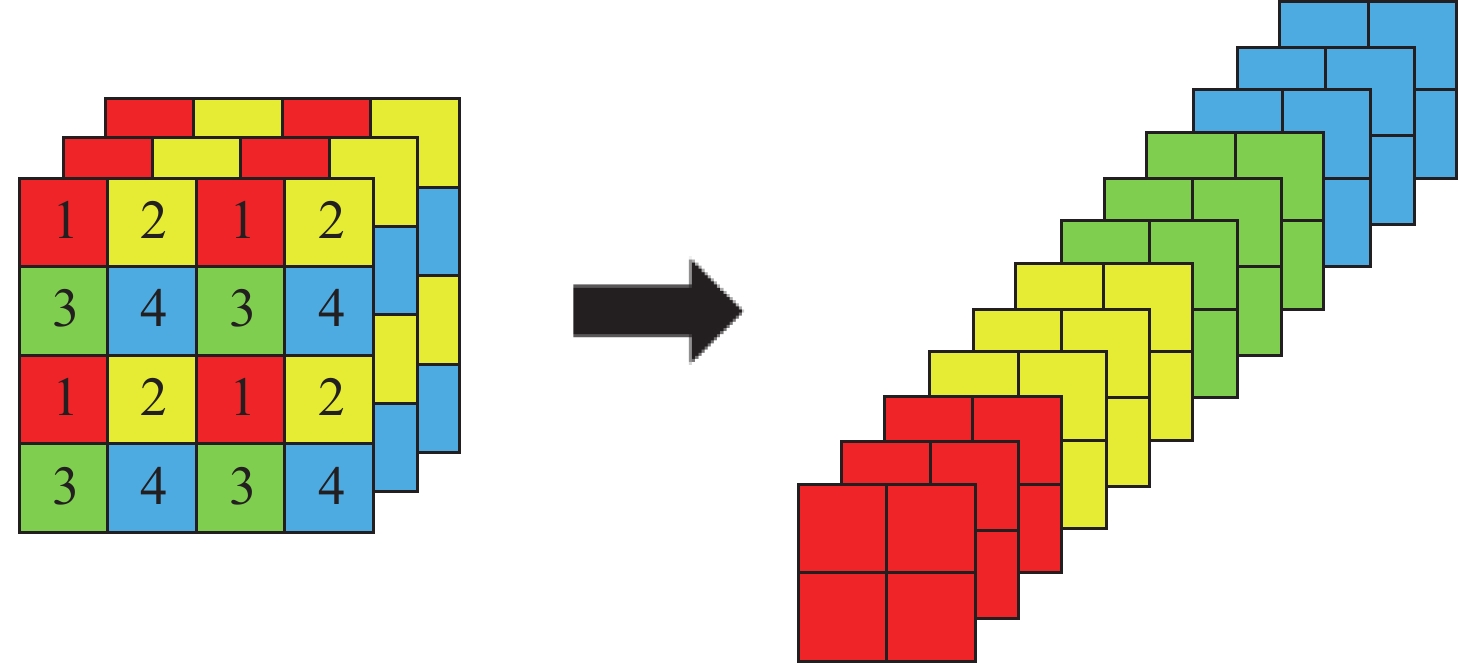
摘要: 由于遥感图像具有分辨率高和背景信息复杂的特点,其对目标检测的精确性和鲁棒性要求越来越高,因此遥感图像处理领域逐渐引入了卷积神经网络算法。然而此类算法通常模型复杂且计算量庞大,难以在空间与资源受限的星上平台高效运行。针对这一问题,提出一种基于宇航级现场可编程门阵列(Filed Programmable Gate Array, FPGA)的卷积神经网络硬件加速架构,并选用YOLOv5s作为目标网络,采用输入与输出通道并行展开以及数据流水线控制的策略进行架构设计。实验结果表明,在使用该处理架构加速YOLOv5s的推理阶段,卷积模块的工作频率可以达到200 MHz,其运算性能高达394.4GOPS(Giga Operations Per Second),FPGA的功耗为14.662 W,数字信号处理(Digital Signal Processing, DSP)计算矩阵的平均计算效率高达96.29%。Abstract: With the rapid development of my country’s remote sensing engineering technology, the resolution of remote sensing images that can be obtained is getting higher and higher, and the image background information is also more complex, which brings great challenges to the accuracy and robustness of traditional target detection methods. With the development of deep learning, the convolutional neural network algorithm has better performance in terms of detection accuracy and robustness than traditional methods. In order to improve the accuracy and robustness of remote sensing image target detection with high resolution and complex background, the remote sensing image target detection algorithm based on convolutional neural network is applied in this field. However, such algorithms usually have complex models and a large amount of calculation, making it difficult to run efficiently on space and resource-constrained on-board platforms. Aiming at this problem, a convolutional neural network forward inference hardware acceleration architecture based on aerospace-grade FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) is proposed, and the YOLOv5s network model is selected as the target algorithm for architecture design. Since the main body of the YOLOv5s network is composed of a large number of convolutional layers, the center of gravity of the accelerator architecture design lies in the convolutional layer. In the design of the architecture, the parallel expansion of input channels and output channels and the optimization strategy of data pipeline control are adopted to effectively improve the real-time processing performance of the inference stage is improved. The experimental results show that when using this processing architecture to accelerate the inference stage of YOLOv5s, the operating frequency of the convolution module can reach 200 MHz, and its computing performance can reach 394.4GOPS (Giga Operations Per Second). The power consumption is 14.662 W, and the average calculation efficiency of the DSP (Digital Signal Processing) calculation matrix is as high as 96.29%. It shows that the use of FPGA for hardware acceleration of convolutional neural networks in resource and power constrained on-board platforms has significant advantages.
-
表 1 不同的CNN在FPGA上实现的情况比较
Table 1. Comparison of different CNN implementations on FPGA
Method 文献[16] 文献[17] 文献[18] 文献[19] 本文 FPGA ZC709 XC7 K325 T ZCU102 VC707 VC709 Network YOLOv2-tiny YOLOv2 YOLOv2 YOLOv2-tiny YOLOv5s 精度/bit 8 32 16 BNN 16 频率/MHz 200 100 300 200 200 DSP 610/900 — 609 168/2800 1024/1200 BRAM 256/545 — 491 1026/1030 1094/1470 LUT 84000/219000 — 95000 86000/304000 166000/433000 FF 65000/437000 — 90000 60000/607000 228000/866000 吞吐量/GOPS 464.5 6.222 102.2 464.7 394.4 功耗/W 10.25 2.555 11.8 8.72 14.662 能耗比
/(GOPS·W–1)45.3 2.435 8.66 53.29 26.90 EDSP 95.2% — — — 96.29% -
[1] ZAIDI S S A, ANSARI M S, ASLAM A, et al. A survey of modern deep learning based object detection models[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022, 126: 103514 doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2022.103514 [2] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90 doi: 10.1145/3065386 [3] HUANG M Y, XU Y, QIAN L X, et al. A bridge neural network-based optical-SAR image joint intelligent interpretation framework[J]. Space: Science & Technology, 2021, 2021: 9841456 [4] KONG T, SUN F C, LIU H P, et al. FoveaBox: Beyound anchor-based object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7389-7398 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3002345 [5] XU Y C, FU M T, WANG Q M, et al. Gliding vertex on the horizontal bounding box for multi-oriented object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(4): 1452-1459 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2974745 [6] LIU Z, CAI Y F, WANG H, et al. Robust target recognition and tracking of self-driving cars with radar and camera information fusion under severe weather conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 6640-6653 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3059674 [7] SINGH B, LI H D, SHARMA A, et al. R-FCN-3000 at 30 fps: Decoupling detection and classification[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 1081-1090 [8] HE K M, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice: IEEE, 2017: 2980-2988 [9] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multiBox detector[C]//14 th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam: Springer, 2016: 21-37 [10] LI Z G, WANG J T. An improved algorithm for deep learning YOLO network based on Xilinx ZYNQ FPGA[C]//2020 International Conference on Culture-oriented Science & Technology (ICCST). Beijing: IEEE, 2020: 447-451 [11] WANG Z X, XU K, WU S X, et al. Sparse-YOLO: Hardware/software Co-design of An FPGA accelerator for YOLOv2[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 116569-116585 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3004198 [12] WANG J, GU S S. FPGA implementation of object detection accelerator based on Vitis-AI[C]//2021 11 th International Conference on Information Science and Technology (ICIST). Chengdu: IEEE, 2021: 571-577 [13] CAI Y F, LUAN T Y, GAO H B, et al. YOLOv4-5 D: An effective and efficient object detector for autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 4503613 [14] 谭显东, 彭辉. 改进YOLOv5的SAR图像舰船目标检测[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(4): 247-254 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2108-0308TAN Xiandong, PENG Hui. Improved YOLOv5 ship target detection in SAR image[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022, 58(4): 247-254 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2108-0308 [15] GAREA A S, HERAS D B, ARGÜELLO F. Caffe CNN-based classification of hyperspectral images on GPU[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2019, 75(3): 1065-1077 doi: 10.1007/s11227-018-2300-2 [16] ZHANG J M, CHENG L F, LI C F, et al. A low-latency FPGA implementation for real-time object detection[C]//2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS). Daegu: IEEE, 2021: 1-5 [17] BI F H, YANG J. Target detection system design and FPGA implementation based on YOLO v2 algorithm[C]//2019 3 rd International Conference on Imaging, Signal Processing and Communication (ICISPC). Singapore: IEEE, 2019: 10-14 [18] ZHANG S G, CAO J, ZHANG Q, et al. An FPGA-based reconfigurable CNN accelerator for YOLO[C]//2020 IEEE 3 rd International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET). Chengdu: IEEE, 2020: 74-78 [19] NGUYEN D T, NGUYEN T N, KIM H, et al. A high-throughput and power-efficient FPGA implementation of YOLO CNN for object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2019, 27(8): 1861-1873 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2019.2905242 [20] 陈浩敏, 姚森敬, 席禹, 等. YOLOv3-tiny的硬件加速设计及FPGA实现[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2021, 43(12): 2139-2149 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2021.12.007CHEN Haomin, YAO Senjing, XI Yu, et al. Design and FPGA implementation of YOLOv3-tiny hardware acceleration[J]. Computer Engineering and Science, 2021, 43(12): 2139-2149 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2021.12.007 [21] 周旗开, 张伟, 李东锦, 等. 基于改进YOLOv5s的光学遥感图像舰船分类检测方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(16): 1628008 doi: 10.3788/LOP202259.1628008ZHOU Qikai, ZHANG Wei, LI Dongjin, et al. Ship classification and detection method for optical remote sensing images based on improved YOLOv5s[J]. Laser and Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(16): 1628008 doi: 10.3788/LOP202259.1628008 [22] 周海, 侯晴宇, 卞春江, 等. 一种FPGA实现的复杂背景红外小目标检测网络[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(2): 295-310 doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0221ZHOU Hai, HOU Qingyu, BIAN Chunjiang, et al. An infrared small target detection network under various complex backgrounds realized on FPGA[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(2): 295-310 doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0221 [23] DODD P E, SHANEYFELT M R, SCHWANK J R, et al. Current and future challenges in radiation effects on CMOS electronics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2010, 57(4): 1747-1763 doi: 10.1109/TNS.2010.2042613 [24] BINDER D, SMITH E C, HOLMAN A B. Satellite anomalies from galactic cosmic rays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1975, 22(6): 2675-2680 doi: 10.1109/TNS.1975.4328188 [25] 胡孔阳, 胡海生, 刘小明. 三模冗余在高性能抗辐射DSP中的应用[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2019, 36(3): 58-60HU Kongyang, HU Haisheng, LIU Xiaoming. The application of TMR on the high performance and anti radiation DSP[J]. Microelectronics & Computer, 2019, 36(3): 58-60 [26] ZHANG X F, WANG J S, ZHU C, et al. DNNBuilder: An automated tool for building high-performance DNN hardware accelerators for FPGAs[C]//2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD). San Diego: IEEE, 2018: 1-8 -
-





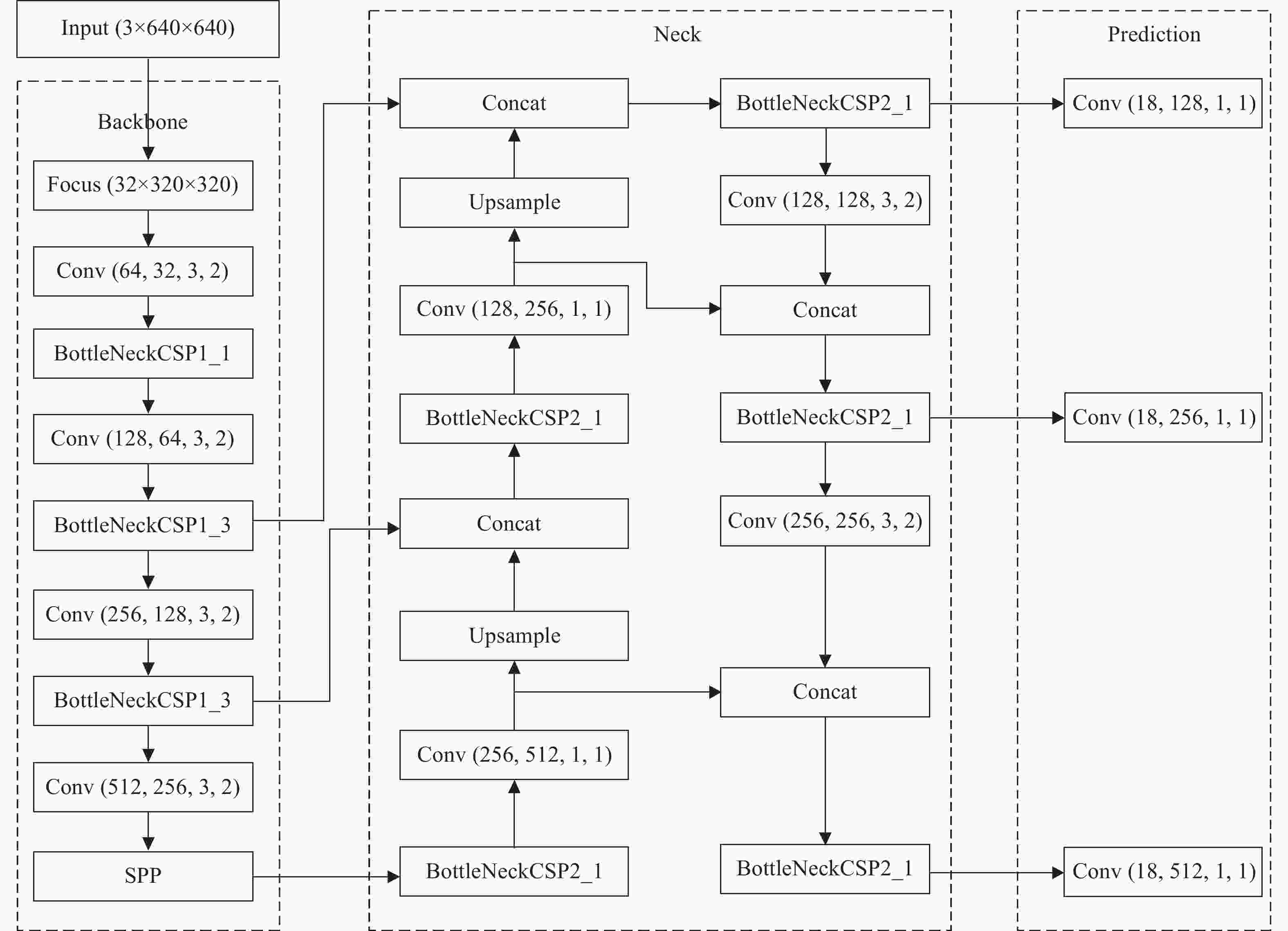
 下载:
下载: