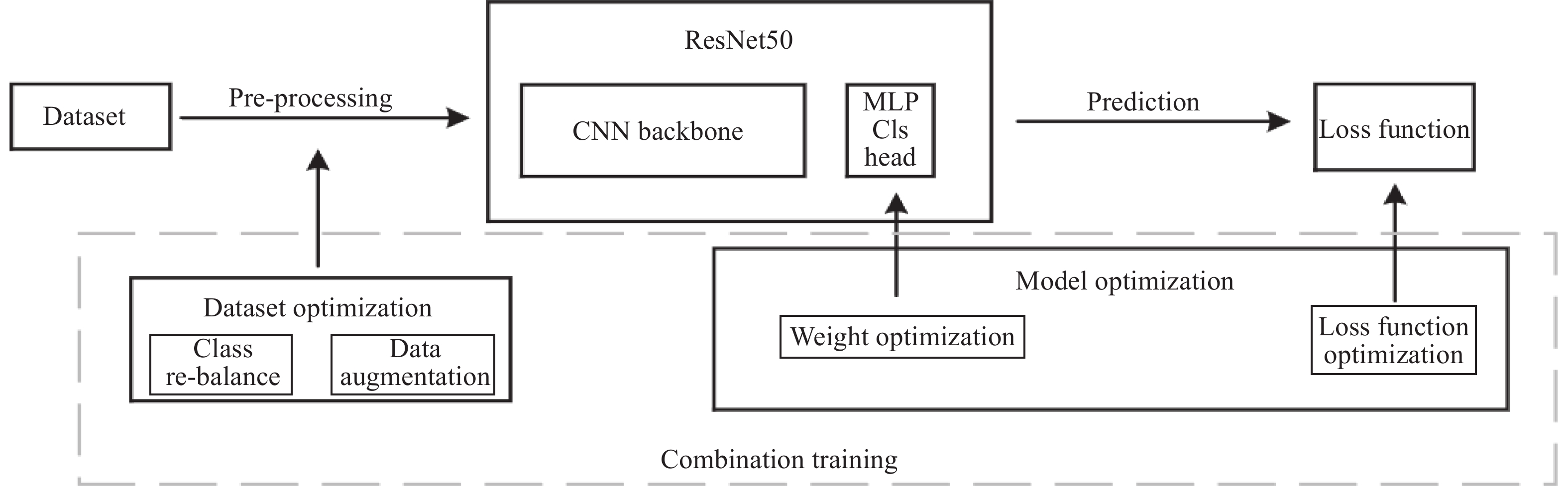
Study of Sample Imbalance in Deep Learning Modeling of Solar Flare Forecasting
-
摘要: 不同等级耀斑发生的频次存在数量级上的差别, 使基于常规卷积神经网络的耀斑预报模型通常难以捕捉M和X类耀斑先兆特征, 导致高等级耀斑预报精度低的问题. 本文对于这种耀斑预报中的长尾分布问题, 通过控制变量法讨论不同深度长尾学习方法对于耀斑预报精度提升. 尝试从训练集优化、损失函数优化、网络权重优化等角度改进模型对于M和X类耀斑的预报性能. 在SDO/HMI太阳磁图预报未来24 h耀斑的实验中, 相比于常规方法训练的基准模型, 改进模型在M和X类耀斑预报的精确率分别有了53.10%和38.50%的提升, 同时在召回率上有64%和52%的提升. 表明在耀斑预报问题中, 数据长尾分布的处理至关重要, 验证了深度长尾学习方法的有效性. 这种提升尾部类预报精确率的方法不仅可以应用于耀斑预报领域, 还可以迁移到其他具有长尾分布现象的空间天气典型事件的预报分析中.Abstract: Solar flares, as violent eruptions occurring in the lower atmosphere of the Sun, exert significant impacts on human activities. Researchers globally have developed multiple prediction models for solar flares, employing empirical, physical, statistical, and other methodologies. There is an order of magnitude difference in the occurrence of different classes of flares. This makes it difficult for traditional convolutional neural network-based flare prediction models to capture M, X class flare features, which leads to the problem of low precision of high level flare prediction. With the breakthrough of deep learning technology in recent years, it has shown strong potential in modelling and prediction of complex problems and a number of works have begun to try to use deep learning methods to construct flare prediction models. In this paper, different deep long-tail learning methods are discussed by us to improve the precision of flare forecasting by controlling the variables for the long-tail distribution phenomenon in flare forecasting. The forecast performance of the model for M and X flares is tried to be improved from the perspectives of training set optimization, loss function optimization and network weight optimization. The experiments on SDO/HMI solar magnetogram data show that the precision of M, X class flare prediction is significantly improved by 53.10% and 38.50%, respectively, and the recall is increased by 64% and 52% compared with the baseline model trained by conventional methods. It shows that the treatment of the long-tailed distribution of data is crucial in the flare forecasting problem, and verifies the effectiveness of the deep long-tailed learning method. This method of improving the precision of tail class forecasts can be applied not only to the field of flare forecasting, but also can be transferred to the analysis of forecasting other typical events of space weather with long-tailed distribution phenomenon.
-
Key words:
- Flare prediction /
- Long-tailed distribution /
- Residual neural network
-
表 1 类重平衡算法
Table 1. Class rebalancing algorithm
算法名称 简称 核心公式 实例采样(标准数据集) Uniform $ {\tilde {n}}_{j}=N \dfrac{{n}_{j}^{q}}{{\displaystyle\sum }_{i=1}^{C}{n}_{i}^{q}},\; q=0,0.5, 1 $ 类平衡采样 Balance 平方根采样 Squreroot 渐进式采样 Shift $ {\tilde {n}}_{j}=N \left[\left(1-\dfrac{t}{T}\right){p}_{j}^{\mathrm{I}\mathrm{B}}+\dfrac{t}{T}{p}_{j}^{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{B}}\right] $ 表 2 数据增强算法
Table 2. Data enhancement algorithms
算法名称 简称 核心公式 RSG算法 RSG - Mixup算法 Mixup $ \tilde {X}=\lambda {X}_{i}+(1-\lambda ) {X}_{j},\;\tilde {Y}=\lambda {Y}_{i}+(1-\lambda ) {Y}_{j} $ Manifold Mixup算法 Manifold $ \tilde {X}=\lambda {X}_{i}+(1-\lambda ) {X}_{j},\;\tilde {Y}=\lambda {Y}_{i}+(1-\lambda ) {Y}_{j} $ 表 3 损失函数优化算法
Table 3. Loss function optimization algorithms
算法名称 简称 核心公式 代价敏感学习方法 IB Loss $ {L}_{\mathrm{I}\mathrm{B}}\left(w\right)=\dfrac{1}{m}\displaystyle\sum _{(x,y)\in {D}_{m}}{\lambda }_{k}\dfrac{L(y,f(x,w\left)\right)}{{\|f\left(x,w\right)-y\|}_{1}\cdot {\|h\|}_{1}} $ LDAM算法 LDAM Loss $ {L}_{\mathrm{L}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{M}}\left(y,z\right)=-\mathrm{ln}\dfrac{{e}^{{z}_{y}-{{\varDelta }}_{y}}}{{e}^{{z}_{y}-{{\Delta }}_{y}}+{\displaystyle\sum }_{j\ne y}{e}^{{z}_{j}}} $ 表 4 权重优化算法统计
Table 4. Weight optimization algorithm statistics table
算法名称 简称 核心公式 类重训练方法 CRT - 最近邻分类器方法 NCM - $ \tau $正则化算法 $ \tau $ $ {\tilde {w}}_{i}=\dfrac{{w}_{i}}{{\|{w}_{i}\|}^{\tau }} $ 可学习权重缩放算法 LWS $ {\tilde {w}}_{i}={f}_{i}\cdot {w}_{i} $ 表 5 太阳耀斑软X射线等级划分
Table 5. Solar flare soft X-ray class classification
太阳耀斑等级 软X射线峰值流量范围/(W·m–2) A $ < {10}^{-7} $ B $ {10}^{-7}\sim{10}^{-6} $ C $ {10}^{-6}\sim{10}^{-5} $ M $ {10}^{-5}\sim{10}^{-4} $ X $ > {10}^{-4} $ 表 6 太阳耀斑预报训练、测试、验证数据集
Table 6. Solar flare forecast training, testing and validation dataset
数据集类型 No-flare C-Class M-Class X-Class 训练集 22766 18478 2422 290 验证集 7532 6003 795 92 测试集 7493 5988 786 89 表 7 不同重采样方法下耀斑预报模型的精确率
Table 7. Precision of flare forecasting models under different resampling methods
Method No-flare/(%) C-Class/(%) M-Class/(%) X-Class/(%) 实例采样(基准) 87.10 83.50 0.00 0.00 类平衡采样 42.20 66.70 7.70 0.00 平方根采样 54.40 70.70 8.50 5.70 渐进式采样 58.20 64.40 18.20 15.30 表 8 不同数据增强方法下耀斑预报模型的精确率
Table 8. Precision of flare forecasting models with different data enhancement methods
Method No-flare/(%) C-Class/(%) M-Class/(%) X-Class/(%) 实例采样(基准) 87.10 83.50 0.00 0.00 RSG算法 54.80 48.20 0.00 0.00 Mixup 76.20 58.10 0.00 0.00 Manifold 42.30 22.90 26.70 17.60 表 9 不同损失函数优化方法下耀斑预报模型的精确率
Table 9. Precision of flare forecasting models with different loss function optimization methods
Method No-flare/(%) C-Class/(%) M-Class/(%) X-Class/(%) 实例采样(基准) 87.10 83.50 0.00 0.00 代价敏感学习 57.90 42.10 15.50 4.30 LDAM算法 63.60 43.10 18.30 15.10 表 10 不同网络权重优化方法下耀斑预报模型的精确率
Table 10. Precision of flare forecasting models with different network weight optimization methods
Method No-flare/(%) C-Class/(%) M-Class/(%) X-Class/(%) 实例采样(基准) 87.10 83.50 0.00 0.00 分类器重训练算法 73.50 78.40 28.40 0.00 最近邻分类器算法 65.70 71.30 30.10 0.00 τ正则化算法 43.50 51.80 28.10 0.00 可学习权重缩放算法 63.10 73.10 26.30 0.00 表 11 不同组合训练方法下耀斑预报模型的精确率
Table 11. Precision of flare forecasting models with different combinations of training methods
Method No-flare/(%) C-Class/(%) M-Class/(%) X-Class/(%) 实例采样(基准) 87.10 83.50 0.00 0.00 组合训练 Uniform+CRT 73.50 78.40 28.40 0.00 Uniform+NCM 65.70 71.30 30.10 0.00 Uniform+$ \tau $ 43.50 51.80 28.10 0.00 Uniform+LWS 63.10 73.10 26.30 0.00 Balance+CRT 78.10 77.50 38.80 0.00 Balance+NCM 73.20 75.80 56.50 0.00 Balance+$ \tau $ 75.30 78.20 33.10 0.00 Balance+LWS 81.20 79.60 35.10 0.00 Squareroot+CRT 42.80 71.50 50.20 2.50 Squareroot+NCM 72.50 75.90 65.20 28.50 Squareroot+$ \tau $ 39.20 44.50 36.80 13.50 Squareroot+LWS 73.80 75.20 30.80 15.60 Shift+CRT 58.40 78.50 23.10 17.30 Shift+NCM 78.20 56.80 35.90 18.30 Shift+$ \tau $ 58.10 38.50 33.70 16.50 Shift+LWS 73.50 78.10 53.10 38.50 表 12 几种表现较优方法召回率
Table 12. Recall rates for several better performing methods
Method No-flare/(%) C-Class/(%) M-Class/(%) X-Class/(%) 实例采样(基准) 83 75 0 0 Balance+LWS 77 71 46 0 Squareroot+NCM 72 73 75 38 Shift+LWS 76 69 64 52 表 13 去除阴影效应后太阳耀斑预报训练、测试、验证数据集
Table 13. Training, testing and validation datasets for solar flare forecasting after removal of shadow effects
数据集类型 No-flare C-Class M-Class X-Class 训练集 16218 14735 2059 199 验证集 6518 4984 719 92 测试集 5676 4861 683 72 表 14 几种表现较优方法在去投影数据集上的精确率统计
Table 14. Precision statistics of several better-performing methods on the deprojected dataset
Method No-flare/(%) C-Class/(%) M-Class/(%) X-Class/(%) 实例采样(基准) 58.6 48.1 16.7 0 Balance+LWS 68.6 64.4 82.4 11.7 Squareroot+NCM 77.8 77.3 75.9 28 Shift+LWS 82.8 90.2 96.7 34.3 表 15 几种表现较优方法在去投影数据集上的召回率统计
Table 15. Recall statistics of several better-performing methods on the deprojected dataset
Method No-flare/(%) C-Class/(%) M-Class/(%) X-Class/(%) 实例采样(基准) 70.7 43.7 0.7 0 Balance+LWS 79.4 58.6 17.1 26.4 Squareroot+NCM 83.8 70 65.3 73.6 Shift+LWS 95.4 77.3 64.3 63.9 -
[1] BLOOMFIELD D S, HIGGINS P A, MCATEER R T J, et al. Toward reliable benchmarking of solar flare forecasting methods[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2012, 747(2): L41 doi: 10.1088/2041-8205/747/2/L41 [2] YUAN Y, SHIH F Y, JING J, et al. Automated flare forecasting using a statistical learning technique[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2010, 10(8): 785-796 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/10/8/008 [3] QAHWAJI R, COLAK T. Automatic short-term solar flare prediction using machine learning and sunspot associations[J]. Solar Physics, 2007, 241(1): 195-211 doi: 10.1007/s11207-006-0272-5 [4] YU D R, HUANG X, WANG H N, et al. Short-term solar flare level prediction using a Bayesian network approach[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2010, 710(1): 869-877 doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/710/1/869 [5] HAZRA S, SARDAR G, CHOWDHURY P. Distinguishing between flaring and nonflaring active regions[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2020, 639: A44 [6] COLAK T, QAHWAJI R. Automated Solar Activity Prediction: A hybrid computer platform using machine learning and solar imaging for automated prediction of solar flares[J]. Space Weather, 2009, 7(6): S06001 [7] PARK E, MOON Y J, SHIN S, et al. Application of the deep convolutional neural network to the forecast of solar flare occurrence using full-disk solar magnetograms[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2018, 869(2): 91 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/aaed40 [8] 何欣燃, 钟秋珍, 崔延美, 等. 基于长短期记忆神经网络的太阳耀斑短期预报[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(5): 862-872 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.05.210315028HE Xinran, ZHONG Qiuzhen, CUI Yanmei, et al. Solar flare short-term forecast model based on long and short-term memory neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(5): 862-872 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.05.210315028 [9] 郭大蕾, 张振, 朱凌锋, 等. 太阳活动区EUV图像的生成式模型耀斑分级与预报[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(1): 60-67. DOI: 10.11728/cjss2023.01.220214015GUO Dalei, ZHANG Zhen, ZHU Lingfeng, et al. Generative model-based of flare hierarchic recognition and forecast of extreme ultraviolet images in solar active region[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(1): 60-67. DOI: 10.11728/cjss2023.01.220214015 [10] HUANG X, WANG H, XU L, et al. Deep learning based solar flare forecasting model. I. results for line-of-sight magnetograms[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2018, 856(1): 7 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/aaae00 [11] ZHENG Y F, LI X B, WANG X S. Solar flare prediction with the hybrid deep convolutional neural network[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2019, 885(1): 73 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ab46bd [12] LI X B, ZHENG Y F, WANG X S, et al. Predicting solar flares using a novel deep convolutional neural network[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2020, 891(1): 10 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ab6d04 [13] WAN J, FU J F, LIU J F, et al. Class imbalance problem in short-term solar flare prediction[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2021, 21(9): 237 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/21/9/237 [14] DENG Z, WANG F, DENG H, et al. Fine-grained solar flare forecasting based on the hybrid convolutional neural networks[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2021, 922(2): 232 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ac2b2b [15] DESHMUKH V, FLYER N, VAN DER SANDE K, et al. Decreasing false-alarm rates in CNN-based solar flare prediction using SDO/HMI data[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2022, 260(1): 9 doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ac5b0c [16] KANEDA K, WADA Y, IIDA T, et al. Flare transformer: solar flare prediction using magnetograms and sunspot physical features[C]//Proceedings of the 16th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Macao, China: Springer, 2022: 1488-1503 [17] WANG Ting. Statistical Analysis of Solar Flares During 22, 23 and 24 Solar Cycles[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021 [18] KANG B Y, XIE S N, ROHRBACH M, et al. Decoupling representation and classifier for long-tailed recognition[C]//8th International Conference on Learning Representations. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: OpenReview. net, 2020 [19] WANG J F, LUKASIEWICZ T, HU X L, et al. RSG: a simple but effective module for learning imbalanced datasets[C]//2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, TN, USA: IEEE, 2021: 3783-3792 [20] ZHANG H Y, CISSE M, DAUPHIN Y N, et al. mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization[C]//6th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, BC, Canada: OpenReview. net, 2018: 1-13 [21] VERMA V, LAMB A, BECKHAM C, et al. Manifold mixup: Better representations by interpolating hidden states[C]//Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach: PMLR, 2019: 6438-6447 [22] PARK S, LIM J, JEON Y, et al. Influence-balanced loss for imbalanced visual classification[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal, QC, Canada: IEEE, 2021: 715-724 [23] CAO K D, WEI C, GAIDON A, et al. Learning imbalanced datasets with label-distribution-aware margin loss[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook, NY, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2019: 140 -
-





 周俊 男, 1999年6月出生于湖南省岳阳市. 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心硕士研究生, 主要研究方向空间大数据处理、基于深度学习的太阳耀斑预报. E-mail:
周俊 男, 1999年6月出生于湖南省岳阳市. 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心硕士研究生, 主要研究方向空间大数据处理、基于深度学习的太阳耀斑预报. E-mail: 
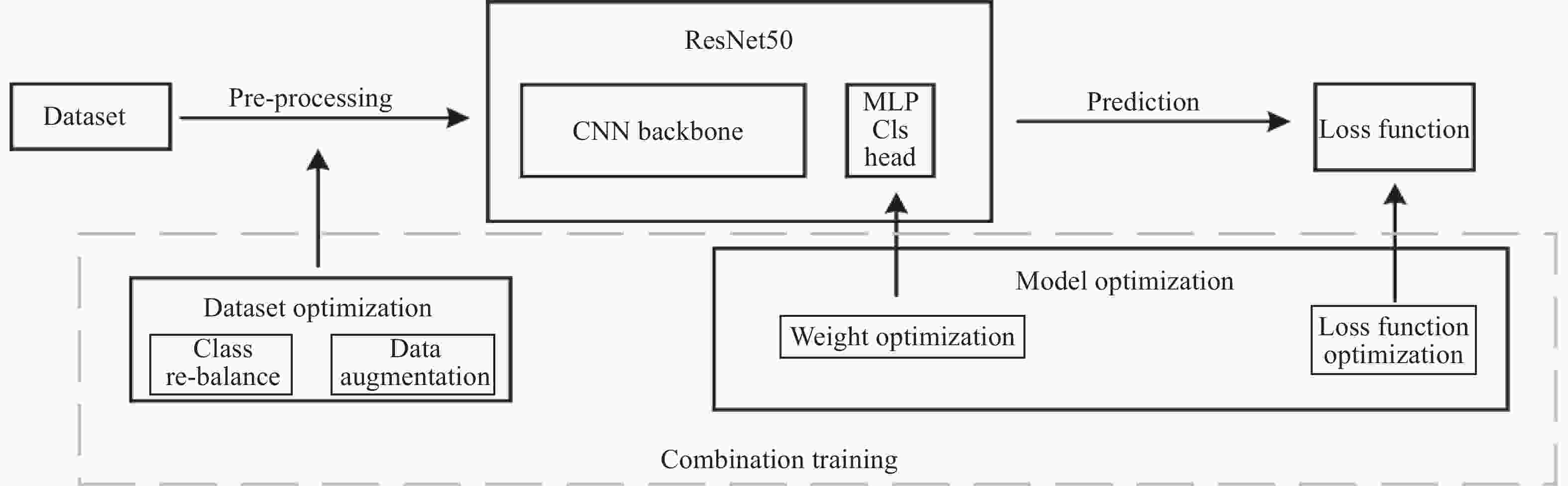
 下载:
下载: