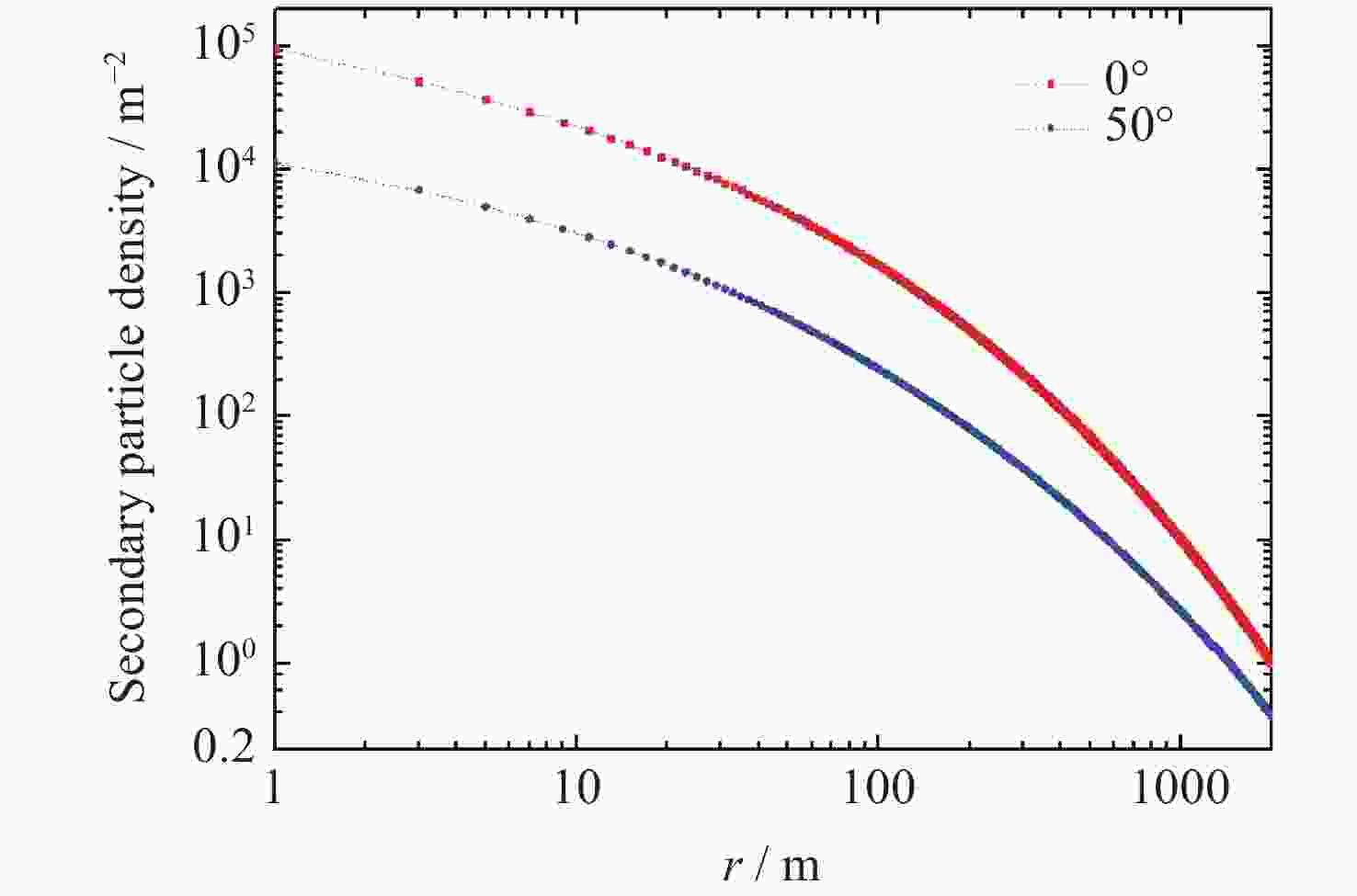
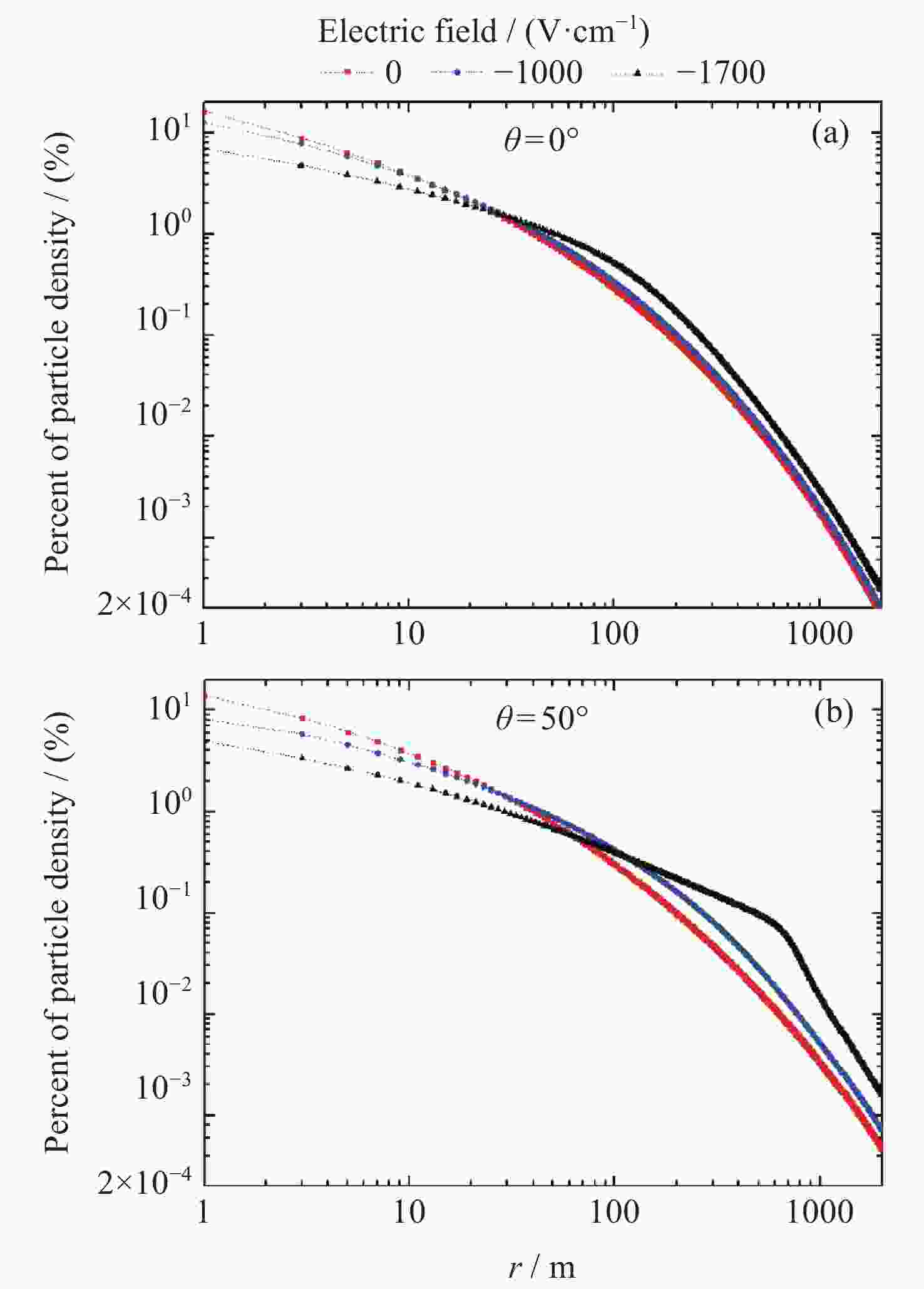
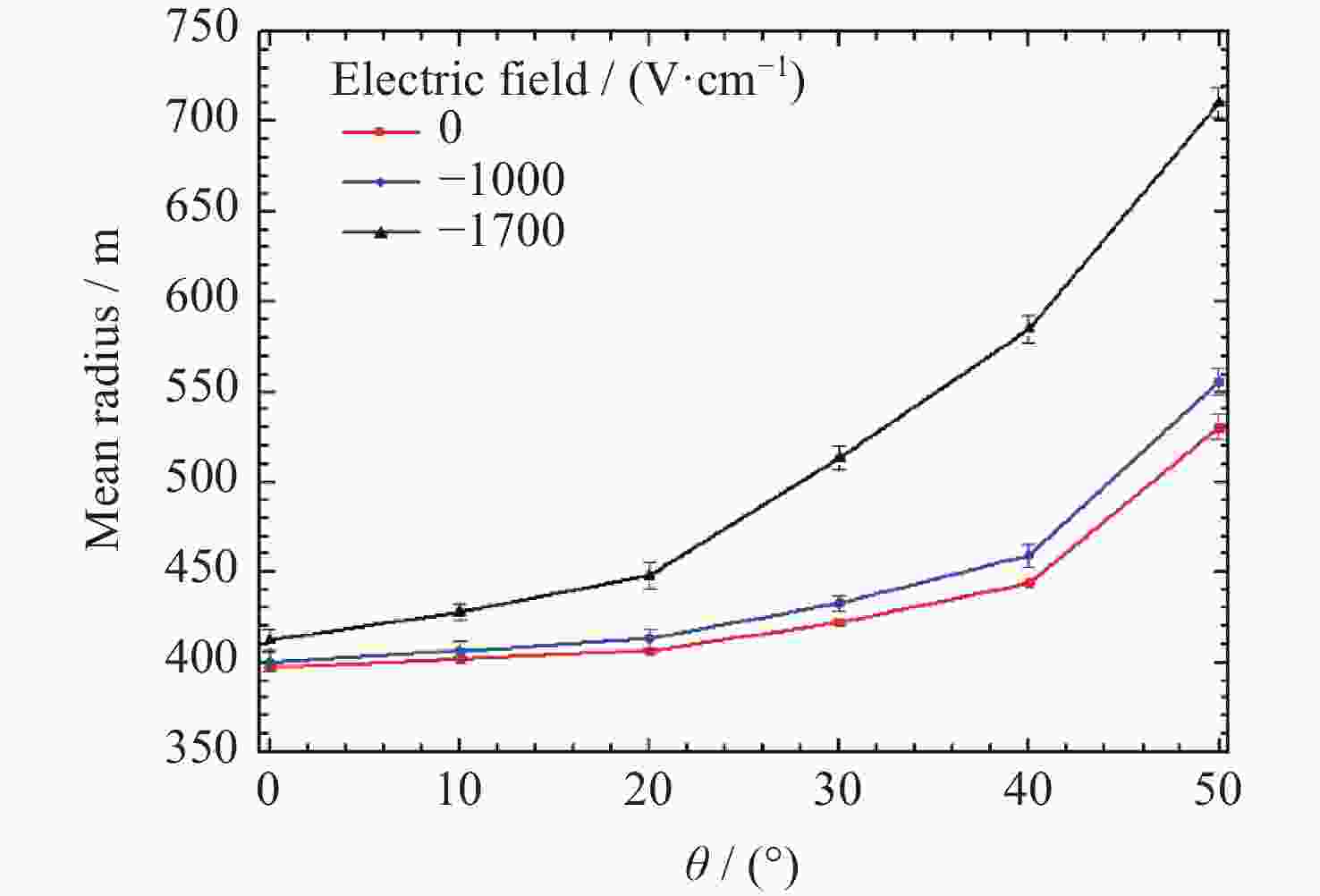
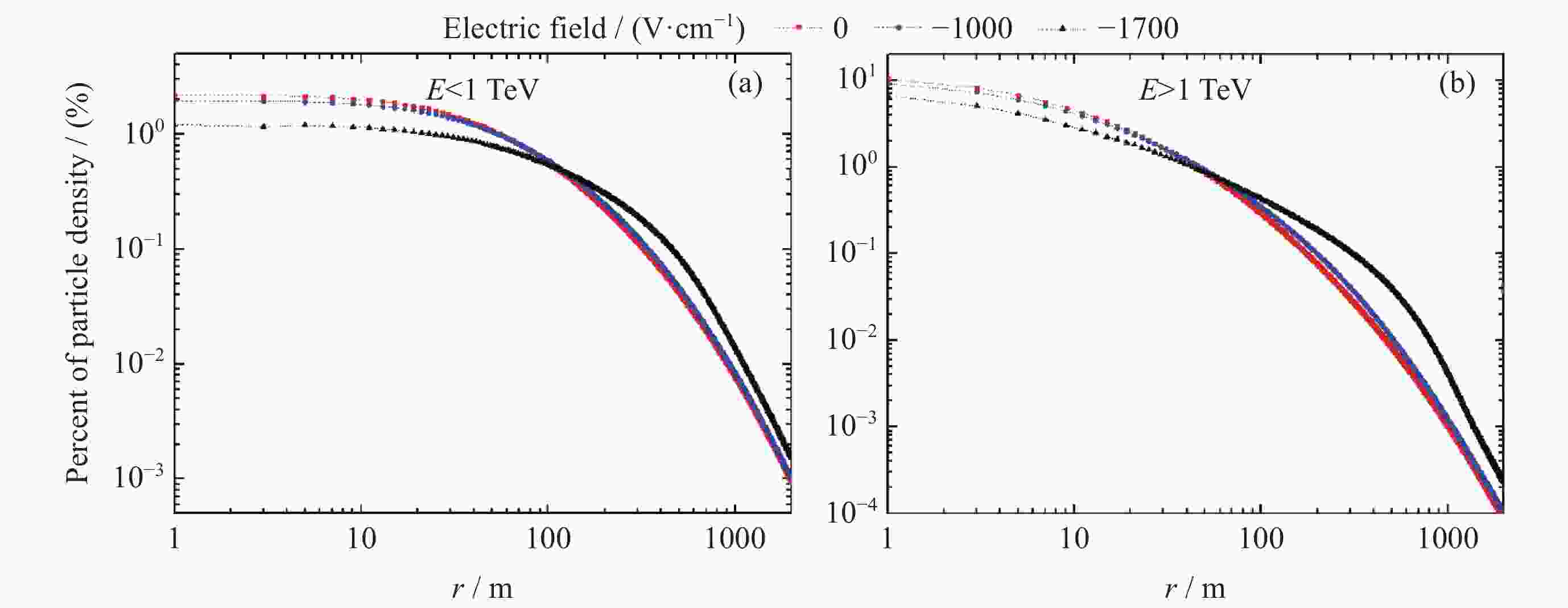
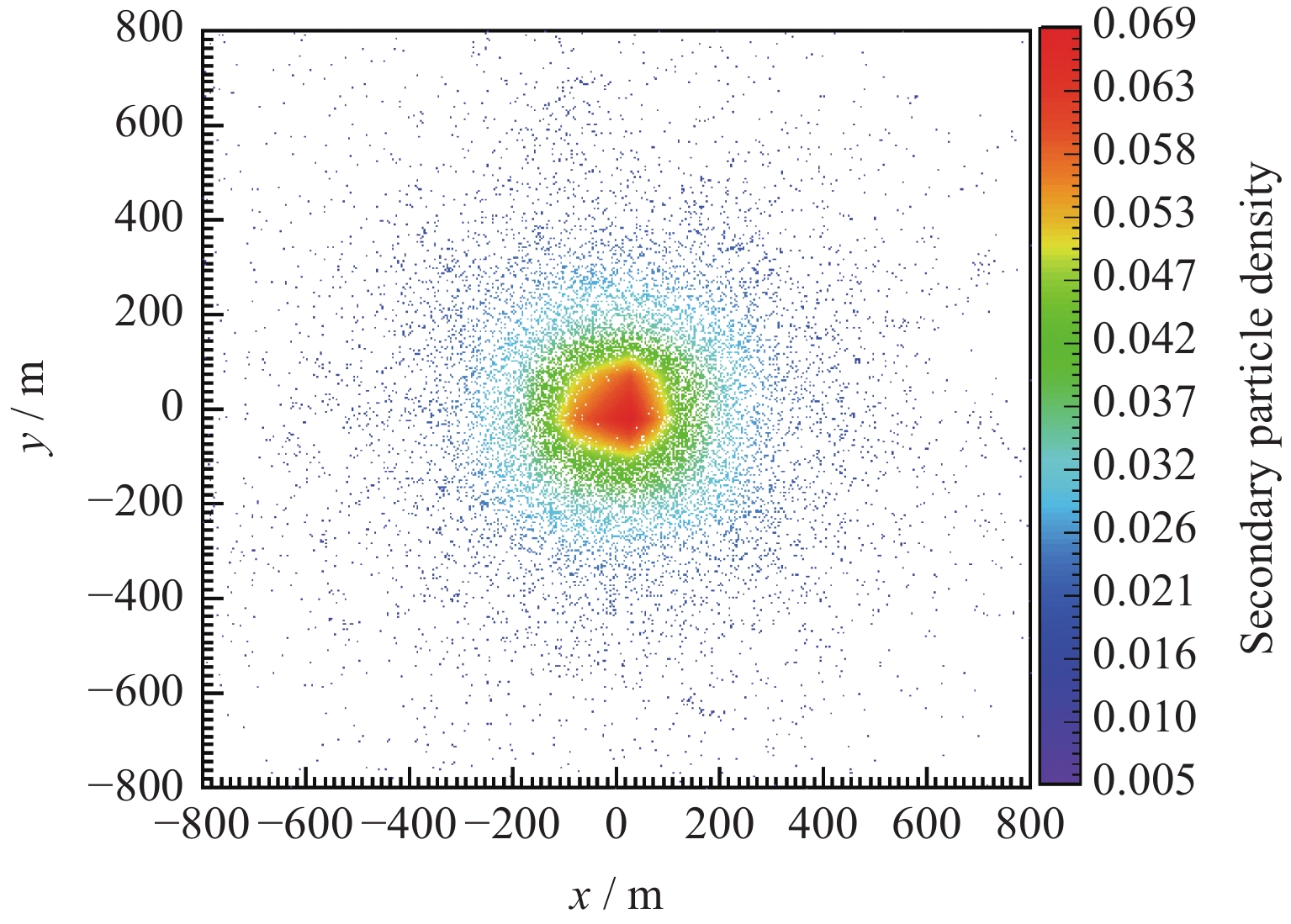
| [1] |
HUANG Zhicheng, ZHOU Xunxiu, HUANG Daihui, et al. Simulation study of scaler mode at large high altitude air shower observatory[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(19): 199301 doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20210632
|
| [2] |
WANG Kongsen, WANG He, HUANG Xingtao, et al. Study on the production characteristics of cosmic ray high energy family events with simulation and experiment[J]. High Energy Physics and Nuclear Physics, 2004, 28(3): 232-238 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3052.2004.03.004
|
| [3] |
MARSHALL T C, RUST W D, STOLZENBURG M. Electrical structure and updraft speeds in thunderstorms over the southern Great Plains[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1995, 100(D1): 1001-1015 doi: 10.1029/94JD02607
|
| [4] |
MARSHALL T C, STOLZENBURG M, MAGGIO C R, et al. Observed electric fields associated with lightning initiation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(3): L03813
|
| [5] |
GUREVICH A V, MILIKH G M, ROUSSEL-DUPRE R. Runaway electron mechanism of air breakdown and preconditioning during a thunderstorm[J]. Physics Letters A, 1992, 165(5/6): 463-468
|
| [6] |
ZHOU Xunxiu, WANG Xinjian, HUANG Daihui, et al. Simulation study on the correlation between the ground cosmic rays and the near earth thunderstorms electric field at Yangbajing (Tibet China)[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(14): 149202 doi: 10.7498/aps.64.149202
|
| [7] |
CHILINGARIAN A, HOVSEPYAN G, ZAZYAN M. Muon tomography of charged structures in the atmospheric electric field[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(17): e2021GL094594 doi: 10.1029/2021GL094594
|
| [8] |
HEUMESSER M, CHANRION O, NEUBERT T, et al. Spectral observations of optical emissions associated with terrestrial gamma-ray flashes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(4): 2020GL090700 doi: 10.1029/2020GL090700
|
| [9] |
WADA Y, MATSUMOTO T, ENOTO T, et al. Catalog of gamma-ray glows during four winter seasons in Japan[J]. Physical Review Research, 2021, 3(4): 043117 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.043117
|
| [10] |
AXIKEGU, BARTOLI B, BERNARDINI P, et al. Cosmic ray shower rate variations detected by the ARGO-YBJ experiment during thunderstorms[J]. Physical Review D, 2022, 106(2): 022008 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.106.022008
|
| [11] |
TSUCHIYA H, HIBINO K, KAWATA K, et al. Observation of thundercloud-related gamma rays and neutrons in Tibet[J]. Physical Review D, 2012, 85(9): 092006 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.85.092006
|
| [12] |
CHILINGARIAN A, HOVSEPYAN G, ASLANYAN D, et al. Thunderstorm ground enhancements: multivariate analysis of 12 years of observations[J]. Physical Review D, 2022, 106(8): 082004 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.106.082004
|
| [13] |
FISHMAN G J, BHAT P N, MALLOZZI R, et al. Discovery of intense gamma-ray flashes of atmospheric origin[J]. Science, 1994, 264(5163): 1313-1316 doi: 10.1126/science.264.5163.1313
|
| [14] |
BRIGGS M S, FISHMAN G J, CONNAUGHTON V, et al. First results on terrestrial gamma ray flashes from the Fermi gamma-ray burst monitor[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115(A7): A07323
|
| [15] |
NEUBERT T, ØSTGAARD N, REGLERO V, et al. A terrestrial gamma-ray flash and ionospheric ultraviolet emissions powered by lightning[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6474): 183-186 doi: 10.1126/science.aax3872
|
| [16] |
TSUCHIYA H, ENOTO T, YAMADA S, et al. Long-duration γ ray emissions from 2007 and 2008 winter thunderstorms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2011, 116(D9): D09113
|
| [17] |
CHILINGARIAN A, MAILYAN B, VANYAN L. Recovering of the energy spectra of electrons and gamma rays coming from the thunderclouds[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2012, 114-115: 1-16 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.05.008
|
| [18] |
YAN Ruirui, HUANG Daihui, ZHAO Bing, et al. Effects of thunderstorms electric field on energy of cosmic rays at LHAASO[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(1): 65-71 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.01.065
|
| [19] |
VANYAN L, CHILINGARYAN A. Simulations of the Relativistic Runaway Electron Avalanches (RREA) in the thunderclouds above the Aragats space Environmental center (ASEC)[C]//Proceedings of the 32 nd International Cosmic Ray Conference. Beijing: International Cosmic Ray Conference, 2011: 338-341
|
| [20] |
MA X H, BI Y J, CAO Z, et al. Chapter 1 LHAASO instruments and detector technology[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2022, 46(3): 030001 doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ac3fa6
|
| [21] |
WANG P H, HUANG D H, ZHOU X X, et al. Characteristics of near-earth thunderstorm electric fields at LHAASO observatory[C]//Proceedings of Science. Berlin: Sissa Medialab Srl, 2022: 1-10
|
| [22] |
JIA H Y, FENG L, RUFFOLO D, et al. Chapter 7 solar and heliospheric physics and interdisciplinary research with LHAASO[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2022, 46(3): 030007 doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ac3fae
|
| [23] |
HECK D, KNAPP J, CAPDEVIELLE J, et al. CORSIKA: a Monte Carlo code to simulate extensive air showers[EB/OL]. [2023-02-15]. https://www.ikp.kit.edu/corsika/70.php
|
| [24] |
DWYER J R. A fundamental limit on electric fields in air[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(20): 2055
|
| [25] |
SYMBALISTY E M D, ROUSSEL-DUPRE R A, YUKHIMUK V A. Finite volume solution of the relativistic Boltzmann equation for electron avalanche studies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 1998, 26(5): 1575-1582 doi: 10.1109/27.736065
|
| [26] |
AXI K G, ZHOU X X, HUANG Z C, et al. Intensity variations of showers with different zenith angle ranges during thunderstorms[J]. Astrophysics and Space Science, 2022, 367(3): 30 doi: 10.1007/s10509-022-04056-3
|
| [27] |
ZHOU X X, WANG X J, HUANG D H, et al. Effect of near-earth thunderstorms electric field on the intensity of ground cosmic ray positrons/electrons in Tibet[J]. Astroparticle Physics, 2016, 84: 107-114 doi: 10.1016/j.astropartphys.2016.08.004
|





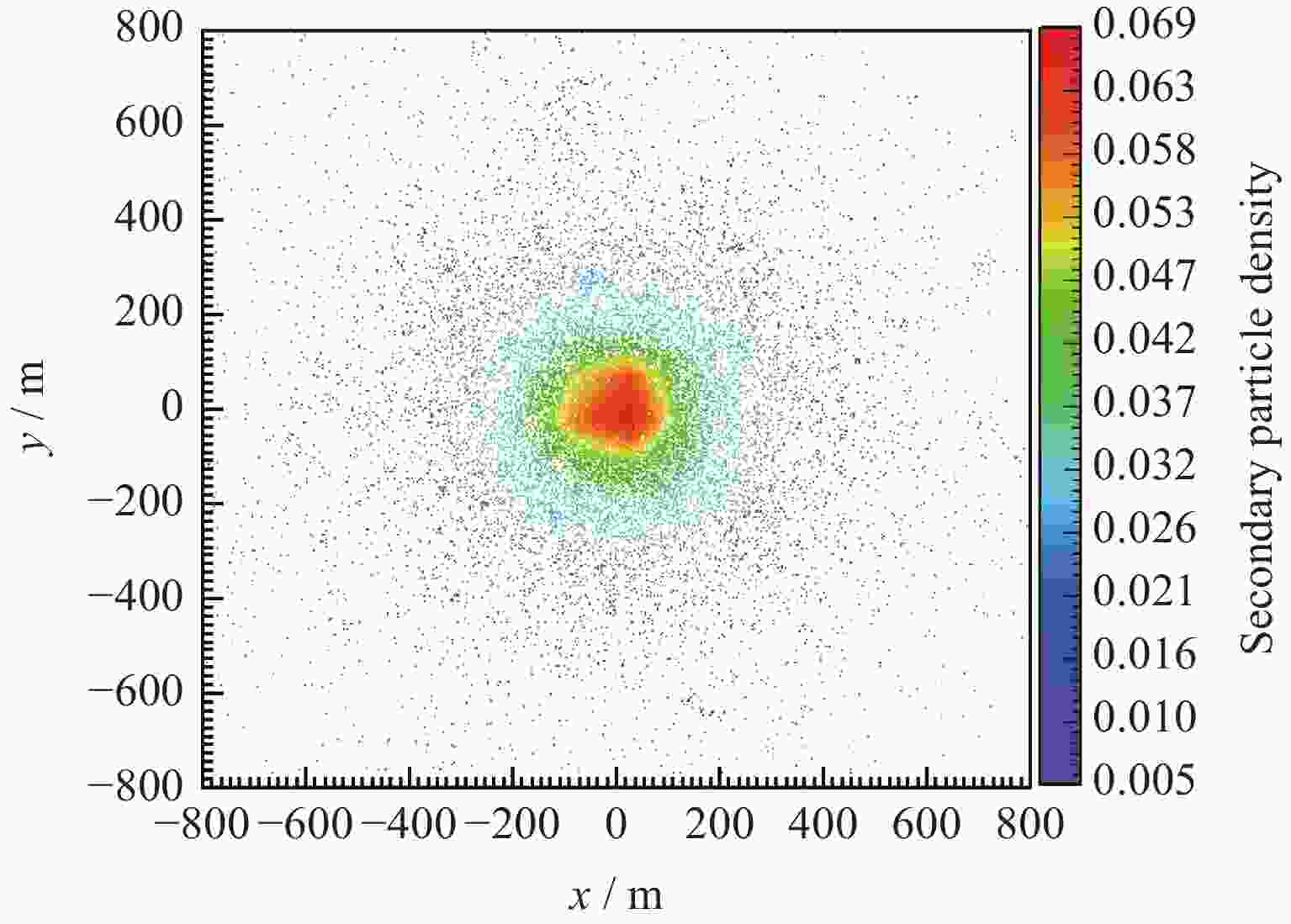
 下载:
下载: