基于银川电离层垂测仪电子浓度反演的一次强电离层暴观测
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.05.2023-0148 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.05.2023-0148
Observation of a Strong Ionospheric Storm Based on Electron Density Inversion of Yinchuan Vertical Ionosonde
-
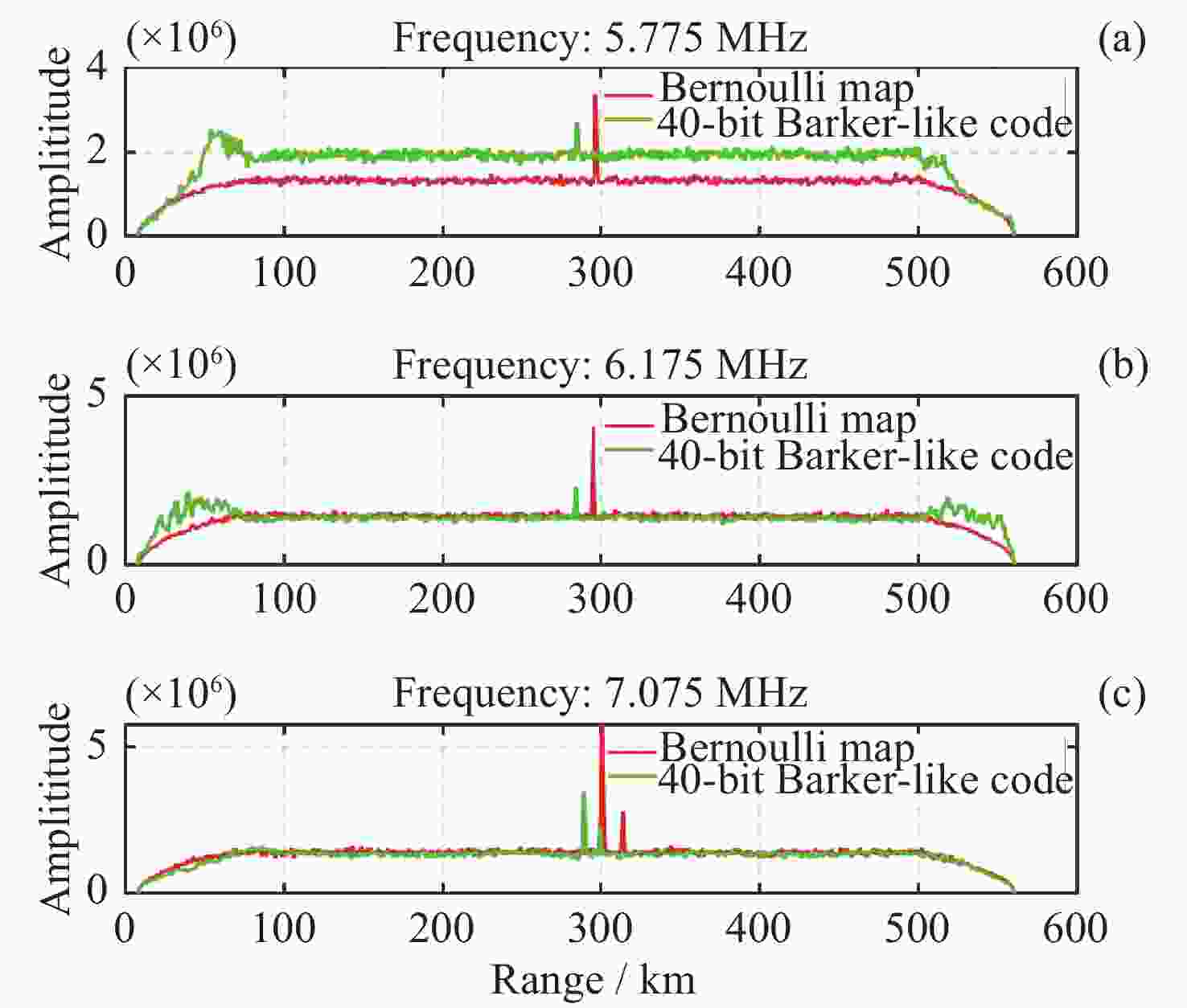
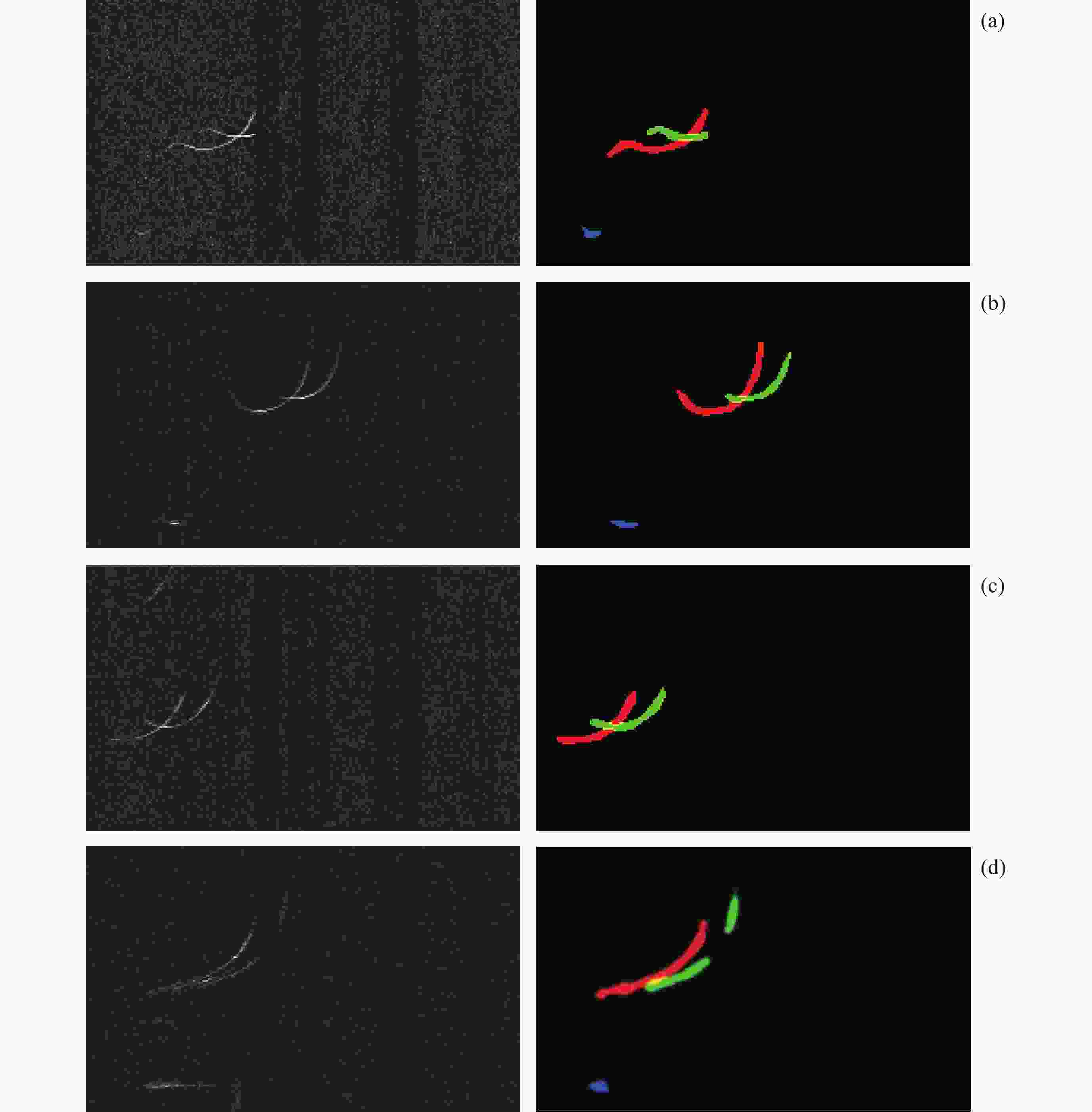
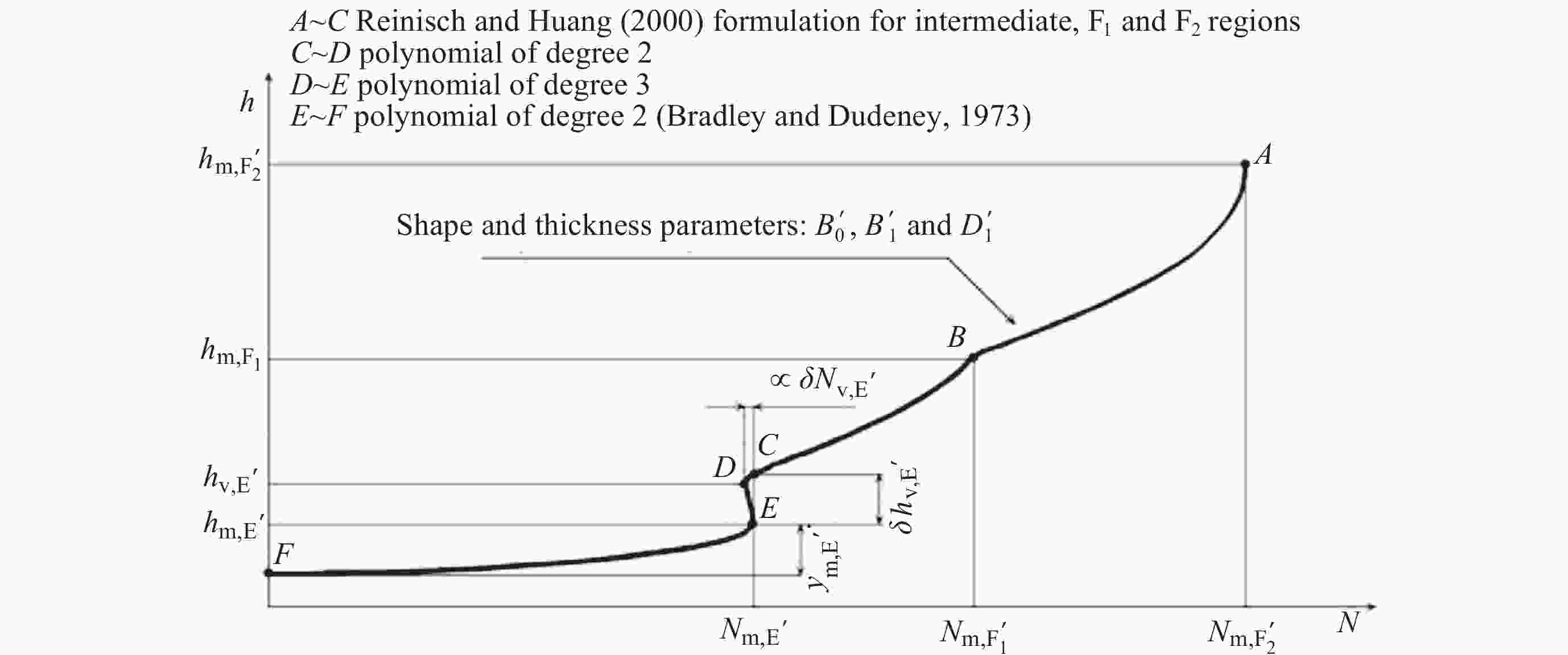
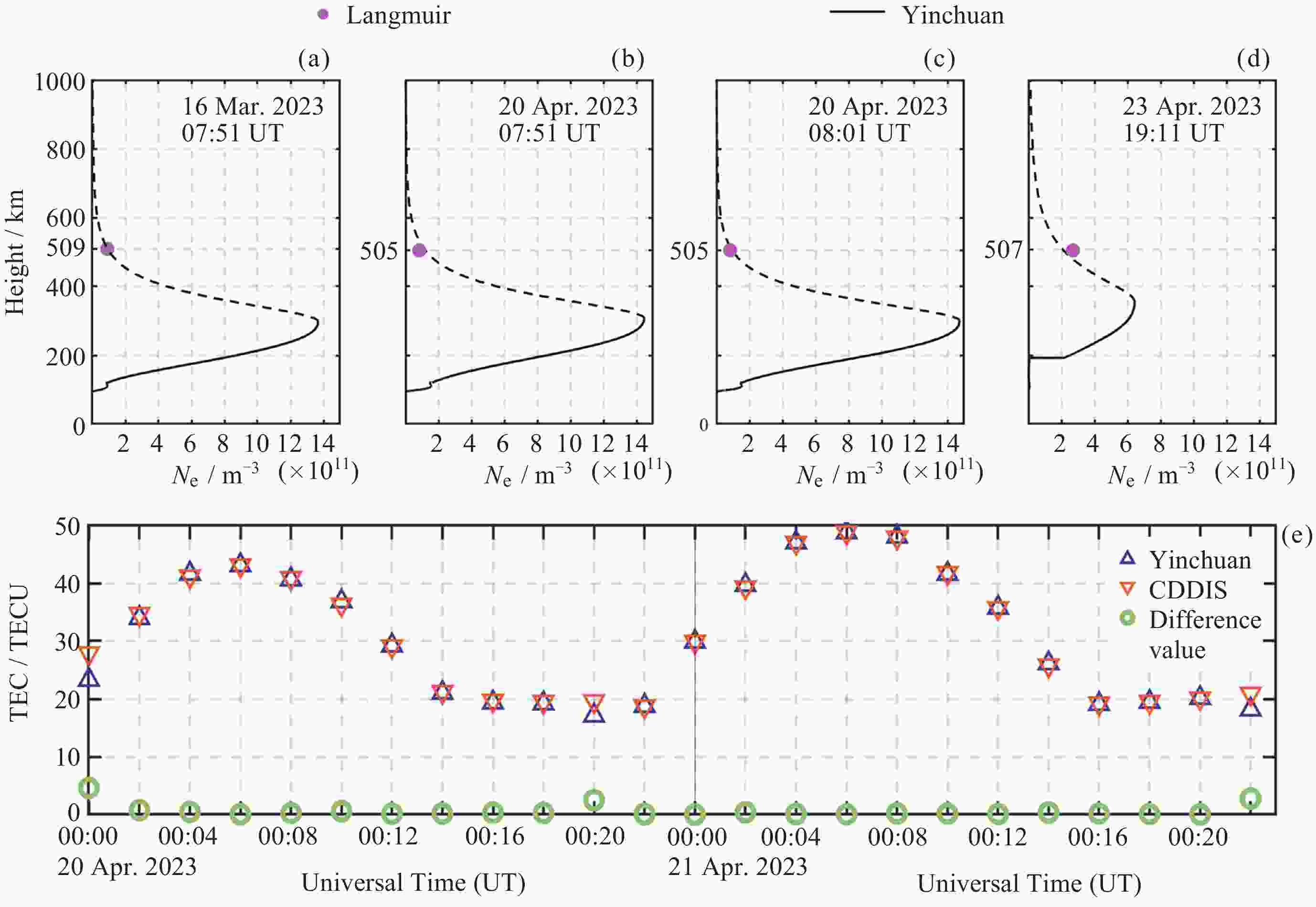
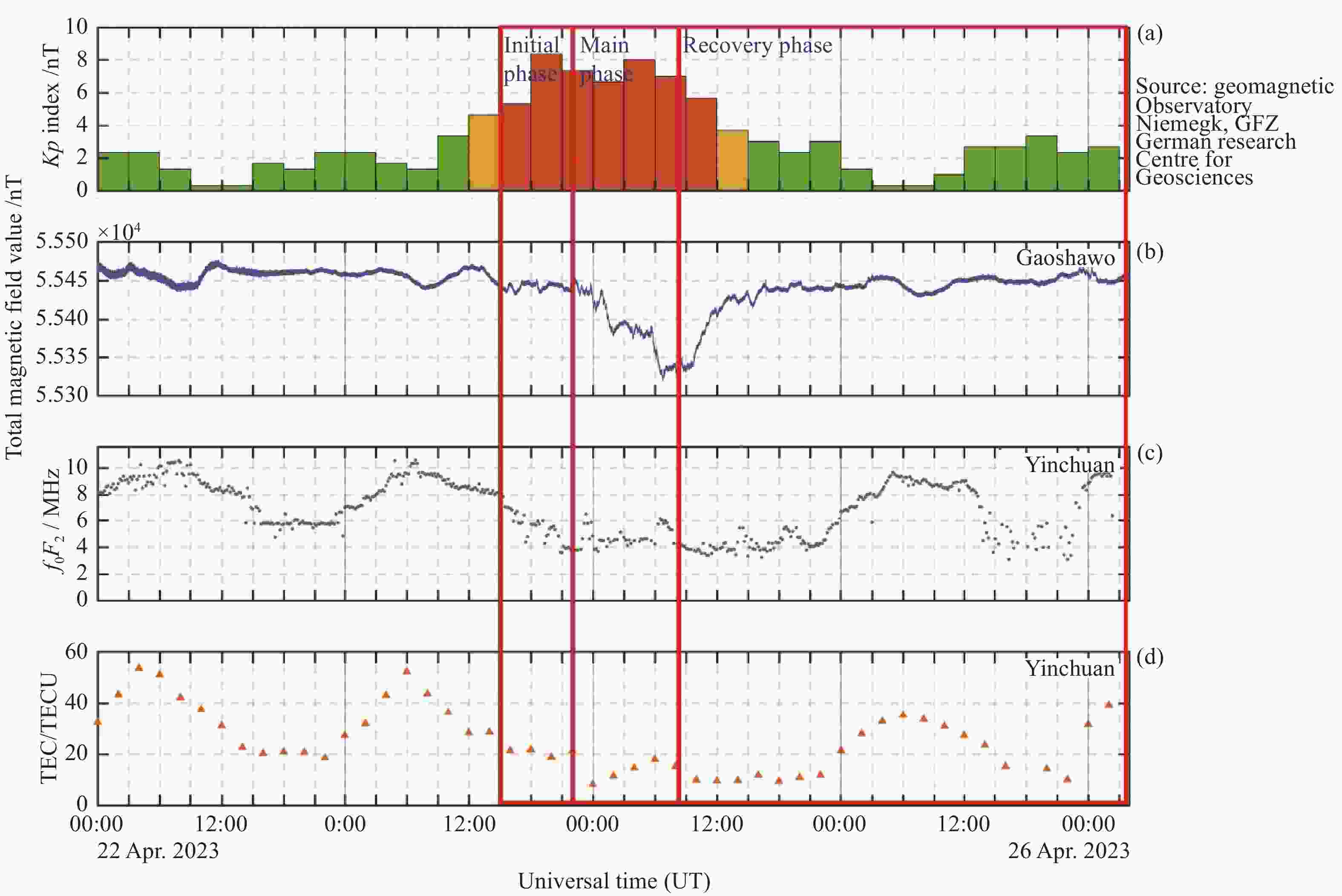
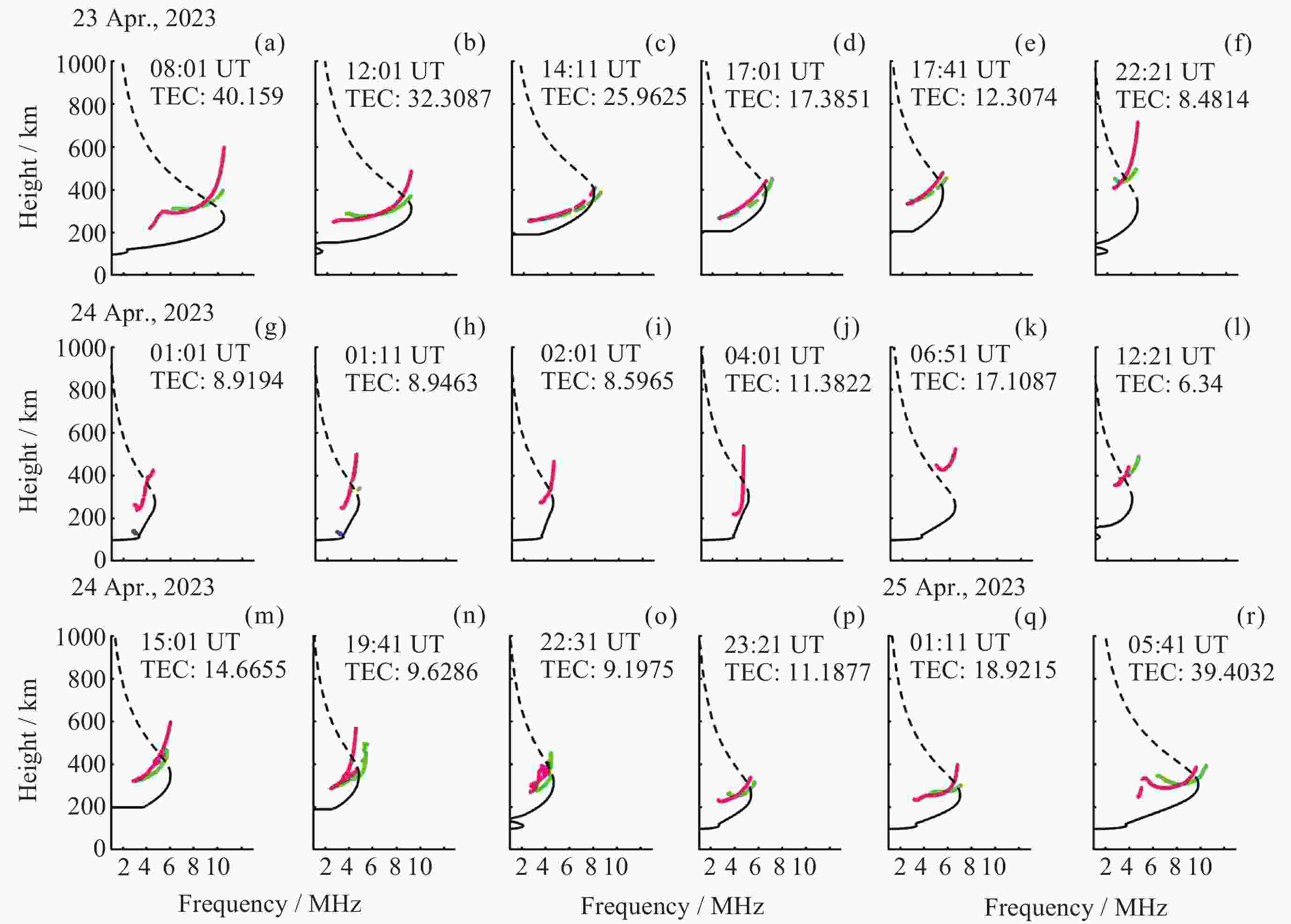
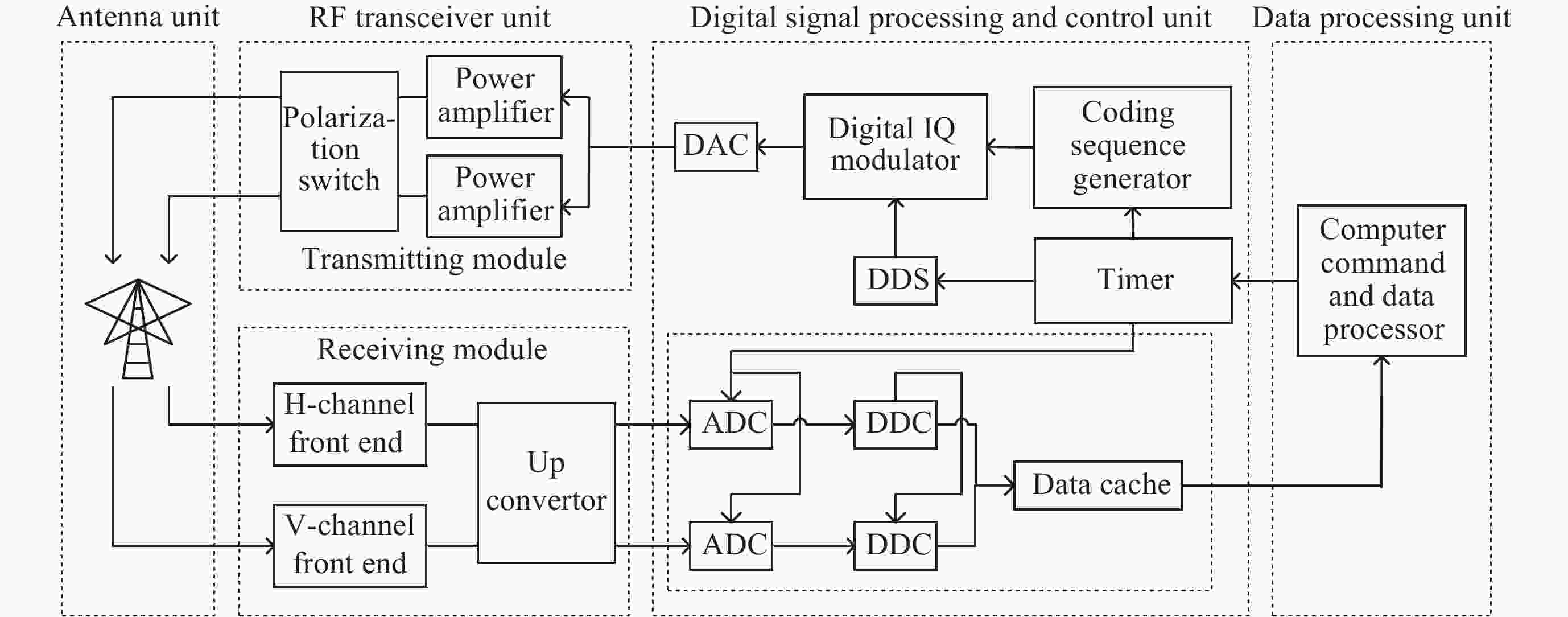
摘要: 根据银川电离层垂测仪的回波数据, 采用脉冲压缩技术, 使用Bernoulli映射序列对发射信号进行编码, 解决实际探测中回波信号混合强杂波干扰的问题, 从而获得高质量频高图. 为从图中提取电离层的关键信息, 将信号处理问题转换成计算机视觉中的语义分割任务, 构建原始频高图数据集, 并进行离散化和人工标注等预处理. 通过训练cGAN神经网络分析得到频高图中各层回波的特征参数, 达到分割不同描迹的目的. 采用改进式国际参考电离层底部反演模型和NeQuick顶部模型对垂测仪上空的电子浓度剖面进行反演, 根据张衡一号卫星的实测数据对顶部的计算结果进行修正. 通过将计算得到的总电子浓度与CDDIS公开的数据结果对比, 验证了垂测仪数据的准确性. 在此基础上, 结合高沙窝磁通门的地磁数据, 垂测仪于2023年4月23-24日的大地磁暴期间成功观测到电离层异常变化的全过程并给出了总电子浓度变化结果, 为探究中国西部电磁环境变化提供准确可靠的观测数据.Abstract: This study is based on the echo data from the Yinchuan vertical ionosonde. The ionosonde supports scanning in the frequency range from 1 to 30 MHz, with a distance resolution of 1.5 km and a reception window ranging from 67.5 km to 560.1 km. It utilizes pulse compression technology and encodes the transmission signal using Bernoulli mapping sequences, successfully resolving the issue of echo signal mixture with strong clutter interference in practical detection, thus obtaining Ionograms of high quality. In order to extract key information of ionosphere from the ionograms, the signal processing problem is transformed into a semantic segmentation task in computer vision, constructing an original ionograms dataset, and undergoing preprocessing such as discretization and manual annotation. By training a cGAN neural network to analyze the characteristic parameters of each layer’s traces in the ionograms, the goal of segmenting different traces is achieved. The network is suitable for processing various types of ionograms under calm conditions, with an accuracy rate of over 95%, effectively saving time in manual parameter measurement and improving processing efficiency. An improved bottom inversion model of the International Reference Ionosphere and the NeQuick top model is used to invert the electron density profile above the ionosonde, while the top calculation results are corrected according to the actual measurement data from “CSES-1”. By comparing the total electron content calculated with the data results publicly available from CDDIS, the accuracy of the ionosonde data is verified. On this basis, combined with the geomagnetic data acquired by the Gaoshaowo magnetometer, the ionosonde successfully observed the entire process of ionospheric anomalies during the geomagnetic storm on 23–24 April, 2023, and provided the results of the total electron content changes, offering accurate and reliable observational data for exploring the electromagnetic environment changes in western China.
-
Key words:
- Vertical ionosonde /
- Bernoulli map code /
- cGAN /
- Ionograms /
- Electron density inversion /
- Magnetic storm observation
-
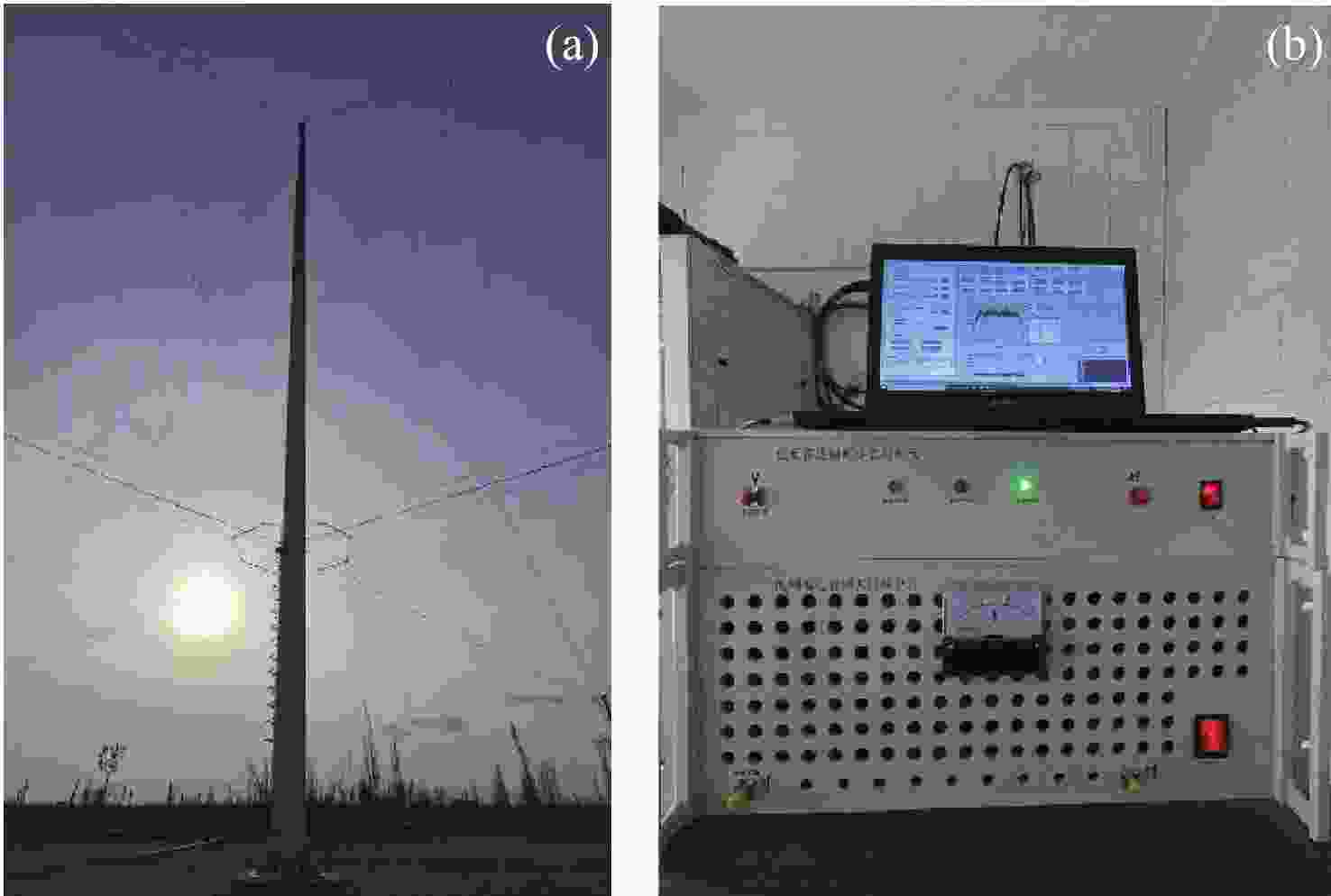
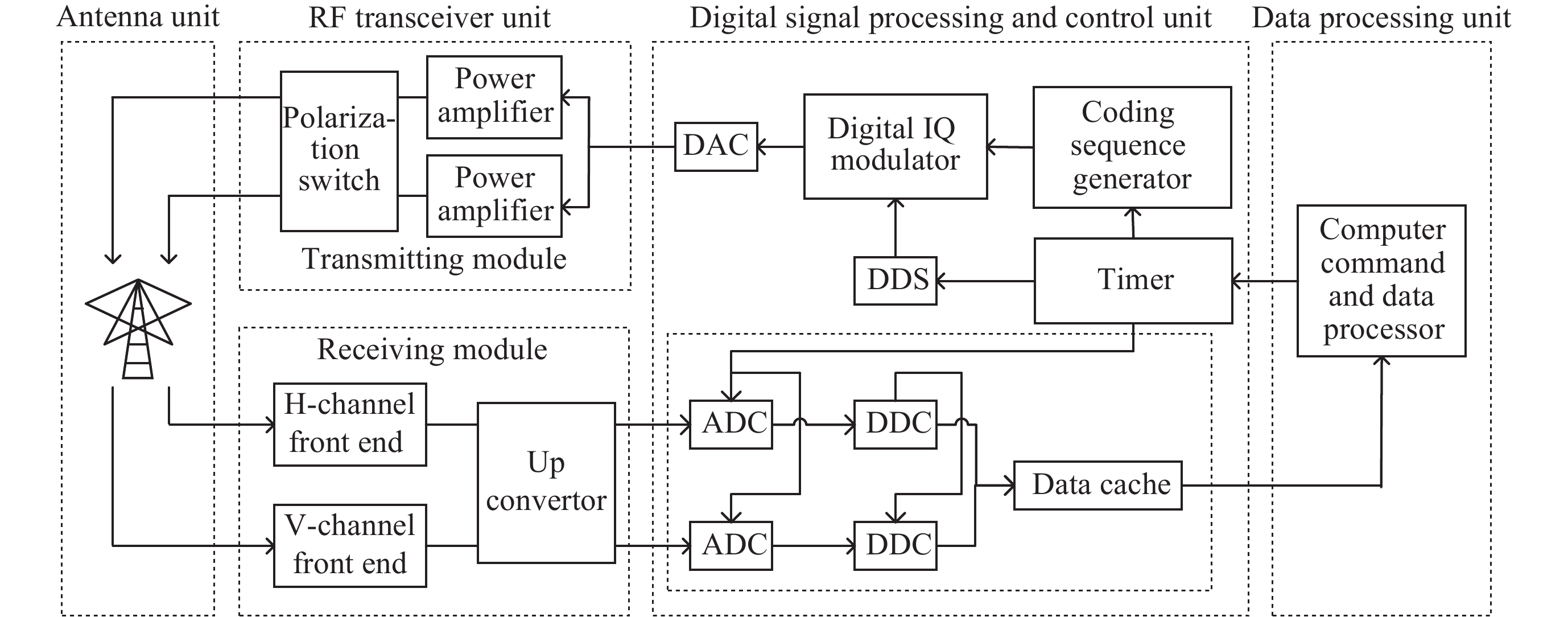
表 1 银川电离层垂测仪系统参数
Table 1. Yinchuan vertical ionosonde system parameters
指标 参数 天线 Delta天线 传输峰值功率/W 500 编码类型 40位Bernoulli序列、
类巴克码、m序列码元时宽/μs 10 工作频率/MHz 1~30 步进频率/kHz 25, 50, 100 接收机带宽/kHz 100 IF/MHz 70 ADC采样/MHz 40 相干累积次数 100 探测距离/km 67.5~560.1 距离分辨率/km 1.5 探测时长/min 7.36, 3.68, 1.84 采样间隔/min 15 -
[1] DAVIES K. Ionospheric Radio[M]. London: P. Peregrinus on Behalf of the Institution of Electrical Engineers, 1990 [2] GHEBREBRHAN O, LUCE H, YAMAMOTO M, et al. Interference suppression factor characteristics of complementary codes for ST/MST radar applications[J]. Radio Science, 2004, 39(3): RS3013 [3] XIAO Z W, WANG J, LI J, et al. Deep-learning for ionogram automatic scaling[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2020, 66(4): 942-950 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2020.05.009 [4] 刘立波, 陈一定, 乐会军, 等. “120°E子午链上空电离层响应和应用模式”一般性科技报告[J]. 科技创新导报, 2016, 13(20): 180-181LIU Libo, CHEN Yiding, YUE Huijun, et al. General aeport on “response and application models of the ionosphere over 120°E meridional chain”[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2016, 13(20): 180-181 [5] 王威, 颜毅华, 谭宝林, 等. 子午工程二期宽波段太阳射电频谱监测[J]. 地球与行星物理论评(中英文), 2024, 55(1): 1-5WANG Wei, YAN Yihua, TAN Baolin, et al. Wide-band solar radio spectral monitoring in the phase II of Chinese meridian project[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2024, 55(1): 1-5 [6] 王铮, 曹光伟, 胡连欢, 等. 子午工程二期GNSS电离层TEC与闪烁监测仪样机测试及数据对比分析[J]. 地球与行星物理论评(中英文), 2024, 55(1): 77-93WANG Zheng, CAO Guangwei, HU Lianhuan, et al. Domestic global navigation satellite system ionospheric total electron content and scintillation monitor prototype testing and data quality comparison analysis for the phase II of Chinese meridian project[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2024, 55(1): 77-93 [7] 朱正平. 电离层垂直探测中的观测模式研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院研究生院(武汉物理与数学研究所), 2006ZHU Zhengping. Studies of Observation Mode in Ionospheric Vertical Sounding[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics (WIPM) of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006 [8] SCOTTO C. A method for processing ionograms based on correlation technique[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part C: Solar, Terrestrial & Planetary Science, 2001, 26 (5): 367-371 [9] PEZZOPANE M, SCOTTO C. Automatic scaling of critical frequency f0F2 and MUF (3000)F2: a comparison between autoscala and ARTIST 4.5 on Rome data[J]. Radio Science, 2007, 42(4): RS4003 [10] PEZZOPANE M, SCOTTO C. Software for the automatic scaling of critical frequency f0F2 and MUF(3000)F2 from ionograms applied at the ionospheric observatory of Gibilmanna[J]. Annals of Geophysics, 2004, 47(6): 1783-1790 [11] 靳梦雅. 一种高性能电离层测高仪的天线设计与数控系统研制[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院国家空间科学中心), 2020JIN Mengya. Antenna Design and Digital Control System Development of a High Performance Ionosonde[D]. Beijing: National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020 [12] 靳梦雅, 郭伟, 刘鹏, 等. 基于FPGA的高性能电离层测高仪数控系统设计[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(4): 580-588 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.04.580JIN Mengya, GUO Wei, LIU Peng, et al. Design of digital control system for high-performance ionosonde based on FPGA[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(4): 580-588 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.04.580 [13] 赵港权. 银川电离层雷达回波数据处理[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院国家空间科学中心), 2022ZHAO Gangquan. Ionospheric Radar Echo Data Processing in Yinchuan Area[D]. Beijing: National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022 [14] 赵港权, 王彩云, 刘大鹏, 等. 低功耗电离层垂测仪系统及在银川地区的试验[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(4): 618-626 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.04.220127011ZHAO Gangquan, WANG Caiyun, LIU Dapeng, et al. Development of a low-power ionosonde in Yinchuan and analysis of preliminary test results[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(4): 618-626 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.04.220127011 [15] HAN S J, GUO W, LIU P, et al. Chaotic coding for interference suppression of digital ionosonde[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(15): 3747 doi: 10.3390/rs15153747 [16] LIU C, GUAN Y B, ZHENG X Z, et al. The technology of space plasma in-situ measurement on the China seismo-electromagnetic satellite[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2019, 62(5): 829-838 doi: 10.1007/s11431-018-9345-8 [17] PEZZOPANE M, PIGNALBERI A. The ESA swarm mission to help ionospheric modeling: a new NeQuick topside formulation for mid-latitude regions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 12253 doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48440-6 [18] SCOTTO C. Electron density profile calculation technique for Autoscala ionogram analysis[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2009, 44(6): 756-766 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2009.04.037 [19] 王华旭, 郭文玲, 蔚娜, 等. 电离层垂直剖面建模方法改进研究[J]. 电波科学学报, 2017, 32(1): 73-78WANG Huaxu, GUO Wenling, WEI Na, et al. The method improvement of ionospheric vertical profile model[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2017, 32(1): 73-78 [20] 泽仁志玛, 刘大鹏, 孙晓英, 等. 张衡一号电磁卫星在轨情况及主要的科学成果[J]. 地球与行星物理论评(中英文), 2023, 54(4): 455-465ZEREN Zhima, LIU Dapeng, SUN Xiaoying, et al. Current status and scientific progress of the Zhangheng-1 satellite mission[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2023, 54(4): 455-465 [21] TSMOTS I, RIZNYK O, RABYK V, et al. Implementation of FPGA-based barker’s-like codes[C]//Proceedings of the XV International Scientific Conference “Intellectual Systems of Decision Making and Problems of Computational Intelligence”. Cham: Springer, 2020: 203-214 [22] 孙直申, 刘小军, 赵博. 互补码在电离层探测中的应用[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2011, 11(21): 5047-5052SUN Zhishen, LIU Xiaojun, ZHAO Bo. Application of complementary codes in ionosphere sounding[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2011, 11(21): 5047-5052 [23] LIU T X, YANG G B, HU Y G, et al. A novel ionospheric sounding network based on complete complementary code and its application[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(4): 779 doi: 10.3390/s19040779 [24] BOSTAN S M, URBINA J V, MATHEWS J D, et al. An HF software‐defined radar to study the ionosphere[J]. Radio Science, 2019, 54(9): 839-849 doi: 10.1029/2018RS006773 [25] SEMETER J, BUTLER T, HEINSELMAN C, et al. Volumetric imaging of the auroral ionosphere: initial results from PFISR[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2009, 71(6/7): 738-743 [26] LI J, LIU M, OU J P, et al. A novel radar waveform design for suppressing autocorrelation side-lobe based on chaotic and single fusion encoding method[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research M, 2022, 111: 77-88 doi: 10.2528/PIERM22042202 [27] 陈锟. 电离层数字测高仪的研制[D]. 武汉: 中南民族大学, 2009CHEN Kun. Design of the Ionosonde[D]. Wuhan: South-Central Minzu University, 2009 [28] 王顺, 陈紫微, 张锋, 等. 一种数字电离层测高仪系统中O波与X波的分离方法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2014, 34(2): 186-193 doi: 10.11728/cjss2014.02.186WANG Shun, CHEN Ziwei, ZHANG Feng, et al. A method for separating O wave and X wave in digital ionosonde[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2014, 34(2): 186-193 doi: 10.11728/cjss2014.02.186 [29] 徐高峰. 基于图像处理的电离层垂测频高图参数提取方法的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014XU Gaofeng. Study on Parameters Extraction in Ionogram Based on Image Processing[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014 [30] 卢红光. 基于图像处理的垂测频高图E、Es层描迹自动判读研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013LU Hongguang. Study on Automatic Scaling of E, Es in Ionogram Based on Image Processing[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2013 [31] REINISCH B W, HUANG X Q. Low latitude digisonde measurements and comparison with IRI[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1996, 18(6): 5-12 doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(95)00892-6 [32] HUANG X Q, REINISCH B W. Vertical electron density profiles from the Digisonde network[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1996, 18(6): 121-129 doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(95)00912-4 [33] HUANG H, MOSES M, VOLK A E, et al. Assessment of IRI-2016 f0F2 and hmF2 model options with digisonde, COSMIC and ISR observations for low and high solar flux conditions[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 68(5): 2093-2103 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.01.033 [34] BILITZA D, PEZZOPANE M, TRUHLIK V, et al. The international reference ionosphere model: a review and description of an ionospheric benchmark[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2022, 60(4): e2022RG000792 doi: 10.1029/2022RG000792 [35] EZQUER R G, SCIDÁ L A, MIGOYA ORUÉ Y O, et al. NeQuick 2 total electron content predictions for middle lati-tudes of north American region during a deep solar mini-mum[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2017, 154: 55-66 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2016.12.014 [36] WATANABE S, MIYOSHI Y, TSUCHIYA F, et al. Modeling of topside ionosphere and plasmasphere[J]. Research Square, 2021 [37] MARINOV P, KUTIEV I, BELEHAKI A, et al. Modeling the plasmasphere to topside ionosphere scale height ratio[J]. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2015, 5: A27 doi: 10.1051/swsc/2015028 [38] SCOTTO C, SABBAGH D. Improvements in bottomside electron density definition in the autoscala program[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2020, 65(5): 1432-1438 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2019.12.004 [39] SCOTTO C, SABBAGH D, IPPOLITO A. Accuracy of hmF2 estimations, including IRI-2020 options and ionograms validated parameters, compared to ISR measurements at Millstone Hill[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 72(8): 3202-3211 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2023.07.012 [40] SCOTTO C, RADICELLA S M, ZOLESI B. An improved probability function to predict the F1 layer occurrence and L condition[J]. Radio Science, 1998, 33(6): 1763-1765 doi: 10.1029/98RS02637 [41] NAVA B, COÏSSON P, RADICELLA S M. A new version of the NeQuick ionosphere electron density model[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2008, 70(15): 1856-1862 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2008.01.015 [42] PIGNALBERI A, PEZZOPANE M, ALBERTI T, et al. Modeling the topside ionosphere effective scale height through in situ electron density observations by low-earth-orbit satellites[J]. Universe, 2023, 9(6): 280 doi: 10.3390/universe9060280 [43] YAN R, GUAN Y B, SHEN X H, et al. The Langmuir probe onboard CSES: data inversion analysis method and first results[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2018, 2(6): 479-488 [44] 孙晓英, 段素平, 刘维宁. 第23太阳活动周太阳极紫外辐射与磁暴相关性分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(5): 697-703 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.05.697SUN Xiaoying, DUAN Suping, LIU Weining. Correlation analysis between magnetic storms and solar extreme ultraviolet radiation during the 23rd solar cycle[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(5): 697-703 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.05.697 [45] ARSLAN TARIQ M, LIU L B, SHAH M, et al. Longitudinal variations of ionospheric responses to the February and April 2023 geomagnetic storms over American and Asian sectors[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2024, 73(6): 3033-3049 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2023.12.039 [46] 熊年禄, 唐存琛, 李行健. 电离层物理概论[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 1999XIONG Nianlu, TANG Cunchen, LI Xingjian. Introduction to Ionospheric Physics[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Press, 1999 -
-





 韩思佳 女, 1994年12月出生于内蒙古自治区包头市. 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心在读博士研究生, 主要研究方向为电离层探测技术、电子浓度反演等. E-mail:
韩思佳 女, 1994年12月出生于内蒙古自治区包头市. 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心在读博士研究生, 主要研究方向为电离层探测技术、电子浓度反演等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: