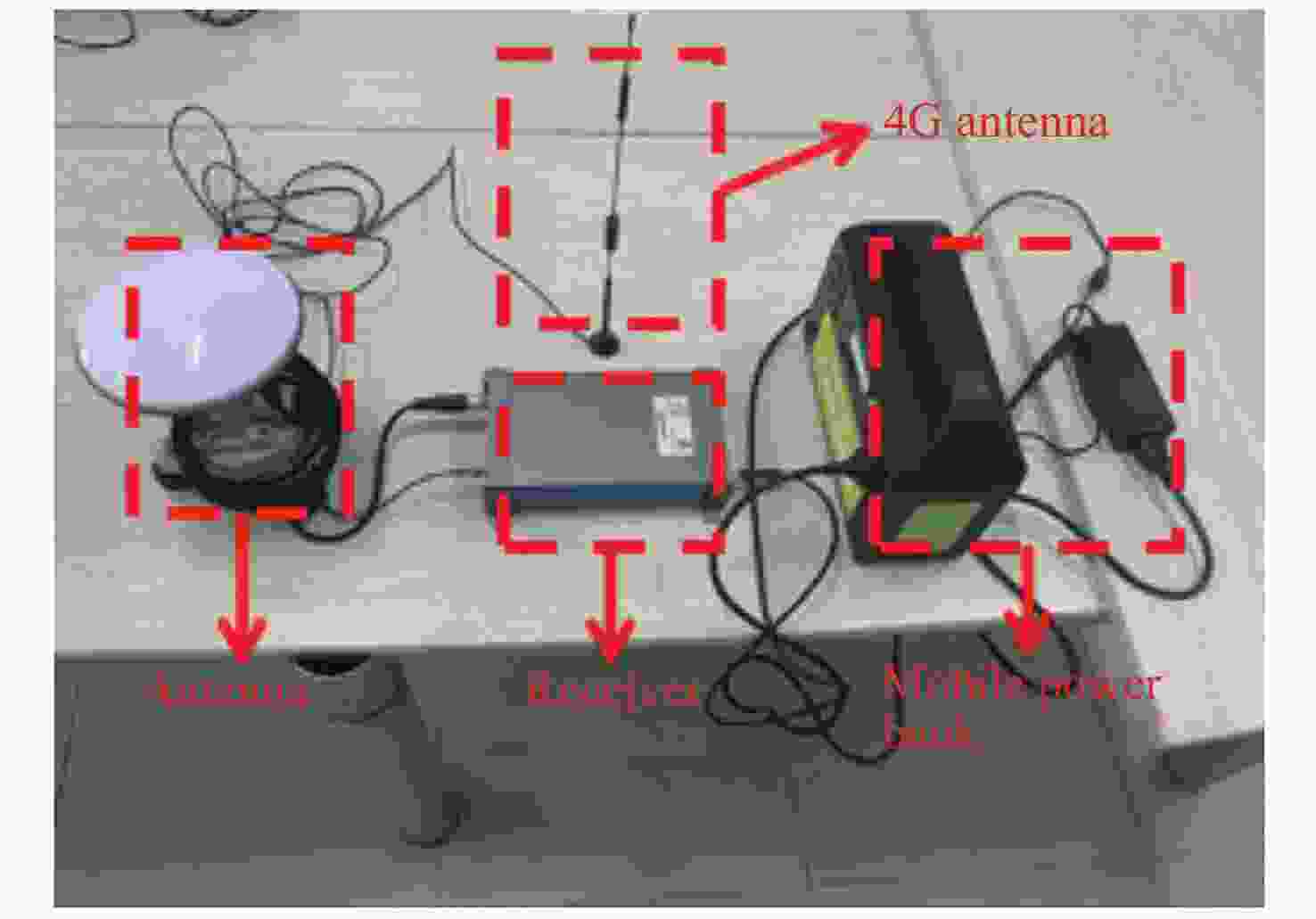
Comparison on Real-time Single Point Positioning Performance of Single Beidou/Multi-mode GNSS in Remote Forested Areas
-
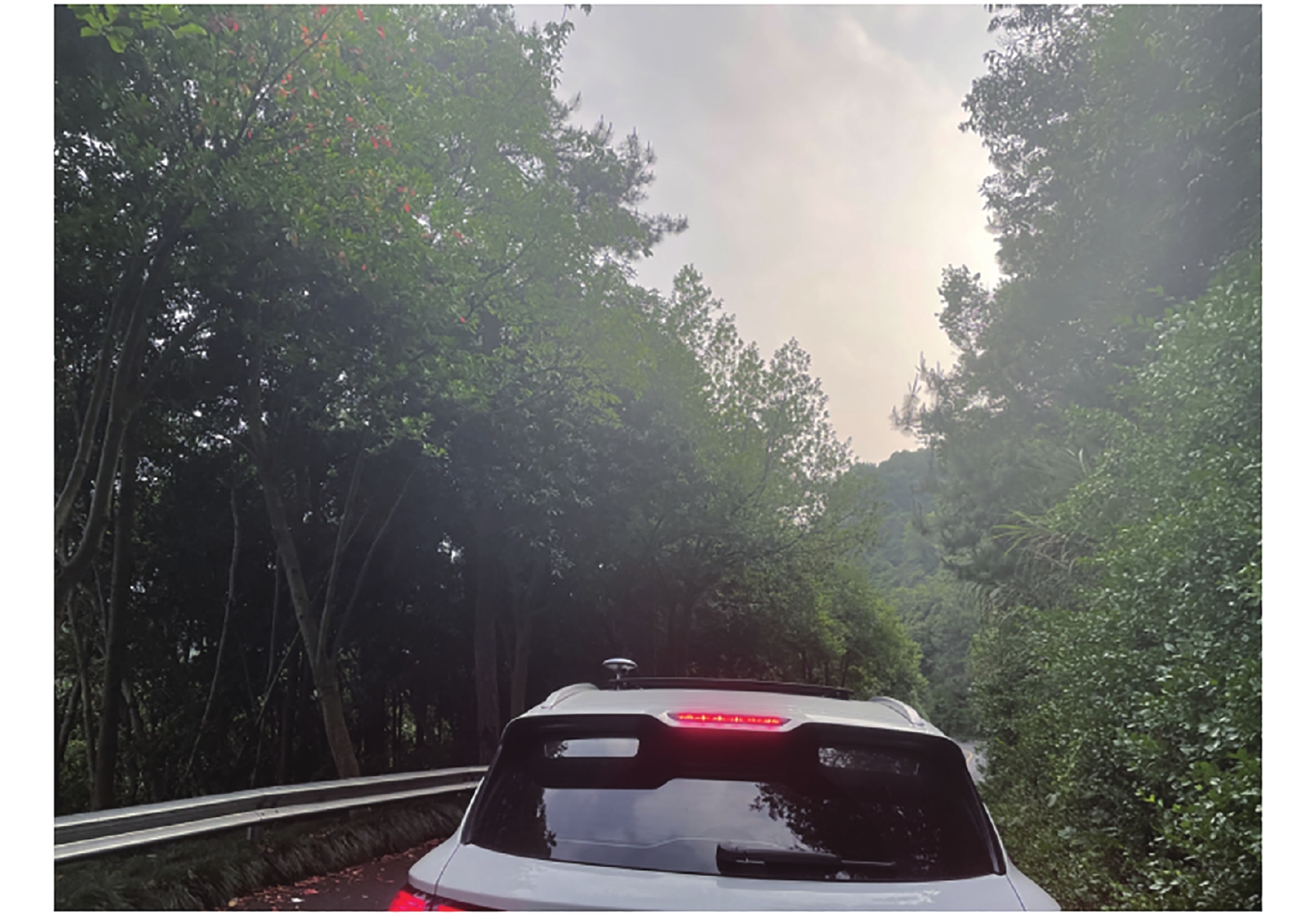
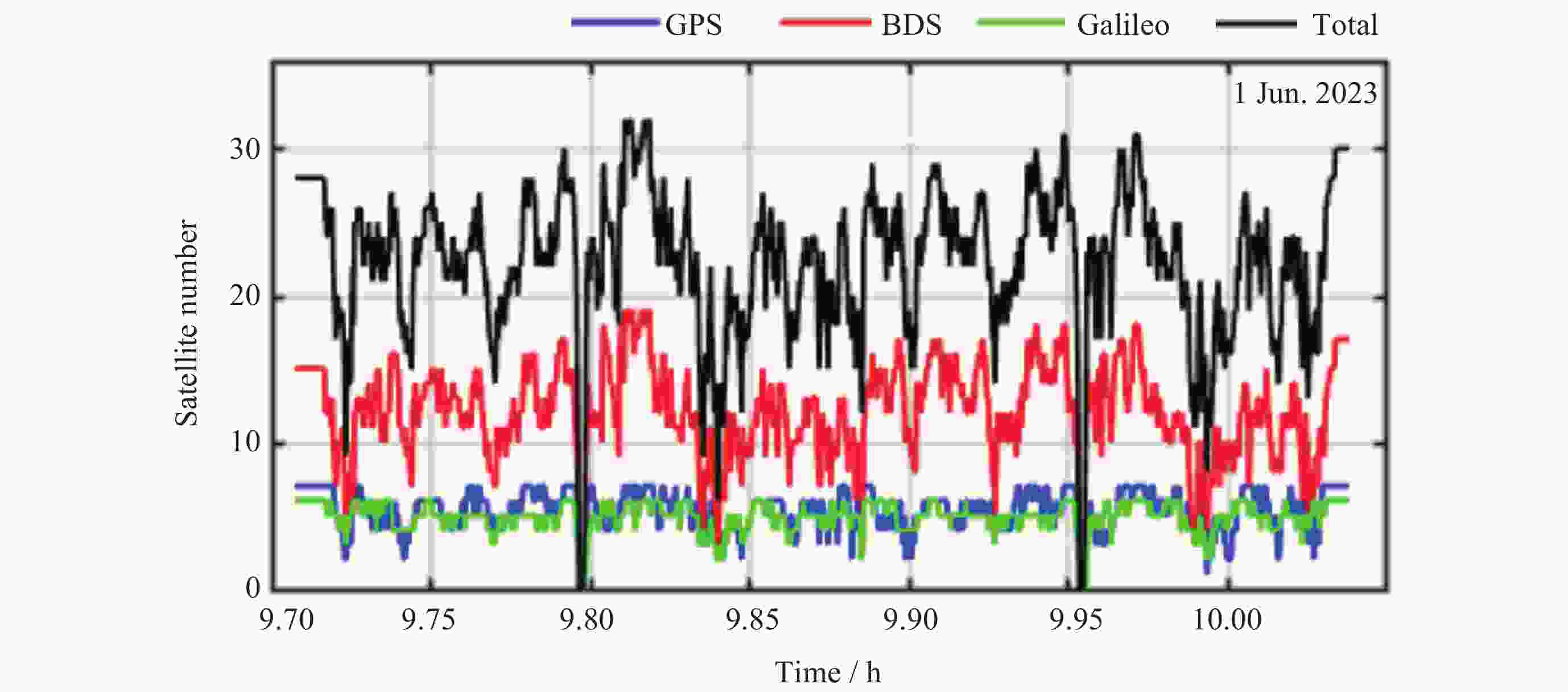
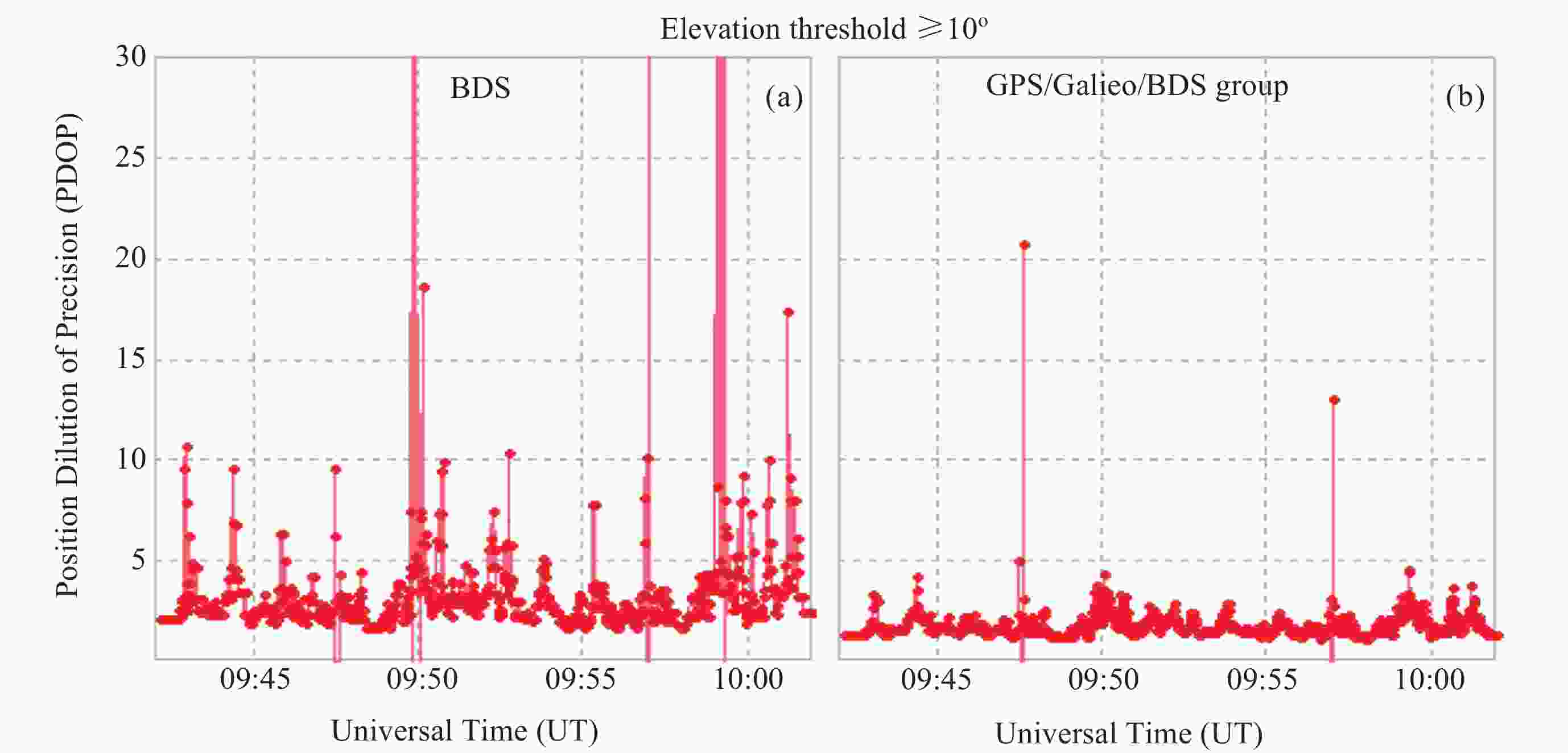
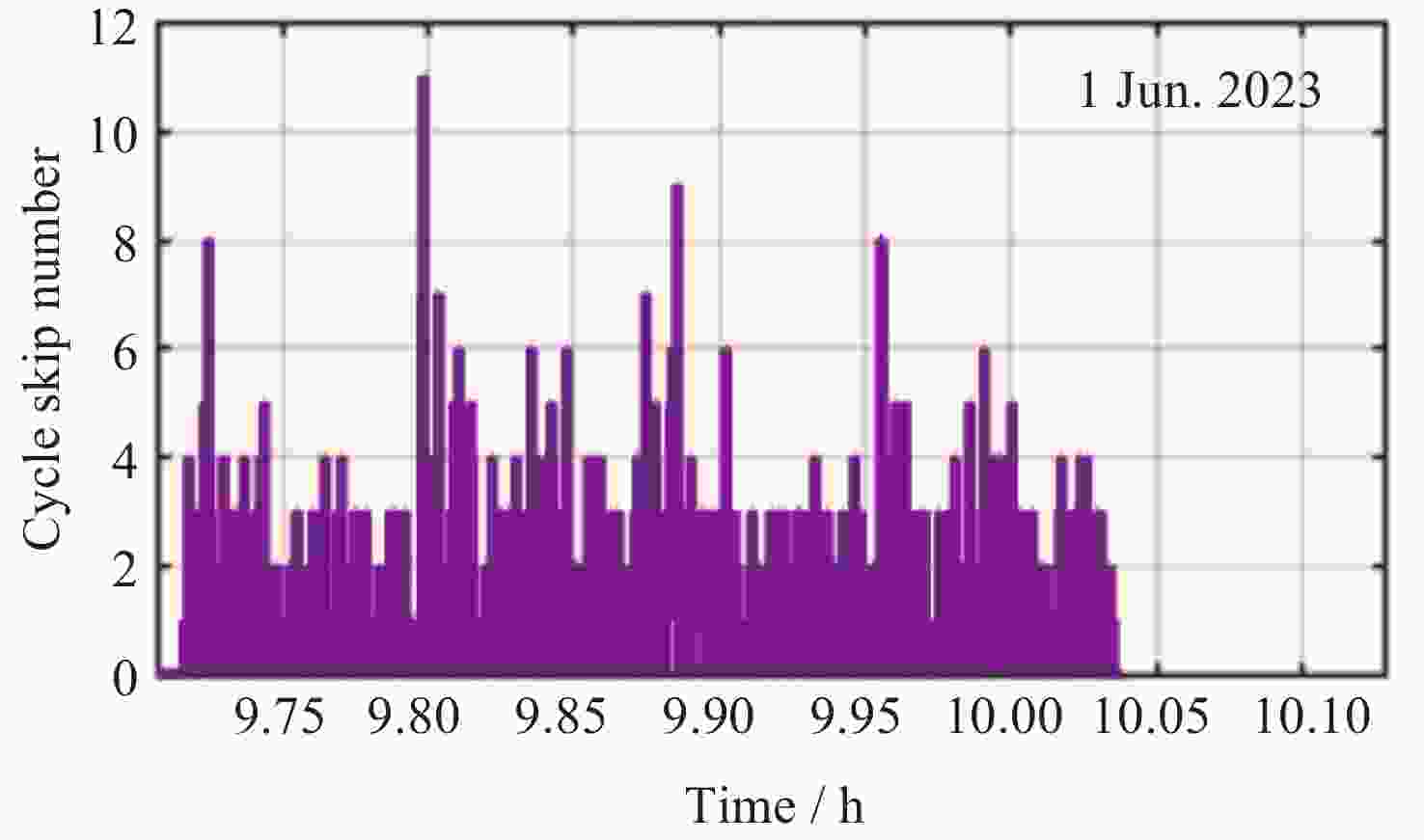
摘要: 在偏远林区, 参考站比较稀疏且较难进行网络通信, 多路径效应大, 观测时卫星周跳数大, 难以利用双差方式进行高精度实时(Real-Time Kinematic, RTK)定位. 为此, 在考虑广播星历钟差引入码硬件延迟的基础上, 推导了单北斗(BDS)/多模全球导航卫星系统(Global Navigation Satellite System, GNSS)单频和消电离层组合的伪距单点定位(Single Point Positioning, SPP)模型, 根据系统钟差基准不同引起的伪距硬件延迟的改正方法, 并采用林区实测的车载动态观测数据进行精度评估, 得出目前卫星导航基于单频SPP和IF SPP在偏远林区可以达到的定位精度. 结果表明, 在林区无参考站改正数的情况下, 单北斗以及GPS/Galileo/ BDS组合的SPP定位平面精度可以达到2 m. 相比单频SPP, 单北斗、GPS/Galileo/BDS消电离层组合SPP的平面精度分别提高约0.5 m和0.4 m, 基于消电离层组合的SPP具有更优的定位性能.Abstract: In remote forested areas, reference stations are sparse, making network communication difficult. There are significant multipath effects, causing large cycle slips during observations, making it challenging to achieve high-precision RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) positioning using double-difference methods. Considering the hardware delay introduced by broadcast ephemeris and clock errors, a pseudorange Single-Point Positioning (SPP) model for single Beidou (BDS)/multi-mode Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) single-frequency and ionosphere-free combinations is derived. Correction methods for pseudorange hardware delays caused by different system clock error references is introduced. Accuracy is evaluated using measured vehicle dynamic observation data in forested areas, and the achievable positioning accuracy of current satellite navigation is determined based on single-frequency SPP and ionosphere-free SPP in remote forested regions. The results show that under the condition of no correction data from reference stations in the forest area, the plane accuracy of BDS and GPS/Galileo/BDS SPP positioning can reach 2 m. Compared with single-frequency SPP, the plane accuracy of Beidou, GPS/Galileo/BDS ionosphere-free SPP is improved by about 0.5 m and 0.4 m respectively, and the SPP based on the ionosphere-free combination has better positioning performance.
-
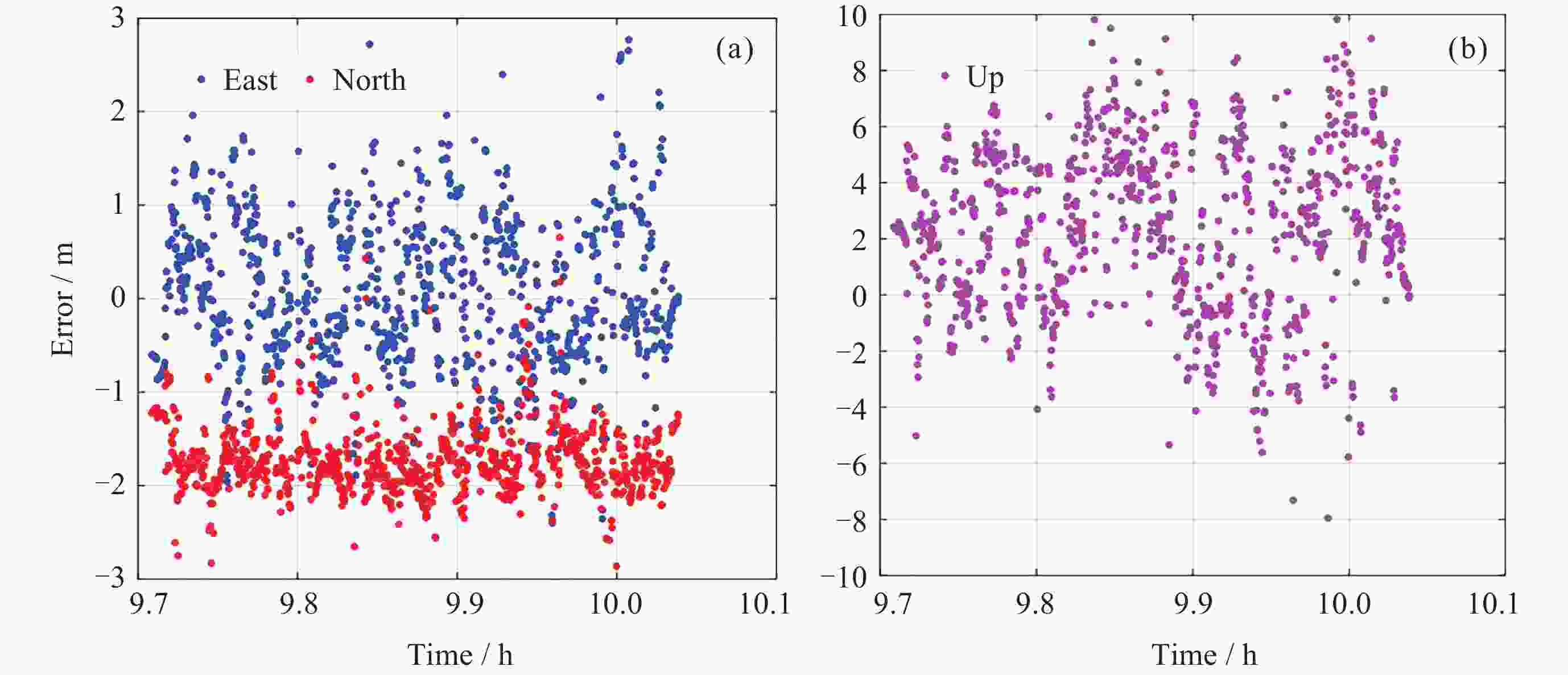
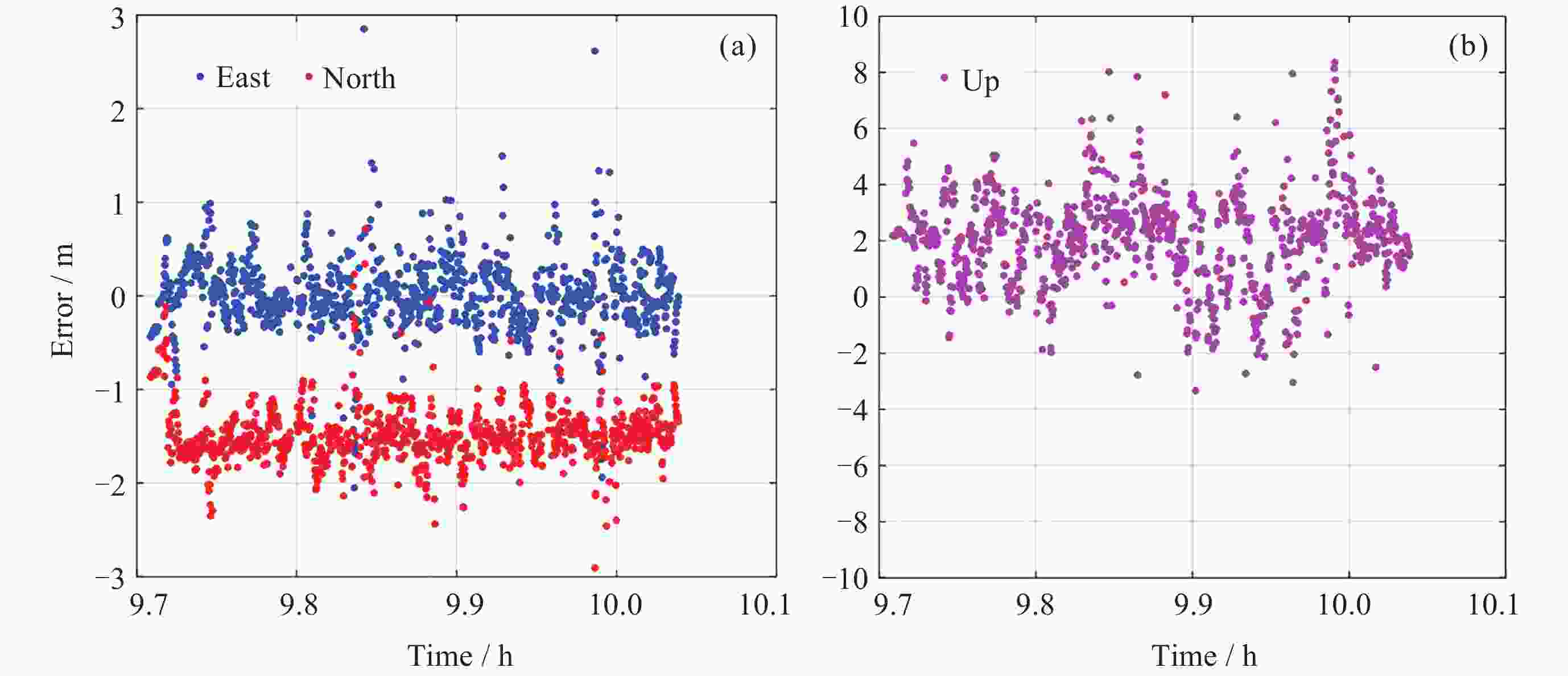
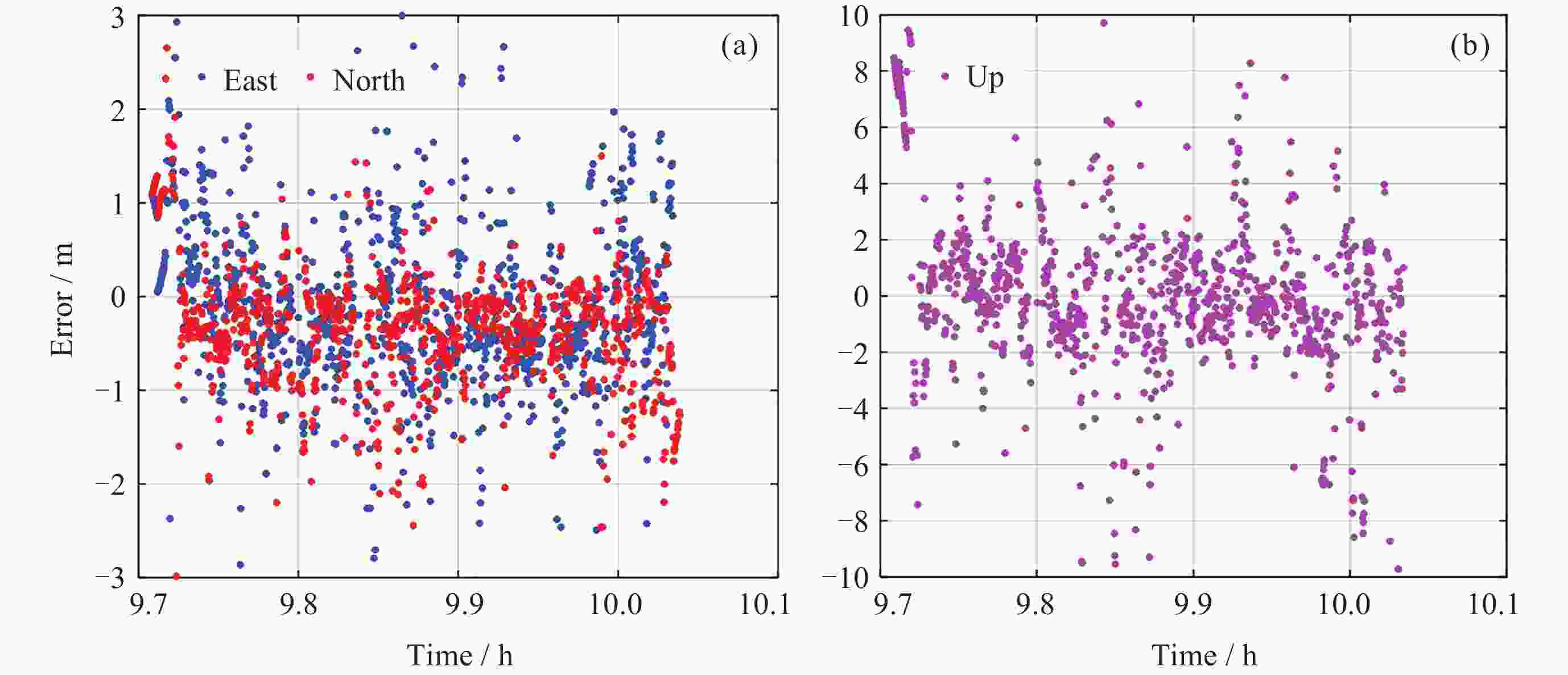
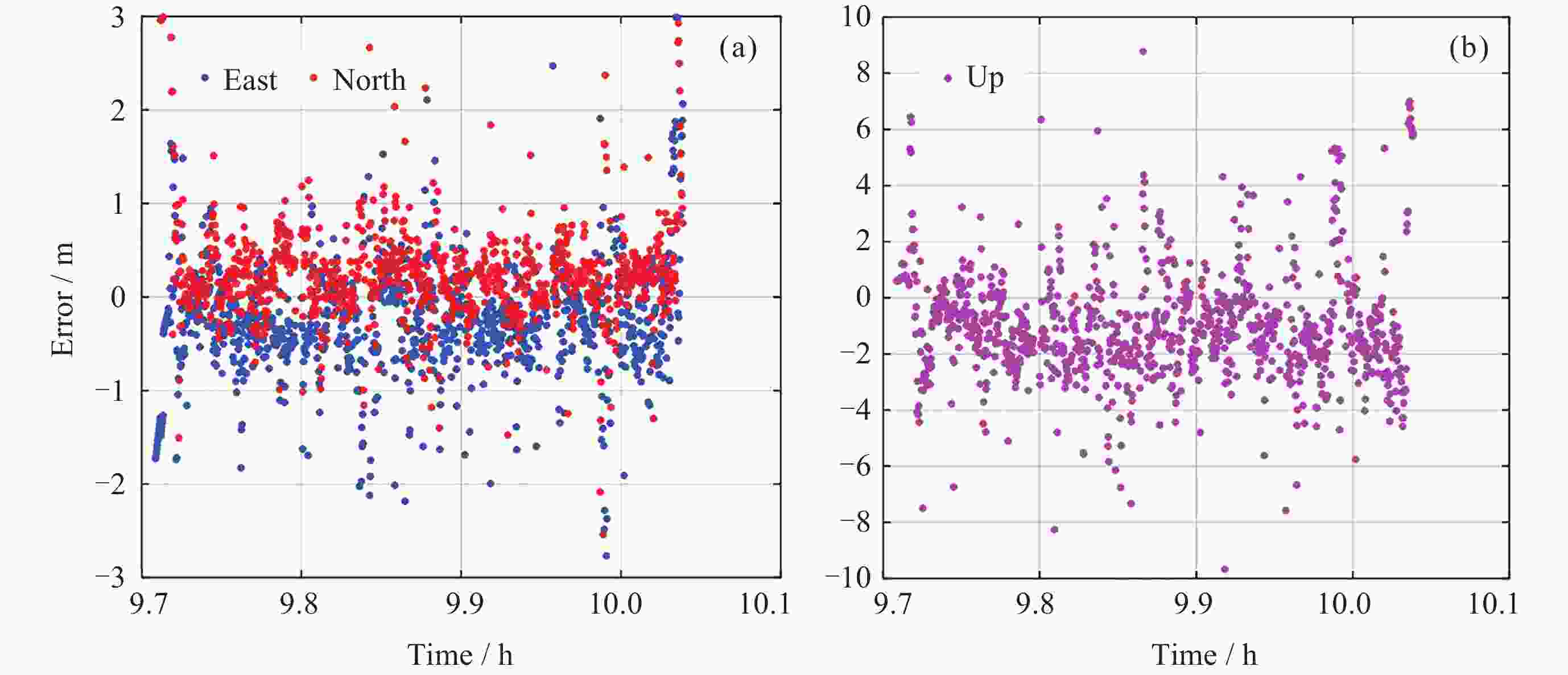
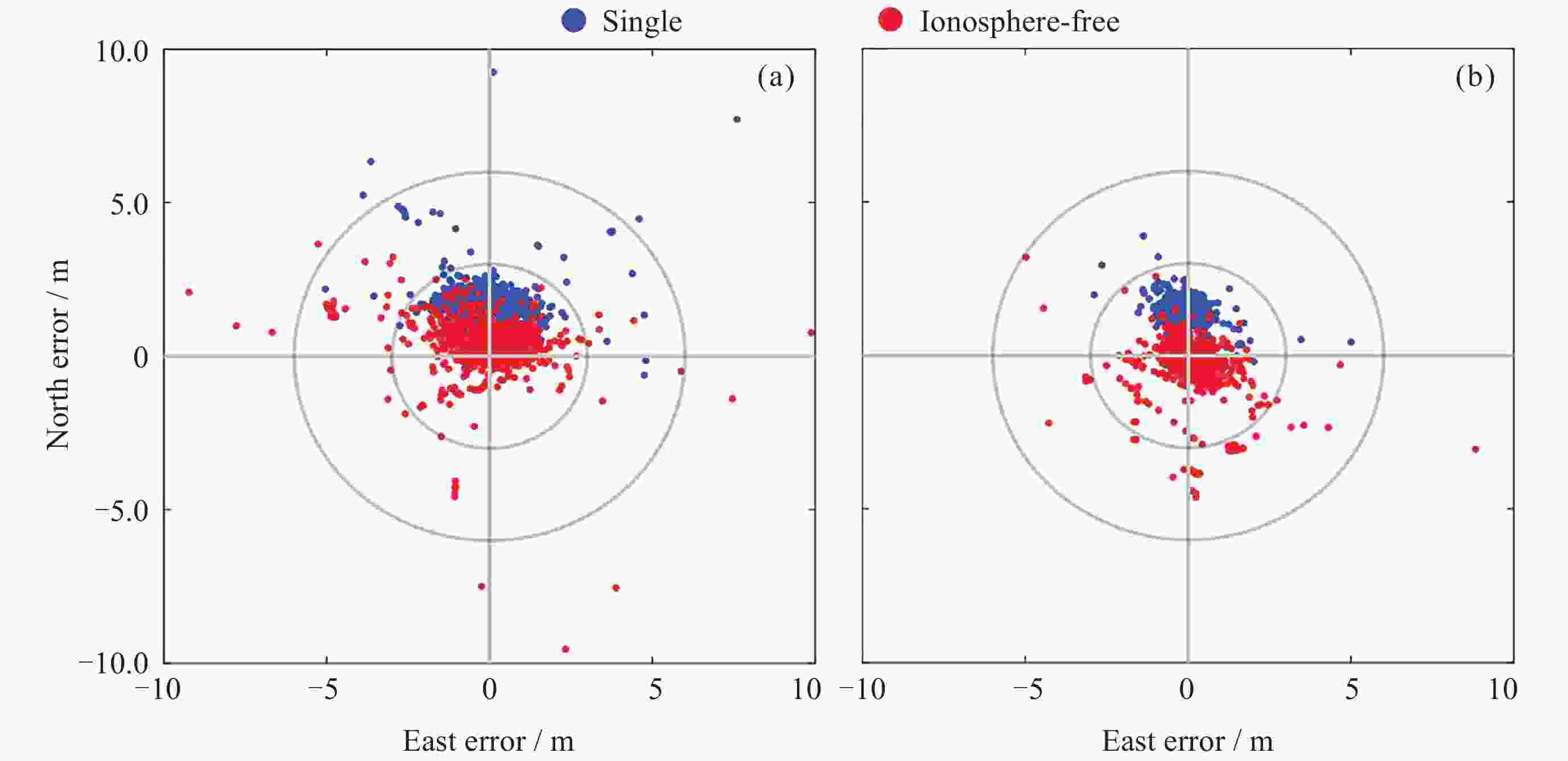
表 1 四个模型在三个方向上的定位误差
Table 1. Positioning errors of four models in three directions
Root mean square error / m 模型 East North Up Horizontal BDS单频SPP 1.0 1.9 3.9 2.1 BDS IFSPP 1.4 0.9 4.5 1.6 三系统单频SPP
三系统IF SPP0.5
0.91.5
0.92.6
2.41.6
1.2 -
[1] 庞丽峰, 黄水生, 李万里, 等. 全球导航卫星系统在我国林业中的应用[J]. 世界林业研究, 2019, 32(5): 41-46PANG Lifeng, HUANG Shuisheng, LI Wanli, et al. Application of GNSS in forestry sector in China[J]. World Forestry Research, 2019, 32(5): 41-46 [2] KATSIGIANNI G, LOYER S, PEROSANZ F. PPP and PPP-AR kinematic post-processed performance of GPS-only, Galileo-only and multi-GNSS[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(21): 2477 doi: 10.3390/rs11212477 [3] 孔豫龙, 柴洪洲, 潘宗鹏, 等. 弱电离层组合SPP在极区定位效果分析[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2017, 34(5): 470-474KONG Yulong, CHAI Hongzhou, PAN Zongpeng, et al. Analysis of SPP result in polar regions based on iono-weak combination[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2017, 34(5): 470-474 [4] 李元鸿, 孙艳丽, 张英, 等. 北斗林业生态移动巡护平台在森林管护中的研发及应用[J]. 林业资源管理, 2020(4): 153-160LI Yuanhong, SUN Yanli, ZHANG Ying, et al. Research and application of Beidou forestry ecological mobile patrol platform in forest management and protection[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2020(4): 153-160 [5] 胡鸿, 杨雪清, 黄静华, 等. 北斗卫星导航在林业中的应用模式研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2017(3): 120-127HU Hong, YANG Xueqing, HUANG Jinghua, et al. Research on application model of Beidou satellite navigation in forestry[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2017(3): 120-127 [6] 黄颖, 唐小明, 黄水生, 等. 林业野外巡护采集信息北斗短报文编码设计及应用[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2014, 34(8): 106-110 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2014.08.022HUANG Ying, TANG Xiaoming, HUANG Shuisheng, et al. BeiDou short message encoding design and application for collected information in forestry patrol[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2014, 34(8): 106-110 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2014.08.022 [7] 闫飞, 王春博, 吴永睿, 等. 森林BDS/GPS组合定位算法与精度分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(4): 221-227,373 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.04.025YAN Fei, WANG Chunbo, WU Yongrui, et al. Algorithm implementation and precision analysis of forest BDS/GPS combined positioning[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(4): 221-227,373 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.04.025 [8] 申丽丽, 郭际明, 王磊. 多GNSS系统组合在城市峡谷中的定位性能分析[J]. 地理空间信息, 2017, 15(1): 50-52,62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4623.2017.01.015SHEN Lili, GUO Jiming, WANG Lei. Performance analysis of multi-GNSS positioning in urban canyon environment[J]. Geospatial Information, 2017, 15(1): 50-52,62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4623.2017.01.015 [9] 张益泽. 北斗实时高精度定位服务系统研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2018, 47(9): 1293 doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20170534ZHANG Yize. Research on real-time high precision BeiDou positioning service system[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2018, 47(9): 1293 doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20170534 [10] 石君杰, 陈忠震, 孟令宇, 等. GNSS RTK 技术在林木定位及微地形测量中的应用[J]. 林业资源管理, 2019(4): 117-123,131SHI Junjie, CHEN Zhongzhen, MENG Lingyu, et al. Applications of GNSS RTK technology to positioning forest location and measuring microtopography[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2019(4): 117-123,131 [11] 武红敢, 罗鹏, 杨云凤, 等. 森林环境下的北斗卫星导航系统性能分析[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(5): 1-7WU Honggan, LUO Peng, YANG Yunfeng, et al. Performance of BeiDou navigation satellite system in forested conditions[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(5): 1-7 [12] YIN X, CHAI H Z, XU W B, et al. Realization and evaluation of real-time uncombined GPS/Galileo/BDS PPP-RTK in the offshore area of China’s Bohai sea[J]. Marine Geodesy, 2022, 45(6): 577-594 doi: 10.1080/01490419.2022.2057628 [13] TEUNISSEN P G, MONTENBRUCK O. Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems[M]. Cham: Springer, 2017 [14] BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document-Open Service Signal (Version 2.1) [Z]. China Satellite Navigation Office, 2016 [15] CHEN J P, ZHANG Y Z, WANG J G, et al. A simplified and unified model of multi-GNSS precise point positioning[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2015, 55(1): 125-134 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2014.10.002 -
-





 叶少春 男, 1998年1月出生于浙江省绍兴市, 现为浙江农林大学环境与资源学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为组合导航和林业测绘. E-mail:
叶少春 男, 1998年1月出生于浙江省绍兴市, 现为浙江农林大学环境与资源学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为组合导航和林业测绘. E-mail:  尹潇 男, 1987年8月出生于山东省济宁市, 现为浙江农林大学环境与资源学院讲师、硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为多源传感器导航与智能感知. E-mail:
尹潇 男, 1987年8月出生于山东省济宁市, 现为浙江农林大学环境与资源学院讲师、硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为多源传感器导航与智能感知. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: