Geomagnetic/Inertial Fusion Navigation Method Based on Magnetic Anomaly Gradient Measurement
-
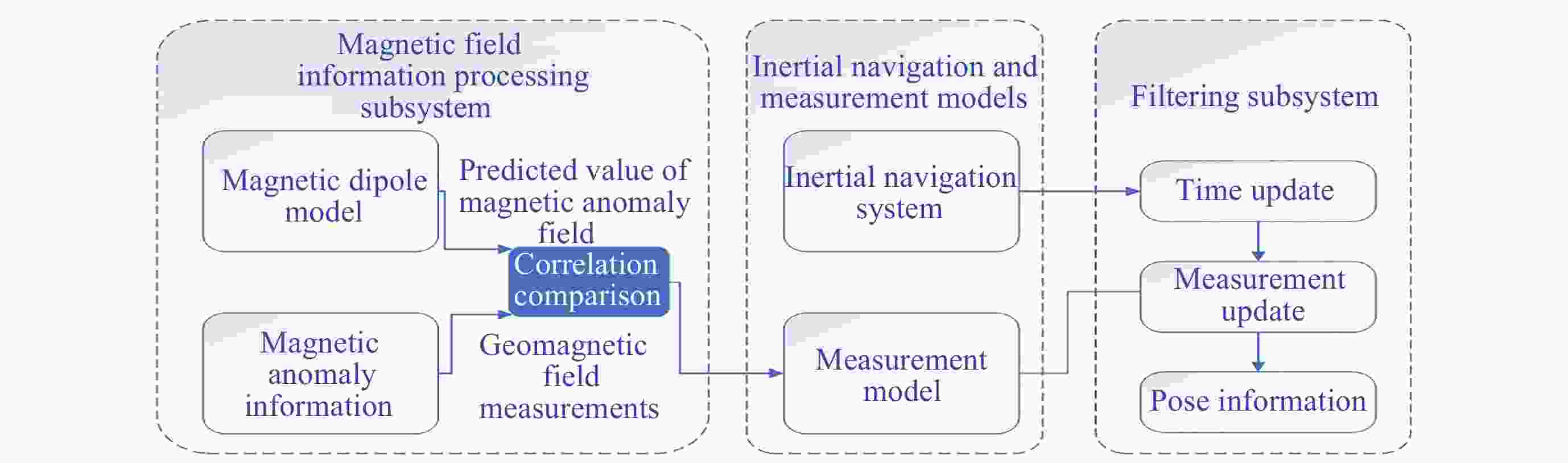
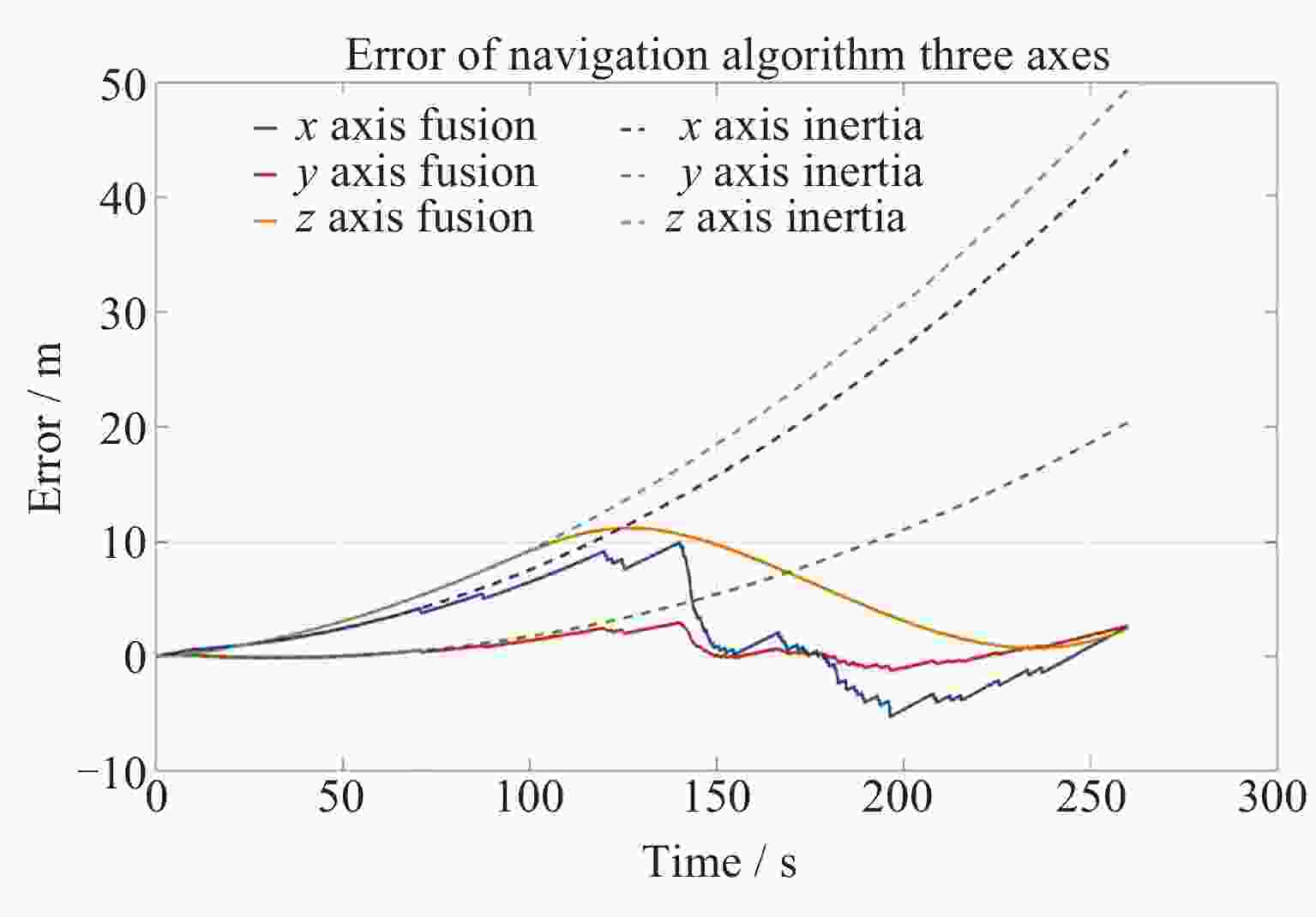
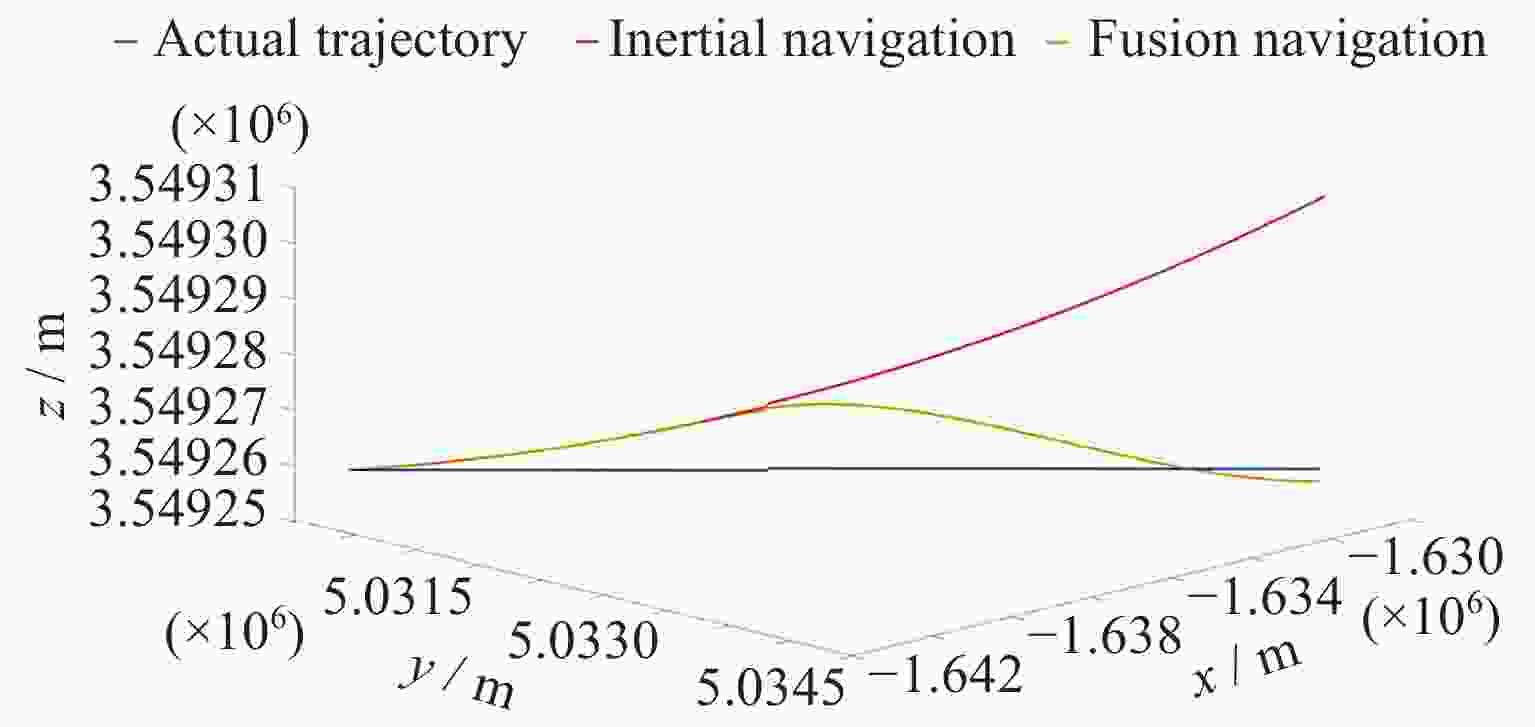
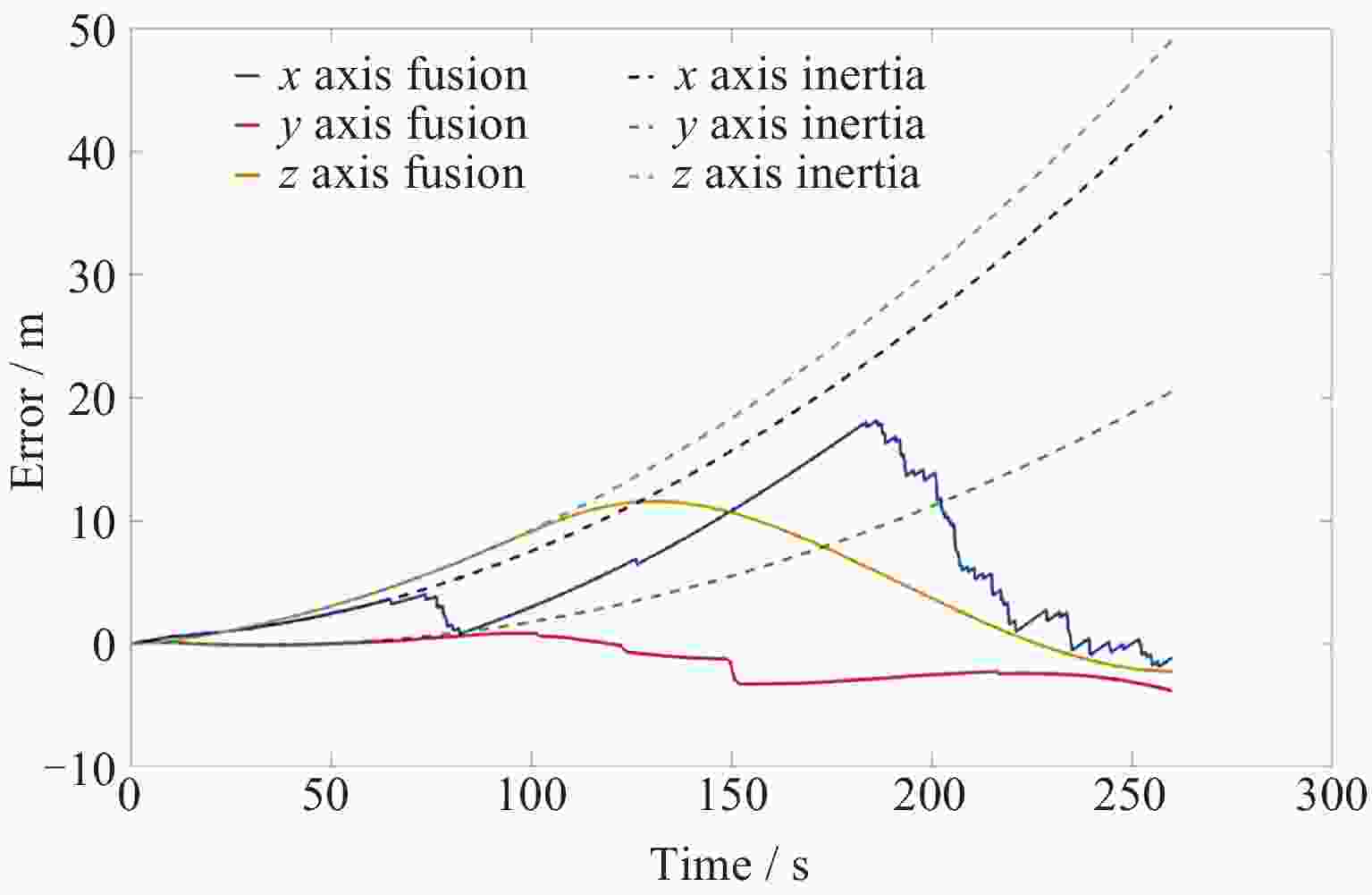
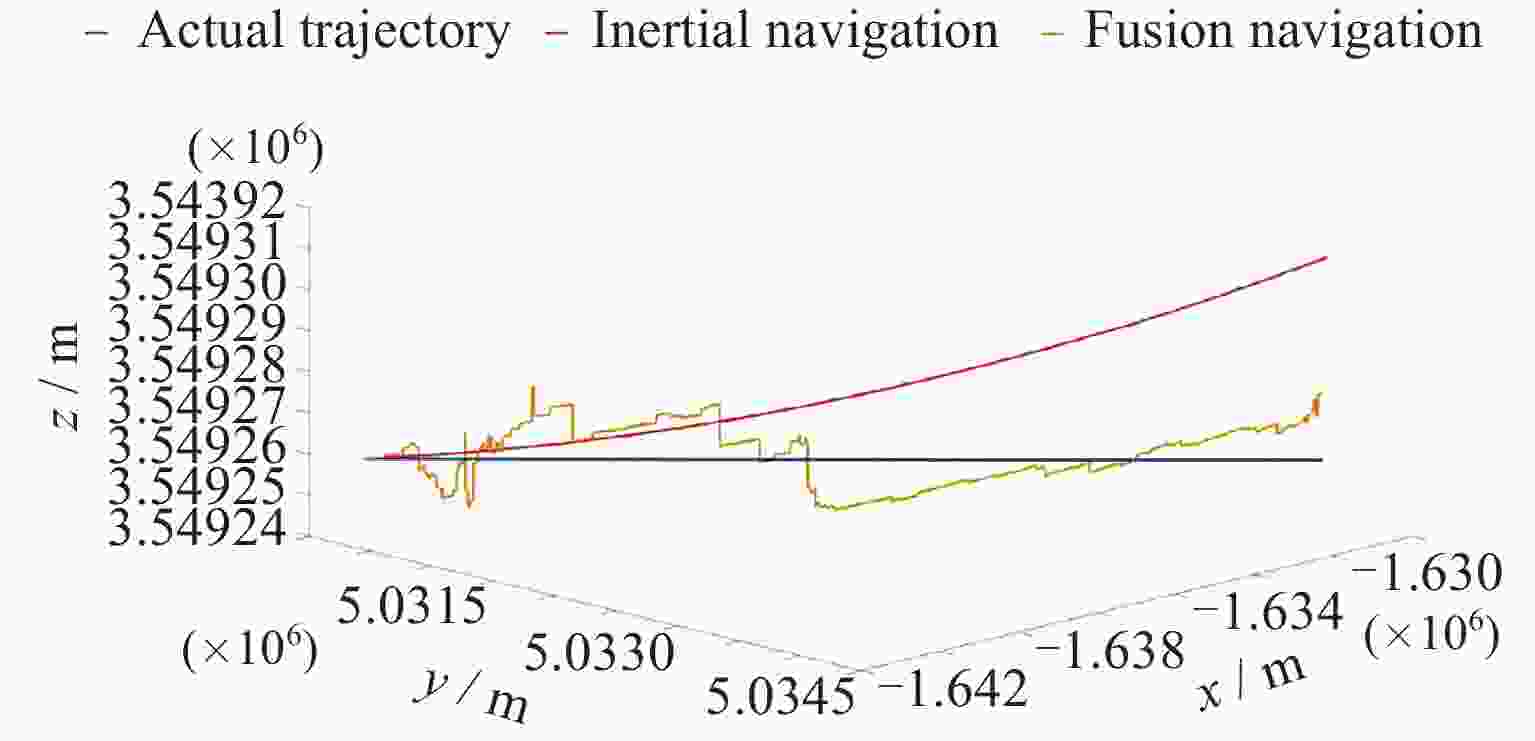
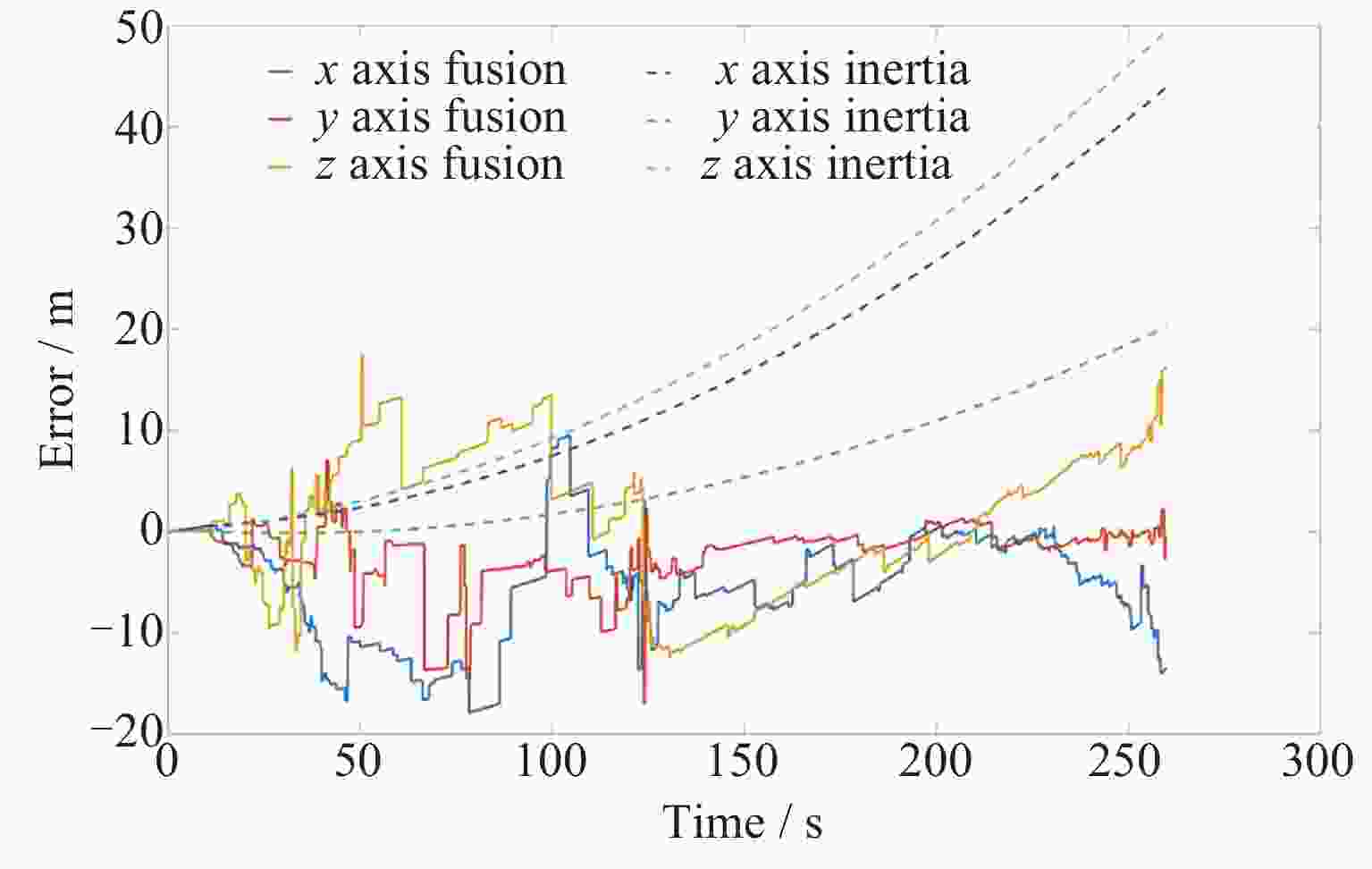
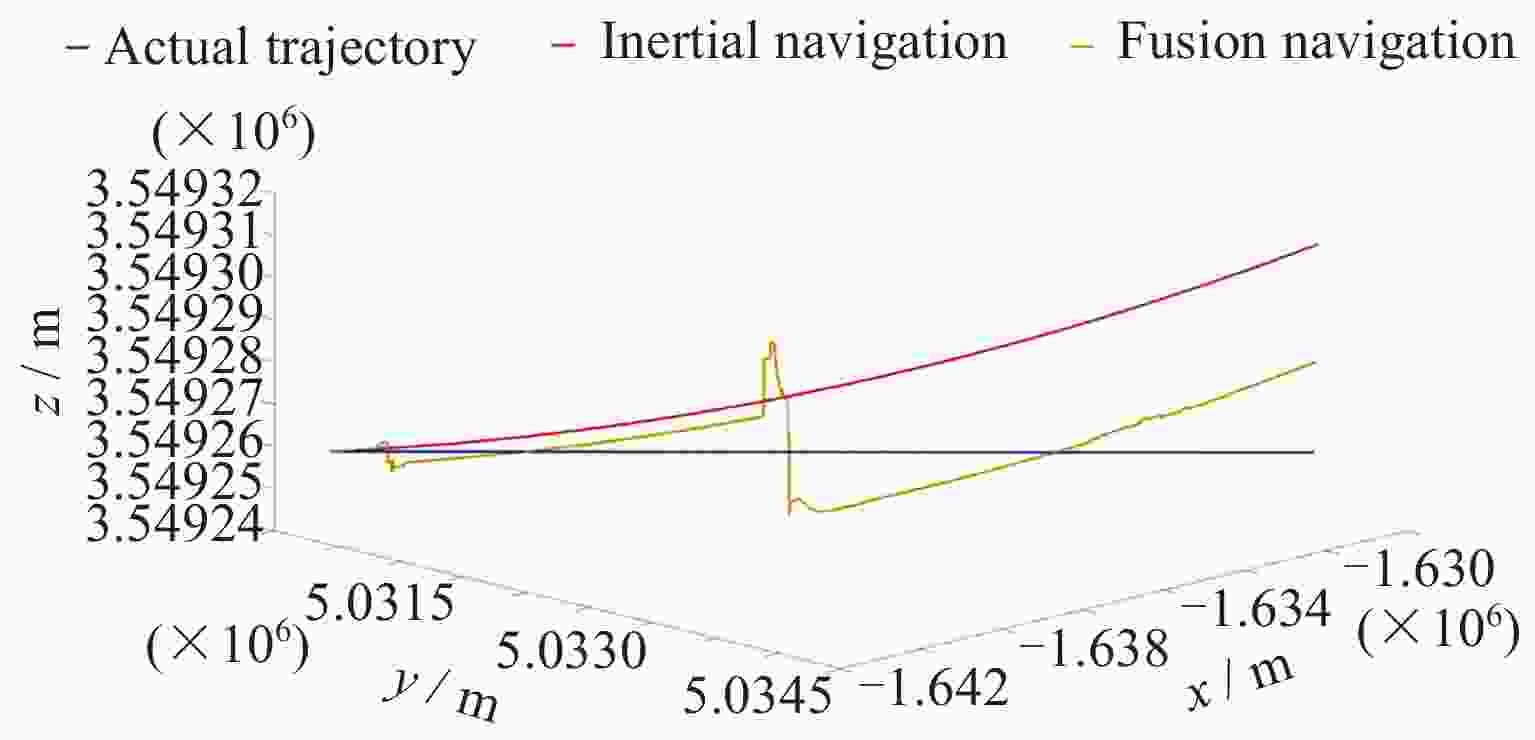
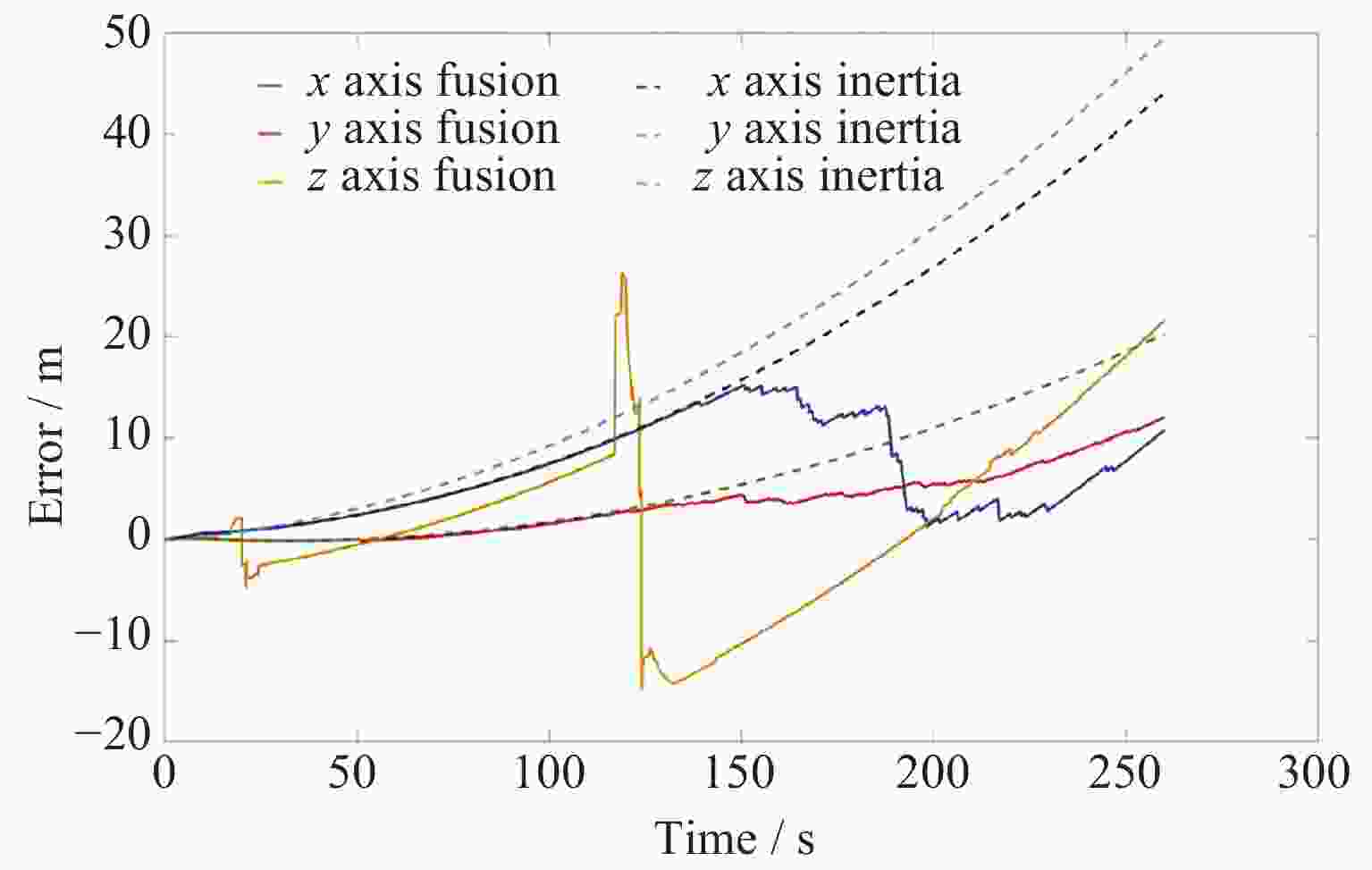
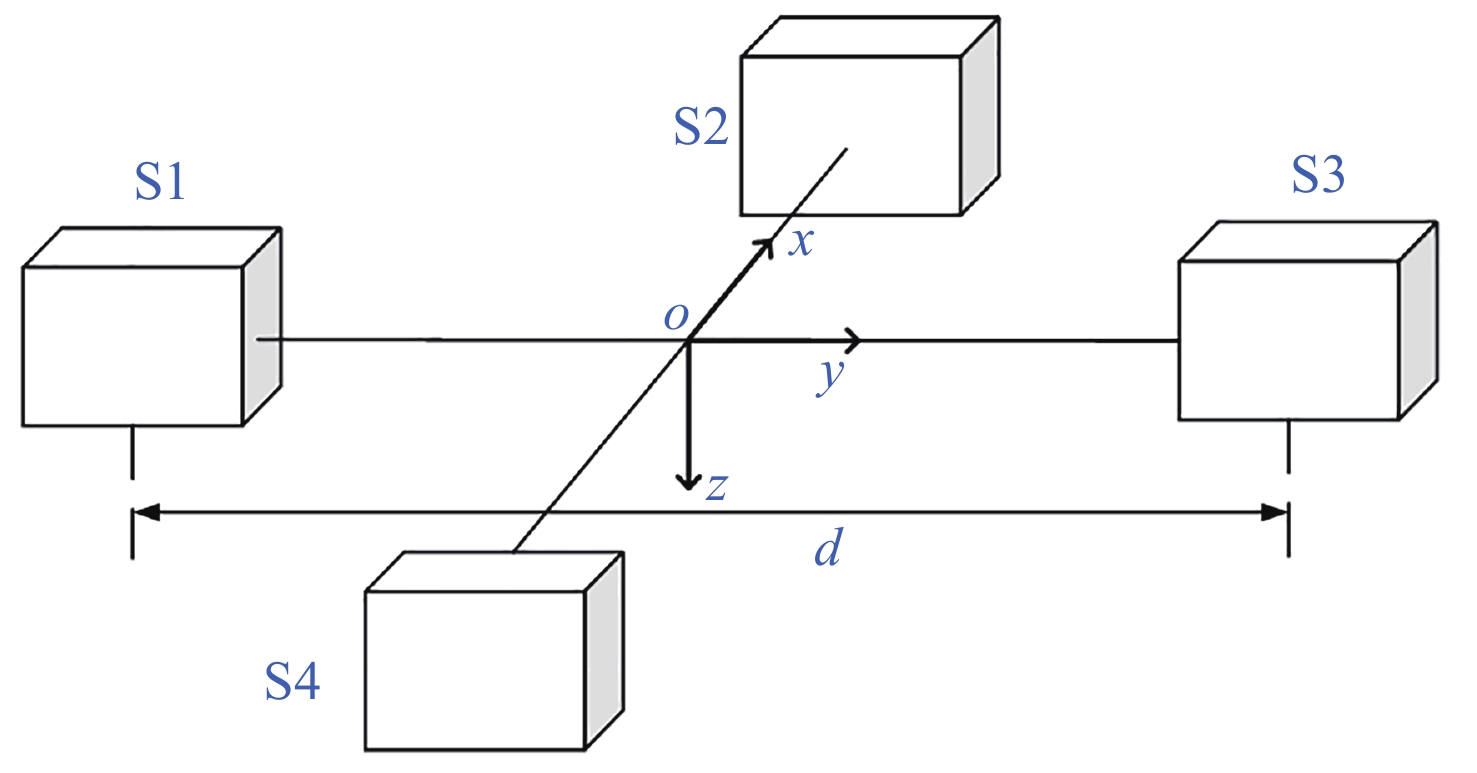
摘要: 地磁导航是一种基于地球天然磁场的导航方法, 其自主性强, 抗干扰性能好, 可以在多种环境下正常工作, 但低空/水下地磁匹配导航需要基于大量测量数据构建地磁图且对于平台计算能力要求较高, 给地磁导航的应用带来不便. 惯性导航在短时间内精度较高, 但随着时间推移会出现较大的累积误差. 本文将从地磁总场中提取的磁异常场前后两次测量间的差分信息作为观测量, 依据磁异常场的偶极子特征, 基于磁偶极子模型理论推导了应用于导航系统滤波器的磁异常梯度测量矩阵, 提出利用磁异常梯度信息修正惯性导航系统的误差的地磁/惯性融合导航方法, 降低了地磁导航对先验地磁图的要求, 同时修正了惯导导航误差. 对比纯惯性导航, 相同条件下该方法的导航位置精度有显著提升, 为运动平台自主导航探索了一种新方法.Abstract: Geomagnetic navigation is an autonomous navigation method that utilizes the natural magnetic field of the Earth. It has various advantages such as strong autonomy and good anti-interference performance, and can work normally in various environments to play its role. However, in the fields of low altitude navigation and underwater navigation, geomagnetic matching navigation requires the construction of geomagnetic maps based on a large amount of measurement data, and requires the motion platform equipped with this navigation method to have high computing power. The above issues bring inconvenience to the application of geomagnetic navigation. Inertial navigation method is a commonly used autonomous navigation method that has high accuracy in a short period of time. However, over time, its navigation results will have significant cumulative errors, which will affect the accuracy of navigation positioning. This article extracts differential information of magnetic anomaly fields from the total measurement information of the Earth's magnetic field through differential measurement information at different positions during platform movement, as the observation of the paper. Meanwhile, based on the magnetic dipole characteristics of the magnetic anomaly field, this article derives a magnetic anomaly gradient measurement matrix that can be applied to navigation system filters on the basis of the magnetic dipole model theory. By using the magnetic anomaly gradient information to correct the cumulative error of the inertial navigation system, a geomagnetic/inertial fusion navigation method is proposed. This method can reduce the requirement for high-precision prior geomagnetic maps in geomagnetic navigation, while also correcting navigation errors in inertial navigation. Comparing the navigation method proposed in this article with the pure inertial navigation method, it was found that the navigation position accuracy of this method has significantly improved under the same conditions. The research conducted in this article explores a new method for autonomous navigation of motion platforms.
-
Key words:
- Geomagnetic navigation /
- Inertial navigation /
- Magnetic dipole /
- Fusion navigation
-
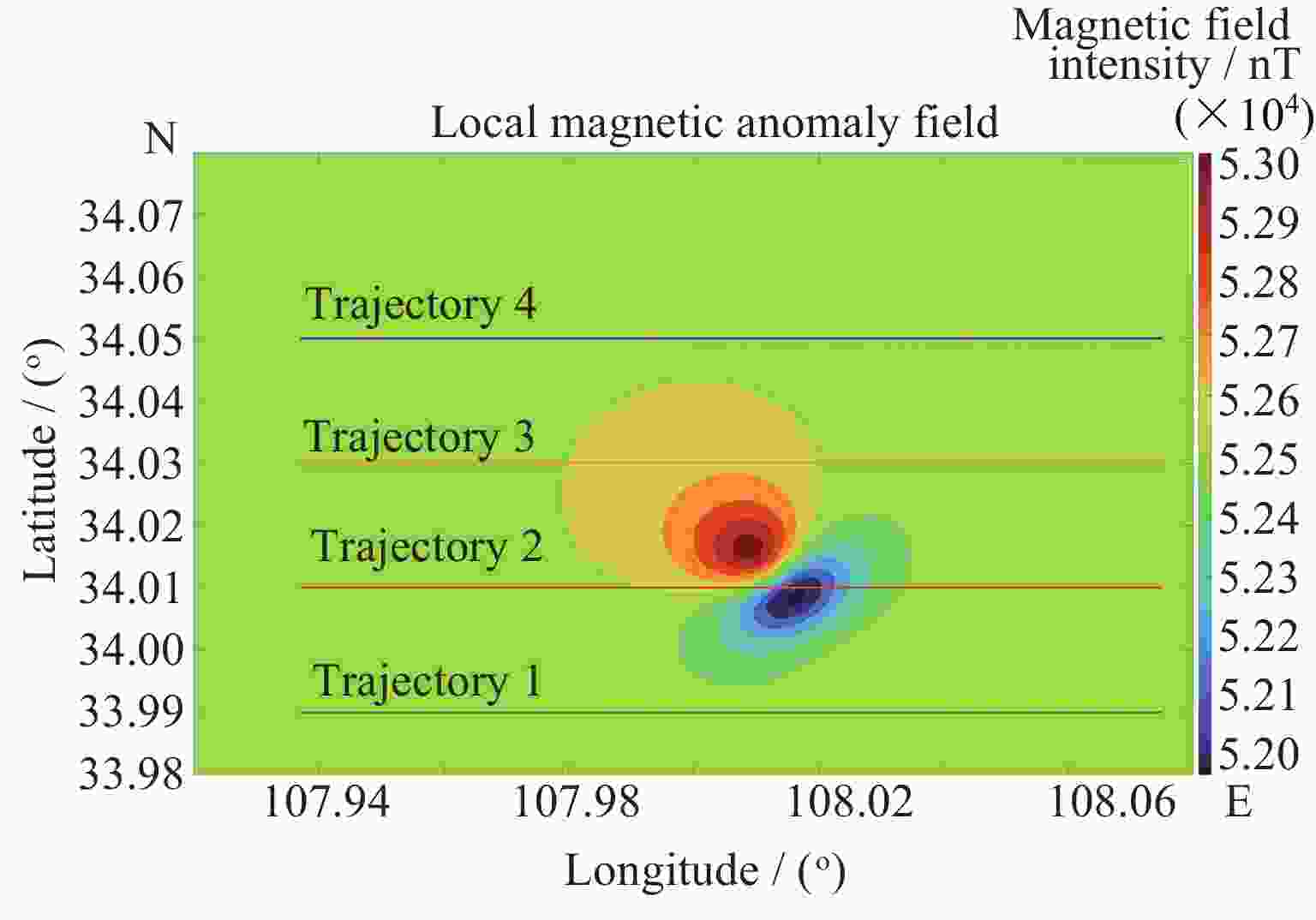
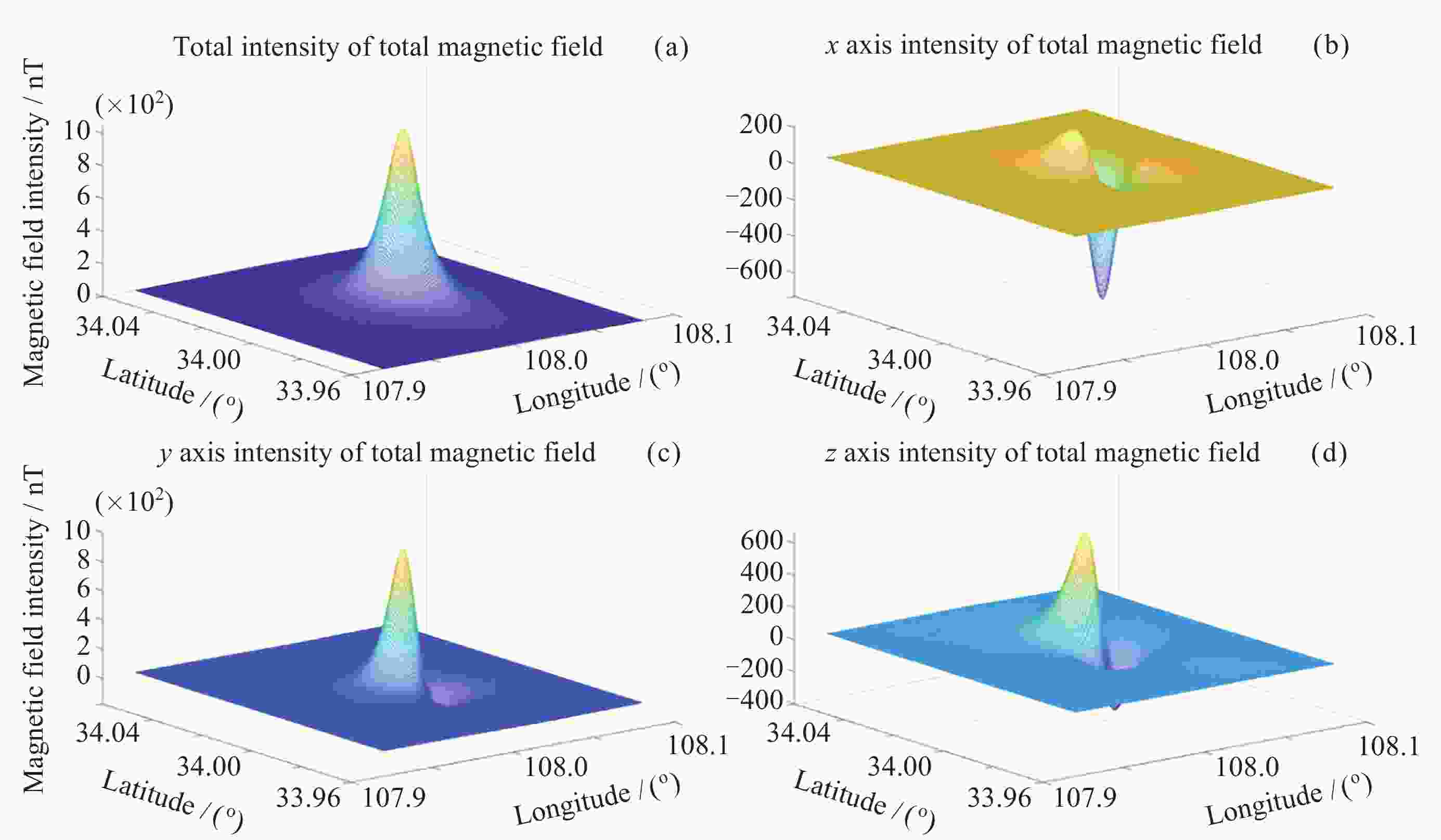
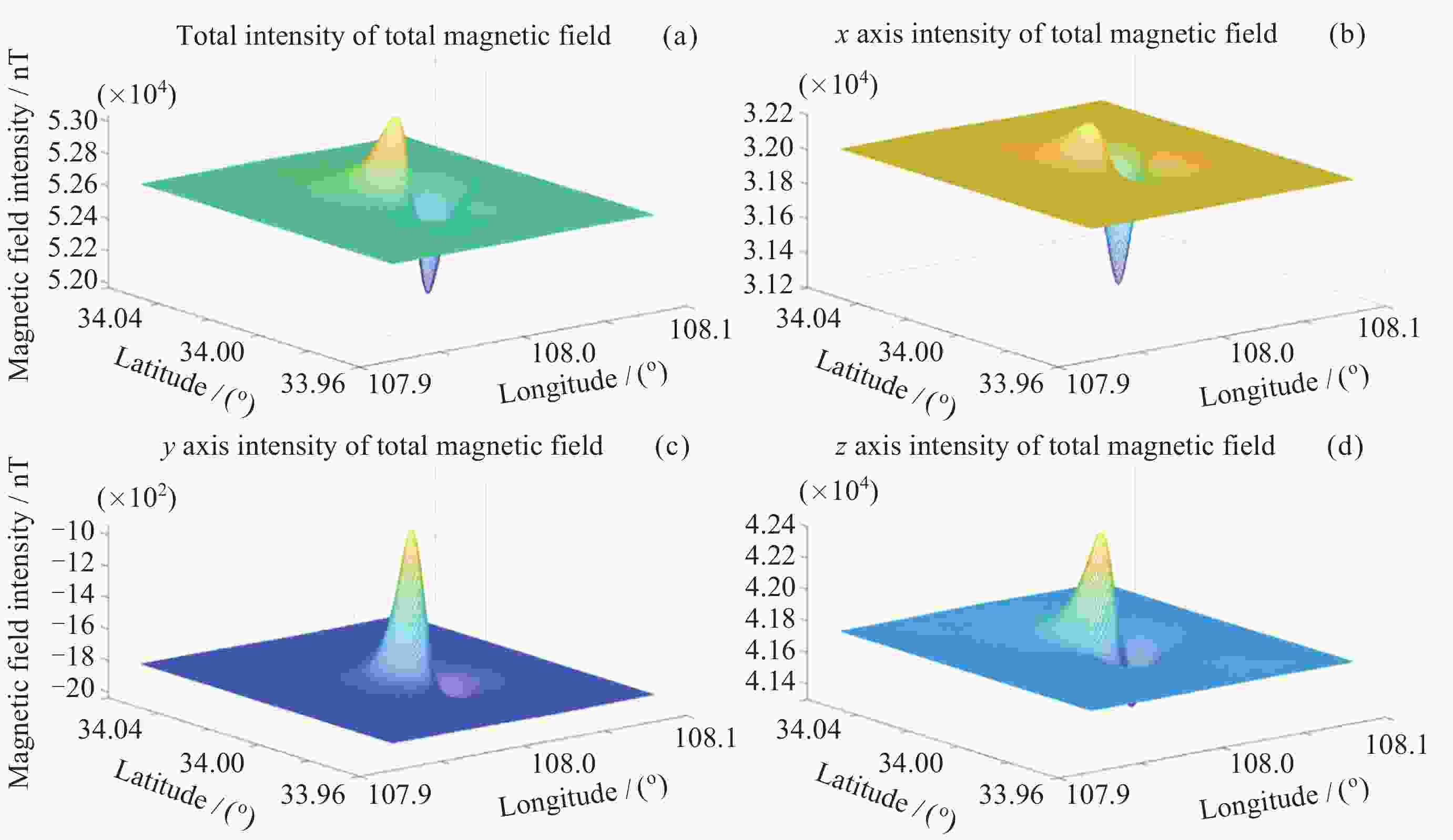
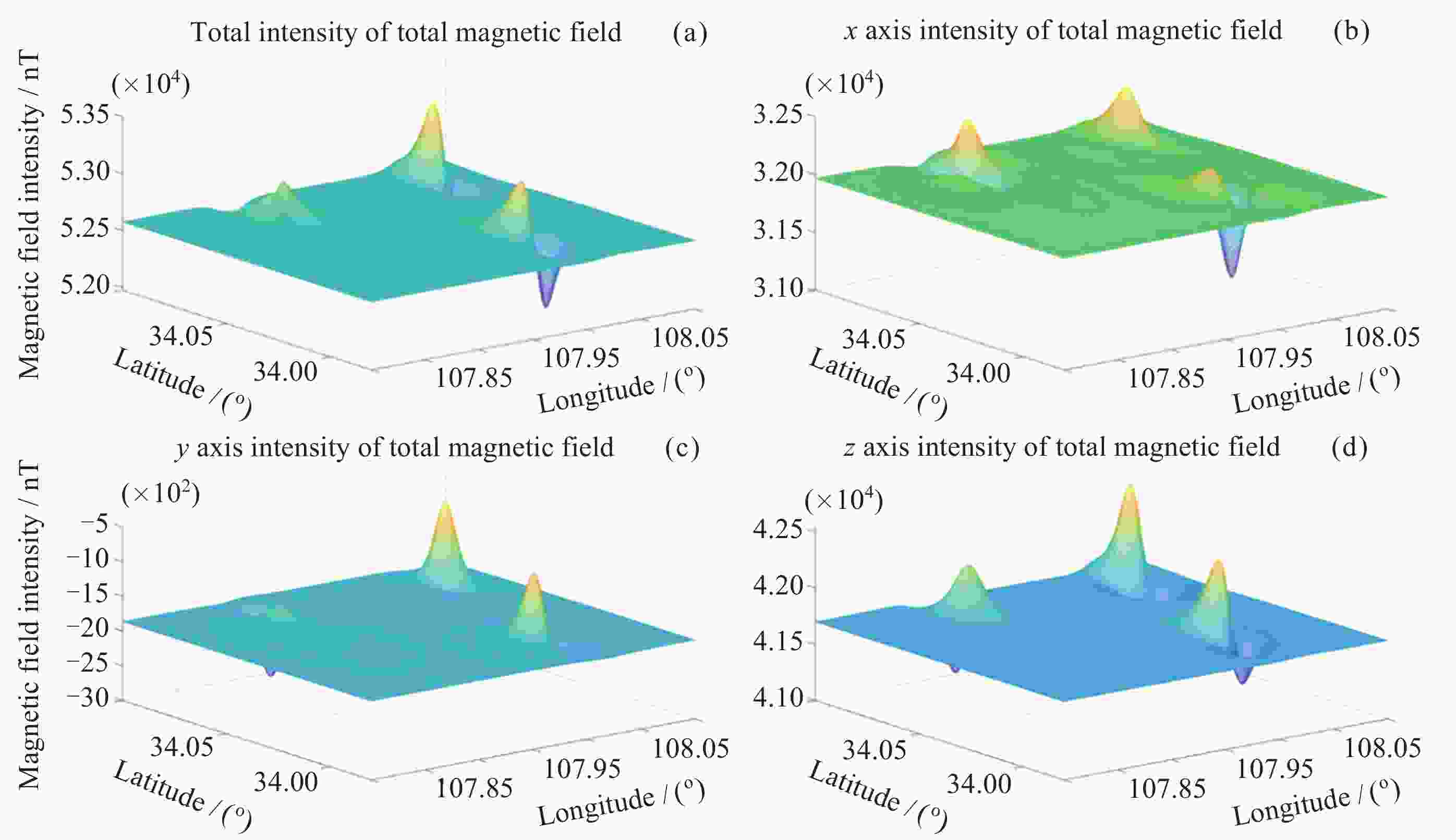
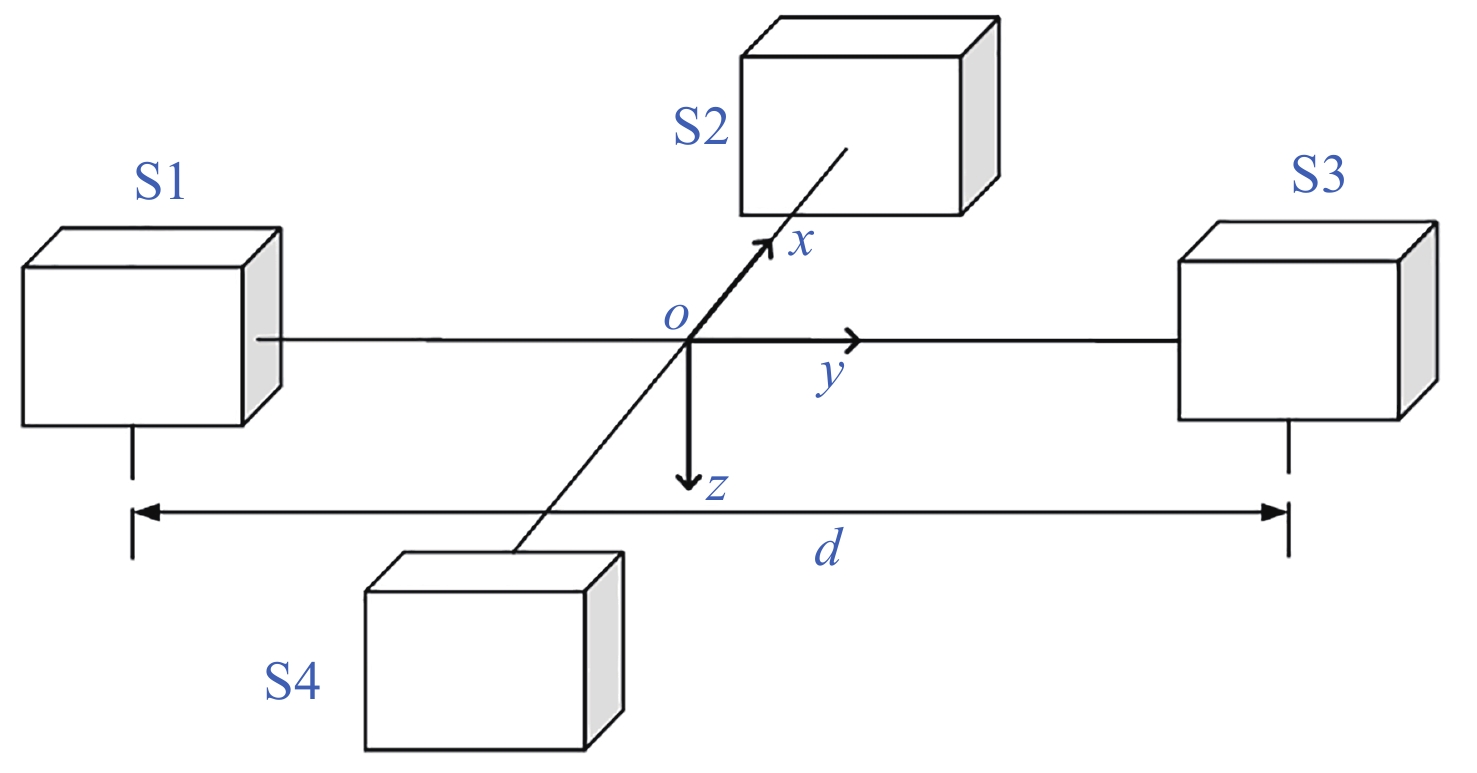
表 1 某地磁异常场梯度幅值统计
Table 1. Amplitude of the gradient of a certain geomagnetic anomaly field
网格点距/kmΔTx 磁异常/( nT⋅km–1) ΔTy 磁异常/( nT⋅km–1) ΔTz 磁异常/( nT⋅km–1) 最大值 最小值 最大值 最小值 最大值 最小值 1 48.3 –71.2 63.6 –40.4 122.3 –68.3 2 43.3 –48.5 44.4 –31.6 81.0 –44.2 3 36.0 –37.0 32.3 –23.0 60.8 –39.0 表 2 仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters
仿真参数 取值 惯导部分参数 陀螺常值零偏: [0.01, 0.015, 0.02] (°) ⋅h–1
陀螺随机游走: [0.001, 0.001, 0.001] (°) ⋅Hz–1/2
加速度常值零偏: [50, 90, 100] μg
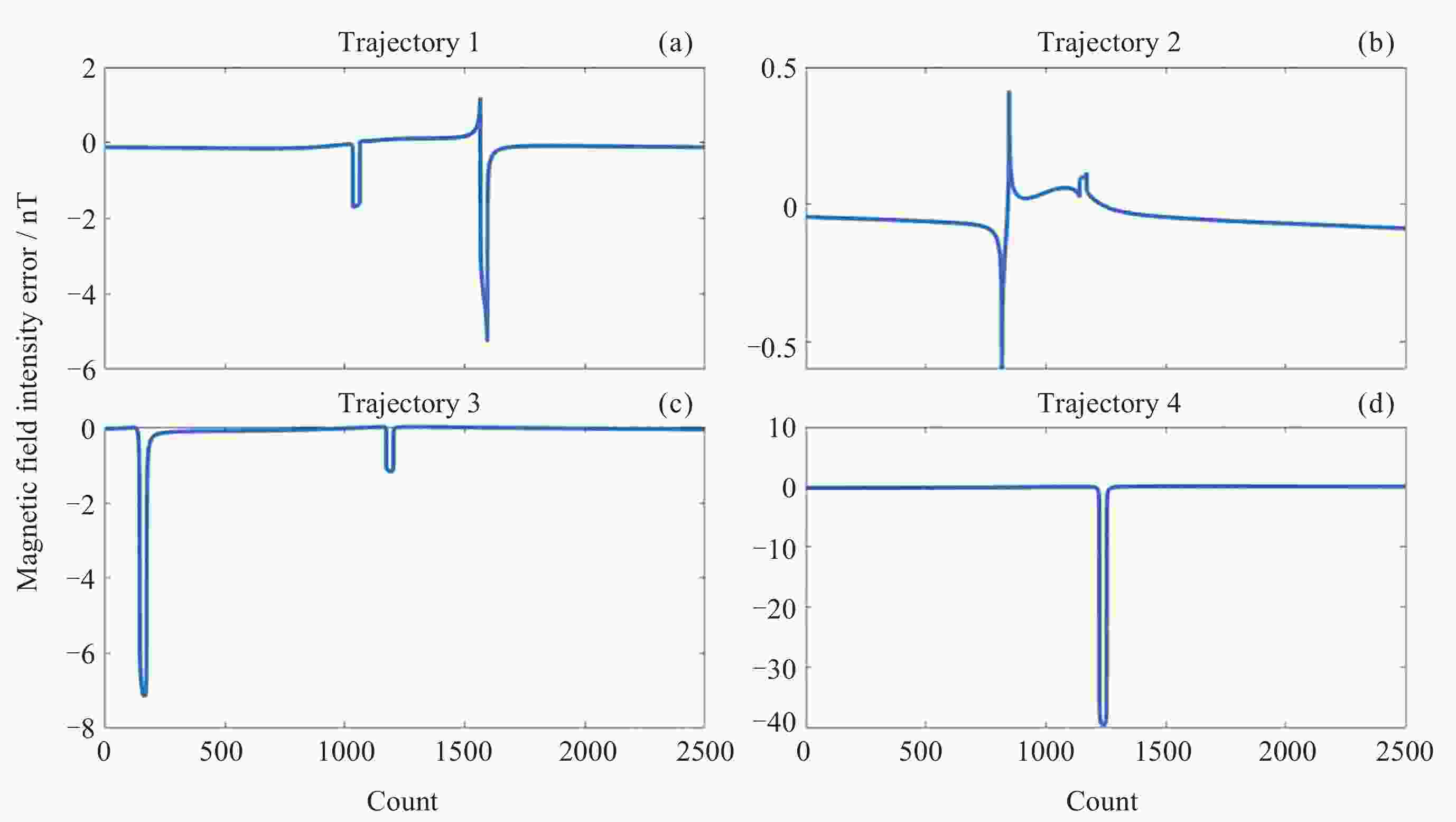
加速度随机游走: [1, 1, 1] μg s–1⋅Hz–1/2磁场部分参数 磁强计测量误差(每轴): 1 nT
磁强计测量频率: 100 Hz
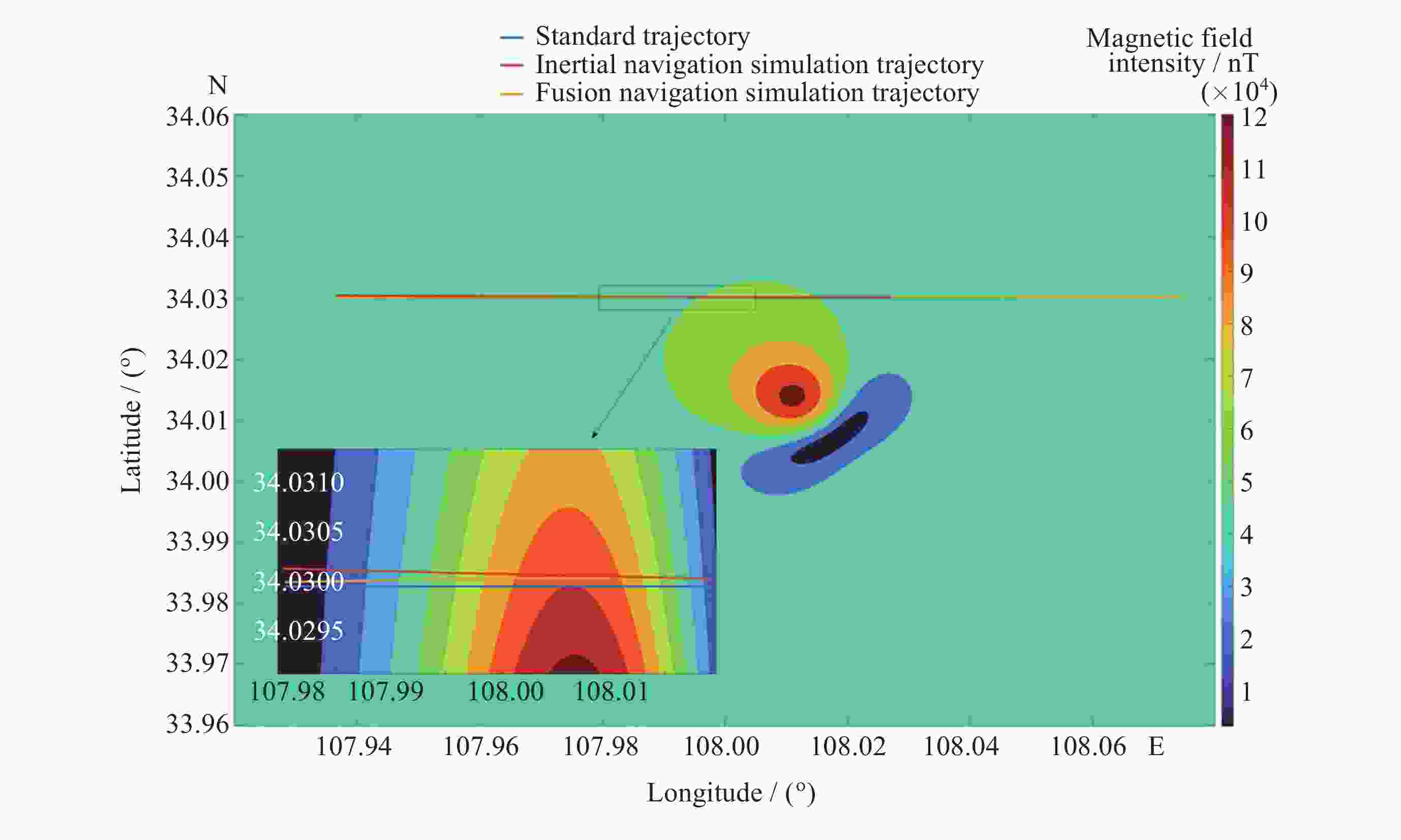
先验磁矩: M=[4.55, 2.5, 7.81]T×109
位置: $ (34.011^\circ {\text{N}},108.014^\circ {\text{E}}, - 1000{\text{m}}) $表 3 多次仿真误差均值
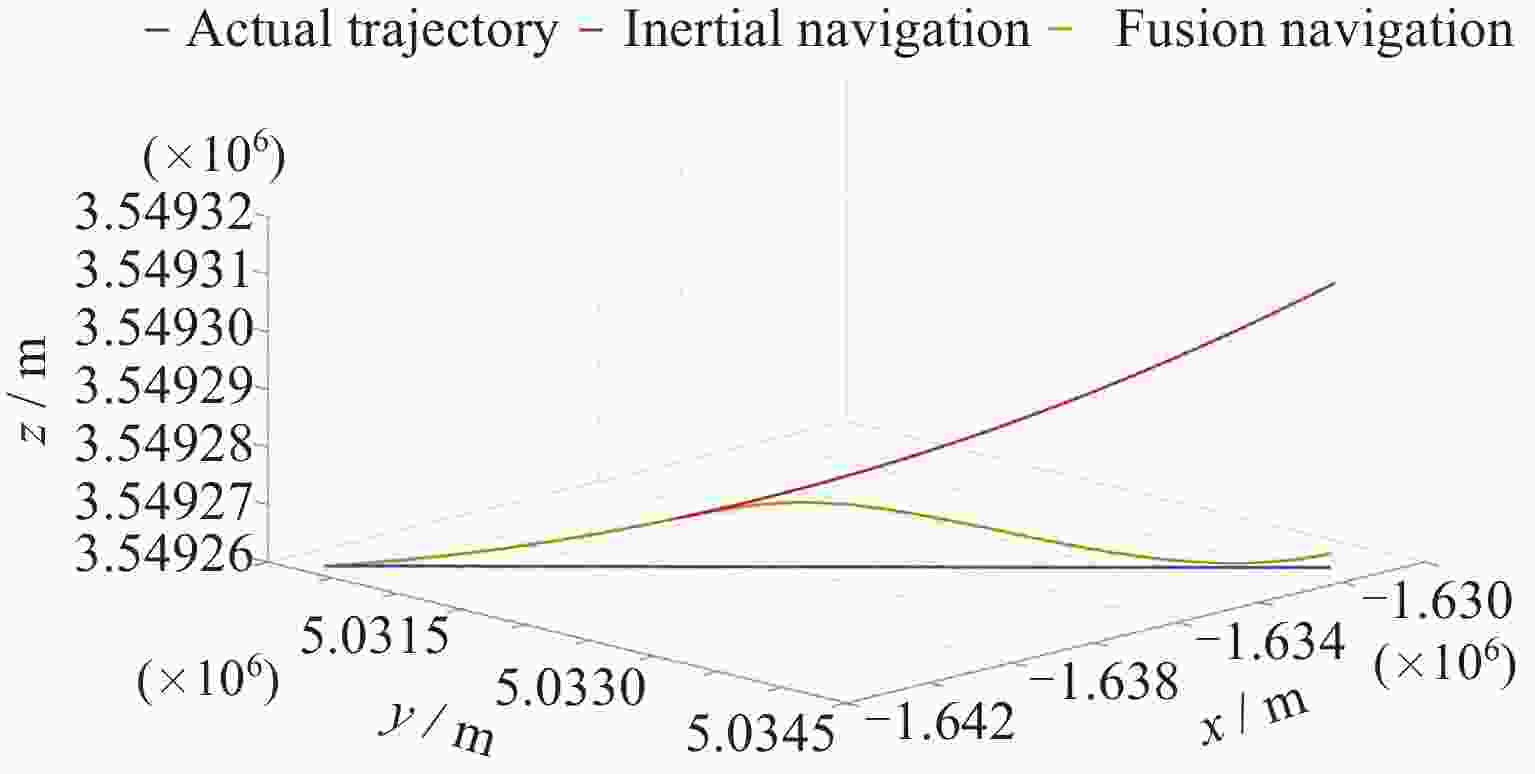
Table 3. Mean error of multiple simulations
仿真
次数误差绝对值均值/m 融合导航 惯性导航 x y z 总 x y z 总 1 3.33 0.80 4.96 3.03 15.47 5.91 17.81 13.06 2 2.60 0.55 5.00 2.72 15.50 5.84 17.93 13.09 3 4.32 1.43 5.14 3.63 15.41 5.68 18.11 13.07 表 4 3 nT磁测噪声下多次仿真误差均值
Table 4. Mean error of multiple simulations under 3 nT magnetic measurement noise
仿真
次数误差绝对值均值 / m 融合导航 惯性导航 x y z 总 x y z 总 1 5.45 1.47 5.93 4.28 15.54 5.89 17.87 13.10 2 5.95 1.84 5.70 4.49 15.33 5.83 17.89 13.02 3 5.52 1.43 5.24 4.06 15.37 5.98 17.67 13.01 表 5 复杂磁环境下多次仿真误差均值
Table 5. Mean error of multiple simulation errors in a complex magnetic environment
仿真
次数误差绝对值均值/m 融合导航 惯性导航 x y z 总 x y z 总 1 5.94 2.57 5.88 4.80 15.39 5.88 17.81 13.03 2 5.95 2.66 5.88 4.83 15.49 5.79 17.99 13.09 3 5.47 2.97 5.93 4.79 15.54 5.85 17.92 13.10 表 6 3 nT噪声复杂环境多次仿真误差均值
Table 6. Mean error value of multiple simulations in a complex environment with 3 nT noise
仿真
次数误差绝对值均值/m 融合导航 惯性导航 x y z 总 x y z 总 1 6.52 3.39 6.49 5.47 15.47 5.90 17.82 13.06 2 6.67 3.40 7.71 5.93 15.38 5.70 18.05 13.04 3 6.33 3.33 7.78 5.81 15.34 5.85 17.84 13.01 -
[1] KOU Yimin. Research of Key Technologies in Geomagnetic Navigation[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010 [2] WANG C, LIU R, LI B. Autonomous navigation algorithm based on celestial and geomagnetism[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2010, 18(4): 429-433 [3] CARLETTA S, TEOFILATTO P, FARISSI M S. A magnetometer-only attitude determination strategy for small satellites: design of the algorithm and hardware-in-the-loop testing[J]. Aerospace, 2020, 7(1): 3 doi: 10.3390/aerospace7010003 [4] SABZEVARI S, ARVAN M R, VALI A R, et al. Symmetry preserving nonlinear observer for attitude estimation with magnetometer only[J]. ISA Transactions, 2020, 102: 314-324 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2020.03.005 [5] CUI Feng. Research on Geomagnetic Navigation Method Based on Measurement Difference and Model Reconstruction & Compensation[D]. Beijing: National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021 [6] GAO Dong, ZHU Minghui, HAN Peng. A geomagnetic/inertial depth fusion navigation method[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2022, 30(4): 437-444 [7] ANDREI C, HEVER M. Q-learning model covariance adaptation of rao-blackwellized particle filtering in airborne geomagnetic navigation[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium. Monterey: IEEE, 2023: 143-149 [8] CHEN Z, LIU K J, ZHANG Q, et al. Geomagnetic vector pattern recognition navigation method based on probabilistic neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5909608 [9] WANG Lihui, XU Ninghui, LIU Qingya. A PSO geomagnetic matching algorithm based on particle constraint[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2020, 28(6): 755-760 [10] 陈斌, 顾左文, 高金田, 等. 2005.0年代中国地区地磁场及其长期变化球冠谐和分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(3): 771-779 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.03.017CHEN Bin, GU Zuowen, GAO Jintian, et al. Analyses of geomagnetic field and its secular variation over China for 2005.0 epoch using spherical cap harmonic method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(3): 771-779 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.03.017 [11] ZHENG Mengling, SONG Xinda, ZHOU Binquan, et al. Research on the adaptive parameter calibration method of SERF atomic magnetometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2022, 43(9): 1-9 [12] ZHU Zhanlong, SHAN Youdong, YANG Yi, et al. INS/GNS integrated method based on innovation orthogonality adaptive Kalman filter[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2015, 23(1): 66-70 [13] 高瑀. 联合Swarm和张衡一号卫星磁测数据建立地球主磁场模型[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2022GAO Yu. Invert the Main Magnetic Field by Combining Swarm and CSES Satellite Data[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2022 [14] 郭才发, 张力军, 蔡洪. 磁暴期间的地磁导航精度分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2011, 31(3): 372-377 doi: 10.11728/cjss2011.03.372GUO Caifa, ZHANG Lijun, CAI Hong. Analysis of geomagnetic navigation accuracy under magnetic storms[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2011, 31(3): 372-377 doi: 10.11728/cjss2011.03.372 [15] 张涛, 高东, 郑建华. 地磁场模型简化计算方法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2018, 38(1): 88-93 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.088ZHANG Tao, GAO Dong, ZHENG Jianhua. Simplified calculation method of geomagnetic field model[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(1): 88-93 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.088 [16] 刘颖, 吴美平, 胡小平, 等. 基于等值线约束的地磁匹配方法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2007, 27(6): 505-511 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2007.06.010LIU Ying, WU Meiping, HU Xiaoping, et al. Contour constraint based geomagnetic matching method[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2007, 27(6): 505-511 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2007.06.010 [17] HAO Boqiang. Design of Magnetic Positioning System Based on Gradient Tensor[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2022 [18] WAN Chengbiao, PAN Mengchun, ZHANG Qi, et al. Magnetic object localization with eigenvalue and eigenvector of tensor[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(2): 655-660 [19] ZHANG Lun. Research on Target Positioning Technology Based on Magnetic Gradient Tensor[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2022 [20] YAN Gongmin, WENG Jun. Strapdown Inertial Navigation Algorithm and Integrated Navigation Principle[M]. Xi’an: Northwest University of Technology Press, 2019 -
-




 梁宇潇 男, 1999年5月出生于重庆市, 现为中国科学院大学国家空间科学中心硕士研究生. 主要研究方向为飞行器自主导航与控制研究. E-mail:
梁宇潇 男, 1999年5月出生于重庆市, 现为中国科学院大学国家空间科学中心硕士研究生. 主要研究方向为飞行器自主导航与控制研究. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: