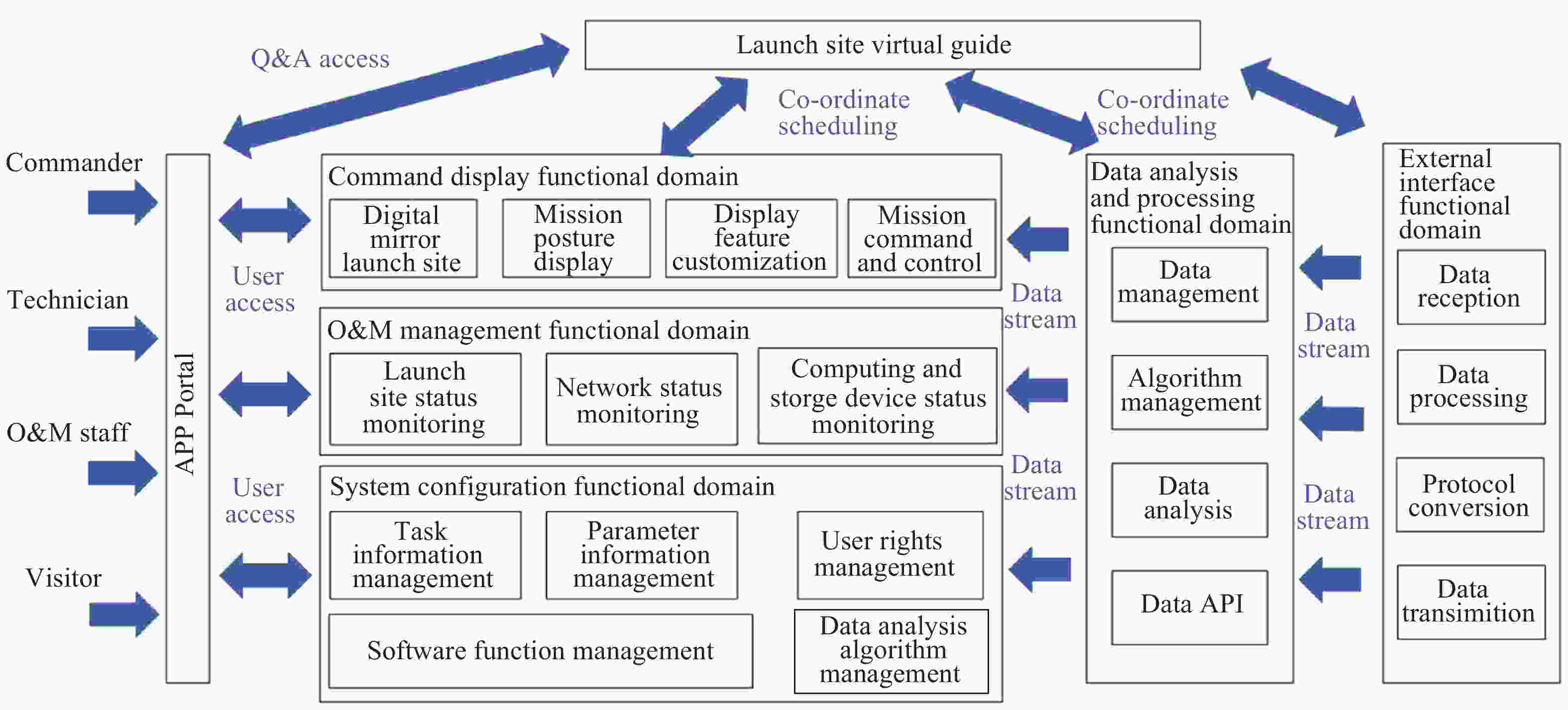
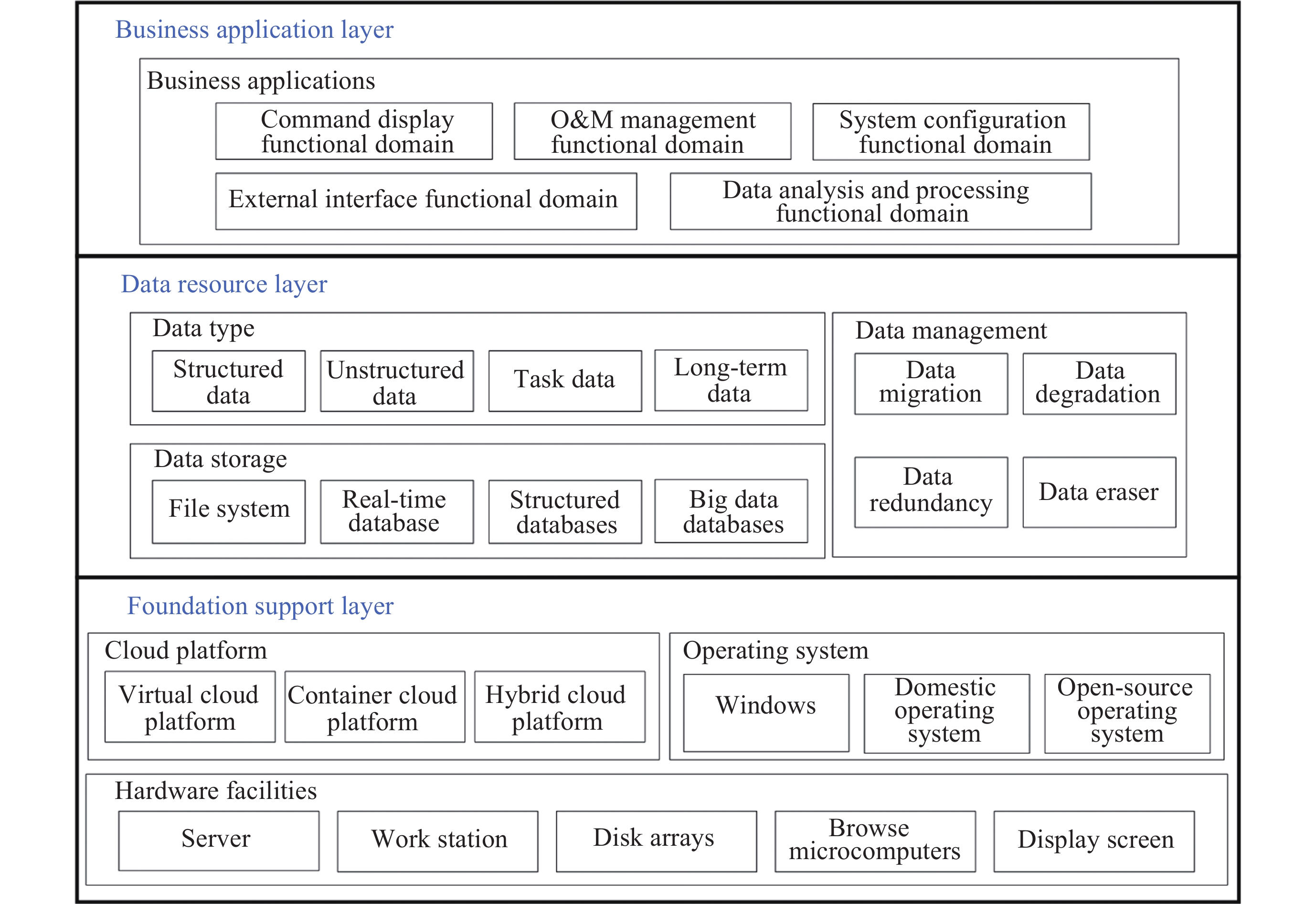
Design of C3I System for Intelligent Space Launch Sites
-
摘要: 中国航天事业的快速发展, 空间科学、空间技术、空间应用的全面突破, 航天发射频率的不断提高, 对航天发射场的服务能力提出了更高的要求. 随着云计算和大数据等技术的飞速发展, 中国航天发射场陆续开展了信息化和数字化转型, 以打造智慧发射场为目标进行升级改造. 在这一背景下, 本文提出智慧发射场指挥监控系统的总体设计思路与技术选型策略, 从系统的可靠性、拓展性与智慧性三个维度进行补充分析并提出后续建设思路, 从发射场信息系统优化设计角度提升发射服务能力, 丰富航天任务、空间科学探测任务的发射资源. 研究成果可为后续发射场建设与升级改造提供参考, 为中国未来的航天任务和空间探测任务提供有力的发射服务保障.Abstract: China’s aerospace industry has been experiencing a swift advancement, pushing the envelope in the realms of space science, technology, and applications. This innovation wave has created a significant influence further bolstering the long-term strategic vision towards the construction of advanced space stations, and has breathed life into ambitious scientific and technological satellite launch missions. Consequently, China is witnessing a surge in the frequency of space launches translating into a substantially heightened demand on the functional capabilities of space launch sites. Aligning closely with the rapidly developing digital technologies, such as cloud computing and big data, the transformation of China’s space launch sites into a modern and dynamic digital and information-based infrastructure has gained momentum. The end-goal fuelling this transformation is the establishment of the so-called “intelligent launch sites”, a vision sought to be achieved through widespread upgrading and renovation efforts. Amid this digital metamorphosis, the launch site information system emerges as a critical pillar, indispensable for catalysing the integration of “intelligence” into the launch site operations, with a key focus on the C3I system, the cornerstone of the entire information infrastructure. In terms of the design approach for intelligent launch site’s C3I systems, this article presents the overall design concept, a three-layer information system architecture consisting of foundation support layer, data resource layer and business application layer and propose a technical selection strategy from the perspectives of software and hardware environment, database selection, data structure design, and the functional and logical design of business applications. It also provides supplementary analyses from the perspectives of system reliability, scalability, and intelligence, and proposes subsequent construction approaches. By optimizing the design of the launch site information system, the launch service capability can be enhanced, and the launch resources for space missions and scientific explorations can be enriched. The research findings can serve as a reference for future launch site construction and upgrade projects, and provide robust launch service guarantees for China's future aerospace missions and space exploration tasks.
-
Key words:
- Intelligent launch sites /
- Information system /
- C3I system /
- System design
-
表 1 云平台选型优劣势分析
Table 1. Analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of cloud platform selection
优势 劣势 虚拟云平台 虚拟机具备图形化界面
虚拟机支持任意操作系统计算资源消耗大, 虚拟机重启速度慢(操作系统重启时间), 虚拟机需预先划分计算资源, 难以实现动态负载均衡或迁移 容器云平台 轻量、计算资源消耗小, 容器重启速度快(秒级), 能够监视容器内进程状态, 能够动态实现负载均衡与节点间容器迁移 容器不提供图形化界面, 容器均使用同一套Linux内核操作系统 表 2 发射场数据类型清单
Table 2. Data types of space launch site
数据类型 任务阶段采集数据 长期采集数据 结构化数据 参数类数据 火箭测试数据
卫星测试数据
加注供气数据
飞行测控数据
本场气象数据空调系统数据
供电系统数据
网络监控数据二维表格类数据 工作调度单 人员履历数据
设备履历数据
系统配置数据非结构化数据 音视频 任务摄像头视频
预案文档安防摄像头视频 -
[1] 王翔, 王为. 我国天宫空间站研制及建造进展[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(34): 4017-4028 doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-0499WANG Xiang, WANG Wei. Development and construction progress of the Tiangong space station in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(34): 4017-4028 doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-0499 [2] 尹怀勤. 探月计划和"嫦娥"系列探测器[J]. 百科探秘: 航空航天, 2017(Z1): 19YIN Huaiqin. Lunar exploration program and “Chang’E” Series Probe[J]. Encyclopedia Exploration: Aerospace , 2017(Z1): 19 [3] 陈丽, 赵聪. 中国首次火星探测任务“天问一号”探测器成功发射[J]. 中国航天: 英文版, 2020, 21 (2): 1CHEN Li, ZHAO Cong. China Successfully Launched Its First Mars Mission, Tianwen 1[J]. Aerospace China, 2020(2): 51-51 [4] 王晓宇, 祁首冰, 赵汉卿. 天琴奏响, 空间引力波探测技术验证传来佳音——访天琴一号技术试验卫星总设计师张立华[J]. 国际太空, 2020(7): 5WANG Xiaoyu, QI Shoubing, ZHAO Hanqing. Tianqin plays, good news comes from the verification of space gravitational wave detection technology——Zhang Lihua, chief designer of Tianqin-1 technical test satellite[J]. Space International, 2020(7): 5 [5] 邓劲松. 爱因斯坦探针卫星——揭秘激荡的X射线宇宙[J]. 现代物理知识, 2020, 32(5): 7DENG Jinsong. Einstein Probe Satellite——Unveiling the turbulent X-ray universe[J]. Modern Physical Knowledge, 2020, 32(5): 7 [6] 陈海鹏, 张兵, 徐文彬. 对我国运载火箭高密度发射应对措施的几点思考[J]. 中国航天, 2015(12): 3CHEN Haipeng, ZHANG Bing, XU Wenbin. Some thoughts on the countermeasures for high-density launch of China’s carrier rockets[J]. China Aerospace, 2015(12): 3 [7] 景骢. 中国航天发射次数首次独占世界第一[J]. 太空探索, 2019(2): 1JING Cong. China's space launch number occupies the first place in the world for the first time[J]. Space Exploration, 2019(2): 1 [8] 肖建军, 董二奎. 我国航天发射场面临的形势与未来发展探讨[J]. 中国航天, 2015(6): 11-17XIAO Jianjun, DONG Erkui. Discussion on the situation and future development of China's space launch site[J]. China Aerospace, 2015(6): 11-17 [9] 惠兴晨, 程博, 陈昌旭, 等. 长征二号丙运载火箭高密度发射研制管理模式探索与展望[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术(中英文), 2023(3): 138-140HUI Xingchen, CHENG Bo, CHEN Changxu, et al. Exploration and prospect of high density launch development and management mode for Long March 2C Launch Vehicle[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles, 2023(3): 138-140 [10] 澄空. 未来五年, 中国将开启全面建设航天强国新征程——《2021中国的航天》白皮书发布[J]. 国际太空, 2022(2): 4-7CHENG Kong. In the next five years, China will embark on a new journey of building a space power in an all-round way——The white paper "China's Aerospace in 2021" was released[J]. Space International, 2022(2): 4-7 [11] 刘党辉, 蔡远文, 李岩, 等. 航天发射场建设技术革新研究[J]. 仪器与设备, 2023, 11(1): 11LIU Danghui, CAI Yuanwen, LI Yan, et al. Research on Technological Innovation for the Construction of Space Launch Sites[J]. Instrumentation and Equipments, 2023, 11(1): 11 [12] 刘阳, 辛腾达, 同江. 下一代智慧发射场发展研究[J]. 宇航总体技术, 2023, 7(2): 61-68LIU Yang, XIN Tengda, TONG Jiang. Research on the Development of the Next Generation Intelligent Launch Site[J]. Astronautical Systems Engineering Technology, 2023, 7(2): 61-68 [13] 肖力田. 智慧火箭发射场系统构建与技术发展研究[C]//第一届航天工程论坛. 上海: 中国宇航学会, 2018XIAO Litian. Research on the construction and technology development of smart rocket launch site system[C]//The 1st Aerospace Engineering Forum. Shanghai: Chinese So-ciety of Astronautics, 2018 [14] TOLK D A , PULLEN D J M. Ideas for a common Framework for Military M&S and C3I Systems[R]. Stockholm: 2023 Euro Simulation Interoperability Workshop, 2003 [15] 罗爱民, 罗雪山, 黄力. C3I系统体系结构框架研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2003, 23(6): 86-90 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.2003.06.013LUO Aimin, LUO Xueshan, HUANG Li. Study on the Architecture Framework of C3I System[J]. Systems Engineering – Theory& Practice, 2003, 23(6): 86-90 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.2003.06.013 [16] 王家伍, 沈怀荣, 唐立文. 现代航天发射场C3I系统探讨[J]. 指挥技术学院学报, 2001WANG Jiawu, SHEN Huairong, TANG Liwen. Discussion on the C3I system of modern space launch sites[J]. Journal of the Academy of Equipment Comm and & Technology, 2001 [17] 万全, 王东锋, 刘占卿, 等. 航天发射场总体设计[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2015.WAN Quan, WANG Dongfeng, LIU Zhanqing, et al. Overall Design of Space Launch[M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2015 [18] 程静, 张逢贵, 庄柯. 大数据与航天发射场[J]. 靶场试验与管理, 2013(6): 1-8CHENG Jing, ZHANG Fenggui, ZHUANG Ke. Big data and space launch sites[J]. Space Launch Sites Test & Ma-nagement, 2013(6): 1-8 [19] 蔡红维, 谢福锋, 胡清忠. 基于云计算的航天发射场业务网络体系架构[J]. 国防科技, 2020, 41(4): 6CAI Hongwei, XIE Fufeng, HU Qingzhong. Cloud computing-based business network architecture for space launch sites[J]. National Defense Technology, 2020, 41(4): 6 [20] 白永强, 申建平, 许寒. 航天发射场测发C3I系统一体化设计[J]. 导弹试验技术, 2010, 000(1): 12-14BAI Yongqiang, SHEN Jianping, XU Han. Integrated design of C3I system for space launch site[J]. Missile test technology, 2010, 000(1): 12-14 [21] GEORGE L. HBase: The definitive guide[J]. Andre, 2011, 12(1): 1-4 [22] 中国人民解放军总装备部. GJB 7337-2011 火箭、航天器与航天发射场信息传输规程[S]. 北京: 中国人民解放军总装备部, 2011 -
-




 刘梓琰 男, 1994年12月出生于北京市, 现为北京宇航系统工程研究所工程师, 主要研究方向为宇航总体技术、指挥信息系统设计等. E-mail:
刘梓琰 男, 1994年12月出生于北京市, 现为北京宇航系统工程研究所工程师, 主要研究方向为宇航总体技术、指挥信息系统设计等. E-mail: 
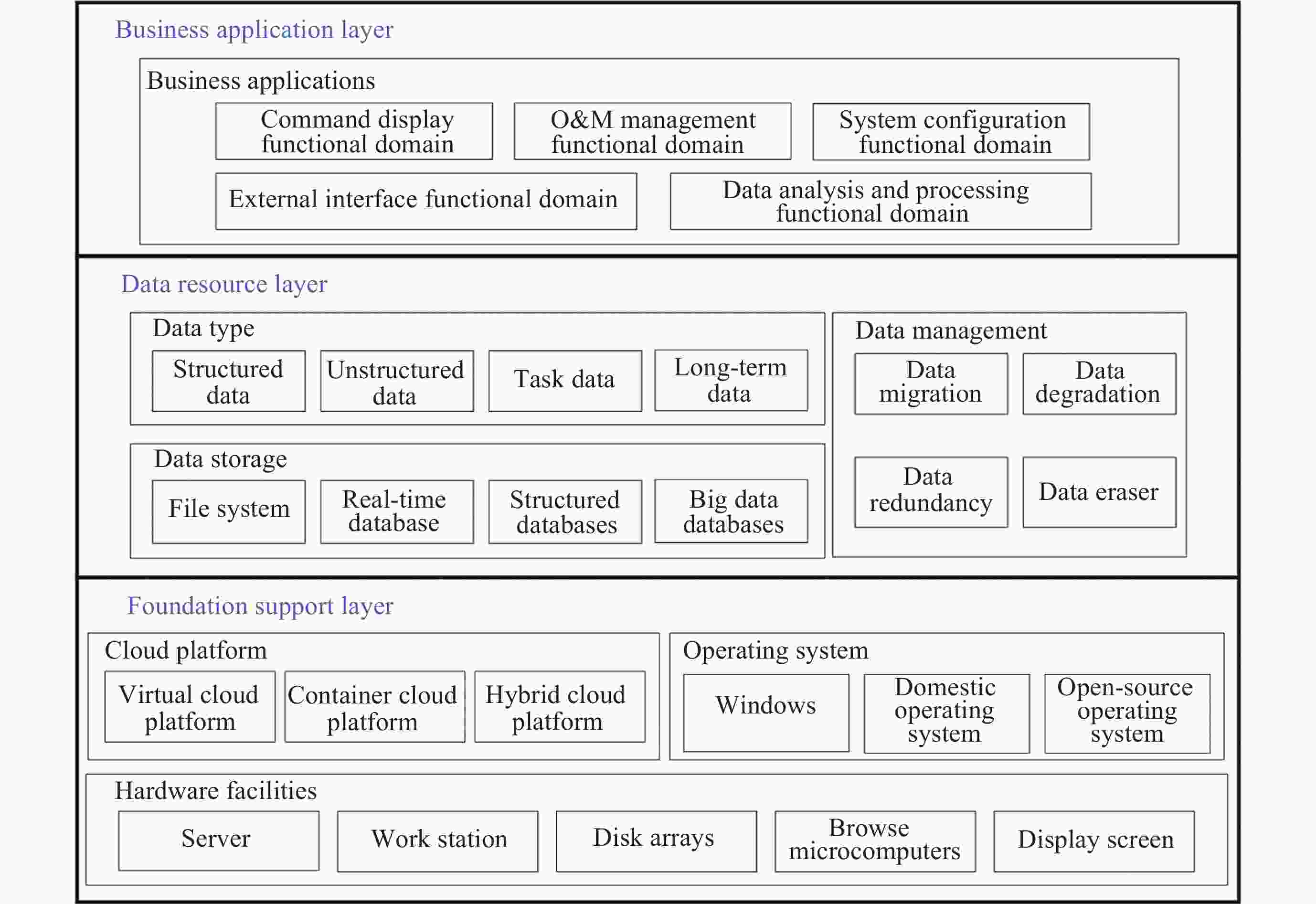
 下载:
下载: