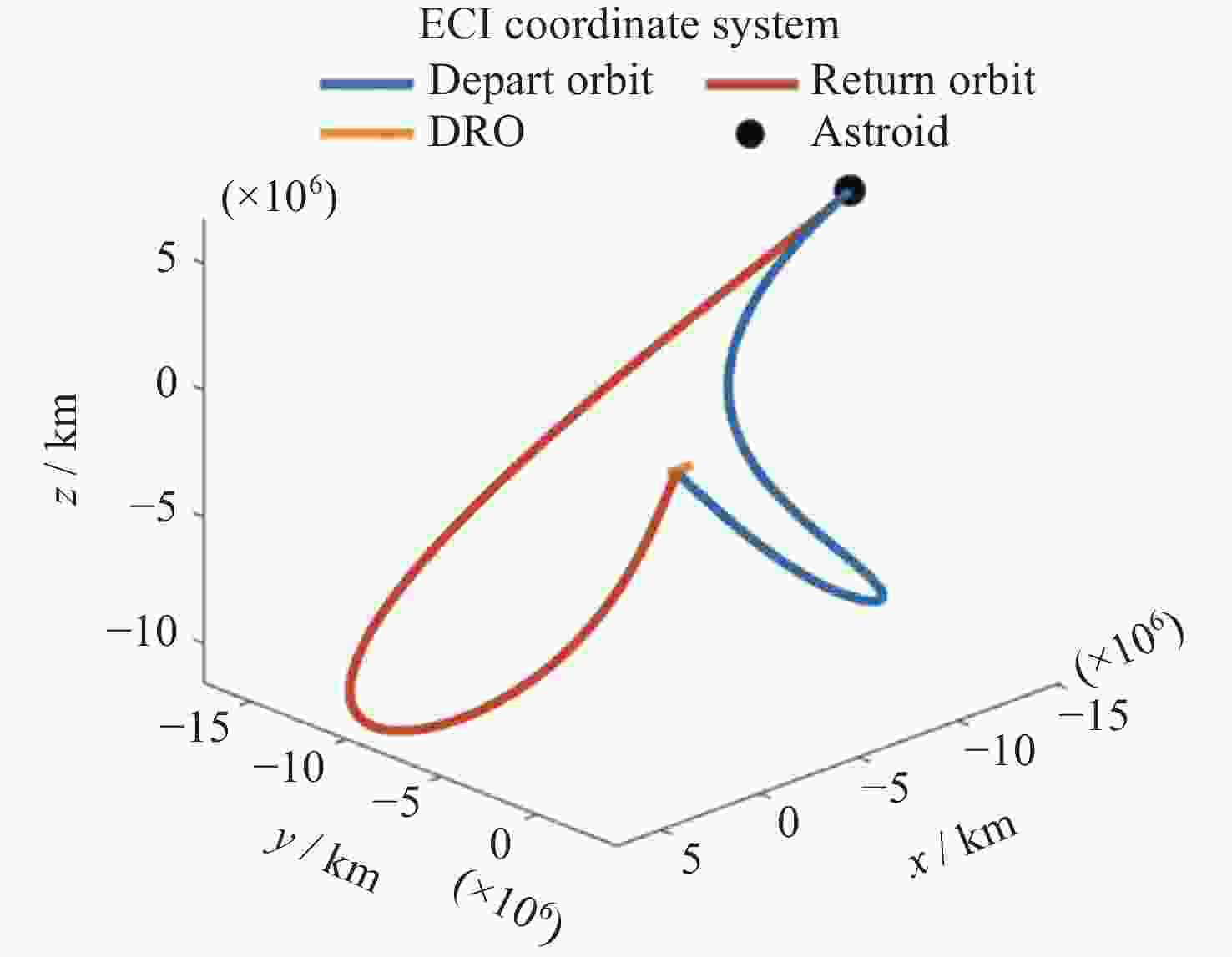
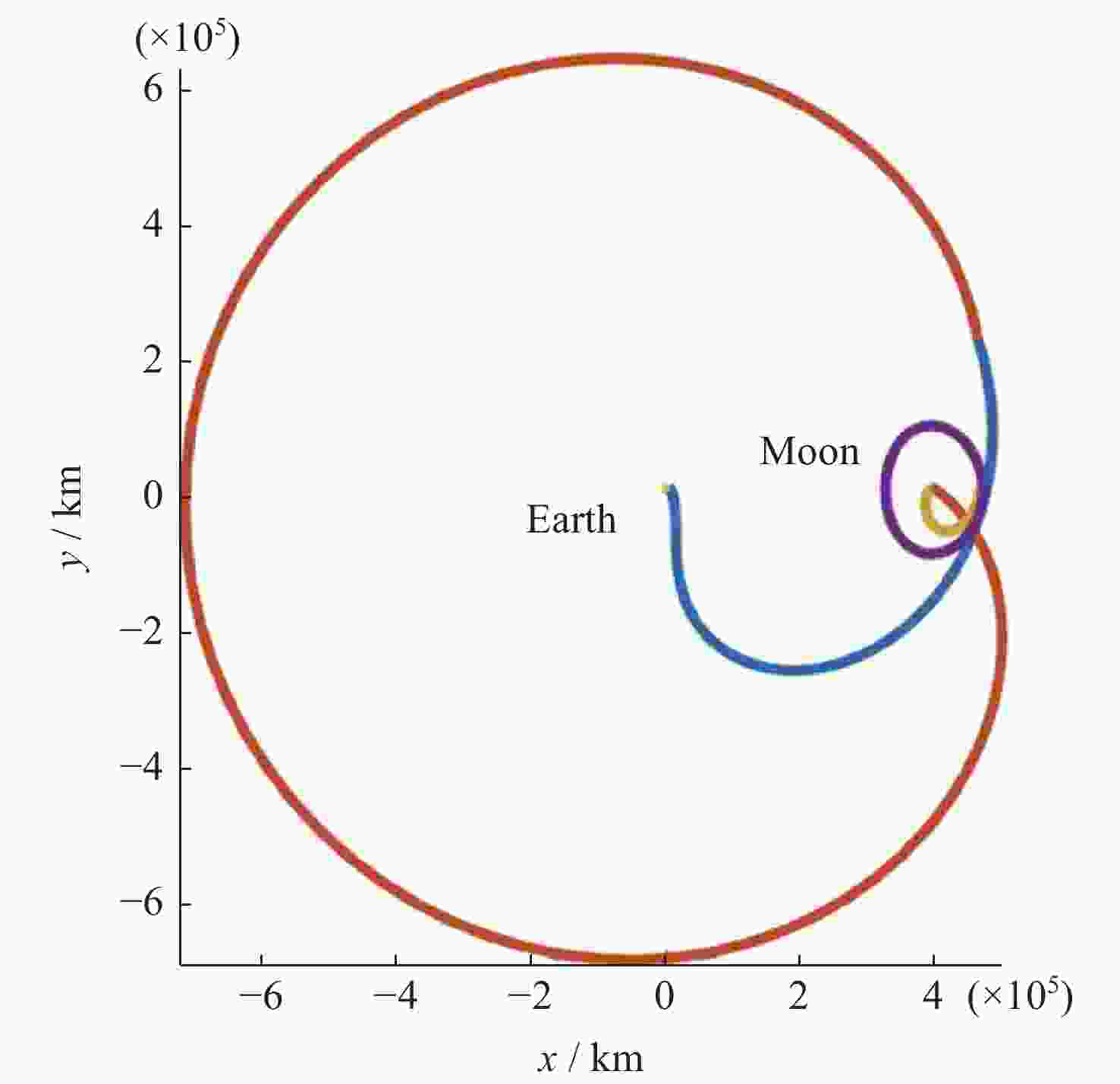
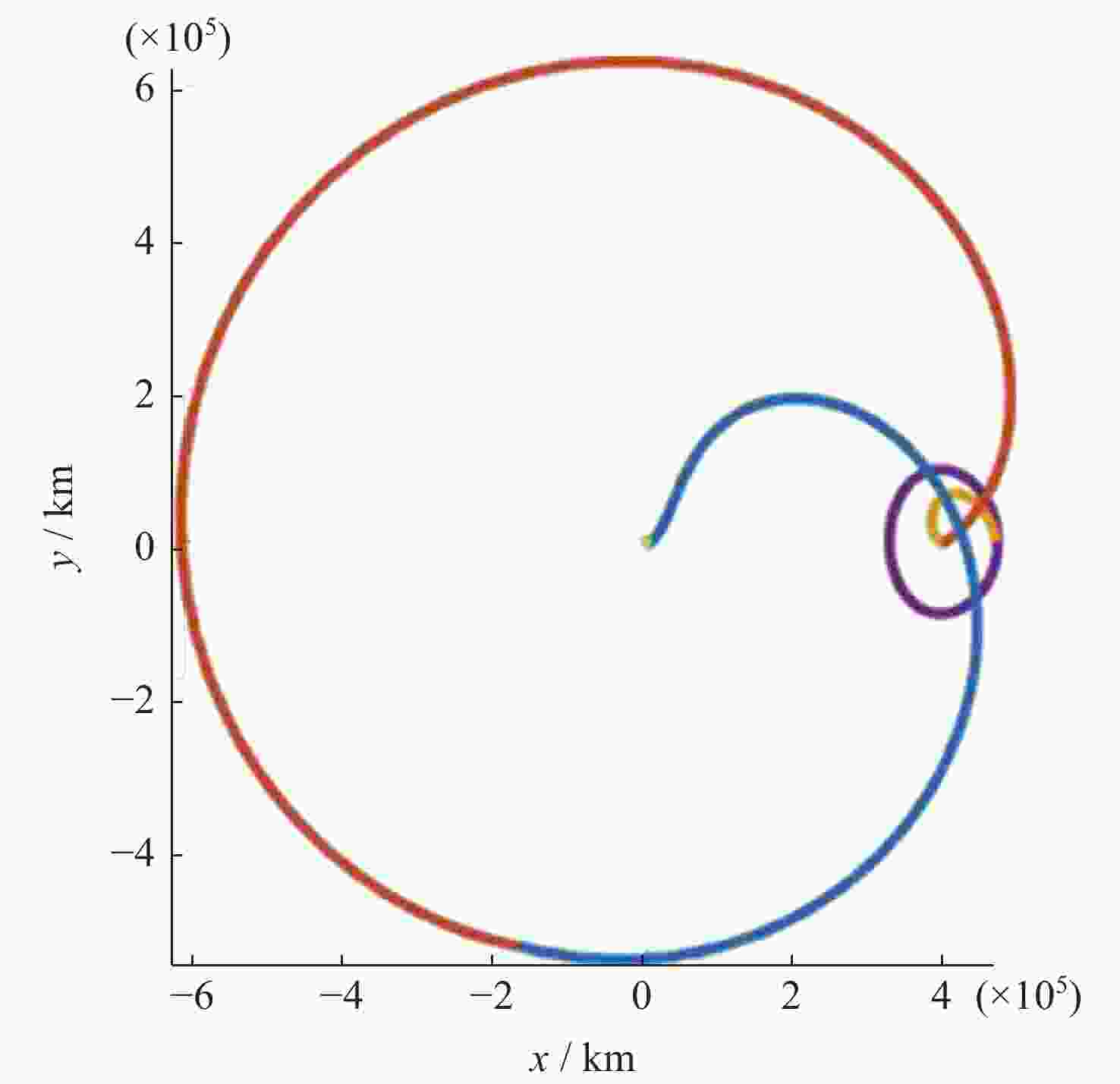
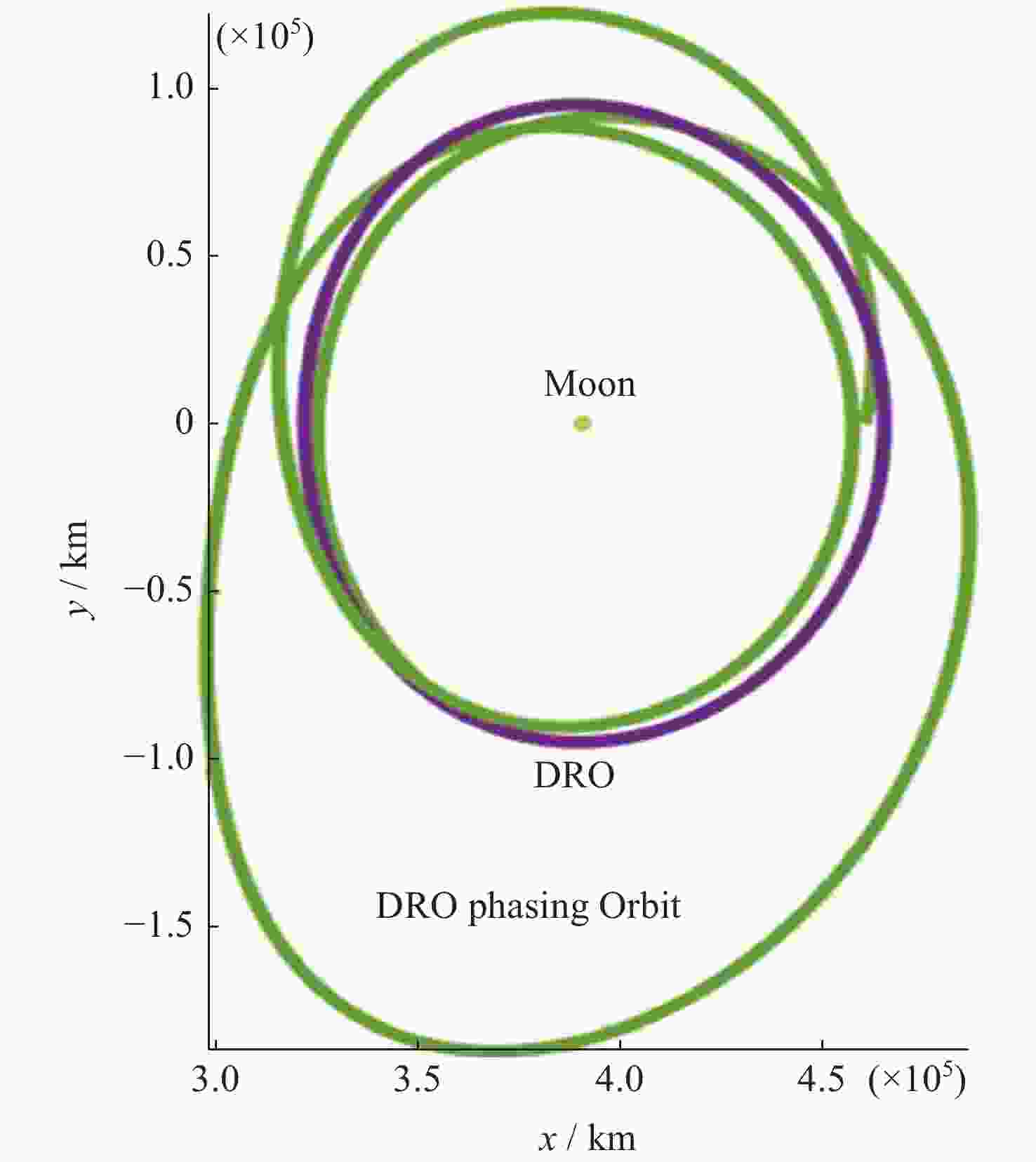
基于DRO的小行星往返飞越探测轨道设计优化方法
doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.05.2023-0011 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2023.05.2023-0011
Orbit Design Optimization Method for an Asteroid Flyby Mission from DRO
-
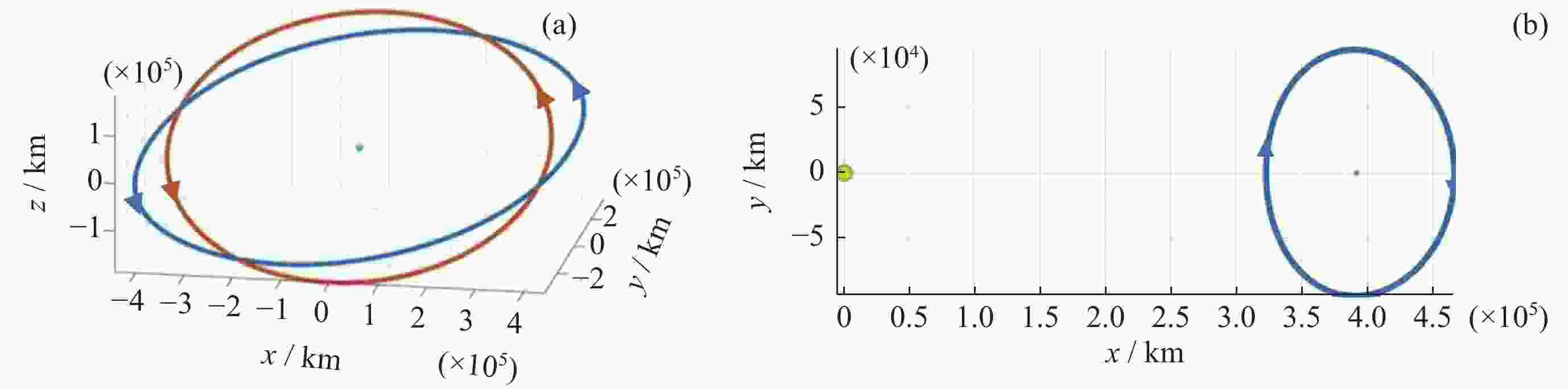
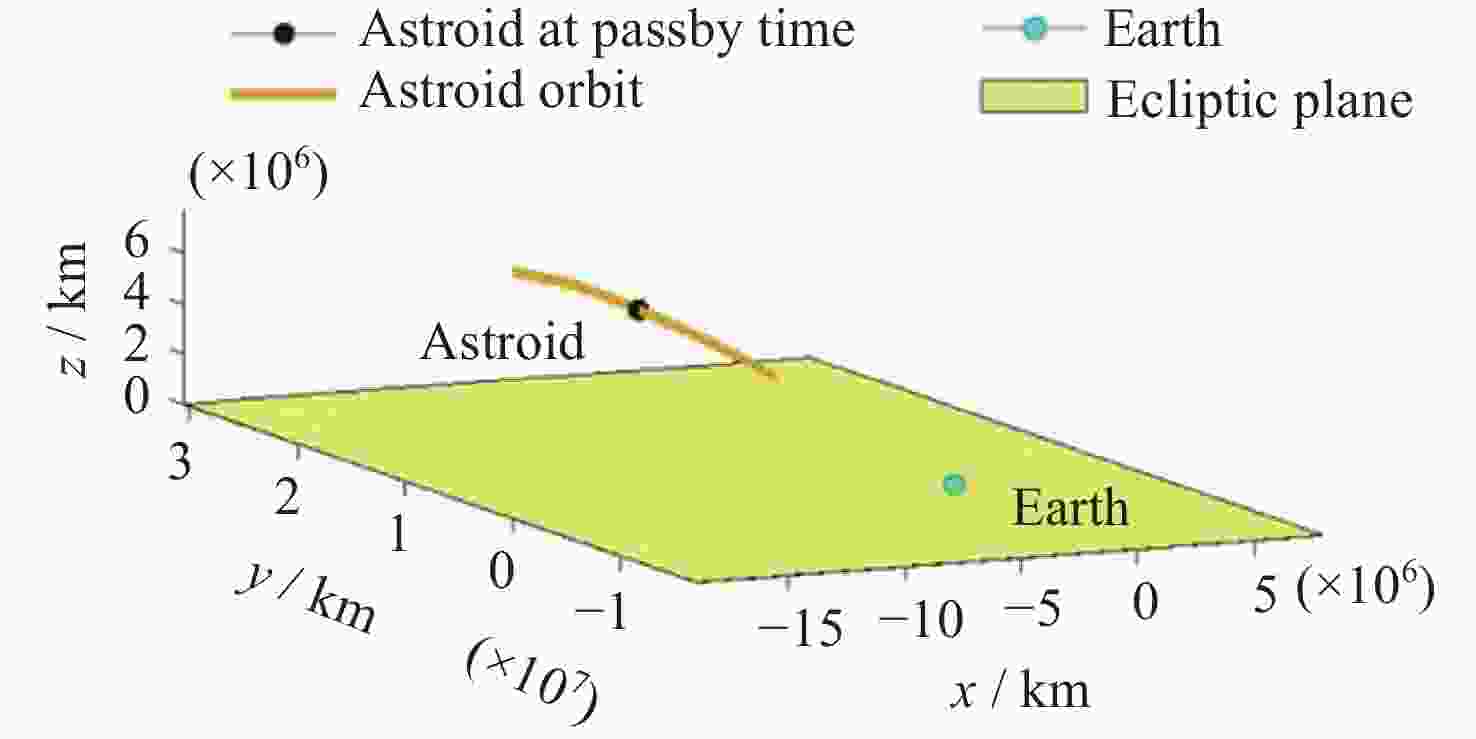
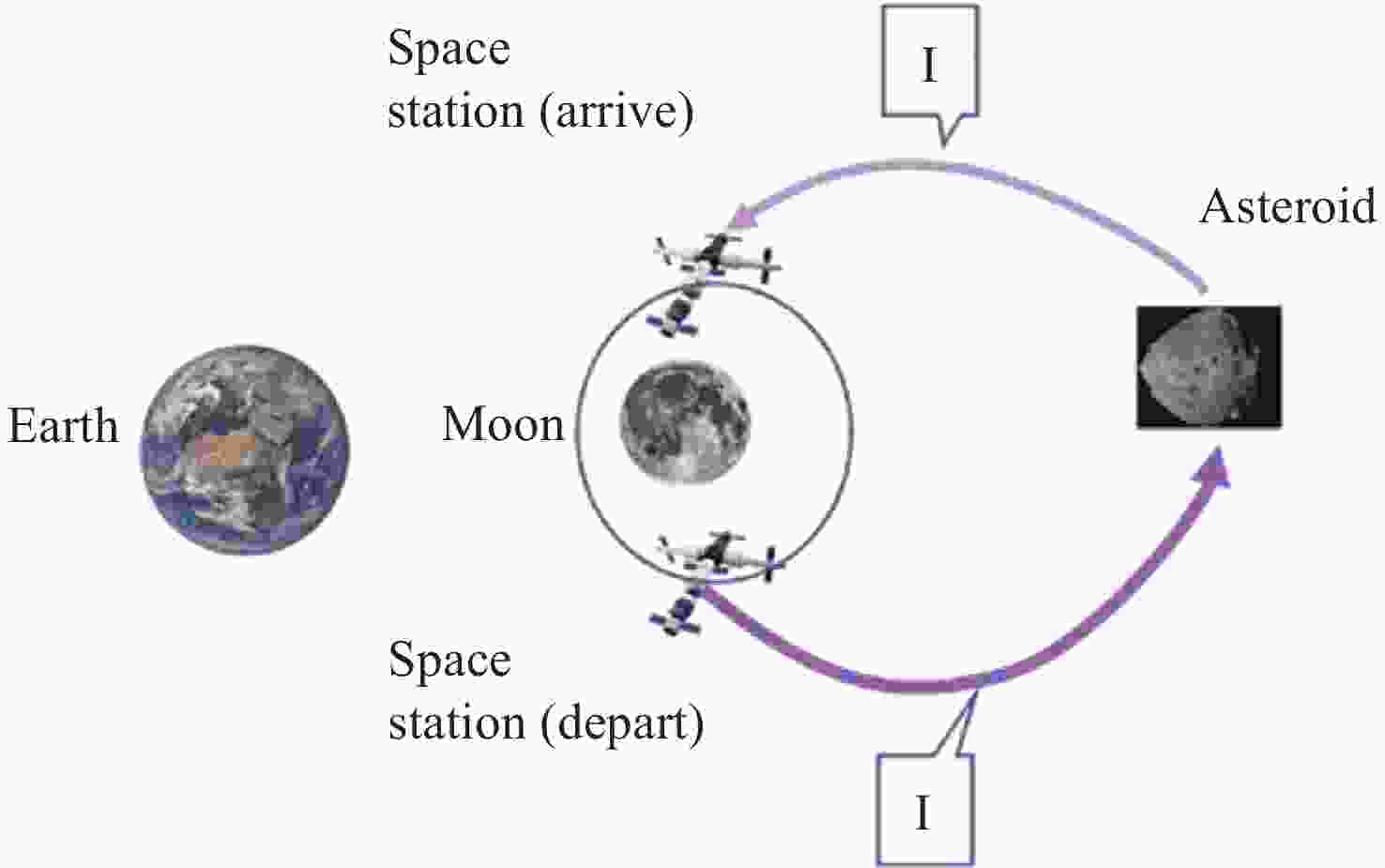
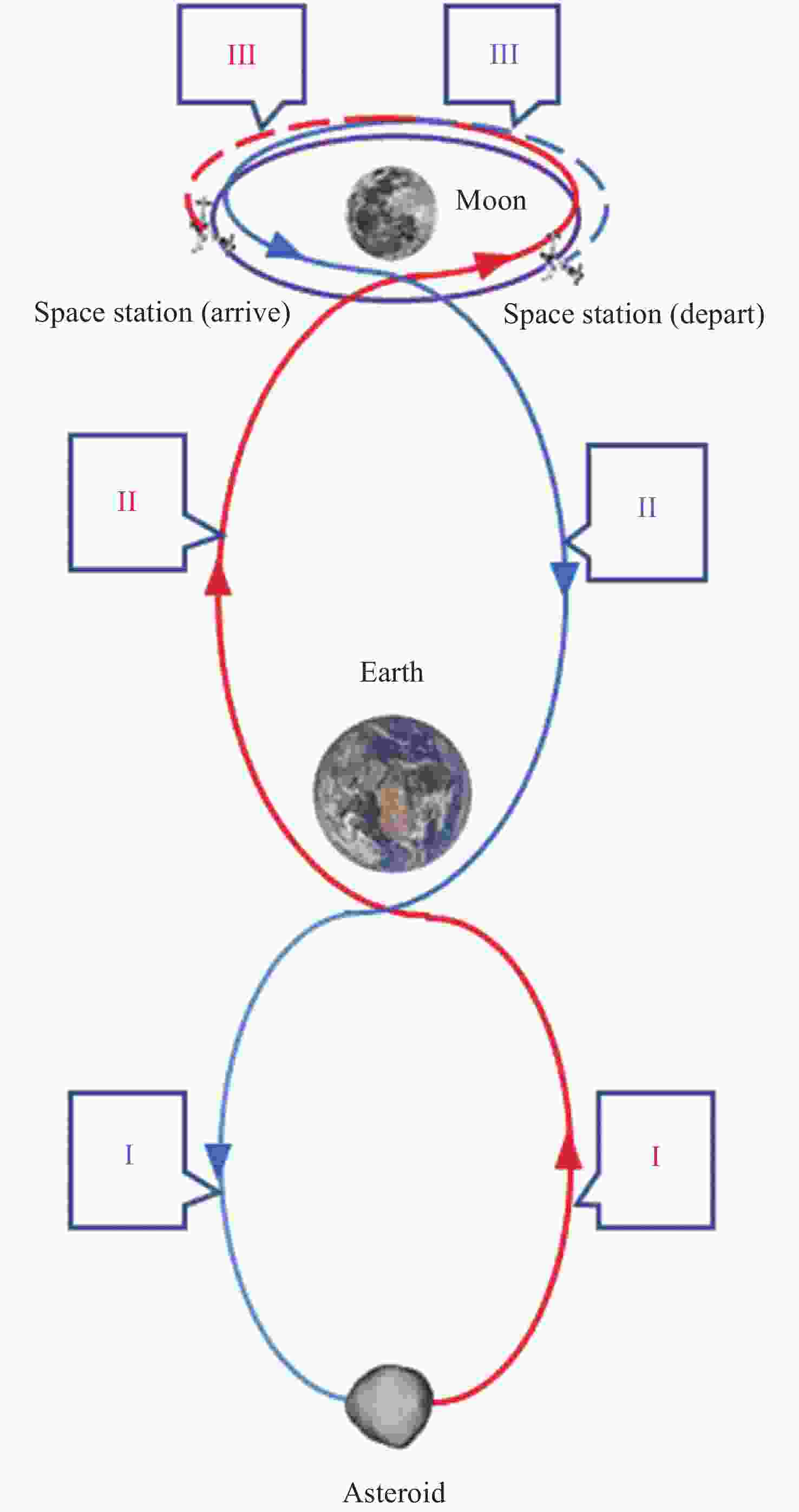
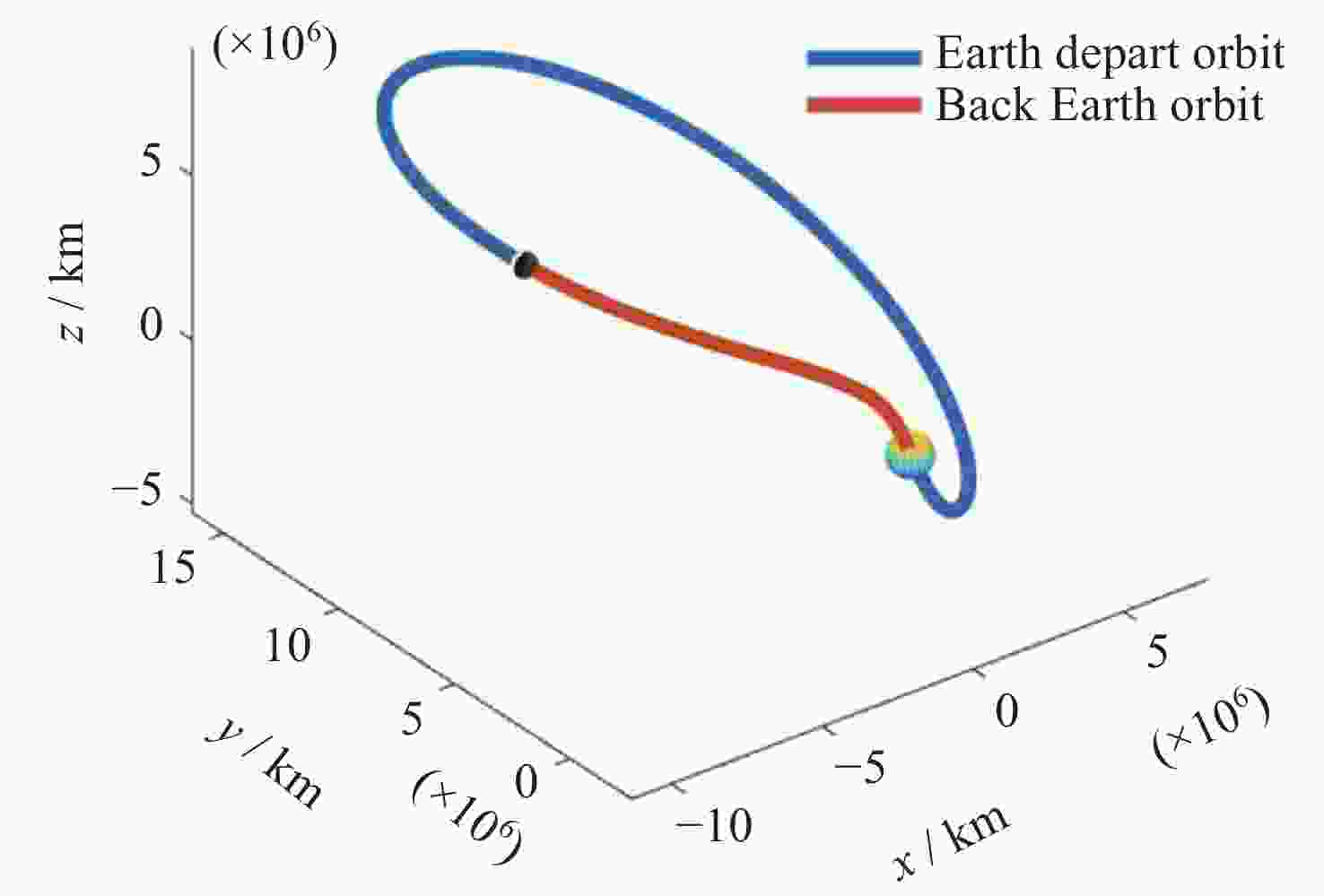
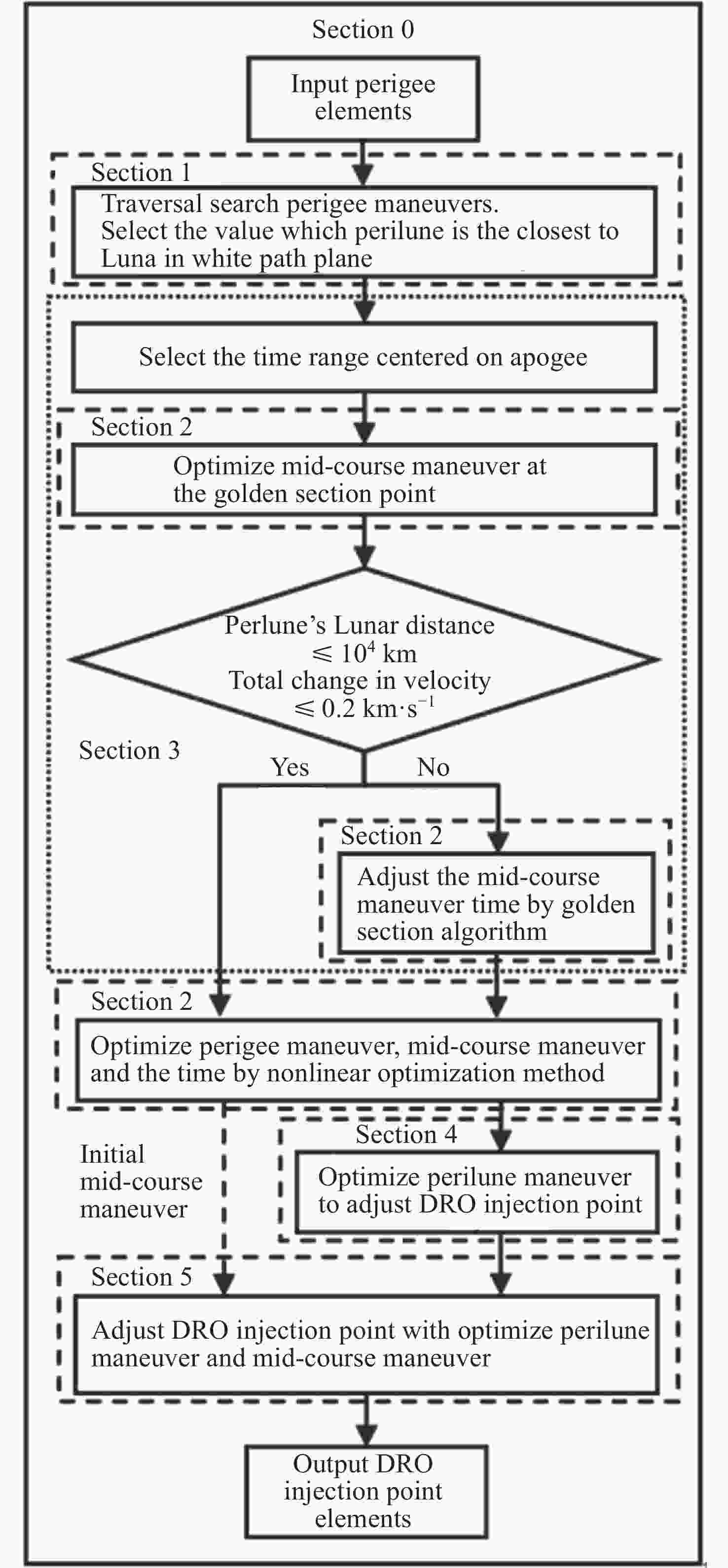
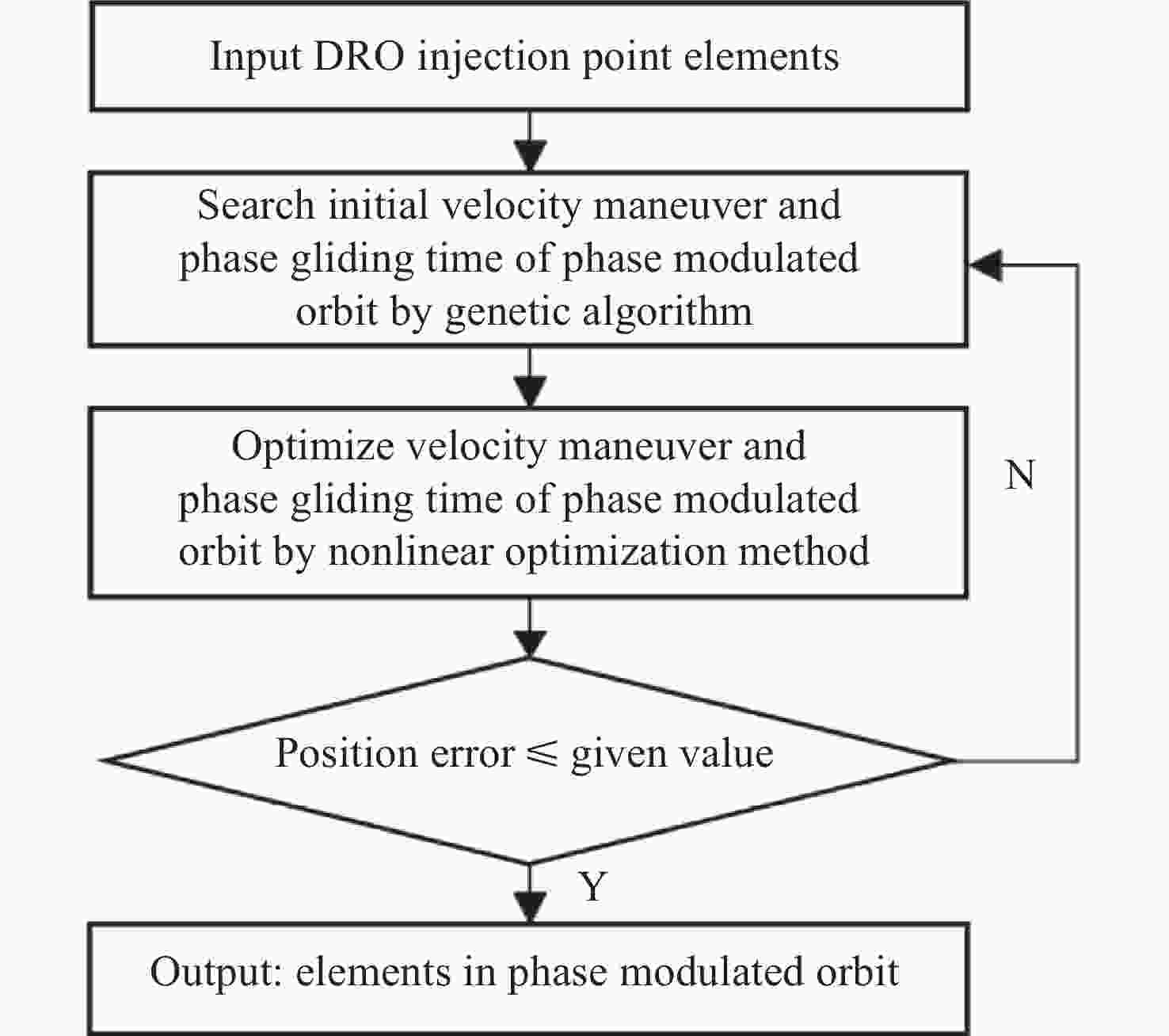
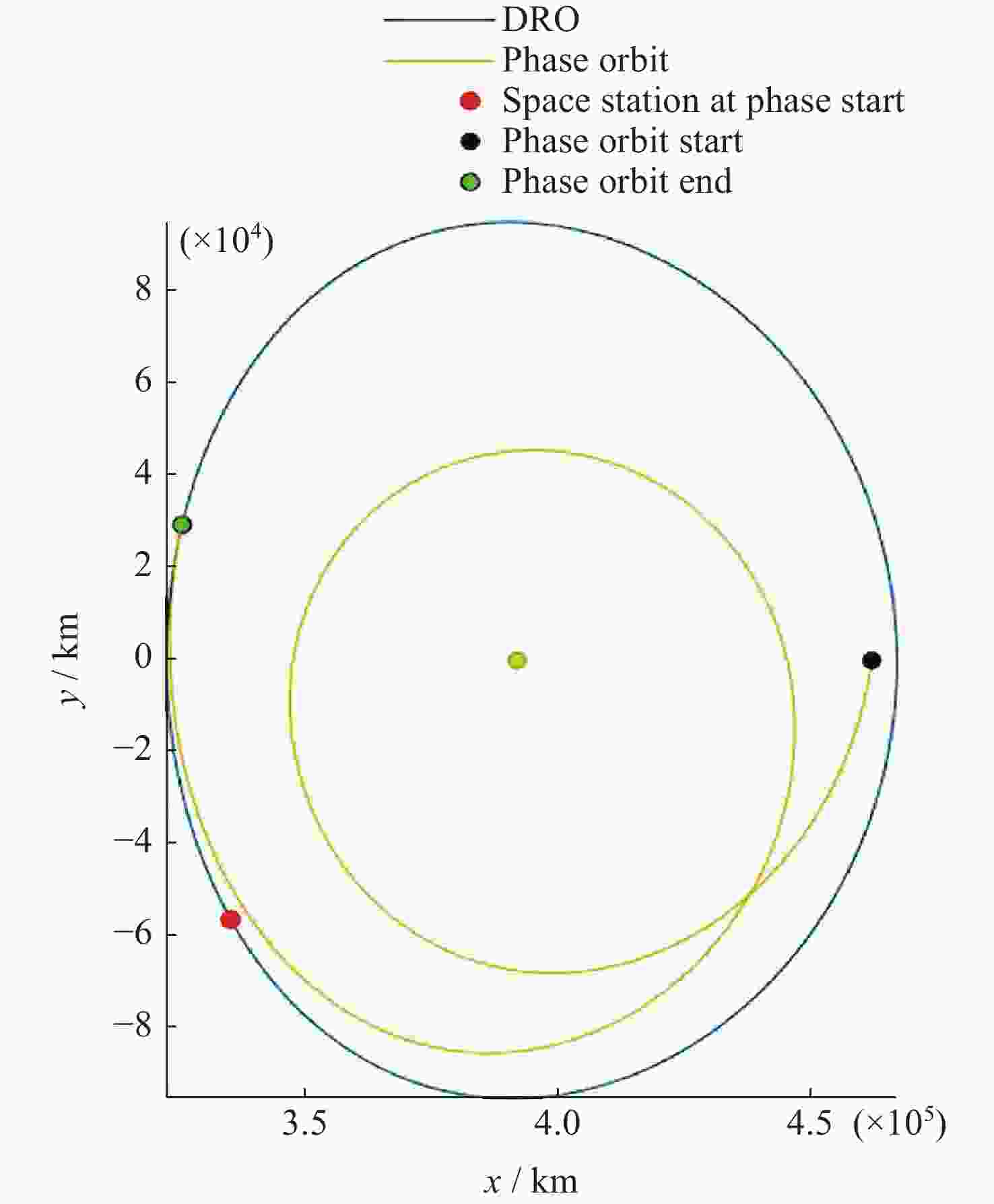
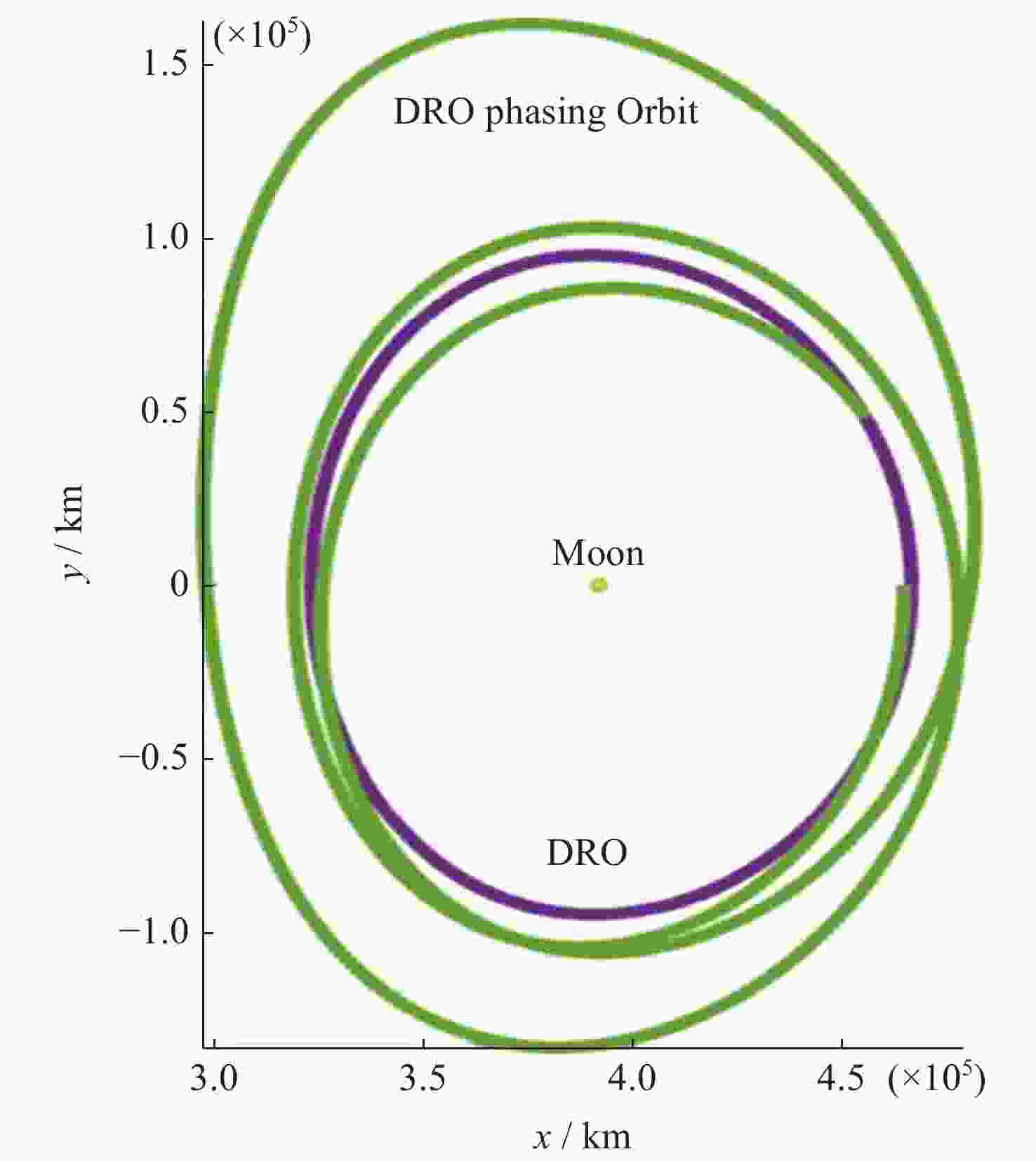
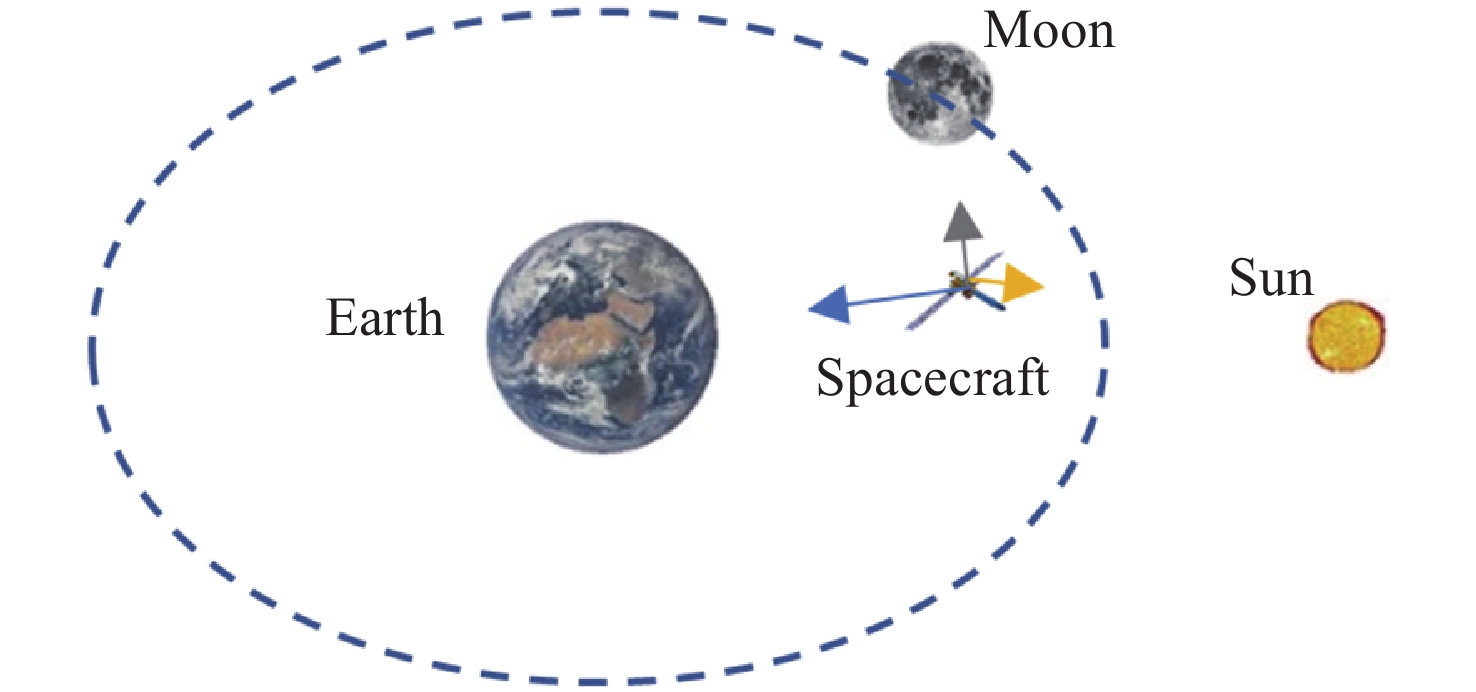
摘要: 远距离逆行轨道(Distant Retrograde Orbits,DRO)是地月系统内一类稳定的周期性轨道,本文研究航天器从DRO轨道站出发,通过月球和地球引力辅助实现飞越探测近地小行星的往返转移轨道设计方法。通过地月引力辅助作用和中途杠杆机动等技术手段减少调整倾角所需的速度增量,扩大在相同速度增量约束下飞越探测小行星的可达范围。同时,通过引入DRO调相轨道,减少DRO逃逸和俘获时的相位约束,将转移轨道段与DRO轨道站的相位解耦,从而降低了该问题的计算复杂度。仿真结果表明,在2 km·s–1的速度增量等约束条件下,通过此研究方法可以实现从DRO轨道站出发飞越探测近地小行星并返回的轨道设计。Abstract: Distant Retrograde Orbit (DRO) is a kind of stable periodic orbit in Earth-Moon system. In this paper, a design method of distant retrograde orbit for spacecraft to fly by and explore near-Earth asteroids by means of the moon and Earth’s gravity assistance starting from DRO orbital station is studied. By means of earth-moon gravity assistance and mid-course lever maneuver, the velocity increment required for adjusting the inclination angle is reduced, and the reachable range of the asteroid flying by exploration under the same velocity increment constraint is expanded. At the same time, the calculation complexity of the problem is reduced by introducing DRO phasing, with reducing the phase constraints of escape and capture in DRO, and decoupling the phase of the transfer track from the DRO orbital station. The simulation results show that under the velocity increment of 2 km·s–1, the method can realize the orbit design of flyby exploration of near-Earth asteroids from DRO orbital station and return.
-
Key words:
- DRO /
- Near-Earth asteroid /
- B plane parameters /
- Lunar gravity assist /
- Orbital phasing
-
表 2 常数取值与约束条件
Table 2. Constant values and constraints
名称 参数 地球引力常数/(km3·s–2) 398600 太阳引力常数/(km3·s–2) 132712440018 月球引力常数/(km3·s–2) 4902.8 地球半径/km 6378 月球半径/km 1738 初始时刻 MJD 60676 最大地球距离/km $ 2\times {10}^{7} $ 最小近地点高度/km 200 最小近月点高度/km 50 两机动间最小间隔时间/d 1 最大总速度增量/(km·s–1) 2 最大总飞行时间/a 4 表 1 虚拟目标小行星轨道参数
Table 1. Target asteroid orbit parameters
参数名称 初始历元(MJD) 半长轴(AU) 偏心率 倾角/(°) 升交点赤经/(°) 近地点幅角/(°) 真近地点角/(°) 数值 59600 1.129 0.366 2.68 163.67 188.14 182.30 表 3 飞越探测轨道近地点参数
Table 3. Perigee parameters of flyby detection orbit
参数名称 近地点出发参数 返回近地点参数 初始历元(MJD) 63882.99 64243.01 ECI x/km –3278.43 3251.21 ECI y/km –4306.81 1011.57 ECI z/km 3739.86 –5628.97 ECI vx/(km·s–1) 0.971 1.070 ECI vy/(km·s–1) –7.688 10.790 ECI vz/(km·s–1) –8.002 2.557 白道面倾角/(o) 59.99 59.88 C3 /(km2·s–2) 2.9068 2.9238 表 4 地球与DRO间转移轨道各项参数
Table 4. Perigee parameters of flyby detection orbit
参数名称 近地点机
动量
/(km·s–1)中途机
动量
/(km·s–1)中途机
动与近地
点间时长
/ d近月点机
动量
/(km·s–1)总速度
增量
/(km·s–1)DRO出发轨道 0.169 0.206 10.693 0.313 0.688 返回DRO轨道 0.166 0.234 15.701 0.271 0.671 表 5 DRO调相轨道各项参数
Table 5. Elements of DRO phasing orbit
参数名称 调相起始
点机动量
/(km·s–1)调相滑行
时间/dDRO轨道站
会和机动
/(km·s–1)总速度增量
/(km·s–1)DRO出发调相轨道 0.132 43.542 0.096 0.228 返回DRO轨道 0.159 47.967 0.142 0.301 -
[1] 张晨. 基于数值延拓的日月综合借力DRO入轨策略[J/OL]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022: 1-17. [2022-12-21]. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0494ZHANG Chen. Low-energy transfer from earth into DRO with hybrid gravity assist and numerical continuation[J/OL]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics. [2022-12-21]. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0494 [2] BROPHY J R, FRIEDMAN L, CULICK F. Asteroid retrieval feasibility[C]//2012 IEEE Aerospace Conference. Big Sky: IEEE, 2012: 1-16 [3] ROA J, HANDMER C J. Quantifying hazards: asteroid disruption in lunar distant retrograde orbits[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1505.03800, 2015 [4] 丁毅, 侯征, 吴云霞. 世界陨石坑研究[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(4): 1095-1104 doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2021.06.045DING Yi, HOU Zheng, WU Yunxia. Research on meteorite craters in the world[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(4): 1095-1104 doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2021.06.045 [5] ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG W. Deep space exploration strategy based on distant retrograde orbits space station[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 2006(1): 012061 doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2006/1/012061 [6] CONTE D, DI CARLO M, HO K, et al. Earth-Mars transfers through Moon distant retrograde orbits[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2018, 143: 372-379 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2017.12.007 [7] OSIRIS-REx mission operations | NASA[EB/OL]. [2018-12-13]. https://www.nasa.gov/content/osiris-rex-mission-operations [8] NASA - NSSDCA - spacecraft – Details[EB/OL]. [2021-12-18] https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=2003-019 A [9] NASA - NSSDCA - spacecraft – Details[EB/OL]. [2021-12-18] https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=2014-076 A [10] CAPDEVILA L, GUZZETTI D, HOWELL K. Various transfer options from Earth into distant retrograde orbits in the vicinity of the Moon[J]. Advances in the Astronautical Sciences, 2014, 152: 3659-3678 [11] FOLTA D C, PAVLAK T A, HAAPALA A F, et al. Preliminary design considerations for access and operations in earth-moon L1/L2 orbits[J]. Advances in the Astronautical Sciences, 2013, 148: 2073-2092 [12] 谭明虎, 张科, 吕梅柏, 等. 基于大幅值Lyapunov轨道的地月转移轨道设计研究[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(5): 1209-1215TAN Minghu, ZHANG Ke, LYU Meibo, et al. Research on earth-moon transfer by using a large amplitude Lyapunov orbit[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(5): 1209-1215 [13] PENG C, ZHANG H, WEN C X, et al. Exploring more solutions for low-energy transfers to lunar distant retrograde orbits[J]. Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy, 2022, 134(1): 4 doi: 10.1007/s10569-021-10056-2 [14] WELCH C M, PARKER J S, BUXTON C. Mission considerations for transfers to a distant retrograde orbit[J]. The Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 2015, 62(2): 101-124 doi: 10.1007/s40295-015-0039-z [15] DEMEYER J, GURFIL P. Transfer to small distant retrograde orbits[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2007, 886(1): 20-31 [16] XU M, XU S J. Exploration of distant retrograde orbits around Moon[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2009, 65(5-6): 853-860 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2009.03.026 [17] 曾豪, 李朝玉, 彭坤, 等. 地月空间NRHO与DRO在月球探测中的应用研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2020, 41(7): 910-919ZENG Hao, LI Zhaoyu, PENG Kun, et al. Research on application of earth-moon NRHO and DRO for lunar exploration[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2020, 41(7): 910-919 [18] REN J, LI M T, ZHENG J H. Families of transfers from the Moon to Distant Retrograde Orbits in cislunar space[J]. Astrophysics and Space Science, 2020, 365(12): 192 doi: 10.1007/s10509-020-03901-7 [19] ZHANG R K, WANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Transfers from distant retrograde orbits to low lunar orbits[J]. Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy, 2020, 132(8): 41 doi: 10.1007/s10569-020-09982-4 [20] BEZROUK C J, PARKER J. Long duration stability of distant retrograde orbits[C]//AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference. San Diego: AIAA, 2014: 4424 [21] 王艾雪, 张晨, 王蜀泉, 等. 基于地月自由返回轨道的DRO入轨策略[J]. 载人航天, 2022, 28(1): 81-89 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2022.01.012WANG Aixue, ZHANG Chen, WANG Shuquan, et al. Design considerations for access in to earth-moon DROs with lunar free-return trajectory[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2022, 28(1): 81-89 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2022.01.012 [22] 赵国强, 宝音贺西, 李俊峰. 基于B平面的火星探测直接转移轨道设计方法[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2012, 32(1): 1-7 doi: 10.3780/j.issn.1000-758X.2012.01.001ZHAO Guoqiang, BAOYIN Hexi, LI Junfeng. Direct transfer trajectory design for mars exploration using B-plane[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2012, 32(1): 1-7 doi: 10.3780/j.issn.1000-758X.2012.01.001 -
-





 下载:
下载: