Insight-HXMT Research Progress Since 2023
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.04.2024-yg12 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.04.2024-yg12
-
Abstract: Since the launch in June 2017, Insight-HXMT has been in service smoothly in orbit and particularly productive in 2023 and 2024. Among a total number of 238 papers published so far based on Insight-HXMT data, 63 were published in 2023, and 32 in the early 2024 (till 2024 April), accounting for 40% of the total. These studies cover a variety of scientific subjects including the basic properties of black holes and neutron stars, the outburst of accreting black hole and neutron star X-ray binaries, thermal nuclear burst probes, isolated pulsars, quasi periodical oscillations, cyclotron resonant scattering features, fast radio bursts and gamma-ray bursts, etc. This paper introduces the overall progress with focus on some potential breakthroughs.
-
Key words:
- Insight-HXMT /
- Black hole /
- Neutron star /
- Outburst
-
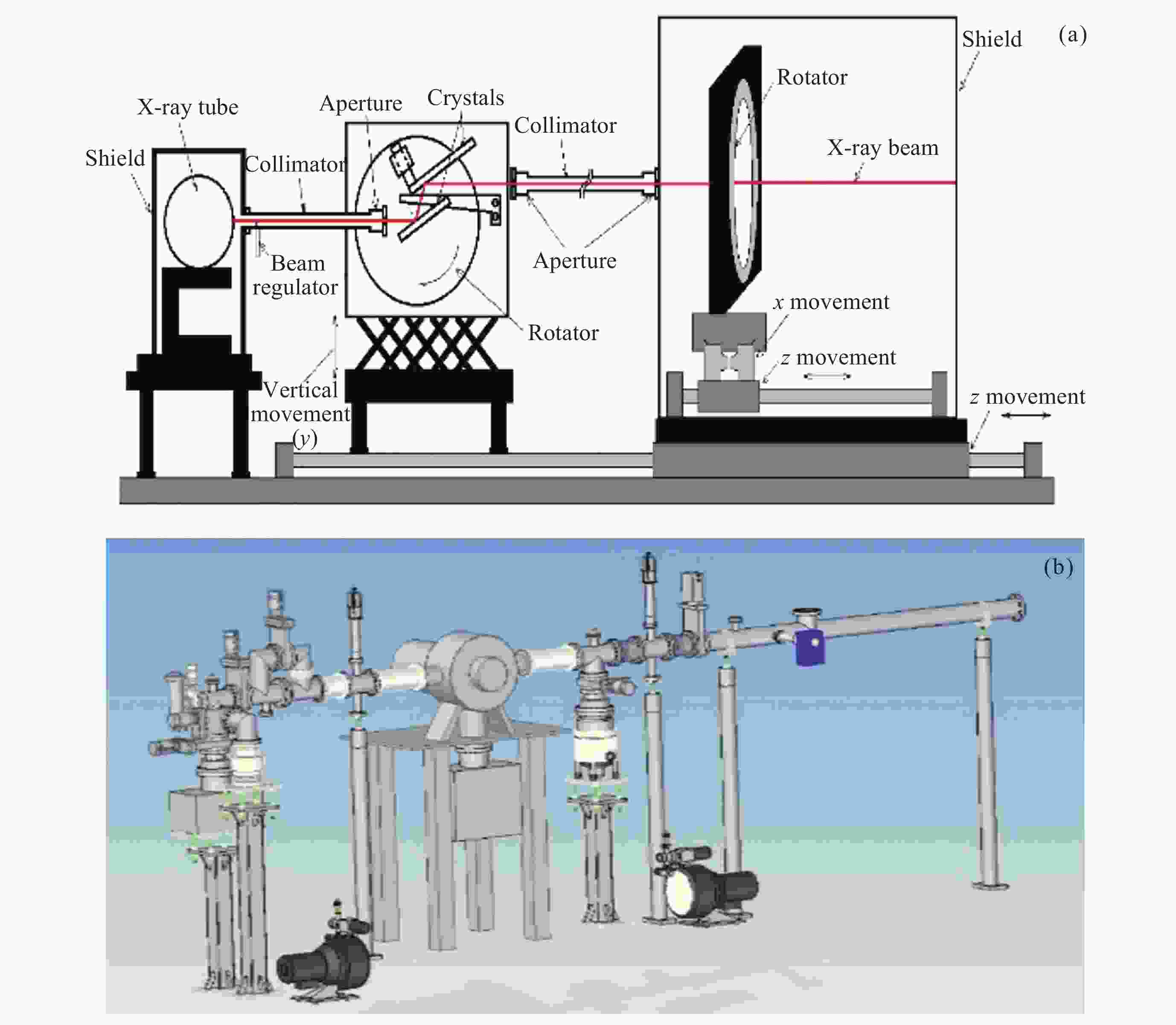
Figure 3. Ground calibration facilities implemented for HE at hard X-rays (a) and for ME/LE at soft X-rays (b)[12]
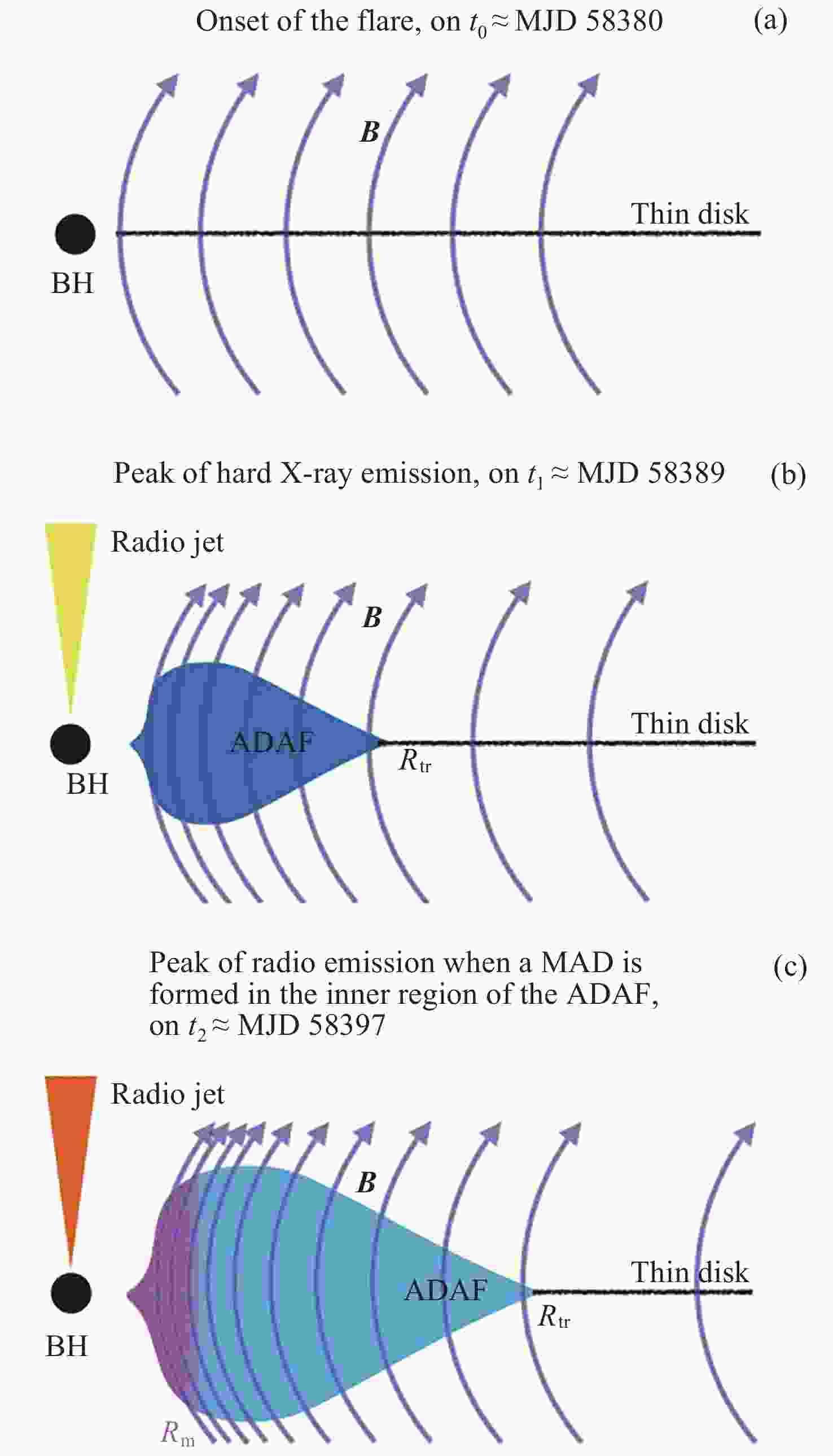
Figure 4. MAD discovered during the decay phase of MAXI J1820+030[18]
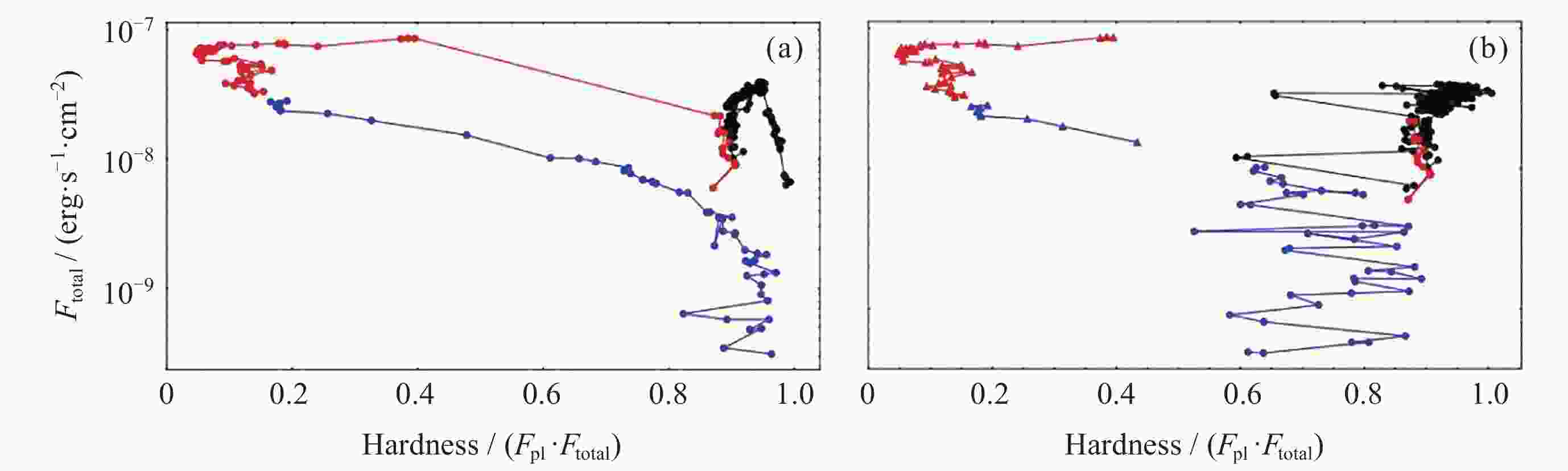
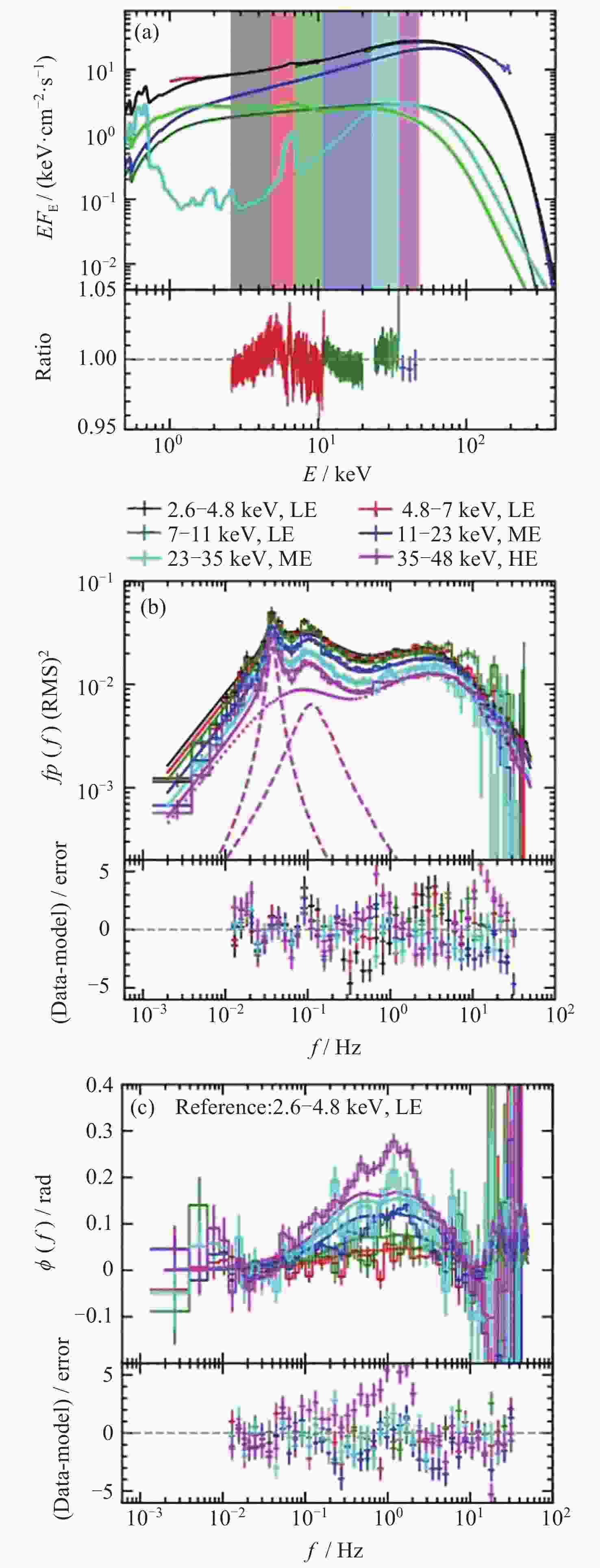
Figure 5. HID modification by accounting for the lag corrections between different energy bands for the outburst of MAXI J1820+070[19]
Figure 6. Joint fits to the spectra in energy, frequency and time lag domains for the outburst of MAXI J1820+070[20]
Figure 7. A standard accretion disk exists during the whole outburst of SLX 1746-331[23]
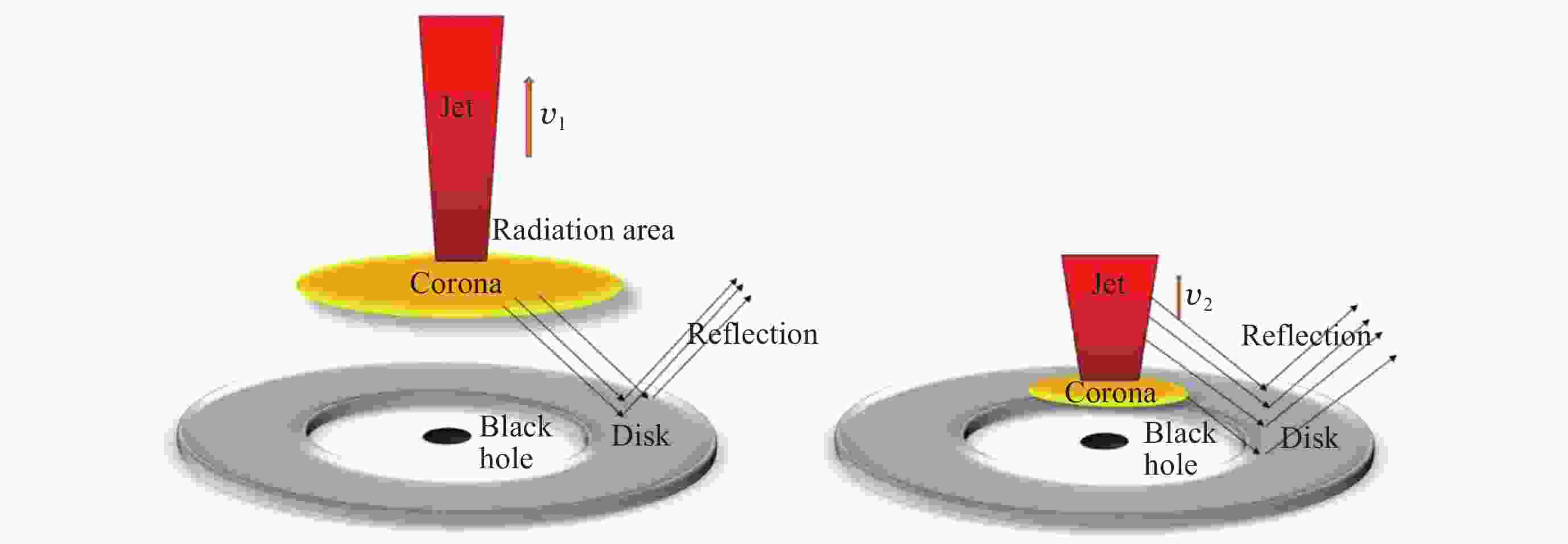
Figure 8. A hybrid jet/corona scenario introduced to the outburst evolution of Swift J1727.8-1613[25]
Figure 9. Mass gap puzzle
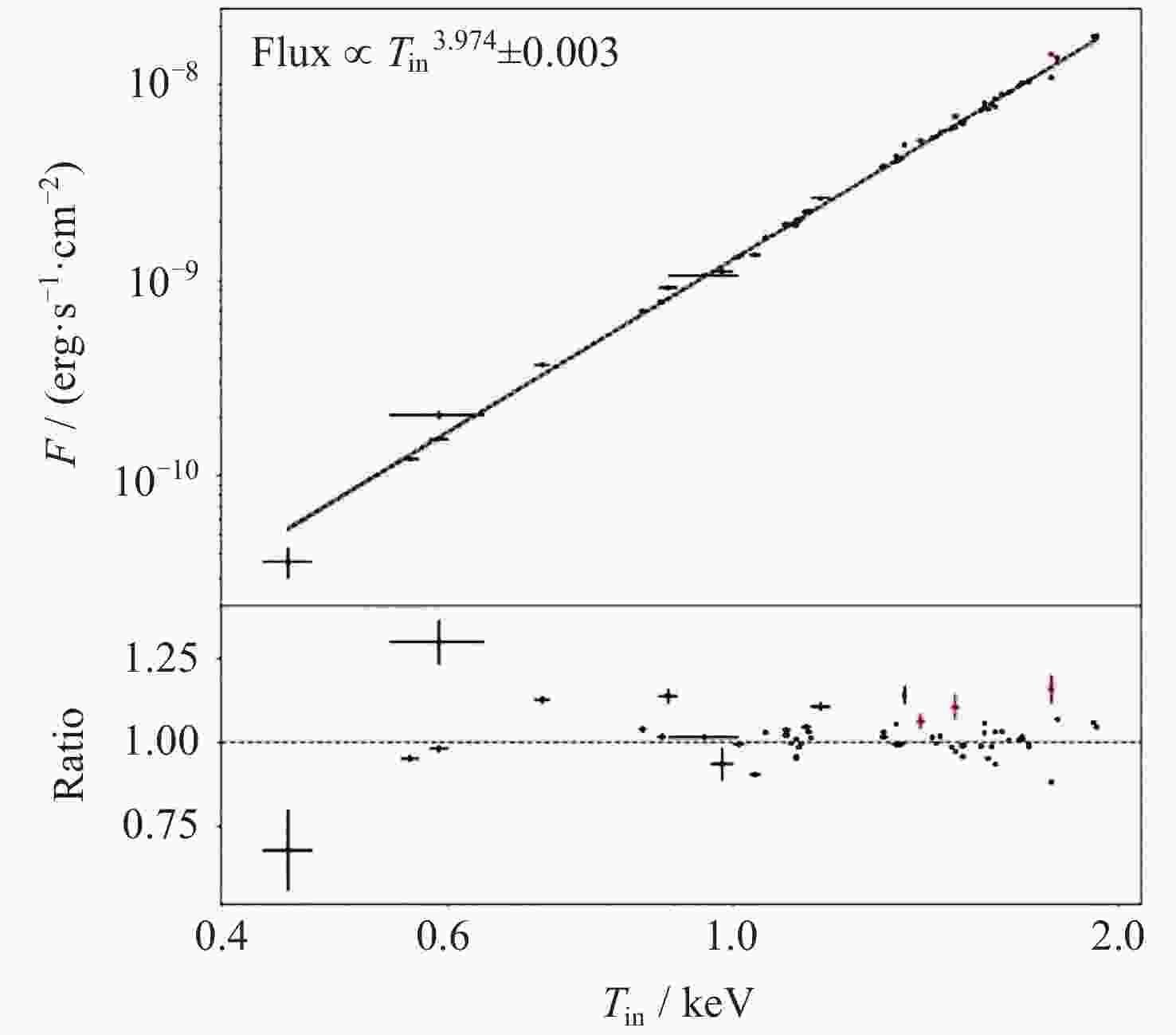
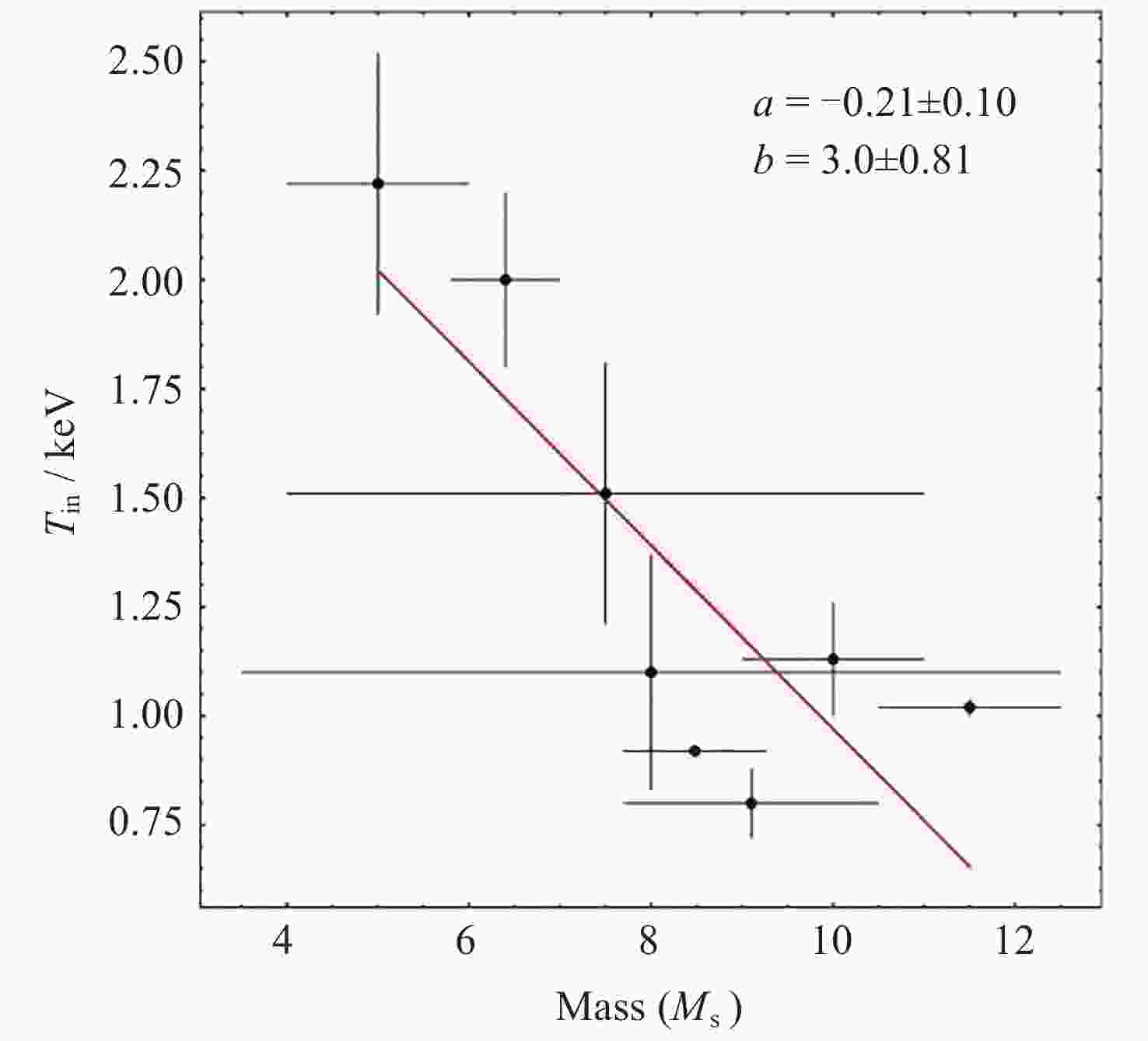
1 Figure 10. BH mass estimated from an empirical correlation between disk temperature and BH mass from a BH outburst sample[22]
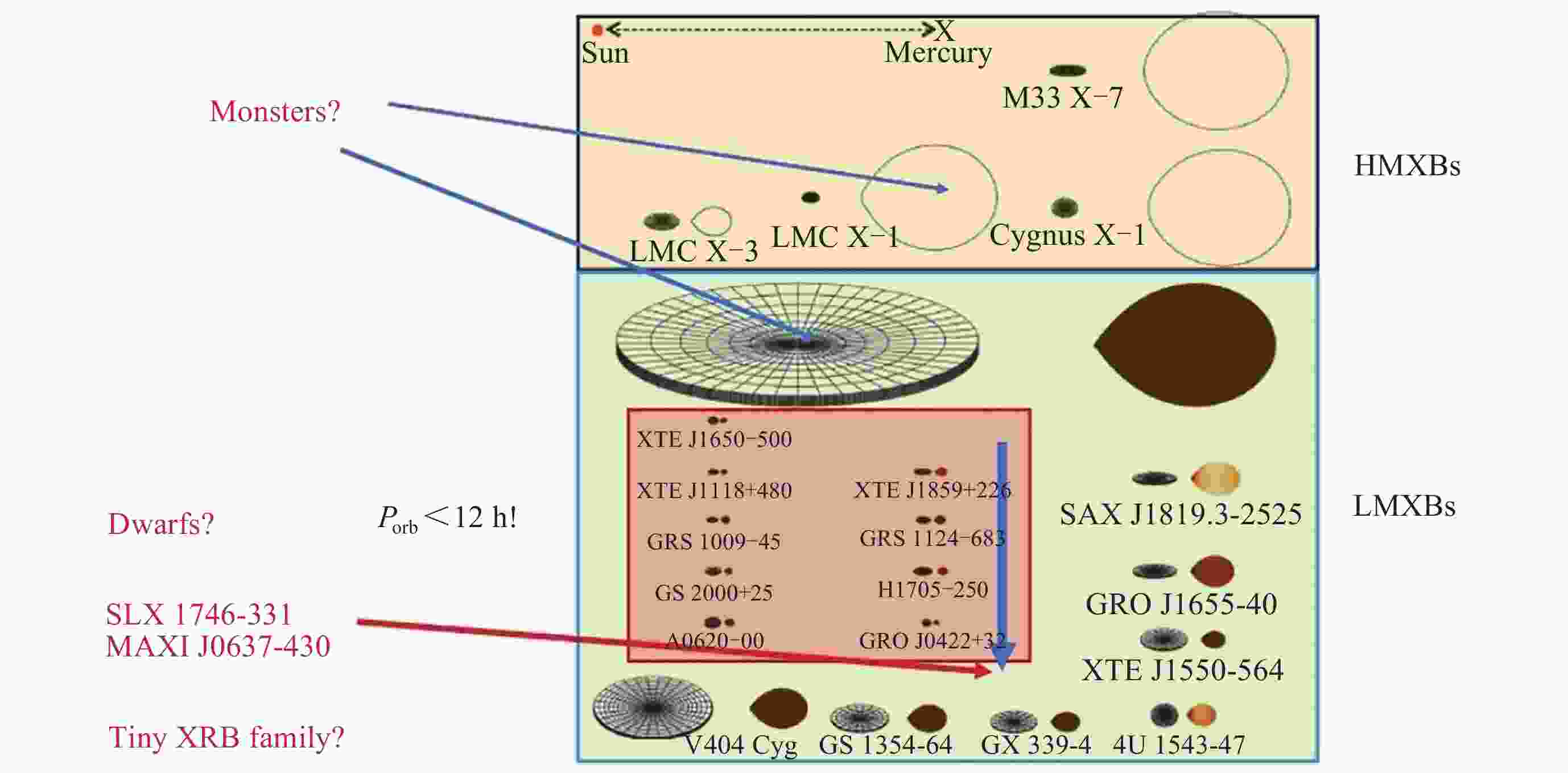
Figure 11. The BH zoo
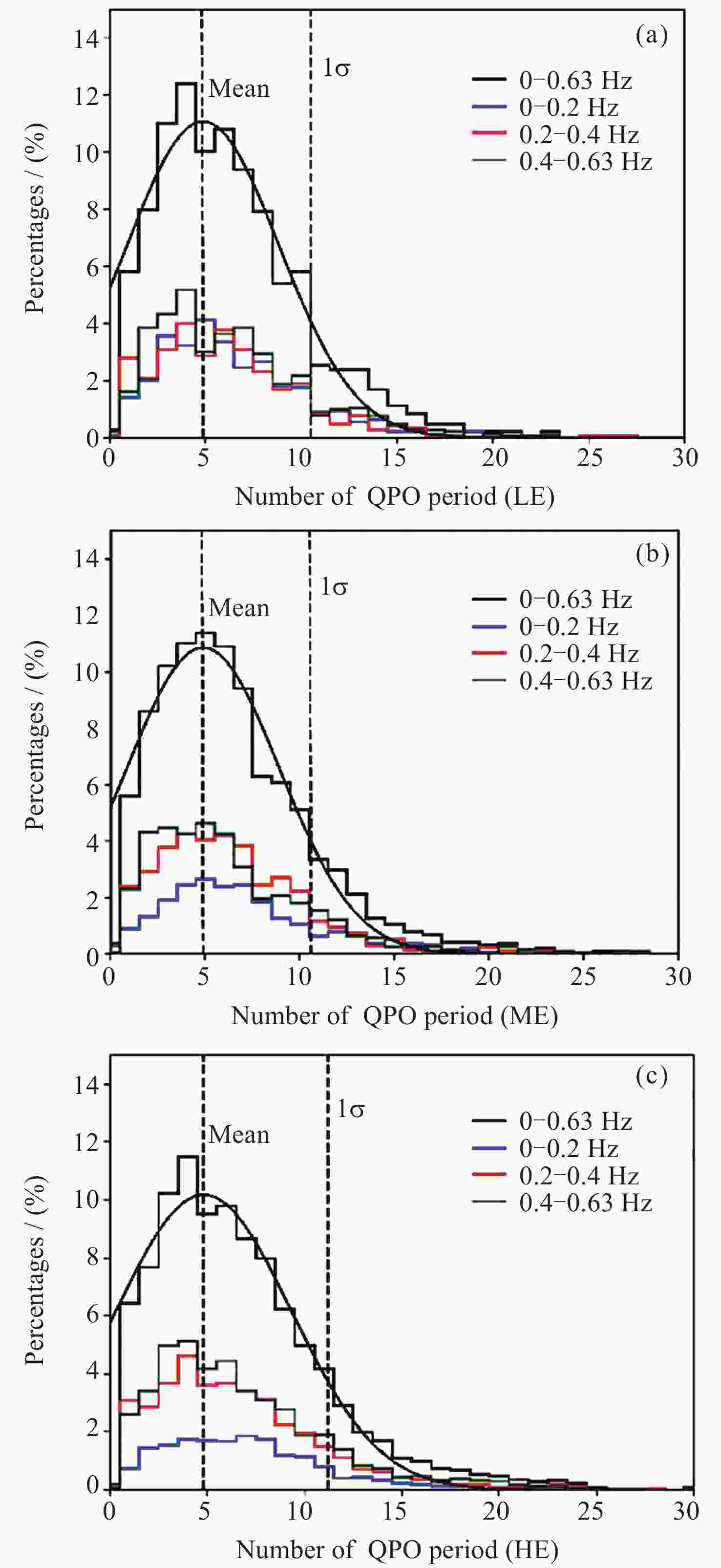
2 Figure 12. QPO lifetime distribution over all the March to June 2018 Insight-HXMT observations in units of cycles[47]
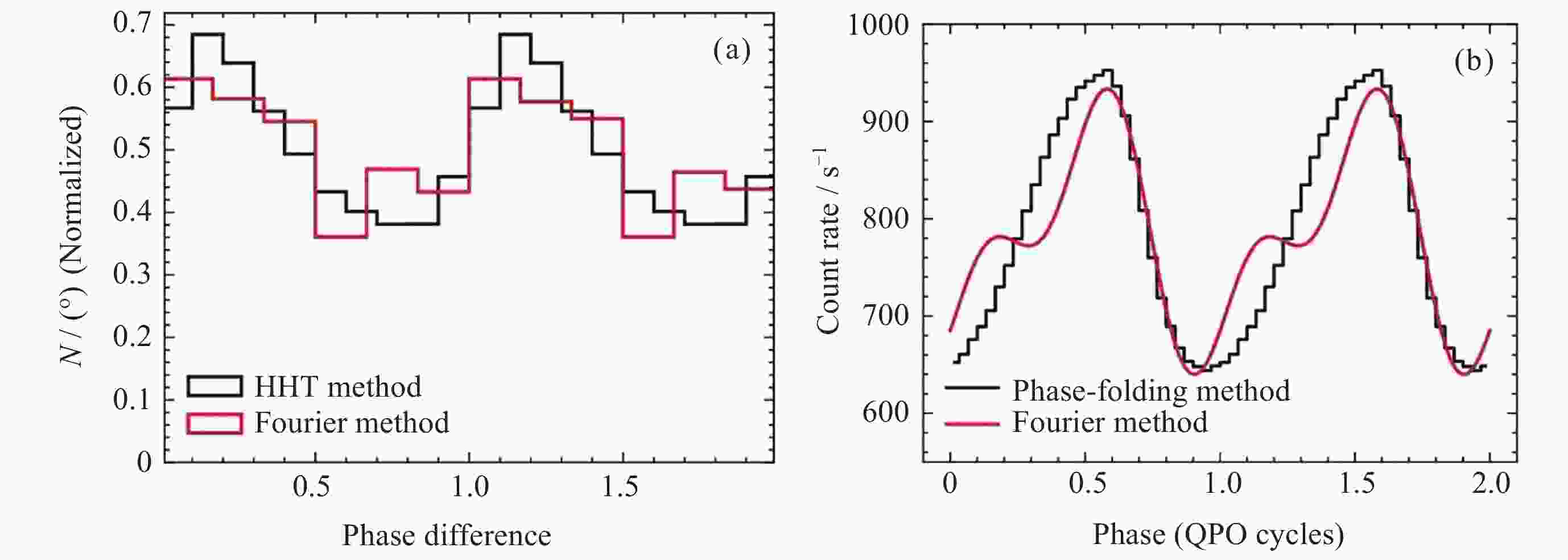
Figure 13. (a) Histogram of measured values of the phase difference between harmonics obtained using the HHT (black) and Fourier (red) methods. To show a clear peak, we repeat the data from 0 to π. (b) Reconstructed QPO waveform derived from the HHT phase-folding (black) and Fourier (red) methods[49]
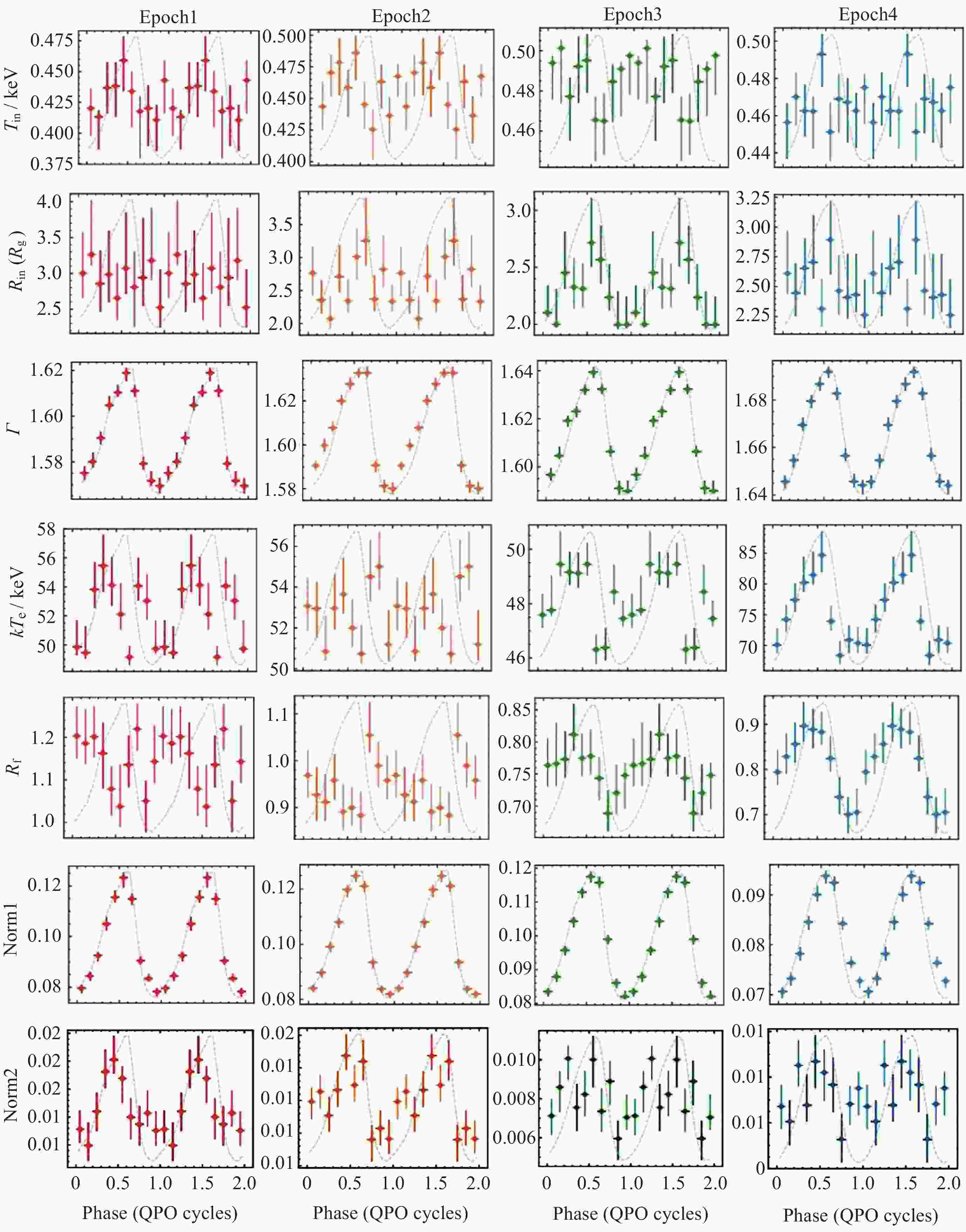
Figure 14. Phase dependence of the seven free spectral parameters, including the temperature of the inner radius of the disk (Tin), inner radius (Rin), spectral index (Γ), electron temperature (kTe), reflection fraction (Rf), and the normalization of relxillCp (Norm1) and xillverCp (Norm2), across the four epochs[49]
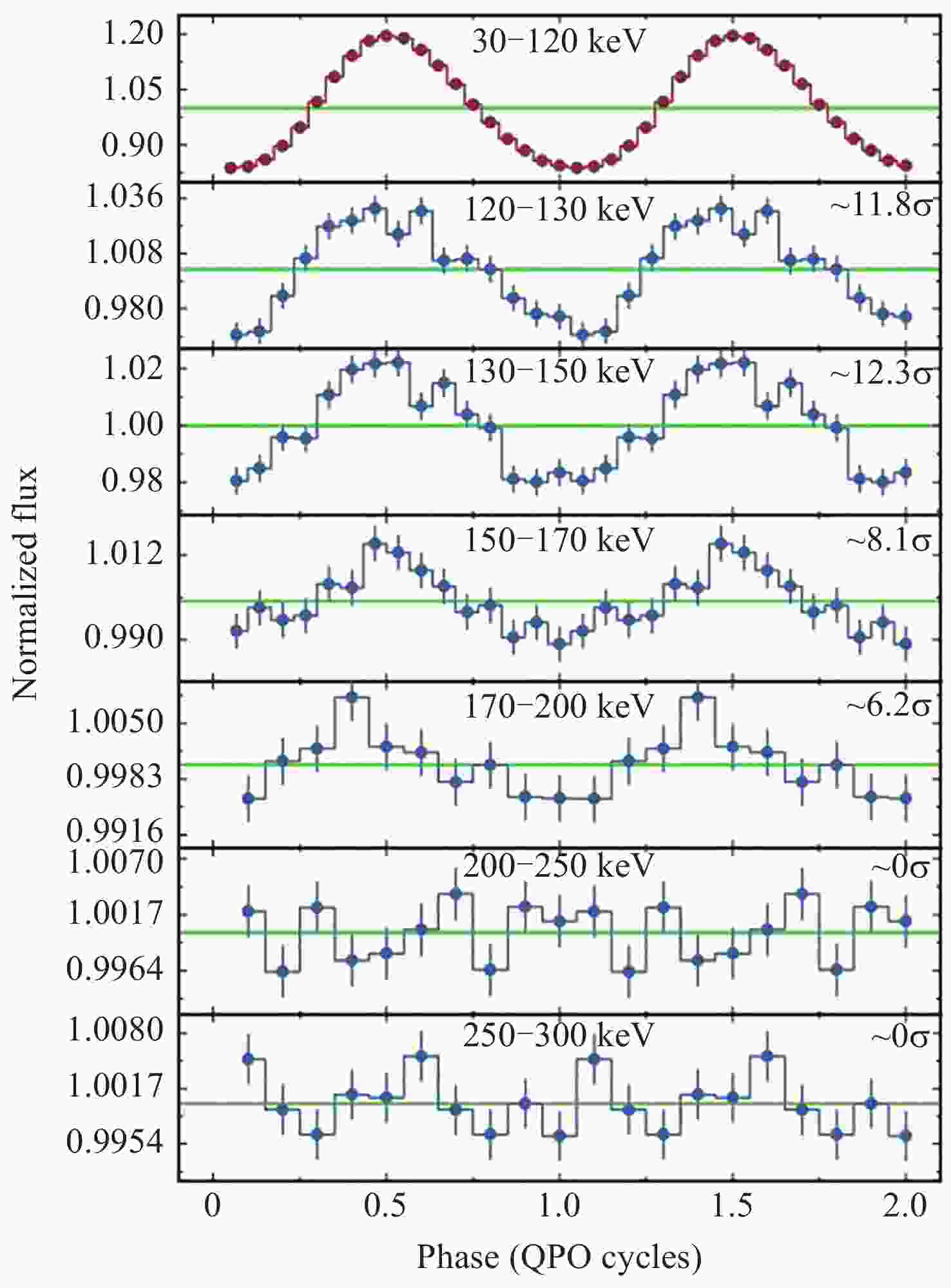
Figure 15. HHT phase-folded QPO waveforms of MAXI J1535-571 from Insight-HXMT/HE light curves[51]
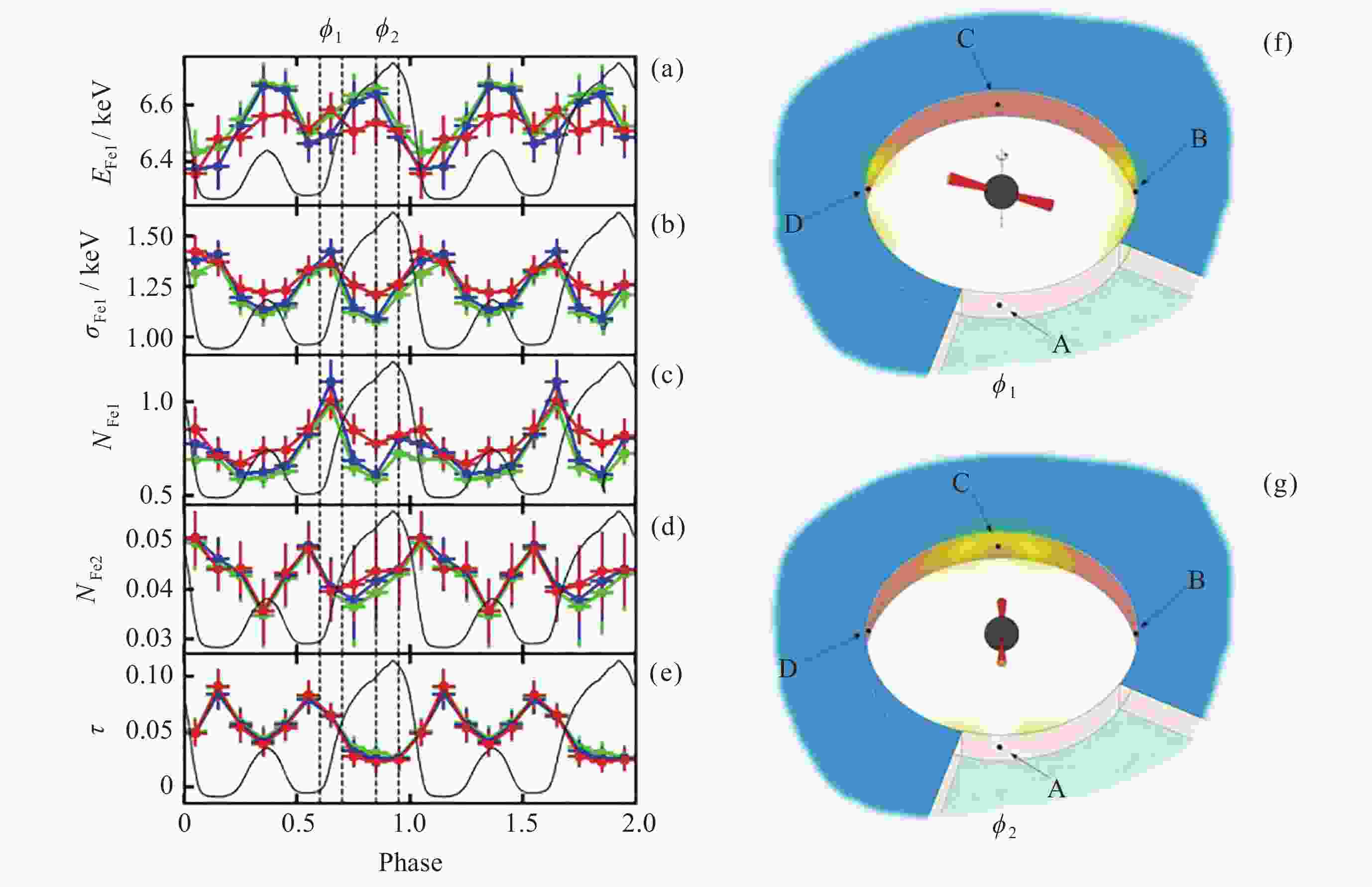
Figure 16. Geometric sketch of the broad iron line emission region on the accretion disk of two specific phase intervals from the observer’s perspective. The accretion disk is divided equally into regions A, B, C, and D toroidally, with the region A being on the side closest to the line of sight of the observer[65]
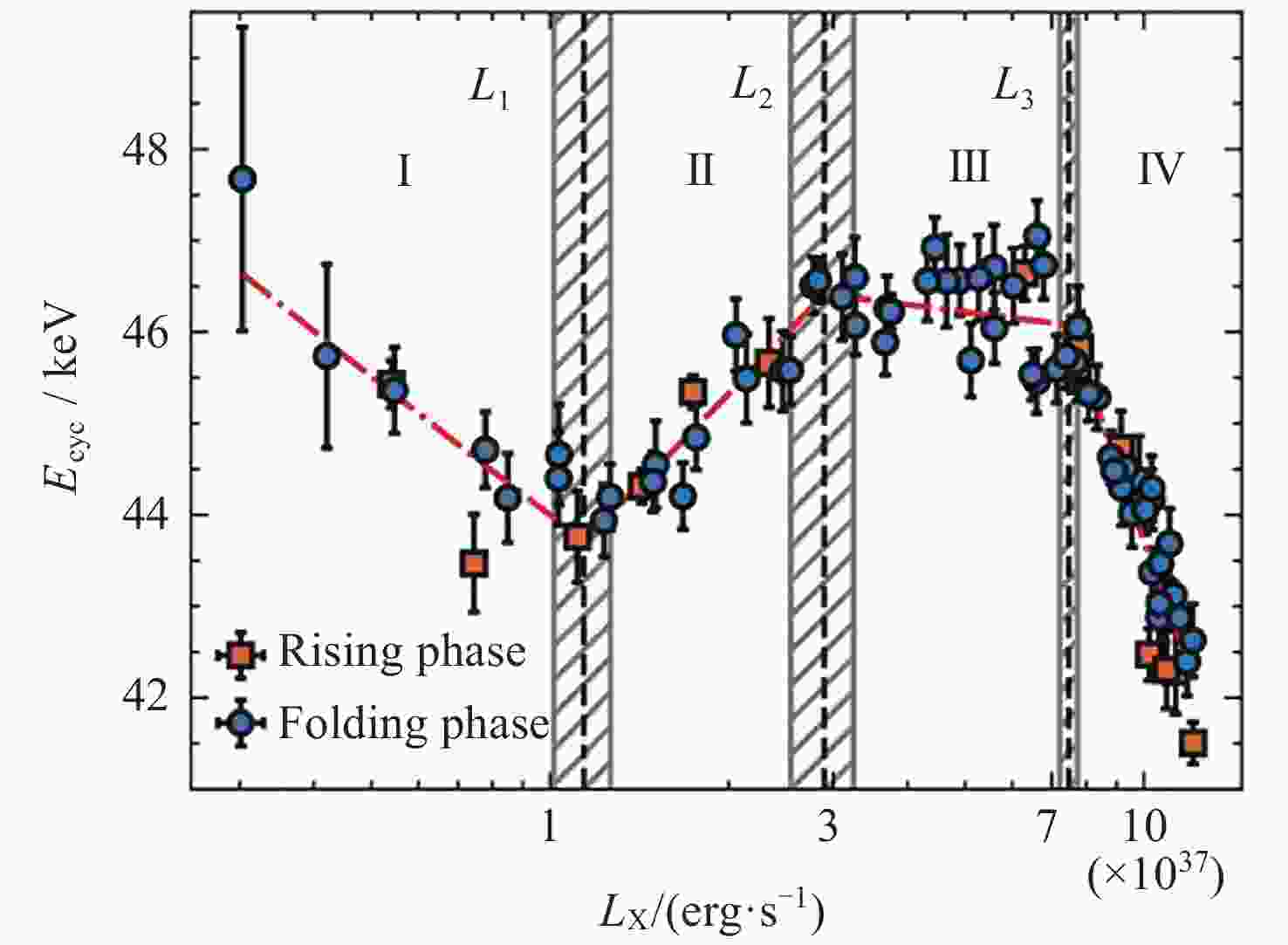
Figure 17. Luminosity dependence of cyclotron line centroid energy with the linear energy drift of Ecyc=0.047 keV·d–1 taken into account. The red dashed line represents the best fitting result with the broken power-law model which has three break luminosities (L1, L2, and L3). These three vertical dashed lines and shaded areas are the best fitting break luminosities and corresponding uncertainties, respectively. These transitional luminosities suggest the division of the Ecyc−LX relation into four zones (Regions I, II, III, and IV) with different types of the Ecyc–LX correlation[75]
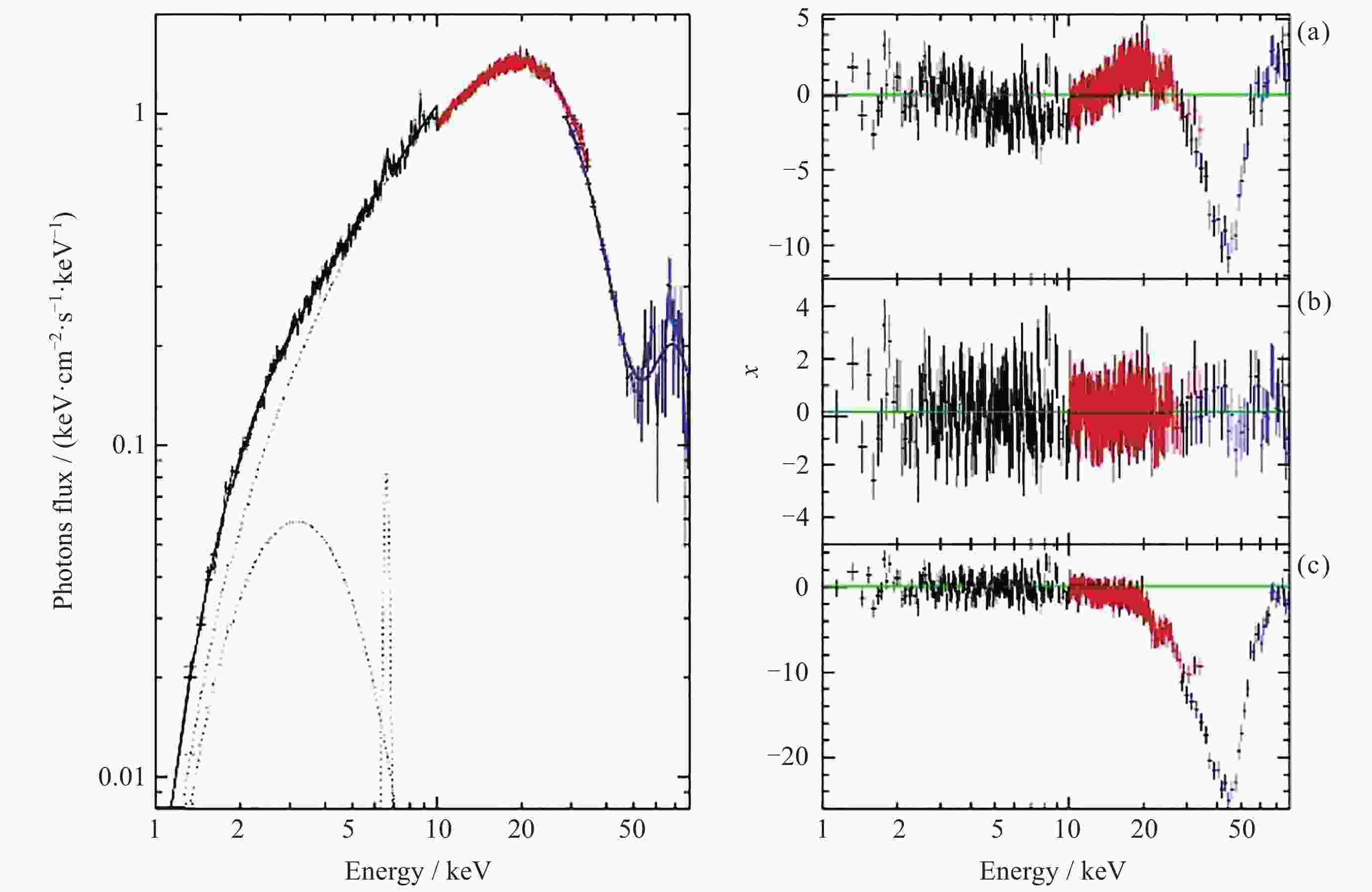
Figure 18. Unfolded spectrum of the HXMT 2018 observation with the best fit of NPEX model is shown on the left panel. The right panel shows the residues[78]
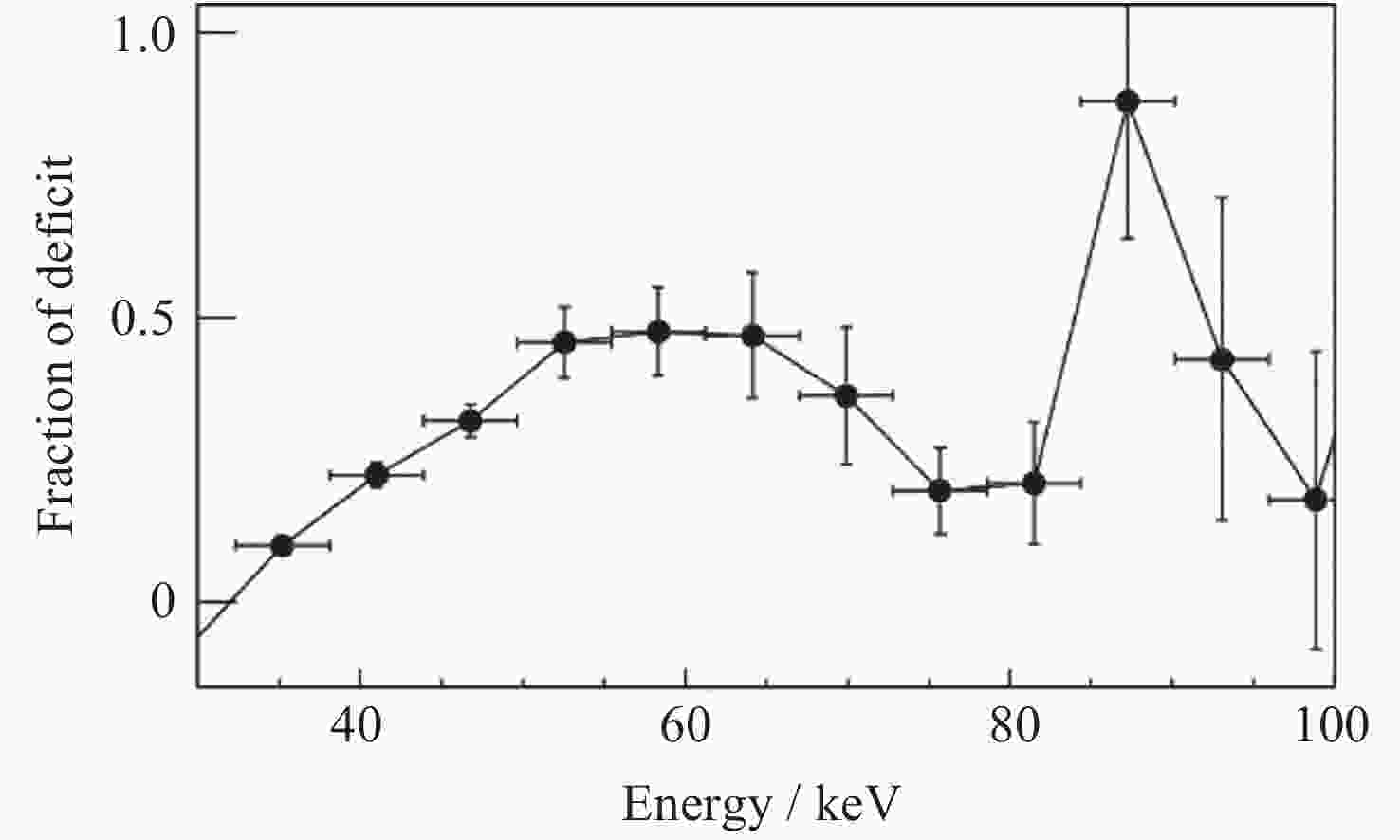
Figure 19. Deficit fraction versus energy during the bursts detected by HE in MAXI J1816-195[86]
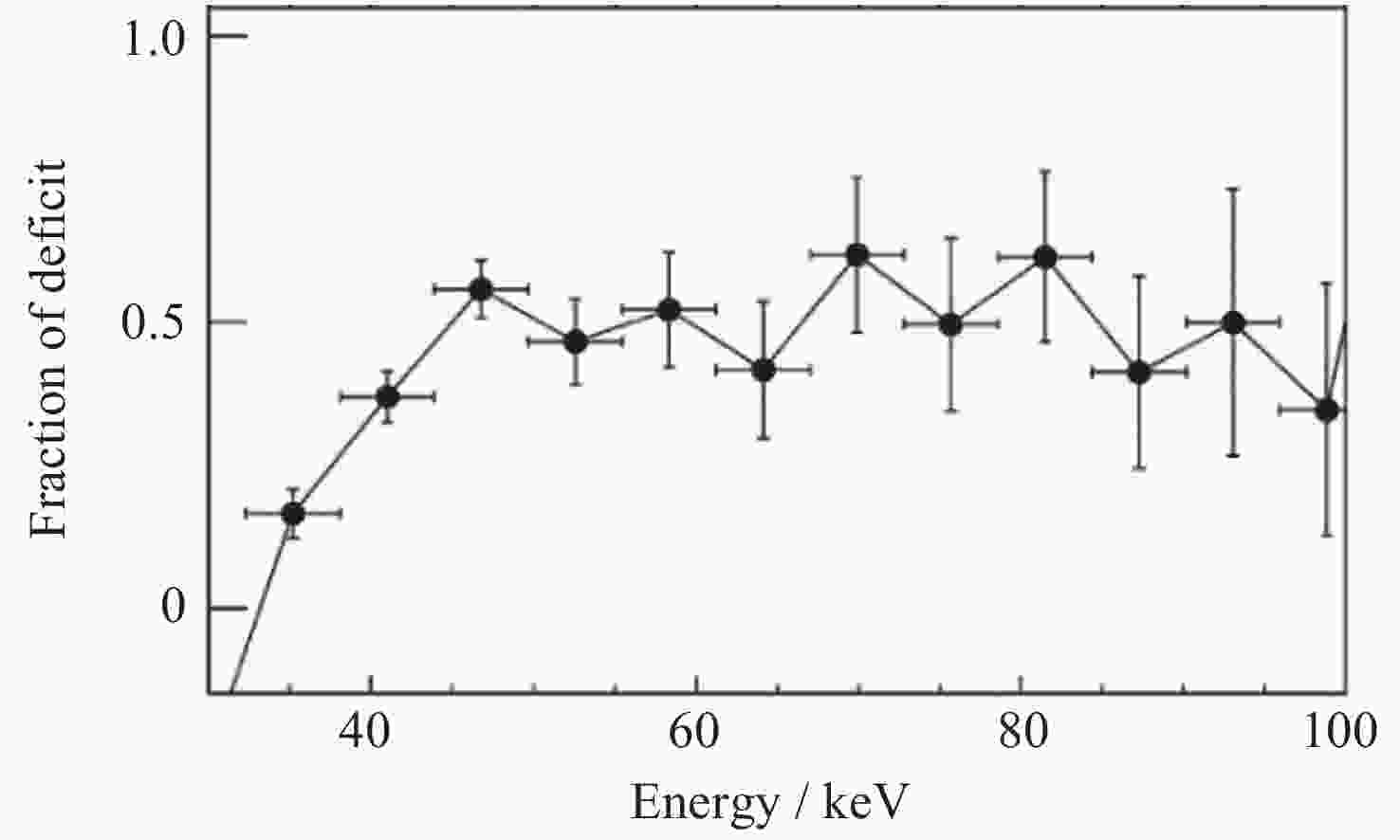
Figure 20. Deficit fraction versus energy during the bursts detected by HE in 4 U 1608-52[87]
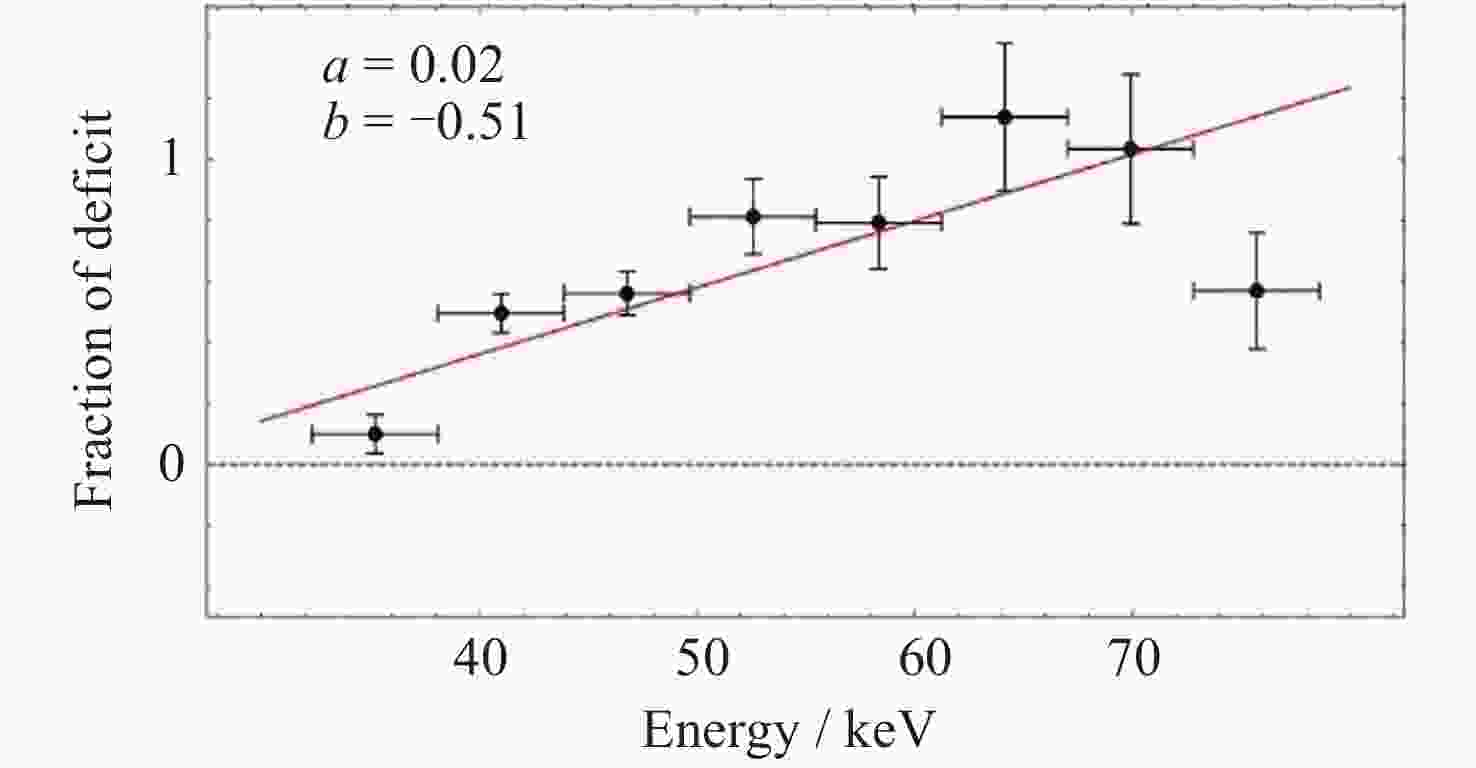
Figure 21. Deficit fraction versus energy during the bursts detected by HE in 4 U 1636-536[88]
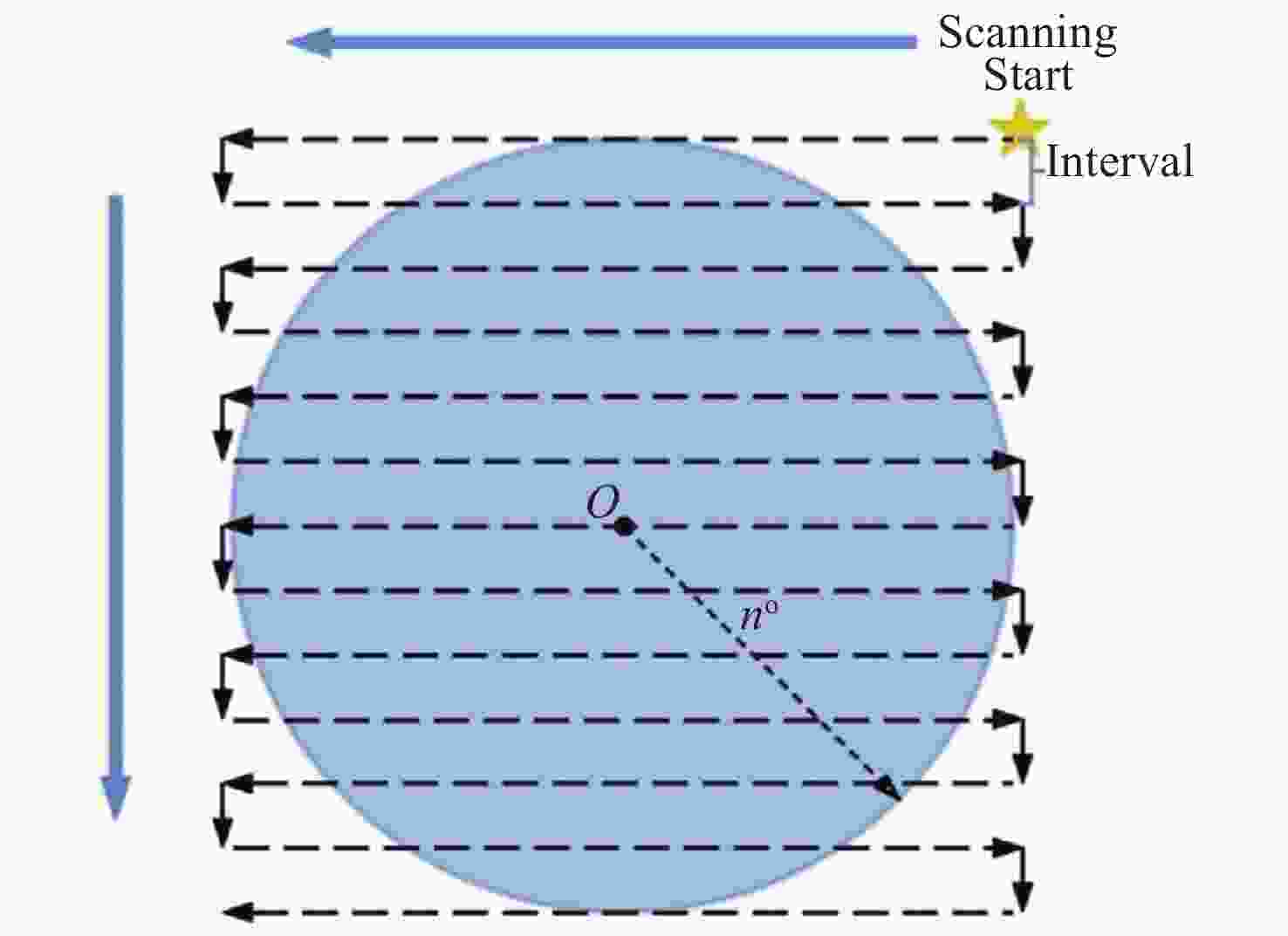
Figure 22. Schematic diagram of the scanning method of a small sky area[92]
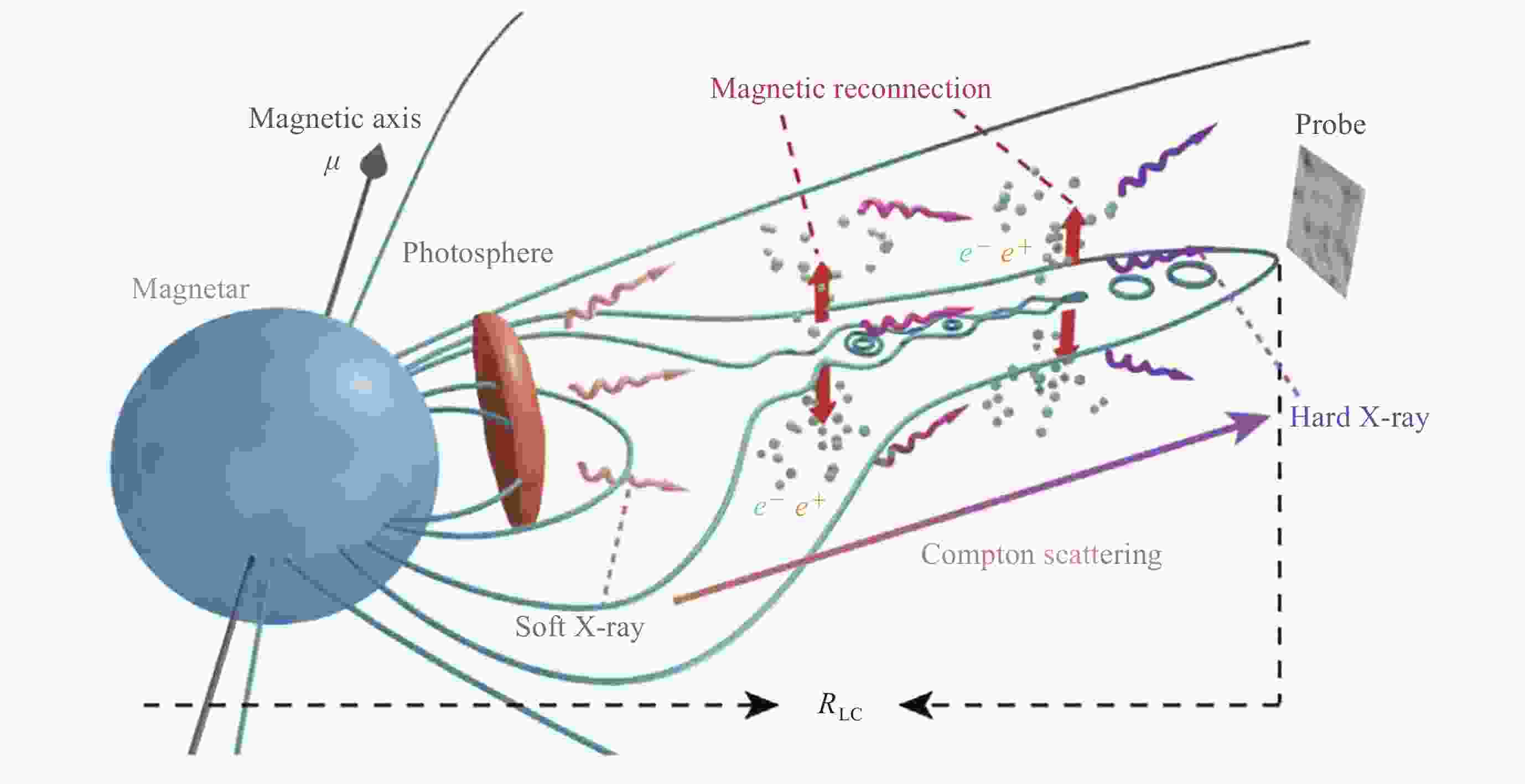
Figure 23. Schematic of the proposed origin model for the FRB 200428-associated X-ray burst[106]
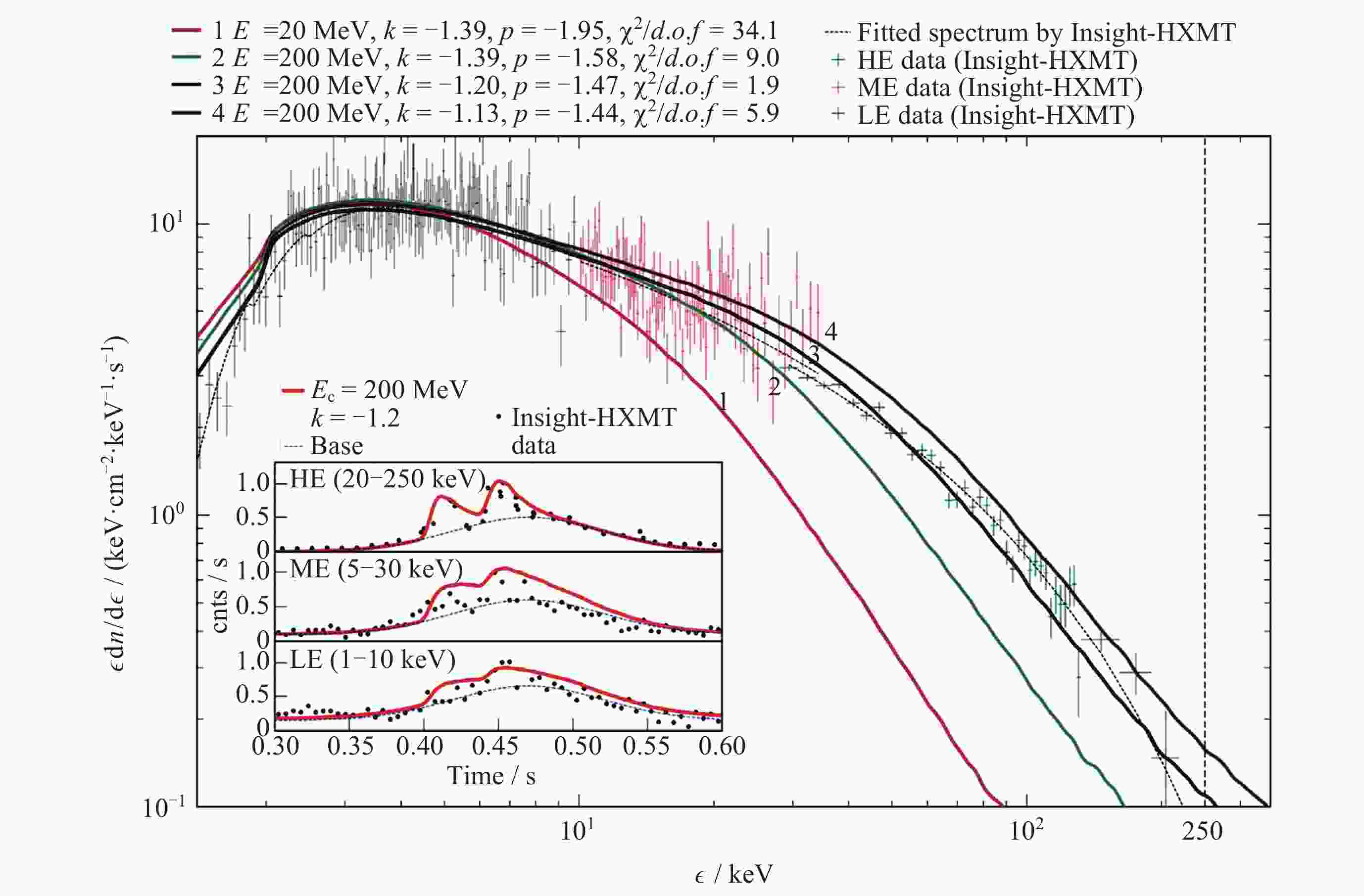
Figure 24. Insight-HXMT X-ray light curves and energy spectrum fitted by the model configured in a QED scenario[106]
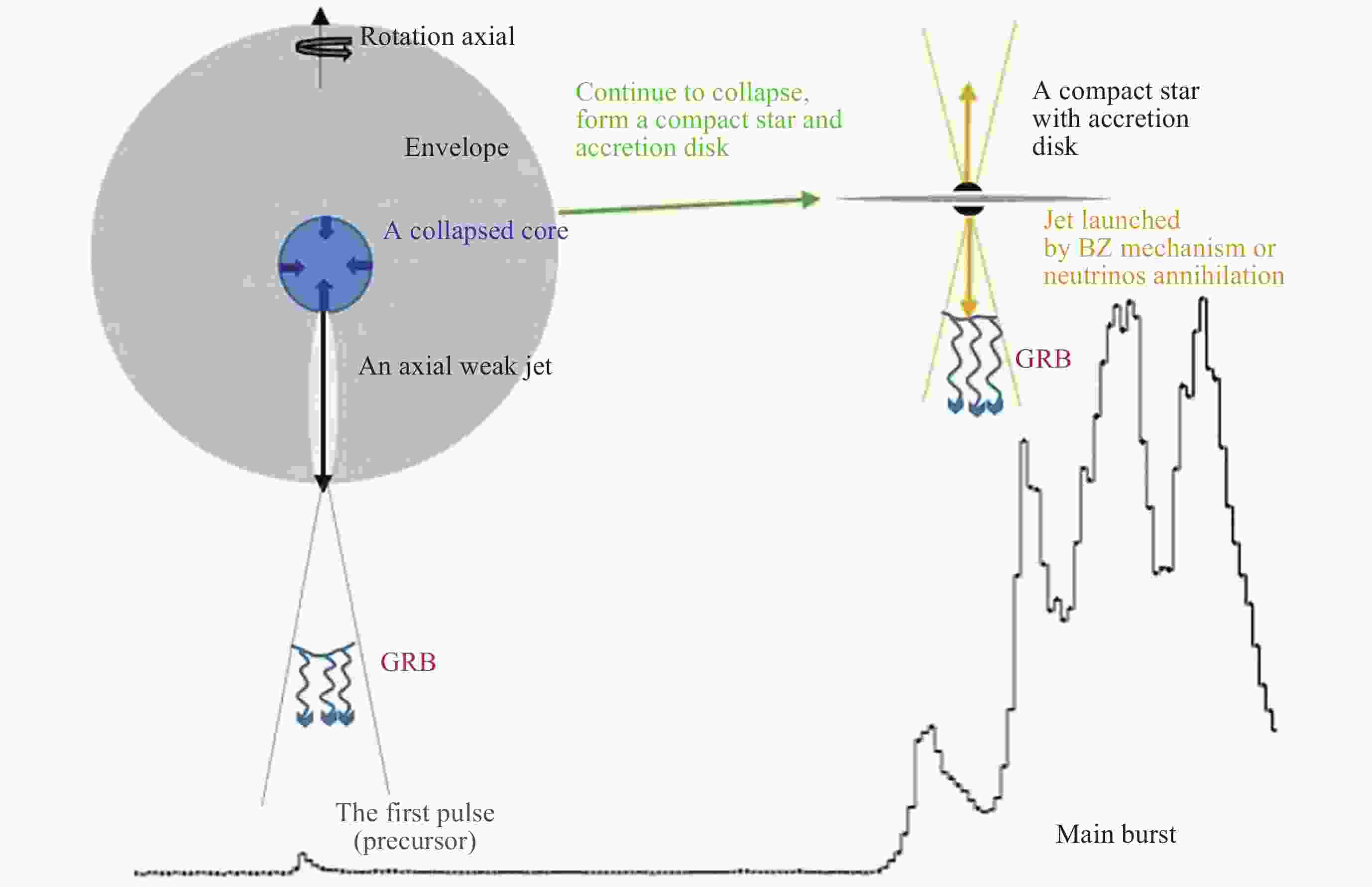
Figure 25. A scenario for the “two-stage” model of precursors for GRB221009 A[114]
-
[1] LI T P, XIONG S L, ZHANG S N, et al. Insight-HXMT observations of the first binary neutron star merger GW170817[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2018, 61 (3): 031011. DOI: 10.1007/s11433-017-9107-5 [2] MA X, TAO L, ZHANG S N, et al. Discovery of oscillations above 200 keV in a black hole X-ray binary with Insight-HXMT[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2021, 5(1): 94-102 [3] YOU B, TUO Y L, LI C Z, et al. Insight-HXMT observations of jet-like corona in a black hole X-ray binary MAXI J1820+070[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1025 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21169-5 [4] DOROSHENKO V, ZHANG S N, SANTANGELO A, et al. Hot disc of the Swift J0243.6+6124 revealed by Insight-HXMT[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2021, 491(2): 1857-1867 [5] KONG L D, ZHANG S, ZHANG S N, et al. Insight-HXMT discovery of the highest-energy CRSF from the first galactic ultraluminous X-ray pulsar swift J0243.6+6124[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2022, 933(1): L3 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ac7711 [6] GE M Y, JI L, ZHANG S N, et al. Insight-HXMT firm detection of the highest-energy fundamental cyclotron resonance scattering feature in the spectrum of GRO J1008-57[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2020, 899(1): L19 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/abac05 [7] LIU C Z, ZHANG Y F, LI X F, et al. The High Energy X-ray telescope (HE) onboard the Insight-HXMT astronomy satellite[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2020, 63 (4): 249503 [8] CAO X L, JIANG W C, MENG B, et al. The Medium Energy X-ray telescope (ME) onboard the Insight-HXMT astronomy satellite[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2020, 63 (4): 249504 [9] CHEN Y, CUI W W, LI W, et al. The Low Energy X-ray telescope (LE) onboard the Insight-HXMT astronomy satellite[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2020, 63 (4): 249505 [10] ZHANG S N, LI T P, LU F J, et al. Overview to the hard X-ray modulation telescope (Insight-HXMT) satellite[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2020, 63 (4): 249502 [11] ZHOU X, LI X Q, XIE Y N, et al. Introduction to a calibration facility for hard X-ray detectors[J]. Experimental Astronomy, 2014, 38(3): 433-441 doi: 10.1007/s10686-014-9393-2 [12] ZHANG S, CHEN Y P, XIE Y N, et al. The X-ray facilities in-building for calibrations of HXMT[C]//Proceedings of the SPIE 9144, Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2014: Ultraviolet to Gamma Ray. Montréal: SPIE, 2014: 914455 [13] ZHANG S, ZHANG S N, LU F J, et al. The Insight-HXMT mission and its recent progresses[C]//Proceedings of the SPIE 10699, Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2018: Ultraviolet to Gamma Ray. Austin: SPIE, 2018: 106991U. DOI: 10.1117/12.2311835 [14] LI X B, LI X F, TAN Y, et al. In-flight calibration of the insight-hard X-ray modulation telescope[J]. Journal of High Energy Astrophysics, 2020, 27: 64-76 doi: 10.1016/j.jheap.2020.02.009 [15] TUO Y L, LI X B, GE M Y, et al. In-orbit timing calibration of the Insight-Hard X-ray modulation telescope[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2022, 259(1): 14 doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ac4250 [16] LIAO J Y, ZHANG S, LU X F, et al. Background model for the high-energy telescope of Insight-HXMT[J]. Journal of High Energy Astrophysics, 2020, 27: 14-23 doi: 10.1016/j.jheap.2020.04.002 [17] YOU Y, LIAO J Y, ZHANG S N, et al. A parametric model to reproduce the background of the Insight-HXMT/HE blind detector[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2021, 256(2): 47 doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ac16db [18] YOU B, CAO X W, YAN Z, et al. Observations of a black hole X-ray binary indicate formation of a magnetically arrested disk[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6661): 961-964 doi: 10.1126/science.abo4504 [19] PENG J Q, ZHANG S, CHEN Y P, et al. A possible overall scenario for the outburst evolution of MAXI J1820+070 revealed by Insight-HXMT[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 518(2): 2521-2528 [20] KAWAMURA T, DONE C, AXELSSON M, et al. MAXI J1820+070 X-ray spectral-timing reveals the nature of the accretion flow in black hole binaries[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 519(3): 4434-4453 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad014 [21] WANG Y N, ZHANG S N. rms-flux slope in MAXI J1820+070: a measure of disk-corona coupling[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2024, 962(1): 53 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad1ab1 [22] PENG J Q, ZHANG S, WANG P J, et al. Back to business: SLX 1746-331 after 13 years of silence[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 955(2): 96 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acf461 [23] PENG J Q, ZHANG S, SHUI Q C, et al. NICER, NuSTAR, and Insight-HXMT views to black hole X-ray binary SLX 1746-331[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2024, 965(2): L22 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad3640 [24] MA R C, SORIA R, TAO L, et al. The peculiar spectral evolution of the new X-ray transient MAXI J0637-430[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2022, 514(4): 5238-5265 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stac1585 [25] PENG J Q, ZHANG S, SHUI Q C, et al. NICER, NuSTAR, and Insight-HXMT views to the newly discovered black hole X-ray binary swift J1727.8-1613[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2024, 960(2): L17 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad17ca [26] DAI X H, KONG L D, BU Q C, et al. Evolution of disc and corona in MAXI J1348-630 during the 2019 reflare: NICER and Insight-HXMT view[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 521(2): 2692-2703 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad714 [27] YU W, BU Q C, LIU H X, et al. A spectral-timing study of the inner flow geometry in MAXI J1535-571 with Insight-HXMT and NICER[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 953(2): 191 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acd9a2 [28] ZHAO S J, TAO L, LI P P, et al. The bright black hole X-ray binary 4U 1543-47 during the 2021 outburst: a thick accretion disk inflated by high luminosity[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2024, 685: A42 [29] JIN P, ZHANG G B, ZHANG Y X, et al. The bright black hole X-ray binary 4U 1543-47 during 2021 outburst. A clear state transition from super-Eddington to sub-Eddington accretion revealed by Insight-HXMT[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 530(1): 929-946 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae686 [30] SHI Z H, WU Q W, YAN Z, et al. A new variability pattern in GRS 1915+105 with NICER and Insight-HXMT observations[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 525(1): 1431-1442 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad2061 [31] BELCZYNSKI K, WIKTOROWICZ G, FRYER C L, et al. Missing black holes unveil the supernova explosion mechanism[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2012, 757(1): 91 doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/757/1/91 [32] GAO S J, LI X D, SHAO Y. Formation of mass-gap black holes from neutron star X-ray binaries with super-Eddington accretion[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2022, 514(1): 1054-1070 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stac1426 [33] YAN Z, YU W F. X-Ray Outbursts of low-mass X-Ray binary transients observed in the RXTE era[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2015, 805(2): 87 doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/805/2/87 [34] SORIA R, MA R C, TAO L, et al. A 2-hr binary period for the black hole transient MAXI J0637-430[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2022, 515(2): 3105-3112 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stac1896 [35] SONG Y J, JIA N, YANG J, et al. The spin measurement of MAXI J1348-630 using the Insight-HXMT data[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 526(4): 6041-6051 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad3166 [36] WU H J, WANG W, SAI N, et al. A moderate spin for the black hole in X-ray binary MAXI J1348-630 revealed by Insight-HXMT[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 522(3): 4323-4331 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad1274 [37] JIA N, ZHAO X S, GOU L J, et al. Detailed analysis on the reflection component for the black hole candidate MAXI J1348-630[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2022, 511(3): 3125-3132 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stac121 [38] KUMAR R, BHATTACHARYYA S, BHATT N, et al. Estimation of spin and mass of the black hole in MAXI J1348-630 from the soft state using NICER and NuSTAR observations[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2022, 513(4): 4869-4874 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stac1170 [39] CHEN J S, WANG W. The spin of a stellar black hole 4U 1543-47 determined by Insight-HXMT[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 527(1): 238-248 [40] YORGANCIOGLU E S, BU Q C, SANTANGELO A, et al. Spin measurement of 4U 1543-47 with Insight-HXMT and NICER from its 2021 outburst. A test of accretion disk models at high luminosities[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2023, 677: A79 [41] STELLA L, VIETRI M. Lense-thirring precession and quasi-periodic oscillations in low-mass X-ray binaries[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 1998, 492(1): L59-L62 doi: 10.1086/311075 [42] KATO S. Trapped one-armed corrugation waves and QPO's[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan, 1990, 42(1): 99-113 [43] TAGGER M, PELLAT R. An accretion-ejection instability in magnetized disks[J]. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 1999, 349: 1003-1016 [44] MOLTENI D, SPONHOLZ H, CHAKRABARTI S K. Resonance oscillation of radiative shock waves in accretion disks around compact objects[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 1996, 457: 805-812 doi: 10.1086/176775 [45] INGRAM A, VAN DER KLIS M. Phase-resolved spectroscopy of low-frequency quasi-periodic oscillations in GRS 1915+105[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2015, 446(4): 3516-3525 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stu2373 [46] GAO C X, YAN Z, YU W F. Low-frequency quasi-periodic oscillation in MAXI J1820+070: revealing distinct Compton and reflection contributions[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 520(4): 5544-5551 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad434 [47] ZHANG P, SORIA R, ZHANG S, et al. Intermittent properties of the quasi-periodic oscillations of MAXI J1820+070 revealed by Insight-HXMT[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2023, 677: A178 [48] HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995 doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193 [49] SHUI Q C, ZHANG S, ZHANG S N, et al. A phase-resolved view of the low-frequency quasiperiodic oscillations from the black hole binary MAXI J1820+070[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 957(2): 84 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acfc42 [50] DRAGOMIRETSKIY K, ZOSSO D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531-547 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675 [51] SHUI Q C, ZHANG S, ZHANG S N, et al. Recovery of high-energy low-frequency quasiperiodic oscillations from black hole X-ray binary MAXI J1535-571 with a Hilbert-Huang transform method[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2024, 965(1): L7 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad374d [52] HUANG Y, QU J L, ZHANG S N, et al. Insight-HXMT observations of the new black hole candidate MAXI J1535-571: timing analysis[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2018, 866 (2): 122 [53] ZHAO Q C, TAO L, LI H C, et al. The first polarimetric view on quasiperiodic oscillations in a black hole X-ray binary[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2024, 961(2): L42 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad1e6c [54] YU W, BU Q C, ZHANG S N, et al. Timing analysis of the newly discovered black hole candidate Swift J1727.8-1613 with Insight-HXMT[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 529(4): 4624-4632 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae835 [55] PSALTIS D, BELLONI T, VAN DER KLIS M. Correlations in quasi-periodic oscillation and noise frequencies among neutron star and black hole X-Ray binaries[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 1999, 520(1): 262-270 doi: 10.1086/307436 [56] YU W, BU Q C, YANG Z X, et al. Hilbert-Huang Transform analysis of quasiperiodic oscillations in MAXI J1820+070[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 951(2): 130 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acd756 [57] MA X, ZHANG L, TAO L, et al. A detailed view of low-frequency quasi-periodic oscillation in the broadband 0.2–200 keV with Insight-HXMT and NICER[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 948(2): 116 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acc4c3 [58] ZHU H F, CHEN X, WANG W. Timing analysis of the new black hole candidate MAXI J1803-298 with Insight-HXMT and NICER[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 523(3): 4394-4404 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad1656 [59] YANG Z X, ZHANG L, ZHANG S N, et al. Fast transitions of X-ray variability in the black hole transient GX 339-4: comparison with MAXI J1820+070 and MAXI J1348-630[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 521(3): 3570-3584 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad795 [60] JIN Y J, WANG W, CHEN X, et al. Quasi-periodic oscillations in GX 339-4 during the 2021 outburst observed with Insight-HXMT[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 953(1): 33 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ace168 [61] DING Q, JI L, BU Q C, et al. Nonlinear variability observed with Insight-HXMT in MAXI J1820+070 and MAXI J1535-571[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2023, 23(8): 085024 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/acdc88 [62] LI P P, TAO L, ZHANG L, et al. Detection of a strong ~2.5 Hz modulation in the newly discovered millisecond pulsar MAXI J1816-195[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 525(1): 595-606 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad2286 [63] LI P P, TAO L, MA R C, et al. Broad-band noise and quasi-periodic oscillation characteristics of the X-ray pulsar RX J0440.9+4431[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 529(2): 1187-1194 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae579 [64] KONG L D, ZHANG S, CHEN Y P, et al. Two complete spectral transitions of swift J0243.6+6124 observed by Insight-HXMT[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2020, 902(1): 18 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/abb241 [65] XIAO Y X, XU Y J, GE M Y, et al. Pulsed iron line emission from the first galactic ultraluminous X-ray pulsar swift J0243.6+6124[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2024, 965(1): 18 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad24f8 [66] HU Y F, JI L, YU C, et al. Beam pattern evolution of accreting X-ray pulsar 1A 0535+262 during its 2020 giant outburst[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 945(2): 138 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acbc7a [67] HOU X, ZHANG W, TORRES D F, et al. Deep search for gamma-ray emission from the accreting X-ray pulsar 1A 0535+262[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 944(1): 57 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acaec7 [68] KLAWIN M, DOROSHENKO V, SANTANGELO A, et al. Centaurus X-3 orbital ephemerides using Insight-HXMT, RXTE, Swift/BAT, and NuSTAR observations[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2023, 675: A135 [69] DING G Q, QU J L, SONG L M, et al. Insight-HXMT detections of hard X-ray tails in scorpius X-1[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 950(1): 69 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/accf91 [70] XIAO H, JI L, ZHANG P, et al. Timing and spectral analysis of HMXB 4U 1700-37 observed with Insight-HXMT[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2024, 963(1): 18 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad1992 [71] LI Z S, KUIPER L, GE M Y, et al. Broadband X-ray timing and spectral characteristics of the accretion-powered millisecond X-ray pulsar MAXIJ1816-195[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 958(2): 177 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad0296 [72] CHEN Y P, ZHANG S, ZHANG S N, et al. Return of 4U 1730-22 after 49 yr silence: the outburst properties observed by NICER and Insight-HXMT[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2023, 942(1): L12 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/aca76a [73] MUSHTUKOV A A, SULEIMANOV V F, TSYGANKOV S S, et al. The critical accretion luminosity for magnetized neutron stars[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2015, 447(2): 1847-1856 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stu2484 [74] BECKER P A, KLOCHKOV D, SCHÖNHERR G, et al. Spectral formation in accreting X-ray pulsars: bimodal variation of the cyclotron energy with luminosity[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2012, 544: A123 [75] SHUI Q C, ZHANG S, WANG P J, et al. Cyclotron line evolution revealed with pulse-to-pulse analysis in the 2020 outburst of 1A 0535+262[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 528(4): 7320-7332 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae352 [76] YANG W, WANG W, LIU Q, et al. Discovery of two cyclotron resonance scattering features in X-ray pulsar cen X-3 by Insight-HXMT[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 519(4): 5402-5409 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad048 [77] LIU Q, WANG W, YANG W, et al. Studying the variations of the cyclotron line in Cen X-3 using Insight-HXMT[J]. Journal of High Energy Astrophysics, 2024, 41: 22-29 doi: 10.1016/j.jheap.2023.12.002 [78] DEVARAJ A, SHARMA R, NAGESH S, et al. Insights into the phase-dependent cyclotron line feature in XTE J1946+274: an AstroSat and Insight-HXMT view[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 527 (4): 11015-11025 [79] DEGENAAR N, BALLANTYNE D R, BELLONI T, et al. Accretion disks and coronae in the X-ray flashlight[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2018, 214(1): 15 doi: 10.1007/s11214-017-0448-3 [80] FRAGILE P C, BALLANTYNE D R, BLANKENSHIP A. Interactions of type I X-ray bursts with thin accretion disks[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2020, 4(5): 541-546 doi: 10.1038/s41550-019-0987-5 [81] RUSSELL T D, DEGENAAR N, VAN DEN EIJNDEN J, et al. Thermonuclear explosions on neutron stars reveal the speed of their jets[J]. Nature, 2024, 627(8005): 763-766 doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07133-5 [82] CHEN Y P, ZHANG S, ZHANG S N, et al. Type-I X-ray bursts reveal a fast co-evolving behavior of the corona in an X-Ray binary[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2012, 752(2): L34 doi: 10.1088/2041-8205/752/2/L34 [83] JI L, ZHANG S, CHEN Y P, et al. Diagnosing the burst influence on accretion in the clocked Burster GS 1826-238[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2015, 806(1): 89 doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/806/1/89 [84] CHEN Y P, ZHANG S, QU J L, et al. Insight-HXMT observations of 4U 1636-536: corona cooling revealed with single short Type-I X-ray burst[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2018, 864(2): L30 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/aadc0e [85] WANG P J, CHEN Y P, JI L, et al. Type-I X-ray burst evolution of the new millisecond pulsar MAXI J1816-195 revealed by Insight-HXMT[J]. Journal of High Energy Astrophysics, 2024, 41: 106-113 doi: 10.1016/j.jheap.2024.02.004 [86] CHEN Y P, ZHANG S, JI L, et al. The prolific thermonuclear X-ray bursts from the outburst of the newly discovered millisecond pulsar MAXI J1816-195 observed by Insight-HXMT and NICER[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2022, 936(2): L21 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ac8c2c [87] CHEN Y P, ZHANG S, JI L, et al. Insight-HXMT observations of thermonuclear X-ray bursts from 4U 1608-52 in the low/hard state: the energy-dependent hard X-ray deficit and cooling saturation of the corona[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 531 (1): 1756-1764 [88] PENG J Q, ZHANG S, CHEN Y P, et al. New insight into the hard X-ray emission influenced by the type I bursts observed by Insight-HXMT during the outburst of 4U 1636-536[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2024, 685: A71 [89] JI L, GE M Y, CHEN Y P, et al. The influence of thermonuclear bursts on polar caps of the accreting X-ray millisecond pulsar MAXI J1816-195[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2024, 966(1): L3 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad3c29 [90] YAN Z, ZHANG G B, CHEN Y P, et al. Insight-HXMT observations of thermonuclear X-ray bursts in 4U 1636-53[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 529 (2): 1585-1596 [91] LU Y Q, LI Z S, PAN Y Y, et al. Type I X-ray bursts' spectra and fuel composition from the atoll and transient source 4U 1730-22[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2023, 670: A87 [92] WANG C, LIAO J Y, GUAN J, et al. The long-term monitoring results of Insight-HXMT in the first 4 yr galactic plane scanning survey[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2023, 265(2): 52 doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/acba94 [93] GUAN J, LU F J, ZHANG S, et al. A modified direct demodulation method applied to Insight-HXMT Galactic plane scanning survey[J]. Journal of High Energy Astrophysics, 2020, 26: 11-20 doi: 10.1016/j.jheap.2020.02.002 [94] SAI N, LIAO J Y, LI C K, et al. Methodology and performance of the two-year galactic plane scanning survey of Insight-HXMT[J]. Journal of High Energy Astrophysics, 2020, 26: 1-10 doi: 10.1016/j.jheap.2020.02.005 [95] WANG C, LIAO J Y, GUAN J, et al. Analysis of bright source hardness ratios in the 4 yr Insight-HXMT galactic plane scanning survey catalog[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2024, 24(2): 025013 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/ad18a3 [96] ZHAO H S, GE M Y, LI X B, et al. Long-term evolution of the X-ray flux of the Crab pulsar[J]. Radiation Detection Technology and Methods, 2023, 7(1): 48-55 [97] TAKATA J, WANG H H, LIN L C C, et al. Efficiency of nonthermal pulsed emission from eight MeV pulsars[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2024, 965(2): 126 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad3213 [98] WANG Y D, ZHENG W, ZHANG S N, et al. Review of X-ray pulsar spacecraft autonomous navigation[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2023, 36(10): 44-63 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2023.03.002 [99] WANG Y D, ZHANG S N, GE M Y, et al. Fast on-orbit pulse phase estimation of X-ray crab pulsar for XNAV flight experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(3): 3395-3404 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3216822 [100] LORIMER D R, BAILES M, MCLAUGHLIN M A, et al. A bright millisecond radio burst of extragalactic origin[J]. Science, 2007, 318(5851): 777-780 doi: 10.1126/science.1147532 [101] LI C K, LIN L, XIONG S L, et al. HXMT identification of a non-thermal X-ray burst from SGR J1935+2154 and with FRB 200428[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2021, 5(4): 378-384 doi: 10.1038/s41550-021-01302-6 [102] GE M Y, LIU C Z, ZHANG S N, et al. Reanalysis of the X-ray-burst-associated FRB 200428 with Insight-HXMT observations[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 953(1): 67 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acda1d [103] CAI C, XUE W C, LI C K, et al. An Insight-HXMT dedicated 33 day observation of SGR J1935+2154. I. burst catalog[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2022, 260(2): 24 doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ac6172 [104] ZHANG W L, LI X J, YANG Y P, et al. Statistical properties of X-ray bursts from SGR J1935+2154 detected by Insight-HXMT[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2023, 23(11): 115013 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/acf979 [105] LU X F, SONG L M, GE M Y, et al. Burst phase distribution of SGR J1935+2154 based on Insight-HXMT[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2023, 23(3): 035007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/acb250 [106] XIE Y, GENG J J, ZHU X W et al. Origin of FRB-associated X-ray burst: QED magnetic reconnection[J]. Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(17): 1857-1861 doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2023.06.005 [107] ZHU W W, XU H, ZHOU D J, et al. A radio pulsar phase from SGR J1935+2154 provides clues to the magnetar FRB mechanism[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(30): eadf6198 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf6198 [108] XIAO S, YANG J J, LUO X H, et al. The minimum variation timescales of X-Ray bursts from SGR J1935+2154[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2023, 268(1): 5 doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ace77c [109] XIAO S, LI X B, XUE W C, et al. Individual and averaged power density spectra of X-ray bursts from SGR J1935+2154: quasi-periodic oscillation search and slopes[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 527(4): 11915-11924 [110] XIAO S, TUO Y L, ZHANG S N, et al. Discovery of the linear energy dependence of the spectral lag of X-ray bursts from SGR J1935+2154[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 521(4): 5308-5333 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad885 [111] TSALLIS C. Possible generalization of Boltzmann-Gibbs statistics[J]. Journal of Statistical Physics, 1988, 52(1): 479-487 [112] XIAO S, ZHANG S N, XIONG S L, et al. The self-organized criticality behaviours of two new parameters in SGR J1935+2154[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 528(2): 1388-1392 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae142 [113] SONG X Y, XIONG S L, ZHANG S N, et al. The first Insight-HXMT gamma-ray burst catalog: the first four years[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2022, 259(2): 46 doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ac4d22 [114] SONG X Y, ZHANG S N. GRB 221009A with an unconventional precursor: a typical two-stage collapsar scenario?[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2023, 957(1): 31 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acfed7 [115] ZHENG C, ZHANG Y Q, XIONG S L, et al. Observation of GRB 221009A early afterglow in X-ray/gamma-ray energy bands[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2024, 962(1): L2 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad2073 [116] KANN D A, AGAYEVA S, AIVAZYAN V, et al. GRANDMA and HXMT observations of GRB 221009A: the standard luminosity afterglow of a hyperluminous gamma-ray burst—in Gedenken a David alexander Kann[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2023, 948(2): L12 doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/acc8d0 [117] CAMISASCA A E, GUIDORZI C, AMATI L, et al. GRB minimum variability timescale with Insight-HXMT and Swift: implications for progenitor models, dissipation physics, and GRB classifications[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2023, 671: A112 [118] GUIDORZI C, SARTORI M, MACCARY R, et al. Distribution of the number of peaks within a long gamma-ray burst[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2024, 685: A34 -
-






 下载:
下载: