Simulation and Experimental Validation of Charge-driven Extreme Ultraviolet Photoelectric Effect
-
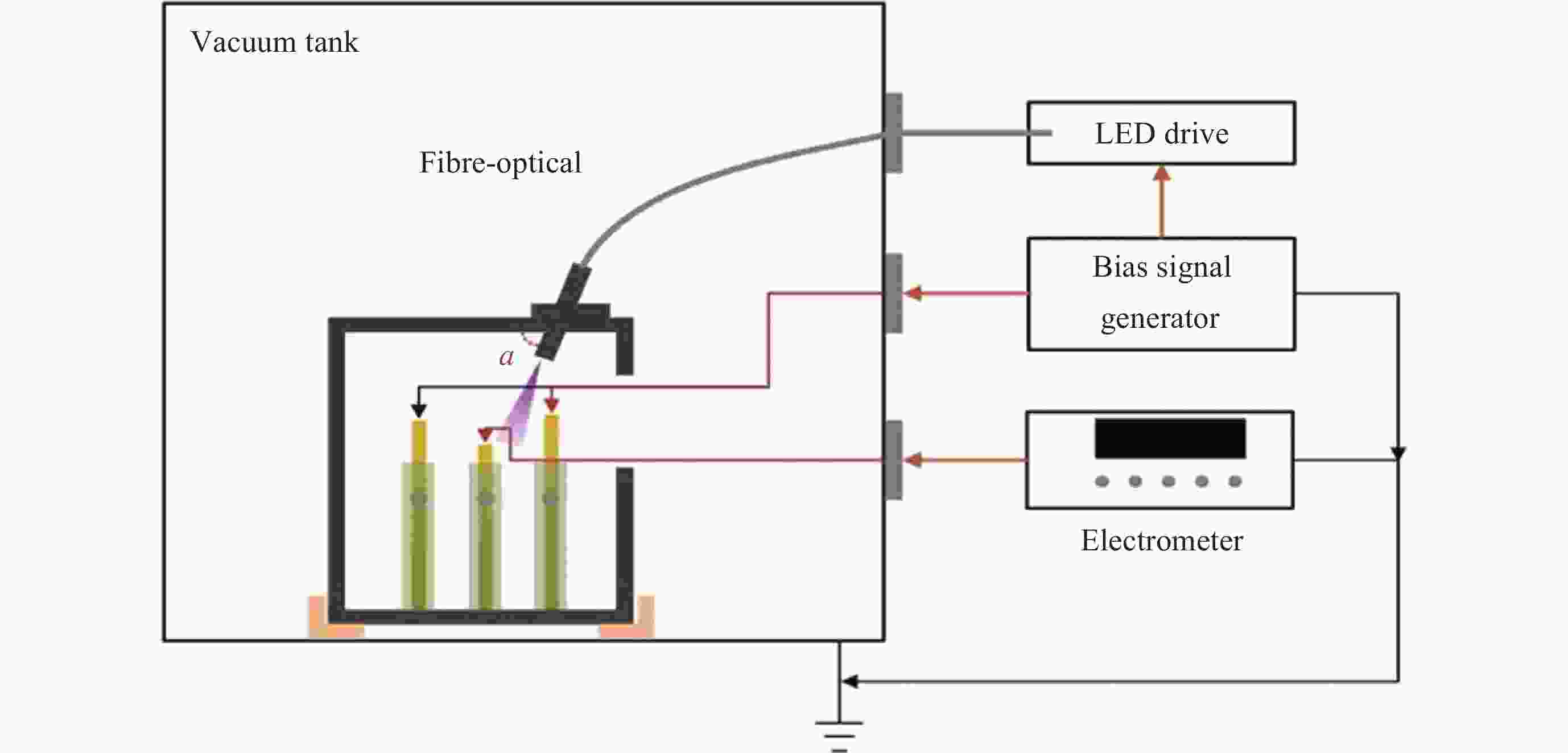
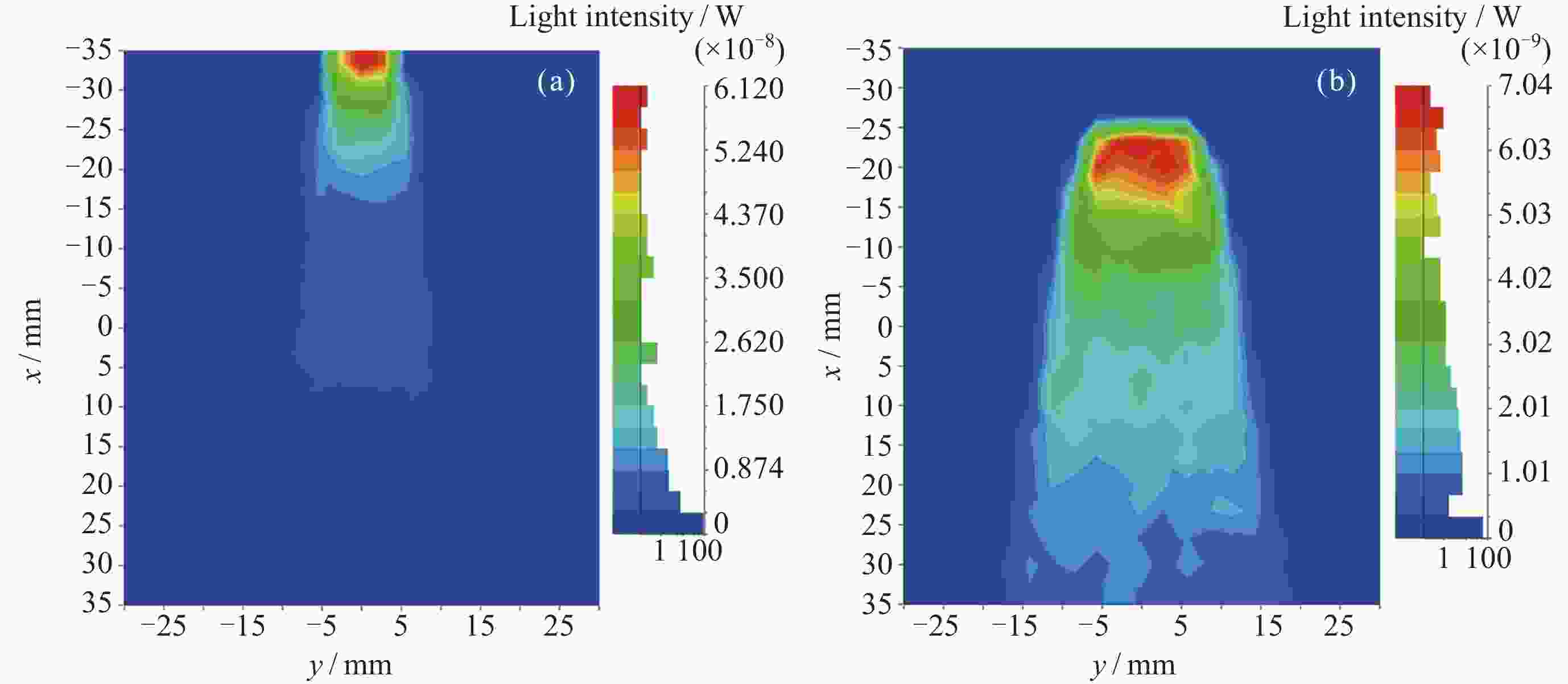
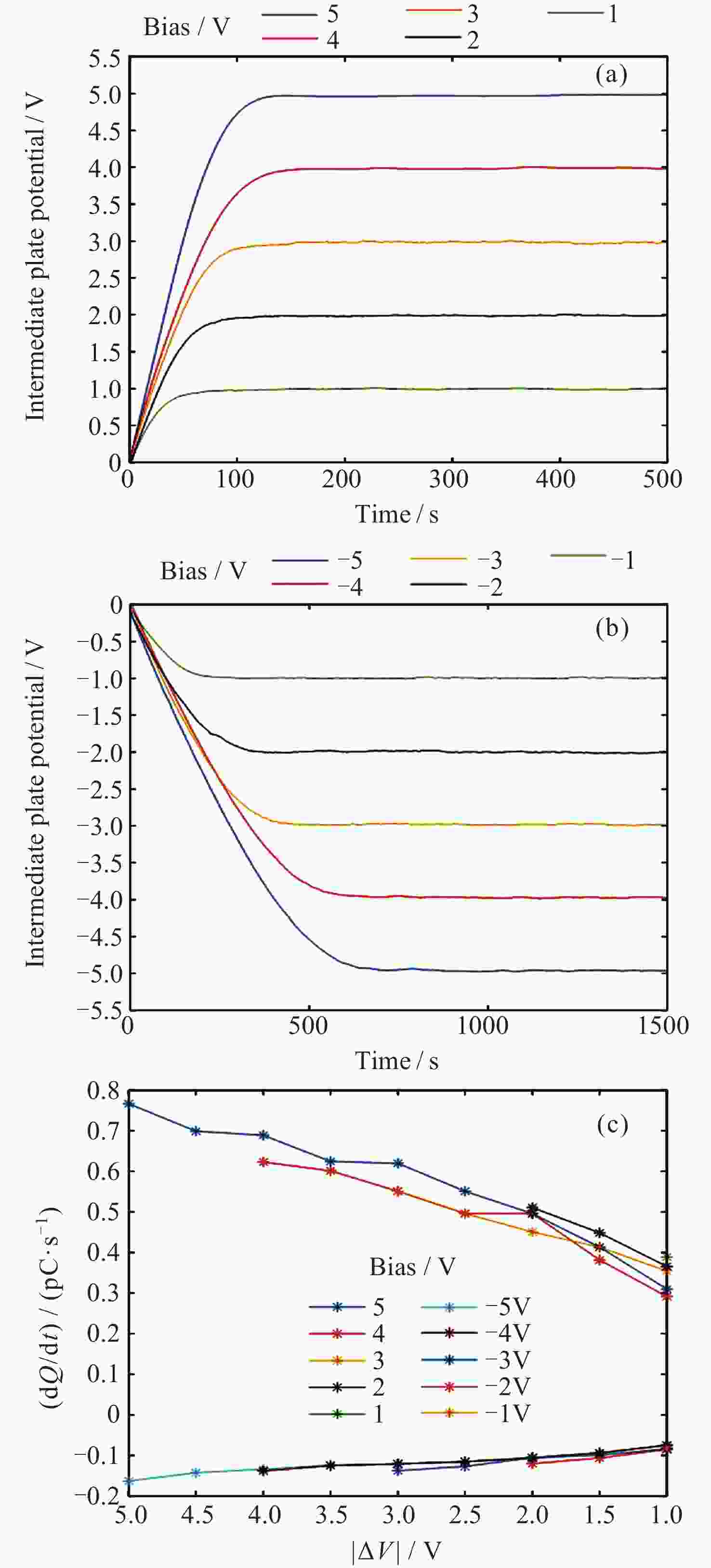
摘要: 惯性传感器中的检验质量是精密引力测量系统中的核心, 其表面会因为宇宙高能粒子持续注入而积累电荷, 在惯性传感器内部电磁场作用下产生杂散噪声, 影响精密引力测量结果. 根据光电效应原理, 用UV LED产生极紫外光照射惯性传感器的电极与检验质量表面, 并在电极间施加适当电场, 就可以在不引入外力作用且无接触条件下改变检验质量的电荷量. 本文基于平行板电容器的简化电极模型, 对极紫外电荷驱动过程进行了理论建模仿真. 在此基础上设计和构建了一套电荷驱动验证试验系统, 针对光功率、偏置电压对充放电速率的影响和交流电荷驱动进行试验. 试验证明电荷充放电速率与极紫外光功率成正比, 其量子产率随极板间电场强度变化. 最终可实现稳定控制检验质量电荷放电速率在0.31~0.76 pC⋅s–1, 检验质量电荷充电速率在–0.05~–0.17 pC⋅s–1. 分析提出的检验质量电荷充放电速率理论模型与地面试验结果一致, 可以有力支撑电荷管理控制系统的研制.Abstract: The test masses of the inertial sensor is the core of the precision gravity measurement system. The surface of test masses accumulates charges due to continuous injection of high-energy particles from space, which generates stray noise under the action of the internal electromagnetic field of the sensor and affects the precision gravity measurement results. According to the principle of photoelectric effect, use UV LED to generate extreme ultraviolet light to irradiate the electrodes of an inertial sensor and the surface of the test masses, and applying an appropriate electric field between the electrodes, it is possible to change the charge amount of the test masses without external forces and under non-contact conditions. Based on the simplified electrode model of the parallel plate capacitor, this paper carried out theoretical modeling and simulation of the extreme ultraviolet charge driving process. Based on this, a set of charge driving verification test system was designed and constructed, and experiments were carried out on the effects of light power and bias voltage on the charging and discharging rates and AC charge driving. The experiment proved that the charge-discharge rate is proportional to the extreme ultraviolet light power, and its quantum yield changes with the electric field strength between the plates. Ultimately, a stable control of the test masses discharge rate between 0.31 pC⋅s–1 and 0.76 pC⋅s–1 and charge rate between –0.05 pC⋅s–1 and –0.17 pC⋅s–1 can be achieved. The theoretical model of charge-discharge rate proposed in this article for the test masses is consistent with the results of ground experiments, which can strongly support the development of charge management and control systems.
-
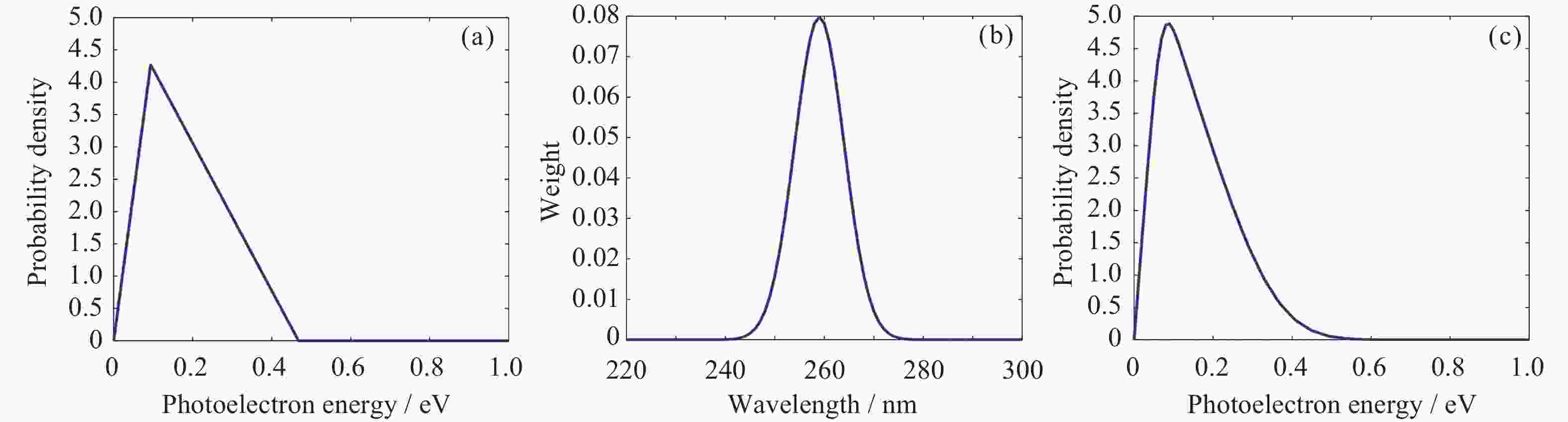
图 2 在单光源波长照射下垂直于表面方向的光电子动能分布(a), 实际使用的UV LED光谱(b)以及在UV LED照射下垂直于表面方向的光电子动能分布 (c)
Figure 2. Distribution of photoelectron kinetic energy perpendicular to the surface direction under single-source wavelength illumination (a), UV LED spectrum actually used (b), distribution of photoelectron kinetic energy perpendicular to the surface direction under UV LED illumination (c)
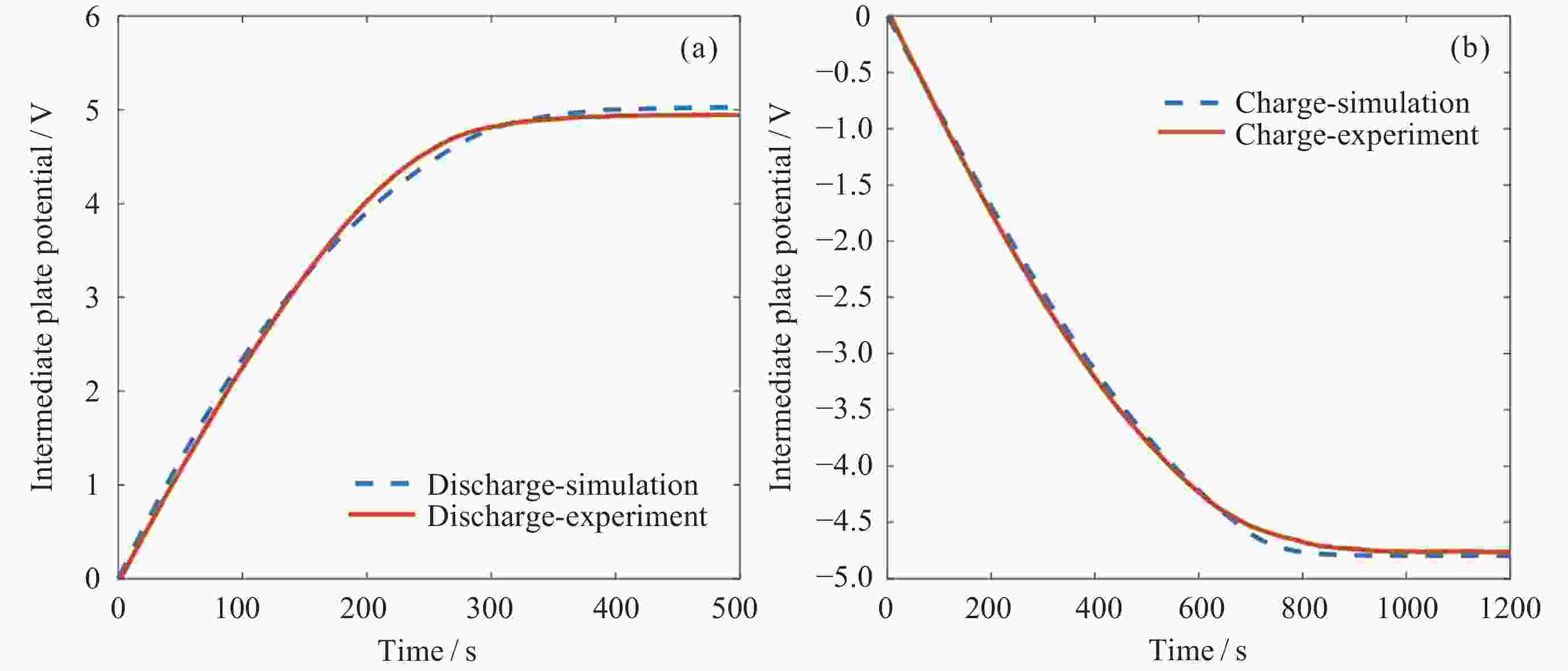
图 11 交流放电试验中2530~2767 s放电与模型放电曲线对比(a)以及3735~4321 s充电曲线与模型充电曲线对比(b)
Figure 11. Comparison of discharge curves from 2530 to 2767 seconds in AC discharge tests with model discharge curves (a) and comparison of charging curves from 3735 to 4321 seconds in AC discharge tests with model charging curves (b)
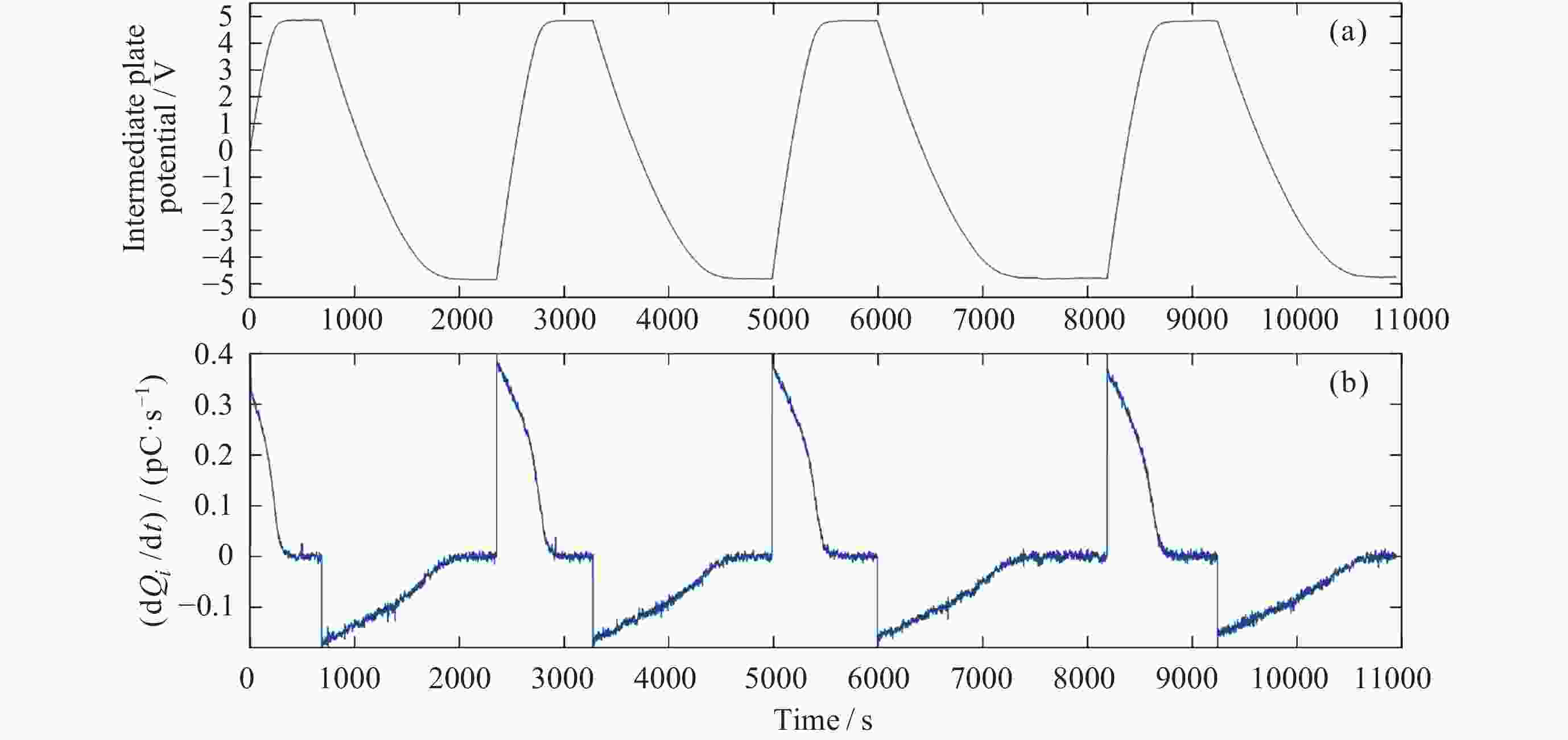
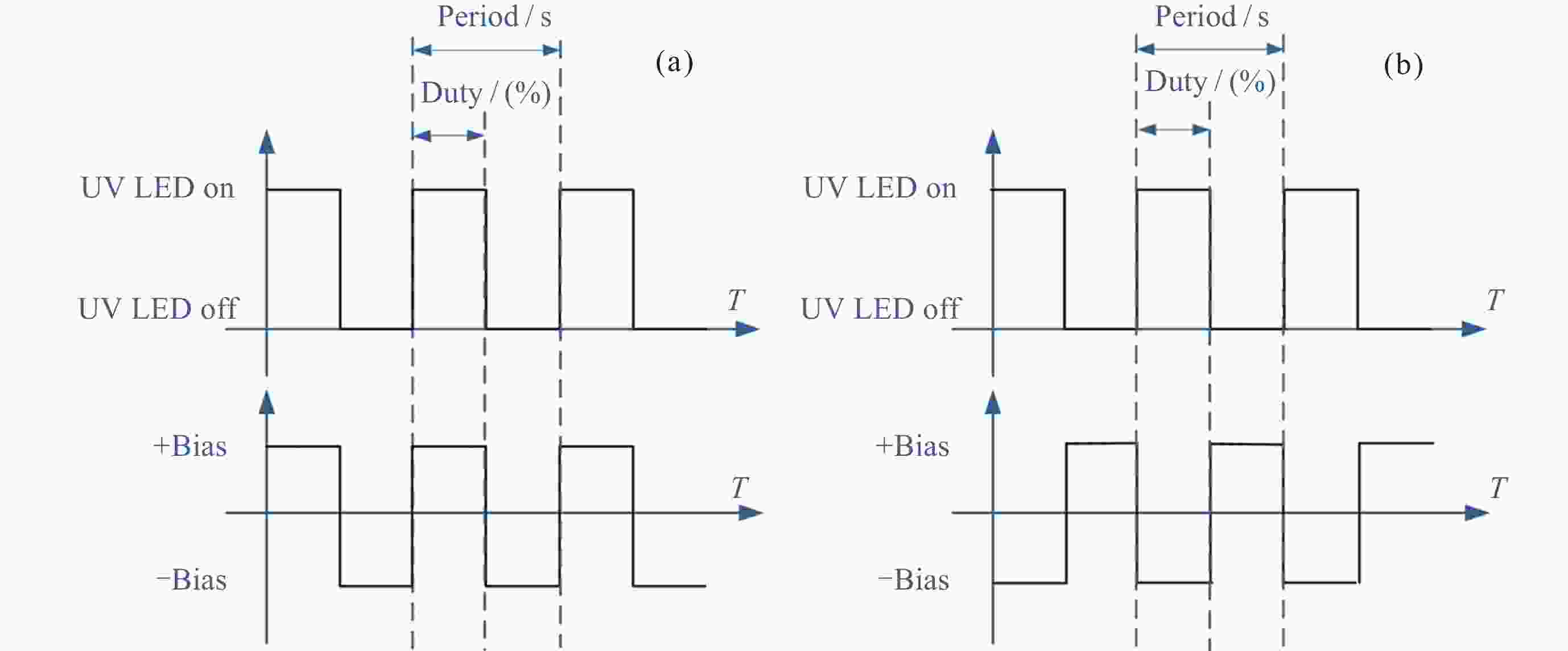
表 1 交流试验时间序列
Table 1. AC experiment time sequence
UV LED 信号相位/(°) 时间/s 0 180 √ √ × 503 × × × 686 √ × √ 2357 √ √ × 3265 √ × √ 5000 √ √ × 5994 √ × √ 8187 √ √ × 9242 √ × √ 10944 注 UV LED: √表示UV LED开启, ×表示UV LED关闭. 信号相位: √位于0°表明UV LED信号与偏压信号同相, 位于180°表明UV LED信号与偏压信号反相. -
[1] ARAÚJO H M, WASS P, SHAUL D, et al. Detailed calculation of test-mass charging in the LISA mission[J]. Astroparticle Physics, 2005, 22(5/6): 451-469 [2] VOCCA H, GRIMANI C, AMICO P, et al. Simulation of the charging process of the LISA test masses due to solar flares[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2004, 21(5): S665-S670 doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/21/5/041 [3] 康伟东, 李得天, 雷军刚, 等. 引力参考传感器检测质量块电荷积累与控制[J]. 真空与低温, 2020, 26(2): 158-164 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2020.02.012KANG Weidong, LI Detian, LEI Jungang, et al. Gravity reference sensor test mass charge accumulation and control[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2020, 26(2): 158-164 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2020.02.012 [4] EWING B E. Charge management in LISA pathfinder: the continuous discharging experiment[Z]. Trento, Italy: Universita di Trento, 2017 [5] ZIEGLER T, BERGNER P, HECHENBLAIKNER G, et al. Modeling and performance of contact-free discharge systems for space inertial sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1493-1510 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120661 [6] 陈浩. 精密扭秤实验中的电荷管理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2013CHEN Hao. The charge management research in the torsion pendulum[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2013 [7] PAIL R, BRUINSMA S, MIGLIACCIO F, et al. First GOCE gravity field models derived by three different approaches[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2011, 85(11): 819-843 doi: 10.1007/s00190-011-0467-x [8] WILLEMENOT E, TOUBOUL P. On-ground investigation of space accelerometers noise with an electrostatic torsion pendulum[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2000, 71(1): 302-309 doi: 10.1063/1.1150197 [9] LI J, BENCZE W, DEBRA D, et al. On-orbit performance of Gravity Probe B drag-free translation control and orbit determination[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2007, 40(1): 1-10 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2007.03.009 [10] SARAF S, BUCHMAN S, BALAKRISHNAN K, et al. Ground testing and flight demonstration of charge management of insulated test masses using UV-LED electron photoemission[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2016, 33(24): 245004 doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/33/24/245004 [11] SUN K X, LEINDECKER N, HIGUCHI S, et al. UV LED operation lifetime and radiation hardness qualification for space flights[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2009, 154: 012028 doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/154/1/012028 [12] HOLLINGTON D, BAIRD J T, SUMNER T J, et al. Characterising and testing deep UV LEDs for use in space applications[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2015, 32(23): 235020 doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/32/23/235020 [13] HOLLINGTON D, BAIRD J T, SUMNER T J, et al. Lifetime testing UV LEDs for use in the LISA charge management system[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2017, 34(20): 205009 doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/aa87eb [14] HECHENBLAIKNER G, ZIEGLER T, BISWAS I, et al. Energy distribution and quantum yield for photoemission from air-contaminated gold surfaces under ultraviolet illumination close to the threshold[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111(12): 124914 doi: 10.1063/1.4730638 [15] WASS P J, HOLLINGTON D, SUMNER T J, et al. Effective decrease of photoelectric emission threshold from gold plated surfaces[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2019, 90(6): 064501 doi: 10.1063/1.5088135 [16] INCHAUSPÉ H, OLATUNDE T, APPLE S, et al. Numerical modeling and experimental demonstration of pulsed charge control for the space inertial sensor used in LISA[J]. Physical Review D, 2020, 102(4): 042002 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.102.042002 [17] HOLLINGTON D. The Charge Management System for LISA and LISA Pathfinder[D]. London: Imperial College London, 2011 [18] 张琦锋, 侯士敏, 邵庆益, 等. BaO半导体薄膜在外加垂直表面电场作用下的近紫外光吸收增强现象研究[J]. 物理学报, 2000, 49(10): 2089-2093 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2000.10.037ZHANG Qifeng, HOU Shimin, SHAO Qingyi, et al. Study of enhanced photoabsorption of BaO thin films in the near-ultraviolet band with applied vertical electric field on the surface[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2000, 49(10): 2089-2093 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2000.10.037 [19] 康伟东, 李得天, 李刚, 等. 引力参考传感器检测质量块电荷UV光调控技术研究[J]. 真空与低温, 2021, 27(4): 407-410 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2021.04.015KANG Weidong, LI Detian, LI Gang, et al. Research on UV light control technology for detecting mass charge with gravitational reference sensor[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2021, 27(4): 407-410 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2021.04.015 -
-





 王子栋:男, 1998年1月出生于山东省菏泽市. 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为空间引力波探测中检验质量电荷管理技术. E-mail:
王子栋:男, 1998年1月出生于山东省菏泽市. 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为空间引力波探测中检验质量电荷管理技术. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: