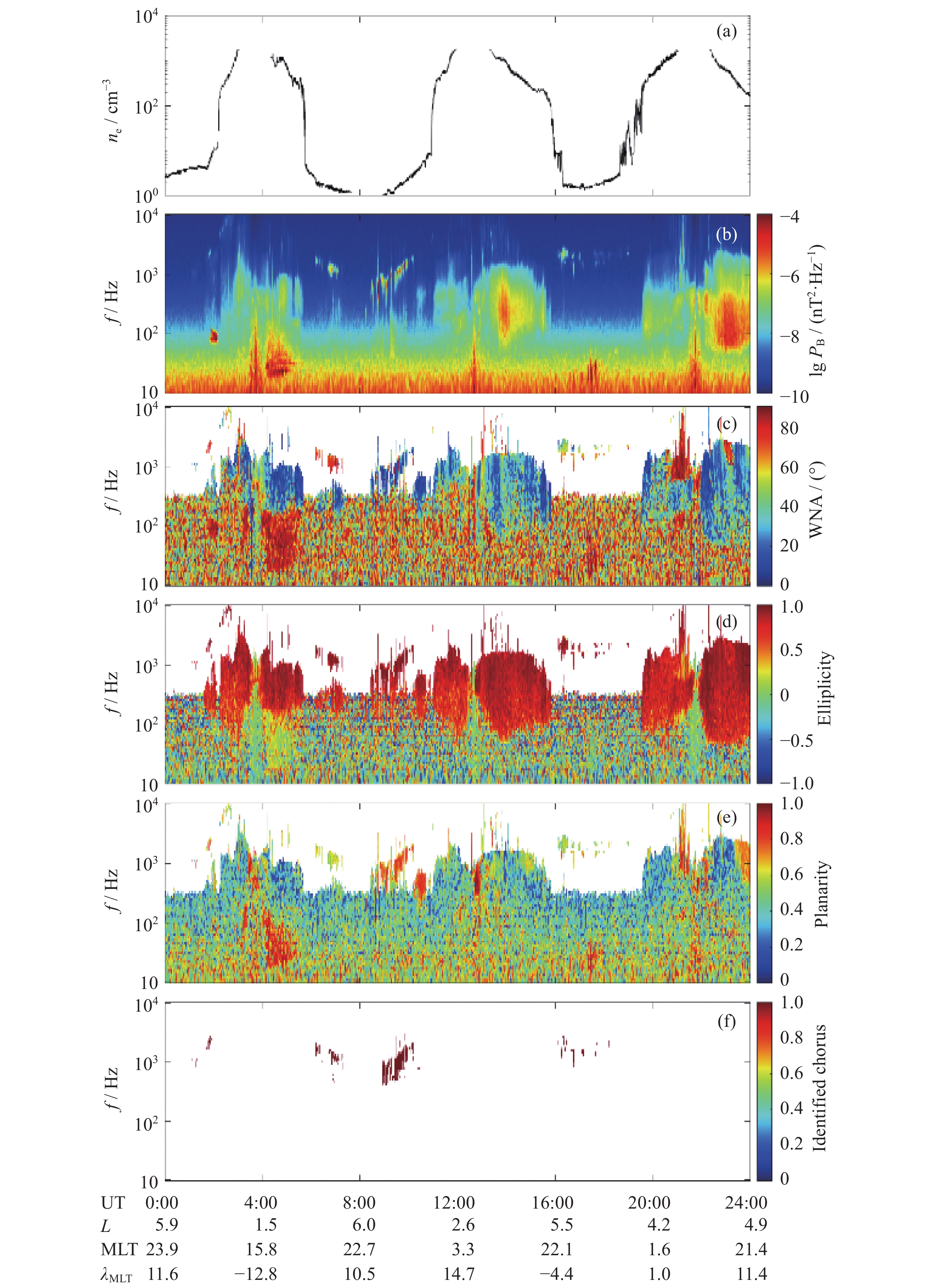
| [1] |
BURTIS W J, HELLIWELL R A. Banded chorus—A new type of VLF radiation observed in the magnetosphere by OGO 1 and OGO 3[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1969, 74(11): 3002-3010 doi: 10.1029/JA074i011p03002
|
| [2] |
HELLIWELL R A. A theory of discrete VLF emissions from the magnetosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1967, 72(19): 4773-4790 doi: 10.1029/JZ072i019p04773
|
| [3] |
OMURA Y, KATOH Y, SUMMERS D. Theory and simulation of the generation of whistler-mode chorus[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2008, 113(A4): A04223
|
| [4] |
SUMMERS D, TANG R X, THORNE R M. Limit on stably trapped particle fluxes in planetary magnetospheres[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2009, 114(A10): A10210
|
| [5] |
SU Z P, ZHU H, XIAO F L, et al. Intense duskside lower band chorus waves observed by Van Allen Probes: Generation and potential acceleration effect on radiation belt electrons[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2014, 119(6): 4266-4273 doi: 10.1002/2014JA019919
|
| [6] |
AGAPITOV O, ARTEMYEV A, KRASNOSELSKIKH V, et al. Statistics of whistler-mode waves in the outer radiation belt: Cluster STAFF-SA measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2013, 118(6): 3407-3420 doi: 10.1002/jgra.50312
|
| [7] |
TSURUTANI B T, SMITH E J. Two types of magnetospheric ELF chorus and their substorm dependences[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1977, 82(32): 5112-5128 doi: 10.1029/JA082i032p05112
|
| [8] |
MEREDITH N P, HORNE R B, ANDERSON R R. Substorm dependence of chorus amplitudes: Implications for the acceleration of electrons to relativistic energies[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2001, 106(A7): 13165-13178 doi: 10.1029/2000JA900156
|
| [9] |
KOONS H C, ROEDER J L. A survey of equatorial magnetospheric wave activity between 5 and 8 RE[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 1990, 38(10): 1335-1341 doi: 10.1016/0032-0633(90)90136-E
|
| [10] |
LI W, BORTNIK J, THORNE R M, et al. Global distribution of wave amplitudes and wave normal angles of chorus waves using THEMIS wave observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2011, 116(A12): A12205
|
| [11] |
LI W, THORNE R M, ANGELOPOULOS V, et al. Global distribution of whistler-mode chorus waves observed on the THEMIS spacecraft[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009, 36(9): L09104
|
| [12] |
TSURUTANI B T, SMITH E J. Postmidnight chorus: a substorm phenomenon[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1974, 79(1): 118-127 doi: 10.1029/JA079i001p00118
|
| [13] |
OMURA Y, HIKISHIMA M, KATOH Y, et al. Nonlinear mechanisms of lower-band and upper-band VLF chorus emissions in the magnetosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2009, 114(A7): A07217
|
| [14] |
LIU K J, GARY S P, WINSKE D. Excitation of banded whistler waves in the magnetosphere[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(14): L14108
|
| [15] |
SUMMERS D, MA C, MEREDITH N P, et al. Model of the energization of outer-zone electrons by whistler-mode chorus during the October 9, 1990 geomagnetic storm[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(24): 2174
|
| [16] |
THORNE R M, LI W, NI B, et al. Rapid local acceleration of relativistic radiation-belt electrons by magnetospheric chorus[J]. Nature, 2013, 504(7480): 411-414 doi: 10.1038/nature12889
|
| [17] |
SU Z P, XIAO F L, ZHENG H N, et al. Nonstorm time dynamics of electron radiation belts observed by the Van Allen Probes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41(2): 229-235 doi: 10.1002/2013GL058912
|
| [18] |
XIAO F L, YANG C, HE Z G, et al. Chorus acceleration of radiation belt relativistic electrons during March 2013 geomagnetic storm[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2014, 119(5): 3325-3332 doi: 10.1002/2014JA019822
|
| [19] |
HE Q, LIU S, XIAO F L, et al. Observations and parametric study on the role of plasma density on extremely low-frequency chorus wave generation[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2022, 65(11): 2649-2657 doi: 10.1007/s11431-021-2030-7
|
| [20] |
HORNE R B, THORNE R M, SHPRITS Y Y, et al. Wave acceleration of electrons in the Van Allen radiation belts[J]. Nature, 2005, 437(7056): 227-230 doi: 10.1038/nature03939
|
| [21] |
Reeves G D, SPENCE H E, HENDERSON M G, et al. Electron acceleration in the heart of the Van Allen radiation belts[J]. Science, 2013, 341(6149): 991-994 doi: 10.1126/science.1237743
|
| [22] |
TU W, CUNNINGHAM G S, CHEN Y, et al. Event-specific chorus wave and electron seed population models in DREAM3D using the Van Allen probes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41(5): 1359-1366 doi: 10.1002/2013GL058819
|
| [23] |
SUMMERS D, MA C, MEREDITH N P, et al. Modeling outer-zone relativistic electron response to whistler-mode chorus activity during substorms[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2004, 66(2): 133-146 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2003.09.013
|
| [24] |
SUMMERS D, NI B B, MEREDITH N P. Timescales for radiation belt electron acceleration and loss due to resonant wave-particle interactions: 2. Evaluation for VLF chorus, ELF hiss, and electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2007, 112(A4): A04207
|
| [25] |
XIAO F L, ZONG Q G, CHEN L X. Pitch-angle distribution evolution of energetic electrons in the inner radiation belt and slot region during the 2003 Halloween storm[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2009, 114(A1): A01215
|
| [26] |
XIAO F L, SU Z P, ZHENG H N, et al. Modeling of outer radiation belt electrons by multidimensional diffusion process[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2009, 114(A3): A03201
|
| [27] |
MIYOSHI Y, KATOH Y, NISHIYAMA T, et al. Time of flight analysis of pulsating aurora electrons, considering wave-particle interactions with propagating whistler mode waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2010, 115(A10): A10312
|
| [28] |
NISHIMURA Y, BORTNIK J, LI W, et al. Identifying the Driver of Pulsating Aurora[J]. Science, 2010, 330(6000): 81-84 doi: 10.1126/science.1193186
|
| [29] |
THORNE R M. Radiation belt dynamics: The importance of wave-particle interactions[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37(22): L22107
|
| [30] |
GOLDSTEIN B E, TSURUTANI B T. Wave normal directions of chorus near the equatorial source region[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1984, 89(A5): 2789-2810 doi: 10.1029/JA089iA05p02789
|
| [31] |
BRENEMAN A W, KLETZING C A, PICKETT J, et al. Statistics of multispacecraft observations of chorus dispersion and source location[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2009, 114(A6): A06202
|
| [32] |
AGAPITOV O, KRASNOSELSKIKH V, KHOTYAINTSEV Y V, et al. Correction to “a statistical study of the propagation characteristics of whistler waves observed by Cluster”[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(24): L24102
|
| [33] |
LU Q M, KE Y G, WANG X Y, et al. Two-dimensional gcPIC simulation of rising-tone chorus waves in a dipole magnetic field[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2019, 124(6): 4157-4167 doi: 10.1029/2019JA026586
|
| [34] |
KE Y G, GAO X L, LU Q M, et al. Deformation of electron distributions due to Landau trapping by the whistler-mode wave[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(3): e2021GL096428 doi: 10.1029/2021GL096428
|
| [35] |
MAUK B H, FOX N J, KANEKAL S G, et al. Science objectives and rationale for the radiation belt storm probes mission[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2013, 179(1/2/3/4): 3-27
|
| [36] |
KURTH W S, DE PASCUALE S, FADEN J B, et al. Electron densities inferred from plasma wave spectra obtained by the waves instrument on Van Allen probes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2015, 120(2): 904-914 doi: 10.1002/2014JA020857
|
| [37] |
LI W O, SANTOLIK J, BORTNIK R M, et al. New chorus wave properties near the equator from Van Allen probes wave observations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43: 4725-4735 doi: 10.1002/2016GL068780
|




 杨立贤 男, 2000年7月出生于广东省揭阳市, 现为长沙理工大学物理与电子科学学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为地球内磁层等离子体波动. E-mail:
杨立贤 男, 2000年7月出生于广东省揭阳市, 现为长沙理工大学物理与电子科学学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为地球内磁层等离子体波动. E-mail: 
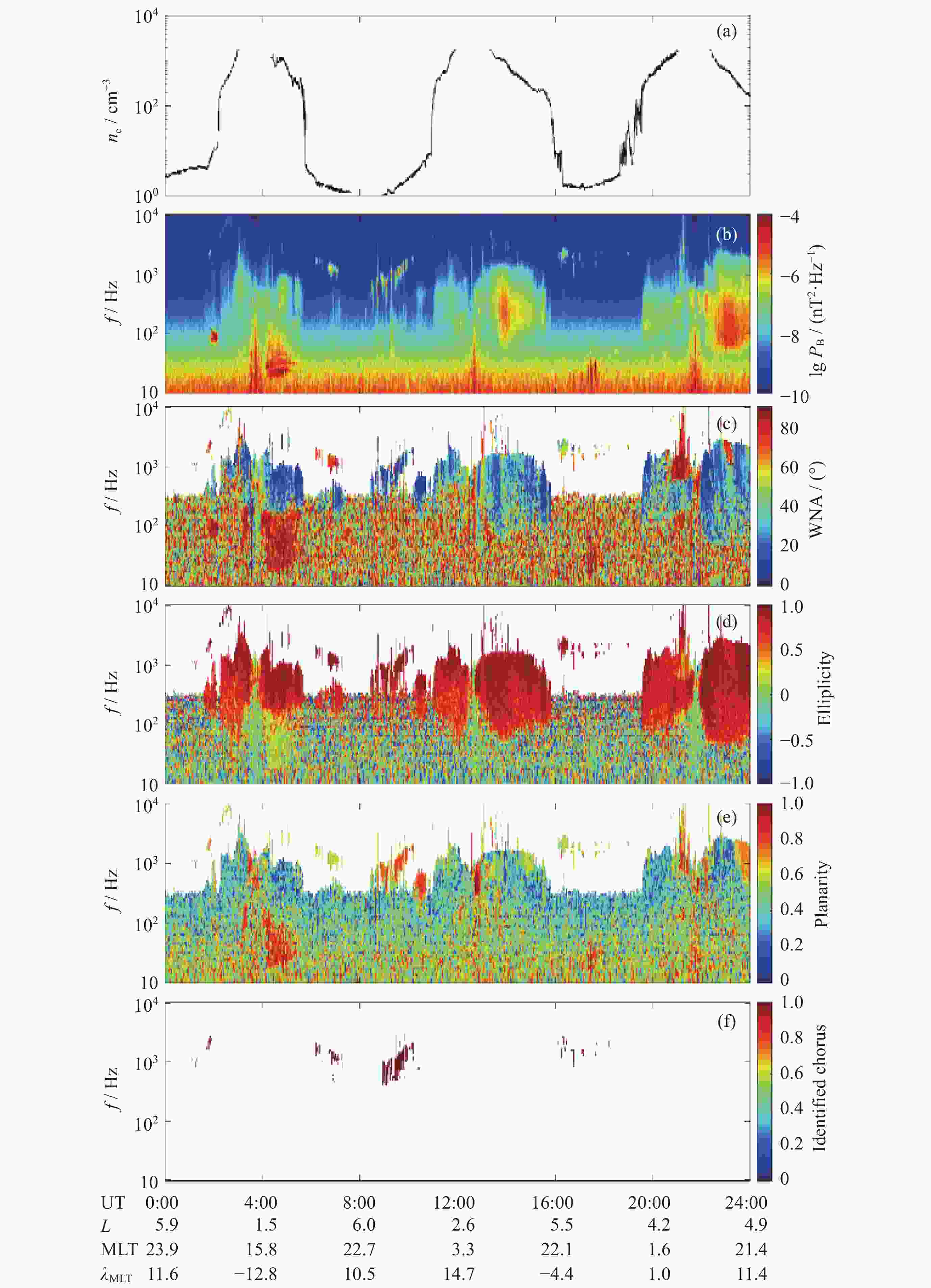
 下载:
下载: