Experimental of Submerged Liquid Cooling Based on Loop Thermosiphon
-
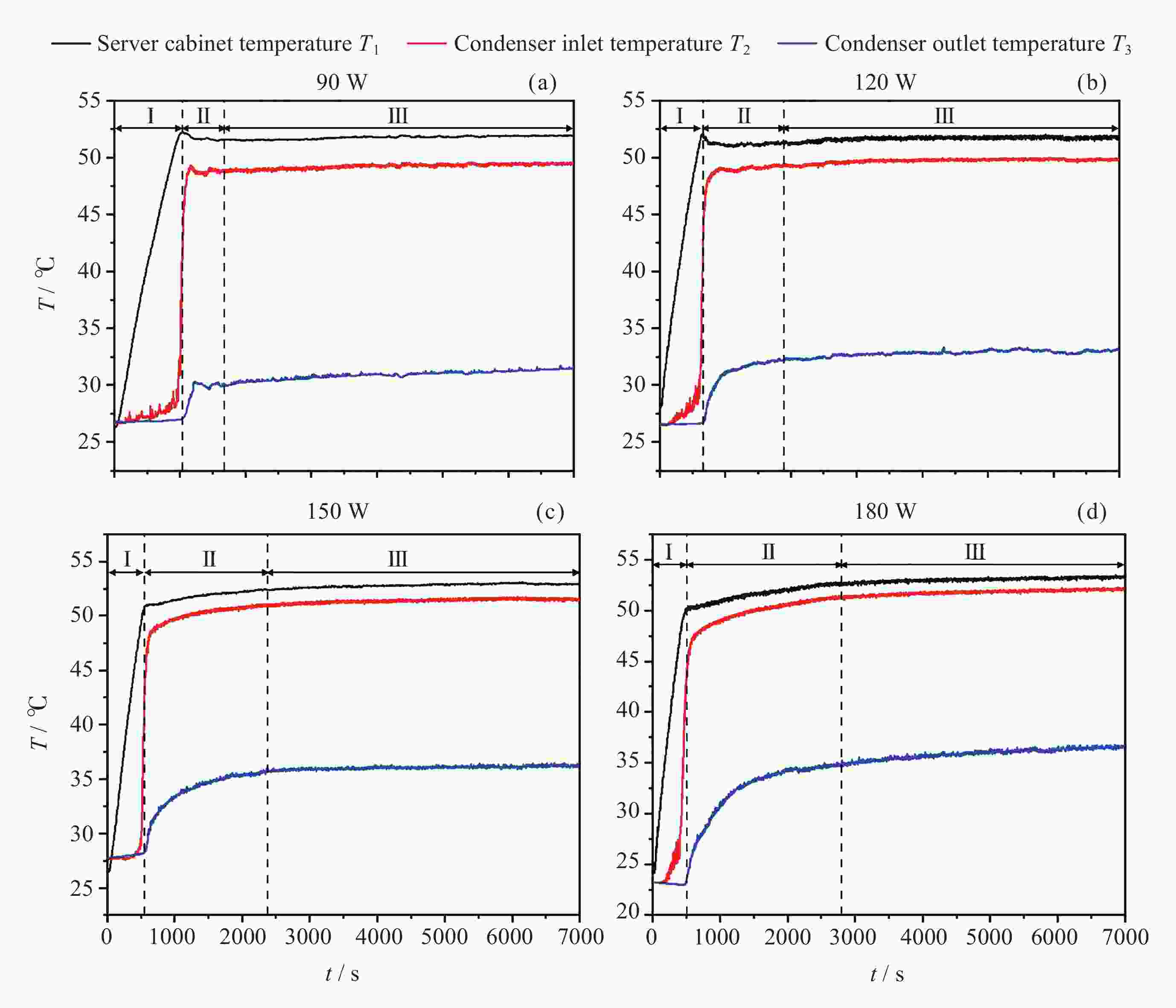
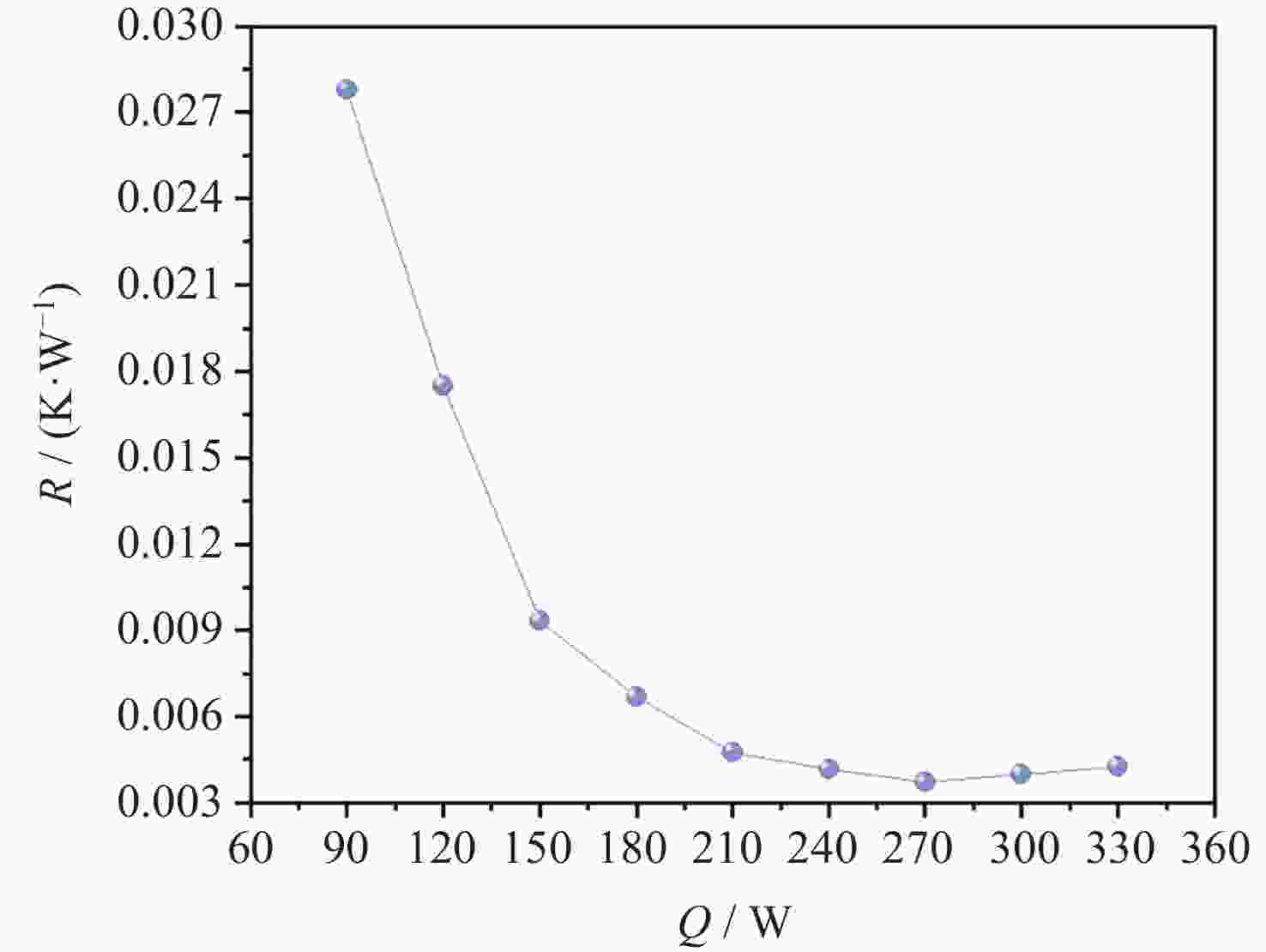
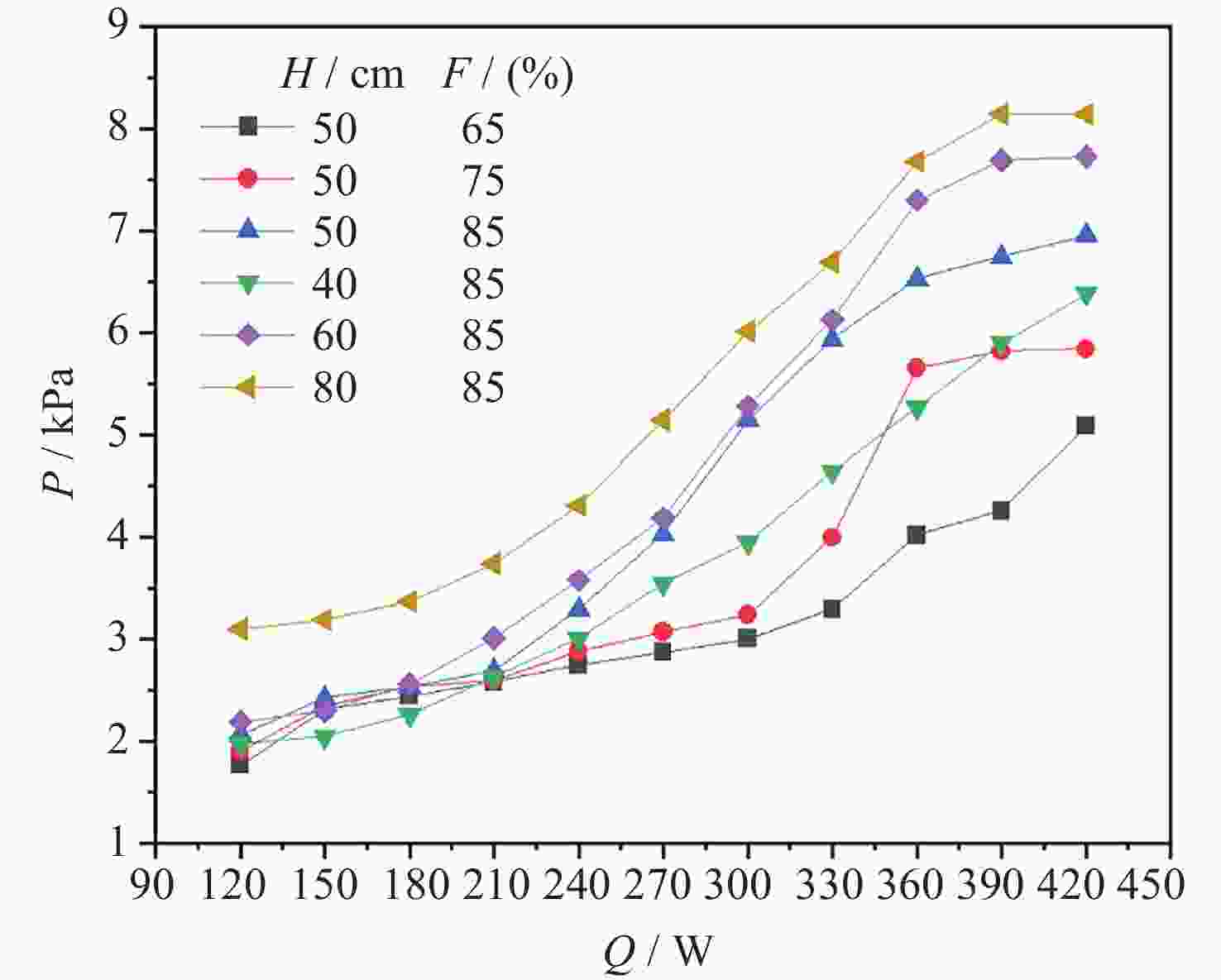
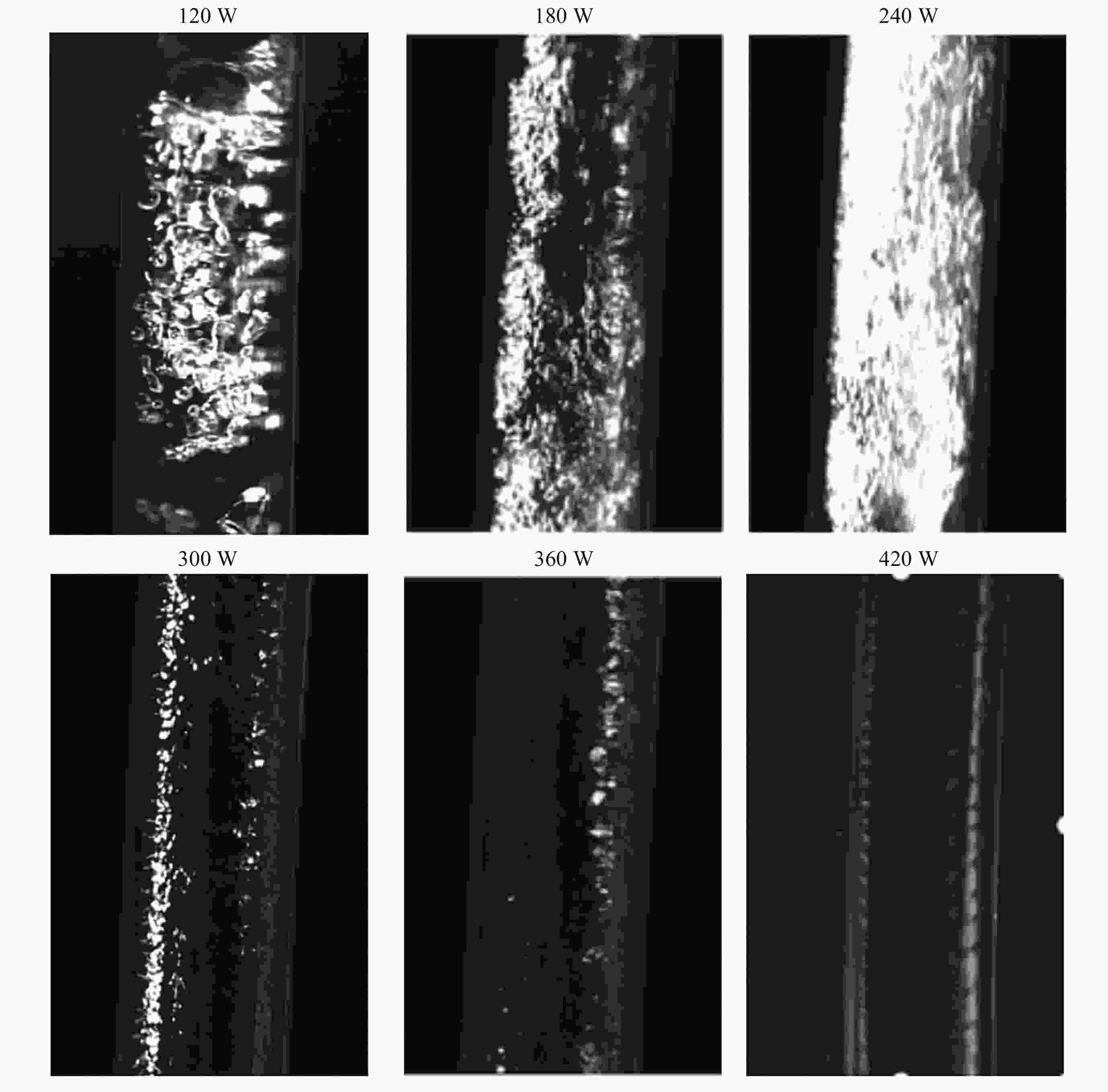
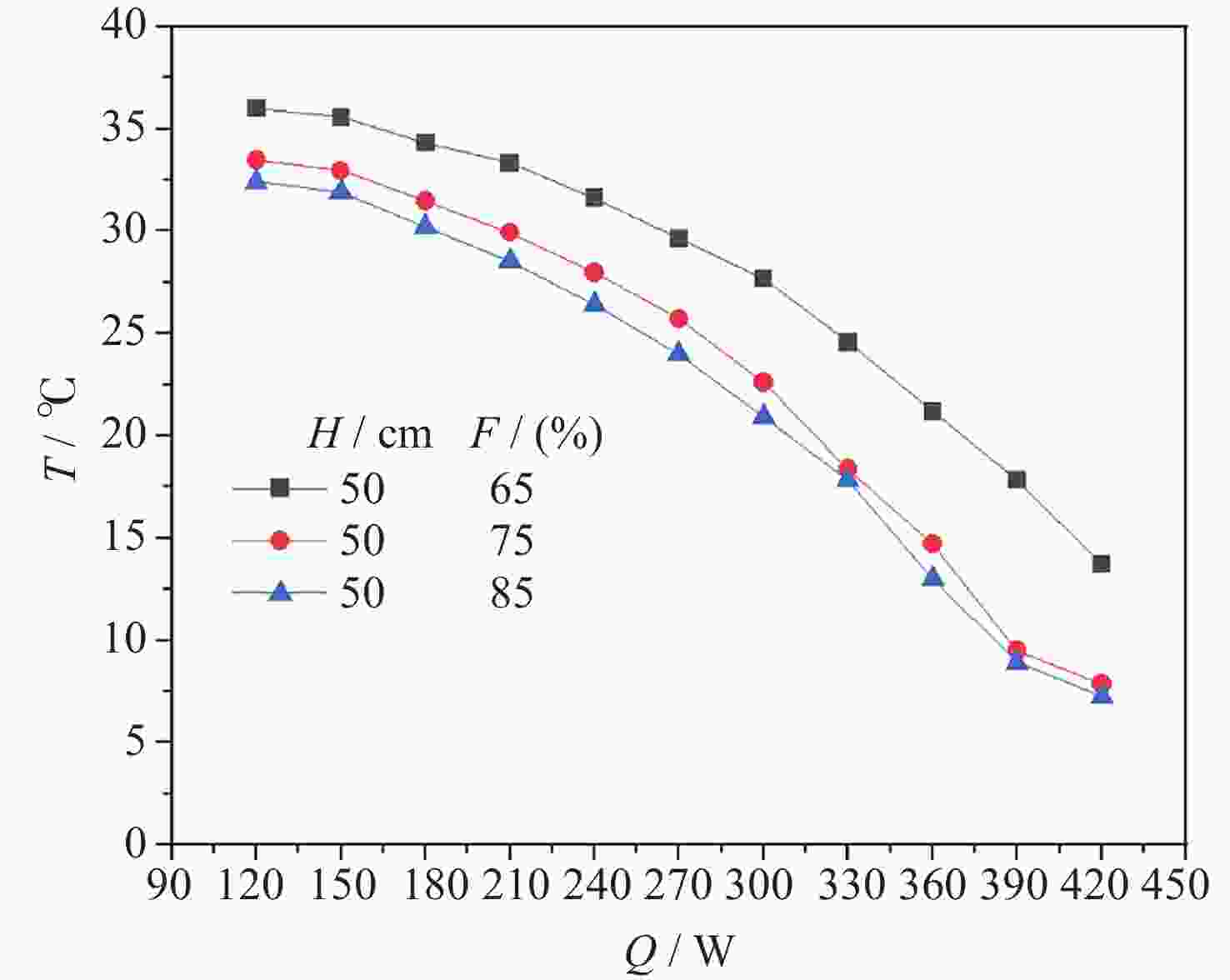
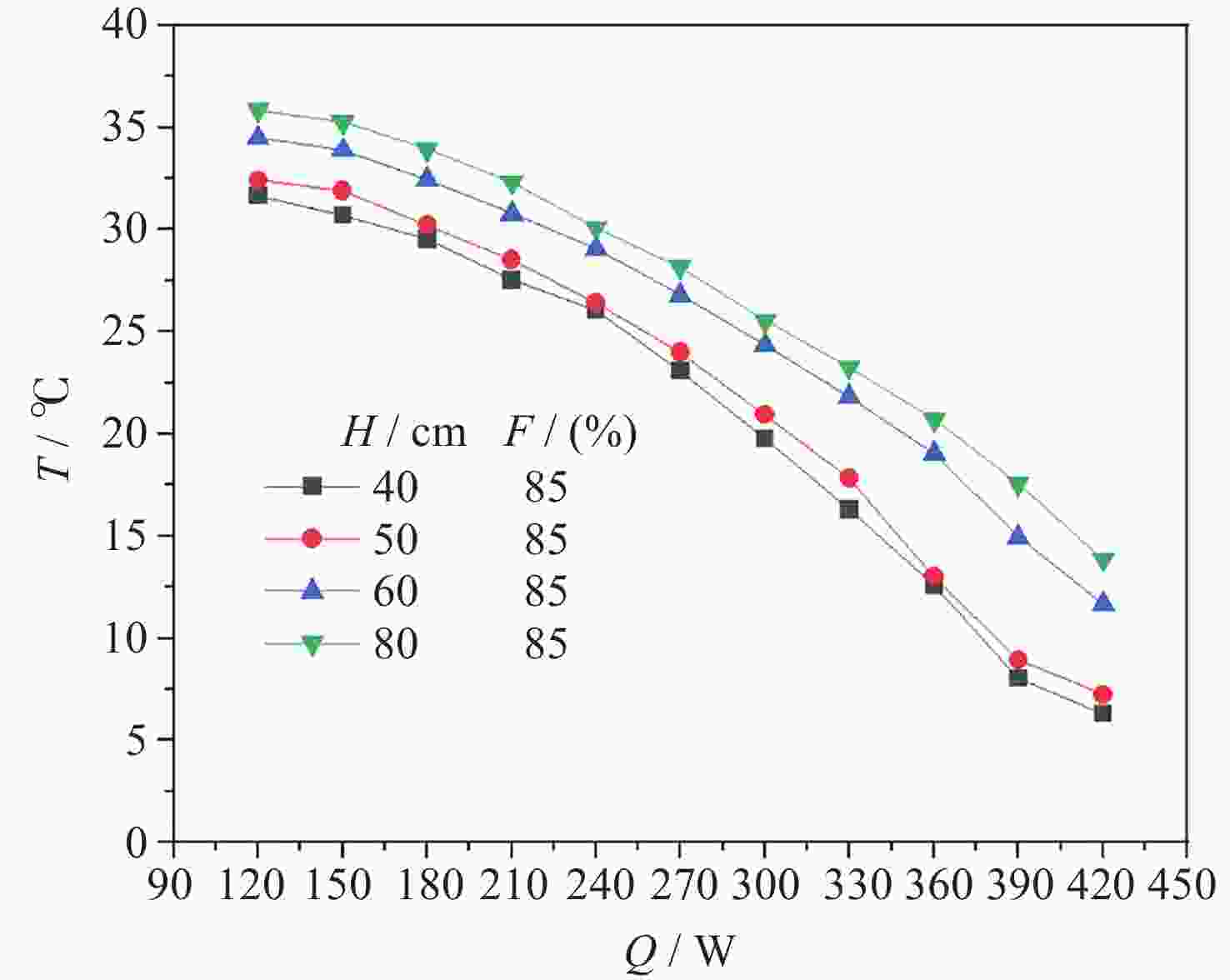
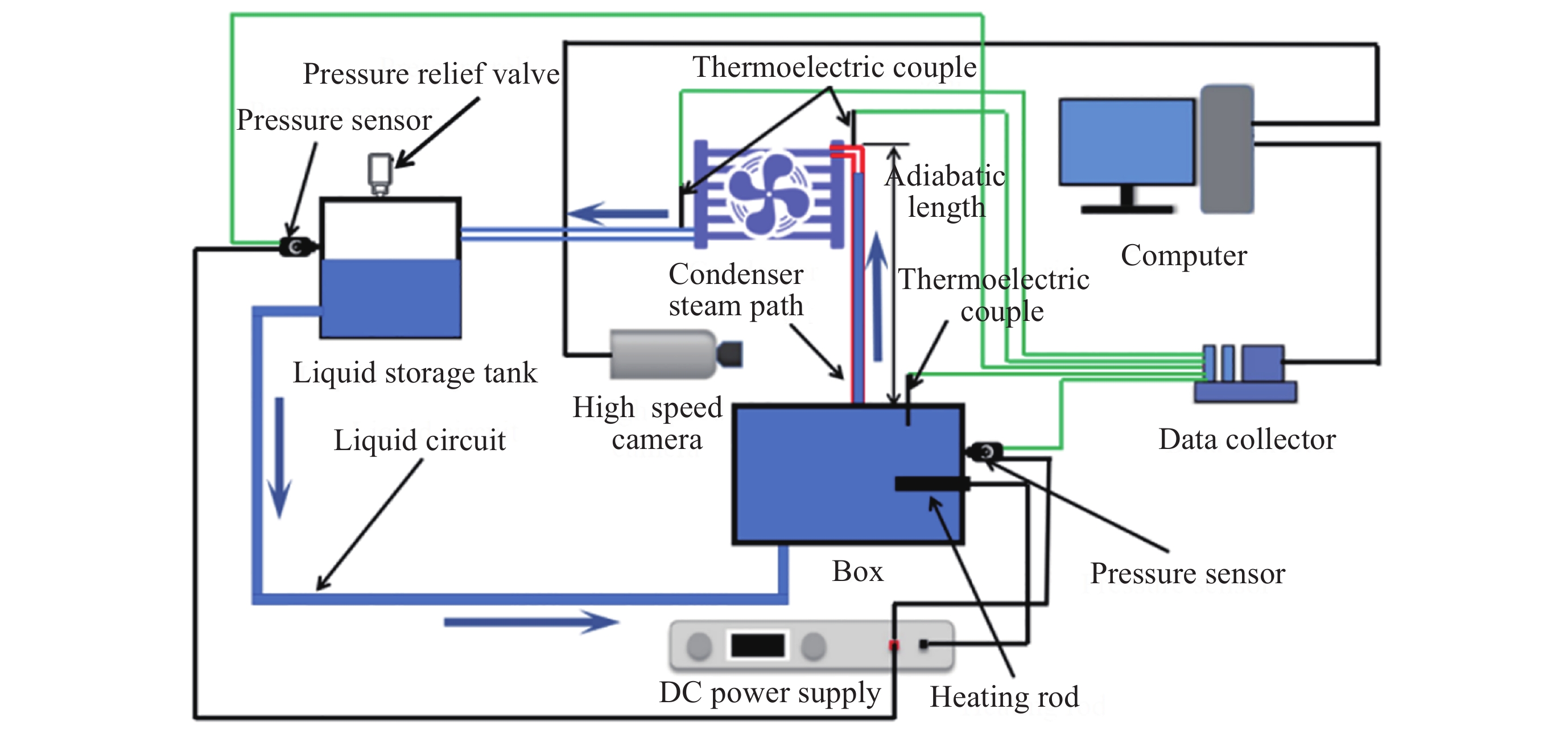
摘要: 将环路热虹吸管与服务器散热相结合, 设计并加工出一种用于模拟服务器液冷的循环冷却系统. 以HFE-7100作为工质, 研究不同加热功率下服务器模拟热启动问题, 并探讨不同注液率、汽路绝热段长度(箱体与冷凝器的高度差)对循环系统传热特性的影响. 此外还对实验过程中汽路内的流动状态进行了分析. 研究结果表明, 在低加热功率下(90~120 W), 服务器箱体温度会出现先升高后降低随后逐渐平稳的现象, 而高加热功率下(≥150 W)则会出现箱体温度先快速升高然后缓慢升高随后逐渐平稳的现象. 热启动过程中的现象可以分为3个阶段. 第1阶段为过冷至蒸发, 第2阶段循环系统初步建立, 第3阶段系统循环完全建立. 其中第2阶段热启动箱体最高温度会随着加热功率的增加而逐渐降低, 系统达到稳定循环的时间会随着加热功率的增加而增加. 此外, 注液率从65%增加到85%时, 系统压差(箱体及储液箱内的压强差)提高34.7%, 但是冷凝器效率降低, 其出口过冷度会降低47.4%; 当汽路绝热段长度从40 cm增加到80 cm时, 系统压差提高26.6%, 冷凝器效率提升, 其出口过冷度提高120.6%.Abstract: This paper combines loop thermosiphon with server cooling to design and fabricate a circulating cooling system for simulating liquid cooling in servers. HFE-7100 was used as the working fluid to investigate the thermal startup issues of the servers under different heating powers and to explore the effects of varying liquid injection rates and the length of the adiabatic section in the vapor line (the height difference between the enclosure and the condenser) on the heat transfer characteristics of the circulation system. Additionally, the flow state within the vapor line during the experiment was analyzed. The research findings indicate that at low heating powers (90~120 W), the temperature of the simulated server enclosure firstly increases, then decreases, and eventually stabilizes. In contrast, at high heating powers (≥150 W), the enclosure temperature initially rises quickly, then increases slowly, and finally stabilizes. The phenomena observed during the thermal startup process can be divided into three stages: Stage 1 (from subcooled to evaporation), Stage 2 (initial establishment of the circulation system), and Stage 3 (full establishment of the system circulation). In Stage 3, the maximum temperature of the enclosure gradually decreases with increasing heating power, while the time required for the system to reach stable circulation increases with higher heating power. Furthermore, when the liquid injection rate is increased from 65% to 85%, the system pressure differential (the pressure difference between the enclosure and the liquid storage tank) increases by 34.7%, but the efficiency of the condenser is reduced, and the outlet supercooling degree will be reduced by 47.4%. When the length of the adiabatic section of the vapor line is increased from 40 cm to 80 cm, the system pressure differential increases by 26.6%, while the efficiency of the condenser improves, and the outlet supercooling degree is increased by 120.6%.
-
表 1 实验装置尺寸
Table 1. Size of the experimental device
设备名称 尺寸 箱体 140 mm×120 mm×44.45 mm 储液箱 120 mm×120 mm×150 mm 管路 1000 mm×10 mm×6.5 mm 冷凝器 180 mm×160 mm×60 mm 表 2 HFE-7100物性参数
Table 2. Physical properties of HFE-7100
物性参数 HFE-7100 沸点/℃ 61 液体密度/(kg·m–3) 1372 比热容/(J·kg–1·K–1) 1094 表面张力/(mN·m–1) 10 蒸汽密度/(kg·m–3) 9.58 导热系数/(W·m–1·K–1) 0.062 汽化潜热/(kJ·kg–1) 111.6 动力黏度/(kg·m–1·s–1) 3.61×10–4 表 3 实验设备性能参数
Table 3. Main performance parameters of the experimental equipment
设备名称 测量范围 误差 T型热电偶/℃ 0~500 ±0.5 NI测温模块/℃ 0~300 ±0.3 直流电源/V 0~350 ±0.5 压力传感器/kPa 0~250 ±0.25 NI测压模块/kPa 0~250 ±0.25 高速摄像机/(frame·s–1) 1000 0 -
[1] 董新伟, 耿永伟, 郝亮. 不同气候区数据中心用间接蒸发冷却空调的耗能分析[J]. 暖通空调, 2023, 53(8): 171-176DONG Xinwei, GENG Yongwei, HAO Liang. Energy consumption analysis of indirect evaporative cooling air conditioning for data centers in different climate zones[J]. Heating Ventilating :Times New Roman;">& Air Conditioning, 2023, 53(8): 171-176 [2] 郭丰, 王娟. 通过团体标准建设工作推动数据中心液冷技术发展及应用的探索[J]. 中国标准化, 2020(8): 173-176GUO Feng, WANG Juan. Promoting the development and application of liquid cooling technology in data center through association standards development[J]. China Standardization, 2020(8): 173-176 [3] 张呈平, 郭勤, 贾晓卿, 等. 数据中心用浸没式冷却液的研究进展[J]. 精细化工, 2022, 39(11): 2184-2195ZHANG Chengping, GUO Qin, JIA Xiaoqing, et al. Research progress of immersion coolant for data centers[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2022, 39(11): 2184-2195 [4] CHENG W L, ZHANG W W, CHEN H, et al. Spray cooling and flash evaporation cooling: the current development and application[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 55: 614-628 [5] ZHU J Q, JIAO Y X, DONG H, et al. Research on the flow and heat transfer characteristics of RP-3 and structural optimization in parallel bending cooling channels[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 241: 122432 [6] 韩冰冰. 数据中心液冷技术发展现状[J]. 智能建筑, 2020(8): 73-76HAN Bingbing. Development status of liquid cooling technology in data center[J]. Intelligent Building, 2020(8): 73-76 [7] LUCCHESE R, VARAGNOLO D, JOHANSSON A. Controlled direct liquid cooling of data servers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2021, 29(6): 2325-2338 [8] EL-GENK M S. Immersion cooling nucleate boiling of high power computer chips[J]. Energy conversion and management, 2012, 53(1): 205-218 [9] WEN S, CHEN G, WU Q, et al. Simulation study on nanofluid heat transfer in immersion liquid-cooled server[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(13): 7575 [10] ZHOU G H, ZHOU J Z, HUAI X L, et al. A two-phase liquid immersion cooling strategy utilizing vapor chamber heat spreader for data center servers[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 210: 118289 [11] ZHANG H N, SHAO S Q, XU H B, et al. Free cooling of data centers: a review[J]. Renewable and sustainable energy reviews, 2014, 35: 171-182 [12] DOBRIANSKY Y. Concepts of self-acting circulation loops for downward heat transfer (reverse thermosiphons)[J]. Energy conversion and management, 2011, 52(1): 414-425 [13] YUE C, ZHANG Q, ZHAI Z Q, et al. CFD simulation on the heat transfer and flow characteristics of a microchannel separate heat pipe under different filling ratios[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 139: 25-34 [14] ZHANG H N, SHAO S Q, GAO Y P, et al. The effect of heating power distribution on the startup time and overshoot of a loop thermosyphon with dual evaporators[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 132: 554-559 [15] DING T, CAO H W, HE Z G, et al. Visualization experiment on boiling heat transfer and flow characteristics in separated heat pipe system[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2018, 91: 423-431 [16] SAMBA A, LOUAHLIA-GUALOUS H, LE MASSON S, et al. Two-phase thermosyphon loop for cooling outdoor telecommunication equipments[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2013, 50(1): 1351-1360 [17] 张红星, 苗建印, 王录, 等. 嫦娥三号两相流体回路的地面试验验证方法及试验结果分析[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2014, 44(6): 589-596ZHANG Hongxing, MIAO Jianyin, WANG Lu, et al. Ground test method and results of closed two-phase thermosyphons for the moon exploration spacecraft Chang’E-3[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2014, 44(6): 589-596 [18] 赵建福, 李震东, 苗建印, 等. 部分重力驱动的两相流体自然循环回路传热性能的数值仿真[J]. 载人航天, 2015, 21(1): 64-68,94 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2015.01.012ZHAO Jianfu, LI Zhendong, MIAO Jianyin, et al. Numerical simulation of heat transfer in closed two-phase natural circulation system driven by partial gravity[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2015, 21(1): 64-68,94 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2015.01.012 [19] GUO Y D, WANG L, MIAO J Y, et al. Design and validation of closed two-phase thermosyphon loop in lunar gravity environment during China lunar project CE-4[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2022, 34(3): 38 [20] EL-GENK M S, BOSTANCI H. Saturation boiling of HFE-7100 from a copper surface, simulating a microelectronic chip[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2003, 46(10): 1841-1854 [21] MOFFAT R J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results[J]. Experimental thermal and fluid science, 1988, 1(1): 3-17 -
-




 王禹 男, 2000年生, 西安交通大学化学工程与技术学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为浸没式相变热管理. E-mail:
王禹 男, 2000年生, 西安交通大学化学工程与技术学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为浸没式相变热管理. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: