基于遥感数据的夏季长江冲淡水年际间扩展规律及其影响因素
doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.06.2023-0059 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2023.06.2023-0059
Analysing Interannual Variation of Changjiang Diluted Water Spreading and Its Influencing Factors Based on Remote Sensing Observations
-
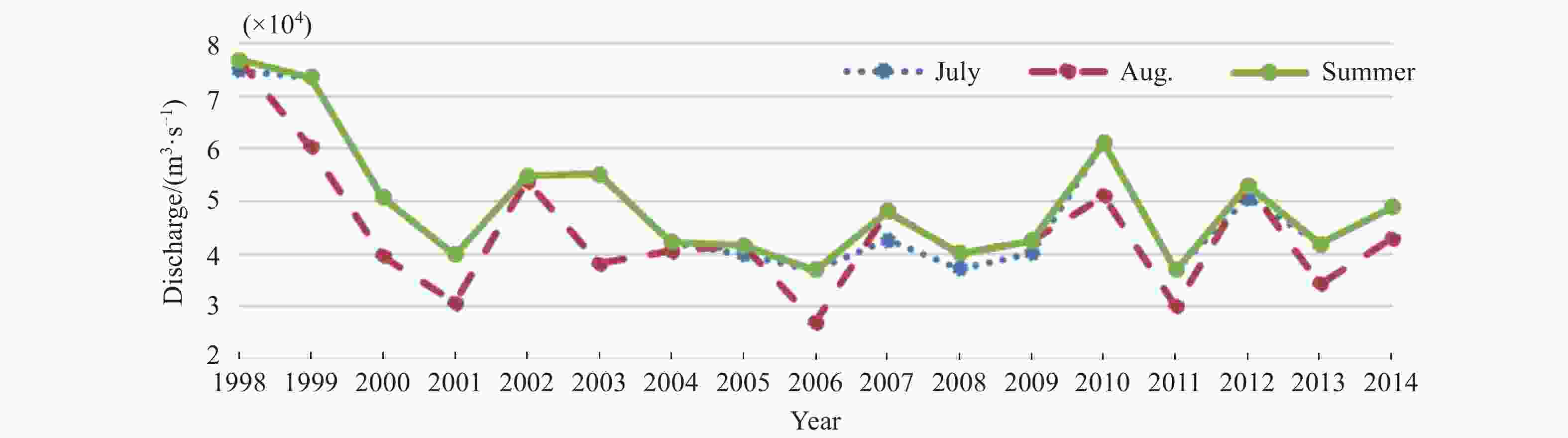
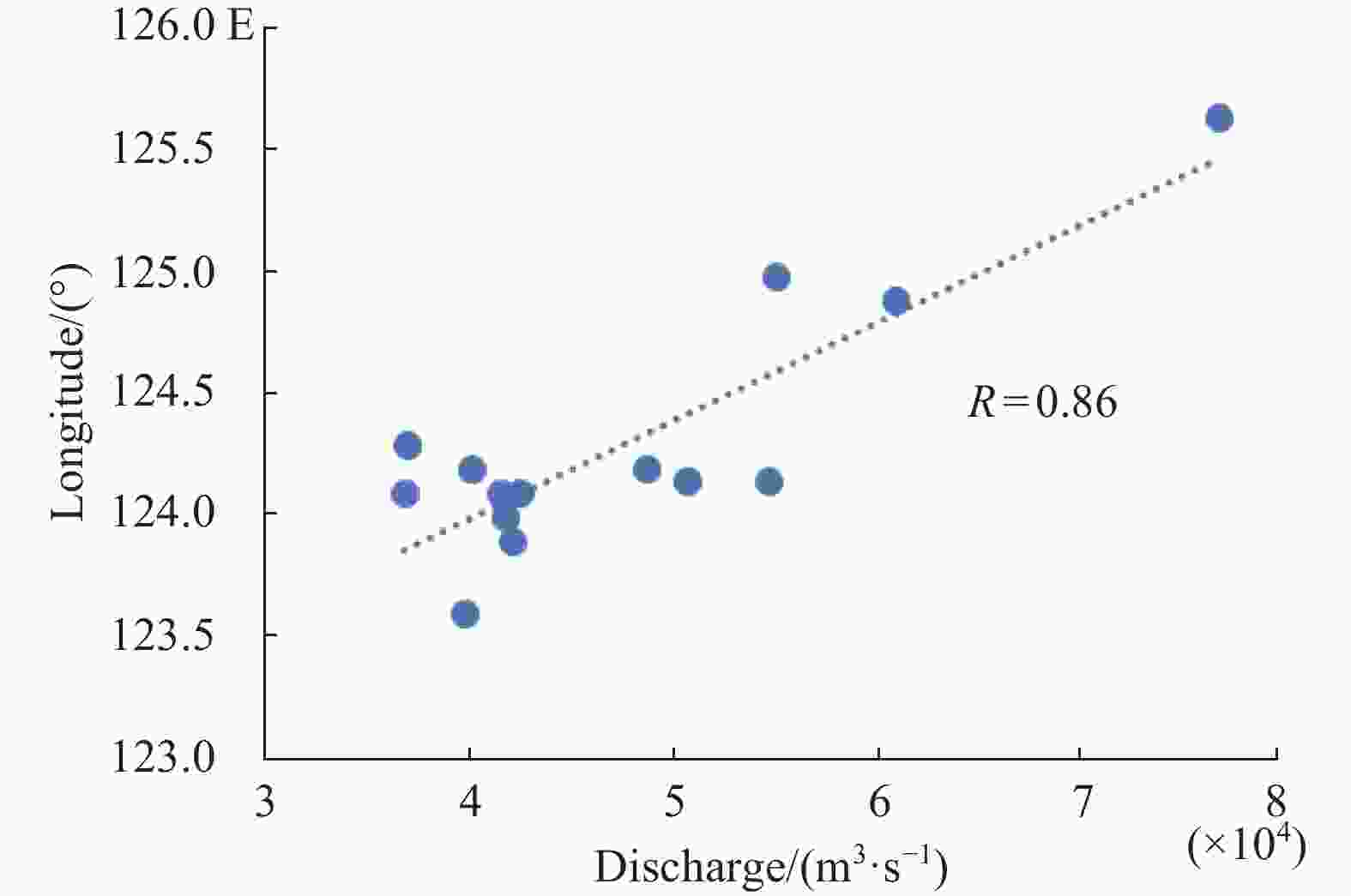
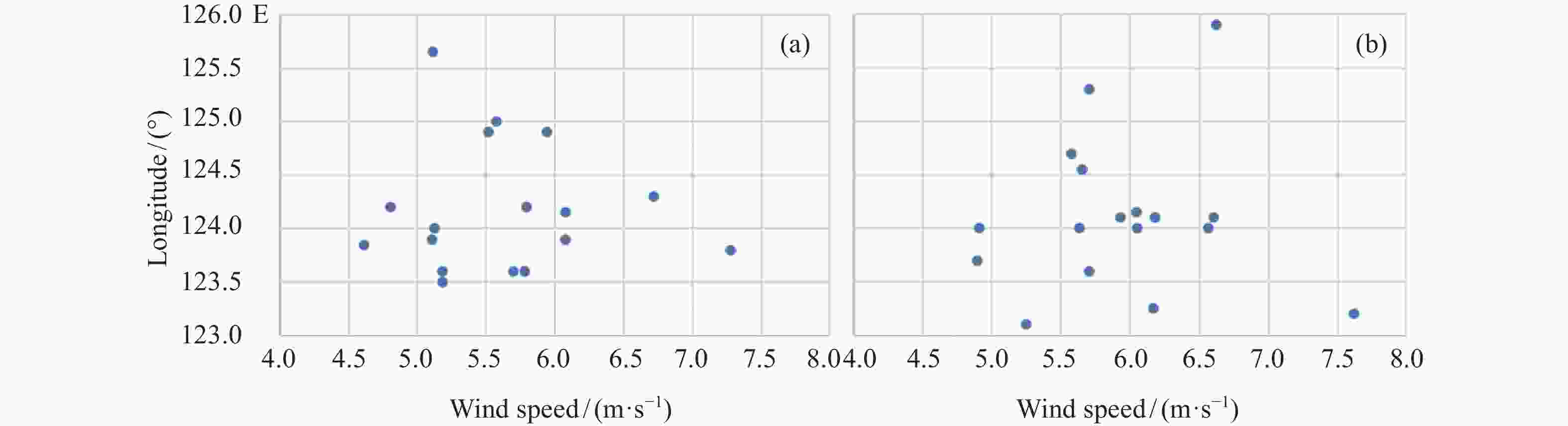
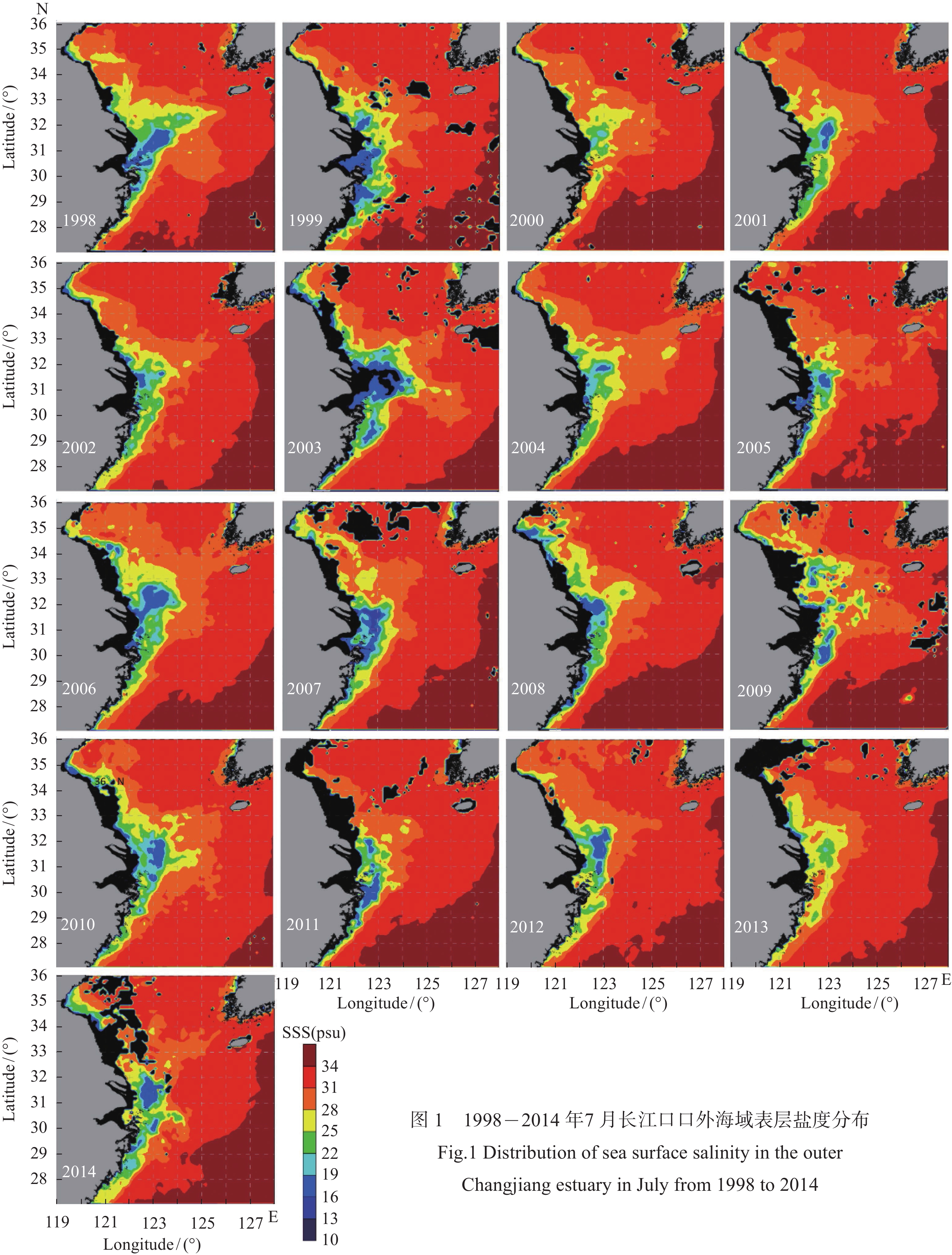
摘要: 长江冲淡水向外海扩展对于黄、东海水文生物环境以及物质循环有重大影响。通过分析1998-2014年连续17年卫星观测结果,研究夏季长江冲淡水向外海扩展的年际间变化规律,分析径流量和风场对其变化的影响。结果显示,夏季长江冲淡水向外海的扩展路径主要有东北偏北型、东北型和偶见型三类,以东北型为主;冲淡水向东扩展位置主要分布在123°-126°E区间,年际间差异显著。扩展过程的年际变化主要体现在扩展路径是否转向、向东扩展的态势呈现7弱8强还是7盛8衰。长江径流量的多寡对冲淡水向外海扩展的远近起到重要影响作用,径流量较大时,冲淡水向东扩展较远,径流量较小时,冲淡水向东扩展的距离会受到明显的限制。风向的变化是导致冲淡水扩展过程呈现多样性的一个重要原因。东南风、东风对于冲淡水向东北方向扩展起到促进作用,对于向东南方向扩展起到一定的阻碍作用,东北风对冲淡水向外海的扩展起到阻碍作用,迫使冲淡水盘踞在长江口近岸海域。Abstract: Expansion of the Changjiang Diluted Water (CDW) to the outer sea has a significant impact on the hydrobiological environment and material cycle in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. Based on 17 years of satellite fusion data from 1998 to 2014, this paper studies the inter-annual variations of the CDW spreading to the outer sea in summer, analyzes the influences of runoff and wind field on these changes. The result shows that the expansion path is mainly divided into three types: northeast-north type, northeast type and occasional type, in which northeast type is in the majority. The eastern boundary of the CDW expansion appears obviously inter-annual variations, and it mainly distributes in the range of 123°E to 126°E. The inter-annual variation of the expansion process is mainly reflected in the changes of expansion path and the distance of eastern expansion from July to August. The amount of runoff plays an important role in the distance of CDW expansion to the outer sea. When the runoff is large, the diluted water expands farther eastward, while when the runoff is small, the diluted water is limited near the Yangtze River estuary. The diversity of expansion process is obviously affected by wind direction. Southeast wind and east wind promote the expansion of diluted water in the northeast direction, and prevent the expansion in the southeast direction to some extent. Northeast wind prevents the expansion to the outer sea, forcing the diluted water staying near the Yangtze River estuary.
-
Key words:
- Remote sensing data /
- Changjiang diluted water /
- Interannual variation
-
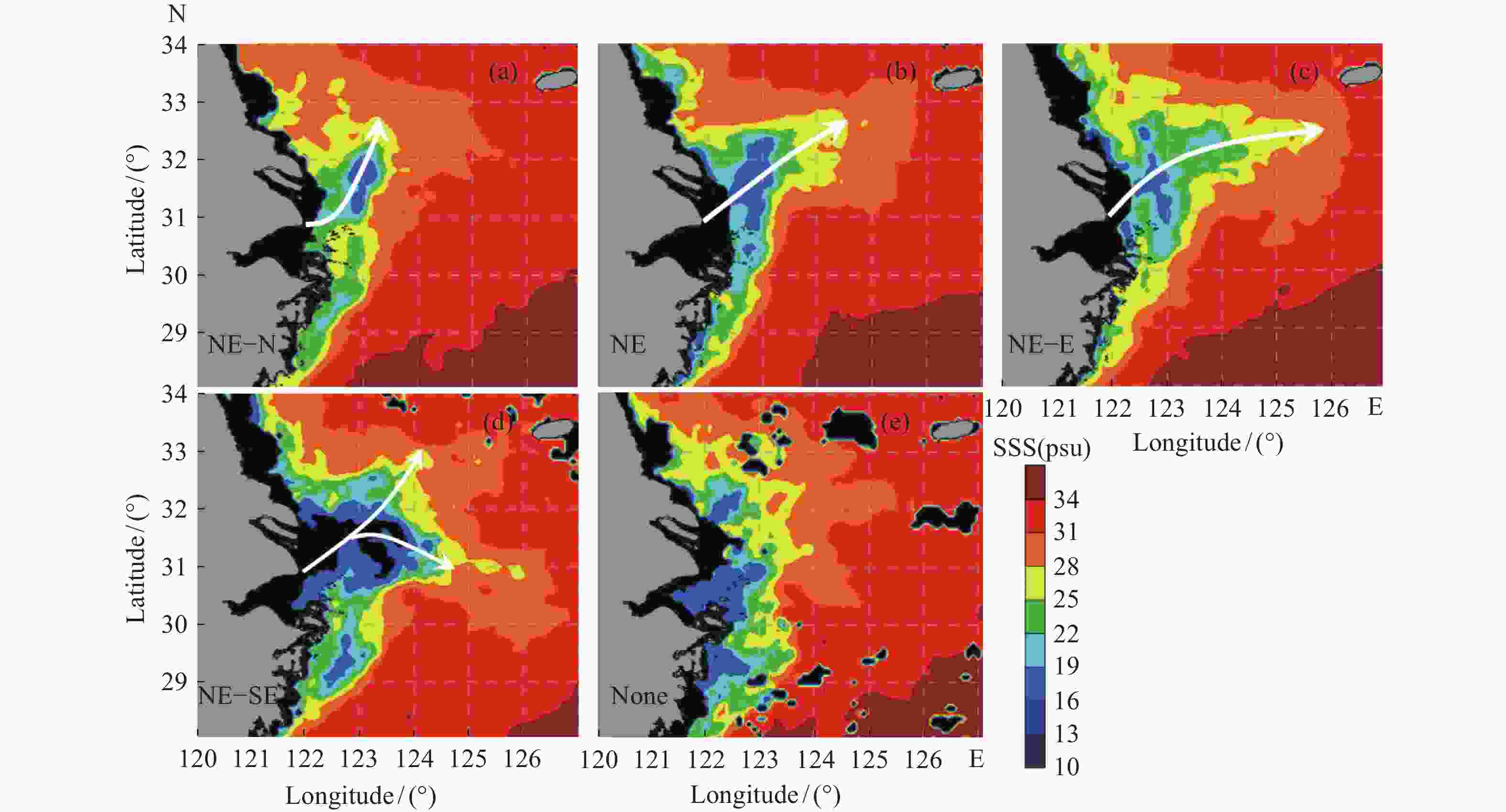
图 3 东北偏北型(NE-N)(a)、东北型(NE)(b)、东北偏东型(NE-E)(c)、东北–东南双向型(NE-SE)(d)和无明显指向型(None)(e)5种扩展路径示例图。白色箭头代表扩展路径
Figure 3. Samples of five types of expansion path: northeast-north type (NE-N), northeast type (NE), northeast-east type (NE-E), northeast-southeast type (NE-SE) and no-direction type (None). White arrow represents expansion path
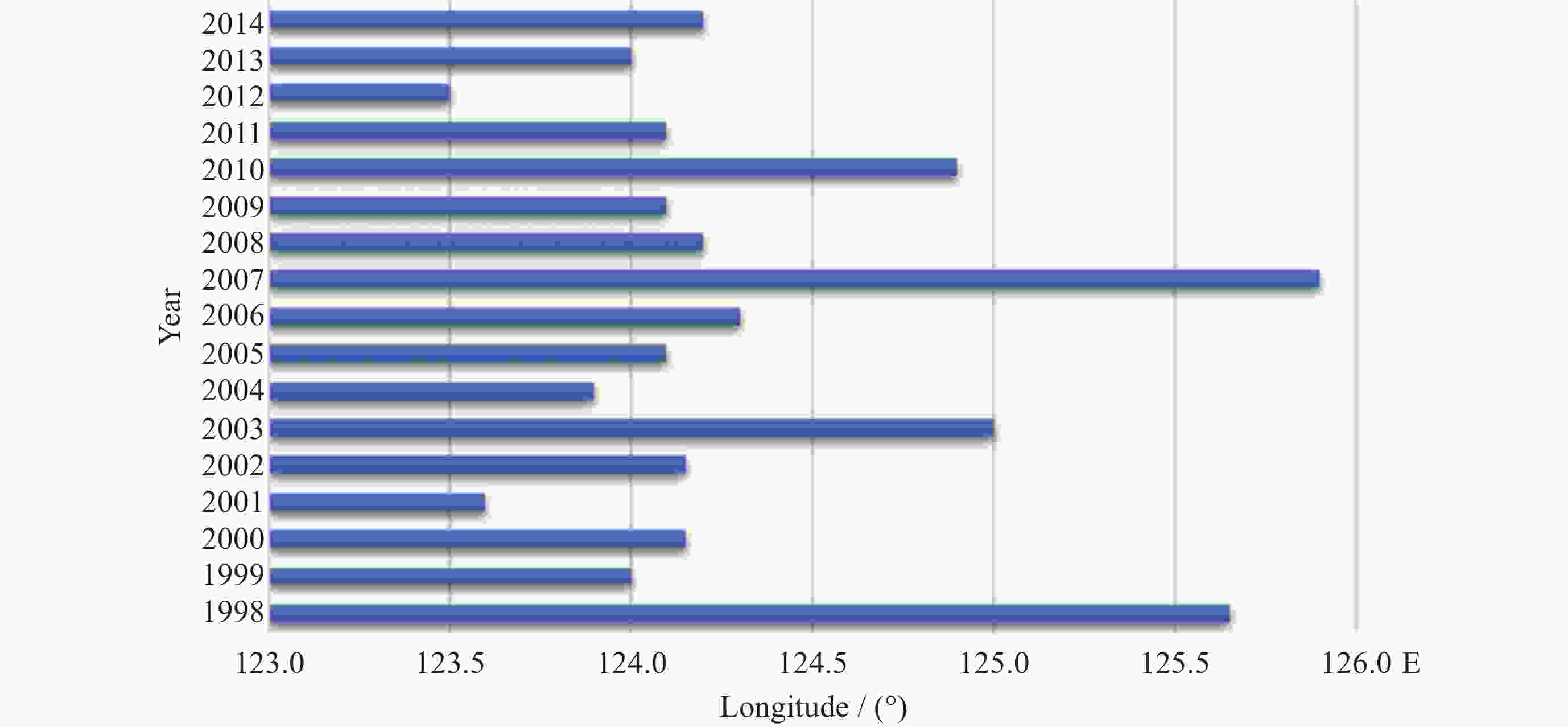
表 1 1998-2014年7月和8月长江冲淡水扩展路径及对应年份
Table 1. CDW expansion path and corresponding year on July and August from 1998 to 2014
冲淡水路径 7月 8月 东北偏北型 2001,2007,2008,2012 2000,2001,2004,2008,2012 东北型 1998,2000,2002,2005,
2006,2009,2011,20131998,2002,2003,2005,
2006,2009,2011,2013偶见型 东北偏东 2010 2007,2010 东北–东南 2003,2004 无明显指向 1999,2014 1999,2014 表 2 7月和8月风向转变情况及对应年份
Table 2. Changes of wind direction from July to August and corresponding year
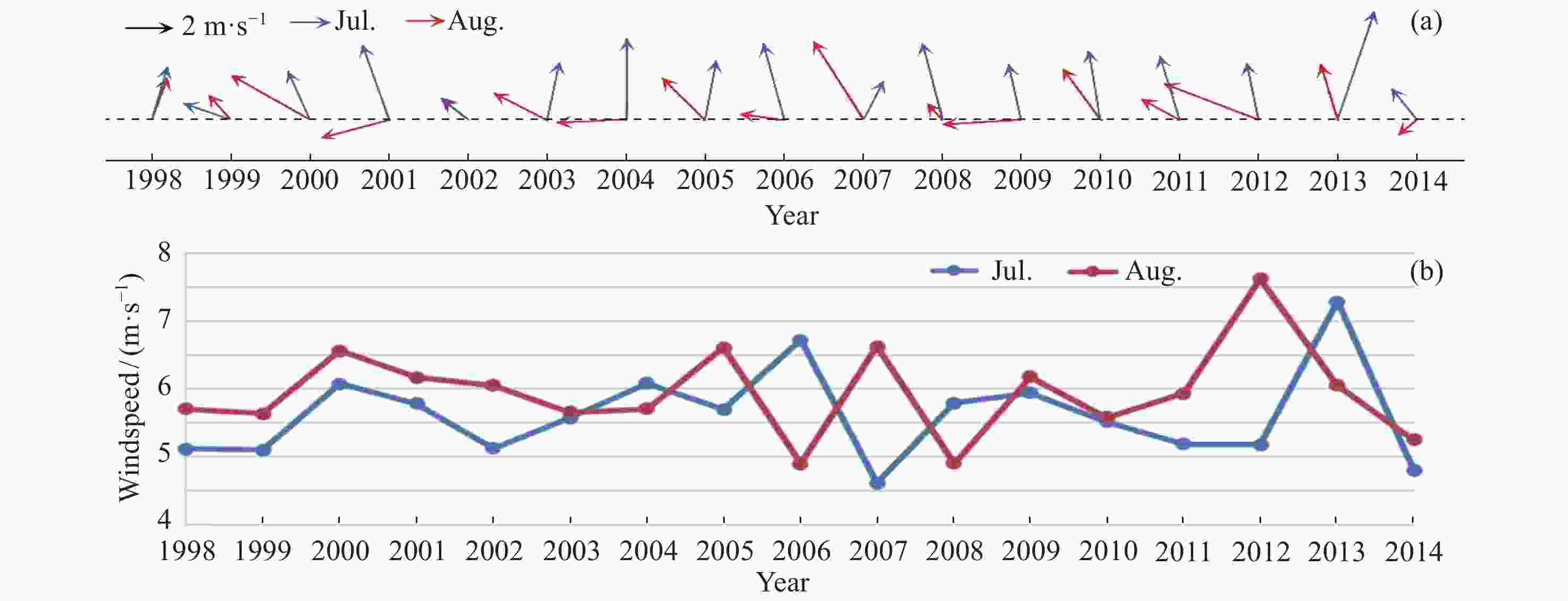
7月和8月风向转变 对应年份 东南–东北 2001,2009,2014 西南–东南 2003,2005,2007,2013 南–东北 2004 未发生转向
(东南–东南)1998,1999,2000,2002,2006,2008,2010,2011,2012 -
[1] Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. 2021 China River Sediment Bulletin[R/OL]. (2022-07-04)[2023-05-30]. http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/zghlnsgb/202207/t20220704_1583075.html [2] 邹娥梅, 郭炳火, 汤毓祥, 等. 南黄海及东海北部夏季若干水文特征和环流的分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2001, 32(3): 340-347ZOU E’mei, GUO Binghuo, TANG Yuxiang, et al. An analysis of summer hydrographic features and circulation in the Southern Yellow Sea and the northern East China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2001, 32(3): 340-347 [3] 朱建荣, 丁平兴, 胡敦欣. 2000年8月长江口外海区冲淡水和羽状锋的观测[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2003, 34(3): 249-255 doi: 10.11693/hyhz200303003003ZHU Jianrong, DING Pingxing, HU Dunxin. Observation of the diluted water and plume front off the Changjiang River Estuary during August 2000[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2003, 34(3): 249-255 doi: 10.11693/hyhz200303003003 [4] ZHOU F, XUAN J L, NI X B, et al. A preliminary study on variations of the Changjiang Diluted Water between August 1999 and 2006[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2009, 31(4): 1-12 [5] WU H, SHEN J, ZHU J R, et al. Characteristics of the Changjiang plume and its extension along the Jiangsu Coast[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 76: 108-123 doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.01.007 [6] 郭亚茹, 荣增瑞, 迟玉涛, 等. 夏季长江冲淡水年际变化的数值研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2020(4): 30-41 doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2020.04.005GUO Yaru, RONG Zengrui, CHI Yutao, et al. The modeling study of interannual variability of Changjiang River plume in summer season[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2020(4): 30-41 doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2020.04.005 [7] 赵玉喜, 王珍岩. 春季长江冲淡水在口门外海域逐月变化及其影响因素分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(10): 81-92 doi: 10.11759/hykx20210107002ZHAO Yuxi, WANG Zhenyan. The monthly changes and its influencing factors of the Changjiang Diluted Water off the estuary in spring[J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(10): 81-92 doi: 10.11759/hykx20210107002 [8] LIU B C, LI J P, FENG L C. A modeling study of the effect of wind on Changjiang (Yangtze) River diluted water in summer[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2013, 35(1): 25-37 [9] MORADI M. Evaluation of merged multi-sensor ocean-color chlorophyll products in the Northern Persian Gulf[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2021, 221: 104415 doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2021.104415 [10] 童如清, 宋庆君, 夏光平, 等. 中国近海多传感器合并叶绿素数据集检验与分析[J]. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 57(1): 69-76 doi: 10.19603/j.cnki.1000-1190.2023.01.007TONG Ruqing, SONG Qingjun, XIA Guangping, et al. Validation and analysis of multi-sensor merged chlorophyll datasets in offshore China[J]. Journal of Central China Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2023, 57(1): 69-76 doi: 10.19603/j.cnki.1000-1190.2023.01.007 [11] 毛汉礼, 甘子钧, 蓝淑芳. 长江冲淡水及其混合问题的初步探讨[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1963, 5(3): 183-206MAO Hanli, GAN Zijun, LAN Shufang. A preliminary study of the Yangtze diluted water and its mixing processes[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1963, 5(3): 183-206 [12] 梁文浩, 王晓春, 吴琼, 等. SMAP卫星海表盐度观测在中国近海的验证与应用[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2019, 37(4): 565-573LIANG Wenhao, WANG Xiaochun, WU Qiong, et al. Validation and application of SMAP SSS observation in Chinese adjacent seas[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2019, 37(4): 565-573 [13] 赵文杰, 李洪平, 刘海行. SMAP卫星的RBF神经网络海表盐度遥感反演[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2022, 40(3): 513-522 doi: 10.12362/j.issn.1671-6647.20210702001ZHAO Wenjie, LI Hongping, LIU Haixing. Remote sensing retrieval of sea surface salinity based on RBF neural network from SMAP satellite[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2022, 40(3): 513-522 doi: 10.12362/j.issn.1671-6647.20210702001 [14] 牛原, 邱志伟, 刘瑞翔, 等. SMAP卫星海表盐度产品精度评定与全球海表盐度特征分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2021, 39(3): 53-62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2021.03.006NIU Yuan, QIU Zhiwei, LIU Ruixiang, et al. Quality assessment and characteristic analysis of global sea surface salinity products based on SMAP[J]. Journal of Oceanographic Research, 2021, 39(3): 53-62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2021.03.006 [15] WANG Z H, ZHANG J, LIU Y X. Retrieval of sea surface salinity from the microwave radiometer onboard HY-2A[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2022, 39(2): 14-19. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2022.02.002 [16] 何颖清, 冯佑斌, 扶卿华, 等. 珠江河口海水表层盐度光学遥感反演研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2020, 36(6): 40-47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2020.06.007HE Yingqing, FENG Youbin, FU Qinghua, et al. A study on optical remote sensing inversion of sea surface salinity in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2020, 36(6): 40-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2020.06.007 [17] SUN D Y, SU X P, QIU Z F, et al. Remote sensing estimation of sea surface salinity from GOCI measurements in the Southern Yellow Sea[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(7): 775 doi: 10.3390/rs11070775 [18] BAI Y, PAN D L, CAI W J, et al. Remote sensing of salinity from satellite-derived CDOM in the Changjiang River dominated East China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(1): 227-243 doi: 10.1029/2012JC008467 [19] YU X, XIAO B, LIU X Y, et al. Retrieval of remotely sensed sea surface salinity using MODIS data in the Chinese Bohai Sea[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 38(23): 7357-7373 doi: 10.1080/01431161.2017.1375570 [20] ZHANG G P. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Yellow Substance in Yellow Sea and East China Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2015 [21] DONG Q, SHANG S L, LEE Z. An algorithm to retrieve absorption coefficient of chromophoric dissolved organic matter from ocean color[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2013, 128: 259-267 doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.10.013 [22] LEE Z P, CARDER K L, ARNONE R A. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: a multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters[J]. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(27): 5755-5772 doi: 10.1364/AO.41.005755 [23] ZHAO B R. Diversion mechanism of diluted water in Changjiang River[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1991, 13(5): 600-610 [24] BEARDSLEY R C, LIMEBURNER R, YU H, et al. Discharge of the Changjiang (Yangtze River) into the East China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1985, 4(1/2): 57 [25] 王建丰, 王玉, 王刚. 基于FVCOM数值模拟和观察资料的长江冲淡水转向机制分析[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(2): 194-201WANG Jianfeng, WANG Yu, WANG Gang. Analysis of direction change mechanism of the Changjiang River diluted water based on FVCOM and observation[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27(2): 194-201 [26] 乐肯堂. 长江冲淡水路径问题的初步研究——Ⅱ. 风场对路径的作用[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1989, 20(2): 139-148LE Kentang. A preliminary study of the path of the Changjiang diluted water – II. The effect of local wind on the path[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1989, 20(2): 139-148 [27] XUAN J L, HUANG D J, ZHOU F, et al. The role of wind on the detachment of low salinity water in the Changjiang Estuary in summer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2012, 117(C10): C10004 [28] WU H, ZHU J R, SHEN J, et al. Tidal modulation on the Changjiang River plume in summer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2011, 116(C8): C08017 [29] 王磊, 黄大吉, 贺双颜. 长江口邻近海域近岸水舌向外海的短期扩展过程分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2013, 31(4): 17-25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2013.04.003WANG Lei, HUANG Daji, HE Shuangyan. A short-term extension process of coastal water tongue adjacent to the Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2013, 31(4): 17-25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2013.04.003 -
-





 下载:
下载: