高精度矢量磁力仪地面测试定标系统大型磁屏蔽室仿真分析
doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.05.2022-0067 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2023.05.2022-0067
Simulation of Large-scale Magnetic Shielding Room for High-precision Vector Magnetometer Ground Test and Calibration System
-
摘要: 利用有限元分析方法开展大型磁屏蔽室的仿真分析,完成了高精度矢量磁力仪地面定标用大型磁屏蔽室的建模和性能仿真计算,从屏蔽效能、开口影响及内部磁场均匀度等方面对磁屏蔽室仿真计算和实测结果进行对比。结果表明,磁屏蔽空间内部中心区域的剩磁实测数值与仿真结果一致性较好,剩磁分布趋势基本一致,证明有限元分析方法在磁屏蔽室屏蔽性能定量分析的可行性。通过有限元分析方法,能够实现磁屏蔽室开口剩磁影响的定量计算,为磁屏蔽室门及通风孔设计提供依据;同时可以对内部磁场均匀区大小、残余梯度进行验证,有效避免工程实施后发现性能不满足设计要求的风险,有利于保障大空间磁屏蔽室的性能和建造效率。Abstract: In this paper, the simulation analysis of a large-scale magnetic shielding room is carried out by using the finite element analysis method, and the modeling and performance simulation calculation of a large-scale magnetic shielding room for ground calibration of a high-precision vector magnetometer are completed, and the simulation calculation and measured results of the magnetic shielding room are compared and analyzed from the aspects of shielding effectiveness, opening influence, internal magnetic field uniformity and other aspects. The results show that the measured value of the remnant magnetism in the central area of the magnetic shielding space is in good agreement with the simulated results, and the remnant magnetism distribution trend is basically the same, which proves the feasibility of the finite element analysis method in the quantitative analysis of the shielding performance of the magnetic shielding room. The finite element analysis method can realize the quantitative calculation of the remnant magnetic influence of the shielding room opening, which provides a basis for the design of shielding room doors and ventilation holes, At the same time, the size of the uniform area of the internal magnetic field and the residual gradient can be verified, which effectively avoids the risk of finding the performance does not meet the requirements after the implementation of the project. Aiming at the design and research of large-space magnetic shielding room, the method based on finite element and ANSYS Maxwell software simulation adopted in this paper is conducive to guarantee the performance and construction efficiency of the large-space magnetic shielding room.
-
Key words:
- Vector magnetometer /
- Ground calibration /
- Magnetic shielding room /
- Simulation
-
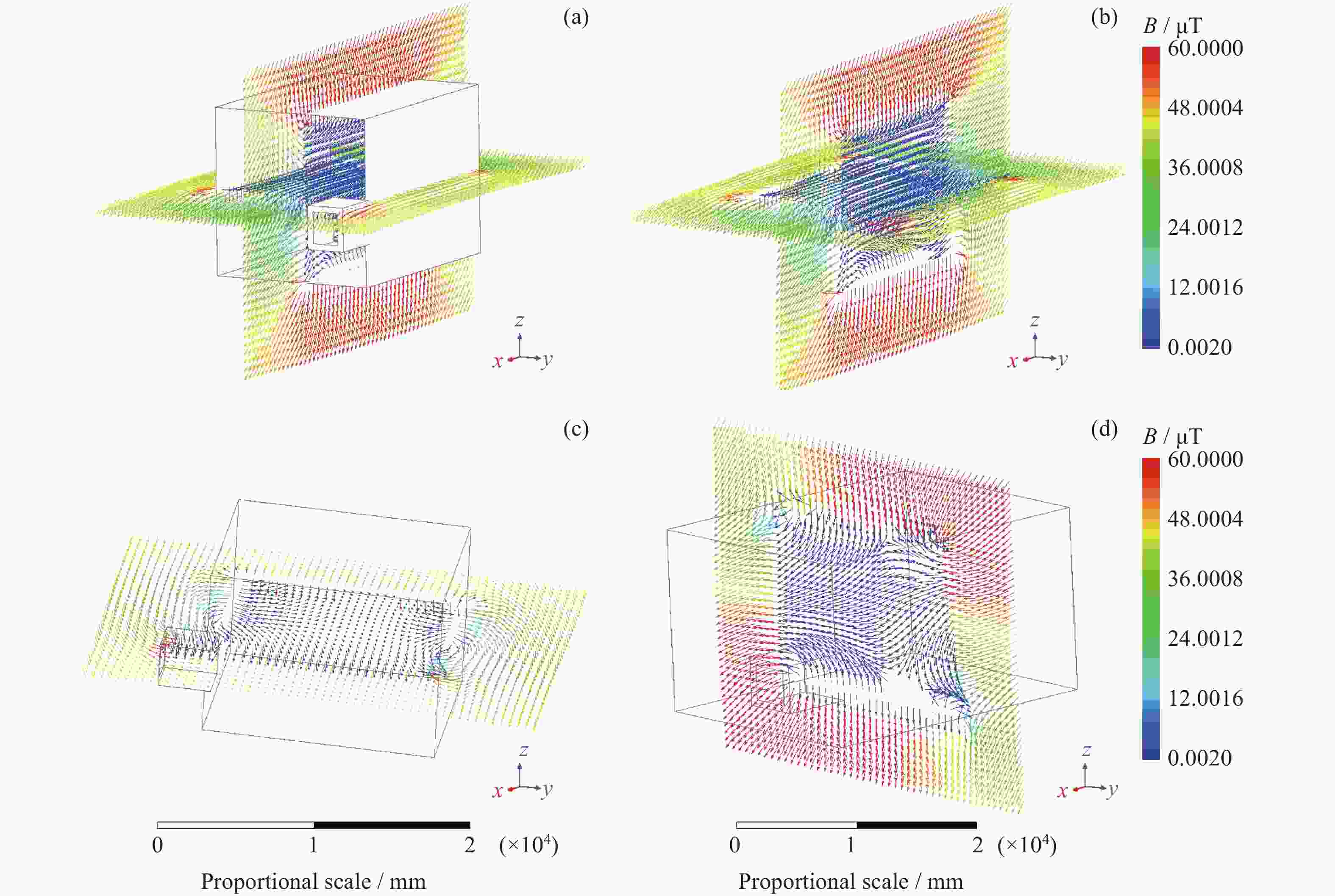
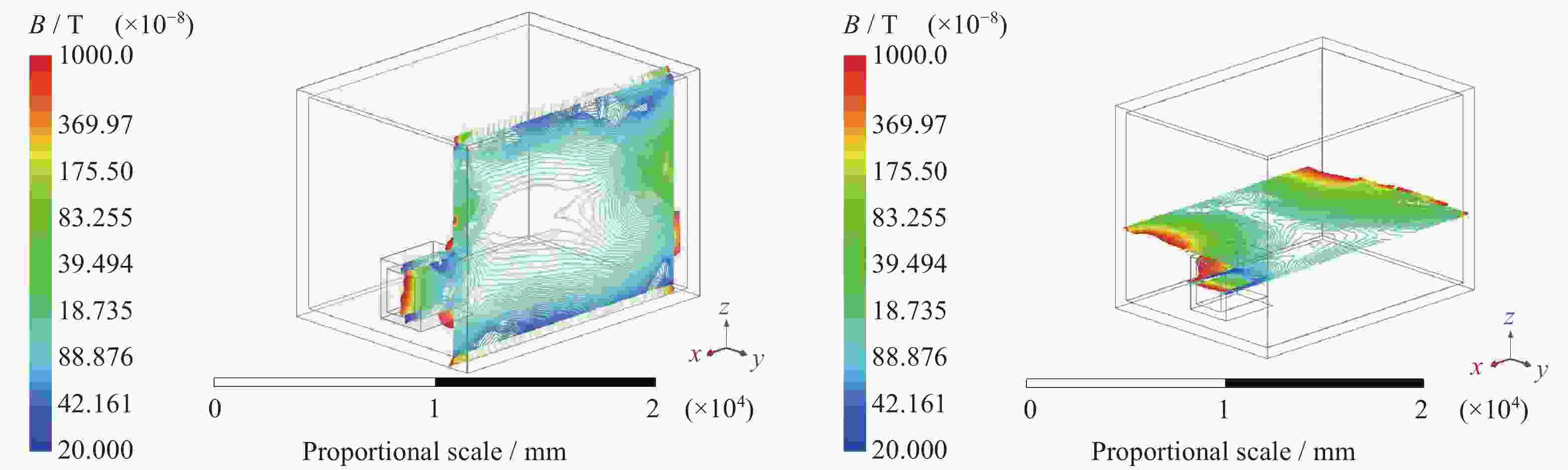
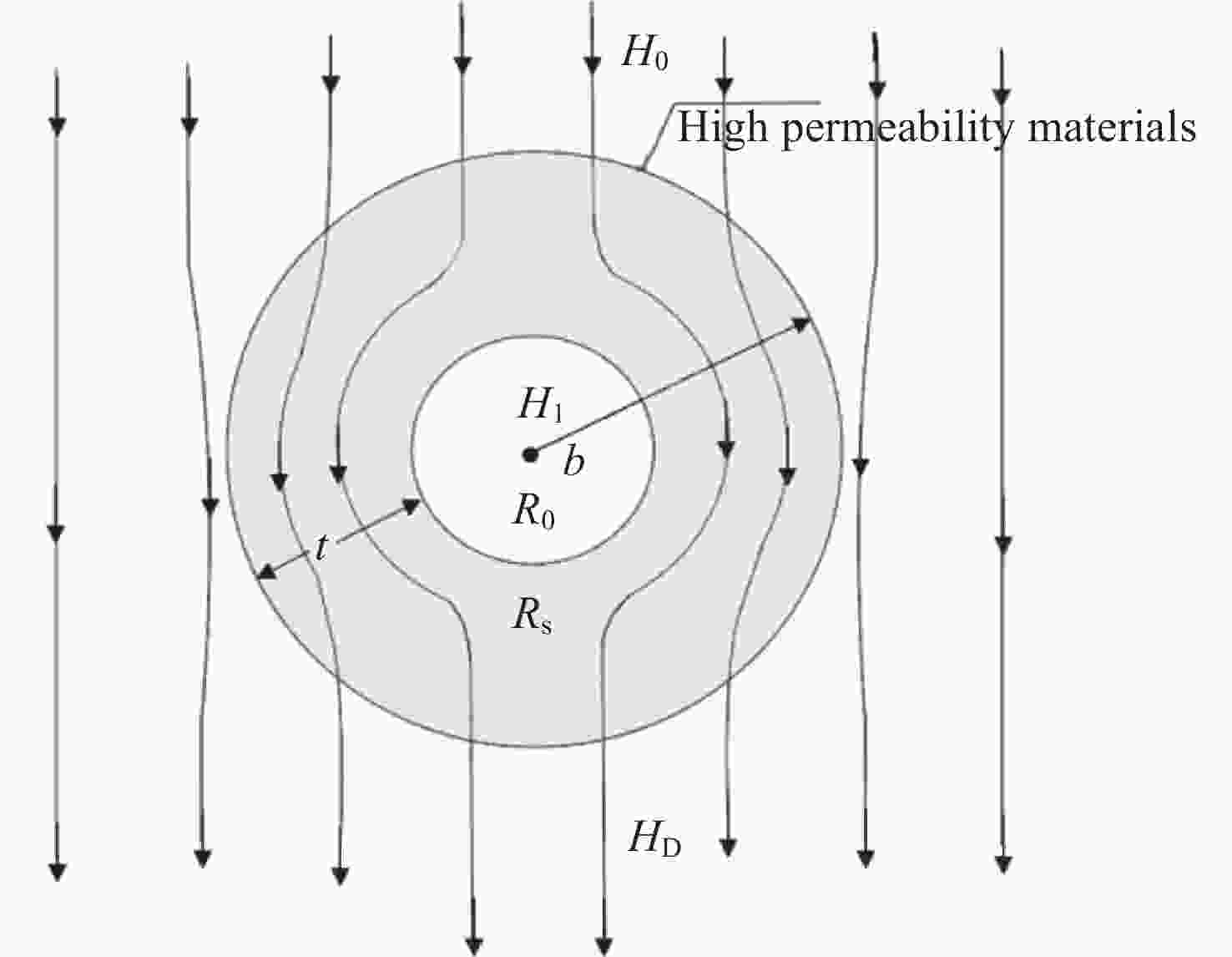
图 3 磁屏蔽室磁场分布 (箭头方向表示外部地磁场方向,颜色代表强度数值)。(a)磁屏蔽室外磁场分布,(b)屏蔽室内部及外部磁场分布(屏蔽室隐藏显示),(c)屏蔽室垂直于z轴的平面磁场分布,(d)屏蔽室垂直于x轴的平面磁场分布
Figure 3. Magnetic shielding room magnetic field distribution (The direction of the arrow indicates the direction of the external geomagnetic field, and the color represents the intensity value). (a) Distribution of external magnetic field of the magnetic shielding room. (b) Distribution of both external and internal magnetic field of the magnetic shielding room (shielding room hidden display). (c) Magnetic field distribution in the plane of the shielded room perpendicular to the z-axis. (d) Magnetic field distribution in the plane of the shielded room perpendicular to the x-axis
表 1 主要大型磁屏蔽室情况对比
Table 1. Comparison of major large space magnetic shielding rooms
序号 名称 屏蔽材料及构成 结构尺寸 1 美国伊利诺大学零磁屏蔽室MSR 1层4.8 mm的铝和2层1.5 mm的坡莫合金共同构成 内部空间为2.23 m×2.23 m× 2.23 m 2 美国麻省理工大学零磁屏蔽室 由2层纯铝和3层高磁导率材料薄板构成 26面类球体,最内层直径2.5 m,最外层直径4 m 3 韩国标准计量与科学研究院零磁室 - 内部尺寸:2 m×2 m×2.5 m 4 德国国家物理技术研究院PTB零磁屏蔽室(BMSR-2) 由1层射频屏蔽、1层铝和7层坡莫合金以及主动补偿线圈共同构成 内部尺寸:2.9 m×2.9 m×2.9 m
建筑尺寸:15 m×15 m×15 m5 哈佛大学联合生物医学中心MSR 共3层,每层均由高导磁和高电导材料构成 内部尺寸:4.0 m ×3.0 m×2.4 m
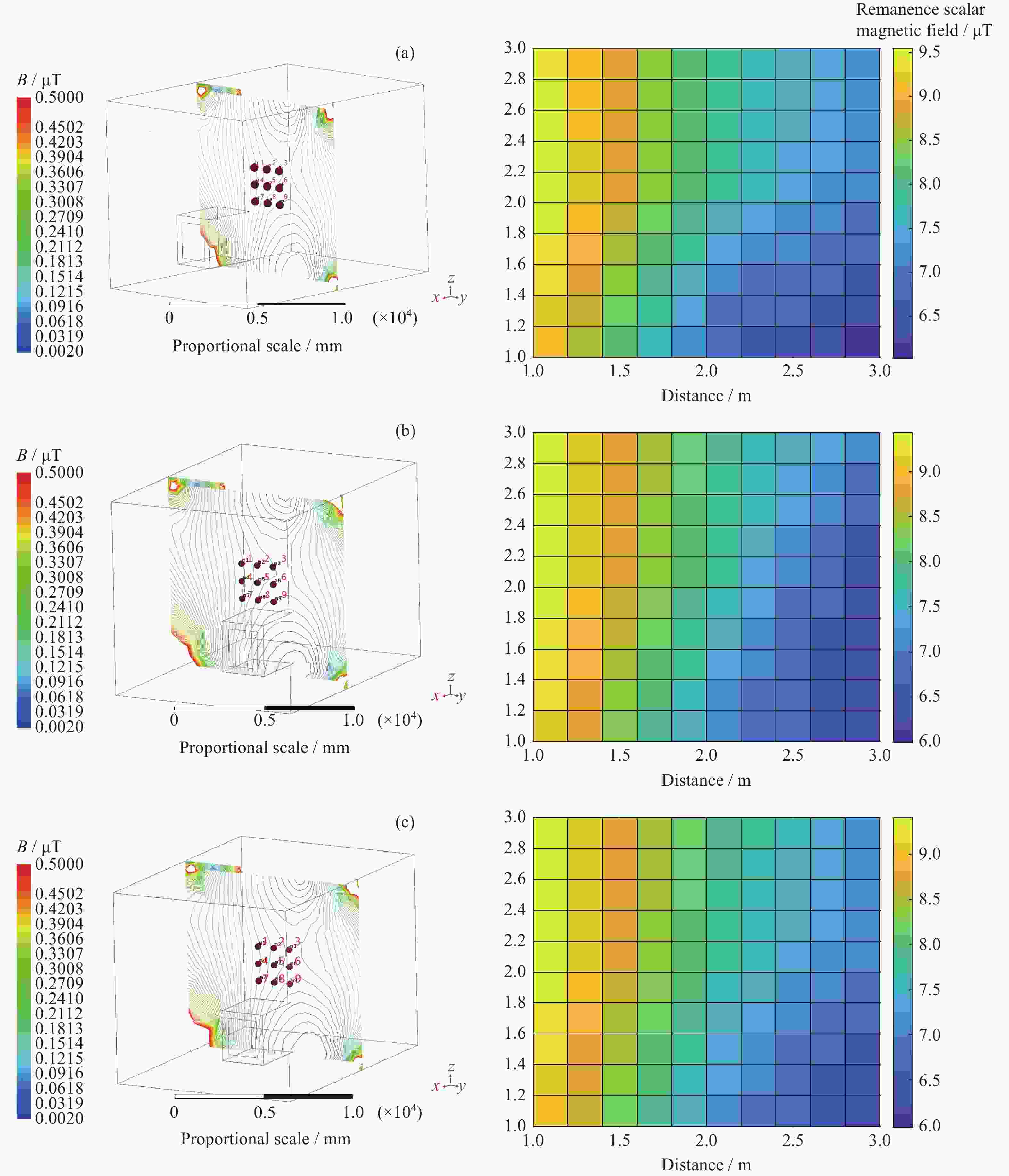
外部尺寸:5.3 m ×4.3 m×4.1 m6 日本超导实验室COSMOS 由1层铝和4层高导磁材料共同构成 外形似足球,内层直径约4 m,外层直径约6.1 m 7 中国地震局与钢铁研究院联合建造的零磁空间实验室 采用高导磁率的坡莫合金构成 外形为类球体,内部直径约2 m Name x y z B (×10–2) /μT m1 0.000 –1000.000 1000.000 9.378 m2 0.000 0.000 1000.000 7.847 m3 0.000 1000.000 1000.000 7.266 m4 0.000 –1000.000 0.000 9.543 m5 0.000 0.000 0.000 7.794 m6 0.000 1000.000 0.000 7.004 m7 0.000 –1000.000 –1000.000 9.107 m8 0.000 000.000 –1000.000 6.806 m9 0.000 1000.000 –1000.000 6.027 注 B 为剩余磁场标量仿真值。 Name x y z B (×10–2) /μT m1 1000.000 –1000.000 1000.000 9.356 m2 1000.000 0.000 1000.000 7.916 m3 1000.000 1000.000 1000.000 7.247 m4 1000.000 –1000.000 0.000 9.431 m5 1000.000 0.000 0.000 7.766 m6 1000.000 1000.000 0.000 6.911 m7 1000.000 –1000.000 –1000.000 9.120 m8 1000.000 000.000 –1000.000 7.087 m9 1000.000 1000.000 –1000.000 5.997 注 B 为剩余磁场标量仿真值。 Name x y z B (×10–2) /μT m1 –1000.000 –1000.000 1000.000 9.338 m2 –1000.000 0.000 1000.000 7.930 m3 –1000.000 1000.000 1000.000 7.087 m4 –1000.000 –1000.000 0.000 9.407 m5 –1000.000 0.000 0.000 7.758 m6 –1000.000 1000.000 0.000 6.871 m7 –1000.000 –1000.000 –1000.000 8.986 m8 –1000.000 000.000 –1000.000 7.140 m9 –1000.000 1000.000 –1000.000 5.975 注 B 为剩余磁场标量仿真值。 表 5 磁屏蔽室剩余磁场标量强度仿真数值与实际测试数值情况及对比(单位nT)
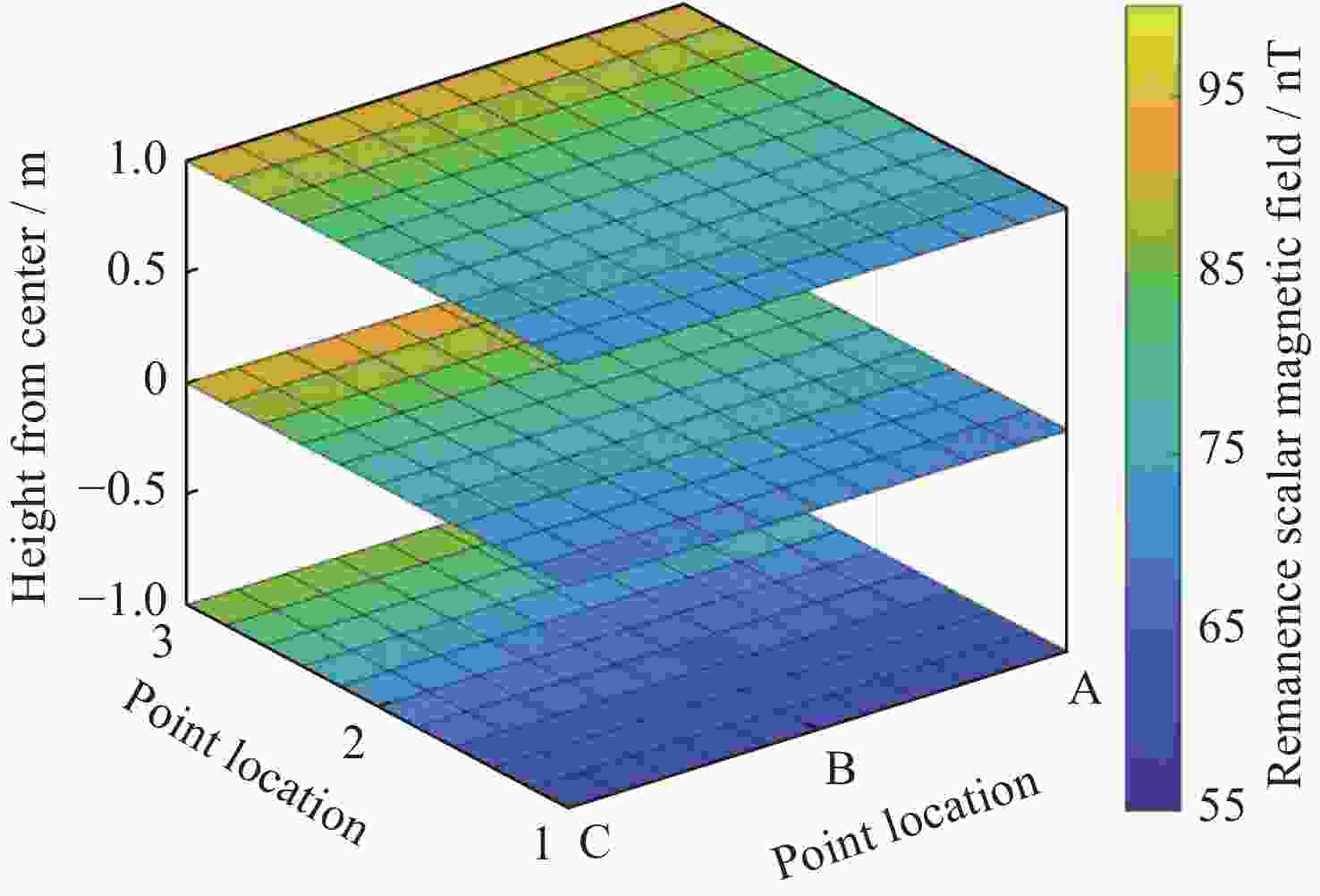
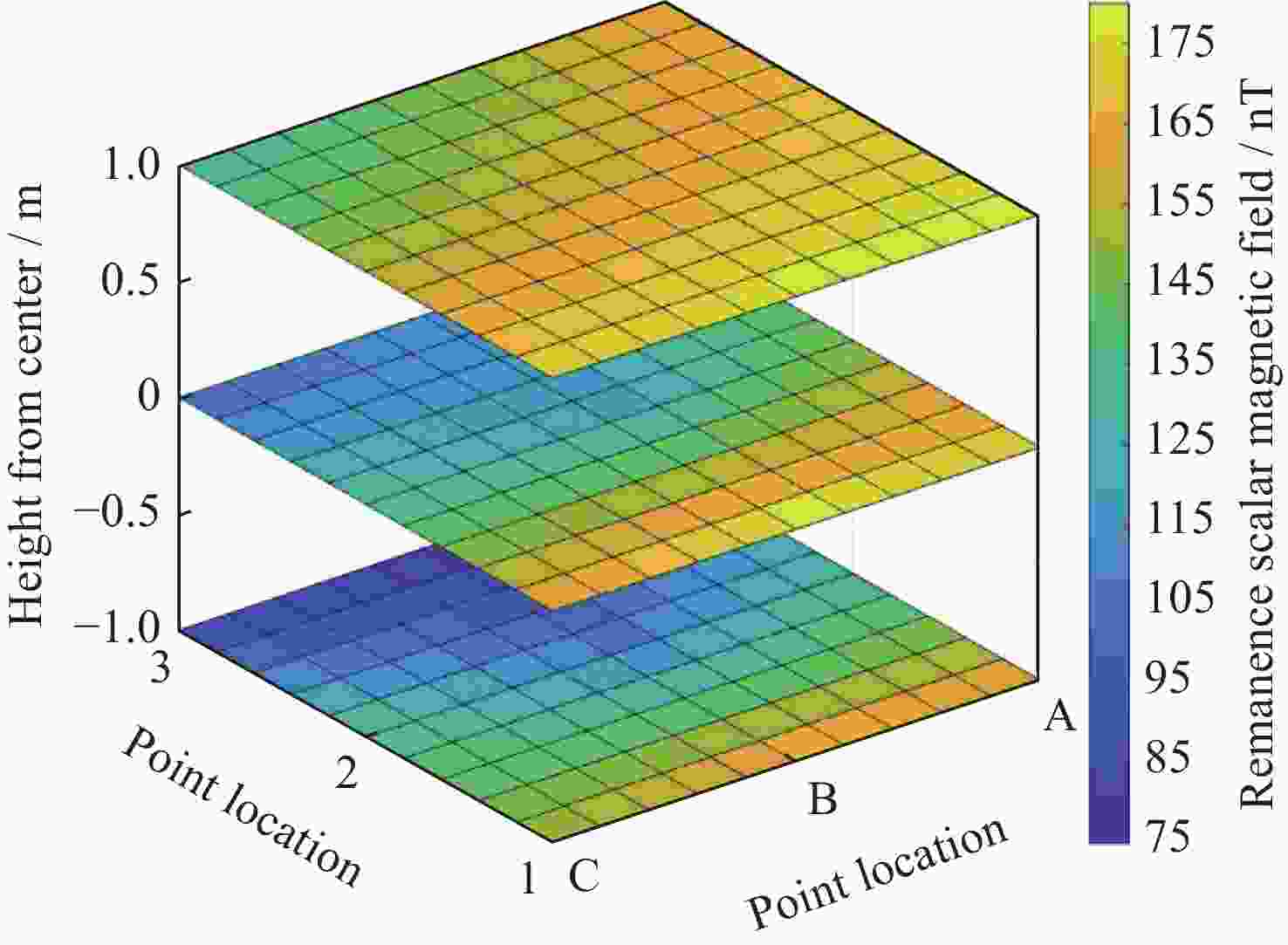
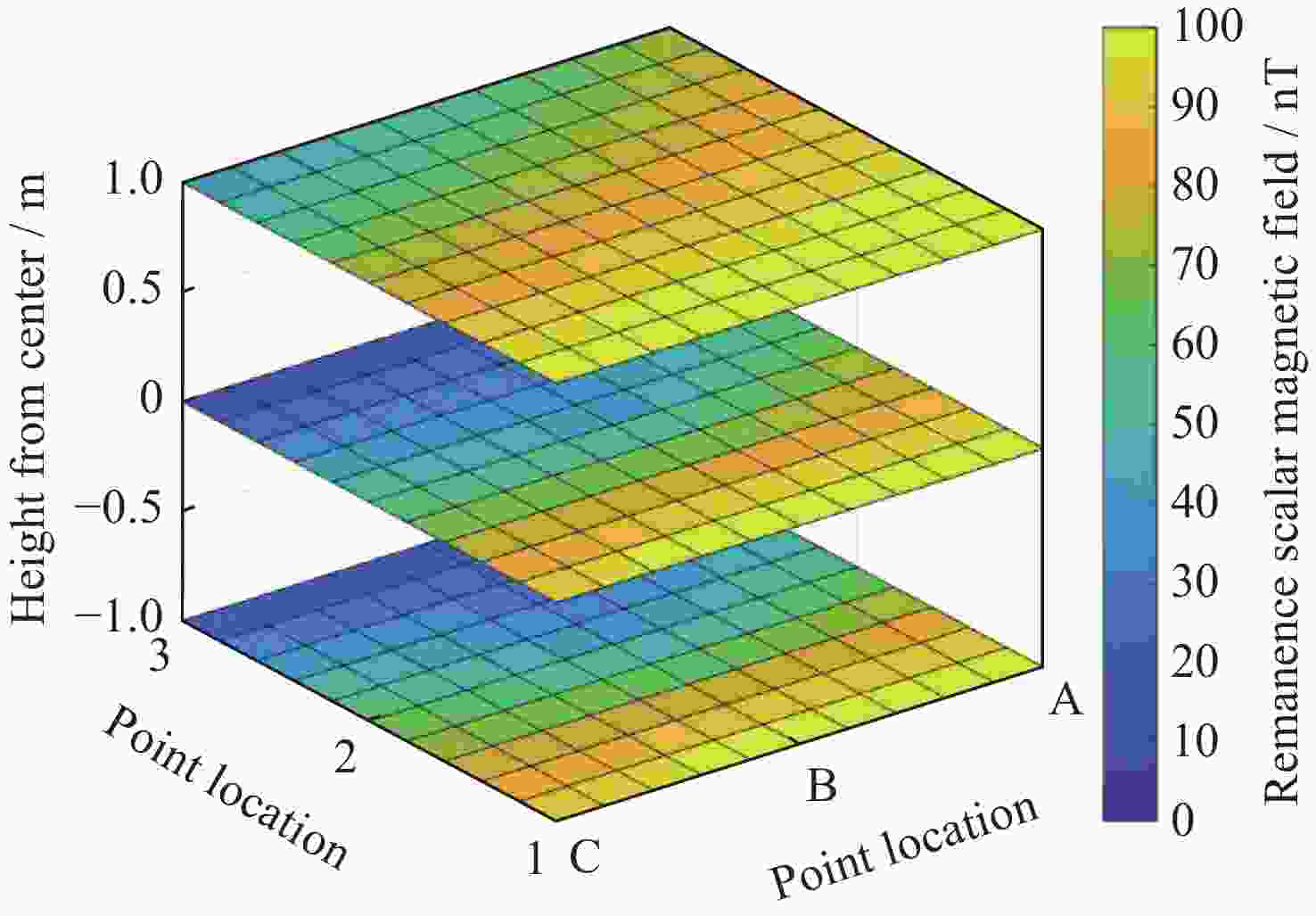
Table 5. Comparison of simulation and measured data of residual magnetic field scalar intensity in magnetic shielding room (Unit nT)
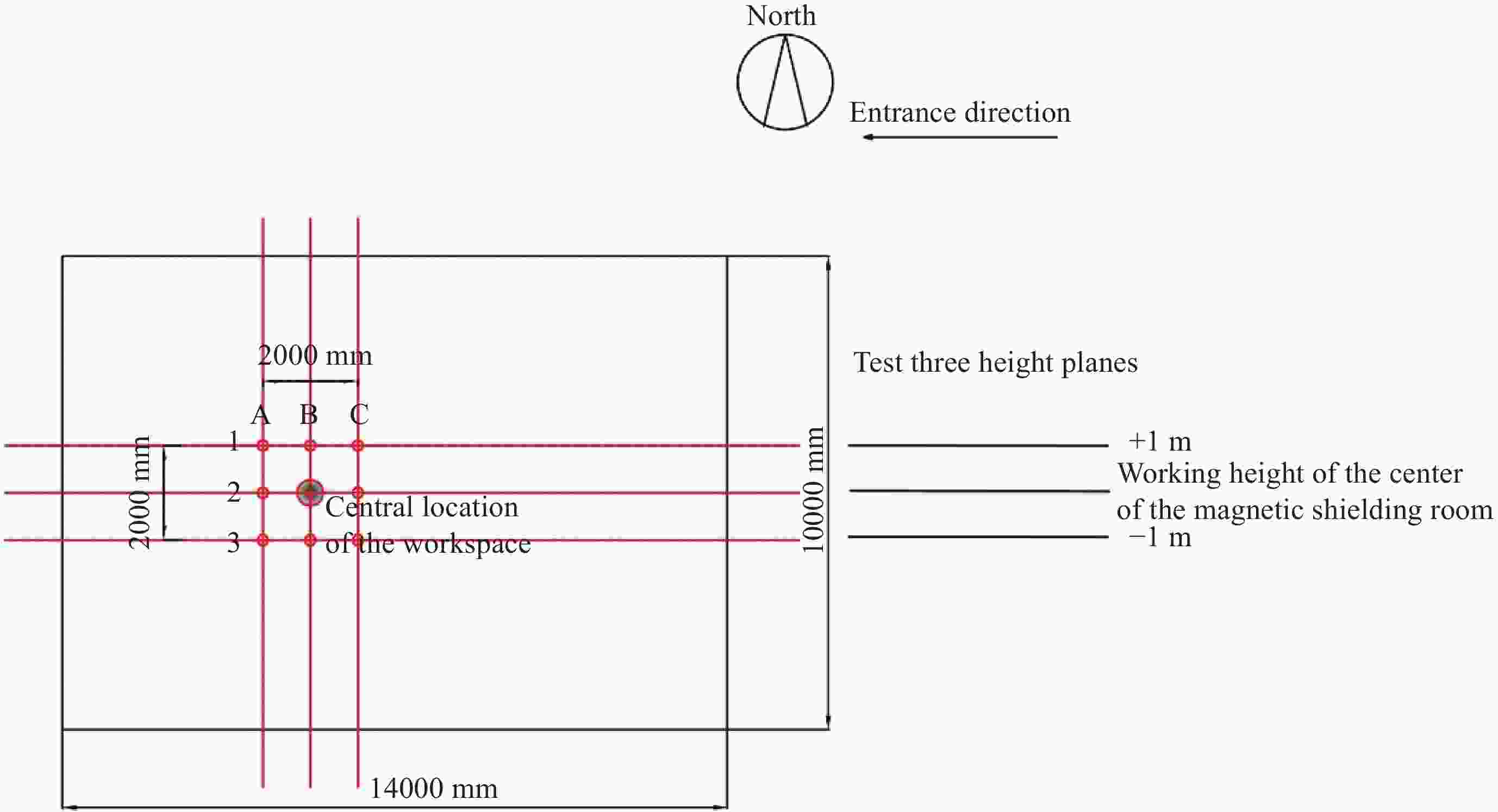
高度 测试点序号
及状态1 2 3 仿真 实测 差值 仿真 实测 差值 仿真 实测 差值 屏蔽室工作中心高度 A 68.71 160.8 92.09 77.58 129.0 51.42 94.07 98.1 4.03 B 70.04 177.8 107.76 77.94 118.8 40.86 95.43 112.8 17.37 C 69.11 169.9 100.79 77.66 149.9 72.24 94.31 136.3 41.99 屏蔽室工作中心高度以下1 m A 59.75 150.1 90.35 71.40 131.5 60.10 89.86 77.0 –12.86 B 60.27 163.8 103.53 68.06 104.9 36.84 91.07 76.5 –14.57 C 59.97 158.4 98.43 70.87 133.0 62.13 97.20 101.1 9.90 屏蔽室工作中心高度以上1 m A 70.87 171.6 100.73 79.30 151.6 72.30 93.38 127.5 34.12 B 72.66 177.2 104.54 78.47 159.0 80.53 93.78 145.4 51.62 C 72.47 178.4 105.93 79.16 170.4 91.24 93.56 165.4 71.84 注 表中点位剩磁测量值实测为矢量数值,为与仿真值有效比对,换算成标量值。 -
[1] 徐文耀. 地球电磁现象物理学[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009XU Wenyao. Physics of Electromagnetic Phenomena of the Earth[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2009 [2] 程华富. 磁通门磁强计校准装置研究[J]. 宇航计测技术, 2018, 38(5): 55-59CHENG Huafu. Study on a calibration device of fluxgate magnetometer[J]. Journal of Astronautic Metrology and Measurement, 2018, 38(5): 55-59 [3] CONNERNEY J E P, BENN M, BJARNO J B, et al. The Juno magnetic field investigation[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2017, 213(1/2/3/4): 39-138 [4] 胡瑞雪, 韩雪艳, 赵占良, 等. 大型磁屏蔽室嵌套拼接结构整体磁导率的分析与研究[J]. 燕山大学学报, 2019, 43(5): 401-407HU Ruixue, HAN Xueyan, ZHAO Zhanliang, et al. Analysis and research on overall permeability of nesting and splicing structures in large magnetic shielding rooms[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 2019, 43(5): 401-407 [5] 张景鑫, 许亚峰, 刘明非. 磁场空间技术概论[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012ZHANG Jingxin, XU Yafeng, LIU Mingfei. Introduction to Magnetic Field Space Technology[M]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2012 [6] 支萌辉. 高精度数字磁通门传感器研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2017ZHI Menghui. Research on High Precision Digital Fluxgate Sensor[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2017 [7] 李巧燕, 王保国, 马通边, 等. 低频高性能屏蔽装置的设计[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2016, 14(4): 591-595LI Qiaoyan, WANG Baoguo, MA Tongbian, et al. Design of shielding device with low-frequency and high-performance[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2016, 14(4): 591-595 [8] 金惕若. 中国的弱磁场标准[J]. 地球物理学报, 1988, 31(6): 713-716JIN Tiruo. The standard of low magnetic field in China[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 1988, 31(6): 713-716 [9] PAAVOLA M A J, ILMONIEMI R J, SOHLSTRÖM L, et al. High performance magnetically shielded room for clinical measurements[C]//Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Biomagnetism on Biomag 96. New York: Springer, 2000: 87-90 [10] 李立毅, 孙芝茵, 潘东华, 等. 近零磁环境装置现状综述[J]. 电工技术学报, 2015, 30(15): 136-140LI Liyi, SUN Zhiyin, PAN Donghua, et al. Status reviews for nearly zero magnetic field environment facility[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(15): 136-140 [11] KUNKEL G M. Shielding effectiveness testing of space blanket[M]//KUNKEL G M. Shielding of Electromagnetic Waves: Theory and Practice. Cham: Springer, 2020: 51-56 [12] EROFEENKOA V T, BONDARENKOB V F. Shielding of a magnetic pulse by the multilayer film shield with alternating magnetic and nonmagnetic layers[J]. Technical Physics, 2017, 62(6): 846-851 doi: 10.1134/S1063784217060081 [13] AHN S. Shielding of magnetic field[M]//SUH N P, CHO D H. The On-line Electric Vehicle. Cham: Springer, 2017: 197-206 -
-





 下载:
下载: