张衡一号卫星探测的赤道附近电场分布及其与电离层分布的关系
doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.05.2023-0020 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2023.05.2023-0020
Distribution of Equatorial Electric Field and Its Relation with Ionosphere Distribution Detected by the ZH-1 Satellite
-
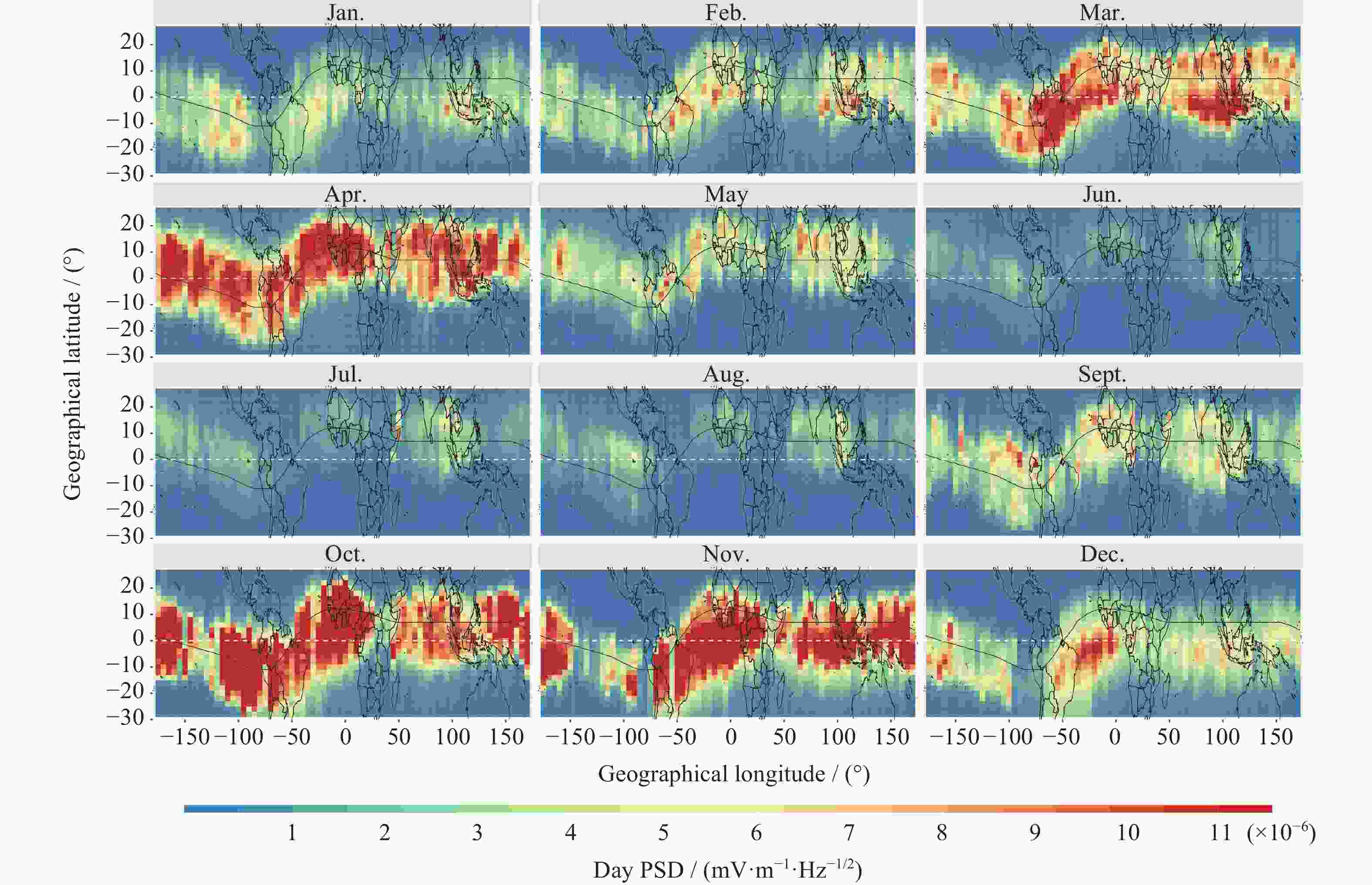
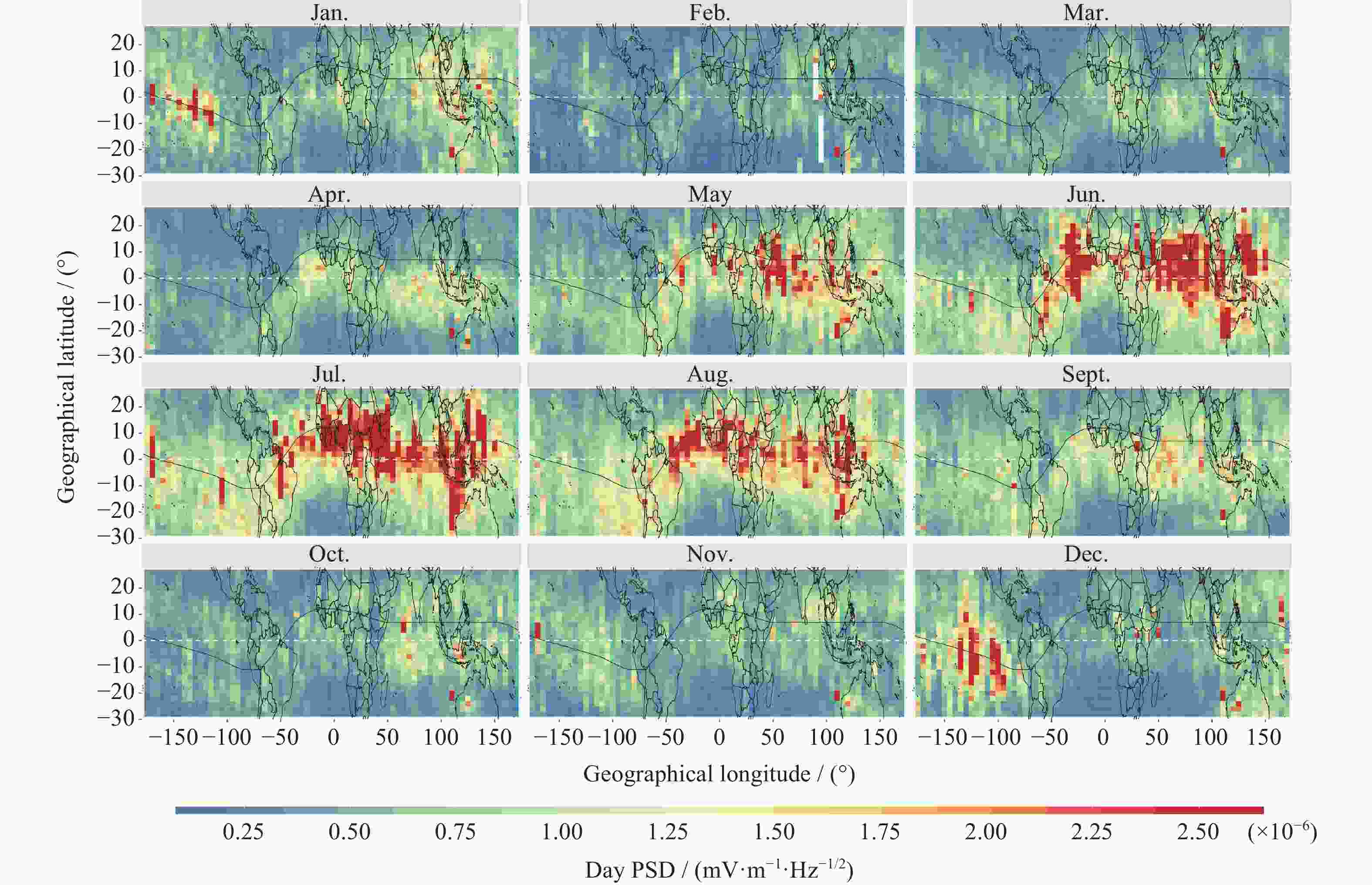
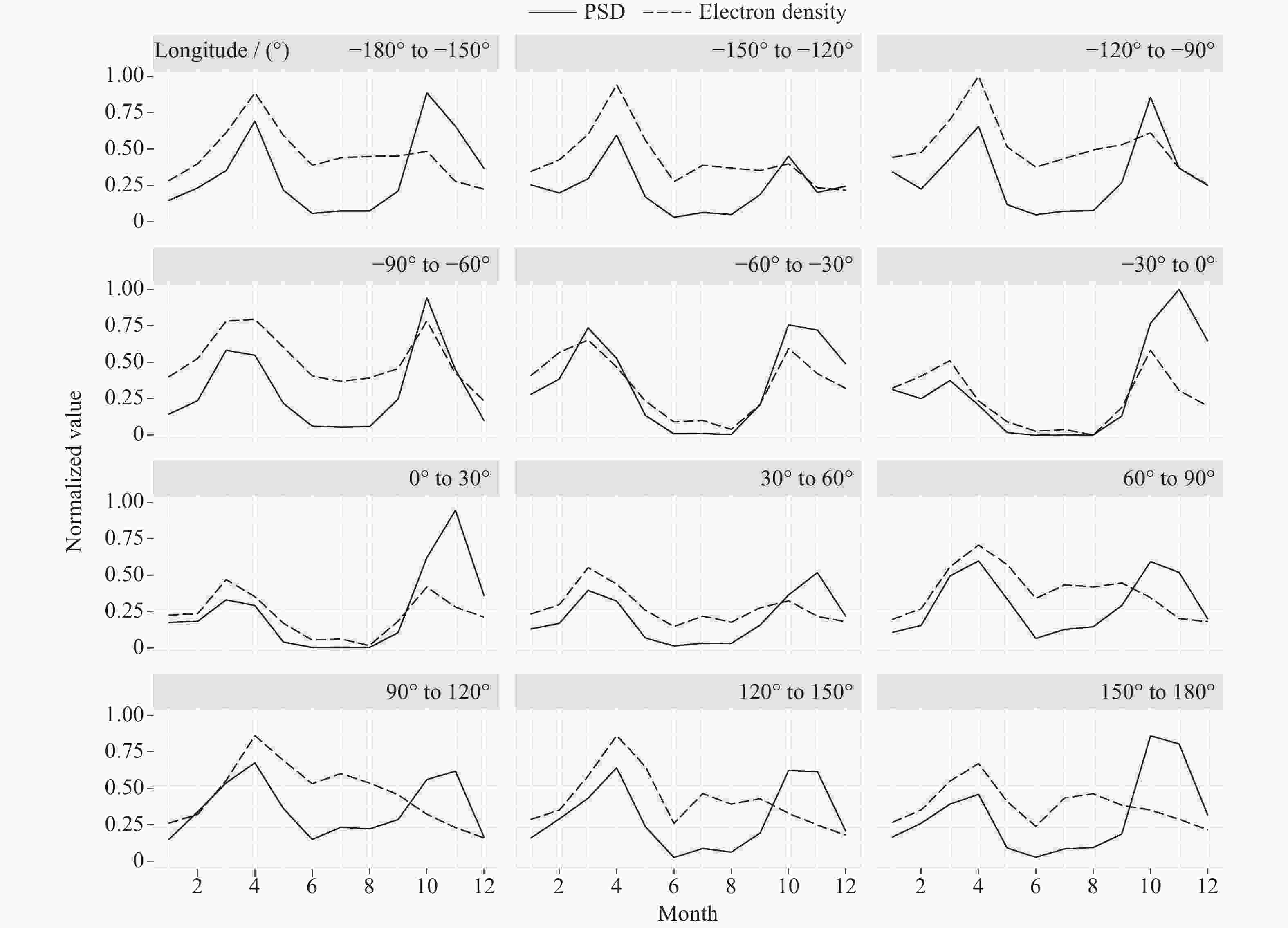
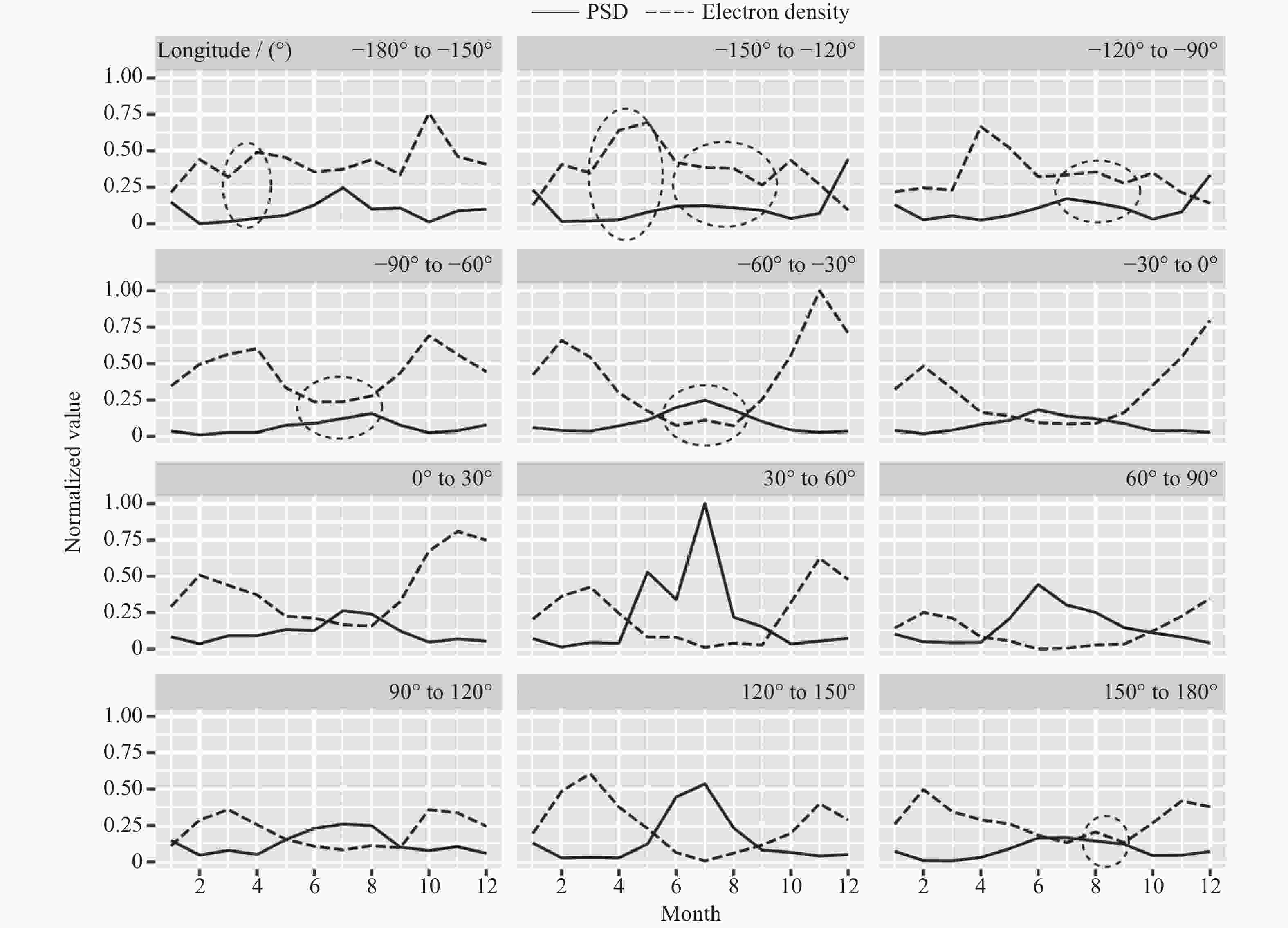
摘要: 利用张衡一号卫星搭载的电场探测仪(Electric Field Detector,EFD)获得的VLF频段2019年电场功率谱数据,研究赤道附近区域近东西向电场的背景分布、季节变化以及与电离层背景的关系。结果表明:白天电场背景在赤道及其附近随季节呈不同波形结构,以3波、4波为主;夜间电场背景规律性稍差,仍呈随季节变化的经向波形结构分布特征;白天电场背景与电离层背景的季节变化呈高度正相关性,春秋季为峰值;夜间电场背景的季节变化特征是夏冬季峰值,与夜间电离层背景整体上呈负相关性。VLF电场功率谱观测数据与电离层观测数据在较大和较小空间尺度上的统计特征上都具有一致性。EFD载荷为电离层相关科学问题的研究及应用提供了一个可以使用的电场观测数据集。Abstract: The nearly east-west power spectral density data of VLF band in 2019, obtained by the Zhangheng-1 satellite, are used to carry out studies on the background distribution of the equatorial electric field, its seasonal variations, as well as its relation with the background ionosphere. The results are as follows: variations of waveform distributions with the season are shown for the daytime equatorial electric field background in the equator and its adjacent regions, with wave number 3 and wave number 4 being the dominant structure; the longitude waveform distribution and its variation with the season can be seen from the spatial distribution of nighttime field background though its regularity is weaker than that of the daytime data; the daytime electric field background has a highly positive correlation with the ionospheric background, with a seasonal variation patter of spring-autumn peaks; Seasonal variation of equatorial nighttime electric field background is characterized by summer and winter peaks, and the correlation between the two is generally negative. Therefore, the spatiotemporal distribution of the electric field background and its correlation with the ionosphere background suggests that the electric field observations are consistent with the ionospheric observations in terms of statistical features obtained both from large as well as relatively small spatial scales. The EFD payload, as one of the payloads that produces the most data, provides a usable dataset for the study of ionosphere-related scientific problems.
-
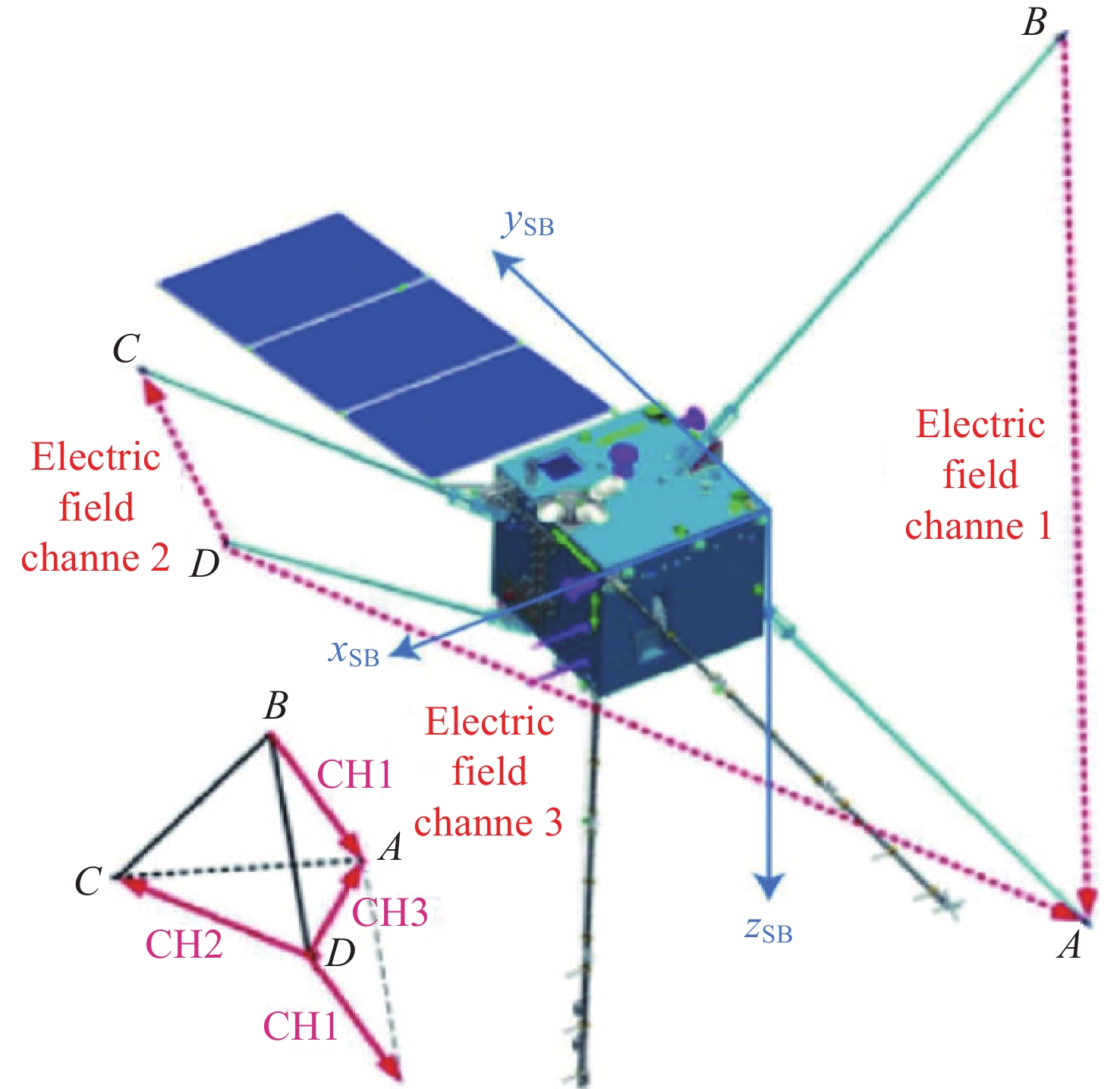
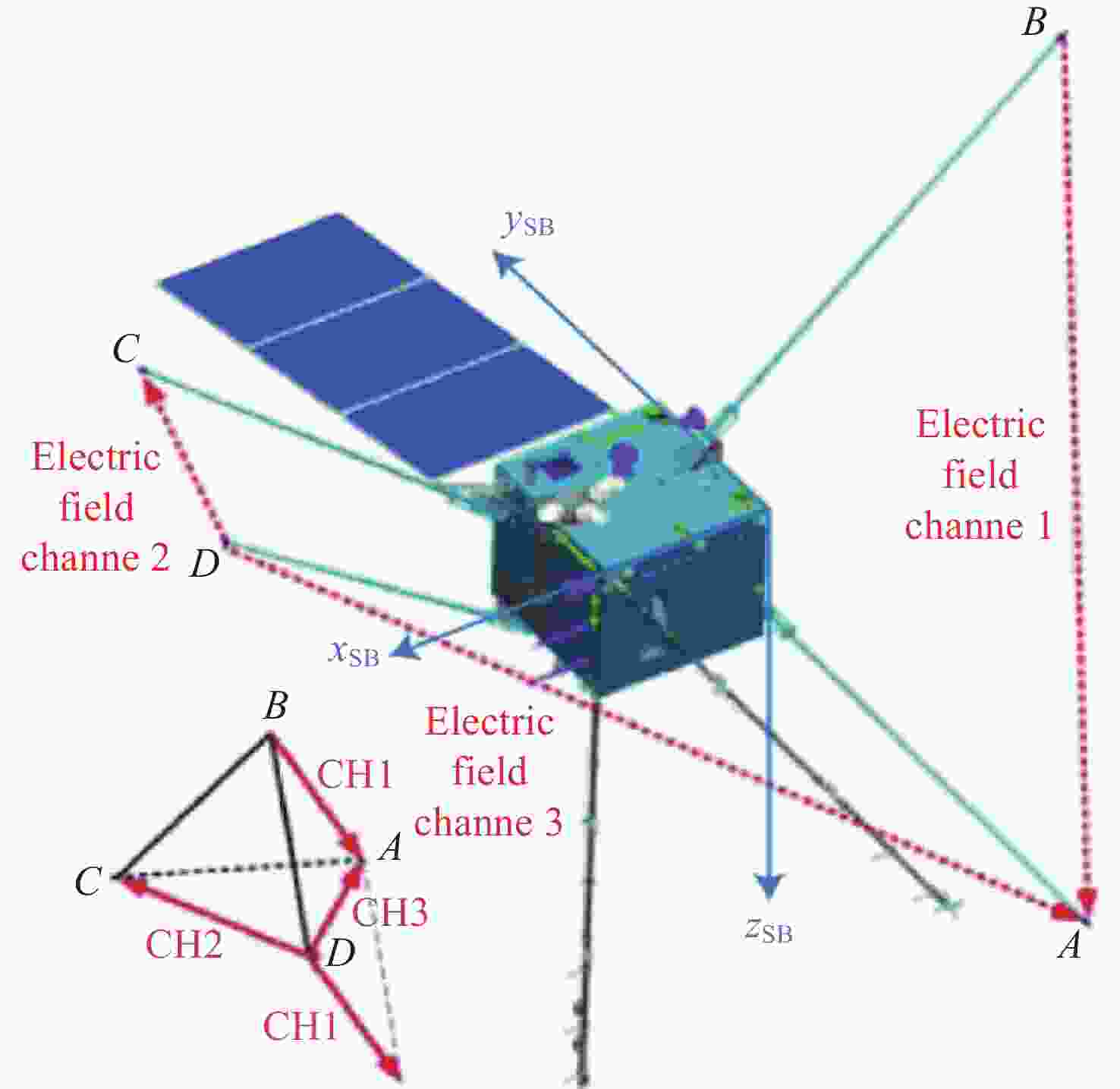
图 1 EFD载荷电场分量及与卫星坐标系关系(xSB,ySB,zSB箭头方向表示卫星坐标系xyz轴的正值方向;A,B,C,D为EFD载荷4个球形探针的位置;CH1,CH2,CH3 表示实际使用的三个电场分量)
Figure 1. Components of EFD payload and their relations with the satellite coordinate (The arrow directions of xSB,ySB,zSB indicate the positive direction of the satellite coordinate xyz; A, B, C, and D represent the position of the 4 sphere probes of the EFD payload; CH1, CH2, and CH3 are the three components of the payload)
表 1 不同经度区功率谱与电子密度观测数据月背景相关系数
Table 1. Pearson correlation coefficients of monthly background for PSD and electron density measurements in different longitude sectors
Longitude sector rd rn Longitude sector rd rn Longitude sector rd rn –180º至–150º 0.2869 –0.4832 –60º至–30º 0.8837 –0.8297 60º至90º 0.4223 –0.7596 –150º至–120º 0.6598 –0.6592 –30º至0º 0.6473 –0.7942 90º至120º 0.2680 –0.7379 –120º至–90º 0.6038 –0.4963 0º至30º 0.6389 –0.7462 120º至150º 0.3263 –0.7359 –90º至–60º 0.8261 –0.7739 30º至60º 0.5513 –0.6174 150º至180º 0.0383 –0.8137 注 rd表示白天数据的相关系数,rn表示夜间数据的相关系数。 -
[1] WOODMAN R F. Vertical drift velocities and east-west electric fields at the magnetic equator[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1970, 75(31): 6249-6259 doi: 10.1029/JA075i031p06249 [2] BALSLEY B B. Electric fields in the equatorial ionosphere: a review of techniques and measurements[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, 1973, 35(6): 1035-1044 doi: 10.1016/0021-9169(73)90003-2 [3] WOODMAN R F, RASTOGI R G, CALDERON C. Solar cycle effects on the electric fields in the equatorial ionosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1977, 82(32): 5257-5261 doi: 10.1029/JA082i032p05257 [4] FEJER B G, FARLEY D T, WOODMAN R F, et al. Dependence of equatorial F region vertical drifts on season and solar cycle[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1979, 84(A10): 5792-5796 doi: 10.1029/JA084iA10p05792 [5] FEJER B G, DE PAULA E R, GONZÁLEZ S A, et al. Average vertical and zonal F region plasma drifts over Jicamarca[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1991, 96(A8): 13901-13906 doi: 10.1029/91JA01171 [6] YEH H C, HILL T W. Mechanism of parallel electric fields inferred from observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1981, 86(A8): 6706-6712 doi: 10.1029/JA086iA08p06706 [7] FEJER B G, DE PAULA E R, HEELIS R A, et al. Global equatorial ionospheric vertical plasma drifts measured by the AE-E satellite[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1995, 100(A4): 5769-5776 doi: 10.1029/94JA03240 [8] BERTHELIER J J, GODEFROY M, LEBLANC F, et al. ICE, the electric field experiment on DEMETER[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2006, 54(5): 456-471 doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2005.10.016 [9] YAO Li, CHEN Huaran, LIU Xiaocan, et al. The global characteristics of VLF electric field frequency spectrum in ionosphere[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research, 2011, 32(4): 27-34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2011.04.006 [10] PFAFF R, URIBE P, FOURRE R, et al. The vector electric field investigation (VEFI) on the C/NOFS satellite[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2021, 217(8): 85 doi: 10.1007/s11214-021-00859-y [11] SHEN X H, ZHANG X M, YUAN S G, et al. The state-of-the-art of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite mission[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2018, 61(5): 634-642 doi: 10.1007/s11431-018-9242-0 [12] WANG X Y, CHENG W L, YANG D H, et al. Preliminary validation of in situ electron density measurements onboard CSES using observations from Swarm Satellites[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2019, 64(4): 982-994 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2019.05.025 [13] SHEN X H, ZEREN Z M, YUAN S G, et al. The CSES mission and its preliminary results[J]. Aerospace China, 2020, 21(1): 5-18 [14] GAO Peng, WANG Xiuying, YANG Dehe, et al. Electric field data storage experiment of the ZH-1 satellite[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(4): 1386-1392 [15] ZHANG X M, FROLOV V, ZHAO S F, et al. The first joint experimental results between SURA and CSES[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2018, 2(6): 527-537 doi: 10.26464/epp2018051 [16] ZHAO S F, ZHOU C, SHEN X H, et al. Investigation of VLF transmitter signals in the ionosphere by ZH-1 observations and full-wave simulation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2019, 124(6): 4697-4709 doi: 10.1029/2019JA026593 [17] LIAO Li, ZHAO Shufan, SHEN Xuhui, et al. Characteristic analysis and full wave simulation of electrical field for China seismo-electromagnetic satellite observations radiated from VLF transmitter[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(4): 1210-1217 doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0504 [18] BOUDJADA M Y, EICHELBERGER H U, ZHANG X M, et al. Analysis of ground-based very low frequency signal recorded onboard CSES satellite[C]//Proceedings of 2021 Kleinheubach Conference. Miltengerg: IEEE, 2021: 1-3 [19] MA Mianjun, LEI Jungang, LI Cheng, et al. Design optimization of zhangheng-1 space electric field detector[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2018, 38(7): 582-589 doi: 10.13922/j.cnki.cjovst.2018.07.06 [20] HUANG J P, LEI J G, LI S X, et al. The Electric Field Detector (EFD) onboard the ZH-1 satellite and first observational results[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2018, 2(6): 469-478 doi: 10.26464/epp2018045 [21] DIEGO P, HUANG J P, PIERSANTI M, et al. The electric field detector on board the china seismo electromagnetic satellite—in-orbit results and validation[J]. Instruments, 2020, 5(1): 1 doi: 10.3390/instruments5010001 [22] CHMYREV V M, SOROKIN V M, SHKLYAR D R. VLF transmitter signals as a possible tool for detection of seismic effects on the ionosphere[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2008, 70(16): 2053-2060 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2008.09.005 [23] HAYOSH M, NĚMEC F, SANTOLÍK O, et al. Propagation properties of quasiperiodic VLF emissions observed by the DEMETER spacecraft[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(3): 1007-1014 doi: 10.1002/2015GL067373 [24] MEREDITH N P, HORNE R B, CLILVERD M A, et al. An investigation of VLF transmitter wave power in the inner radiation belt and slot region[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2019, 124(7): 5246-5259 doi: 10.1029/2019JA026715 [25] ABDU M A. Electrodynamics of ionospheric weather over low latitudes[J]. Geoscience Letters, 2016, 3(1): 11 doi: 10.1186/s40562-016-0043-6 [26] WANG Xiuying, YANG Dehe, ZHOU Zihan, et al. Features of topside ionospheric background over China and its adjacent areas obtained by the ZH-1 satellite[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(2): 391-409 [27] ADENIYI J O. Magnetic storm effects on the morphology of the equatorial F2-layer[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, 1986, 48(8): 695-702 doi: 10.1016/0021-9169(86)90019-X [28] FEJER B G. Low latitude ionospheric electrodynamics[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2011, 158(1): 145-166 doi: 10.1007/s11214-010-9690-7 [29] KIL H, OH S J, KELLEY M C, et al. Longitudinal structure of the vertical E×B drift and ion density seen from ROCSAT-1[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(14): L14110 doi: 10.1029/2007GL030018 [30] FATKULLIN M N. The seasonal anomaly in the electron density of the topside F2-region[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, 1970, 32(6): 1067-1075 doi: 10.1016/0021-9169(70)90118-2 [31] BALAN N, OTSUKA Y, BAILEY G J, et al. Equinoctial asymmetries in the ionosphere and thermosphere observed by the MU radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1998, 103(A5): 9481-9495 doi: 10.1029/97JA03137 [32] LIU L B, ZHAO B Q, WAN W X, et al. Yearly variations of global plasma densities in the topside ionosphere at middle and low latitudes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2007, 112(A7): A07303 [33] BURNS A G, SOLOMON S C, WANG W, et al. Daytime climatology of ionospheric NmF2 and hmF2 from COSMIC data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2012, 117(A9): A09315 [34] WANG Xiuying, YANG Dehe, ZHANG Xueqing, et al. Spatiotemporal features of topside ionospheric irregularities during low solar activity period detected by the ZH-1 Satellite[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(3): 862-881 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0327 [35] SAGAWA E, IMMEL T J, FREY H U, et al. Longitudinal structure of the equatorial anomaly in the nighttime ionosphere observed by IMAGE/FUV[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2005, 110(A11): A11302 doi: 10.1029/2004JA010848 [36] IMMEL T J, SAGAWA E, ENGLAND S L, et al. Control of equatorial ionospheric morphology by atmospheric tides[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(15): L15108 doi: 10.1029/2006GL026161 [37] BURKE W J, DE LA BEAUJARDIÈRE O, GENTILE L C, et al. C/NOFS observations of plasma density and electric field irregularities at post-midnight local times[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009, 36(18): L00C09 [38] YIZENGAW E, ZESTA E, MOLDWIN M B, et al. Longitudinal differences of ionospheric vertical density distribution and equatorial electrodynamics[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2012, 117(A7): A07312 [39] HUANG C S, LU G, ZHANG Y L, et al. Space Physics and Aeronomy, Ionosphere Dynamics and Applications[M]. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2021 -
-





 下载:
下载: