Research on Response Regulation of Pressure-driven Multi-droplet Wetting State
-
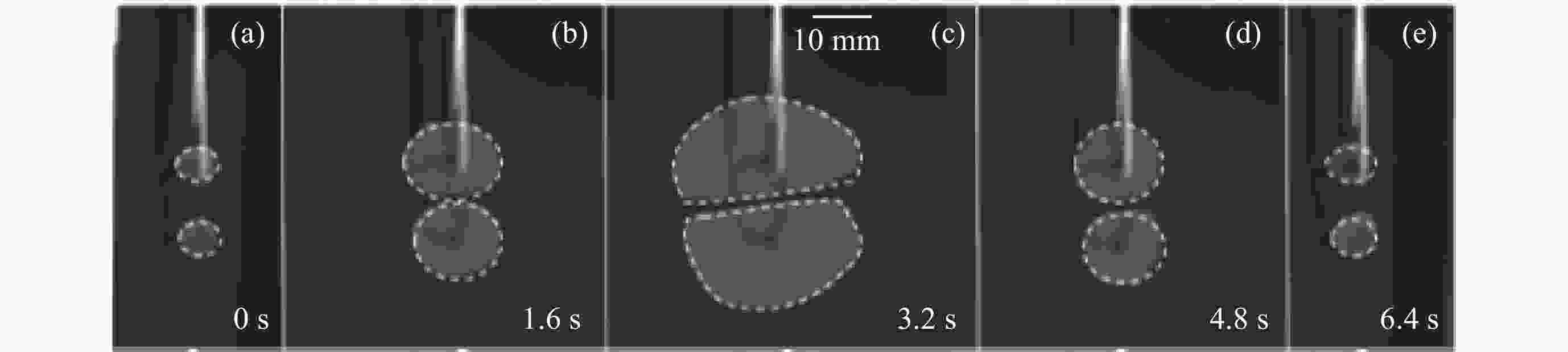
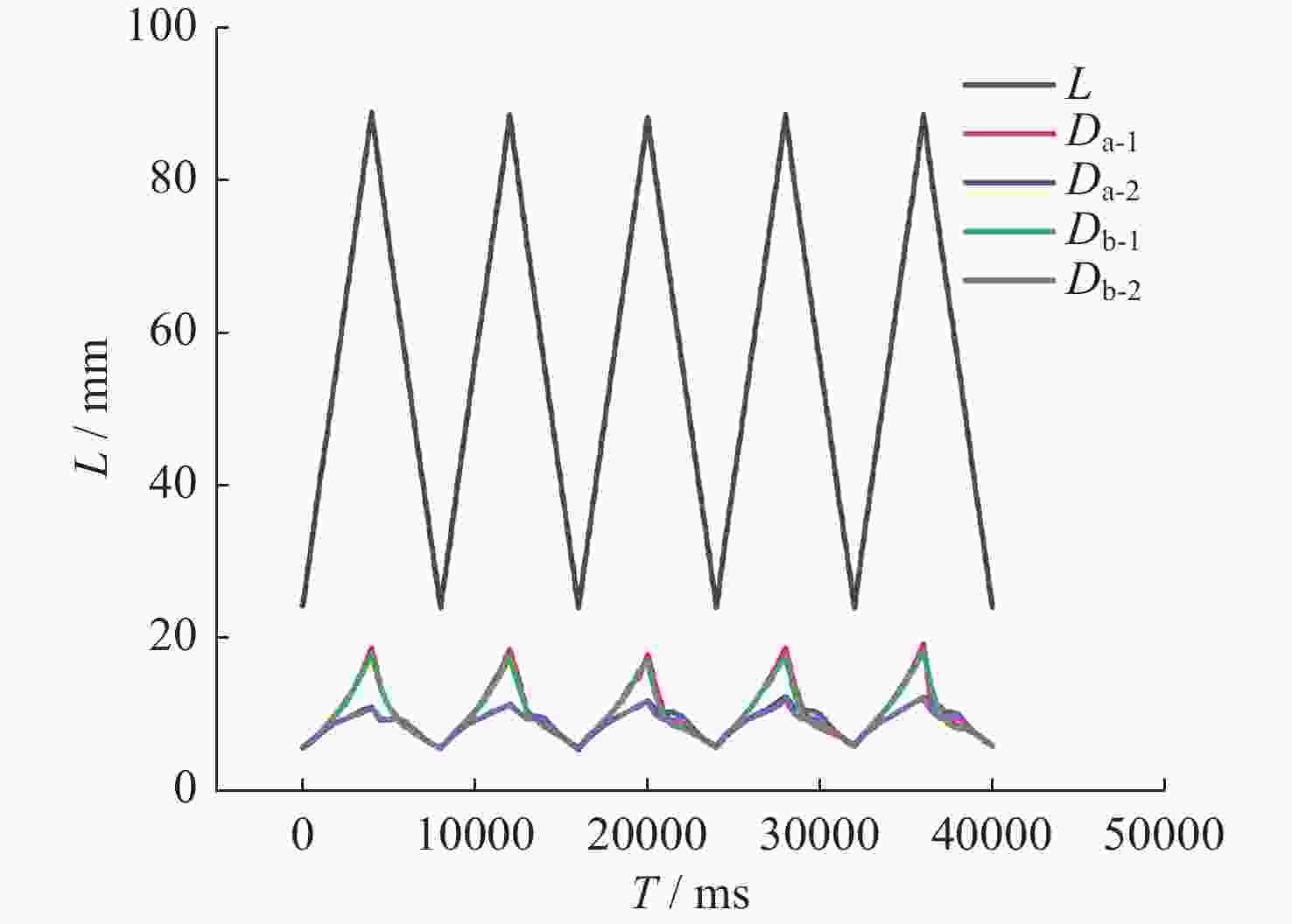
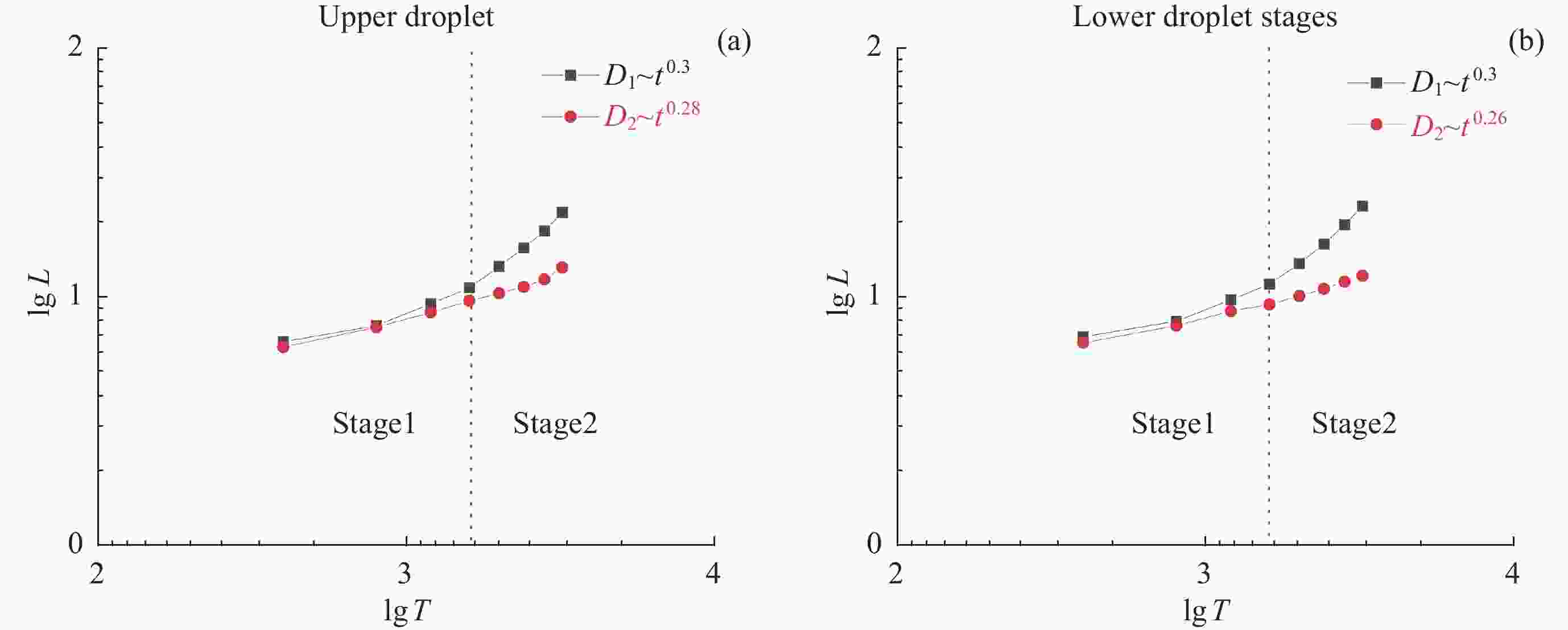
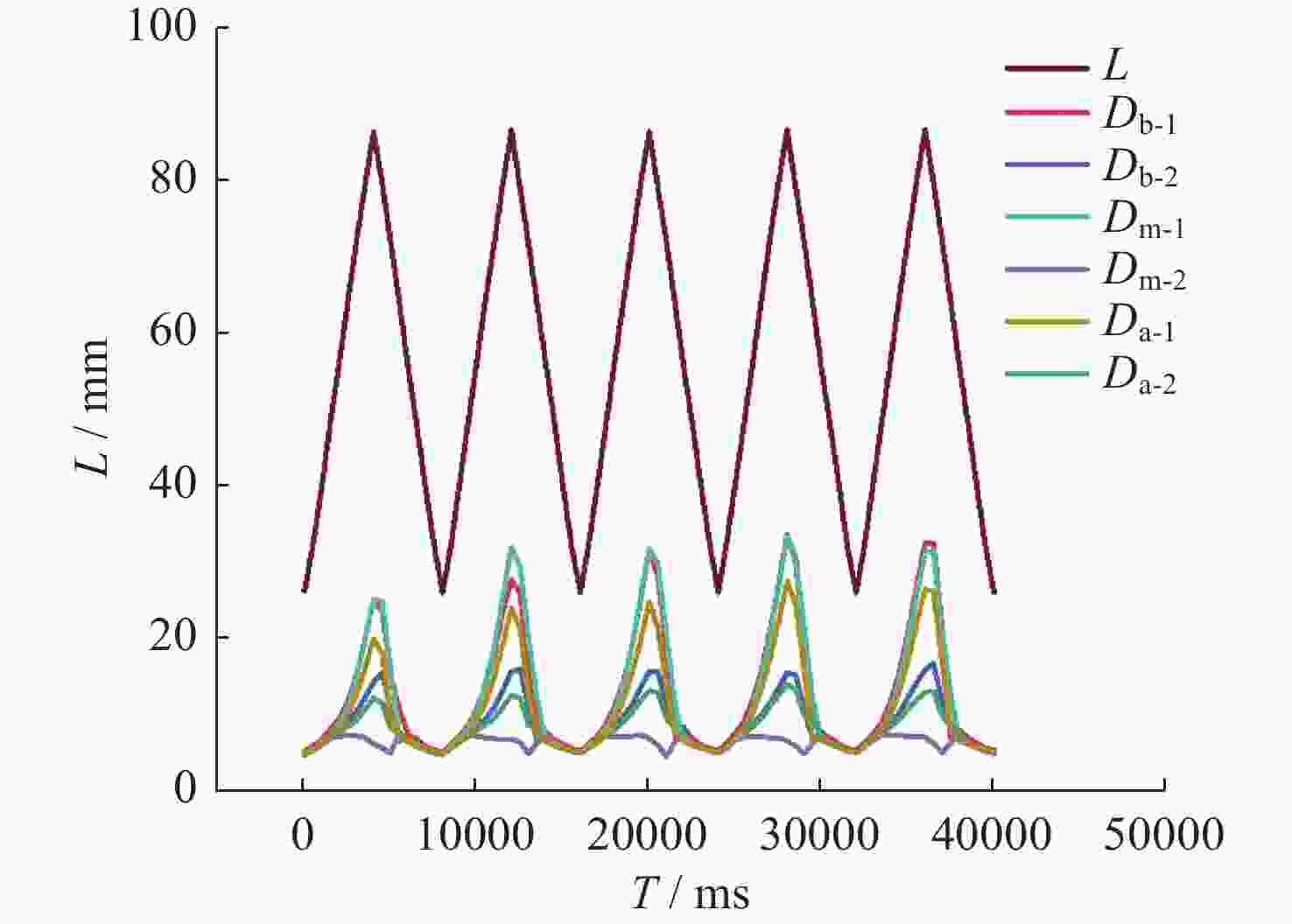
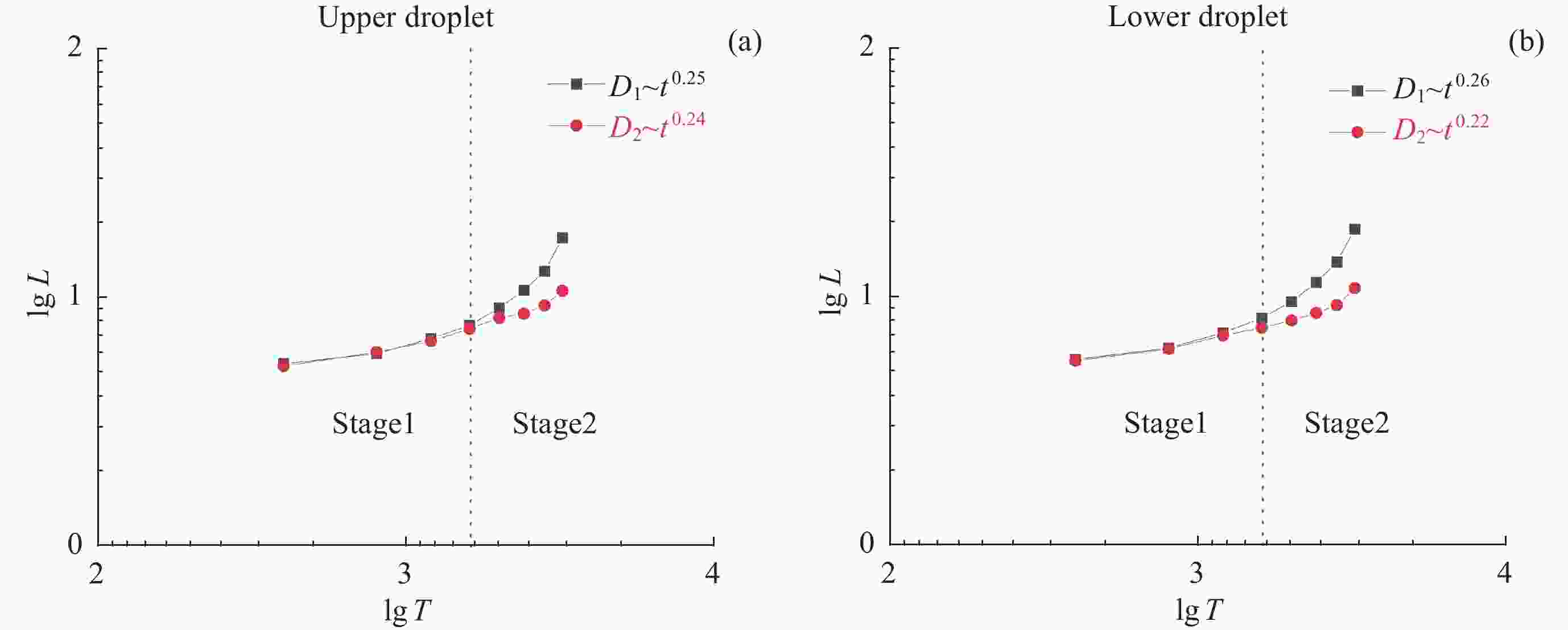
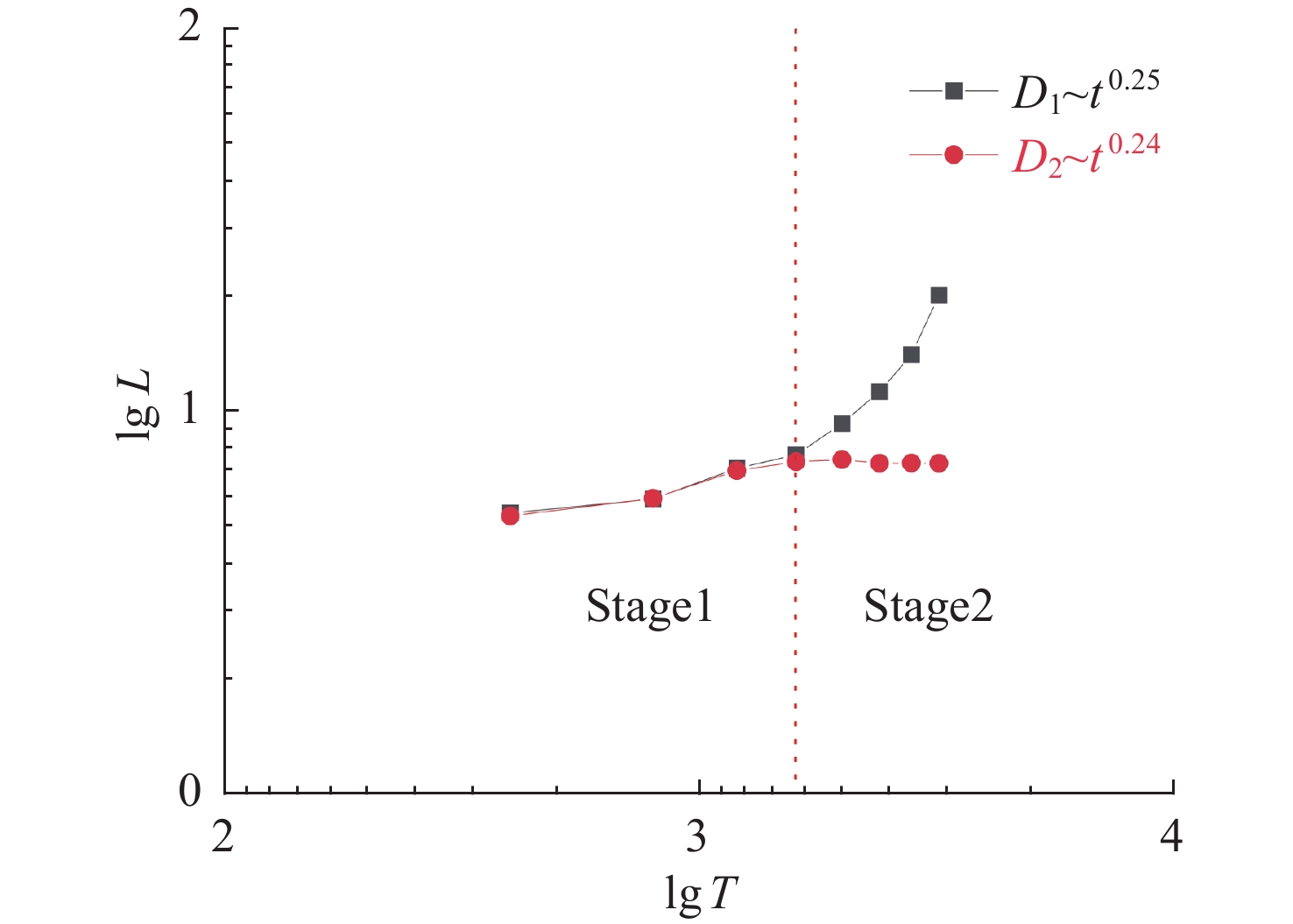
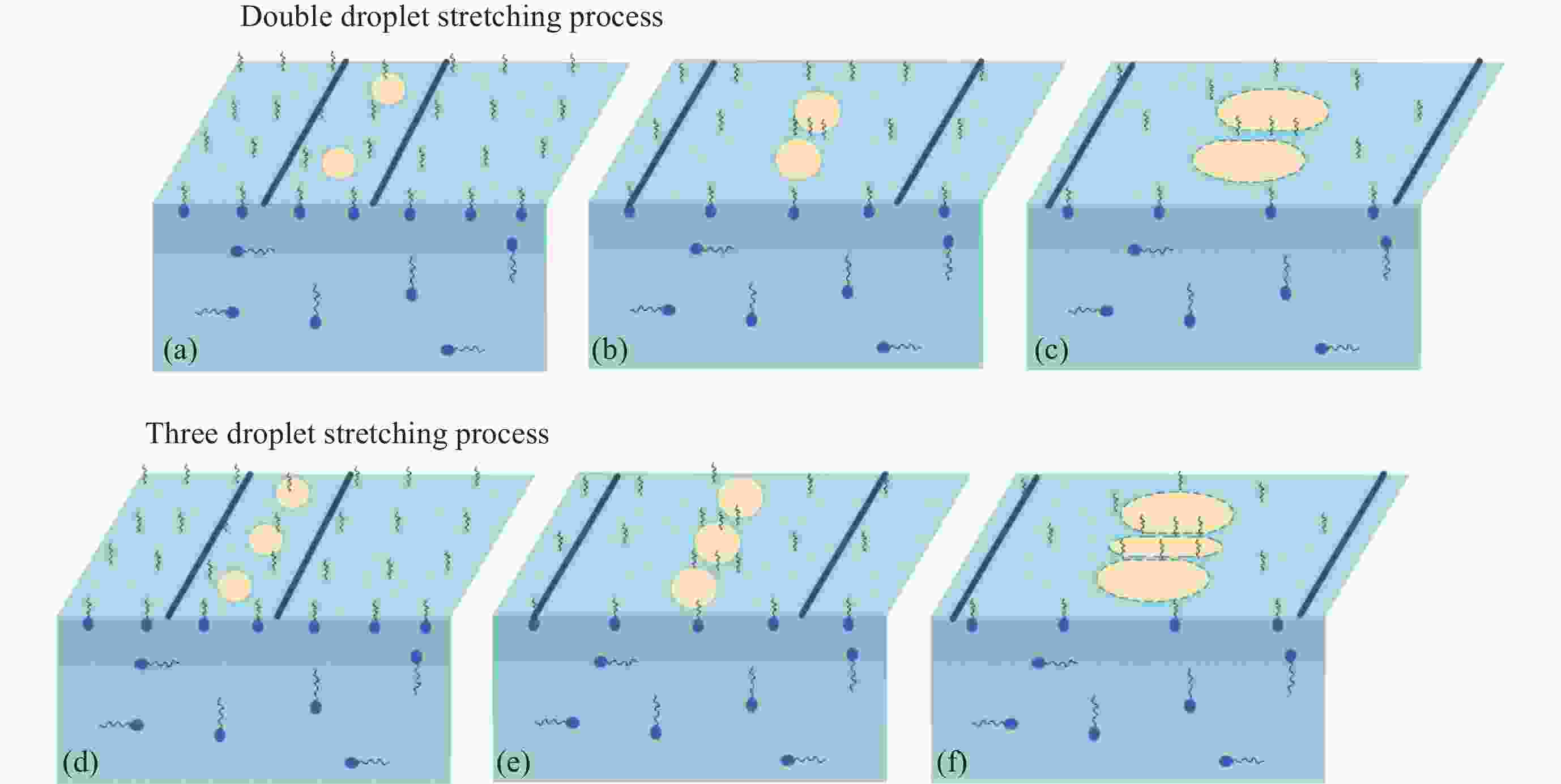
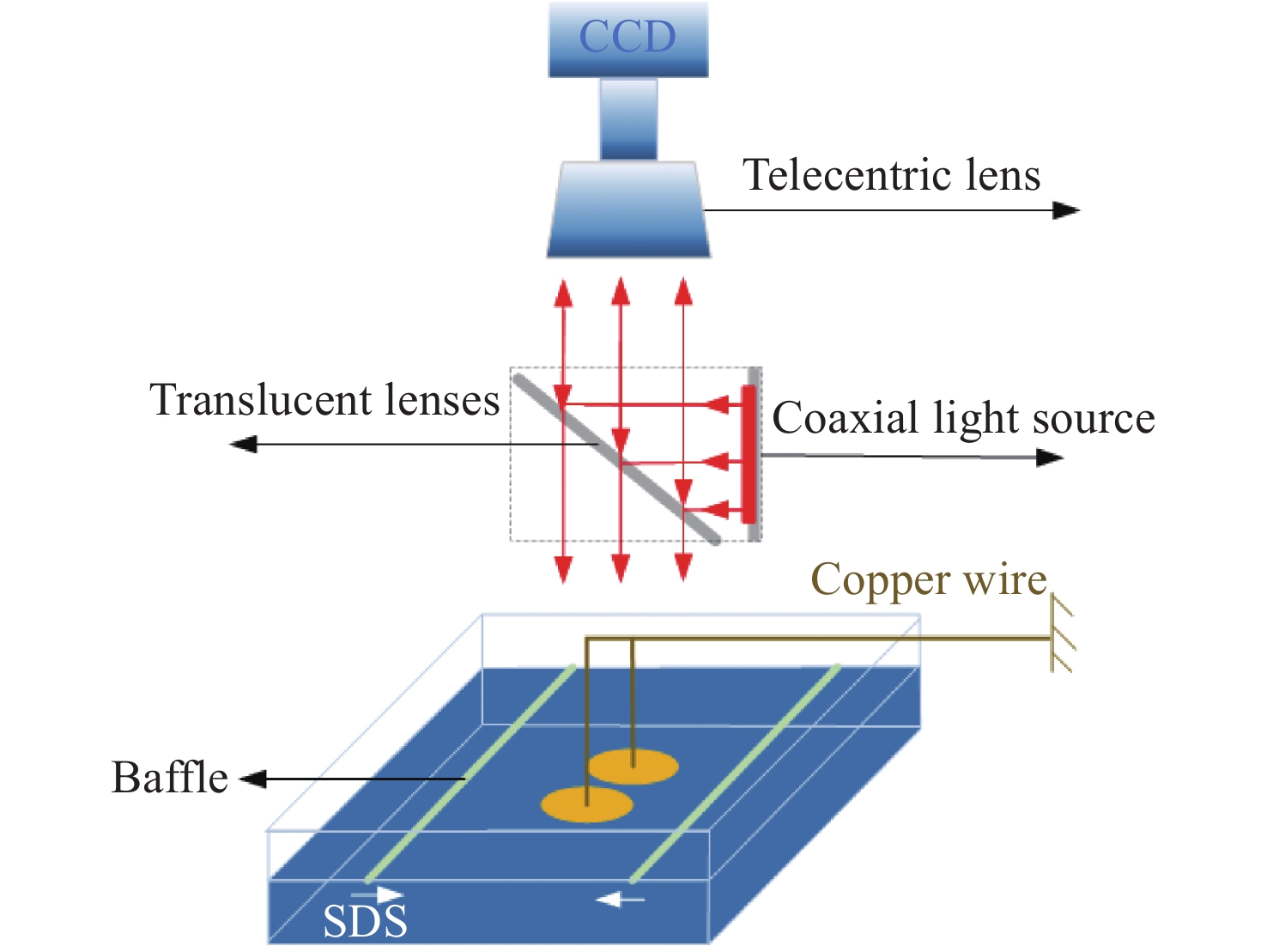
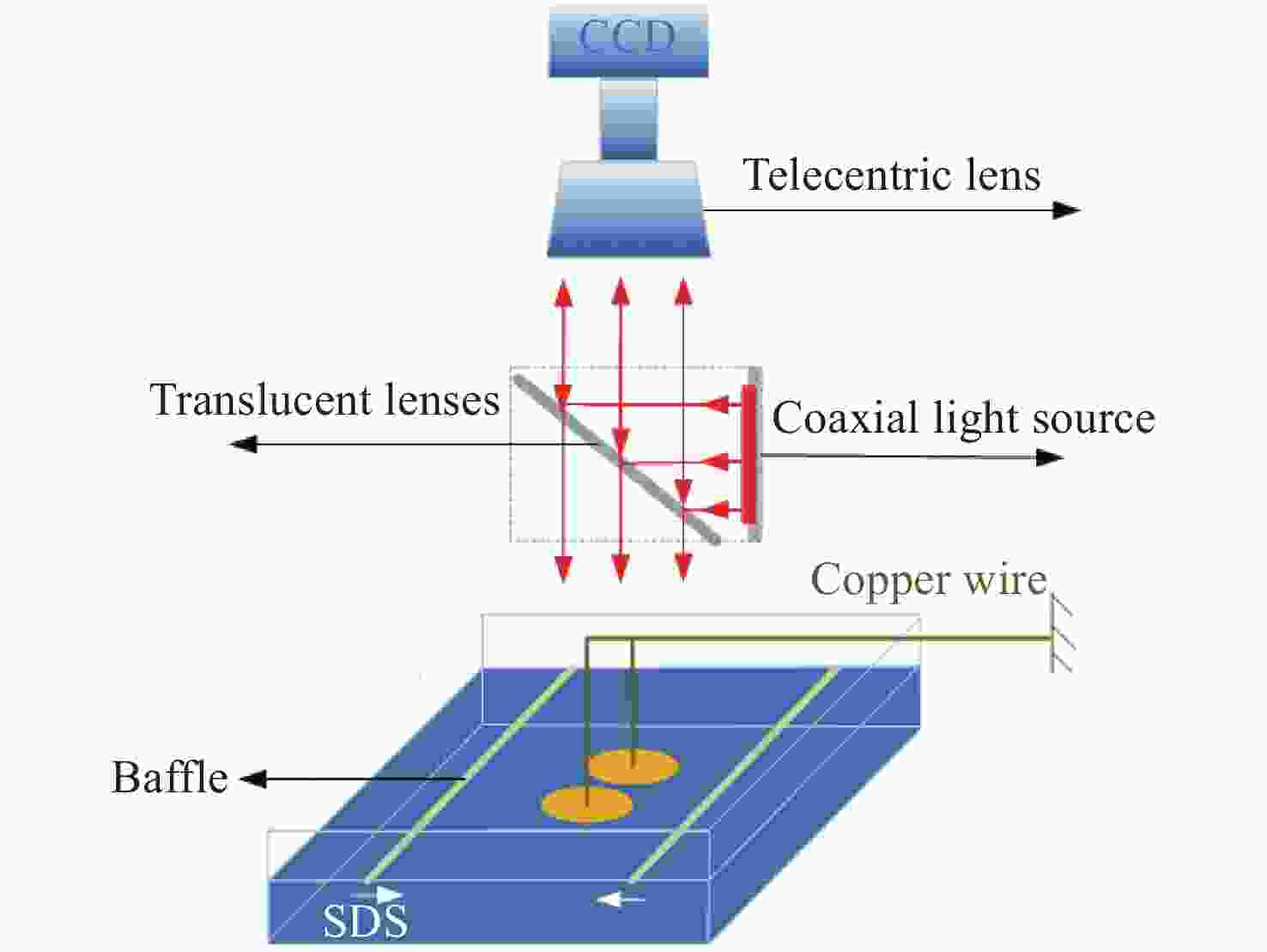
摘要: 液液界面浸润性可控操作的实现,在界面纳米有序结构组装、液体透镜调节、航空航天等方面具有重要意义。从宏观尺度研究了以表面活性剂溶液为底液的液液界面浸润问题,进行以表面活性剂溶液为底液、正十六烷为操控对象的浸润可控调节研究,分析界面单层活性剂分子在液体动态浸润性变化过程中的内在机理,选择固定浓度的表面活性剂溶液,以此匹配最佳的正十六烷铺展状态。通过拉压驱动液面的方式改变液滴铺展状态:挡板拉伸时,每个液滴浸润面积增大,并产生液滴形变;挡板压缩后,浸润面积减小,恢复圆环形状。实现了浸润状态的动态响应。通过拉压,实现了对单液滴的铺展–收缩的控制,在单液滴的基础上实现了双液滴、三液滴浸润状态的协同。Abstract: The liquid-liquid interface spreading engineering has a wide range of applications. Surfaces with controllable wettability can be stimulated to realize the modulation of the wettability state, which is of great importance in nanofluidics, medical field, and materials science. The motion of the three-phase contact line has self-similarity, and the spreading radius and the spreading time are proportional to the power exponential relationship of R~tn and the dynamic mechanism of spreading during infiltration can be reflected through the power index n. In this paper, the liquid-liquid interface wetting problem with surfactant solution as the substrate is investigated on a macroscopic scale, and the intrinsic mechanism of the interfacial monolayer of active agent molecules in the process of changing the dynamic wettability of the liquid is analyzed. The wetting experimental system composed of n-hexadecane as the driven droplet and sodium dodecyl sulfate solution as the base solution was established by changing the droplet spreading state by pulling pressure to drive the liquid surface, and the dynamic response of the wetting state was realized. On the basis of single droplet, the synergistic wetting state of double droplet and triple droplet was realized. The work of this paper gives new ideas and means for liquid interface manipulation, which is expected to be applied in interface assembly technology.
-
Key words:
- Liquid-liquid interface /
- Surfactant /
- Interface control /
- Multiple droplet deformation
-
-
[1] CONCUS P, FINN R. On capillary free surfaces in the absence of gravity[J]. Acta Math., 1974, 132: 177-198 doi: 10.1007/BF02392113 [2] 陈凡红. 固体表面气/液浸润及相关电化学行为研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2020CHEN Fanhong. Wetting of gas/liquid on solid surfaces and related electrochemical behaviors[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2020 [3] JI W J, LI W B, WANG Y R, et al. Tunable spreading and shrinking on photocontrolled liquid substrate[J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(26): 21967-21974 doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b03039 [4] WILKINSON K M, BAIN C D, MATSUBARA H, et al. Wetting of surfactant solutions by alkanes[J]. Chem. Phys. Chem., 2005, 6(3): 547-555 doi: 10.1002/cphc.200400514 [5] BROCHARD-WYART F, DI MEGLIO J M, QUERE D, et al. Spreading of nonvolatile liquids in a continuum picture[J]. Langmuir, 1991, 7(2): 335-338 doi: 10.1021/la00050a023 [6] BONN D, ROSS D. Wetting transitions[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2001, 64(9): 1085-1163 doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/64/9/202 [7] XU X H, ZHENG H X, LIU Y, et al. A droplet-based electricity generator with high instantaneous power density[J]. Nature, 2020, 578(7795): 392-396 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1985-6 [8] LANDT E, VOLMER M. Über die ausbreitungsgeschwindigkeit von Öl auf wasser[J]. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 1926, 122U(1): 398-404 [9] HOULT D P. Oil spreading on the sea[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1972, 4: 341-368 doi: 10.1146/annurev.fl.04.010172.002013 [10] 陈聪, 王进, 纪文杰, 等. 表面活性剂溶液界面拉压驱动液滴浸润性响应[J]. 力学与实践, 2023, 45(1): 67-74CHEN Cong, WANG Jin, JI Wenjie, et al. Response of the droplet wettability driven by interfacial tension of surfactant solution[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 2023, 45(1): 67-74 -
-





 下载:
下载: