Distribution and Characteristics of Martian Precipitating H-ENA
-
摘要: 能量中性原子(Energetic Neutral Atom, ENA)是由能量离子与中性背景成分电荷交换产生. 火星的外逸层扩展范围远高于弓激波, 上游太阳风质子与其相互作用并转化为太阳风氢ENA(Hydrogen-ENA, H-ENA), 新生的H-ENA可直接进入低层大气, 成为新的物质与能量输运通道. 本文基于单流体多成分MHD模型与中性外逸层模型, 计算了火星200 km等高面沉降H-ENA通量的空间分布, 统计了多种太阳风条件下沉降H-ENA的粒子与能量沉降率, 分析影响因素. 结果表明, 在一定模拟条件下, 产生于弓激波上游的太阳风H-ENA, 呈cosZ分布(Z为天顶角), 受磁异常影响较小, 是沉降H-ENA的主要成分, 占ENA总沉降量的59%, 占能量沉降的81%; 产生于磁鞘的磁鞘H-ENA受磁异常阻碍影响较大, 在最强磁异常上方其沉降通量显著下降; 沉降H-ENA与上游太阳风的通量呈正比例关系; 2.1%~3.5%上游太阳风质子转化为太阳风H-ENA.Abstract: Energetic Neutral Atom (ENA) is generated by charge exchange between energetic ions and background neutrals. As Martian exosphere extends far above the bow shock, hydrogen ENA (H-ENA) produced by solar wind proton may enter the lower atmosphere directly, depositing mass and energy in the atmosphere. Based on the single-fluid multispecies MHD model and exosphere model, this paper calculates the spatial distribution of the precipitating H-ENA flux at the height of 200 km on Mars, evaluates the particle and energy deposition rate of the precipitating H-ENA under different solar wind conditions, analyzes their controlling factors. The results show that the solar wind H-ENA generated upstream of the bow shock is less affected by the crustal fields, and shows a cosZ distribution. As a major mass and energy source, the precipitating solar wind H-ENAs account for 59% particle deposition and 81% energy deposition of the total precipitating ENAs. Magnetosheath H-ENA generated in the magnetosheath is greatly affected by the crustal fields, and their precipitating flux decreases significantly above the strongest magnetic anomalies. The precipitating H-ENA flux is proportional to the upstream solar wind flux, and 2.1%~3.5% of upstream solar wind protons are estimated to be converted into the solar wind H-ENAs.
-
Key words:
- Mars /
- Precipitating H-ENA /
- MHD model /
- Crustal
-
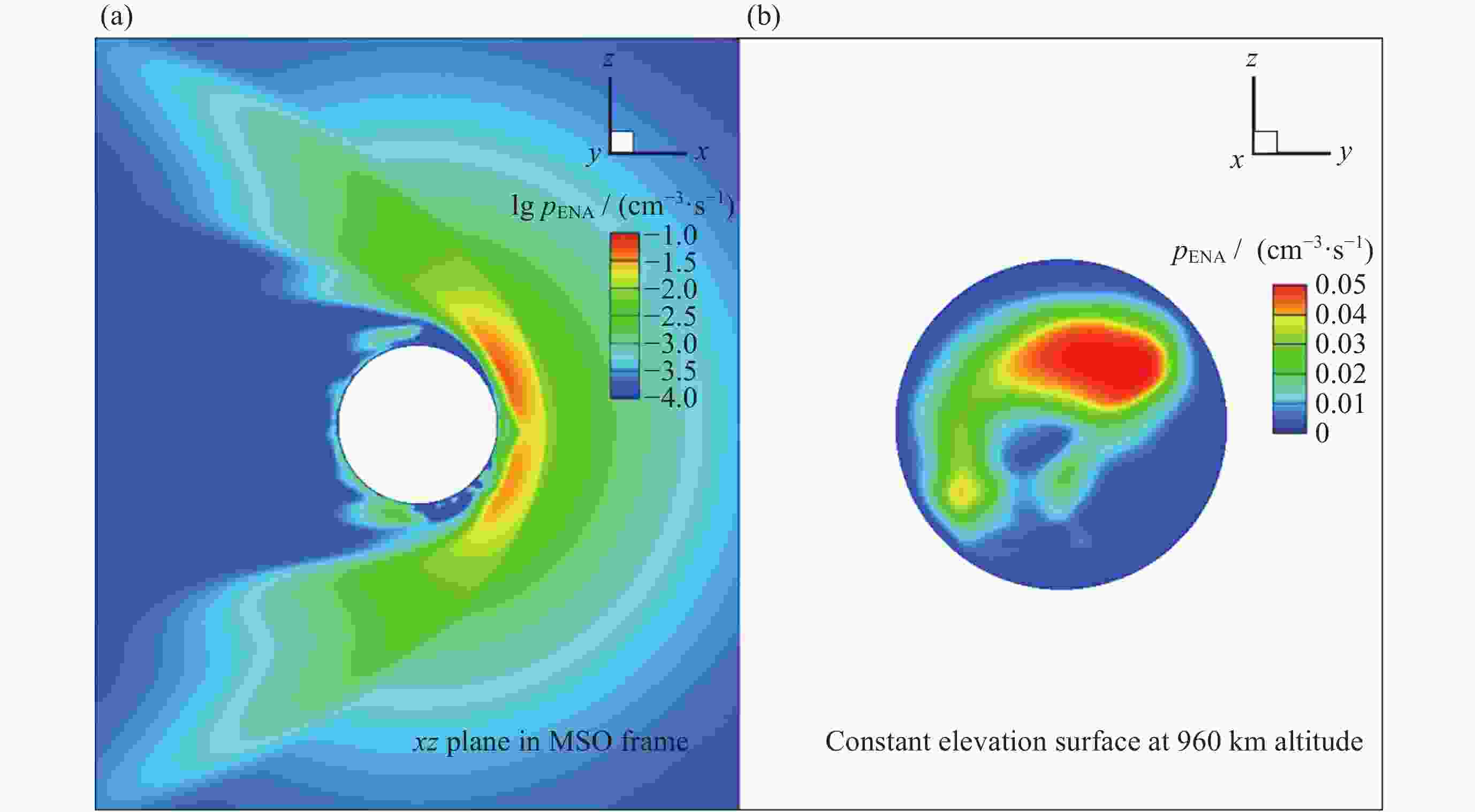
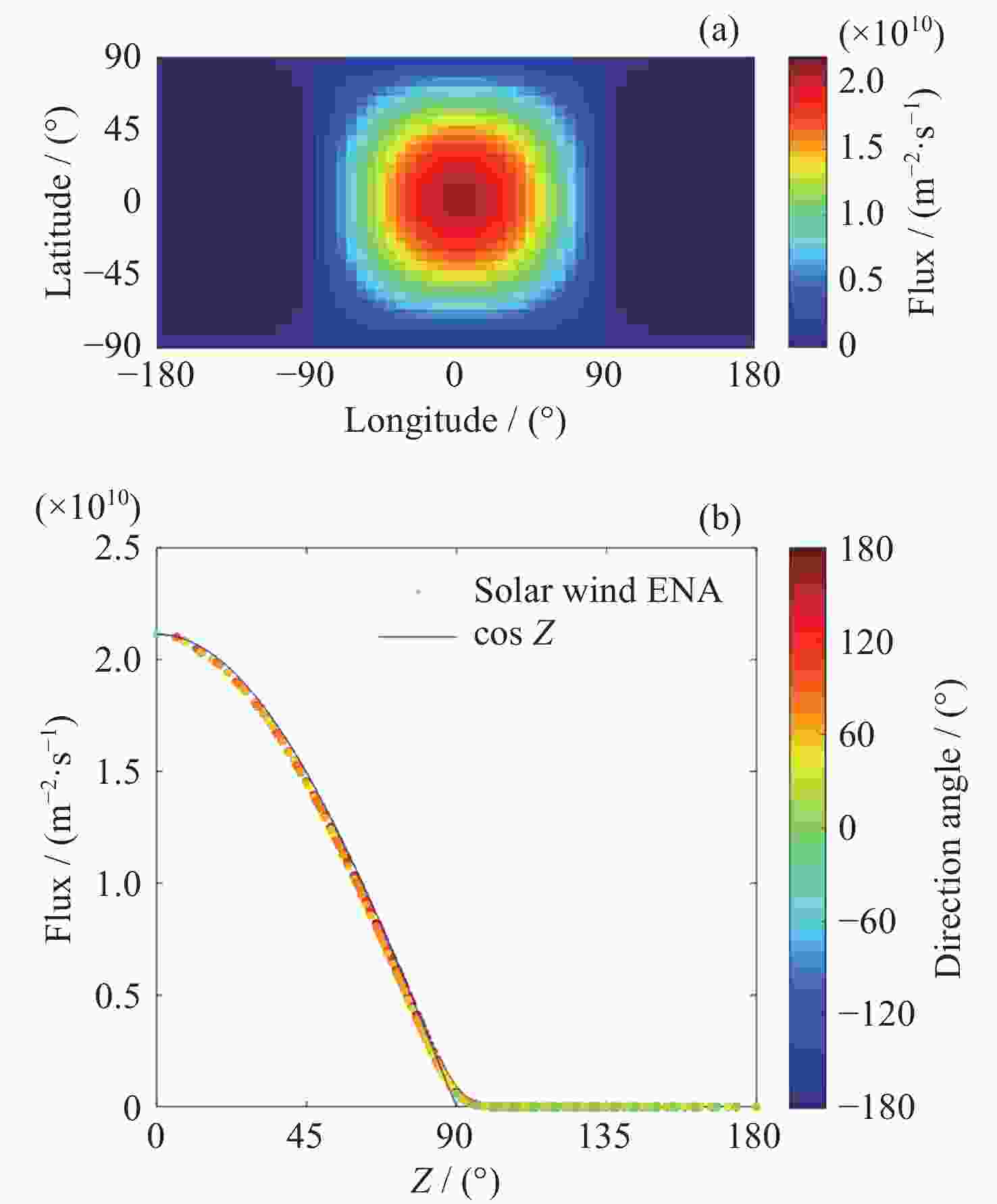
图 4 200 km等高面上沉降太阳风H-ENA通量的空间分布. (a)沉降太阳风H-ENA通量的经纬度分布, (0, 0)表示日下点. (b)沉降太阳风H-ENA通量随太阳天顶角(Z)的变化
Figure 4. Spatial distribution of solar wind H-ENA flux at 200 km. (a) Longitude and latitude distribution of the precipitating solar wind H-ENA flux, and (0, 0) represents the subsolar point. (b) Variation of the precipitating solar wind H-ENA flux with the solar zenith angle (Z)
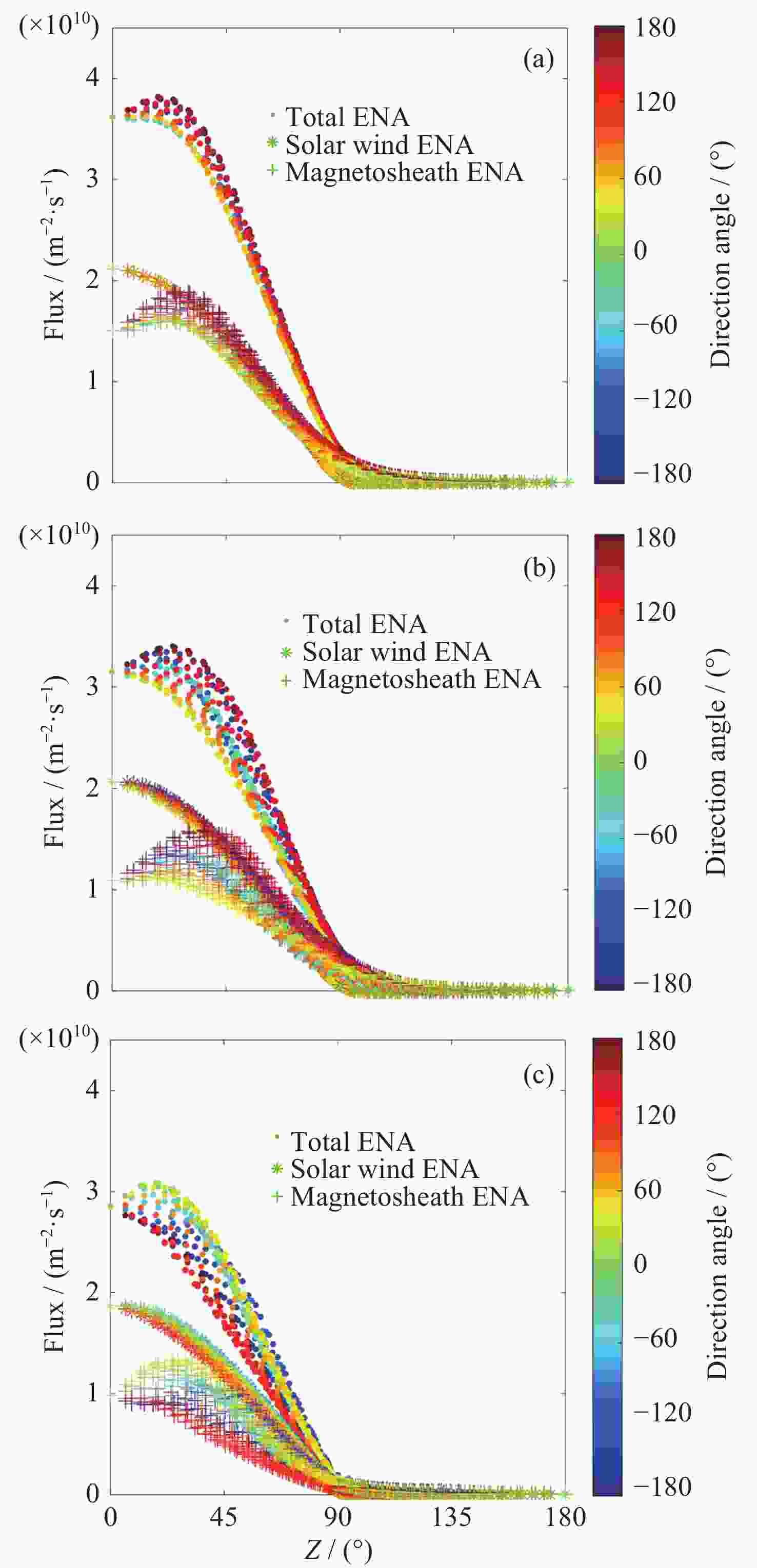
图 6 200 km等高面上沉降H-ENA通量随太阳天顶角Z的变化(方向角为该位置与日下点连接弧线相对于日下点地理北向的方向角)
Figure 6. Variation of precipitating H-ENA flux on 200 km constant elevation surface with solar zenith angle Z (Direction angle is from the connection arc between the precipitating position and subsolar point to the geography north of the subsolar point)
表 1 MHD模型的参数
Table 1. Parameters of MHD model
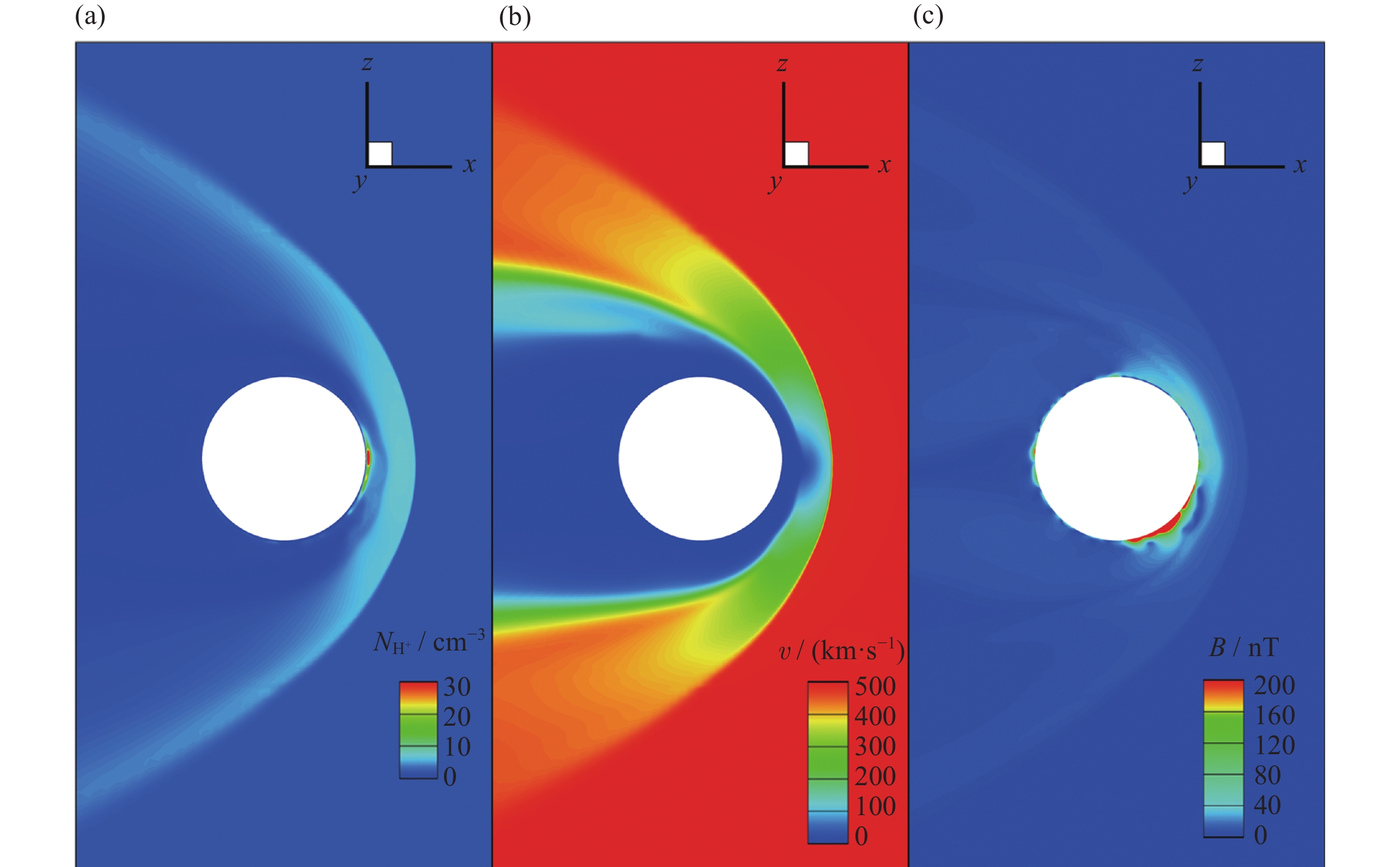
太阳风参数 值 密度/cm–3 1.8 速度/(km·s–1) (500, 0, 0) 质子温度/K 1.5×105 磁场/nT (–1.6, 2.5, 0) 表 2 临界高度170 km处外逸层模型参数
Table 2. Model parameters at exospheric critical altitude 170 km
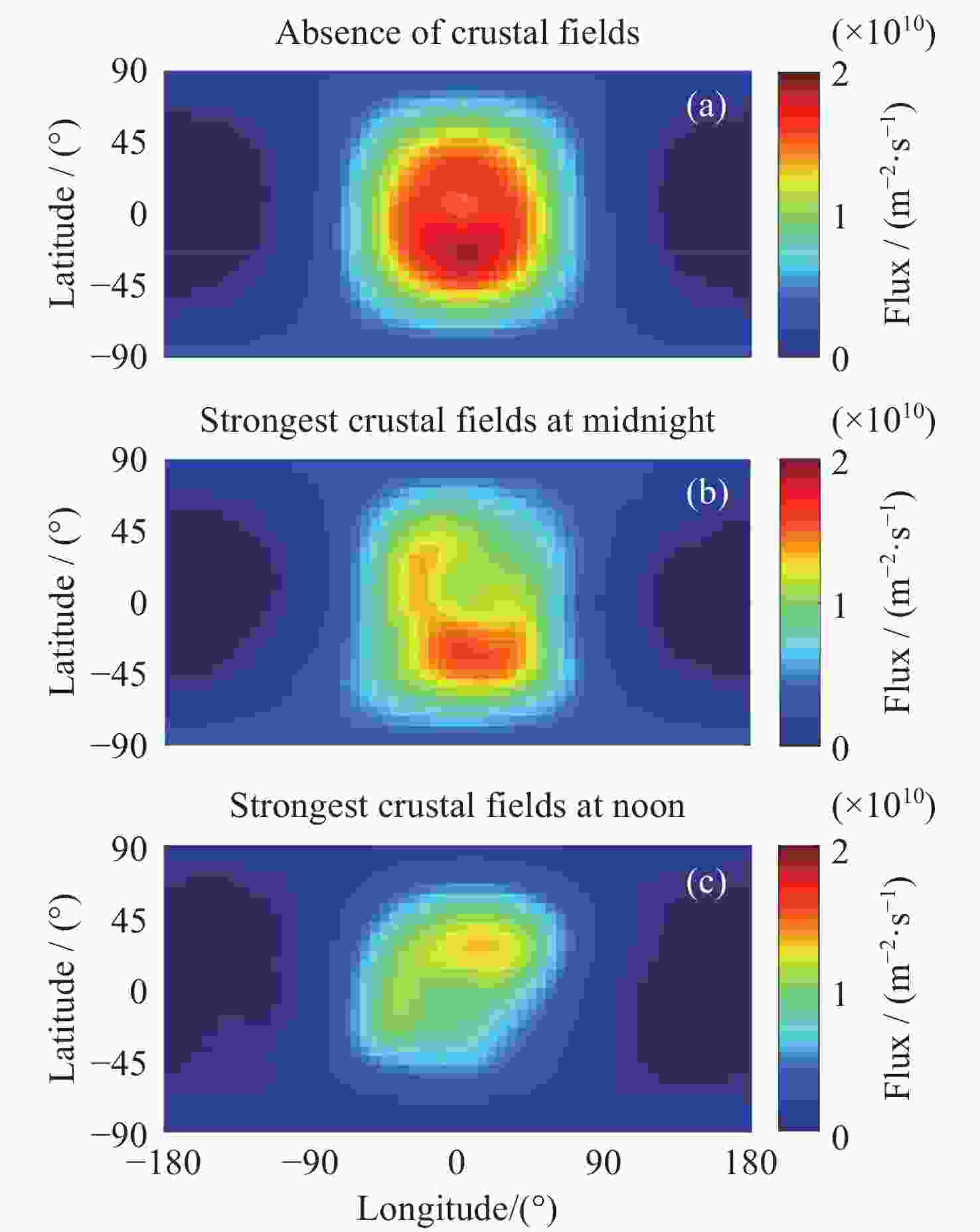
成分 温度/K 密度/cm–3 H 192 9.9×105 H2 192 3.8×106 O(thermal) 173 1.4×108 O(hot) 4.4×103 5.5×103 表 3 不同磁异常条件下沉降H-ENA物理量统计
Table 3. Statistics on precipitating H-ENA parameters under different crustal field conditions
模型条件
(最强磁异常)沉降太阳风 H-ENA 沉降磁鞘 H-ENA 最大通量(×1010)/(m–2·s–1) 沉降率
(×1024)/ s–1能量沉降率(×1027)/(eV·s–1) 最大通量(×1010)/(m–2·s–1) 沉降率
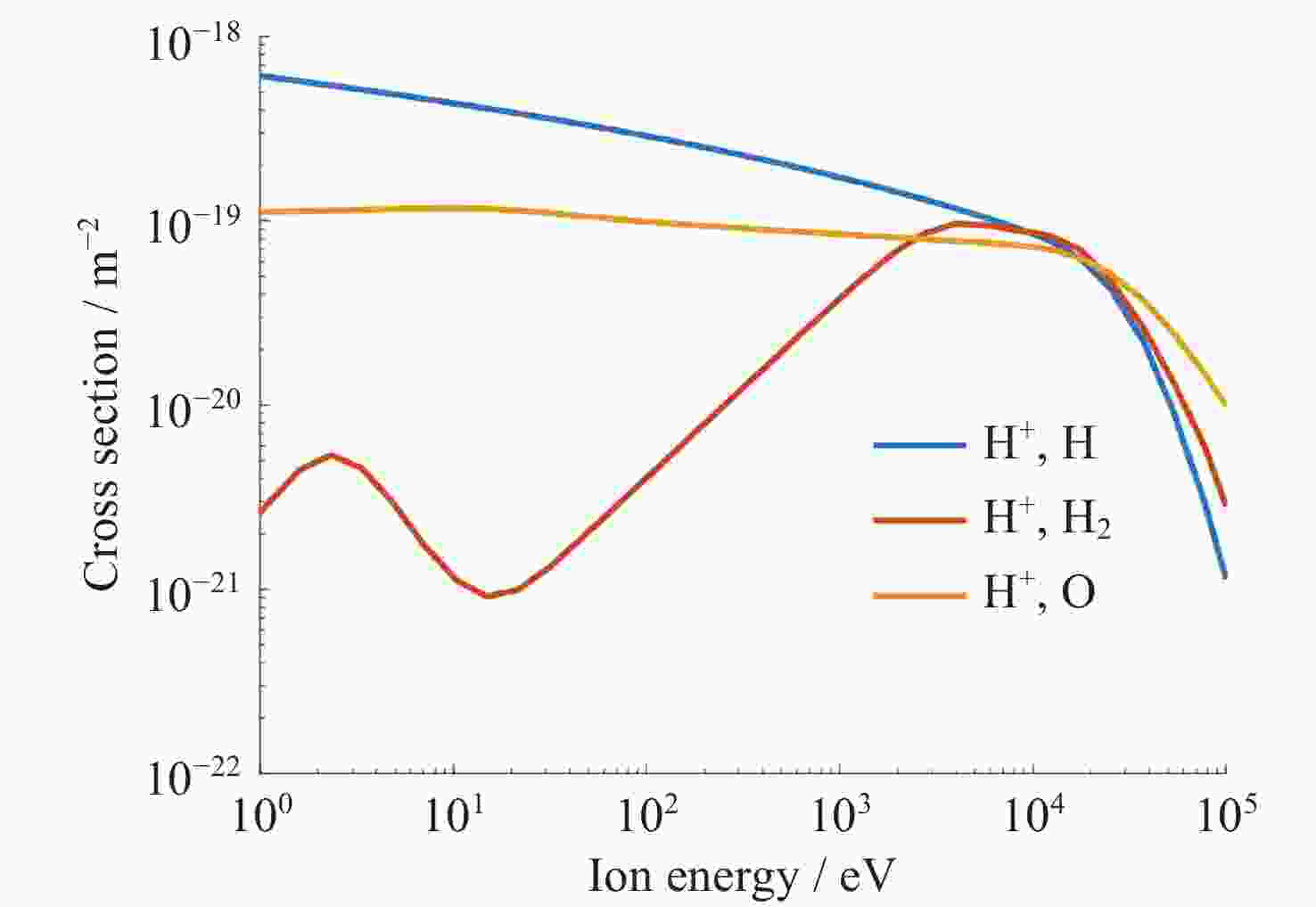
(×1024)/ s–1能量沉降率
(×1027) /(eV·s–1)Case 1 无 2.11 0.84 1.06 1.89 0.83 0.57 Case 2 位于子夜 2.06 0.80 1.01 1.59 0.70 0.47 Case 3 位于正午 1.87 0.72 0.91 1.33 0.50 0.21 表 4 不同太阳风条件下沉降H-ENA物理量统计
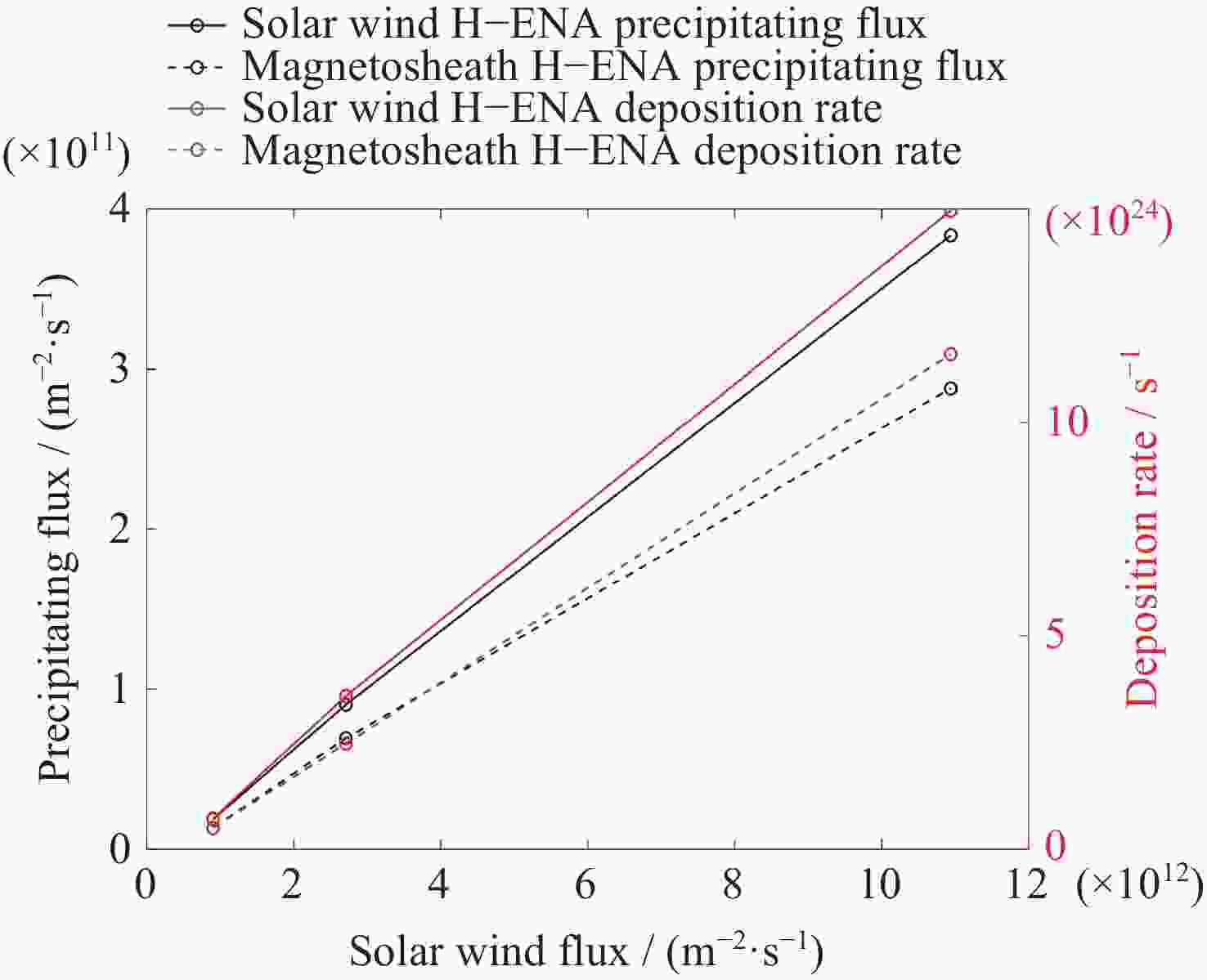
Table 4. Statistics on precipitating H-ENA parameters under different solar wind conditions
模型说明 太阳风 沉降太阳风 H-ENA 沉降磁鞘 H-ENA 通量
(×1012)/( m–2·s–1)最大通量
(×1010 )/(m–2·s–1)沉降率
(×1024)/ s–1最大通量
(×1010)/(m–2·s–1)沉降率
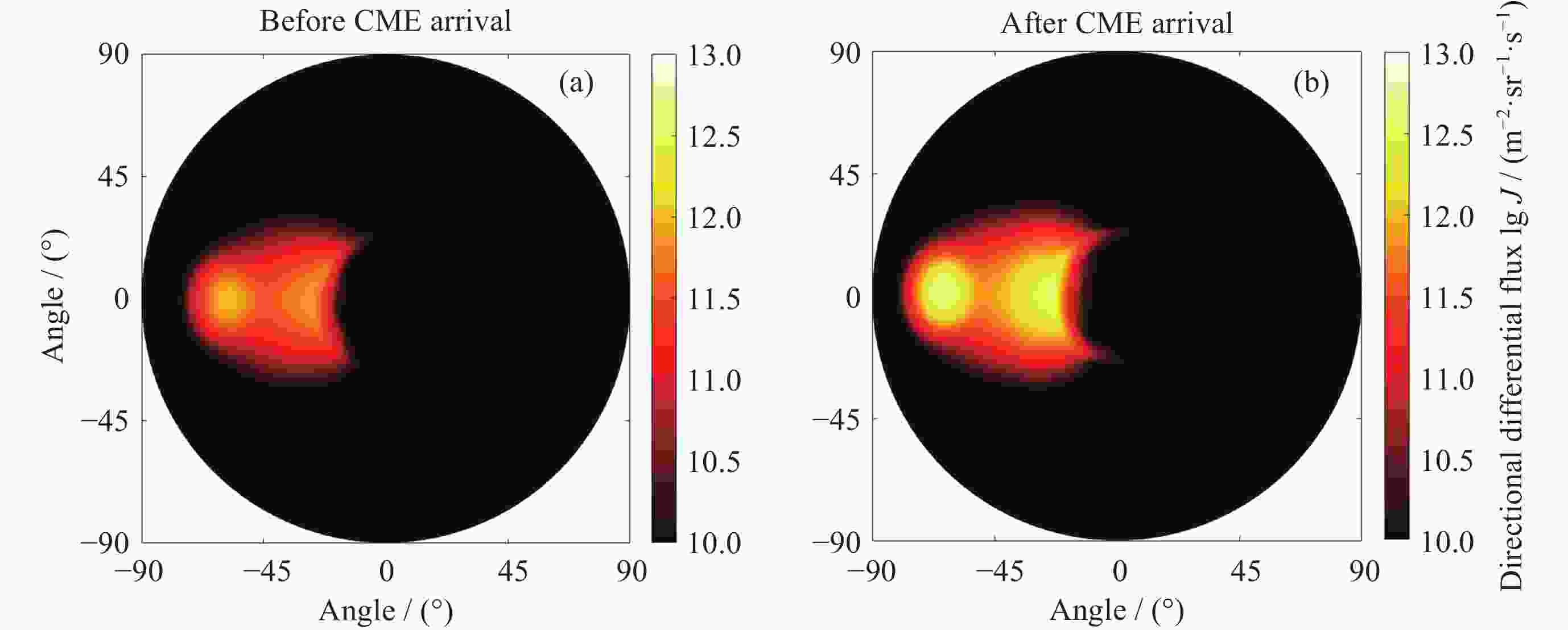
(×1024)/s–1表3中Case 3 0.90 1.87 0.72 1.33 0.50 CME到达前 2.71 9.03 3.59 6.93 2.47 CME到达后 10.94 38.36 14.96 28.80 11.60 -
[1] GRUNTMAN M. Energetic neutral atom imaging of space plasmas[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1997, 68(10): 3617-3656 doi: 10.1063/1.1148389 [2] WURZ P. Detection of energetic neutral atoms[M]//The Outer Heliosphere: Beyond the Planets. Germany, 2000: 251-288 [3] 郭志忠, 符慧山, 刘杨洋. 火星空间环境中电子通量的统计研究[J]. 地球与行星物理论评, 2022, 53(4): 488-496 doi: 10.19975/j.dqyxx.2022-004GUO Zhizhong, FU Huishan, LIU Yangyang. Statistical study of electron flux in Martian space environment[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2022, 53(4): 488-496 doi: 10.19975/j.dqyxx.2022-004 [4] VIGNES D, MAZELLE C, RME H, et al. The solar wind interaction with Mars: locations and shapes of the bow shock and the magnetic pile-up boundary from the observations of the MAG/ER Experiment onboard Mars Global Surveyor[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2000, 27(1): 49-52 doi: 10.1029/1999gl010703 [5] DEIGHAN J, JAIN S K, CHAFFIN M S, et al. Discovery of a proton aurora at Mars[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2018, 2(10): 802-807 doi: 10.1038/s41550-018-0538-5 [6] RITTER B, GÉRARD J C, HUBERT B, et al. Observations of the proton aurora on Mars with SPICAM on board Mars express[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(2): 612-619 doi: 10.1002/2017gl076235 [7] HALEKAS J S. Seasonal variability of the hydrogen exosphere of Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2017, 122(5): 901-911 doi: 10.1002/2017JE005306 [8] KALLIO E, LUHMANN J G, BARABASH S. Charge exchange near Mars: The solar wind absorption and energetic neutral atom production[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1997, 102(A10): 22183-22197 doi: 10.1029/97ja01662 [9] WANG X D, ALHO M, JARVINEN R, et al. Precipitation of hydrogen energetic neutral atoms at the upper atmosphere of Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2018, 123(10): 8730-8748 doi: 10.1029/2018ja025188 [10] BARABASH S, LUNDIN R, ZARNOWIECKI T, et al. Diagnostic of energetic neutral particles at Mars by the ASPERA-C instrument for the Mars 96 mission[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1995, 16(4): 81-86 doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(95)00212-w [11] FUTAANA Y, BARABASH S, GRIGORIEV A, et al. First ENA observations at Mars: ENA emissions from the martian upper atmosphere[J]. Icarus, 2006, 182(2): 424-430 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2005.09.019 [12] FUTAANA Y, BARABASH S, GRIGORIEV A, et al. First ENA observations at Mars: Subsolar ENA jet[J]. Icarus, 2006, 182(2): 413-423 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2005.08.024 [13] GUNELL H, BRINKFELDT K, HOLMSTRÖM M, et al. First ENA observations at Mars: Charge exchange ENAs produced in the magnetosheath[J]. Icarus, 2006, 182(2): 431-438 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2005.10.027 [14] GALLI A, WURZ P, BARABASH S, et al. Energetic hydrogen and oxygen atoms observed on the nightside of Mars[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2006, 126(1): 267-297 doi: 10.1007/s11214-006-9088-8 [15] GALLI A, WURZ P, KALLIO E, et al. Tailward flow of energetic neutral atoms observed at Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2008, 113(E12): E12012 doi: 10.1029/2008je003139 [16] WANG X D, BARABASH S, FUTAANA Y, et al. Directionality and variability of energetic neutral hydrogen fluxes observed by Mars Express[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2013, 118(12): 7635-7642 doi: 10.1002/2013JA018876 [17] MA J J, LI W Y, KONG L G, et al. Solar wind energetic neutral atom observation at Mars by MINPA onboard the Tianwen-1 orbiter[C]//Proceedings of the Fall Meeting 2022. Chicago, American: AGU [18] ZHANG Y T, LI L, XIE L H, et al. Inversion of upstream solar wind parameters from ENA observations at Mars[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(7): 1721 doi: 10.3390/rs15071721 [19] RAMSTAD R, BRAIN D A, DONG Y X, et al. Energetic neutral atoms near Mars: Predicted distributions based on MAVEN measurements[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2022, 927(1): 11 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ac4606 [20] MA Y J, NAGY A F, SOKOLOV I V, et al. Three-dimensional, multispecies, high spatial resolution MHD studies of the solar wind interaction with Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2004, 109(A7): A07211 doi: 10.1029/2003ja010367 [21] MA Y J, RUSSELL C T, FANG X, et al. MHD model results of solar wind interaction with Mars and comparison with MAVEN plasma observations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(21): 9113-9120 doi: 10.1002/2015GL065218 [22] CHAMBERLAIN J W, HUNTEN D M. Theory of Planetary Atmospheres[M] Orlando FL: Academic Press, 1987 [23] RINSUKE I, TATSUO T, TOSHIZO S, et al. Analytic cross sections for collision of H, H2, He and Li atoms and ions with atoms and melecules; 1993 [24] LINDSAY B G, STEBBINGS R F. Charge transfer cross sections for energetic neutral atom data analysis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2005, 110(A12): A12213 doi: 10.1029/2005ja011298 [25] SWACZYNA P, MCCOMAS D J, ZIRNSTEIN E J, et al. Angular scattering in charge exchange: Issues and implications for secondary interstellar hydrogen[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2019, 887(2): 223 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ab5440 [26] HAIDER S A, MAHAJAN K K, BOUGHER S W, et al. Observations and modeling of martian auroras[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2022, 218(4): 32 doi: 10.1007/s11214-022-00906-2 -
-





 张艺腾:男, 1981年11月出生于辽宁省沈阳市. 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心副研究员, 硕士生导师. 主要研究方向为火星空间环境、高精度磁场探测与应用等. E-mail:
张艺腾:男, 1981年11月出生于辽宁省沈阳市. 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心副研究员, 硕士生导师. 主要研究方向为火星空间环境、高精度磁场探测与应用等. E-mail:  李磊:女, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心研究员. 主要从事行星空间环境探测研究. E-mail:
李磊:女, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心研究员. 主要从事行星空间环境探测研究. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: