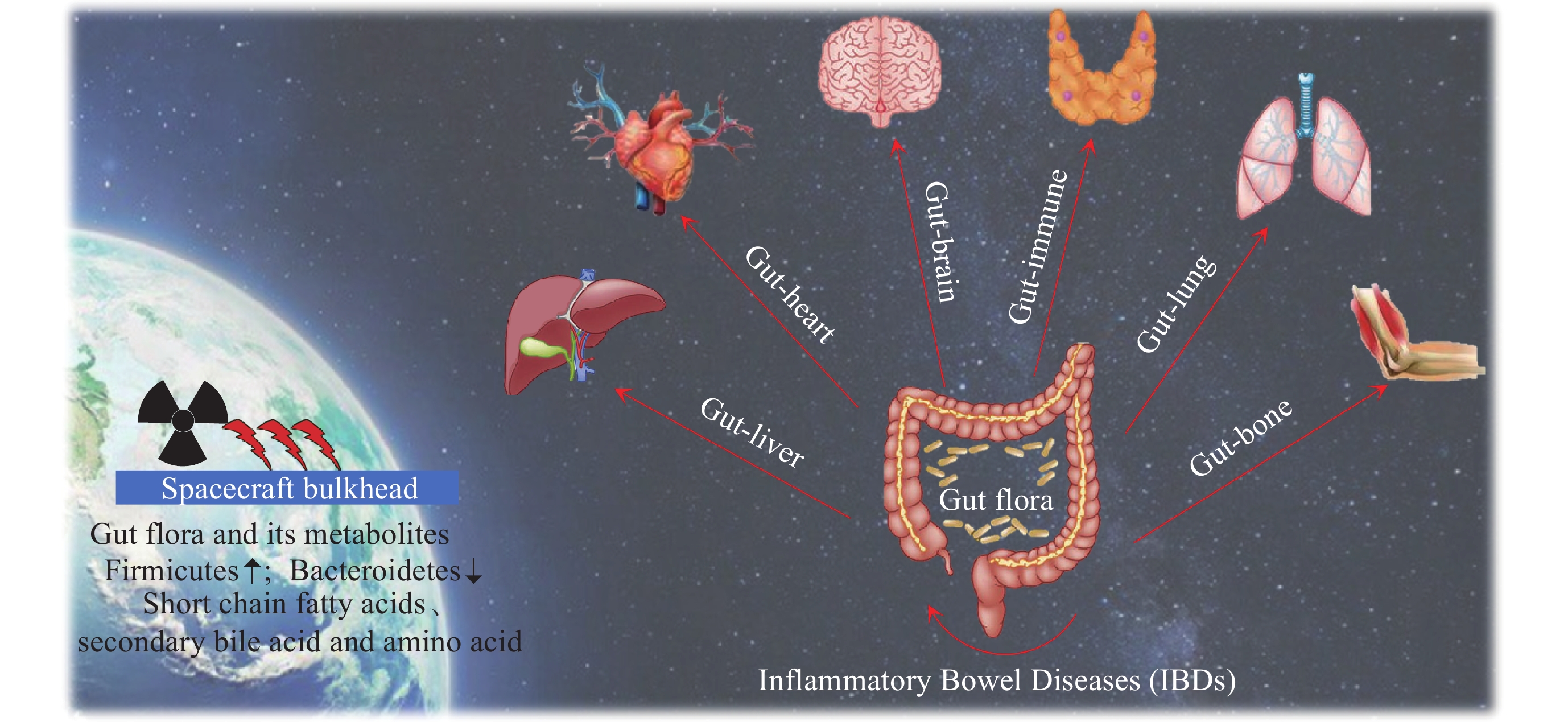
空间辐射对肠道菌群及其代谢产物和多系统疾病的影响
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.05.2023-0126 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.05.2023-0126
Space Radiation-induced Impacts on Gut Flora, Metabolites and Multisystem Diseases
-
摘要: 维持肠道菌群的稳态对保障人体健康具有重要意义. 肠道菌群在调节机体功能方面发挥着关键作用, 例如消化、新陈代谢、免疫及认知等, 这些生理功能通常依赖于肠道菌群的多样性、菌群结构的稳定性与微生态的平衡性. 在空间环境中, 航天员会受到包括空间辐射在内的诸多特殊环境因素的影响. 空间辐射会造成肠道菌群失衡及其代谢产物变化, 使肠道屏障功能受损, 进一步引起肠道、心血管、脑及肺等多系统病理损伤. 本文分析了空间飞行或模拟空间辐射下肠道菌群稳态及其代谢产物的特征性变化, 以及辐射效应下肠道菌群与肠道损伤及其他多系统疾病之间的相互影响, 为研究空间辐射病理机制及辐射防护措施提供参考.Abstract: Maintaining the homeostasis of gut flora is of great significance to protecting human health. Gut flora plays a key role in regulating body functions, such as digestion, metabolism, immunity, and cognition. These physiological functions often depend on the diversity of gut flora, the stability of the bacterial flora structure, and the balance of the microecology. In the outer space, astronauts face many special environmental factors including the space radiation. Space radiation can cause imbalance of gut flora and changes in metabolites, damaging the intestinal barrier function, and further lead to pathological injury to multiple systems such as the intestine, cardiovascular, brain, and lungs. This paper reviews the characteristic changes in gut flora homeostasis and its metabolites under space flight or simulated space radiation, as well as the interaction between gut flora and intestinal damage and other multi-system diseases under radiation effects. It is expected to provide a reference for the further study of the pathological mechanisms upon space radiation and radiation protection measures.
-
Key words:
- Space radiation /
- Gut flora /
- Microbial metabolites /
- Radiation injuries /
- Multisystem diseases
-
表 1 辐射对肠道菌群变化的影响
Table 1. Effects of radiation on gut flora
物种 辐射类型 辐射后肠道菌群变化 文献 人 未知 拟杆菌↑变形杆菌↑, 厚壁菌↓ [37] 人 未知 厚壁菌/拟杆菌比例↓ [38] 人 未知 厚壁菌↓, 梭杆菌↑ [31] 人 未知 梭杆菌、玫瑰杆菌和裂头杆菌↑ [39] GMP、中国恒河猴 高能电子束 拟杆菌和变形杆菌↓, GMP的厚壁菌门↑ [32,40] Wistar 大鼠 X射线 拟杆菌科、乳酸杆菌科和链球菌科↑, 梭状芽孢杆菌↓ [26] BALB/c 小鼠 Co60 梭杆菌↑, 拟杆菌↓ [29] C57 BL/6小鼠 Co60 拟杆菌、厚壁菌↑, 厚壁菌门、放线菌门↓ [27] C57 BL/6 J 小鼠 X射线 厚壁菌、乳酸杆菌科、葡萄球菌中的常见细菌↑,
厚壁菌、乳酸杆菌科、葡萄球菌中的常见细菌↓[28] 河堤田鼠 放射性核素 拟杆菌↑ [30] 表 2 辐射对肠道菌群代谢产物的影响
Table 2. Effects of radiation on gut microbial metabolites
代谢物及其变化 辐射类型 功能 文献 吲哚-3-丙酸↓ 空间辐射 促进黏蛋白表达, 增强肠道黏液层功能; 促进神经再生和修复 [24] 吲哚乳酸↓ 抗氧化活性, 促进肠上皮细胞紧密连接 3-硫酸吲哚酚↑ 抑制肠上皮细胞紧密连接, 引发线粒体自噬,
导致动脉粥状硬化, 损伤肾脏硫代石胆酰甘氨酸↓ 说明菌群紊乱 硫酸苯酯、
硫酸对甲酚、
对甲酚葡糖苷酸↑肠源性尿毒症毒素, 损伤肾脏 组氨酸丙酸咪唑↓ γ射线 在质子缓冲、金属离子螯合、去除活性氧和氮物质以及
红细胞生成和组胺能系统中具有独特的作用[42] 衍生吲哚3-丙酸↓ γ射线 较低的系统炎症水平、恢复造血器官、缓解性骨髓抑制、
胃肠功能改善以及照射后的上皮完整性[43] 短链脂肪酸↓ 铯-137 促进癌症细胞凋亡, 抗炎等 [44] -
[1] 吴季. 深空探测的现状、展望与建议[J]. 科技导报, 2021, 39(3): 80-87WU Ji. Deep space exploration: status, expectation and suggestion[J]. Science Technology Review, 2021, 39(3): 80-87 [2] 张颖一, 张伟. 国外载人深空探测现状及发展趋势分析[J]. 中国航天, 2019(11): 54-59ZHANG Yingyi, ZHANG Wei. Analysis of the status and development trend of manned deep space exploration[J]. Aerospace China, 2019(11): 54-59 [3] GRIGORIEV A I, KOZLOVSKAYA I B, POTAPOV A N. Goals of biomedical support of a mission to mars and possible approaches to achieving them[J]. Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine, 2002, 73(4): 379-384 [4] SETLOW R B. The hazards of space travel[J]. EMBO Reports, 2003, 4(11): 1013-1016 doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400016 [5] TESEI D, JEWCZYNKO A, LYNCH A M, et al. Understanding the complexities and changes of the astronaut microbiome for successful long-duration space missions[J]. Life, 2022, 12(4): 495 doi: 10.3390/life12040495 [6] DEMONTIS G C, GERMANI M M, CAIANI E G, et al. Human pathophysiological adaptations to the space environment[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2017, 8: 547 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00547 [7] GRIMM D, GROSSE J, WEHLAND M, et al. The impact of microgravity on bone in humans[J]. Bone, 2016, 87: 44-56 doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.12.057 [8] KOKHAN V S, MATVEEVA M I, MUKHAMETOV A, et al. Risk of defeats in the central nervous system during deep space missions[J]. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 2016, 71: 621-632 [9] BEVELACQUA J J, MORTAZAVI S M J. Commentary: immune system dysregulation during spaceflight: potential countermeasures for deep space exploration missions[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2018, 9: 2024 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02024 [10] BENTON E R, BENTON E V. Space radiation dosimetry in low-earth orbit and beyond[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2001, 184(1/2): 255-294 [11] ARENA C, DE MICCO V, MACAEVA E, et al. Space radiation effects on plant and mammalian cells[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2014, 104(1): 419-431 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2014.05.005 [12] 张朝宁, 李金田, 刘永琦. 辐射旁效应及其机制研究进展[J]. 辐射防护通讯, 2015, 35(3): 19-24ZHANG Chaoning, LI Jintian, LIU Yongqi. Advances in research of radiation induced bystander effect and its mechanism[J]. Radiation Protection Bulletin, 2015, 35(3): 19-24 [13] YATAGAI F, ISHIOKA N. Are biological effects of space radiation really altered under the microgravity environment?[J]. Life Sciences in Space Research, 2014, 3: 76-89 doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2014.09.005 [14] 徐绸, 何平, 刘长庭. 空间环境对肠道菌群的影响[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2016, 29(4): 297-300XU Chou, HE Ping, LIU Changting. Effects of space environment on intestinal flora[J]. Space Medicine & Medical Engineering, 2016, 29(4): 297-300 [15] SIDDIQUI R, AKBAR N, KHAN N A. Gut microbiome and human health under the space environment[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2021, 130(1): 14-24 doi: 10.1111/jam.14789 [16] JIANG P, GREEN S J, CHLIPALA G E, et al. Reproducible changes in the gut microbiome suggest a shift in microbial and host metabolism during spaceflight[J]. Microbiome, 2019, 7(1): 113 doi: 10.1186/s40168-019-0724-4 [17] KING S J, MCCOLE D F. Epithelial-microbial diplomacy: escalating border tensions drive inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Intestinal Research, 2019, 17(2): 177-191 doi: 10.5217/ir.2018.00170 [18] YANG J Q, JIANG N, LI Z P, et al. The effects of microgravity on the digestive system and the new insights it brings to the life sciences[J]. Life Sciences in Space Research, 2020, 27: 74-82 doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2020.07.009 [19] LI Y J, LIU S, LIU H Y, et al. Dragon's blood regulates Rac1-WAVE2-Arp2/3 signaling pathway to protect rat intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction induced by simulated microgravity[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(5): 2722 doi: 10.3390/ijms22052722 [20] VOORHIES A A, LORENZI H A. The challenge of maintaining a healthy microbiome during long-duration space missions[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2016, 3: 23 [21] VOORHIES A A, MARK OTT C, MEHTA S, et al. Study of the impact of long-duration space missions at the international space station on the astronaut microbiome[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 9911 doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46303-8 [22] SHREINER A B, KAO J Y, YOUNG V B. The gut microbiome in health and in disease[J]. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology, 2015, 31(1): 69-75 doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000139 [23] STOJANOV S, BERLEC A, ŠTRUKELJ B. The influence of probiotics on the firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio in the treatment of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(11): 1715 doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111715 [24] GARRETT-BAKELMAN F E, DARSHI M, GREEN S J, et al. The NASA twins study: a multidimensional analysis of a year-long human spaceflight[J]. Science, 2019, 364 (6436): eaau8650 doi: 10.1126/science.aau8650 [25] SAEI A A, BARZEGARI A. The microbiome: the forgotten organ of the astronaut’s body - probiotics beyond terrestrial limits[J]. Future Microbiology, 2012, 7(9): 1037-1046 doi: 10.2217/fmb.12.82 [26] LAM V, MOULDER J E, SALZMAN N H, et al. Intestinal microbiota as novel biomarkers of prior radiation exposure[J]. Radiation Research, 2012, 177(5): 573-583 doi: 10.1667/RR2691.1 [27] KIM Y S, KIM J, PARK S J. High-throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing reveals alterations of mouse intestinal microbiota after radiotherapy[J]. Anaerobe, 2015, 33: 1-7 doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2015.01.004 [28] GOUDARZI M, MAK T D, JACOBS J P, et al. An integrated multi-omic approach to assess radiation injury on the host-microbiome axis[J]. Radiation Research, 2016, 186(3): 219-234 doi: 10.1667/RR14306.1 [29] LIU X D, ZHOU Y, WANG S Z, et al. Impact of low-dose ionizing radiation on the composition of the gut microbiota of mice[J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2019, 171(1): 258-268 doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz144 [30] LAVRINIENKO A, MAPPES T, TUKALENKO E, et al. Environmental radiation alters the gut microbiome of the bank vole Myodes glareolus[J]. The ISME Journal, 2018, 12(11): 2801-2806 doi: 10.1038/s41396-018-0214-x [31] NAM Y D, KIM H J, SEO J G, et al. Impact of pelvic radiotherapy on gut microbiota of gynecological cancer patients revealed by massive pyrosequencing[J]. Plos One, 2013, 8(12): e82659 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082659 [32] CARBONERO F, MAYTA A, BOLEA M, et al. Specific members of the gut microbiota are reliable biomarkers of irradiation intensity and lethality in large animal models of human health[J]. Radiation Research, 2019, 191(1): 107-121 [33] LI Y C, SUI L, ZHAO H L, et al. Differences in the establishment of gut microbiota and metabolome characteristics between BALB/c and C57BL/6J mice after proton irradiation[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 874702 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.874702 [34] RABER J, FUENTES ANAYA A, TORRES E R S, et al. Effects of six sequential charged particle beams on behavioral and cognitive performance in B6D2F1 female and male mice[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2020, 11: 959 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00959 [35] FERNANDES A, OLIVEIRA A, GUEDES C, et al. Effect of radium-223 on the gut microbiota of prostate cancer patients: a pilot case series study[J]. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 2022, 44(10): 4950-4959 doi: 10.3390/cimb44100336 [36] LI Y Y, ZHANG Y M, WEI K X, et al. Review: effect of gut microbiota and its metabolite SCFAs on radiation-induced intestinal injury[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2021, 11: 577236 doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.577236 [37] WANG Z Q, WANG Q X, WANG X, et al. Gut microbial dysbiosis is associated with development and progression of radiation enteritis during pelvic radiotherapy[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2019, 23(5): 3747-3756 doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14289 [38] WANG A P, LING Z X, YANG Z X, et al. Gut microbial dysbiosis may predict diarrhea and fatigue in patients undergoing pelvic cancer radiotherapy: a pilot study[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(5): e0126312 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126312 [39] FERREIRA M R, ANDREYEV H J N, MOHAMMED K, et al. Microbiota- and Radiotherapy-induced gastrointestinal Side-effects (MARS) study: a large pilot study of the microbiome in acute and late-radiation enteropathy[J]. Clinical Cancer Research, 2019, 25(21): 6487-6500 doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0960 [40] CARBONERO F, MAYTA-APAZA A C, YU J Z, et al. A comparative analysis of gut microbiota disturbances in the gottingen minipig and rhesus macaque models of acute radiation syndrome following bioequivalent radiation exposures[J]. Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 2018, 57(4): 419-426 doi: 10.1007/s00411-018-0759-0 [41] 郑颖, 殷祥昶, 赵阳, 等. 电离辐射对肠道菌群的影响及基于菌群调节的辐射防护研究进展[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2020, 34(7): 549-558ZHENG Ying, YIN Xiangchang, ZHAO Yang, et al. Effects of ionizing radiation on gut microbiota and radioprotection based on gut microbiota[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2020, 34(7): 549-558 [42] CHEN Z Y, WANG B, DONG J L, et al. Gut microbiota-derived L-histidine/imidazole propionate axis fights against the radiation-induced cardiopulmonary injury[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(21): 11436 doi: 10.3390/ijms222111436 [43] XIAO H W, CUI M, LI Y, et al. Gut microbiota-derived indole 3-propionic acid protects against radiation toxicity via retaining Acyl-CoA-binding protein[J]. Microbiome, 2020, 8(1): 69 doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00845-6 [44] MORGAN J L L, RITCHIE L E, CRUCIAN B E, et al. Increased dietary iron and radiation in rats promote oxidative stress, induce localized and systemic immune system responses, and alter colon mucosal environment[J]. The FASEB Journal, 2014, 28(3): 1486-1498 doi: 10.1096/fj.13-239418 [45] LEY R E, TURNBAUGH P J, KLEIN S, et al. Microbial ecology - human gut microbes associated with obesity[J]. Nature, 2006, 444(7122): 1022-1023 doi: 10.1038/4441022a [46] GENTILE C L, WEIR T L. The gut microbiota at the intersection of diet and human health[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6416): 776-780 doi: 10.1126/science.aau5812 [47] MARCHESI J R, ADAMS D H, FAVA F, et al. The gut microbiota and host health: a new clinical frontier[J]. Gut, 2016, 65(2): 330-339 doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309990 [48] KOH A, DE VADDER F, KOVATCHEVA-DATCHARY P, et al. From dietary fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(6): 1332-1345 doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.041 [49] LOUIS P, HOLD G L, FLINT H J. The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2014, 12(10): 661-672 doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3344 [50] CUMMINGS J H, POMARE E W, BRANCH W J, et al. Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood[J]. Gut, 1987, 28(10): 1221-1227 doi: 10.1136/gut.28.10.1221 [51] SMITH E A, MACFARLANE G T. Dissimilatory amino acid metabolism in human colonic bacteria[J]. Anaerobe, 1997, 3(5): 327-337 doi: 10.1006/anae.1997.0121 [52] TIAN T, ZHAO Y Z, YANG Y, et al. The protective role of short-chain fatty acids acting as signal molecules in chemotherapy- or radiation-induced intestinal inflammation[J]. American Journal of Cancer Research, 2020, 10(11): 3508-3531 [53] MONTASSIER E, GASTINNE T, VANGAY P, et al. Chemotherapy-driven dysbiosis in the intestinal microbiome[J]. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2015, 42(5): 515-528 [54] MÁJER F, SHARMA R, MULLINS C, et al. New highly toxic bile acids derived from deoxycholic acid, chenodeoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2014, 22(1): 256-268 [55] WANG L N, ZHOU Y, WANG X H, et al. Mechanism of asbt (Slc10a2)-related bile acid malabsorption in diarrhea after pelvic radiation[J]. International Journal of Radiation Biology, 2020, 96(4): 510-519 doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1707324 [56] LAURSEN M F, SAKANAKA M, VON BURG N, et al. Bifidobacterium species associated with breastfeeding produce aromatic lactic acids in the infant gut[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2021, 6(11): 1367-1382 [57] LEVI I, GUREVICH M, PERLMAN G, et al. Potential role of indolelactate and butyrate in multiple sclerosis revealed by integrated microbiome-metabolome analysis[J]. Cell Reports Medicine, 2021, 2(4): 100246 doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100246 [58] AGUS A, PLANCHAIS J, SOKOL H. Gut microbiota regulation of tryptophan metabolism in health and disease[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2018, 23(6): 716-724 [59] XIN J Y, WANG J, DING Q Q, et al. Potential role of gut microbiota and its metabolites in radiation-induced intestinal damage[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 248: 114341 doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114341 [60] YU Y Q, LIN X, FENG F Y, et al. Gut microbiota and ionizing radiation-induced damage: is there a link?[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 229: 115947 doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115947 [61] WANG Z N, KLIPFELL E, BENNETT B J, et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease[J]. Nature, 2011, 472(7341): 57-63 doi: 10.1038/nature09922 [62] TANG W H W, KITAI T, HAZEN S L. Gut microbiota in cardiovascular health and disease[J]. Circulation Research, 2017, 120(7): 1183-1196 doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.309715 [63] HAUER-JENSEN M, DENHAM J W, ANDREYEV H J N. Radiation enteropathy-pathogenesis, treatment and prevention[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2014, 11(8): 470-479 [64] MOSCA A, LECLERC M, HUGOT J P. Gut microbiota diversity and human diseases: should we reintroduce key predators in our ecosystem[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 455 [65] CUI M, XIAO H W, LI Y, et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation protects against radiation-induced toxicity[J]. EMBO Molecular Medicine, 2017, 9(4): 448-461 doi: 10.15252/emmm.201606932 [66] CRAWFORD P A, GORDON J I. Microbial regulation of intestinal radiosensitivity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(37): 13254-13259 [67] FERREIRA M R, MULS A, DEARNALEY D P, et al. Microbiota and radiation-induced bowel toxicity: lessons from inflammatory bowel disease for the radiation oncologist[J]. The Lancet Oncology, 2014, 15(3): e139-e147 doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70504-7 [68] MOUSSA L, USUNIER B, DEMARQUAY C, et al. Bowel radiation injury: complexity of the pathophysiology and promises of cell and tissue engineering[J]. Cell Transplantation, 2016, 25(10): 1723-1746 doi: 10.3727/096368916X691664 [69] STARZEWSKI J J, PAJĄK J T, PAWEŁCZYK I, et al. The radiation-induced changes in rectal mucosa: hyperfractionated vs. hypofractionated preoperative radiation for rectal cancer[J]. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics, 2006, 64(3): 717-724 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.009 [70] GRÉMY O, BENDERITTER M, LINARD C. Acute and persisting Th2-like immune response after fractionated colorectal γ-irradiation[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2008, 14(46): 7075-7085 doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.7075 [71] FRANCOIS A, MILLIAT F, GUIPAUD O, et al. Inflammation and immunity in radiation damage to the gut mucosa[J]. Biomed Research International, 2013, 2013: 123241 [72] BLIRANDO K, MILLIAT F, MARTELLY I, et al. Mast cells are an essential component of human radiation proctitis and contribute to experimental colorectal damage in mice[J]. The American Journal of Pathology, 2011, 178(2): 640-651 doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.10.003 [73] DUERKOP B A, VAISHNAVA S, HOOPER L V. Immune responses to the microbiota at the intestinal mucosal surface[J]. Immunity, 2009, 31(3): 368-376 doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.08.009 [74] NEUFELD K M, KANG N, BIENENSTOCK J, et al. Reduced anxiety-like behavior and central neurochemical change in germ-free mice[J]. Neurogastroenterology & Motility, 2011, 23(3): 255-e119 [75] WANG S, HUANG X F, ZHANG P, et al. Dietary teasaponin ameliorates alteration of gut microbiota and cognitive decline in diet-induced obese mice[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 71(1): 12203 [76] PARASHAR A, UDAYABANU M. Gut microbiota: implications in Parkinson’s disease[J]. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 2017, 38: 1-7 [77] SONG C, GAO X, SONG W, et al. Simulated spatial radiation impacts learning and memory ability with alterations of neuromorphology and gut microbiota in mice[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(27): 16196-16208 doi: 10.1039/D0RA01017K [78] NOOR R, NAZ A, MANIHA S M, et al. Microorganisms and cardiovascular diseases: importance of gut bacteria[J]. Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark, 2021, 26(5): 22-28 doi: 10.52586/4921 [79] MULLER A M, FISCHER A, KATUS H, et al. Mouse models of autoimmune diseases-autoimmune myocarditis[J]. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2015, 21(18): 2498-2512 doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150316123711 [80] CONNOLLY S E, BENACH J L. The versatile roles of antibodies in Borrelia infections[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2005, 3(5): 411-420 doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1149 [81] HILLMAN E T, LU H, YAO T M, et al. Microbial ecology along the gastrointestinal tract[J]. Microbes and Environments, 2017, 32(4): 300-313 doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME17017 [82] HUSE S M, DETHLEFSEN L, HUBER J A, et al. Exploring microbial diversity and taxonomy using SSU rRNA hypervariable tag sequencing[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2008, 4(11): e1000255 doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000255 [83] JIE Z Y, XIA H H, ZHONG S L, et al. The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 845 doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00900-1 [84] ANKER S D, EGERER K R, VOLK H D, et al. Elevated soluble CD14 receptors and altered cytokines in chronic heart failure[J]. The American Journal of Cardiology, 1997, 79(10): 1426-1430 doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(97)00159-8 [85] ZHAO L B, XING C Y, SUN W Q, et al. Lactobacillus supplementation prevents cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity possibly by inflammation inhibition[J]. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, 2018, 82(6): 999-1008 [86] YANG T, SANTISTEBAN M M, RODRIGUEZ V, et al. Gut dysbiosis is linked to hypertension[J]. Hypertension, 2015, 65(6): 1331-1340 doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05315 [87] QIN J J, LI Y R, CAI Z M, et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes[J]. Nature, 2012, 490(7418): 55-60 doi: 10.1038/nature11450 [88] PLUZNICK J L, PROTZKO R J, GEVORGYAN H, et al. Olfactory receptor responding to gut microbiota-derived signals plays a role in renin secretion and blood pressure regulation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(11): 4410-4415 [89] URIBE-HERRANZ M, RAFAIL S, BEGHI S, et al. Gut microbiota modulate dendritic cell antigen presentation and radiotherapy-induced antitumor immune response[J]. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2020, 130(1): 466-479 [90] ZHANG Q, RAN X, HE Y, et al. Acetate downregulates the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes and attenuates lung injury in neonatal mice with bronchopulmonary dysplasia[J]. Frontiers in Pediatrics, 2021, 8: 595157 doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.595157 [91] WYPYCH T P, PATTARONI C, PERDIJK O, et al. Microbial metabolism of L-tyrosine protects against allergic airway inflammation[J]. Nature Immunology, 2021, 22(3): 279-286 doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-00856-3 [92] LI W J, LU L N, LIU B, et al. Effects of phycocyanin on pulmonary and gut microbiota in a radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis model[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2020, 132: 110826 -
-





 吴竹君 女, 1994年4月出生于湖北省荆州市, 博士研究生, 主要研究方向为航天特殊环境对肠道细菌的影响. E-mail:
吴竹君 女, 1994年4月出生于湖北省荆州市, 博士研究生, 主要研究方向为航天特殊环境对肠道细菌的影响. E-mail:  张昕 女, 1997年1月出生于河南省鹤壁市, 硕士, 主要研究方向为航天微重力环境对脑组织唾液酸糖代谢的影响. E-mail:
张昕 女, 1997年1月出生于河南省鹤壁市, 硕士, 主要研究方向为航天微重力环境对脑组织唾液酸糖代谢的影响. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: