空间引力波探测无拖曳卫星有限频域抗扰控制器设计
doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.05.2024-0022 cstr: 32142.14.cjss2024.05.2024-0022
Design of Finite Frequency Domain Disturbance Rejection Controller for the Drag-free Spacecraft in Space-borne Gravitational Wave Detection
-
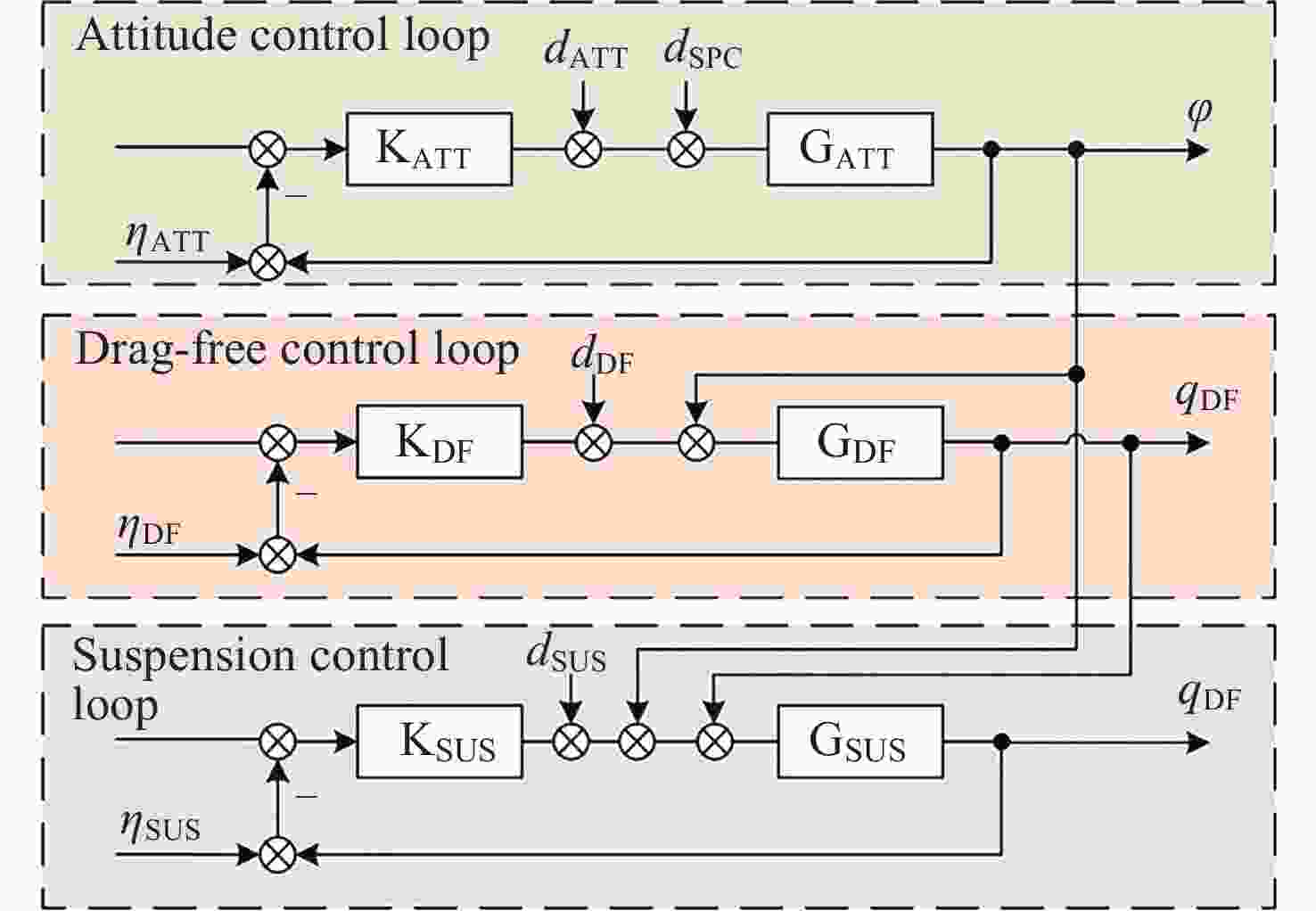
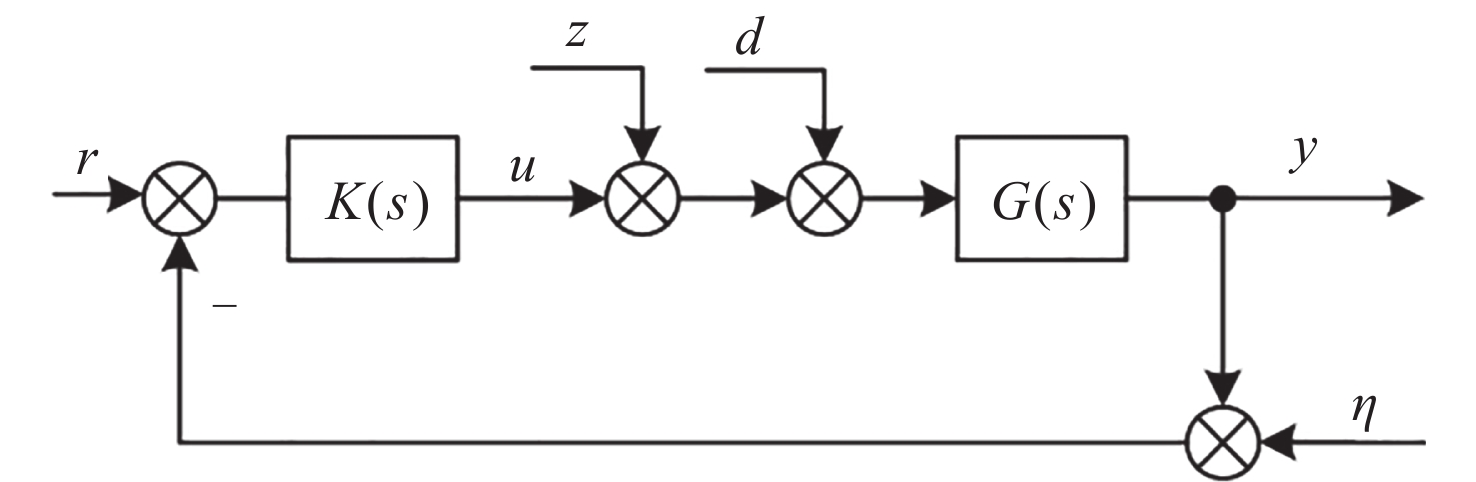
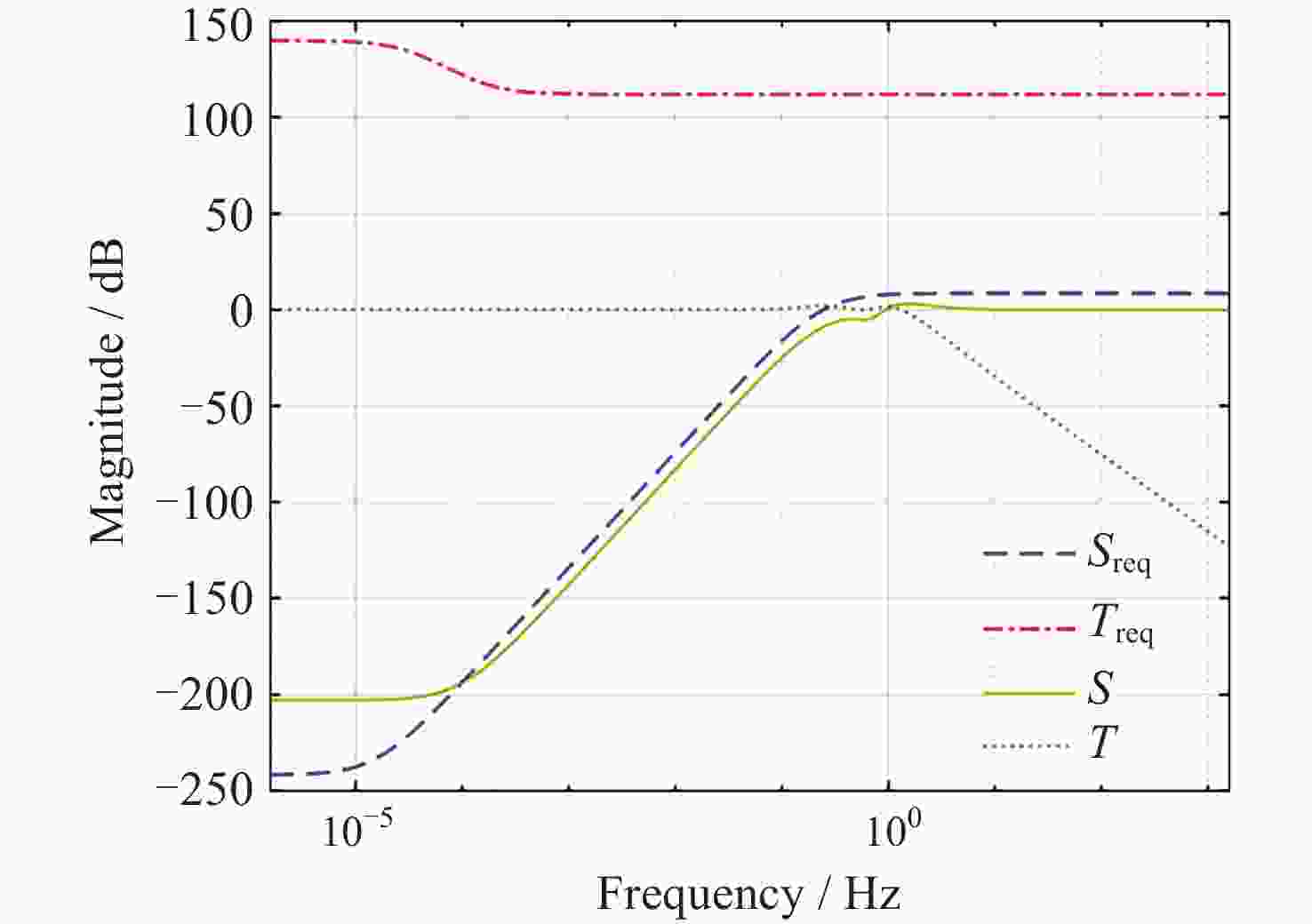
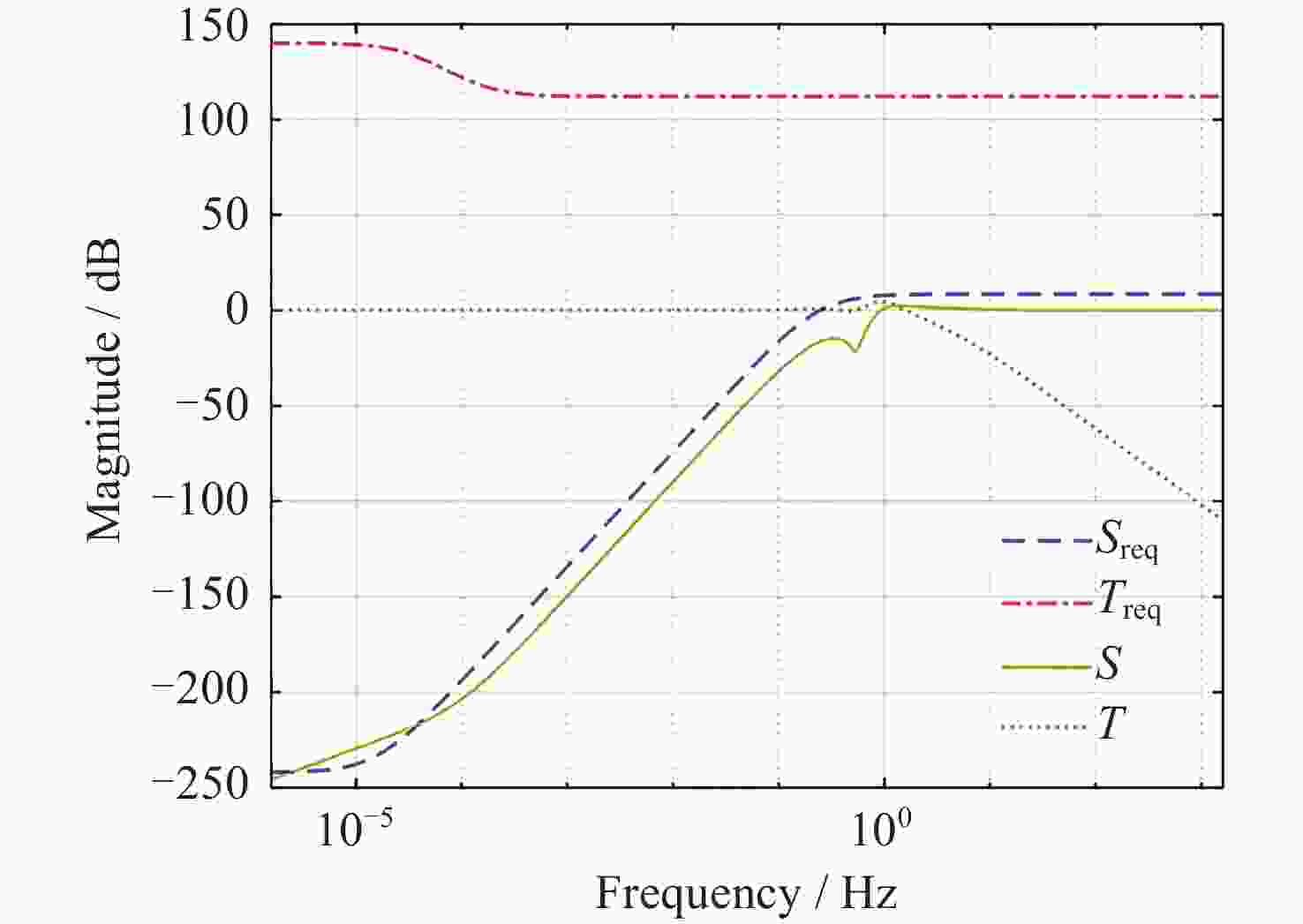
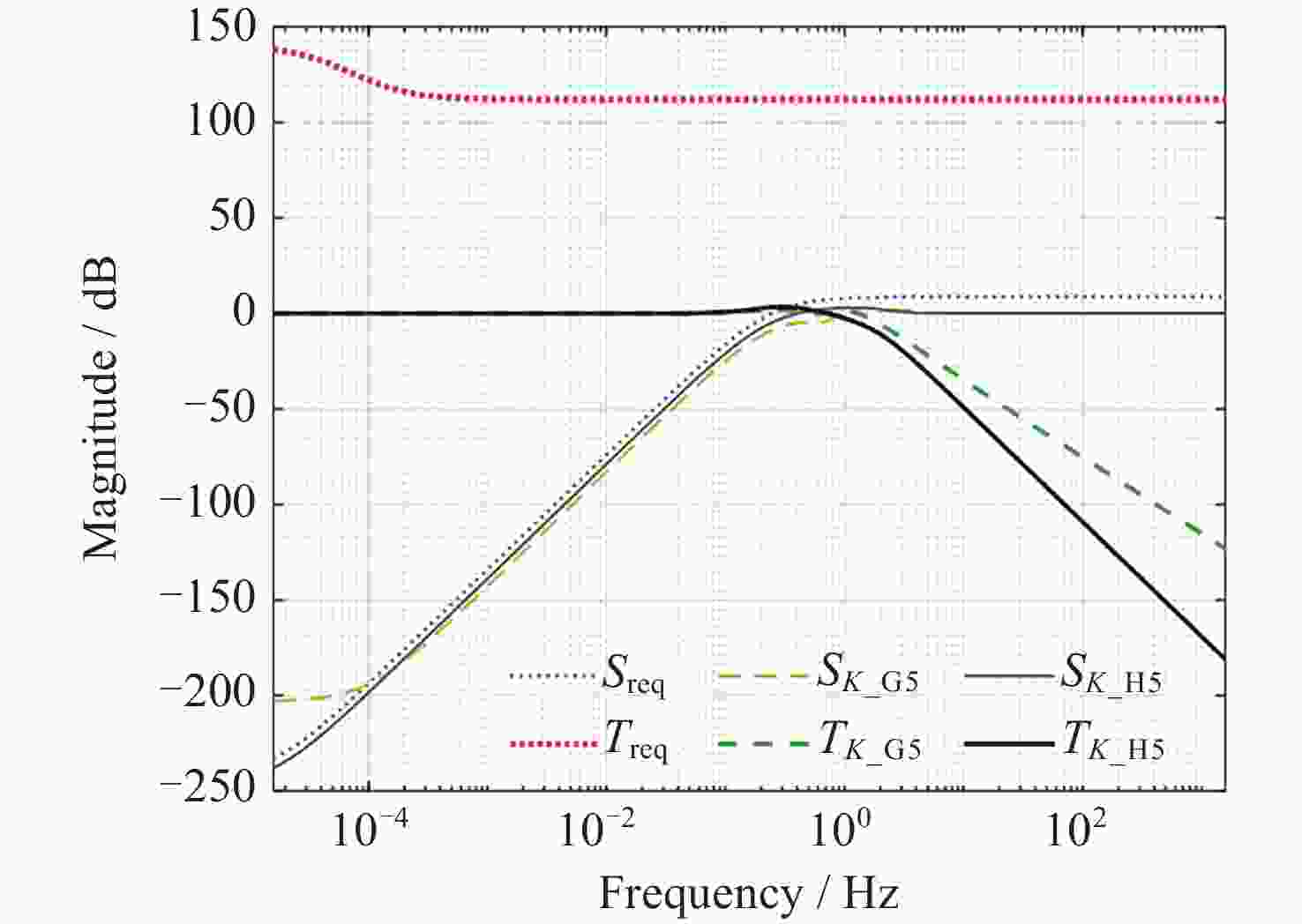
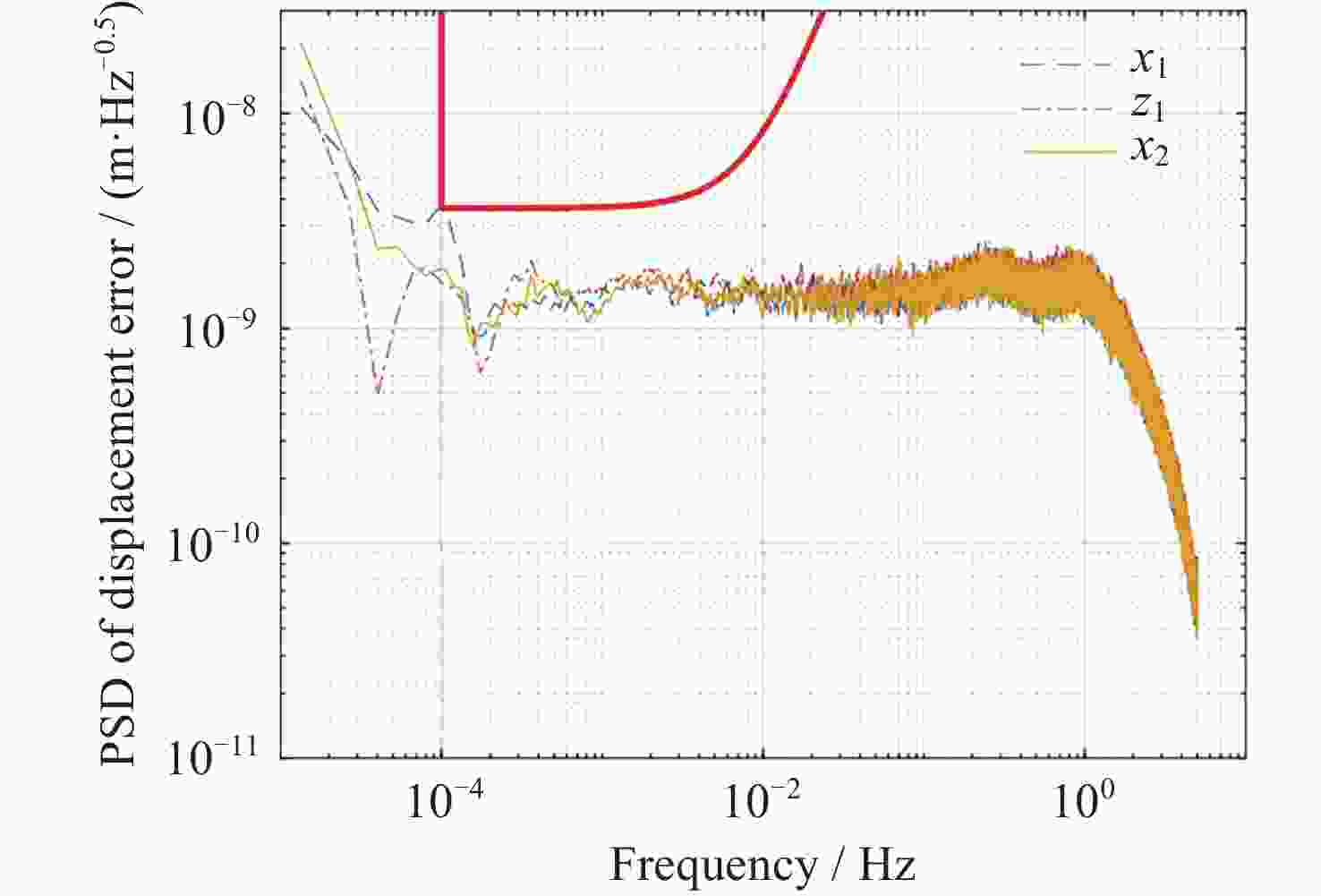
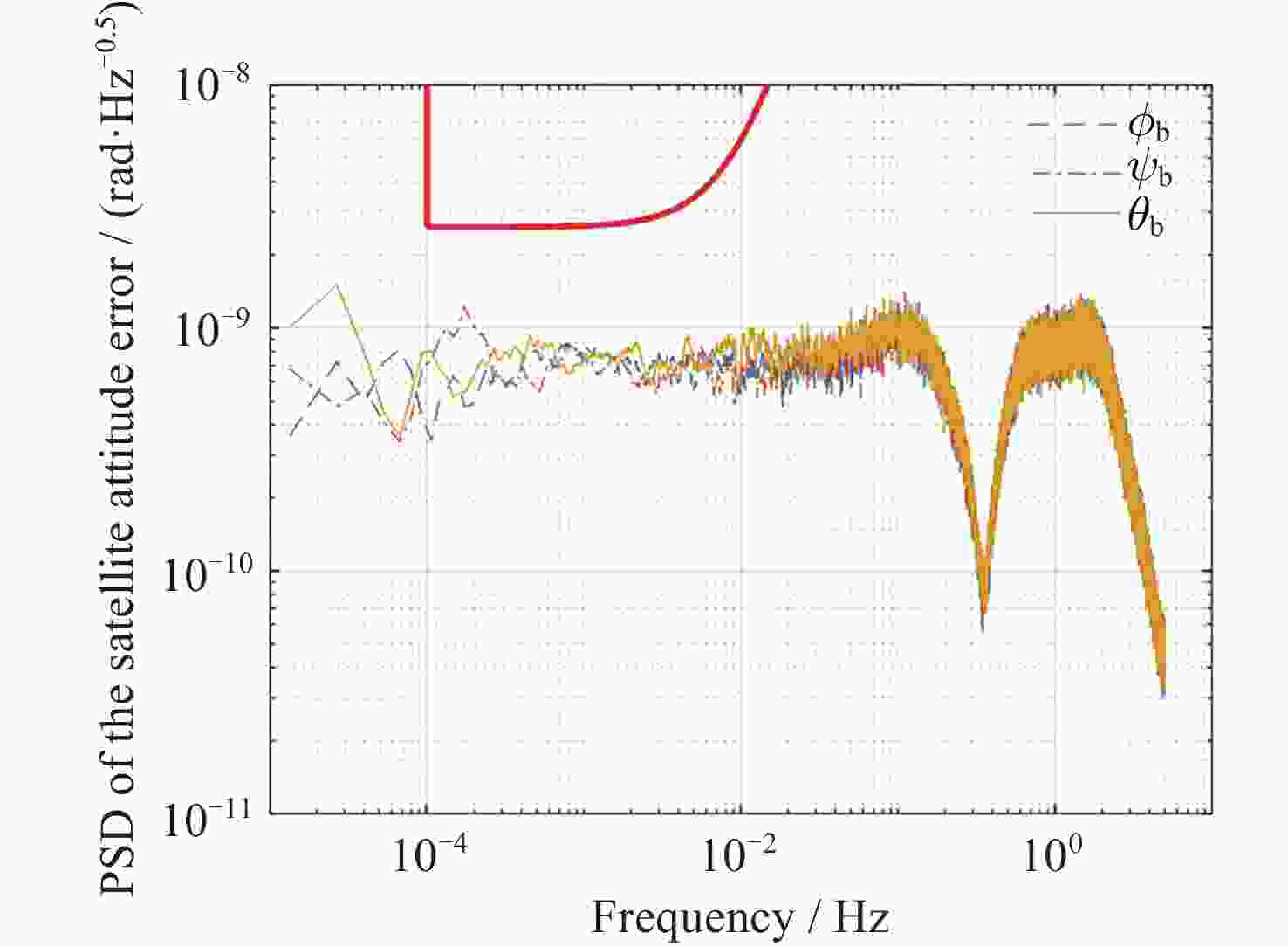
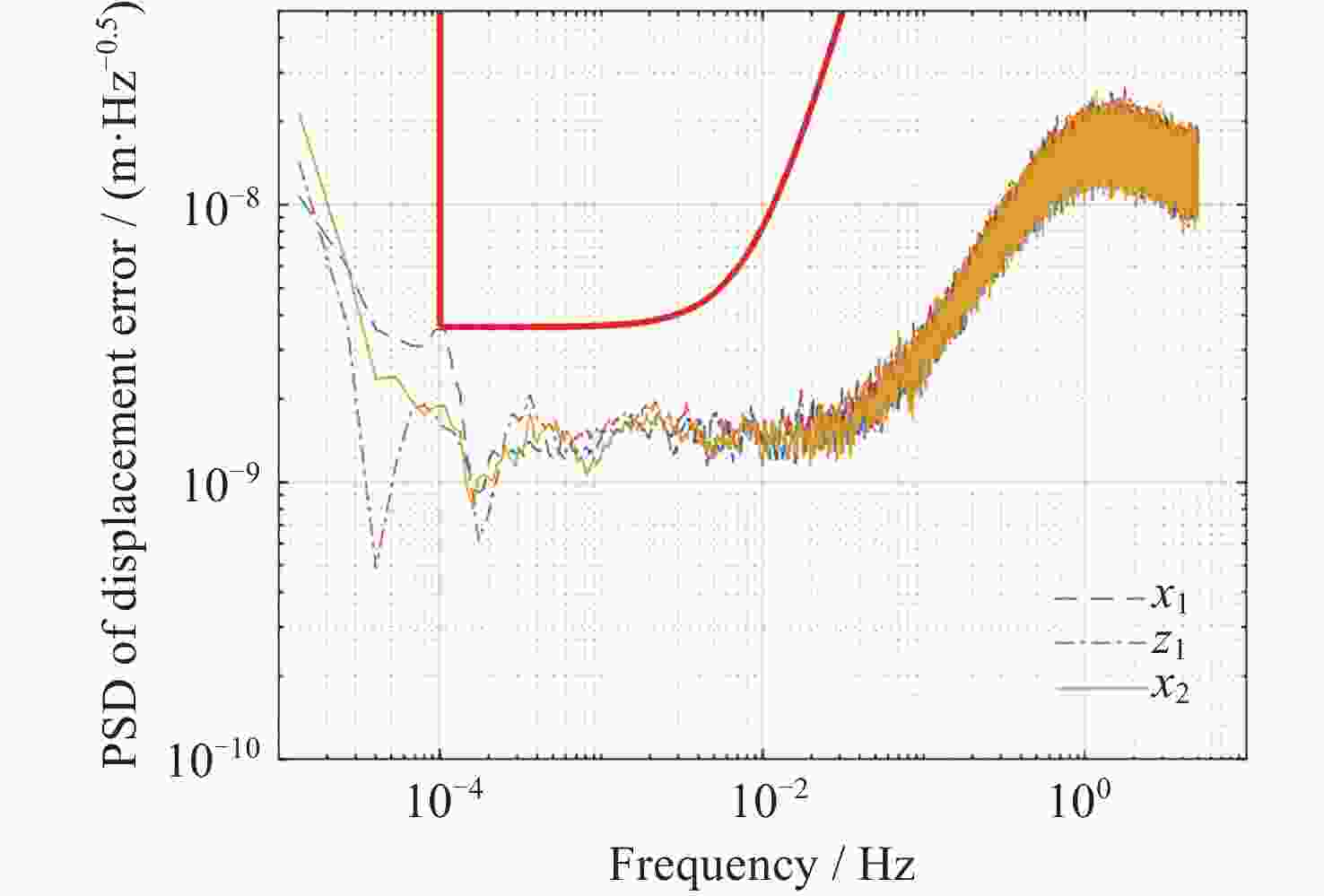
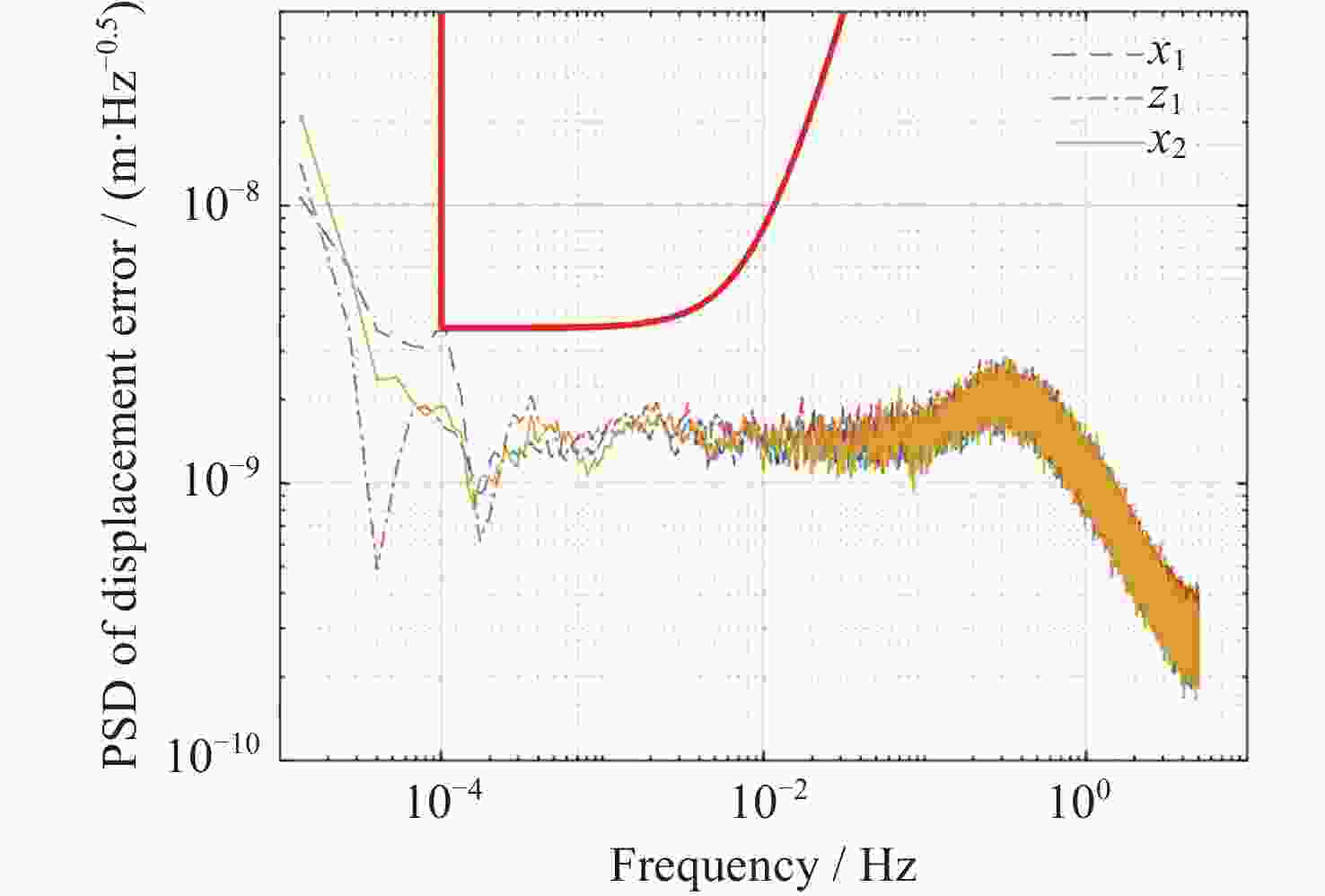
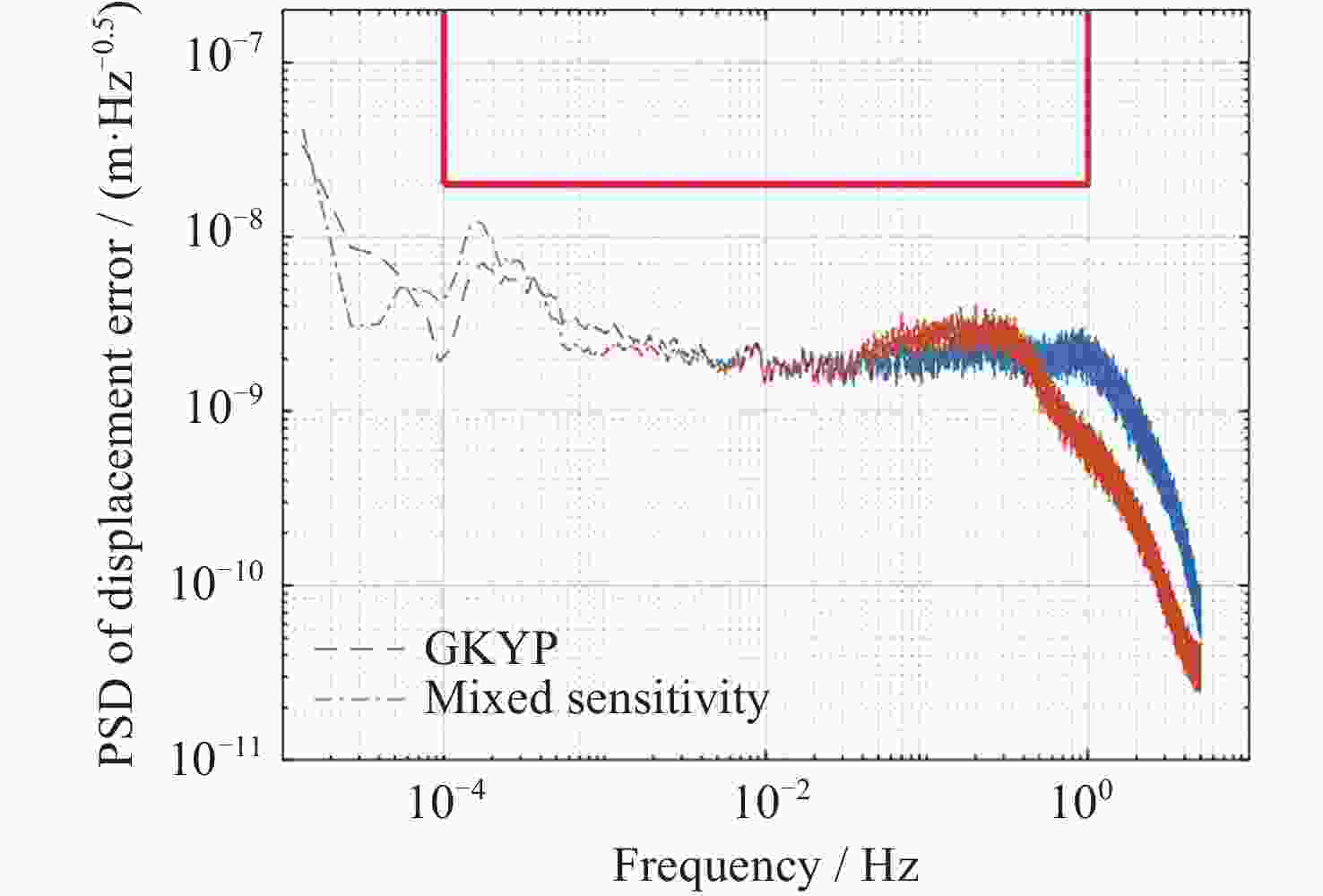
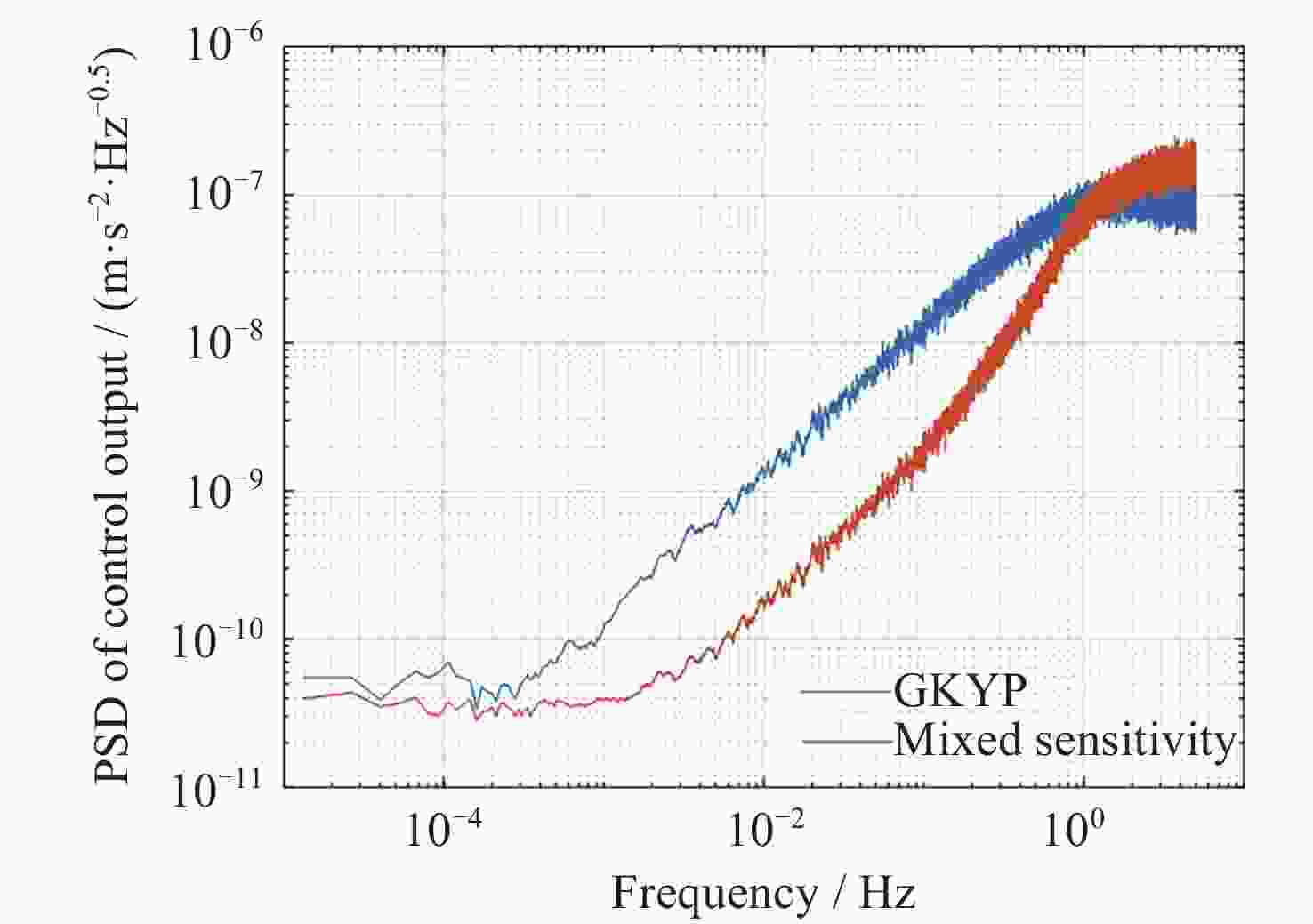
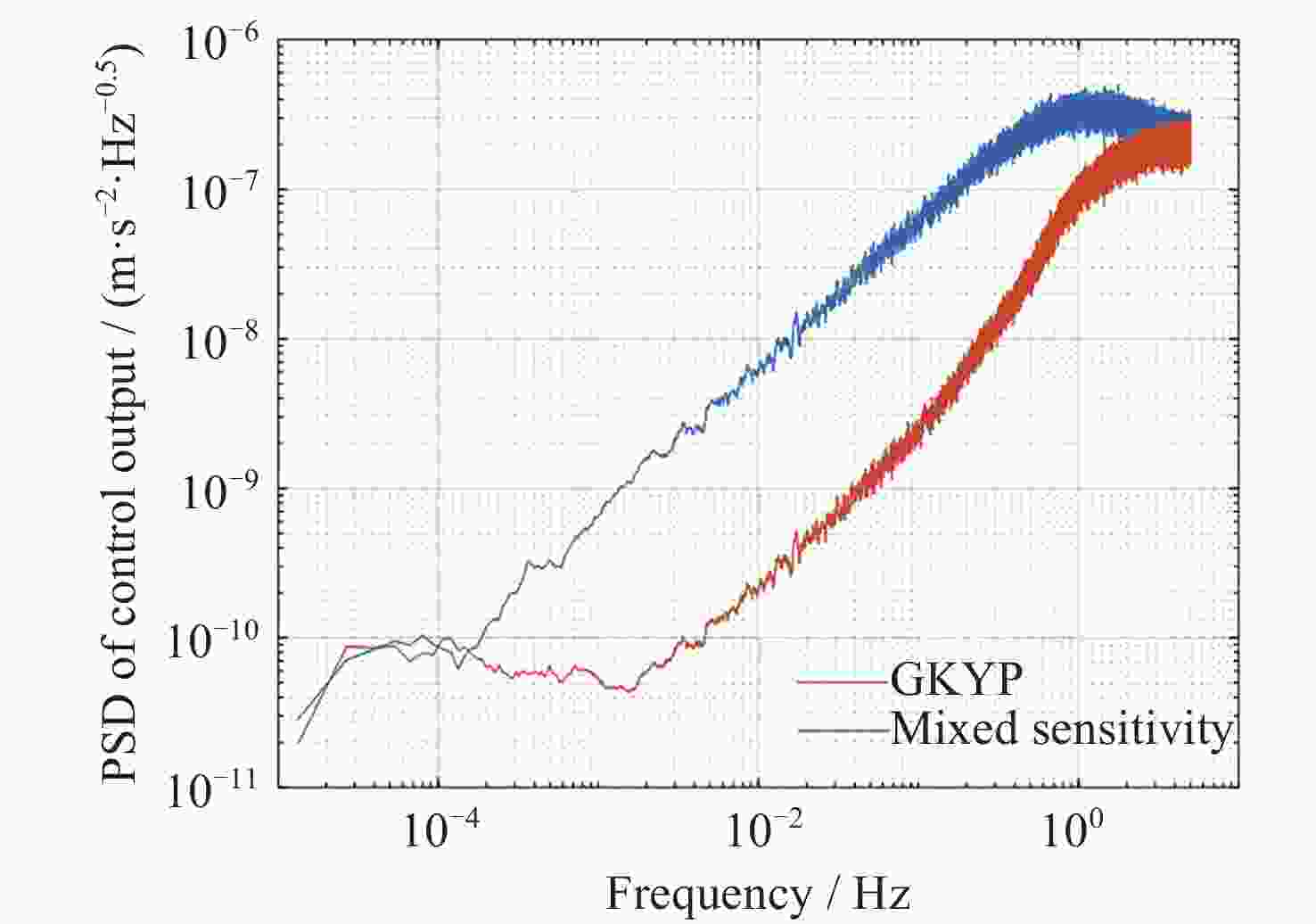
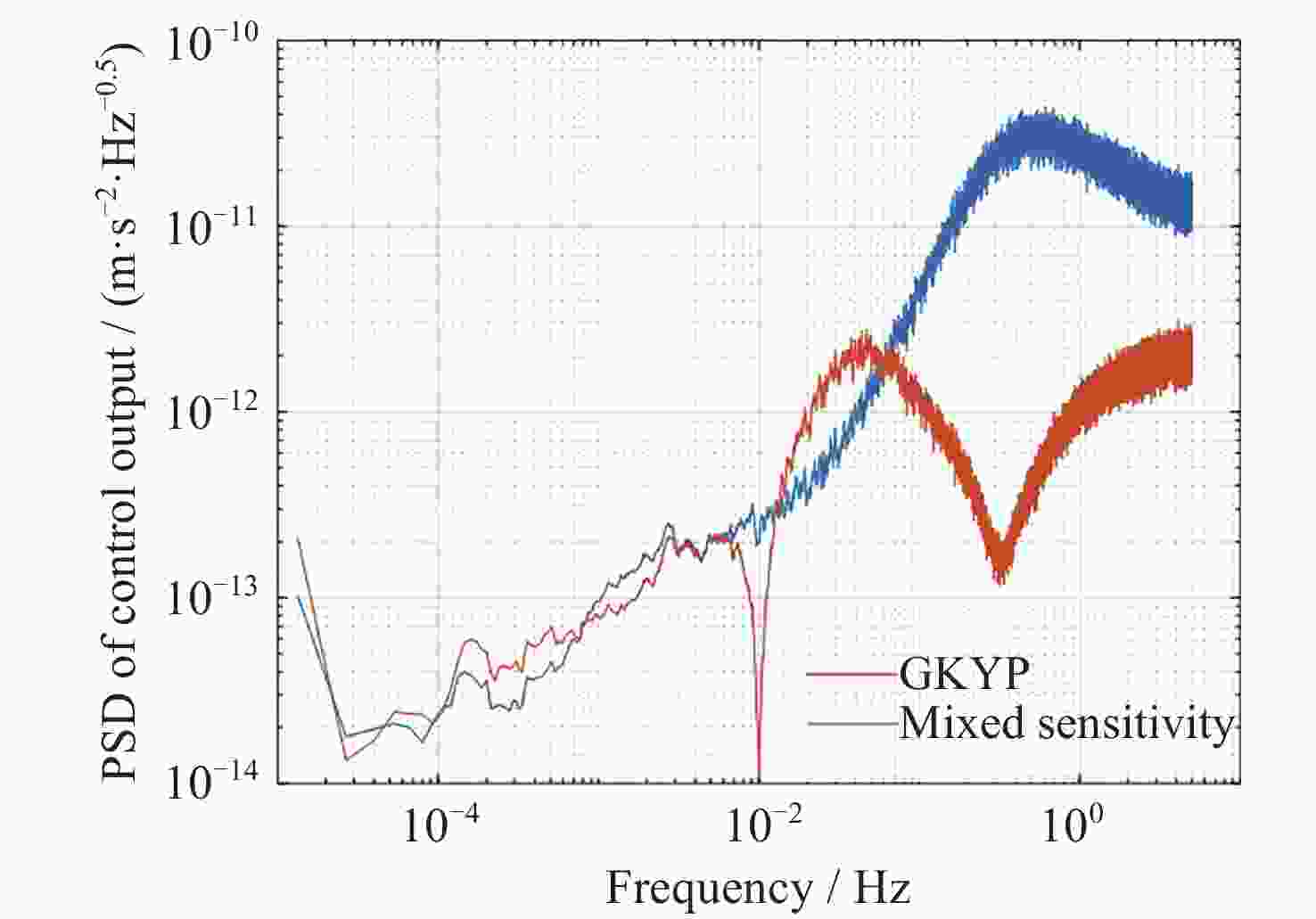
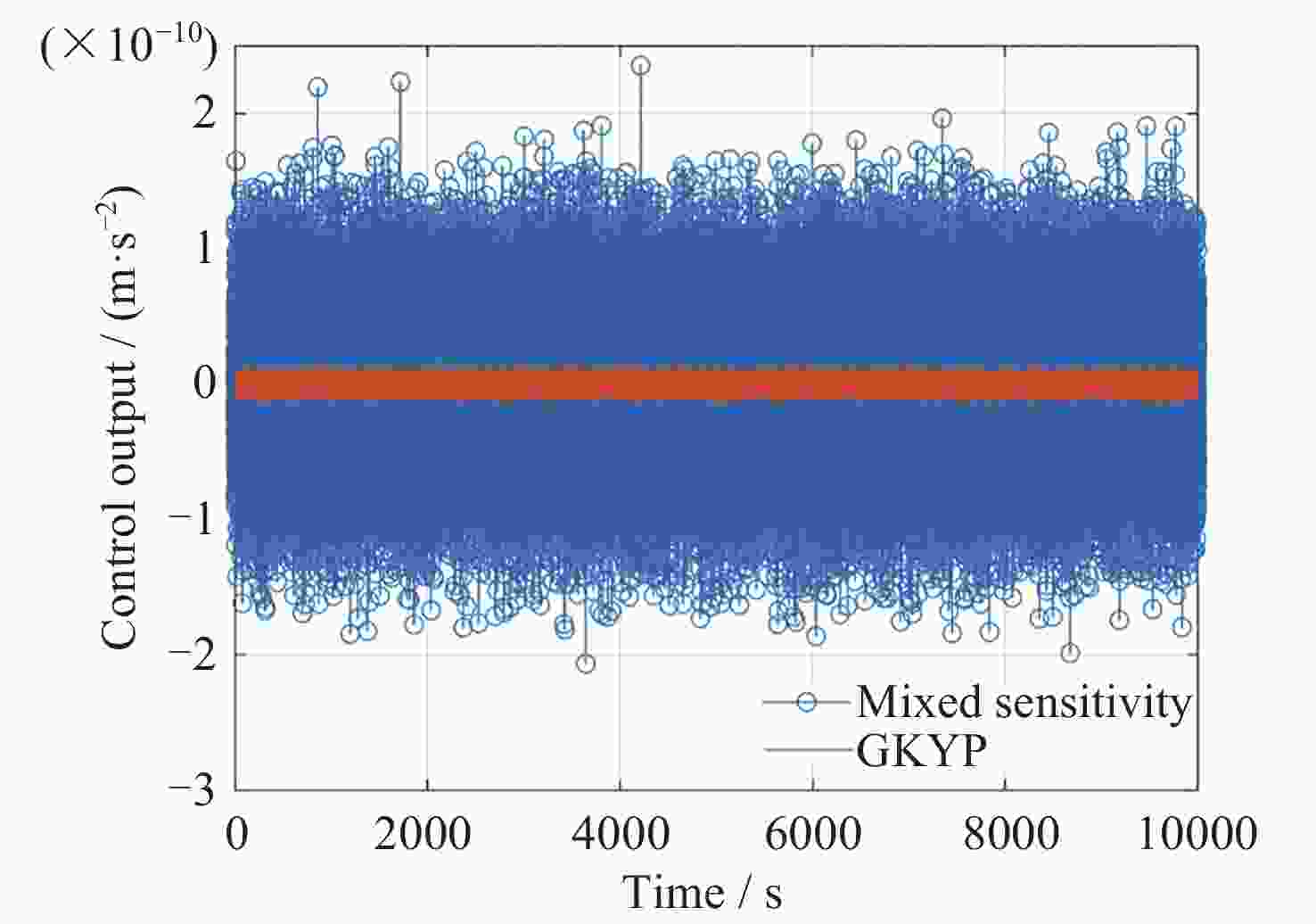
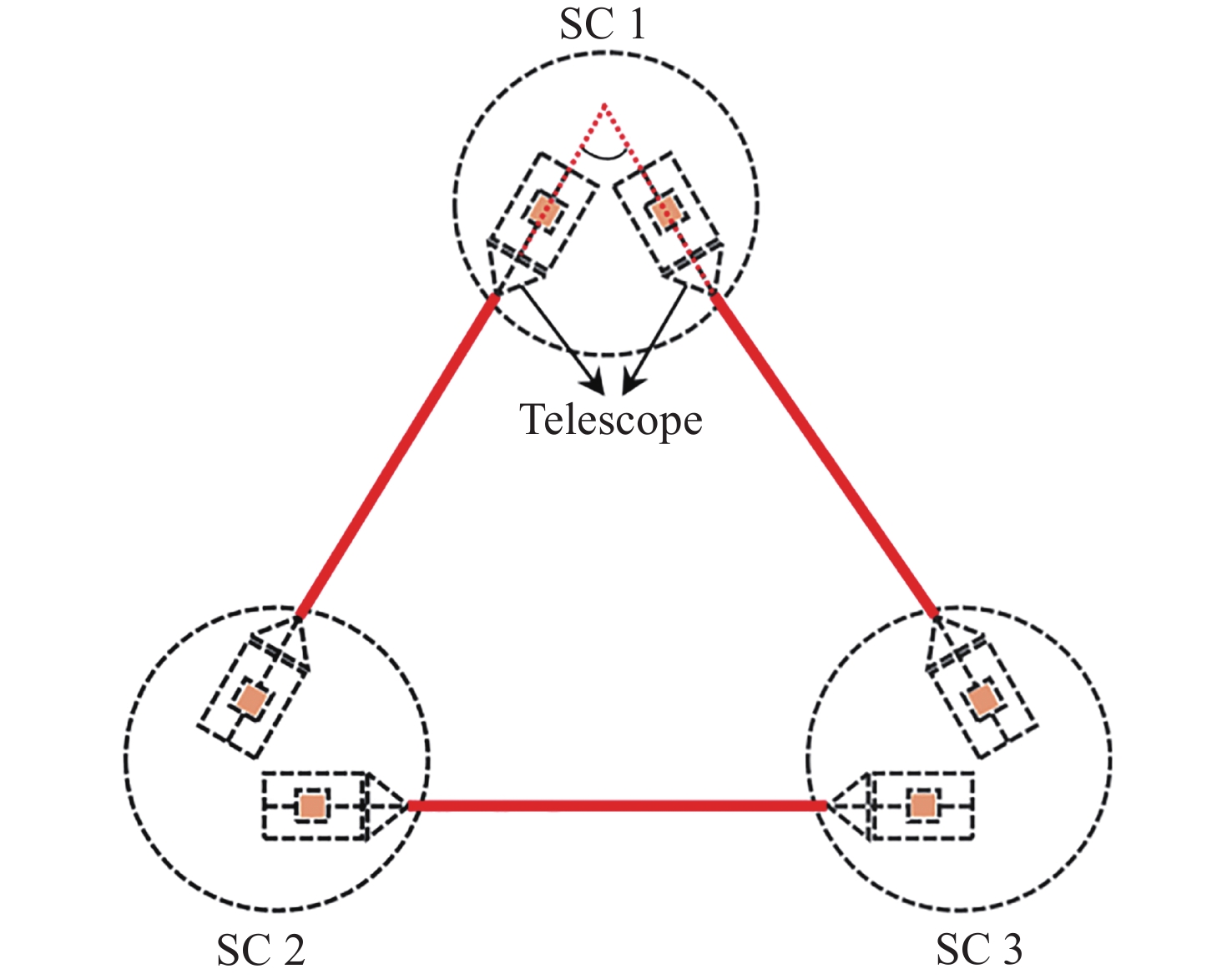
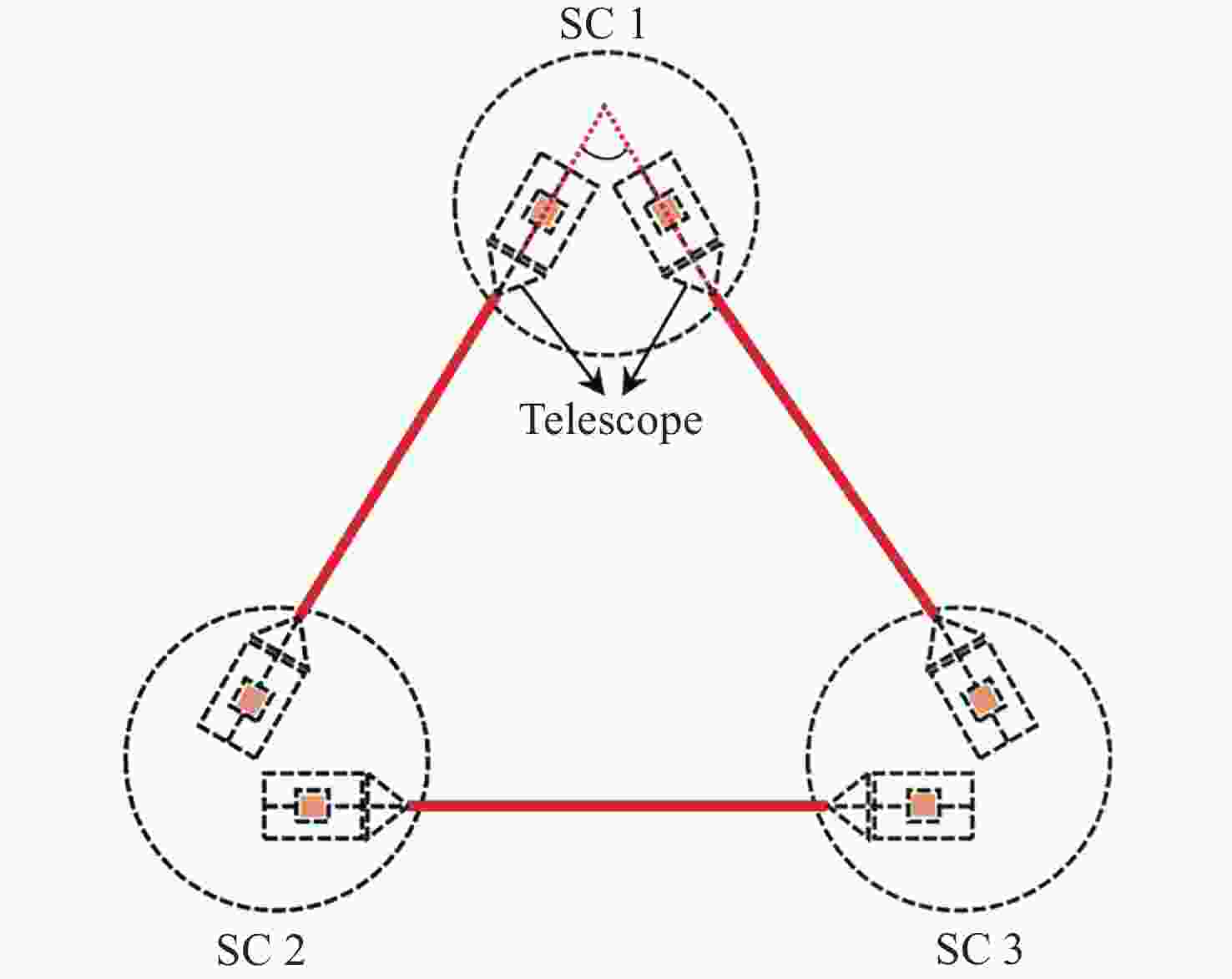
摘要: 在空间引力波探测任务中, 有限测量频域约束以及高精度控制指标使双参考质量无拖曳卫星控制器设计面临诸多技术难题. 基于此, 本文提出了一种基于广义Kalman-Yakubovich-Popov(GKYP)引理的有限频域抗扰控制器设计方法. 针对探测任务中指定频段内的性能约束, 结合灵敏度和补灵敏度控制指标, 在指定频段下构建了具有频率响应函数形式的有限频域控制性能指标. 提出了具有固定阶数特性的输出反馈控制结构, 并基于GKYP引理建立了控制器参数选取方法, 构建了有限频域抗扰控制器设计方法. 不同于现有的无拖曳控制器设计方法, 该设计方法可以有效降低控制指标的保守性, 同时在指定频段下实现了控制器的精确设计, 从而降低控制器阶数. 数值仿真表明, 本文所提方法在复杂扰动和噪声影响下可以满足无拖曳系统各回路控制性能指标.Abstract: In space-borne gravitational wave detection, there are technical challenges in designing the controller for the drag-free spacecraft with dual test masses. These difficulties arise from constraints within the limited measurement frequency domain and the necessity for a high-precision control index. In this paper, a design method of disturbance rejection controller in the finite frequency domain based on the generalized Kalman-Yakubovich-Popov (GKYP) lemma is proposed. Firstly, to address the performance constraints within the designated frequency band of the detection mission, a finite frequency domain control performance index in the form of a frequency response function is constructed. This index is meticulously developed by amalgamating the sensitivity and complementary sensitivity control indexes. Then, a control structure with fixed-order characteristics for output feedback is proposed, and a method for selecting controller parameters based on the GKYP lemma is established. By this, a finite frequency domain disturbance-resistant controller design method is constructed. In contrast to current drag-free controller design methods, the proposed approach significantly diminishes the conservatism in the control index. This realizes the precise design of the controller in the specified frequency band, ultimately resulting in a reduction in the order of the controller. Finally, numerical simulations demonstrate that the proposed method successfully meets the control performance index for each loop of the drag-free system even in the presence of complex disturbances and noises.
-
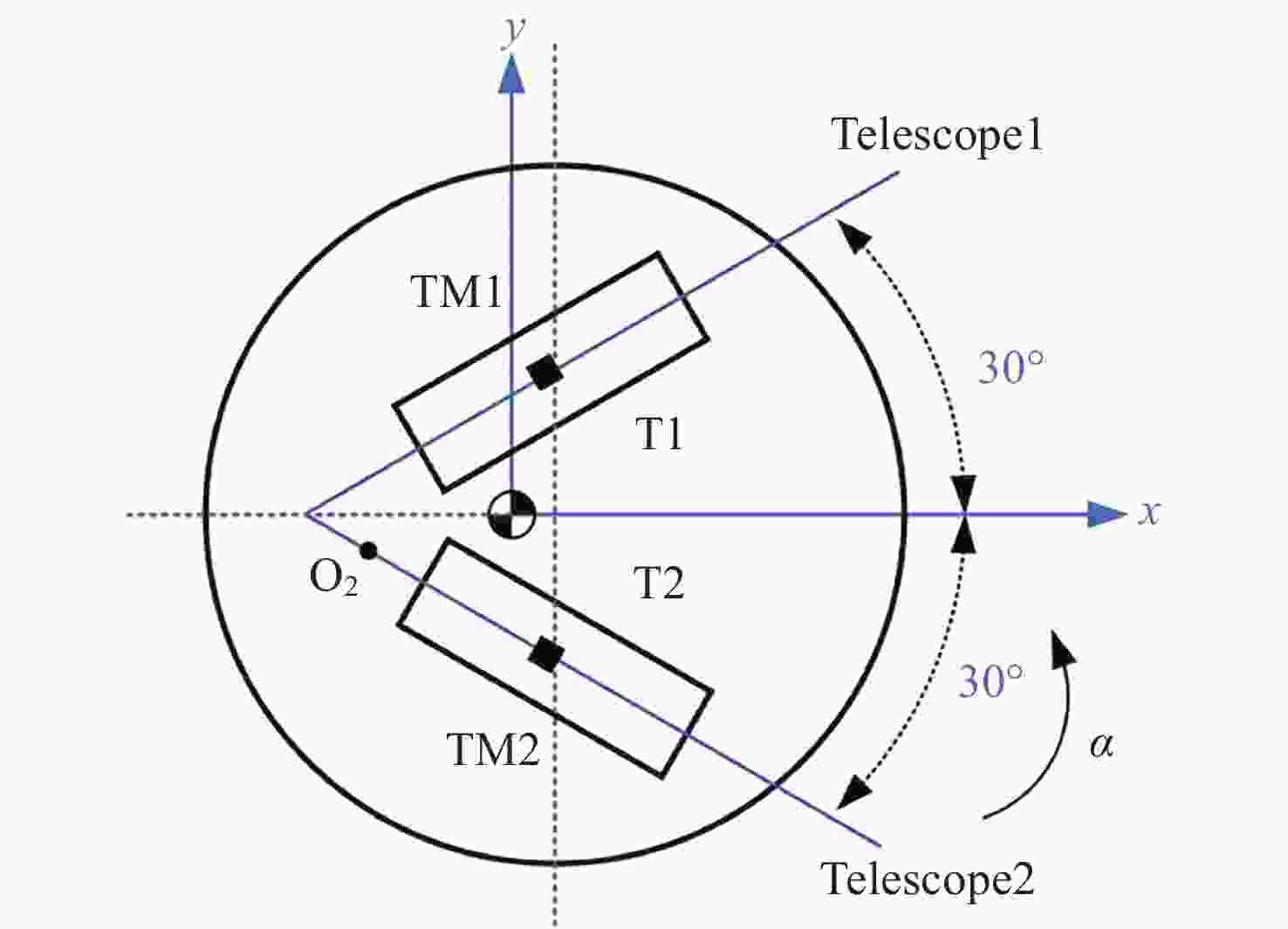
表 1 各自由度控制要求
Table 1. Control requirement for each degree of freedom
控制回路 控制自由度 位姿误差要求/
(m·rad·Hz–0.5)控制输入要求/
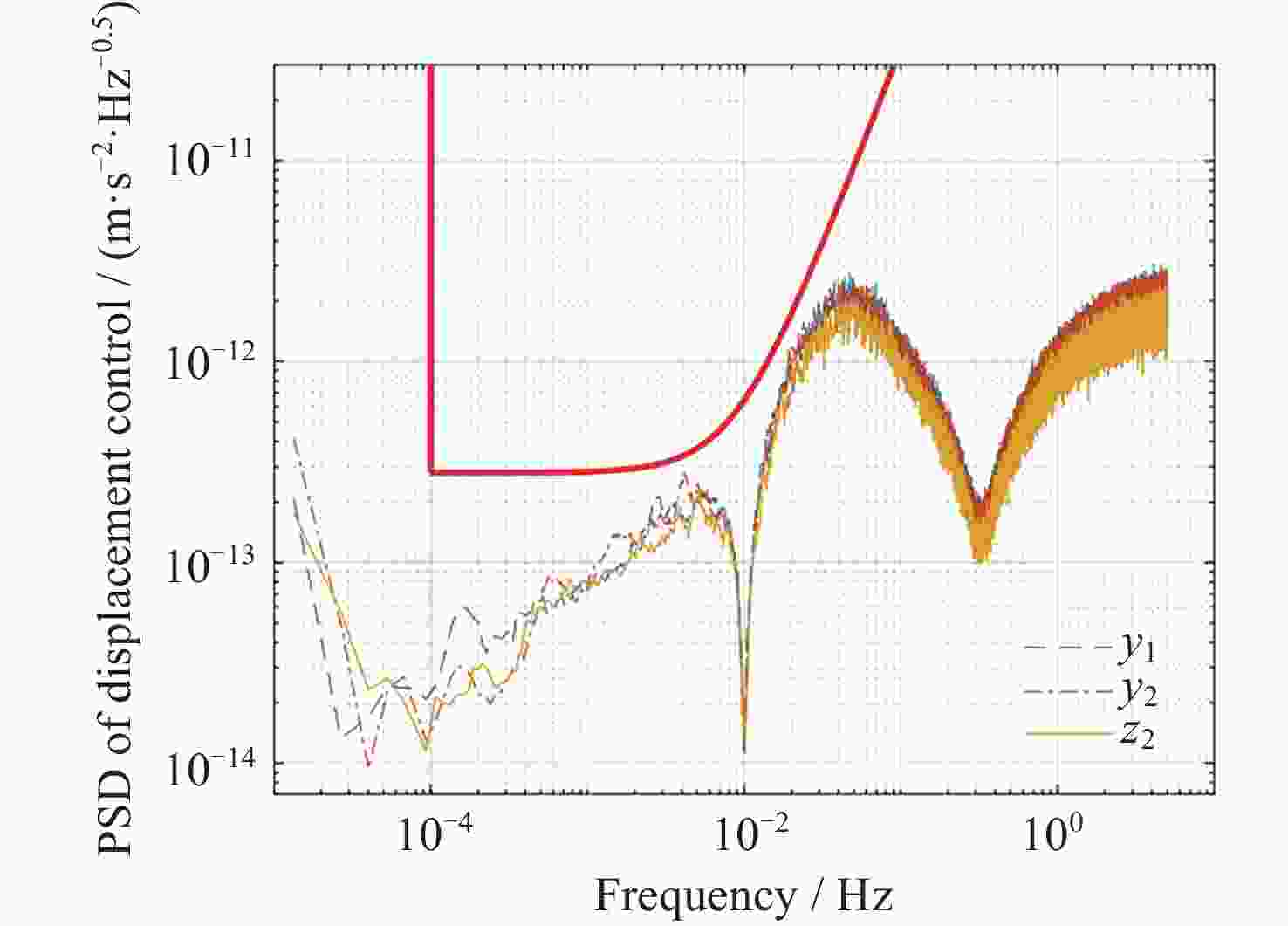
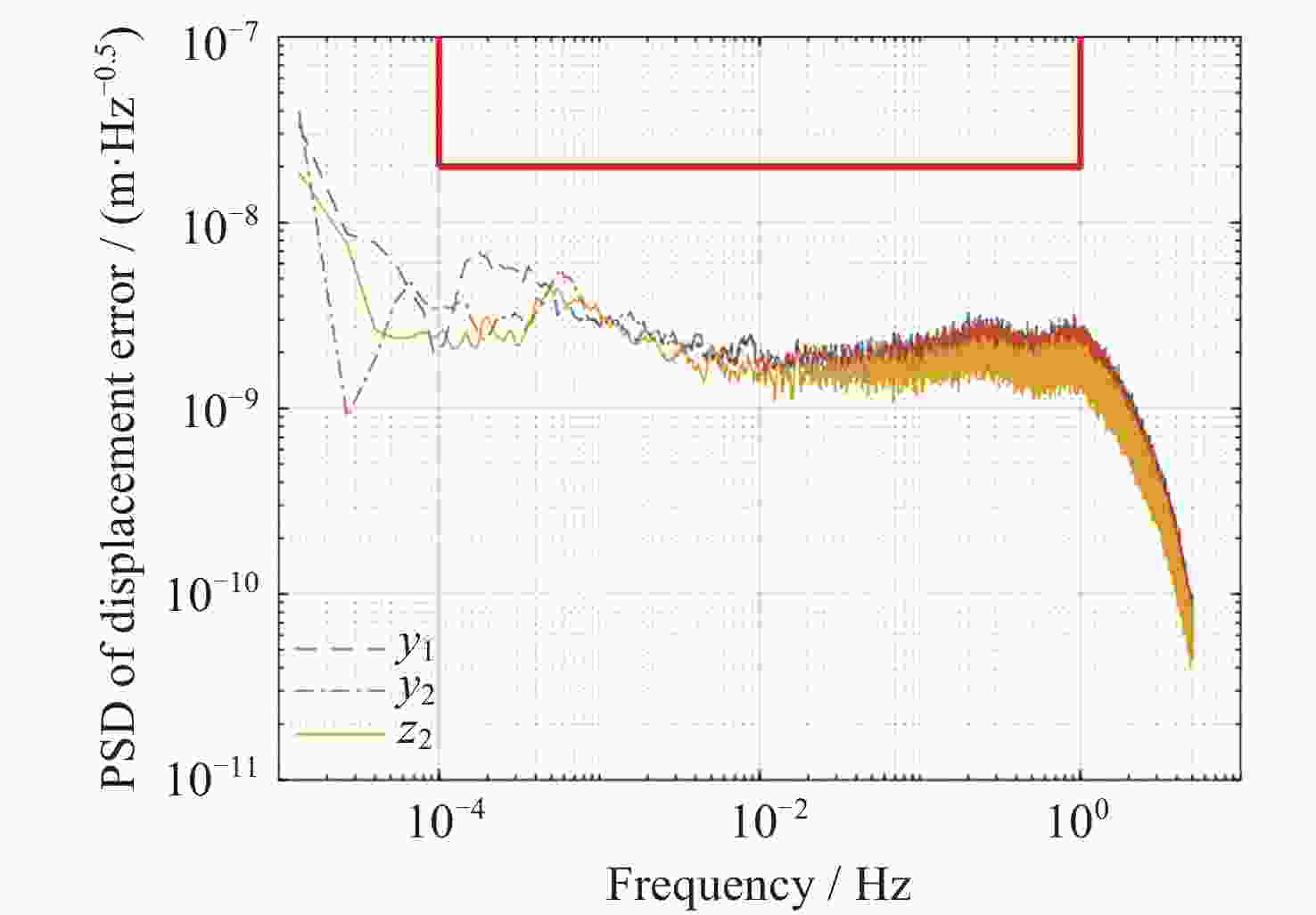
(m·rad·s–2Hz–0.5)无拖曳控制回路 x1, x2, z1 $4 \times {10^{ - 9}}$ - 静电悬浮
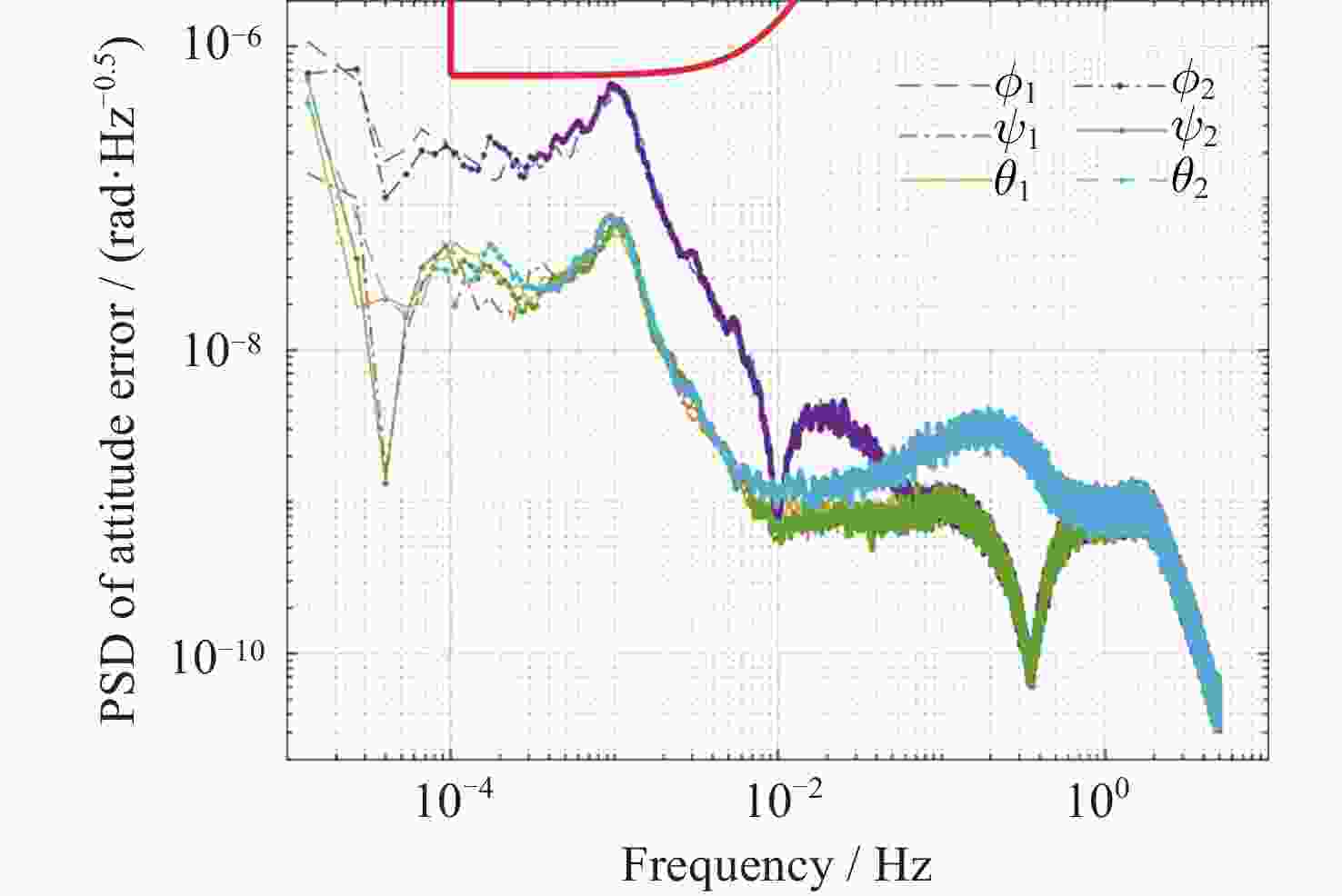
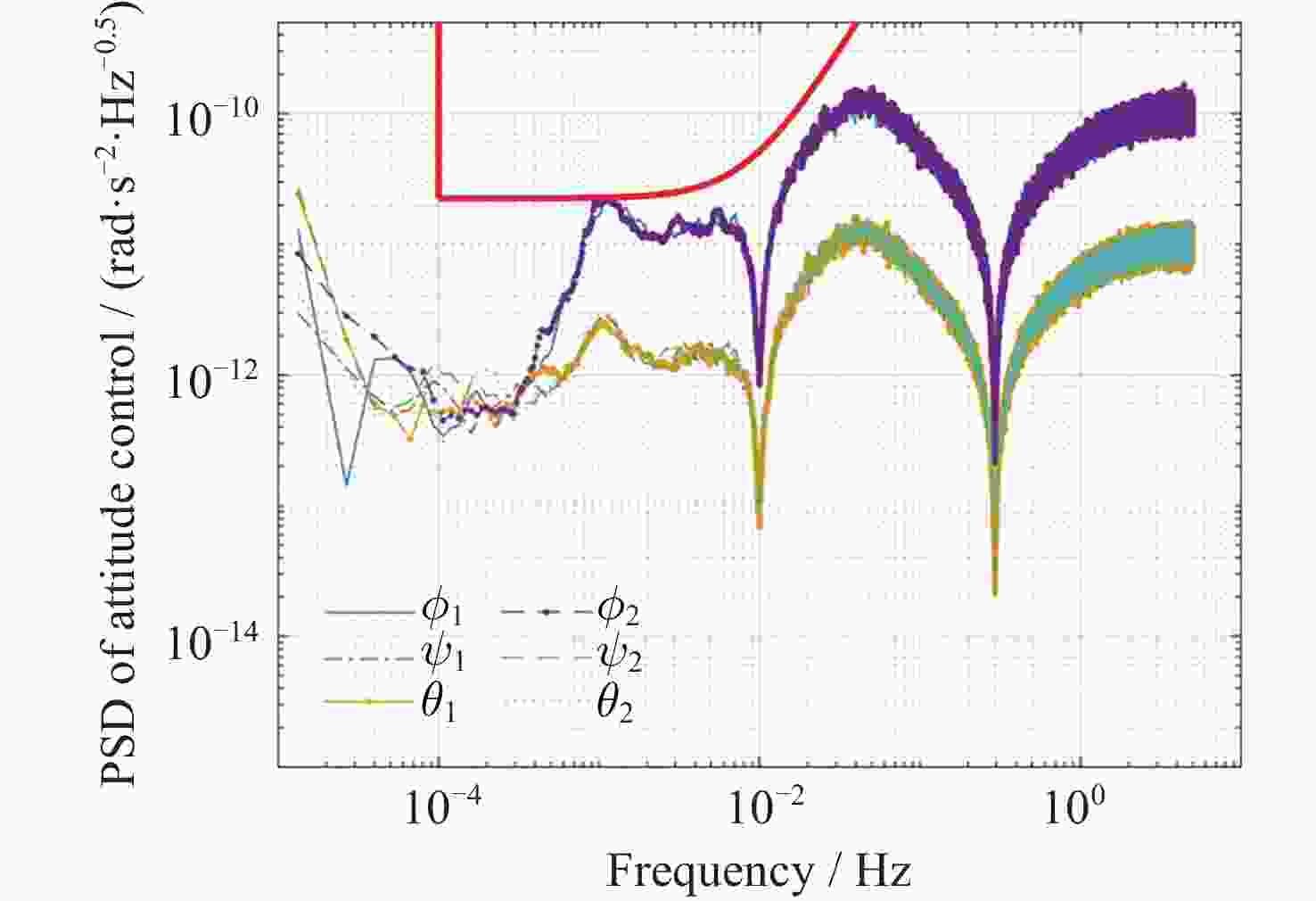
控制回路y1, y2, z2 $2 \times {10^{ - 8}}$ $ 3 \times {10^{ - 13}} $ $ {\phi _1}, $$ {\psi _1}, $$ {\theta _1} $
$ {\phi _2}, $$ {\psi _2}, $$ {\theta _2} $$6 \times {10^{ - 7}}$ $2.5 \times {10^{ - 11}}$ 姿态控制回路 $ {\phi _{\text{b}}} $, $ {\psi _{\text{b}}} $, $ {\theta _{\text{b}}} $ $3 \times {10^{ - 9}}$ - 表 2 ${\boldsymbol{\varPsi}} $在不同频域条件下的取值
Table 2. Values of ${\boldsymbol{\varPsi}} $ under the different frequency domain conditions
低频 中频 高频 $w$ $ 0 \leqslant \left| w \right| \leqslant {w_{\text{l}}} $ ${w_1} \leqslant w \leqslant {w_2}$ $\left| w \right| \geqslant {w_{\text{h}}} \geqslant 0$ ${\boldsymbol{\varPsi}} $ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} { - 1}&0 \\ 0&{w_{\text{l}}^{\text{2}}} \end{array}} \right]$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} { - 1}&{j{w_{\text{c}}}} \\ { - j{w_{\text{c}}}}&{ - {w_1}{w_2}} \end{array}} \right]$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0 \\ 0&{ - w_{\text{h}}^2} \end{array}} \right]$ 表 3 仿真参数
Table 3. Simulation parameters
参数 取值 卫星平台 质量/kg 350 转动惯量/${\text{(kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}})$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {158.1}&{ - 8.626}&{0.8819} \\ { - 8.626}&{163.1}&{0.1913} \\ {0.8819}&{0.1913}&{297.1} \end{array}} \right]{\text{ }}$ 检测质量 质量/kg 1.96 转动惯量/${\text{(kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}})$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {6.913}&0&0 \\ 0&{6.913}&0 \\ 0&0&{6.913} \end{array}} \right] \times {10^{ - 4}}$ – 仿真时间/s ${10^5}$ – 控制周期/s 0.1 -
[1] 万小波, 张晓敏, 黎明. 天琴计划轨道构型长期漂移特性分析[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2017, 37(3): 110-116WAN Xiaobo, ZHANG Xiaomin, LI Ming. Analysis of long-period drift characteristics for orbit configuration of the Tianqin mission[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2017, 37(3): 110-116 [2] 吴岳良, 胡文瑞, 王建宇, 等. 空间引力波探测综述与拟解决的科学问题[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(4): 589-599 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.04.yg08WU Yueliang, HU Wenrui, WANG Jianyu, et al. Review and scientific objectives of spaceborne gravitational wave detection missions[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(4): 589-599 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.04.yg08 [3] BASILE F. Modeling and Design for the Attitude Control Phase of the LISA Drag-Free Mission[D]. Torino: Politecnico di Torino, 2019 [4] LUO Z R, GUO Z K, JIN G, et al. A brief analysis to Taiji: science and technology[J]. Results in Physics, 2020, 16: 102918 doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102918 [5] GONG Y G, LUO J, WANG B. Concepts and status of Chinese space gravitational wave detection projects[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2021, 5(9): 881-889 doi: 10.1038/s41550-021-01480-3 [6] SWEETSER T H. An end-to-end trajectory description of the LISA mission[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2005, 22(10): S429-S435 doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/22/10/039 [7] CIRILLO F. Controller Design for the Acquisition Phase of the LISA Mission Using a Kalman Filter[D]. Lungarno Antonio Pacinotti: Università di Pisa, 2007 [8] 胡启阳, 陈君, 龙军, 等. 无拖曳卫星推力器动态模型研究[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2016, 42(1): 52-56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2016.01.010HU Qiyang, CHEN Jun, LONG Jun, et al. The dynamic model of thruster for drag-free satellite[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2016, 42(1): 52-56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2016.01.010 [9] 胡明, 李洪银, 周泽兵. 无拖曳控制技术及其应用[J]. 载人航天, 2013, 19(2): 61-69 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2013.02.010HU Ming, LI Hongyin, ZHOU Zebing. Drag-free control technology and its applications[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2013, 19(2): 61-69 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2013.02.010 [10] DITTUS H, LÄMMERZAHL C, TURYSHEV S G. Lasers, Clocks and Drag-Free Control: Exploration of Relativistic Gravity in Space[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2008 [11] ZHOU J X, LIU L, WANG Z G. Modeling and analysis of ultra-low frequency dynamics of drag-free satellites[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2019, 31(2): 151-160 doi: 10.1007/s12217-019-9672-7 [12] WORDEN P W, EVERITT C W F. A testing ground for fundamental physics: gravity probe B and other fundamental physics experiments in space[J]. Nuclear Physics B-Proceedings Supplements, 2013, 243: 172-179 [13] ROBERT A, CIPOLLA V, PRIEUR P, et al. MICROSCOPE satellite and its drag-free and attitude control system[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2022, 39(20): 204003 doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ac09cd [14] 邹奎, 苟兴宇, 薛大同. 重力梯度测量卫星无拖曳控制技术[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2017, 43(02): 28-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2017.02.005ZOU Kui, GOU Xingyu, XUE Datong. An overview on drag-free control for gravitational gradiometry satellites[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2017, 43(02): 28-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2017.02.005 [15] CANUTO E. Drag-free and attitude control for the GOCE satellite[J]. Automatica, 2008, 44(7): 1766-1780 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2007.11.023 [16] LI H Y, BAI Y Z, HU M, et al. A novel controller design for the next generation space electrostatic accelerometer based on disturbance observation and rejection[J]. Sensors, 2016, 17(1): 21 doi: 10.3390/s17010021 [17] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, AUGER G, et al. Sub-femto-g free fall for space-based gravitational wave observatories: LISA pathfinder results[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016, 116(23): 231101 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.231101 [18] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. Beyond the required LISA free-fall performance: new LISA pathfinder results down to 20 μHz[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(6): 061101 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.061101 [19] FICHTER W, GATH P, VITALE S, et al. LISA pathfinder drag-free control and system implications[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2005, 22(10): S139 doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/22/10/002 [20] WU S F, FERTIN D. Spacecraft drag-free attitude control system design with quantitative feedback theory[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2008, 62(12): 668-682 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2008.01.038 [21] GATH P, SCHULTE H R, WEISE D, et al. Drag free and attitude control system design for the LISA science mode[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference and Exhibit. Hilton Head: AIAA, 2007: 6731 [22] LUPI F. Precise Control of LISA with Quantitative Feedback Theory[D]. Delft: Delft University of Technology, 2019 [23] 叶建成, 周斌, 张艺腾, 等. 航天器内部磁场环境主动补偿方法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(1): 93-101 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.01.093YE Jiancheng, ZHOU Bin, ZHANG Yiteng, et al. Active compensation method of spacecraft internal magnetic field environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(1): 93-101 doi: 10.11728/cjss2020.01.093 [24] 李卓, 郑建华, 李明涛, 等. 太阳系天体引力对空间引力波探测日心编队构型的影响分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(3): 457-466 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.03.457LI Zhuo, ZHENG Jianhua, LI Mingtao, et al. Analysis of celestial gravity influence on heliocentric formation flying of gravitational wave observatory[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(3): 457-466 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.03.457 [25] LIAN X B, ZHANG J X, LU L, et al. Frequency separation control for drag-free satellite with frequency-domain constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 4085-4096 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3088456 [26] 范一迪, 王鹏程, 卢苇, 等. 双检验质量无拖曳卫星鲁棒控制[J]. 深空探测学报(中英文), 2023, 10(03): 310-321FAN Yidi, WANG Pengcheng, LU Wei, et al. Robust controller design for drag-free satellites with two test masses[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2023, 10(03): 310-321 [27] XIAO C Y, CANUTO E, HONG W, et al. Drag-free design based on embedded model control for TianQin project[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2022, 198: 482-494 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2022.06.031 [28] MA H J, ZHENG J H, HAN P, et al. Robust composite control design of drag-free satellite with Kalman filter-based extended state observer for disturbance reduction[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 70(10): 3034-3050 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.07.048 [29] 章楚, 贺建武, 段俐. 基于扩张状态观测器的无拖曳系统参数辨识[J]. 空间科学学报, 2019, 39(5): 670-676 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.05.670ZHANG Chu, HE Jianwu, DUAN Li. Parameter identification of drag-free system based on extended state observer[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2019, 39(5): 670-676 doi: 10.11728/cjss2019.05.670 [30] The Taiji Scientific Collaboration. China’s first step towards probing the expanding universe and the nature of gravity using a space borne gravitational wave antenna[J]. Communications Physics, 2021, 4(1): 34 doi: 10.1038/s42005-021-00529-z [31] HU Z Q, WANG P C, DENG J F, et al. The drag-free control design and in-orbit experimental results of “Taiji-1”[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics A, 2021, 36(11/12): 2140019 [32] LUO J, BAI Y Z, CAI L, et al. The first round result from the TianQin-1 satellite[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2020, 37(18): 185013 doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/aba66a [33] XIAO C Y, BAI Y Z, LI H Y, et al. Drag-free control design and in-orbit validation of TianQin-1 satellite[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2022, 39(15): 155001 doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ac79f5 [34] IWASAKI T, HARA S. Generalized KYP lemma: unified frequency domain inequalities with design applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2005, 50(1): 41-59 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.840475 [35] DUN A, XU Q J, LEI F. Finite frequency domain H ∞ consensus control of neutral multi-agent systems with input delay[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2023, 54(1): 136-152 doi: 10.1080/00207721.2022.2111234 [36] TAKAKU Y, NAGASHIO Y, KIDA T. An optimal h-infinity design using GKYP lemma for DVDFB controller and its application to flexible spacecraft[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, Aerospace Technology Japan, 2012, 10(28): Pd_53-Pd_60 [37] ZHANG Y Z, LIU M C, ZHANG C Z. Robust fault‐tolerant H ∞ output feedback control of active suspension and dynamic vibration absorber with finite‐frequency constraint[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020, 14(14): 1935-1945 doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2020.0364 [38] ZHANG J X, LU L, LIAN X B, et al. GKYP-based finite frequency control for relative motion of drag-free satellite[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2023, 36(4): 04023031 doi: 10.1061/JAEEEZ.ASENG-4524 [39] VIDANO S, NOVARA C, COLANGELO L, et al. The LISA DFACS: a nonlinear model for the spacecraft dynamics[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 107: 106313 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.106313 [40] GATH P, FICHTER W, KERSTEN M, et al. Drag free and attitude control system design for the LISA pathfinder mission[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit. Providence: AIAA, 2004: 5430 [41] HENRION D, SEBEK M, KUCERA V. Positive polynomials and robust stabilization with fixed-order controllers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2003, 48(7): 1178-1186 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2003.814103 [42] SAFONOV M G, CHIANG R Y, LIMEBEER D J. N. Optimal Hankel model reduction for nonminimal systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1990, 35(4): 496-502 doi: 10.1109/9.52314 -
-





 徐乾蛟 男, 1994年11月出生于山东省德州市, 现为北京理工大学自动化学院在读博士研究生, 主要研究方向为频域控制、连续系统控制、引力波探测三星无拖曳控制等. E-mail:
徐乾蛟 男, 1994年11月出生于山东省德州市, 现为北京理工大学自动化学院在读博士研究生, 主要研究方向为频域控制、连续系统控制、引力波探测三星无拖曳控制等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: