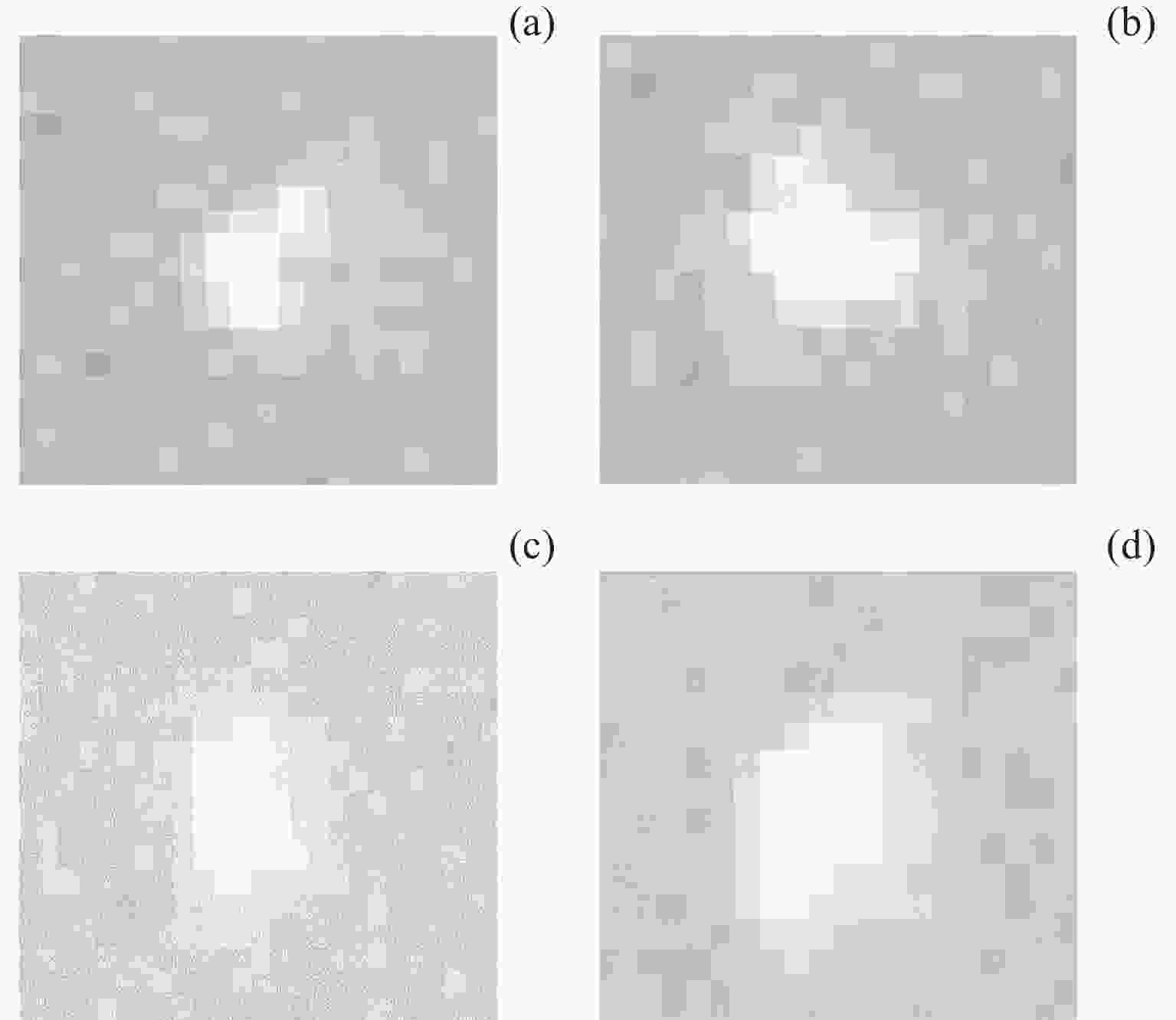
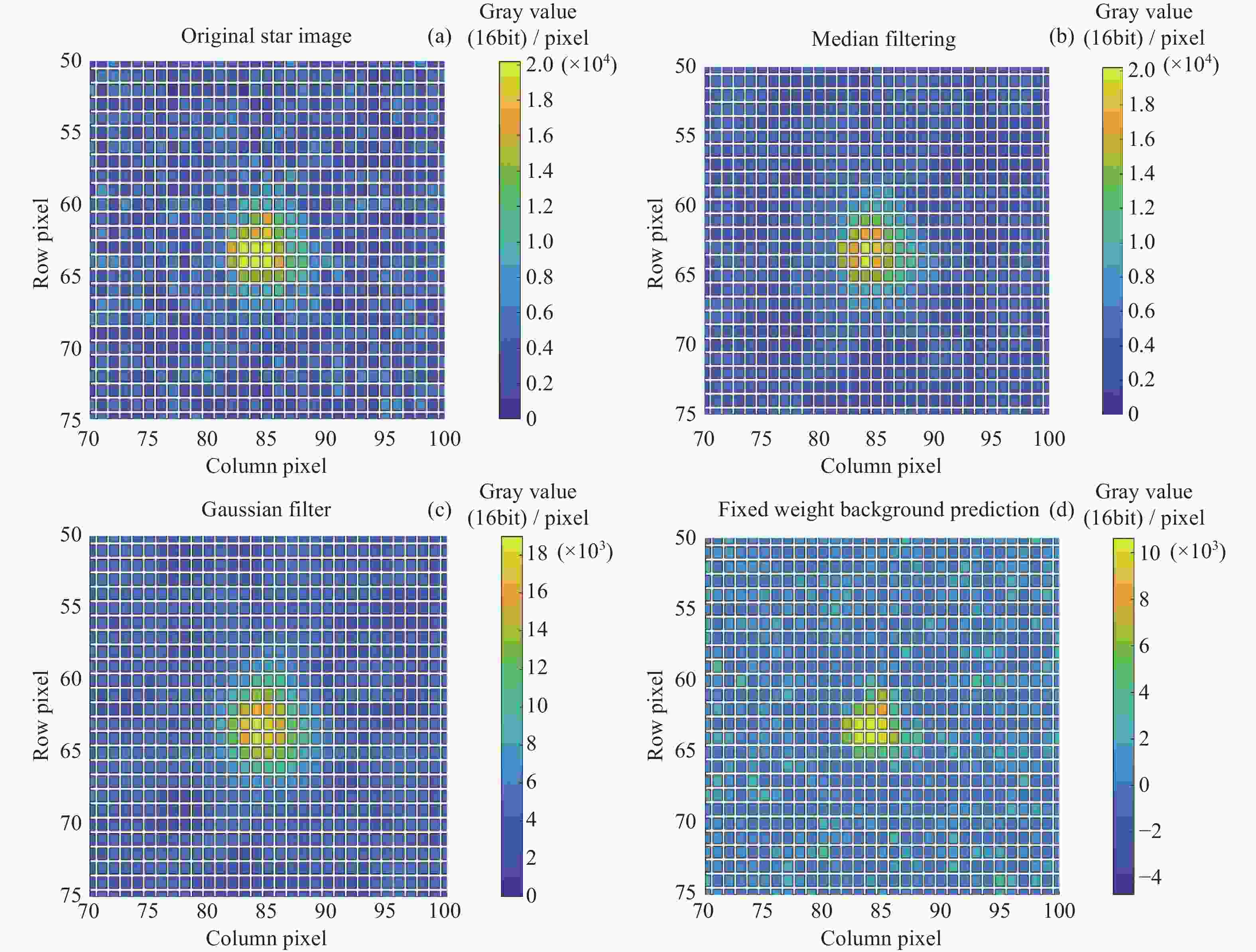
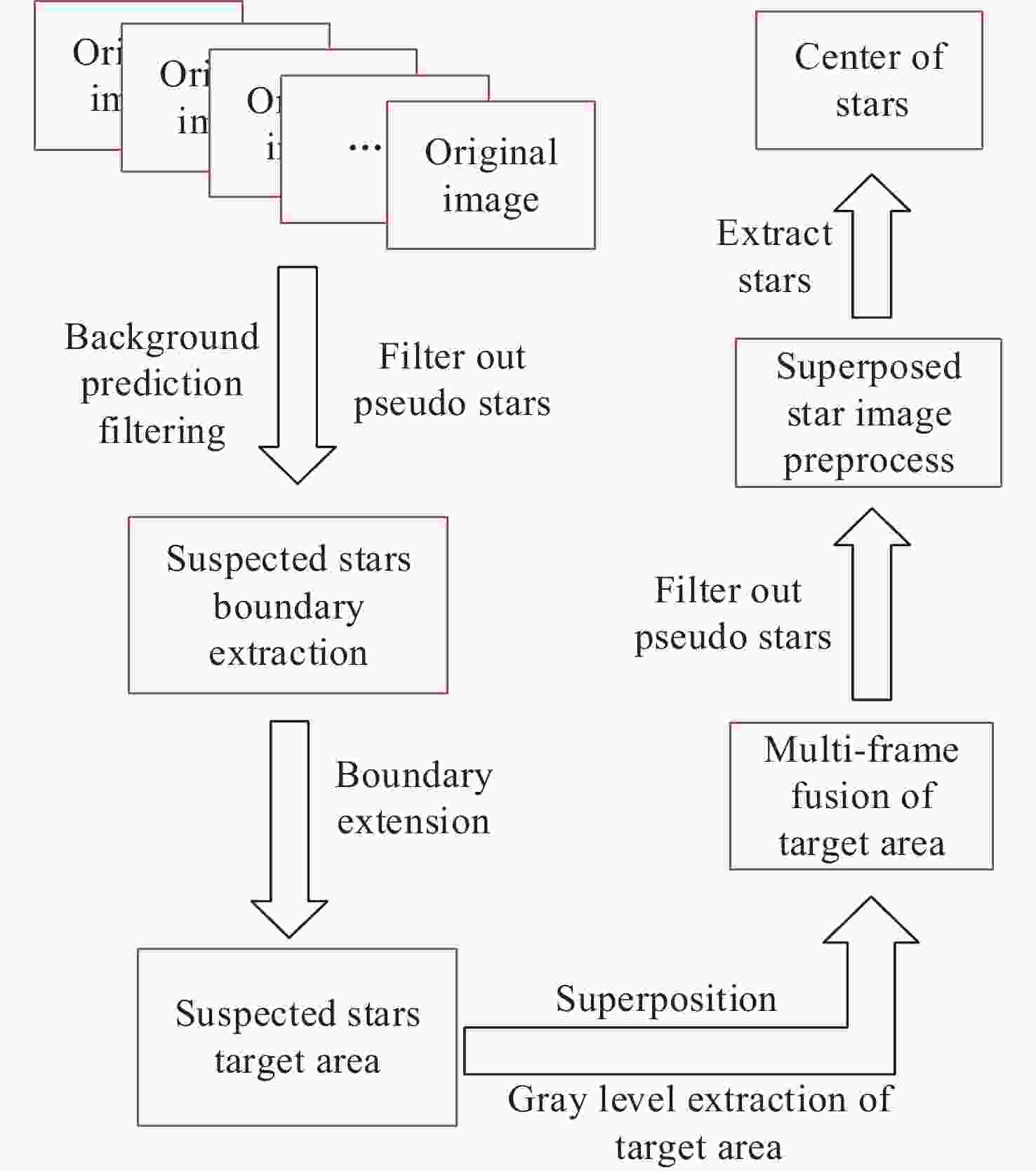
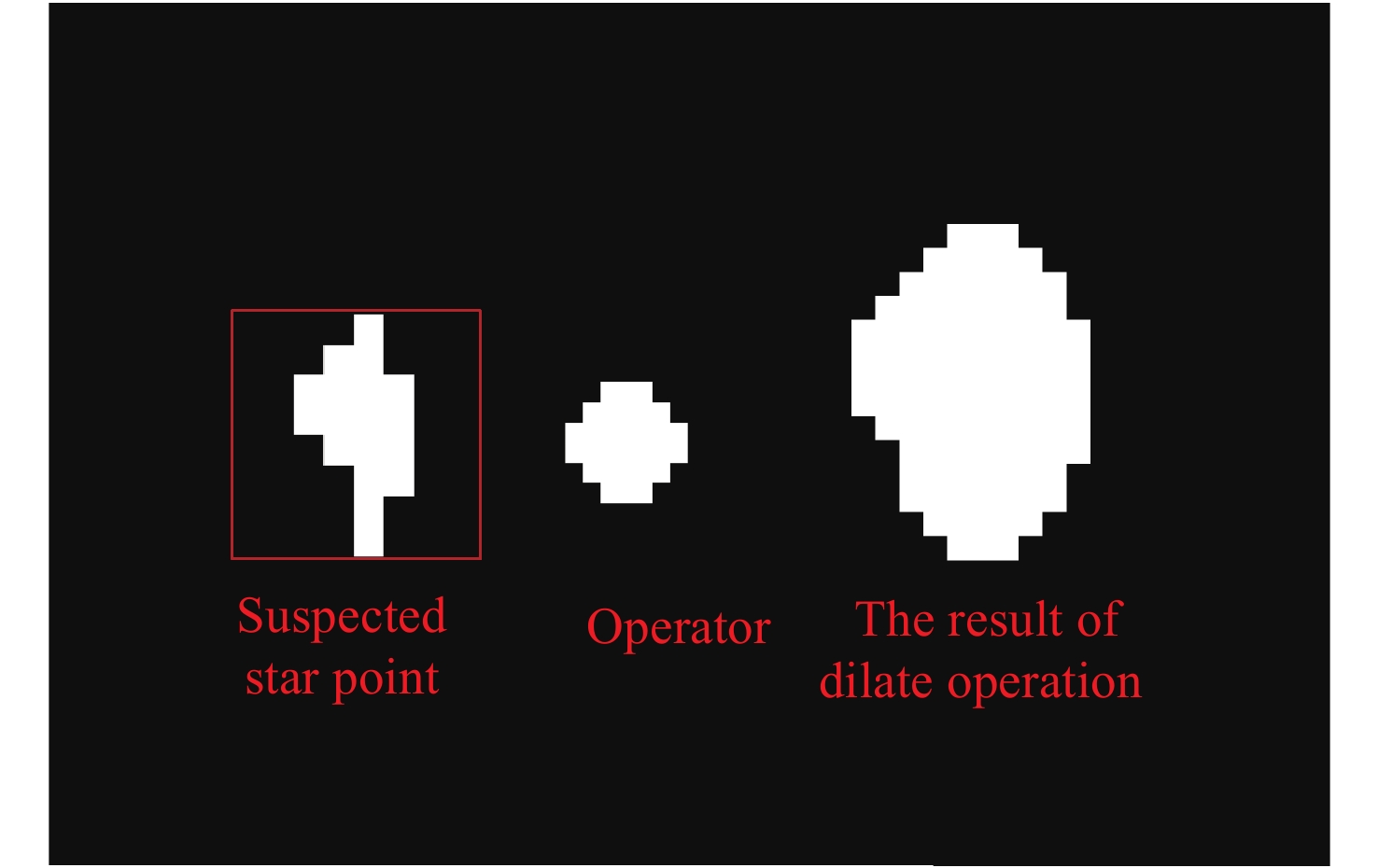
Method of Star Point Extraction for Daytime Infrared Star Image
-
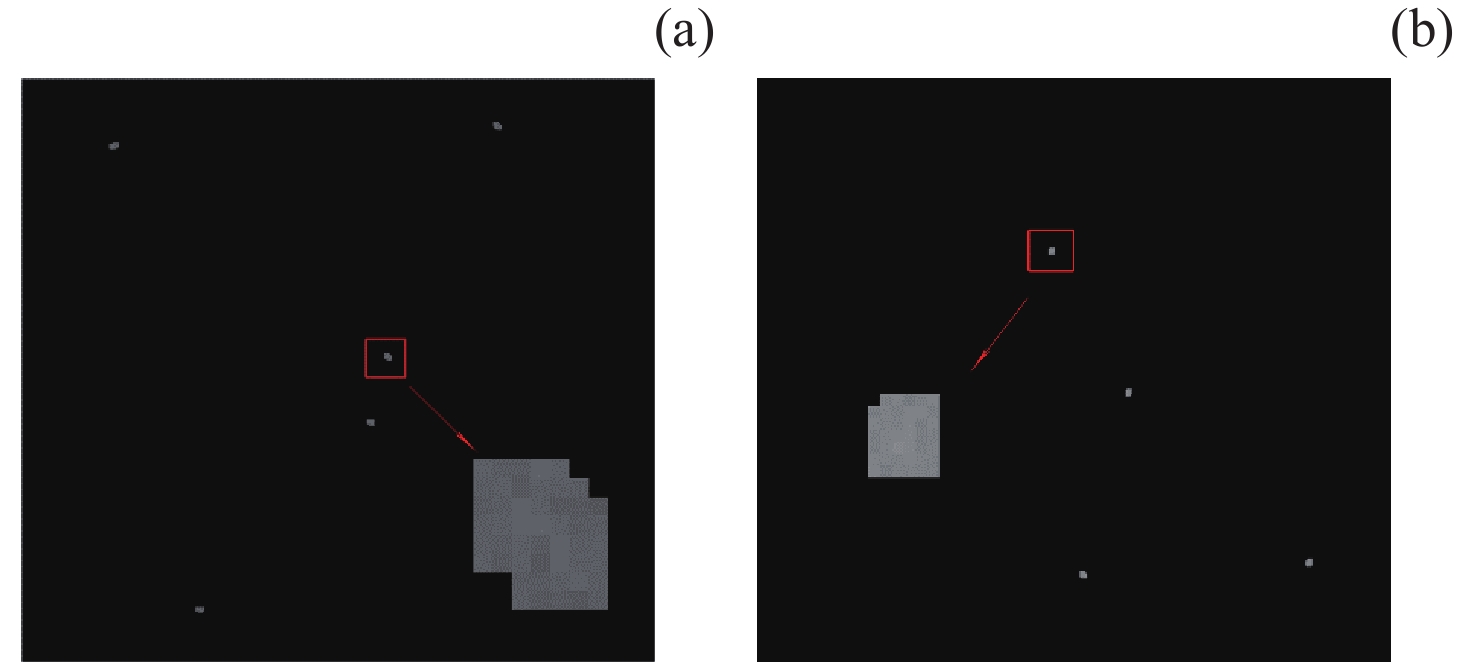
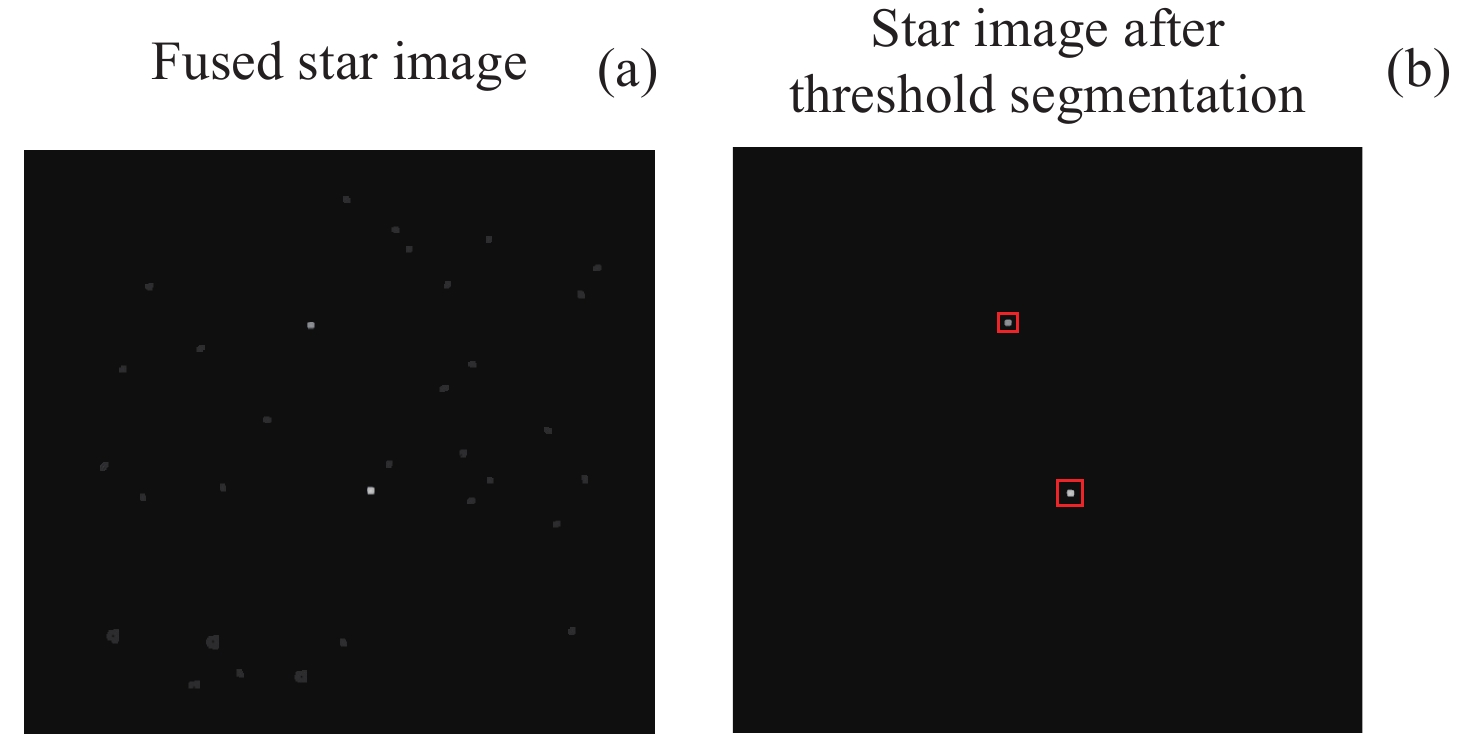
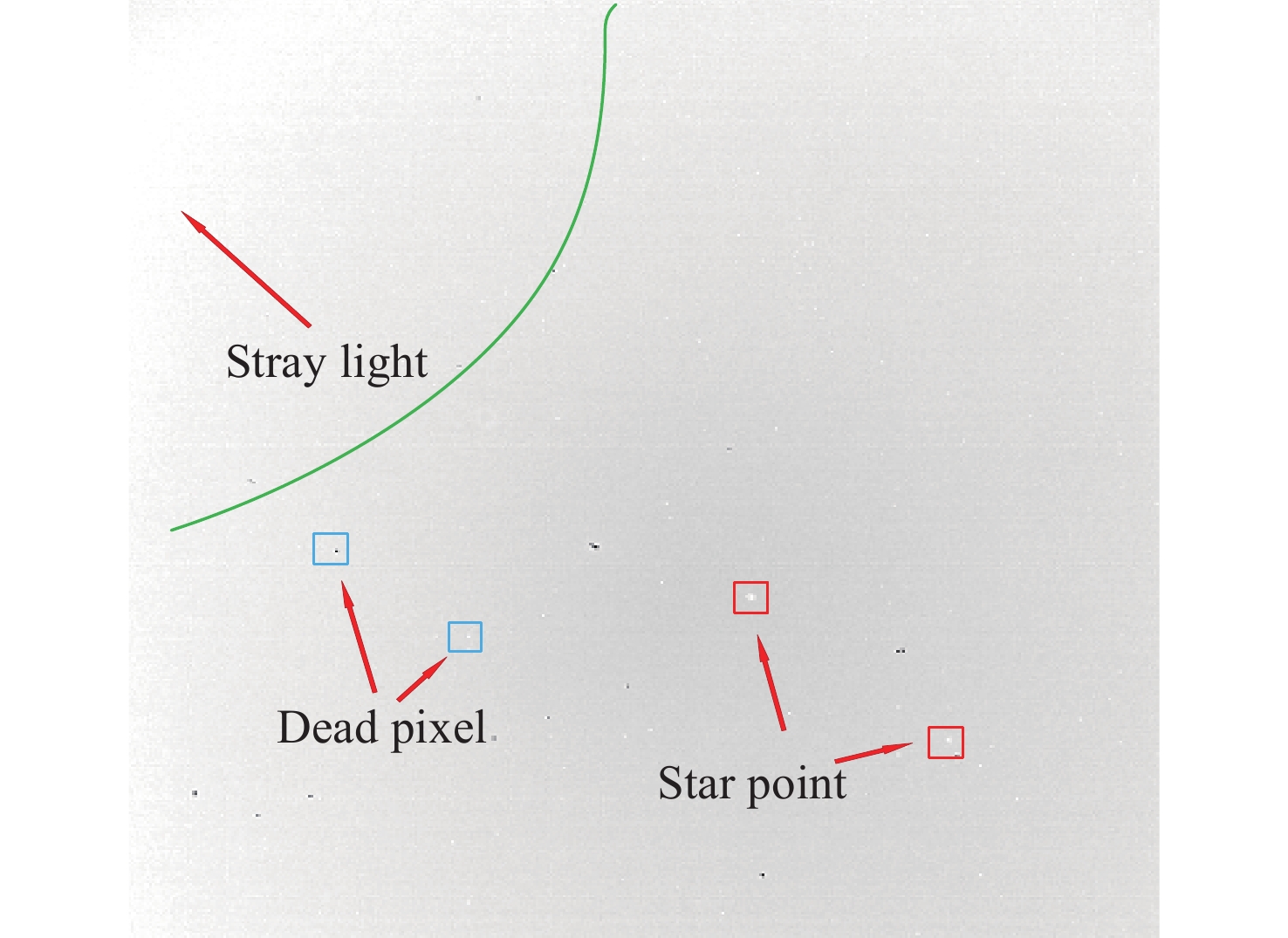
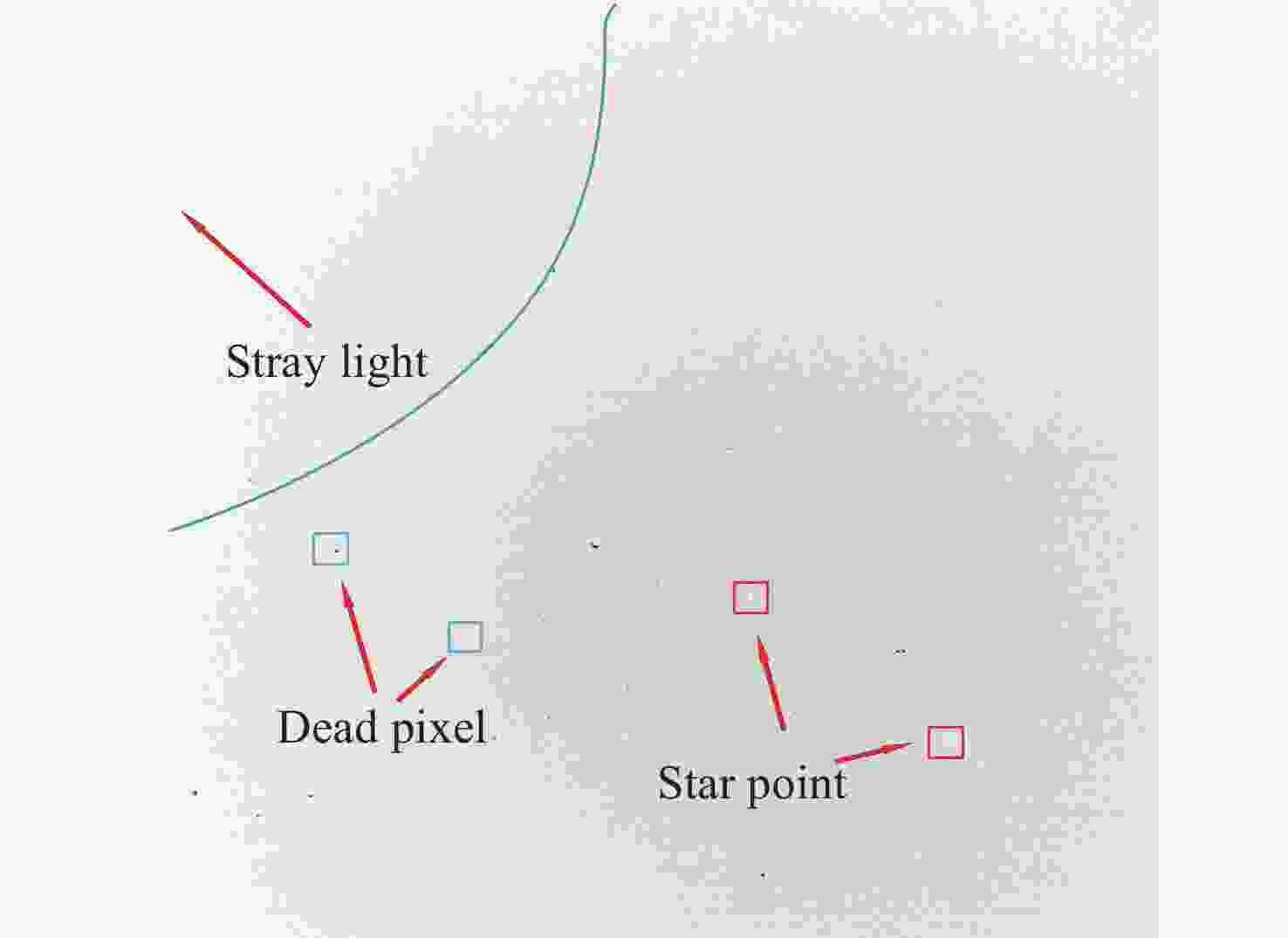
摘要: 白昼红外星图具有高背景噪声、低信噪比、弱目标的特征, 采用传统单帧提取方法很难准确提取星点. 且由于星点为弱小目标, 对噪声极为敏感, 星点成像多为随机不规则图形, 采用单帧提取星点质心鲁棒性较差. 传统多帧叠加法虽能克服单帧提取星点质心鲁棒性较差的问题, 但对于高背景噪声红外星图, 叠加星图并不能明显提高信噪比, 星点提取成功率依然较低. 为此, 提出利用背景预测方法确定疑似星点位置, 并对边界进行膨胀, 然后利用膨胀后的边界进行单帧星图能量提取, 并将提取星图进行叠加形成高信噪比星图, 最后进行星点质心提取. 实验表明, 该方法星点提取正确率为99.5%, 较自适应阈值分割法和多帧叠加法分别提升84.2%和37.9%, 较背景预测法正确率提升14.5%. 同时该方法较自适应阈值分割法和背景预测法、多帧叠加法精度分别提升12.8%, 41.4%, 33.3%, 具有明显优势.Abstract: The daytime infrared star image has the characteristics of high background noise, low signal-to-noise ratio and weak target, so it is difficult to accurately extract the star centroid by using the traditional single frame extraction method. Because the stars are weak and small targets, they are extremely sensitive to noise, and the star imaging is mostly random and irregular, so the robustness of extracting the star centroid by single frame is poor. Although the traditional multi-frame superposition method can overcome the problem of poor robustness of star centroid extraction in single frame, for infrared star images with high background noise, the superposition star image cannot significantly improve the signal-to-noise ratio, and the success rate of star extraction is still low. Therefore, this paper proposes a method that uses background prediction method to determine the position of suspected stars, expands the boundary, and then uses the expanded boundary to extract the energy of single frame star image, and superimposes the extracted energy star image to form a high signal-to-noise ratio star image, and finally extracts the star centroid. Experiments show that the accuracy of star extraction is 99.5%, which is 84.2% and 37.9% higher than that of adaptive threshold segmentation method and multi-frame superposition method, respectively, and 14.5% higher than that of background prediction method. At the same time, the accuracy of this method is improved by 12.8%, 41.4% and 33.3%, respectively, compared with the adaptive threshold segmentation method, background prediction method and multi-frame superposition method, which has obvious advantages over the traditional method.
-
表 1 单帧提取星点质心对比
Table 1. Comparison of star centroids extracted from single frame
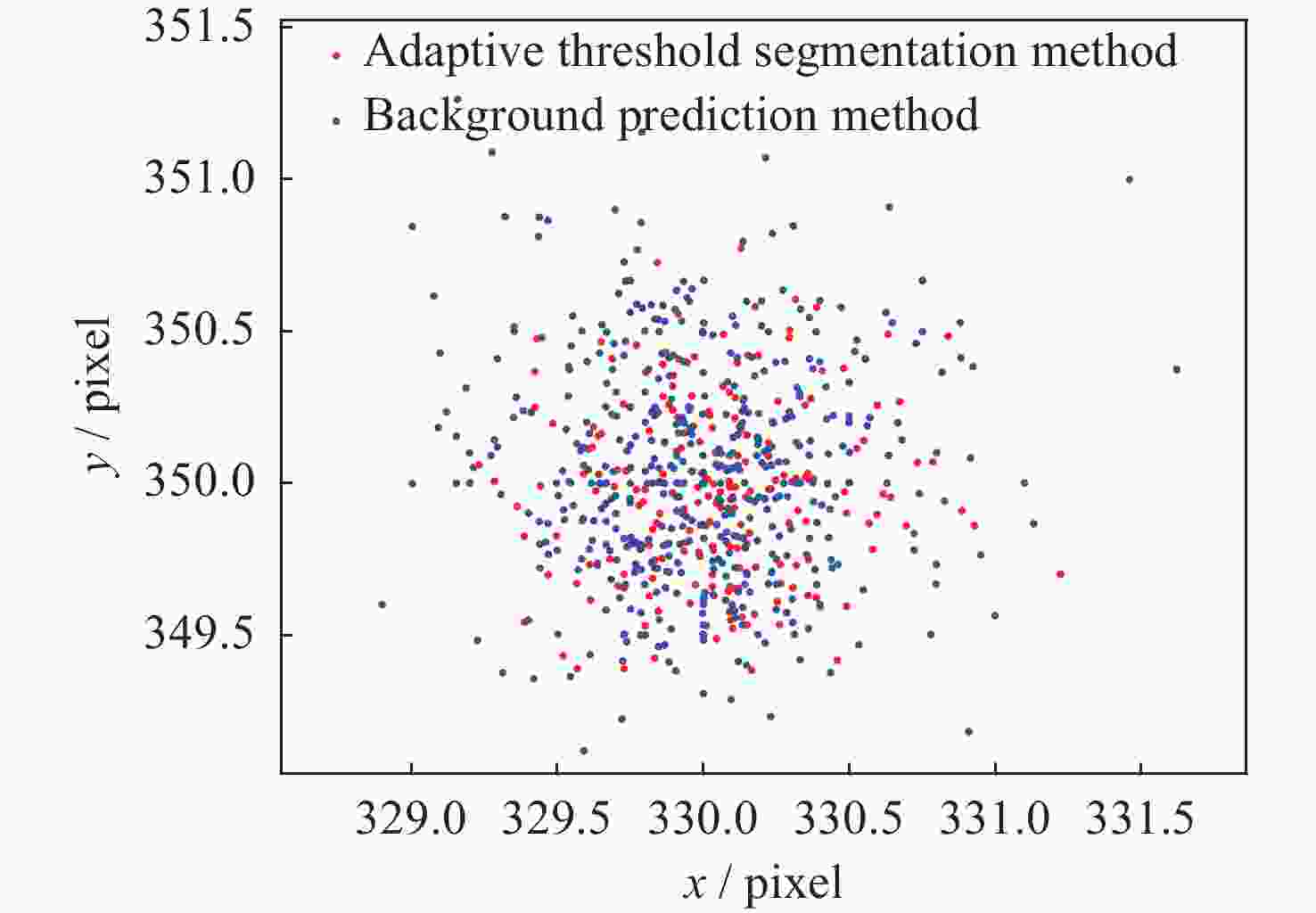
单帧提取方法 x 坐标均值/pixel y 坐标均值/pixel 距离误差均值/pixel 均方根误差/pixel 提取成功帧数 成功率/(%) 自适应阈值分割法 330.01 349.99 0.39 0.21 92 15.3 背景预测法 329.99 350.03 0.46 0.28 486 81.0 表 2 各帧提取星点统计
Table 2. Statistics of extracted star points for each frame
方法 自适应阈值分割法 背景预测法 提取星点数 0 1 2~3 4~7 ≥8 0 1 2 3 帧数 82 92 182 119 117 25 486 78 11 表 3 多帧叠加法提取星点质心对比
Table 3. Comparison of star centroids extracted by multi-frame superposition method
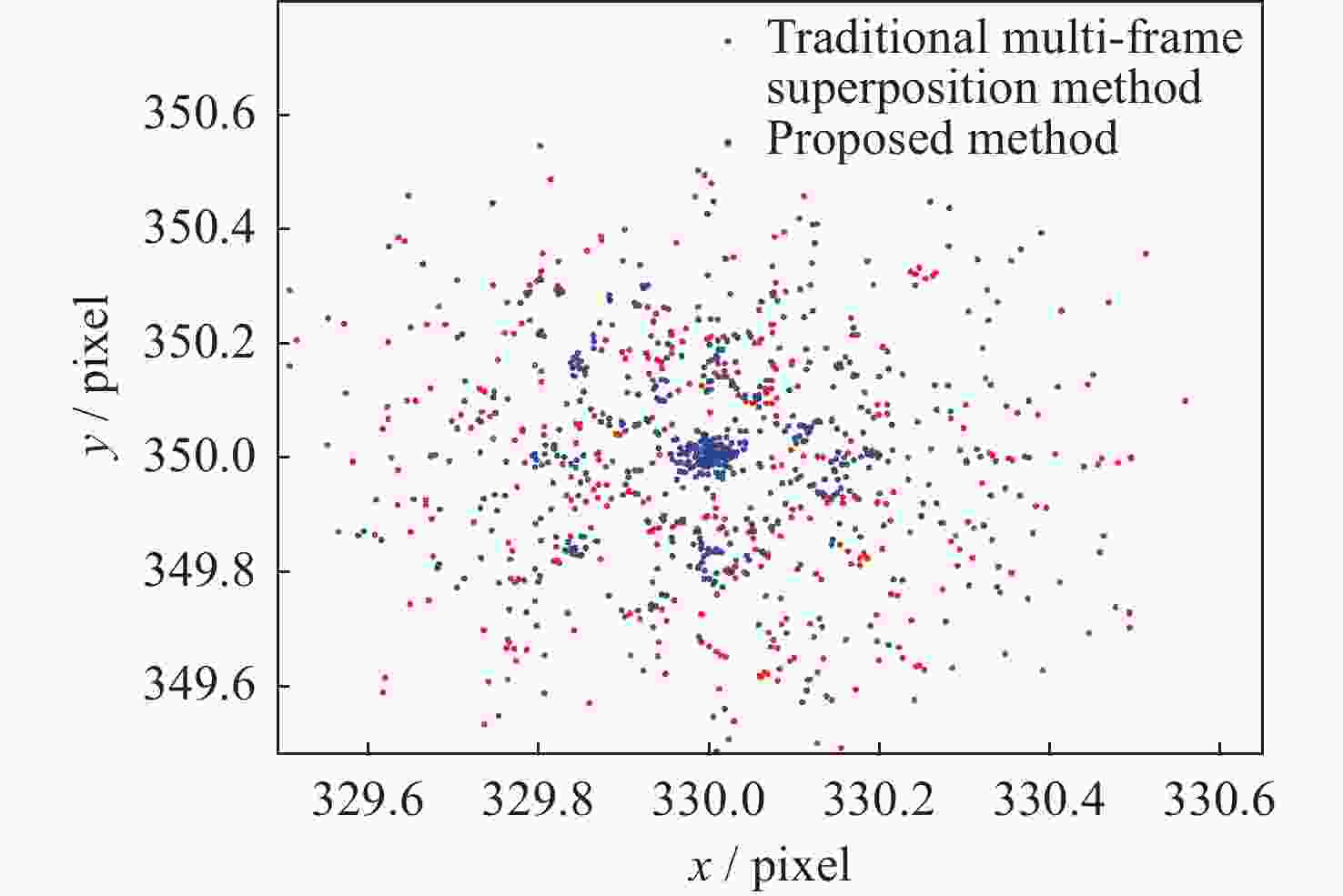
多帧叠加提取法 x 坐标均值
/pixely 坐标均值
/pixel信噪比均值 距离误差均值
/pixel均方根误差
/pixel提取成功帧数 成功率/(%) 传统多帧叠加法 330.01 350.01 0.6379 0.18 0.12 346 57.6 本文所提方法 330.00 350.01 1.1322 0.12 0.07 597 99.5 表 4 多帧叠加提取质星点统计
Table 4. Statistics of multi-frame superposition extraction of mass star points
方法 传统单帧星点提取法 本文所提方法 提取星点数 0 1 2 3 4~8 ≥8 0 1 帧数 70 346 37 23 82 42 3 597 -
[1] 韩金辉, 魏艳涛, 彭真明, 等. 红外弱小目标检测方法综述[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2022, 51(4): 20210393 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210393HAN Jinhui, WEI Yantao, PENG Zhenming, et al. Infrared dim and small target detection: a review[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(4): 20210393 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210393 [2] 张耿, 张超, 李崇辉, 等. 短波红外星图的星点边界提取算法[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2020, 37(5): 447-453ZHANG Geng, ZHANG Chao, LI Chonghui, et al. Star point boundary extraction algorithm based on shortwave infrared star image[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2020, 37(5): 447-453 [3] 吴州平. 全天时星敏感器星图信噪比增强与星点提取研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2018WU Zhouping. Star Image Signal-to-Noise Ratio Enhancement Technology and Star Centroid Estimation for Daytime Star Tracker[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2018 [4] ZHENG X J, HUANG Y Q, MAO X N, et al. Research status and key technologies of all-day star sensor[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1510(1): 012027 doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1510/1/012027 [5] 徐军. 红外图像中弱小目标检测技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2003XU Jun. Research on the Detection of Small and Dimtargets in Infrared Images[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2003 [6] PILLAI A, RAJKUMAR S, MARIMUTHU K, et al. Adaptive new top-hat transform and multi-scale sequential toggle operator based infrared image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of 2017 Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies. Vellore: IEEE, 2017: 1-5 [7] CHEN C L P, LI H, WEI Y T, et al. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 574-581 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242477 [8] WANG H, XIN Y H. Wavelet-based contourlet transform and kurtosis map for infrared small target detection in complex background[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(3): 755 doi: 10.3390/s20030755 [9] ZHANG H, NIU Y X, LU J Z, et al. Accurate and autonomous star acquisition method for star sensor under complex conditions[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2017, 2017: 1643967 doi: 10.1155/2017/1643967 [10] 金柱璋, 方旭源, 黄彦慧, 等. 基于深度度量学习的卫星云图检索[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(4): 210307JIN Zhuzhang, FANG Xuyuan, HUANG Yanhui, et al. Satellite cloud image retrieval based on deep metric learning[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2022, 49(4): 210307 [11] 聂青凤, 刘应杰, 梁赟. 基于稀疏约束神经网络的红外弱小目标检测技术[J]. 电光与控制, 2022, 29(8): 40-44NIE Qingfeng, LIU Yingjie, LIANG Yun. Infrared dim target detection based on neural network model with sparsity constraint[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2022, 29(8): 40-44 [12] 万丽丽. 基于背景预测的红外目标检测[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2015WAN Lili. Infrared Target Detection Based on Background Prediction[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2015 [13] 练达, 毛晓楠, 郑循江, 等. 星敏感器恒星成像模型迭代估计方法[J]. 光子学报, 2019, 48(1): 0104002 doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194801.0104002LIAN Da, MAO Xiaonan, ZHENG Xunjiang, et al. Iterative estimation algorithm of star tracker's star imaging model[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2019, 48(1): 0104002 doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194801.0104002 [14] 张辉, 钟建勇, 袁家虎, 等. 电路噪声对星敏感器星点定位精度的影响[J]. 光学精密工程, 2006, 14(6): 1052-1056ZHANG Hui, ZHONG Jianyong, YUAN Jiahu, et al. Circuit noise effects on star sensor position accuracy[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2006, 14(6): 1052-1056 [15] 梁敏. 红外弱小目标检测与跟踪技术研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2007LIANG Min. Research on Detection and Tracking for Small Dim Targets in Infrared Images[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2007 [16] 徐卿, 赵春晖, 白山, 等. 面向天文/惯性组合导航的全天时星敏感器研究现状及关键技术[C]//惯性技术与智能导航学术研讨会论文集, 2019: 66-274XU Qing, ZHAO Chunhui, BAI Shan, et al. Research status and key technologies of all-sky star sensor for astronomical/inertial integrated navigation[C]//Proceedings of the Symposium on Inertial Technology and Intelligent Navigation, 2019: 266-274 [17] 刘帅, 王铎, 孙腾飞. 基于SUSAN算子的白天红外星目标检测[J]. 红外技术, 2013, 35(9): 571-574, 586LIU Shuai, WANG Duo, SUN Tengfei. Daytime infrared star target detection based on SUSAN operator[J]. Infrared Technology, 2013, 35(9): 571-574, 586 [18] 马鹏阁, 魏宏光, 孙俊灵, 等. 基于高斯-拉普拉斯滤波的增强局部对比度红外小目标检测算法[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(4): 1041-1049MA Pengge, WEI Hongguang, SUN Junling, et al. A LOG filter based enhanced local contrast algorithm to detect infrared small targets[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(4): 1041-1049 [19] 原玉磊. 鱼眼相机恒星法检校技术研究[D]. 郑州: 解放军信息工程大学, 2012YUAN Yulei. Research on Fish-Eye Camera Stellar Calibration Technology[D]. Zhengzhou: PLA Information Engineering University, 2012 [20] 吴州平, 谭文锋, 戴东凯, 等. 一种基于多重滤波的近红外星图星点提取方法[J]. 光学与光电技术, 2019, 17(1): 25-30WU Zhouping, TAN Wenfeng, DAI Dongkai, et al. A method of star extraction for near-infrared star imagebased on multi-filter[J]. Optics & Optoelectronic Technology, 2019, 17(1): 25-30 [21] BAI X Z, ZHANG S, DU B B, et al. Survey on dim small target detection in clutter background: wavelet, inter-frame and filter based algorithms[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 15: 479-483 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.08.091 [22] DONG W K, ZHANG J Q, YANG D D, et al. Homogeneous background prediction algorithm for detection of point target[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2011, 54(2): 70-74 [23] CAO Y, LIU R M, YANG J. Small target detection using two-dimensional least mean square (TDLMS) filter based on neighborhood analysis[J]. International Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2008, 29(2): 188-200 doi: 10.1007/s10762-007-9313-x [24] SHIRVAIKAR M V, TRIVEDI M M. A neural network filter to detect small targets in high clutter backgrounds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1995, 6(1): 252-257 doi: 10.1109/72.363430 [25] HANCOCK B R, STIRBL R C, CUNNINGHAM T J, et al. CMOS active pixel sensor specific performance effects on star tracker/imager position accuracy[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 4284, Functional Integration of Opto-Electro-Mechanical Devices and Systems. San Jose, CA: SPIE, 2001: 43-53 [26] 于劲松, 万九卿, 高秀林. 红外图像弱小点目标检测技术研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2008, 29(12): 1518-1521YU Jinsong, WAN Jiuqing, GAO Xiulin. Research on dim point moving target detection in infrared image[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2008, 29(12): 1518-1521 [27] 杨丽萍, 冯晓毅. 一种基于背景预测的红外弱小目标检测方法[J]. 红外技术, 2007, 29(7): 404-408YANG Liping, FENG Xiaoyi. Weak and small infrared targets detection based on background prediction[J]. Infrared Technology, 2007, 29(7): 404-408 -
-





 杨原 男, 1994年11月出生于河南省渑池县, 现为信息工程大学在读研究生, 主要研究方向为天文导航、空间目标检测等. E-mail:
杨原 男, 1994年11月出生于河南省渑池县, 现为信息工程大学在读研究生, 主要研究方向为天文导航、空间目标检测等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: