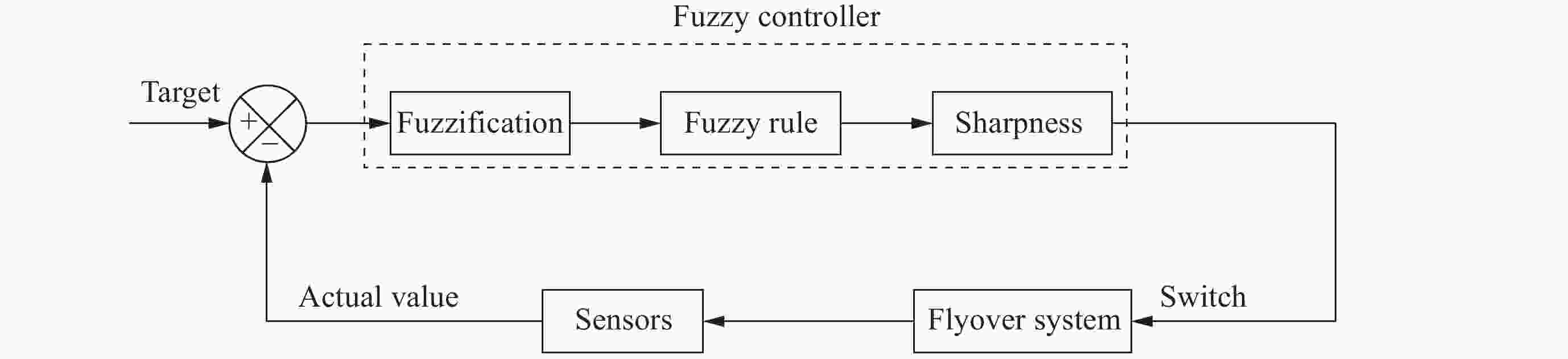
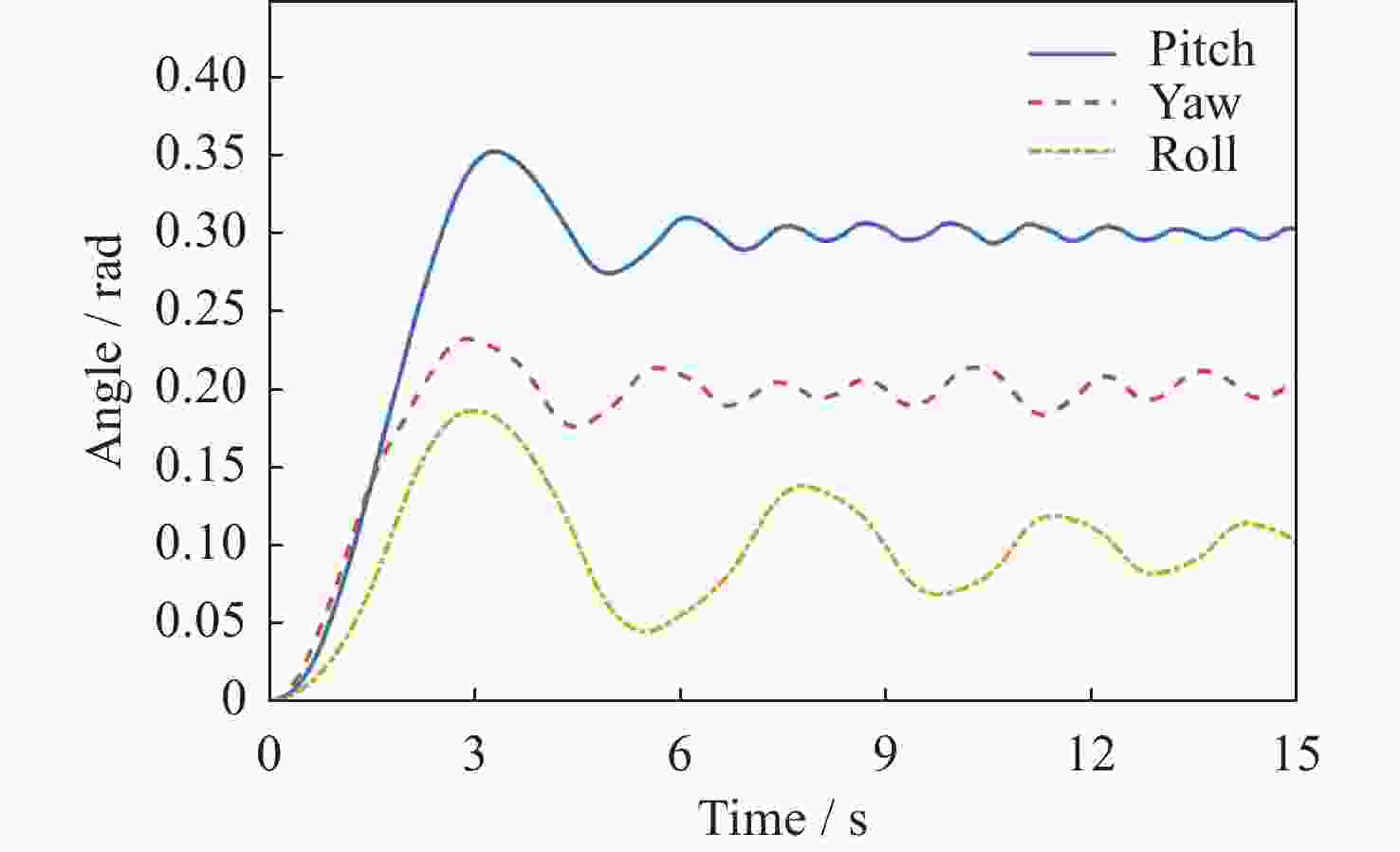
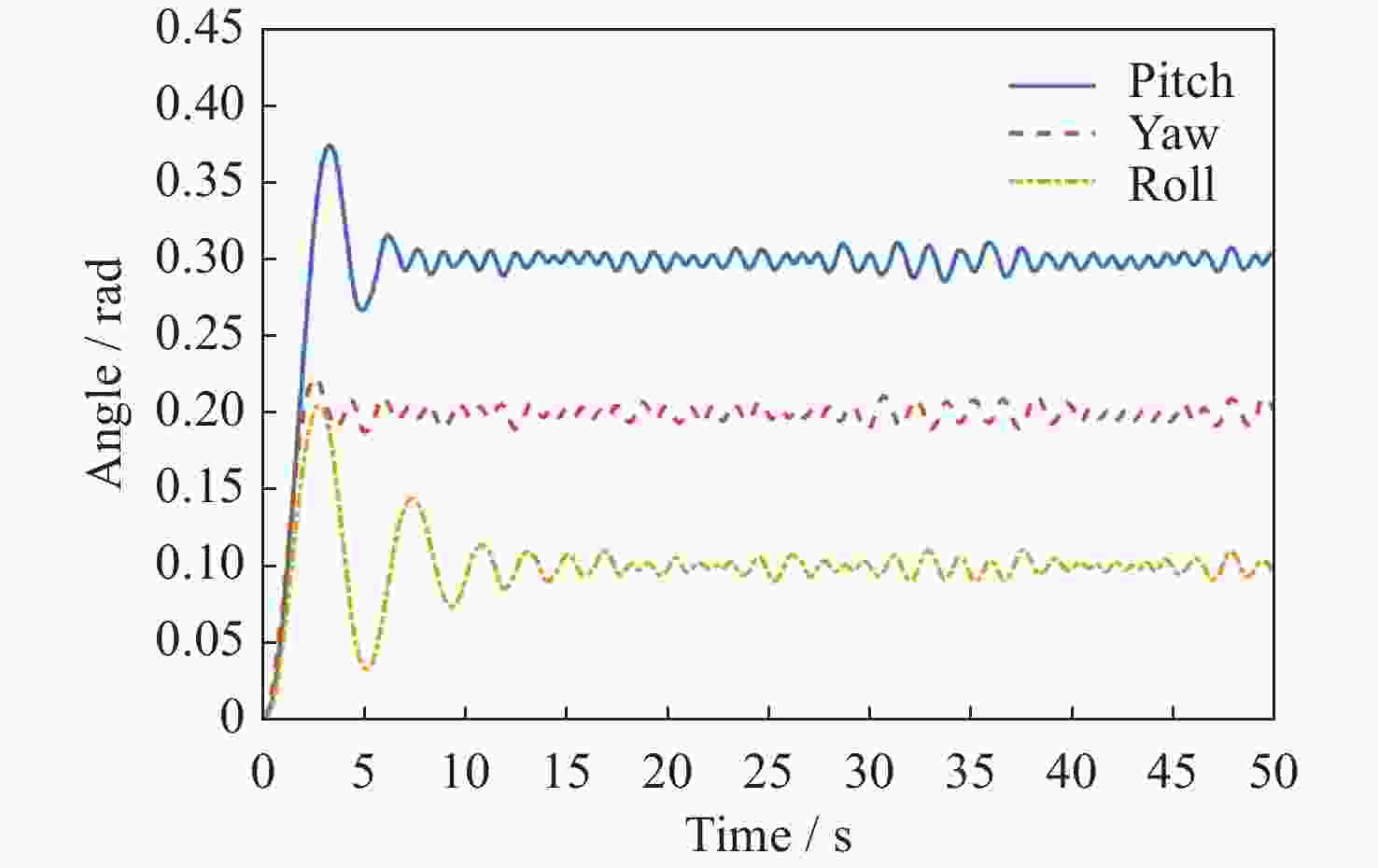
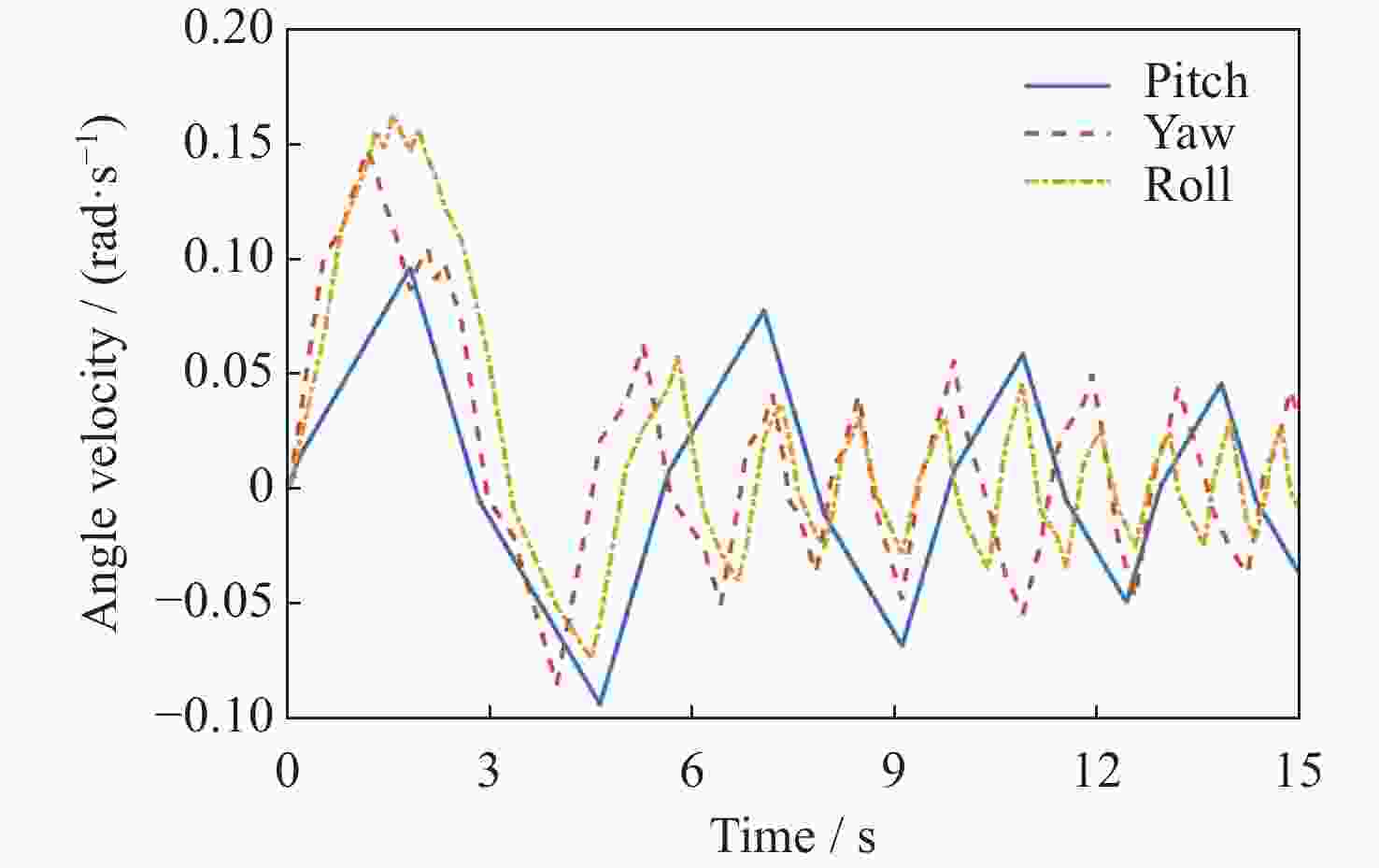
基于模糊控制的深空探测器不确定姿态控制方法设计
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.05.2023-0128 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.05.2023-0128
Design of Uncertain Attitude Control Method for Deep Space Probe Based on Fuzzy Control
-
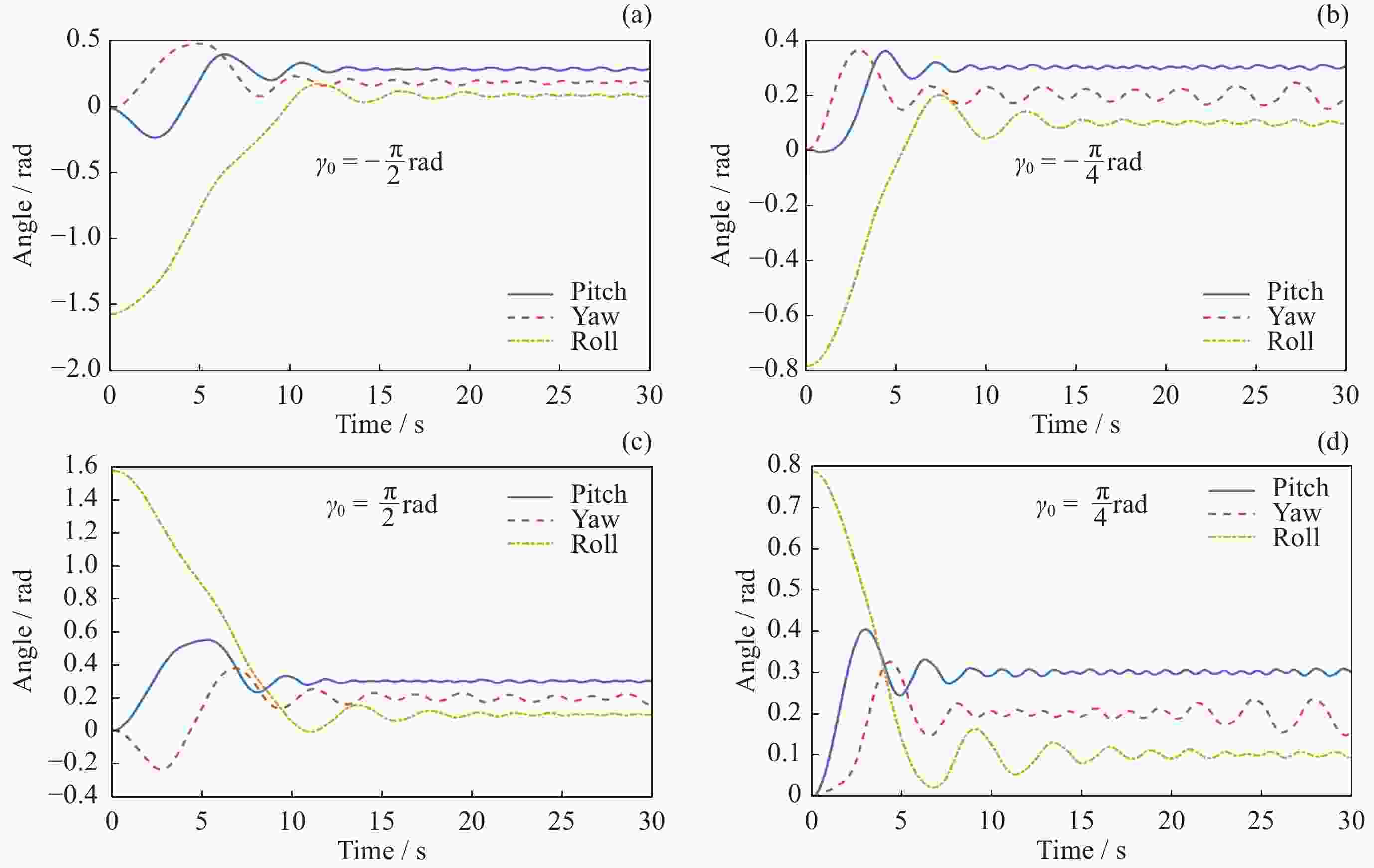
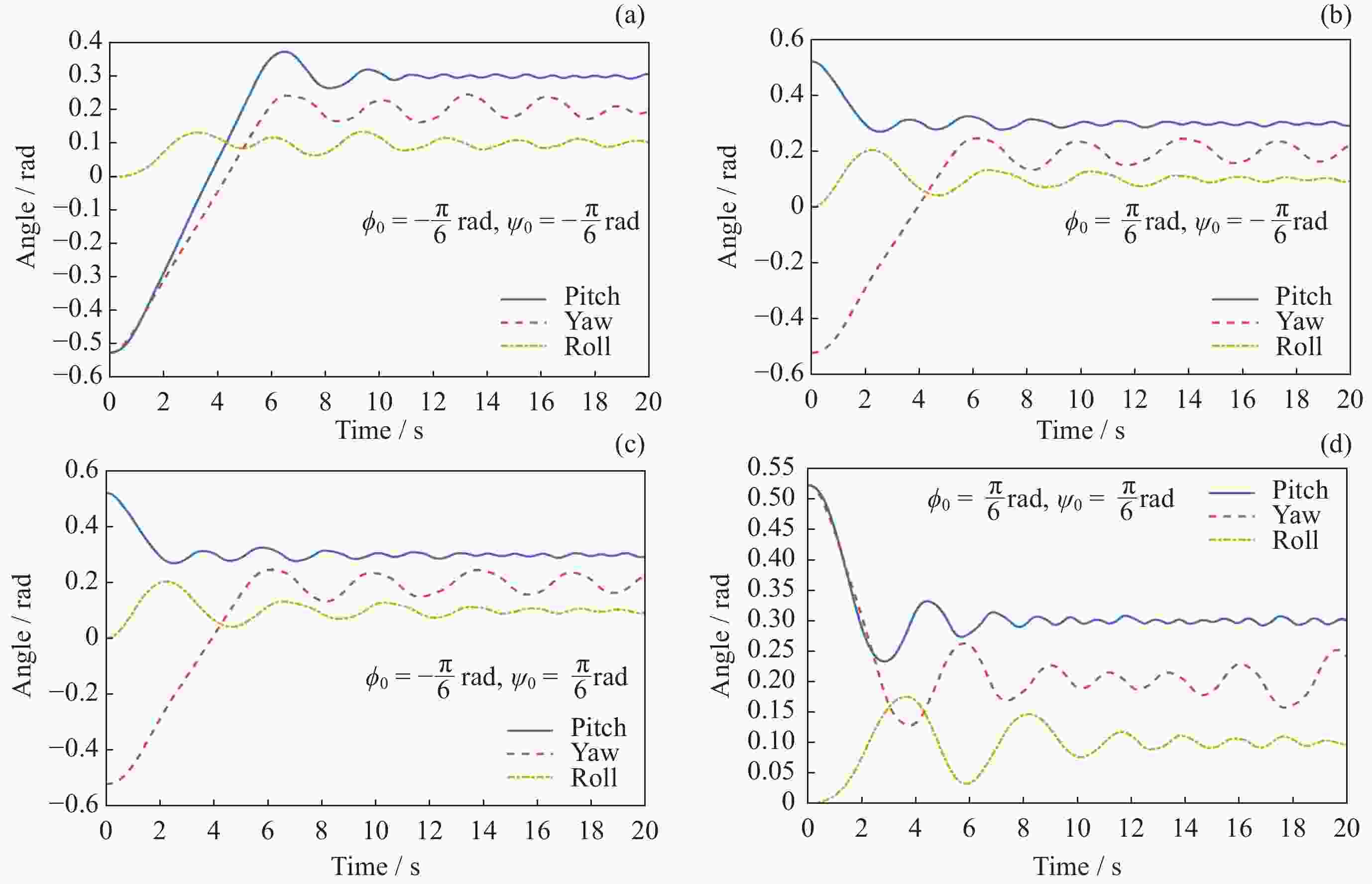
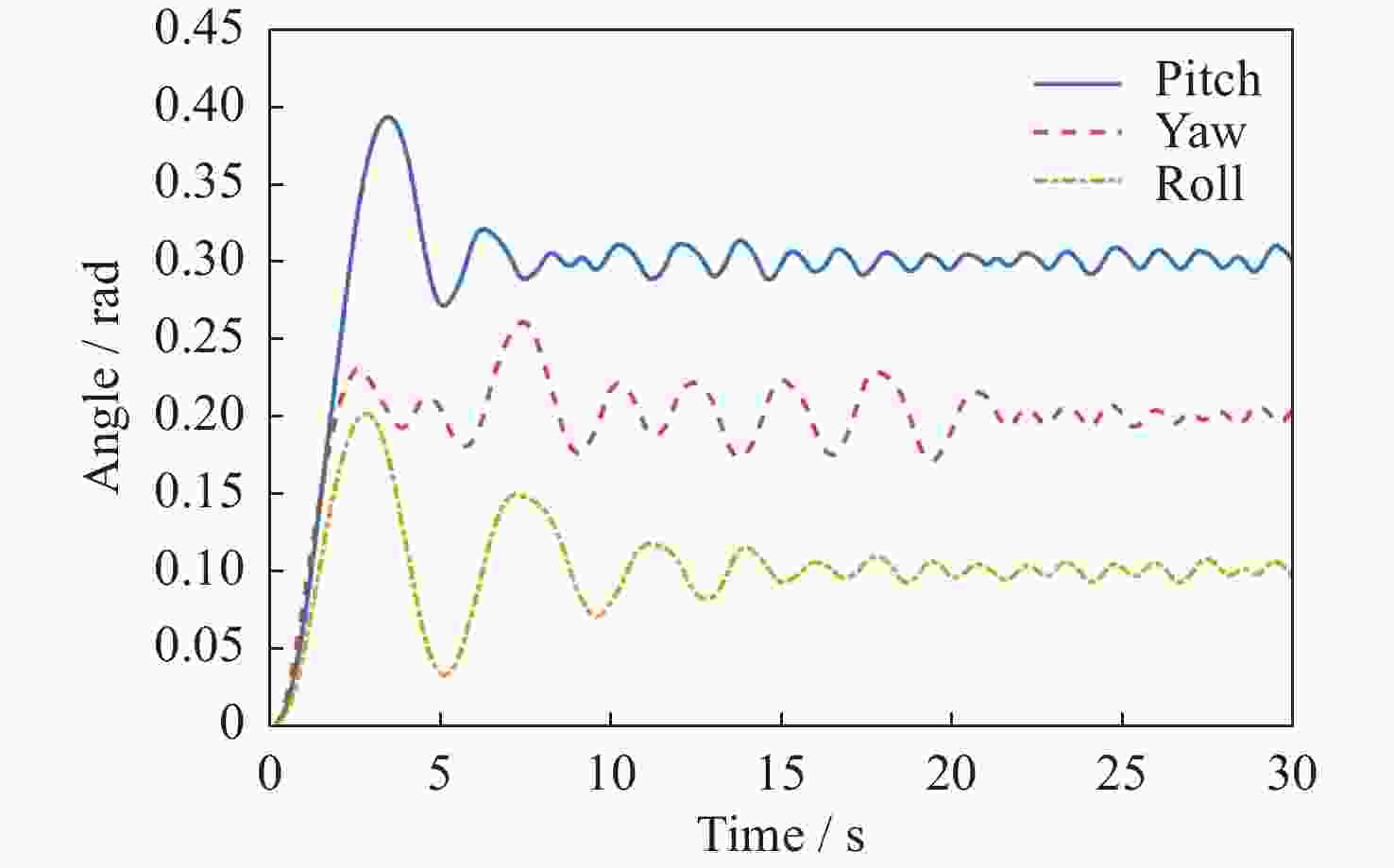
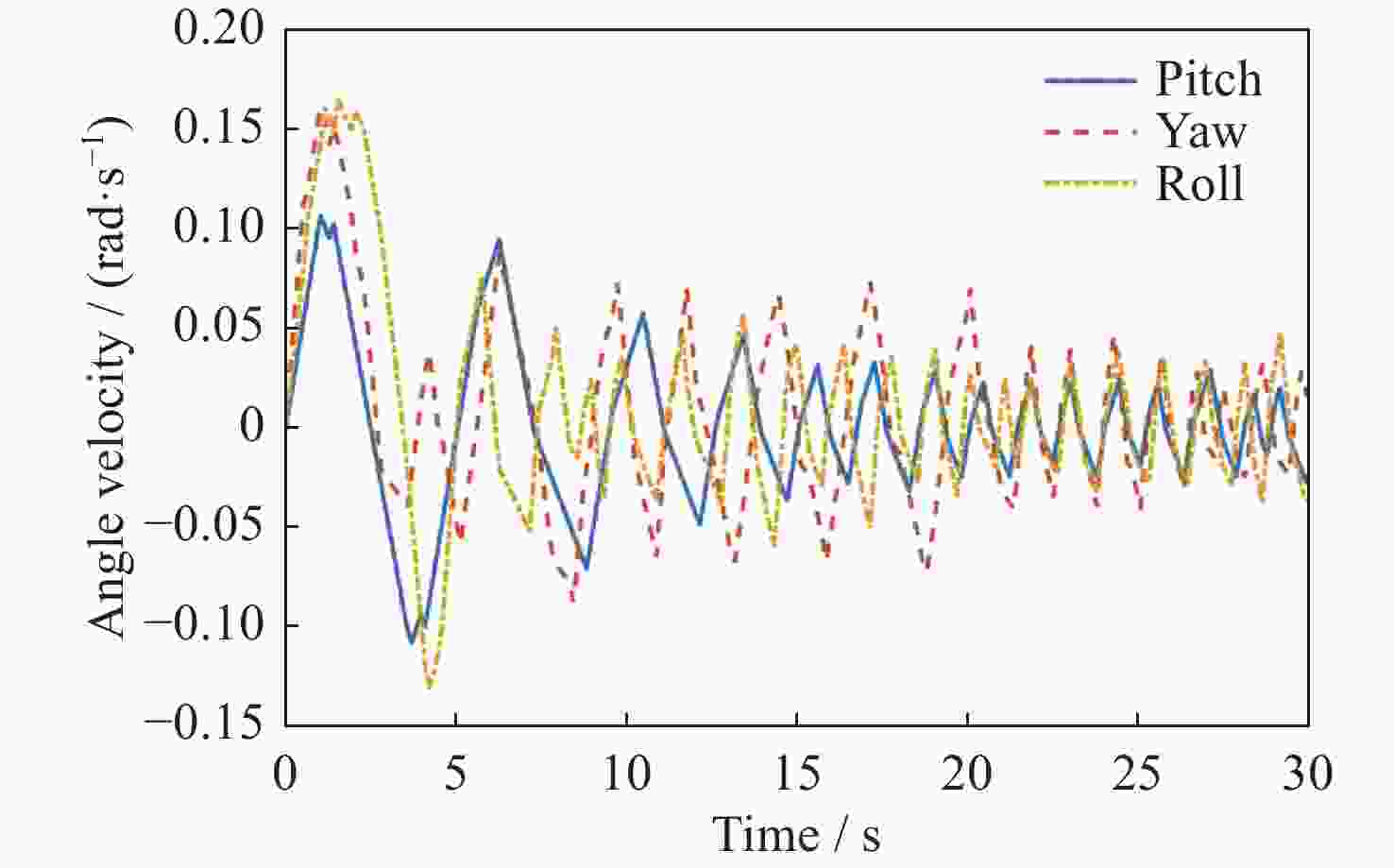
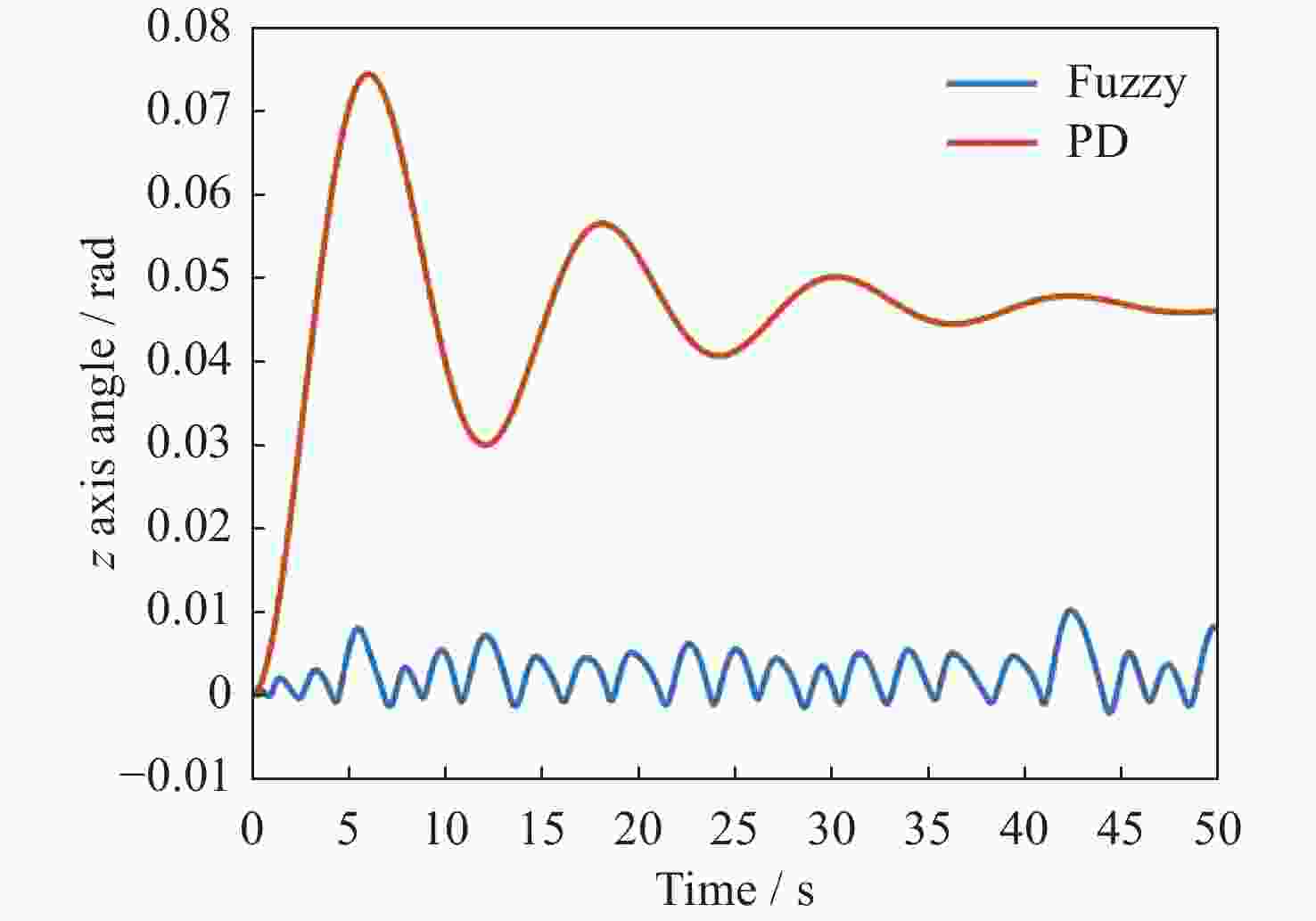
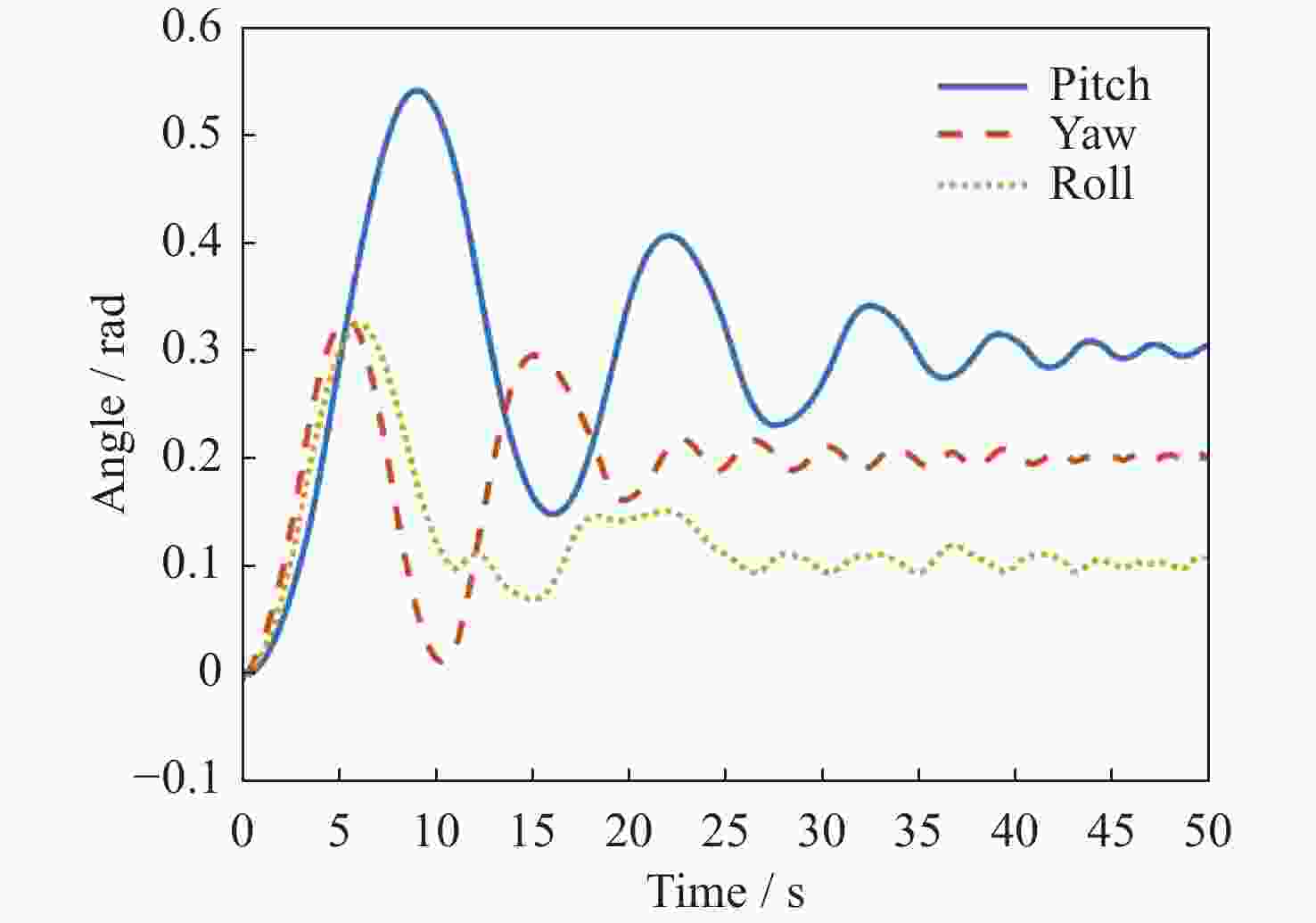
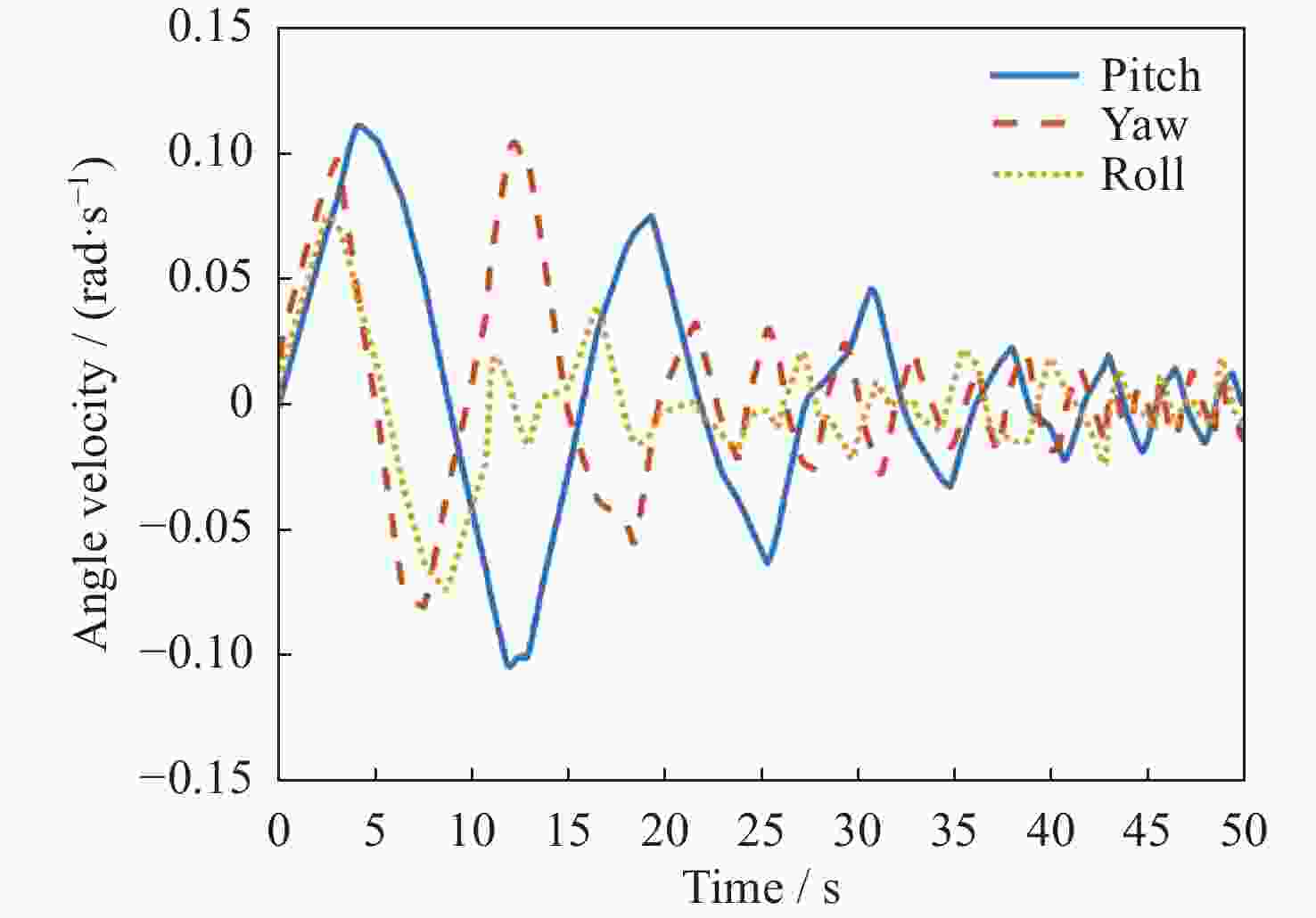
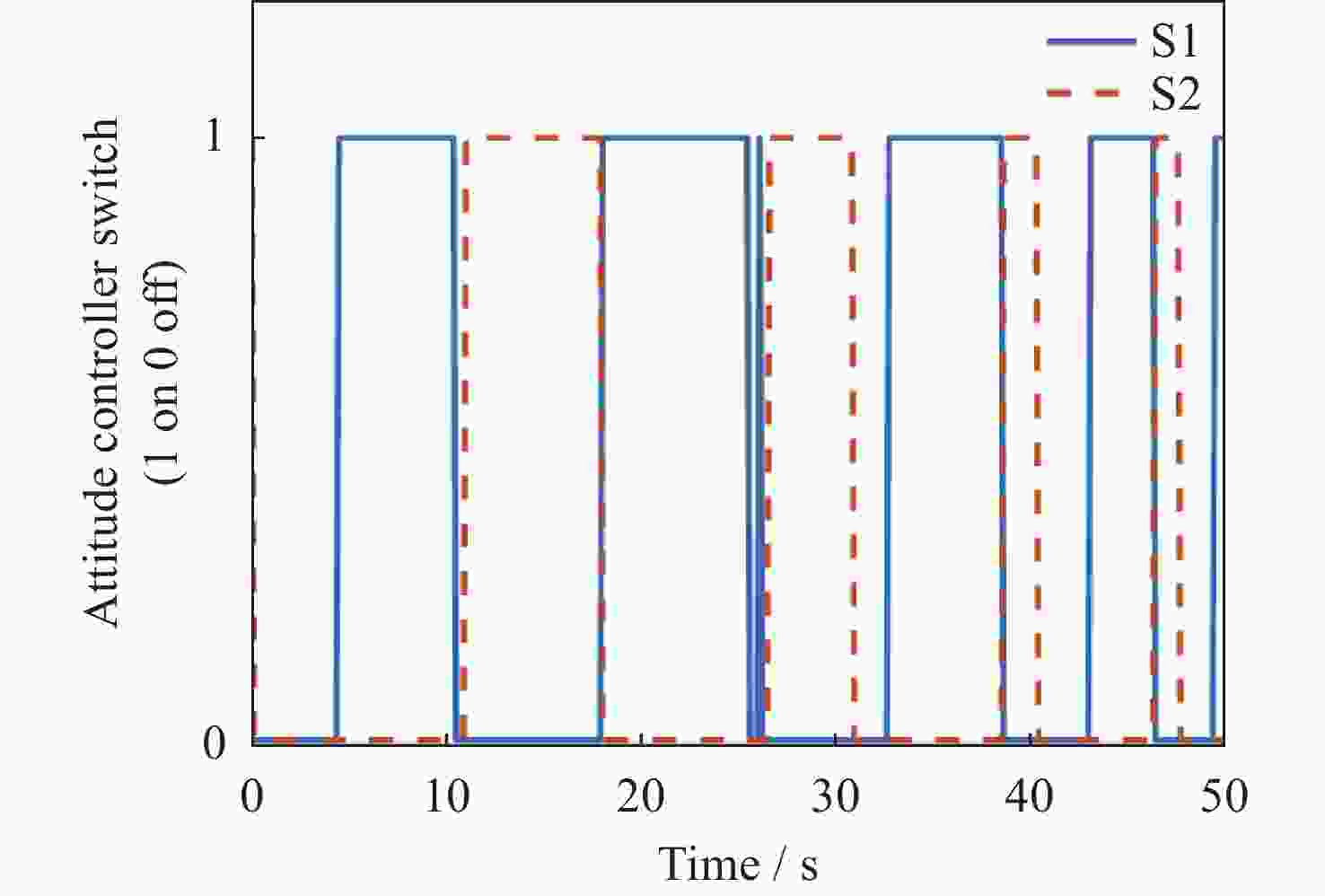
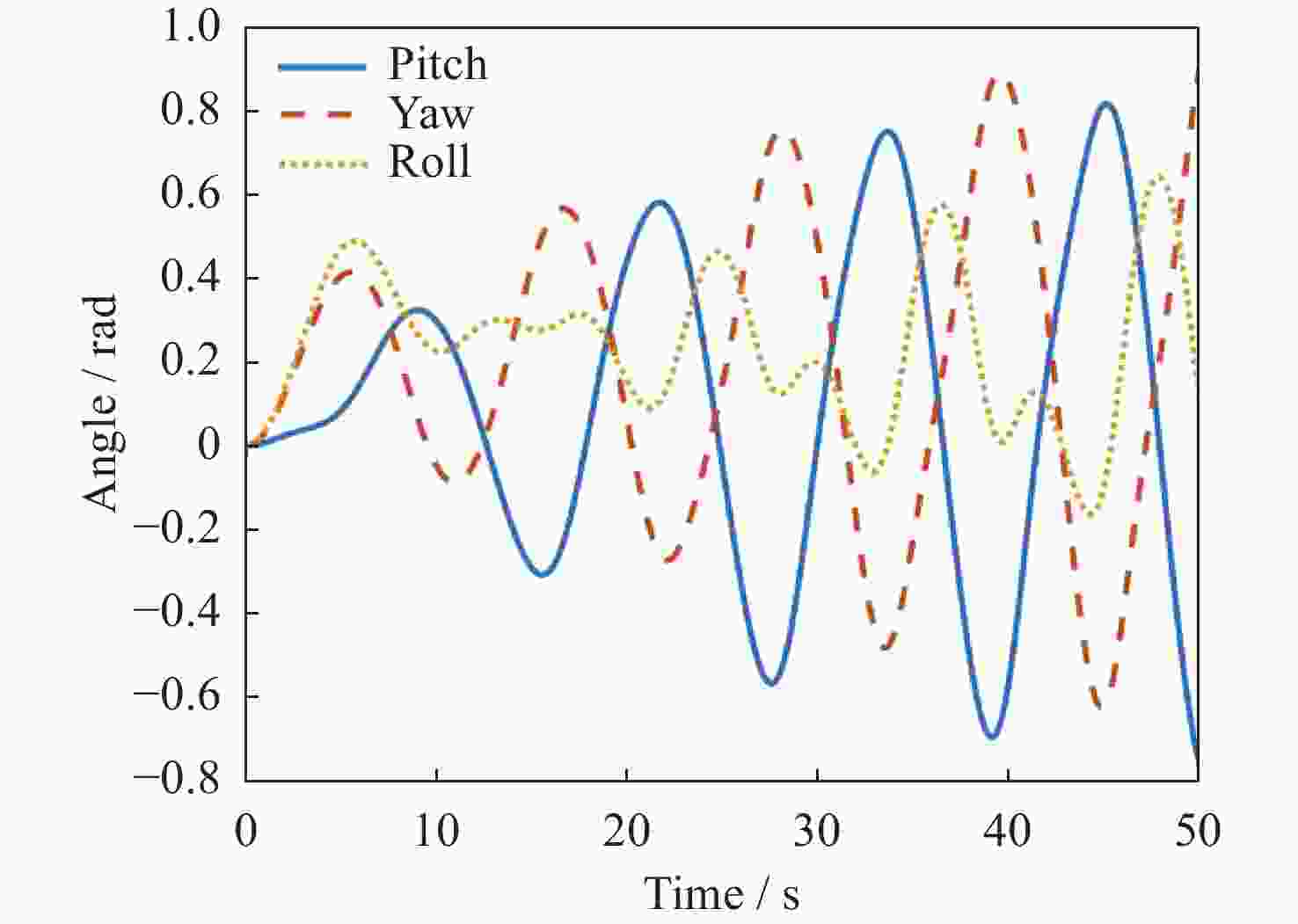
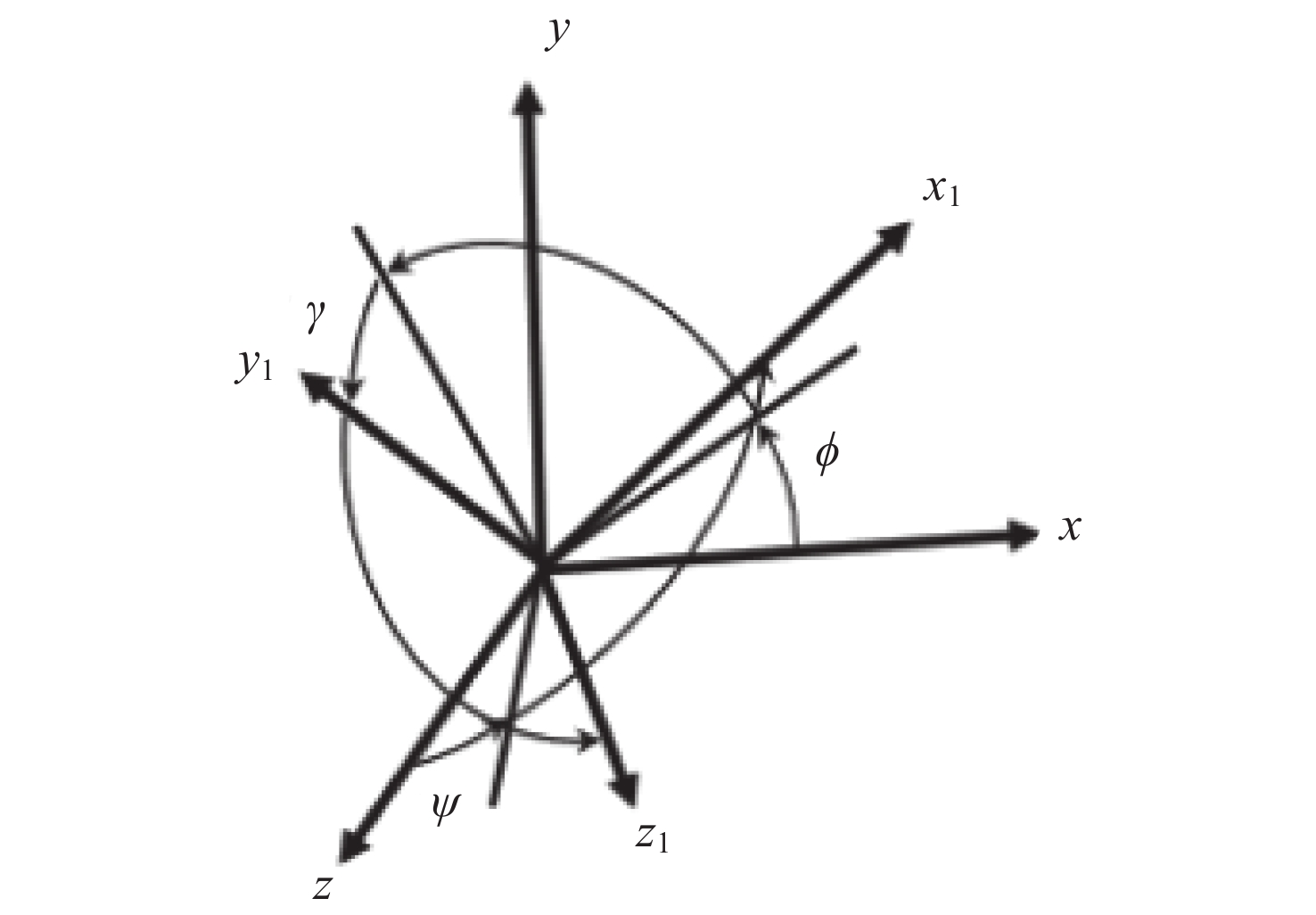
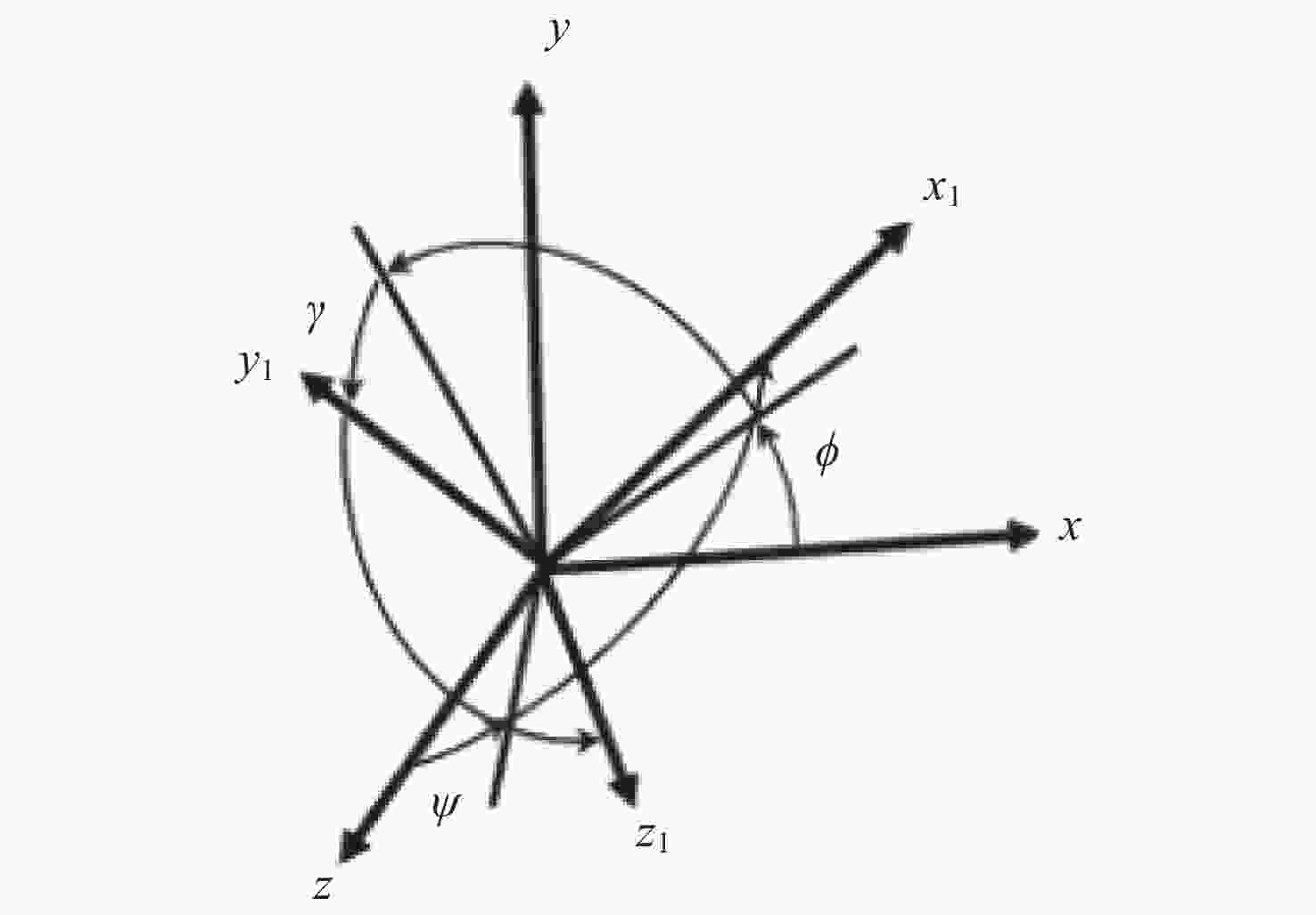
摘要: 在空间探测任务中, 探测器的姿态控制是保证各项任务完成的基础, 虽然探测器的着陆控制技术已日趋成熟, 但地外起飞阶段的姿态控制研究还相对较少. 本文设计了一种适用于深空探测器在外星不确定性环境下起飞时的模糊控制器, 通过对姿态角与角速度进行分档模糊化处理降低计算量; 建立将姿态角和角速度映射到输出力矩的模糊控制规则; 根据模糊规则输出的模糊量, 通过去模糊化得到控制器的开关状态输出, 实现对探测器姿态的快速有效控制. 利用数值仿真测试了控制器的控制效果, 以及在起飞初始姿态和发动机安装存在偏差时的鲁棒性, 在ADAMS环境下对探测器起飞过程进行物理仿真. 结果表明, 相比于经典PD控制方法在实际模型与理想模型有差别时导致的控制发散, 该控制器在参数不确定下具有更强的鲁棒性, 满足了深空探测器自主起飞时对姿态控制的需求.Abstract: In space exploration missions, attitude control is the basis to ensure the completion of various tasks, especially in the take-off and landing stage plays a key role. Although the landing control technology of the spacecraft is becoming more and more mature, the attitude control of the extraterrestrial take-off stage is still less studied. In this paper, a fuzzy controller is designed for the launch of a deep space probe in the alien uncertain environment. Firstly, the detector model used in this paper is summarized, and the attitude description method and corresponding kinematic equation are given. Then, according to the fuzzy control principle, the fuzzy control rules which map the attitude Angle and angular velocity to the output torque are established. Finally, the fuzzy attitude Angle and angular velocity are taken as the input, and the corresponding fuzzy output is obtained according to the fuzzy rule, and the switch state output of the controller engine is obtained by deblurring, so as to realize the fast and effective control of the detector attitude. Then, numerical simulation was used to test the control effect of the controller and its robustness when there is a deviation between the initial attitude and the engine installation. Finally, physical simulation of the probe take-off process was carried out in ADAMS environment combined with Simulink module. According to the above analysis and simulation, the results show that compared with the control divergence caused by the classical PD control method when the actual model is different from the ideal model, the controller has stronger robustness under parameter uncertainty, and meets the demand for attitude control during the autonomous take-off of deep space probes. This study provides an effective fuzzy control scheme for extraterrestrial liftoff, which provides a theoretical and methodological basis for further research.
-
Key words:
- Probe take-off /
- Fuzzy control /
- Uncertainty /
- Attitude control
-
表 1 姿态角误差$ {\Delta }{\boldsymbol{\phi}} $, $ {\Delta }{\boldsymbol{\psi }}$, $ {\Delta }{\boldsymbol{\gamma }}$的模糊化
Table 1. Fuzzy attitude angle error $ {\Delta }{\boldsymbol{\phi}} $, $ {\Delta }{\boldsymbol{\psi }}$, $ {\Delta }{\boldsymbol{\gamma }}$
姿态角误差 模糊控制集 论域 $ (-\mathrm{\infty },-{\theta }_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{r}}] $ NB –2 $ \left(-{\theta }_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{r}},0\right) $ NS –1 $ 0 $ ZO 0 $ \left(0,{\theta }_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{r}}\right) $ PS 1 $ \left[{\theta }_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{r}},\infty \right) $ PB 2 表 2 姿态角误差$ {\Delta }{\dot{{\boldsymbol{\theta }}}}_{z} $, $ {\Delta }{\dot{{\boldsymbol{\theta }}}}_{y} $, $ {\Delta }{\dot{{\boldsymbol{\theta }}}}_{x} $的模糊化
Table 2. Fuzzy attitude angular velocity error ${\Delta }{\dot{{\boldsymbol{\theta }}}}_{z} $, ${\Delta }{\dot{{\boldsymbol{\theta }}}}_{y} $, ${\Delta }{\dot{{\boldsymbol{\theta }}}}_{x} $
姿态角误差 模糊控制集 论域 $ \left(-\mathrm{\infty },-{\omega }_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{p}}\right] $ NB –3 $ \left(-{\omega }_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{p}},-{\omega }_{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{f}}\right] $ NM –2 $ \left(-{\omega }_{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{f}},0\right) $ NS –1 $ 0 $ ZO 0 $ \left(0,{\omega }_{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{f}}\right) $ PS 1 $ \left[{\omega }_{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{f}},{\omega }_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{p}}\right) $ PM 2 $ \left[{\omega }_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{p}},\mathrm{\infty }\right) $ PB 3 表 3 模糊规则控制表
Table 3. Fuzzy rule control table
姿态角
误差角速度误差 PB PM PS ZO NS NM NB PB PB PB PB PB PB PS NS PS B PB PB PB PS NS NS ZO PB PB PB ZO NS NS NS NS PS PS NS NS NB NB NB NB PS NS NB NB NB NB NB 表 4 探测器俯仰与偏航通道姿控发动机组合输出力矩
Table 4. Combined output torque of the attitude control engine of the detector pitch and yaw channel
启动的姿控发动机编号 $ {M}_{y} $论域 $ {M}_{z} $论域 3, 7 NB NB 4, 7 NB PS 4, 8 NB PB 7 NB NS 3 NS NS 4 NS PS 8 NS PB 3, 6 NS NB 1, 8 PS PB 6 PS NB 2 PS NS 5 PB PS 1 PS PS 2, 6 PB NB 2, 5 PB NS 1, 5 PB PB 表 5 探测器滚转通道姿控发动机组合输出力矩
Table 5. Detector roll channel attitude control engine combination output torque
启动的姿控发动机编号 $ {M}_{x} $论域 10, 12 NB 12 NS 9 PS 9, 11 PB -
[1] ZHANG Rongqiao, HUANG Jiangchuan, HE Rongwei, et al. The development overview of asteroid exploration[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2019, 6(5): 417-423,455 [2] ZHENG Wei, XU Houze, ZHONG Min, et al. Progress in international lunar exploration programs[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2012, 27(6): 2296-2307 doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.06.004 [3] HU Jianguo, SHI Yaozu, ZHAO Yi, et al. Study on take-off stability boundaries of lunar detector[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2016, 36(5): 40-47 [4] WU Weiren, YU Dengyun. Development of deep space exploration and its future key technologies[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2014, 1(1): 5-17 [5] CHEN Chao, XU Rui, LI Zhaoyu, et al. Plan repair method of deep space probe based on the expected state sequence[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(11): 1385-1395 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.11.005 [6] WANG Xin, ZHAO Qingjie, YU Chongchong, et al. Path planning method of soft landing for multi-node probe[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2022, 43(3): 366-373 [7] HUANG Wenhu, CAO Dengqing, HAN Zengyao. Advances and trends in dynamics and control of spacecrafts[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2012, 42(4): 367-394 [8] WIDNALL W S. The minimum-time thrust-vector control law in the Apollo lunar-module autopilot[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1970, 3(1): 136-153 doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)68773-1 [9] ZHANG Honghua, GUAN Yifeng, HUANG Xiangyu, et al. Guidance navigation and control for Chang’E-3 powered descent[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2014, 44(4): 377-384 doi: 10.1360/092014-43 [10] ZHANG Honghua, LI Ji, YU Ping, et al. Guidance navigation and control technology for the lunar ascent vehicle of the Chang’E-5 mission[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2021, 51(8): 921-937 doi: 10.1360/SST-2021-0102 [11] TEWARI A. Optimal nonlinear spacecraft attitude control through Hamilton-Jacobi formulation[J]. The Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 2002, 50(1): 99-112 doi: 10.1007/BF03546332 [12] LIANG Y W, XU S D, CHU T C, et al. Application of VSC reliable design to spacecraft attitude tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2005, American Control Conference, 2005. Portland: IEEE, 2005 [13] SUN Liang, HUO Wei. Satellite attitude robust nonlinear stabilization and tracking control with constrained inputs[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2011, 37(4): 24-30 [14] ZOU A M, KUMAR K D, HOU Z G. Quaternion-based adaptive output feedback attitude control of spacecraft using Chebyshev neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2010, 21(9): 1457-1471 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2050333 [15] GUAN P, LIU X J, LIU J Z. Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control for flexible satellite[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2005, 18(4): 451-459 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2004.11.003 [16] OH H S, YOON Y D, CHANG Y K, et al. Near-eigenaxis rotation control law design for moving-to-rest maneuver[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2001, 24(6): 1228-1231 doi: 10.2514/2.4840 [17] SEO D, AKELLA M R. Separation property for the rigid-body attitude tracking control problem[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2007, 30(6): 1569-1576 doi: 10.2514/1.30296 [18] ALIABBASI M, TALEBI H A, KARRARI M. A satellite attitude controller using nonlinear H∞ approach[C]//Proceedings of the 41st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, 2002. Las Vegas: IEEE, 2002 [19] SUN Duoqing. Adaptive fuzzy fault-tolerant coordinated driving control for a six-wheeled rocker-arm lunar rover[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2012, 33(1): 76-84 [20] WANG Guotao, WANG Siyi, LIANG Ansheng, et al. Research of space relay remainders-detection technique based on ADAMS[J]. Low Voltage Apparatus, 2013(3): 11-16, 54 [21] ZHANG Wei. Research on Multi-body Dynamics and Vibration Control of Spacecraft Solar Array System[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021 -
-





 杜宇 男, 1987年1月出生于吉林省长春市, 现为北京空间飞行器总体设计部总体副主任设计师, 主要研究方向为航天器总体设计. E-mail:
杜宇 男, 1987年1月出生于吉林省长春市, 现为北京空间飞行器总体设计部总体副主任设计师, 主要研究方向为航天器总体设计. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: