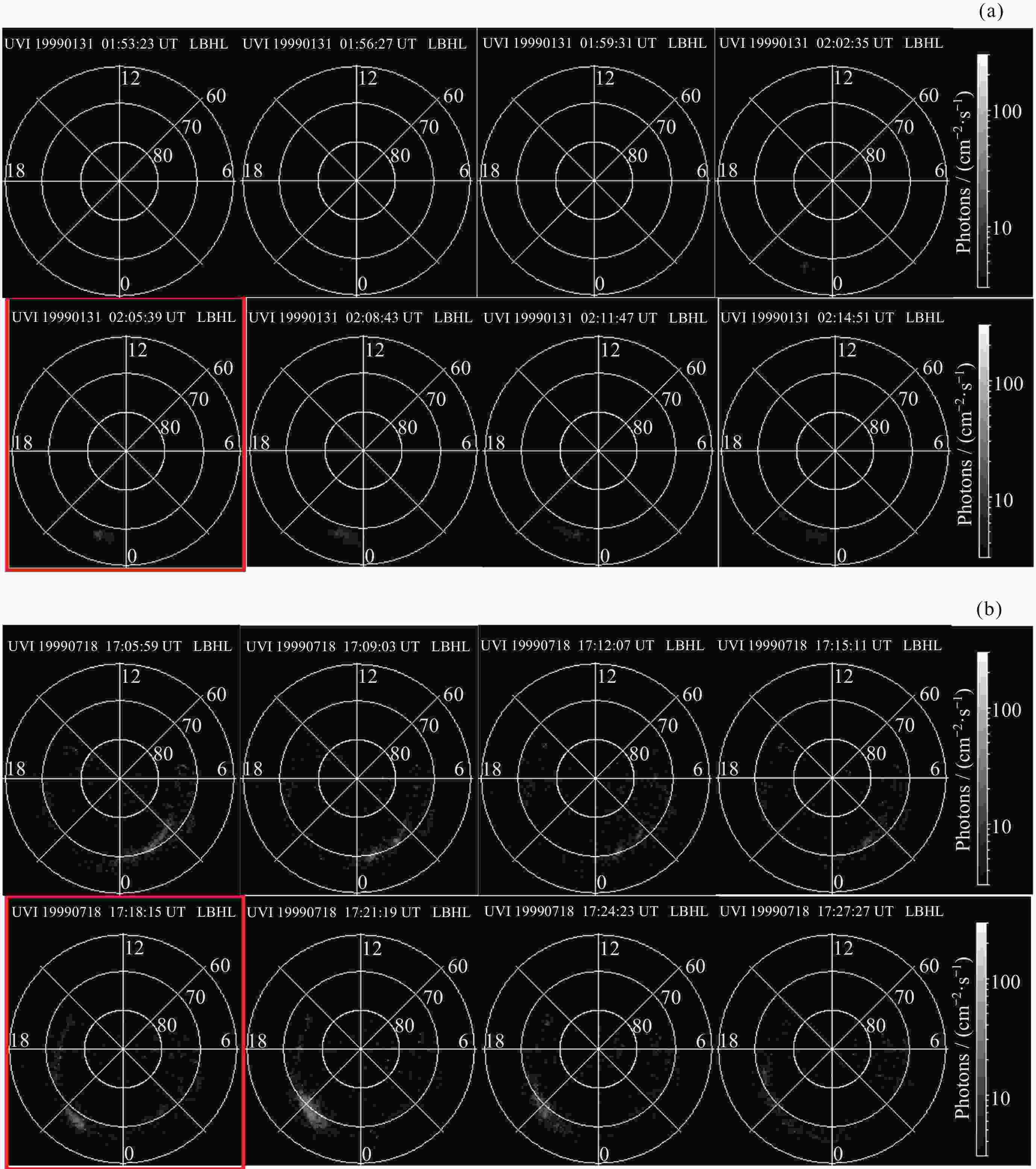
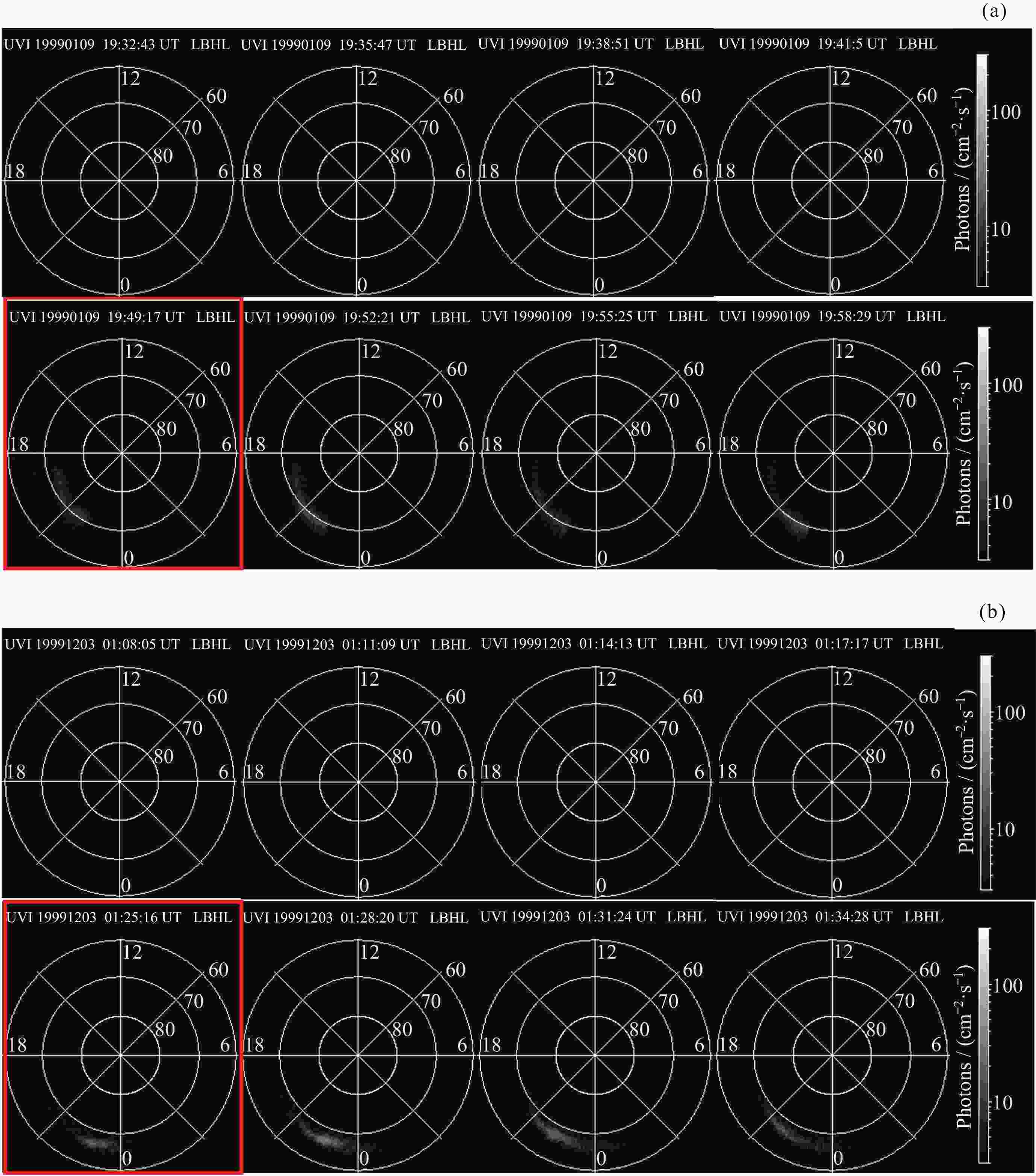
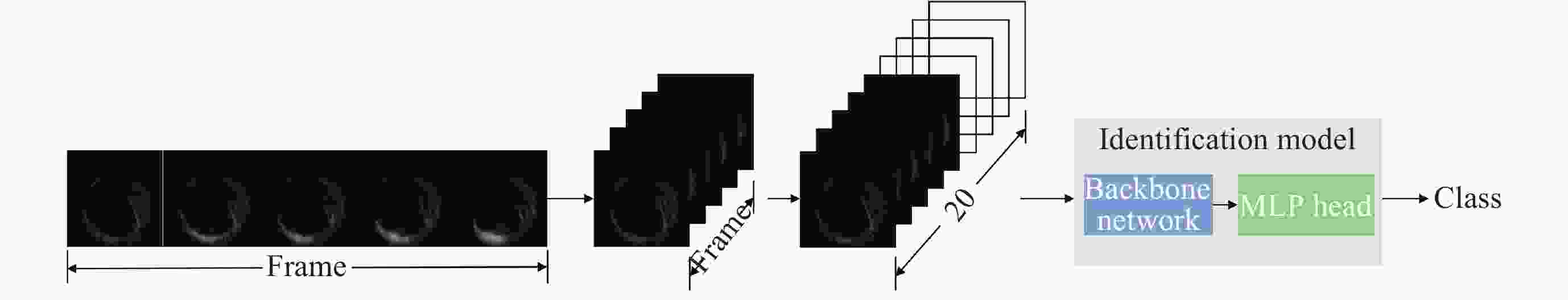
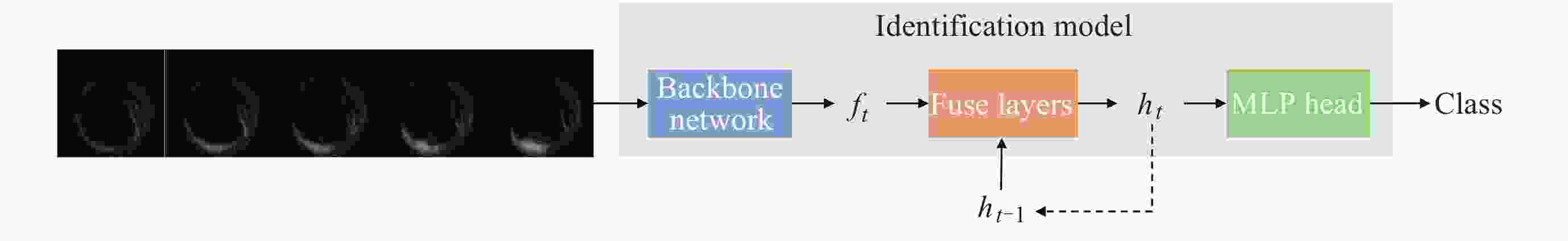
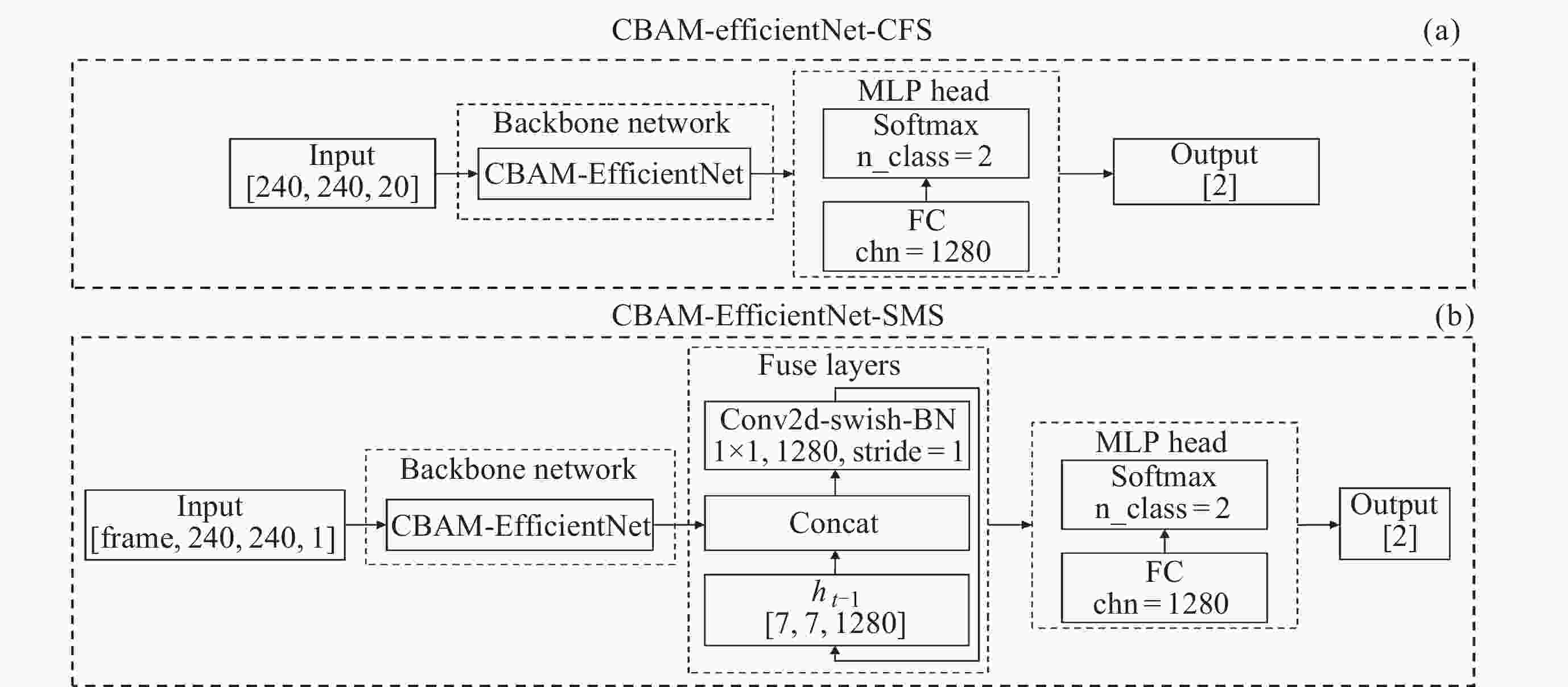
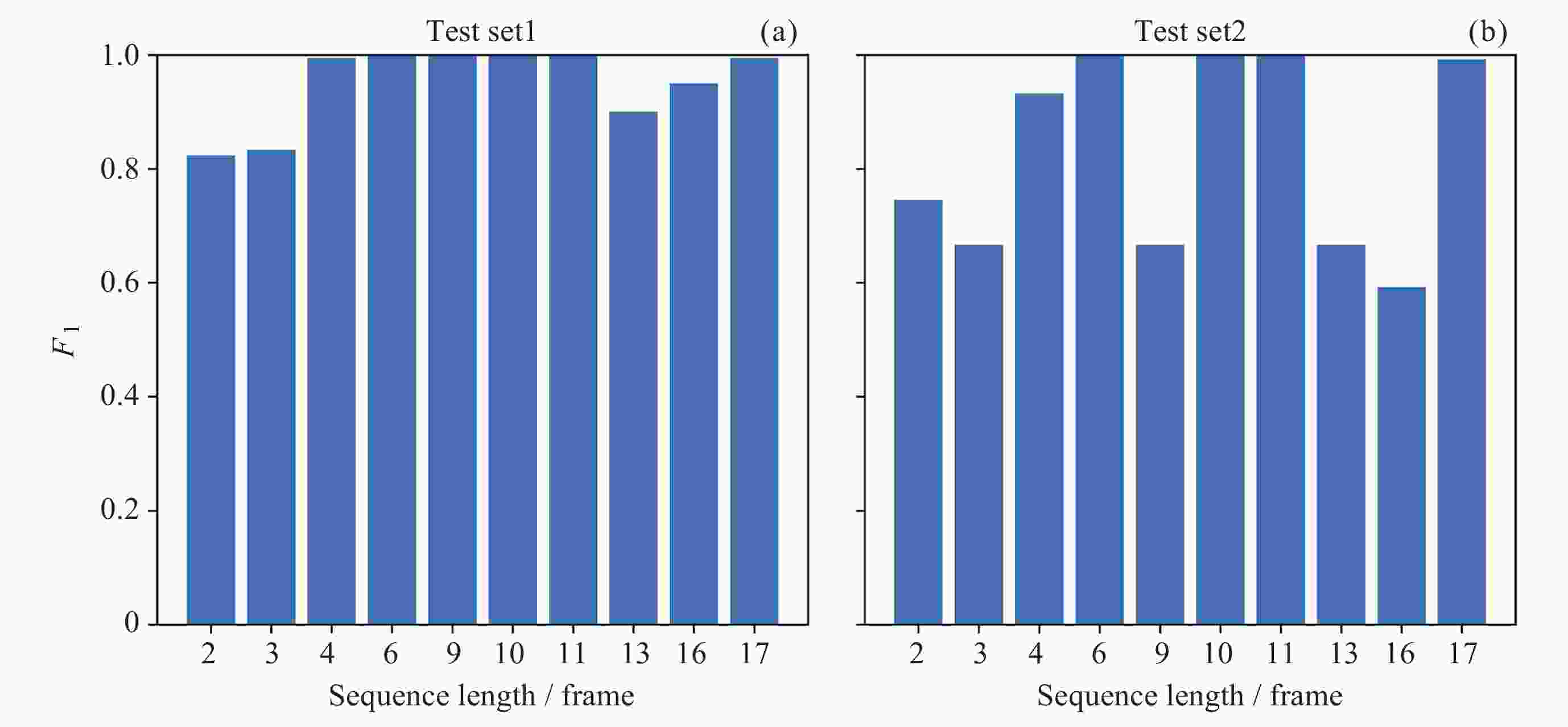
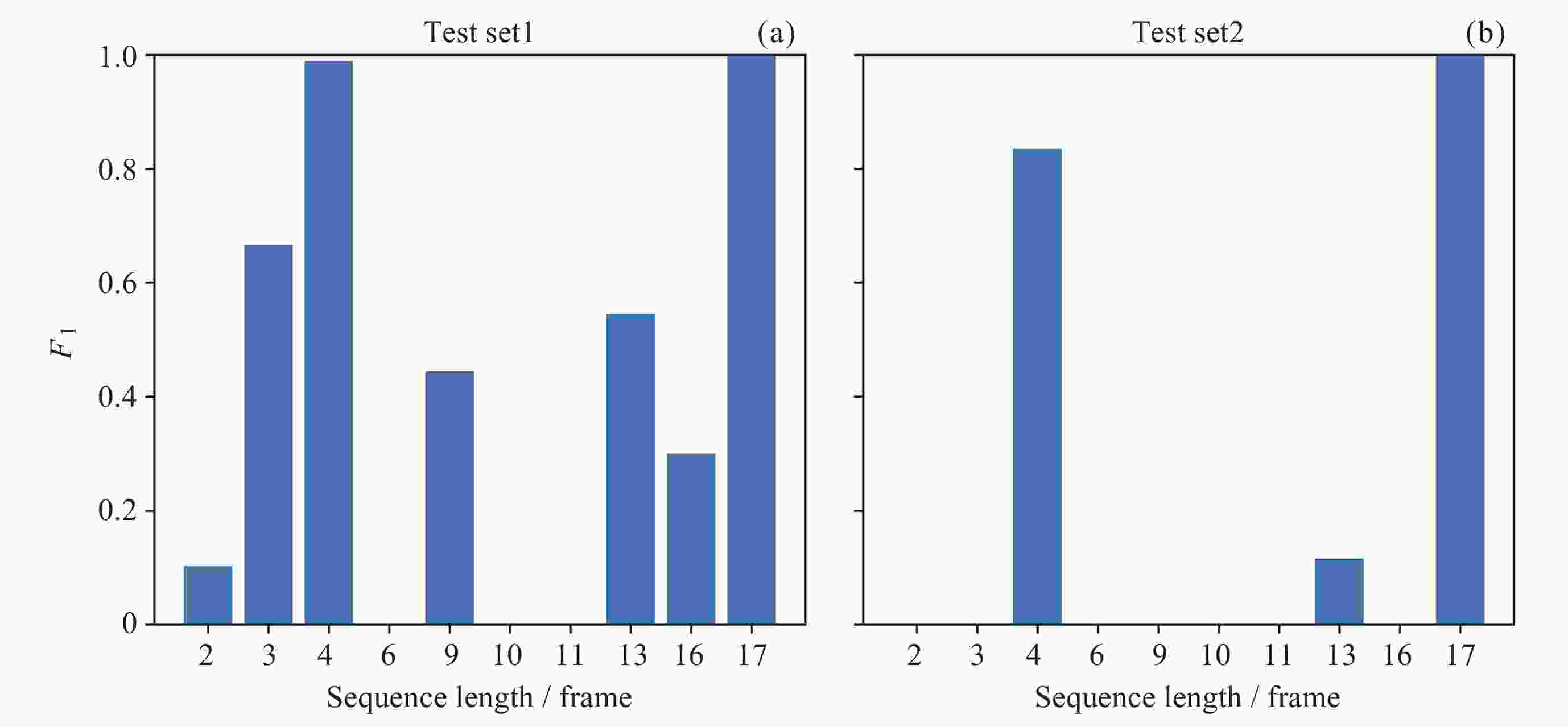
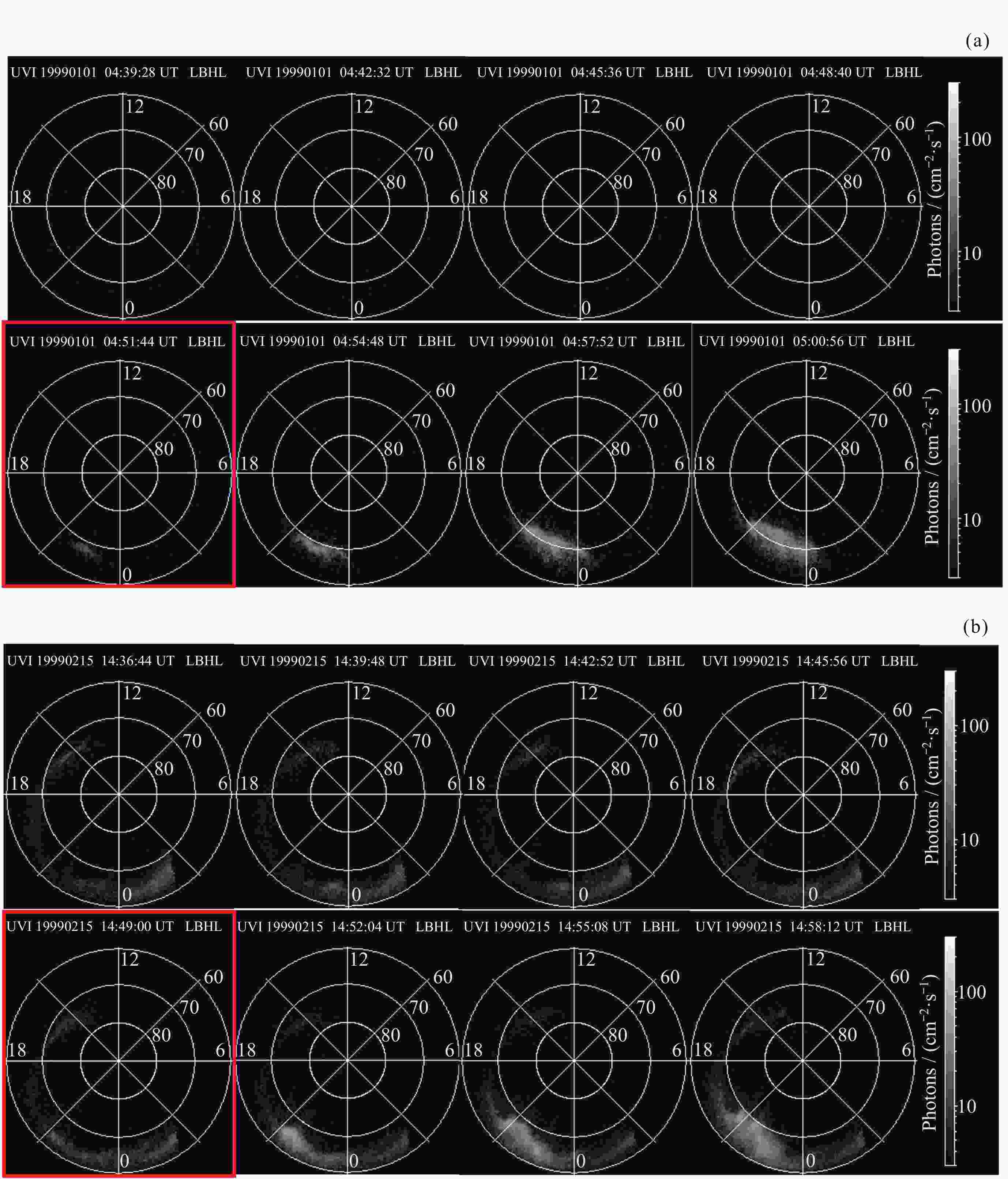
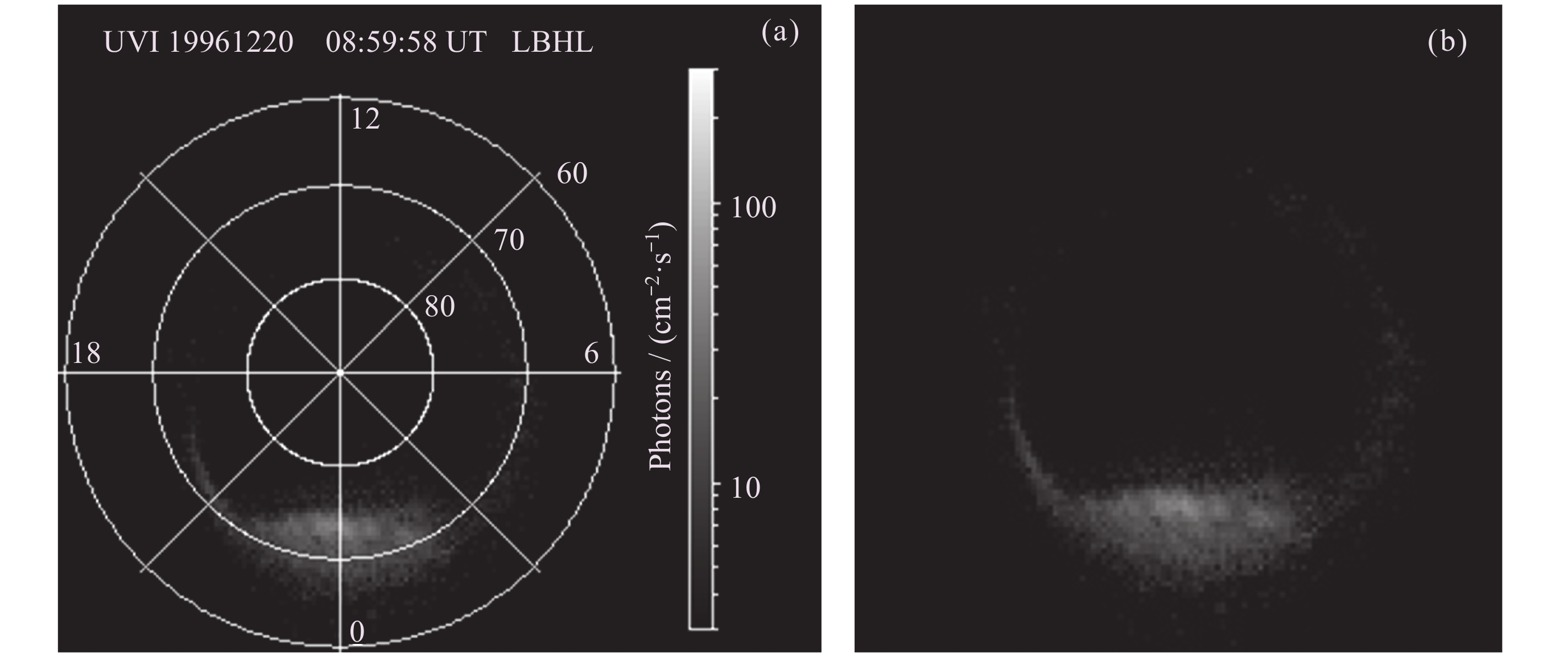
Machine Identification Method of Auroral Substorm Onset Time
-
摘要: 极光亚暴是地球磁场与太阳风相互作用产生的一种地磁扰动现象, 对于其爆发时点的准确识别有助于深入理解其背后的物理机制. 现有的极光亚暴爆发时点机器识别方法在标准上与人工识别存在差异, 且通常需要经过复杂的图像预处理和人工调参. 为了实现与人工识别标准一致的极光亚暴爆发时点机器识别方法, 设计了两种识别策略, 旨在解决在复现人工识别标准时遇到的图像序列长度不定长问题. 研究采用深度学习方法, 并提出了一种基于CBAM注意力的EfficientNet, 以此作为重要组件来构建模型. 使用Polar卫星1996-1998年的紫外极光图像对模型进行训练, 并在1999-2000年的图像数据上进行测试. 模型识别精确率可达0.98, 识别效率可达36.93 frame·s–1. 该模型不仅摆脱了现有模型对于图像预处理的依赖, 还能够适用于真实观测下图像序列不等长以及暴时序列与非暴时序列样本数量极端不均衡的情况, 具有较高的实用性.Abstract: Auroral substorm is a geomagnetic disturbance resulting from the interaction between Earth’s magnetic field and the solar wind. The accurate identification of the onset times is crucial for a deep understanding of the underlying physical mechanisms. The existing machine methods for auroral substorm identification differ from manual identification standards and typically require complex image preprocessing and parameter tuning by manual. To achieve a machine model consistent with manual identification standards, this paper designs two identification strategies aimed at addressing the issue of variable image sequence lengths encountered in replicating manual standards. Based on deep learning methods, this paper proposes an EfficientNet model featuring CBAM attention as a key component for model construction. The model is trained using ultraviolet auroral images from the Polar satellite between 1996 and 1998 and tested on image data from 1999 to 2000. The model achieves an identification accuracy of up to 0.98 and an efficiency of 36.93 frames per second. This model not only eliminates the reliance on image preprocessing present in existing models but also adapts to real-world observations with unequal image sequence lengths and extreme imbalances in the number of samples between substorm and non-substorm sequences, demonstrating its high practicality.
-
Key words:
- Auroral substorm /
- Onset time /
- Machine identification /
- Deep learning
-
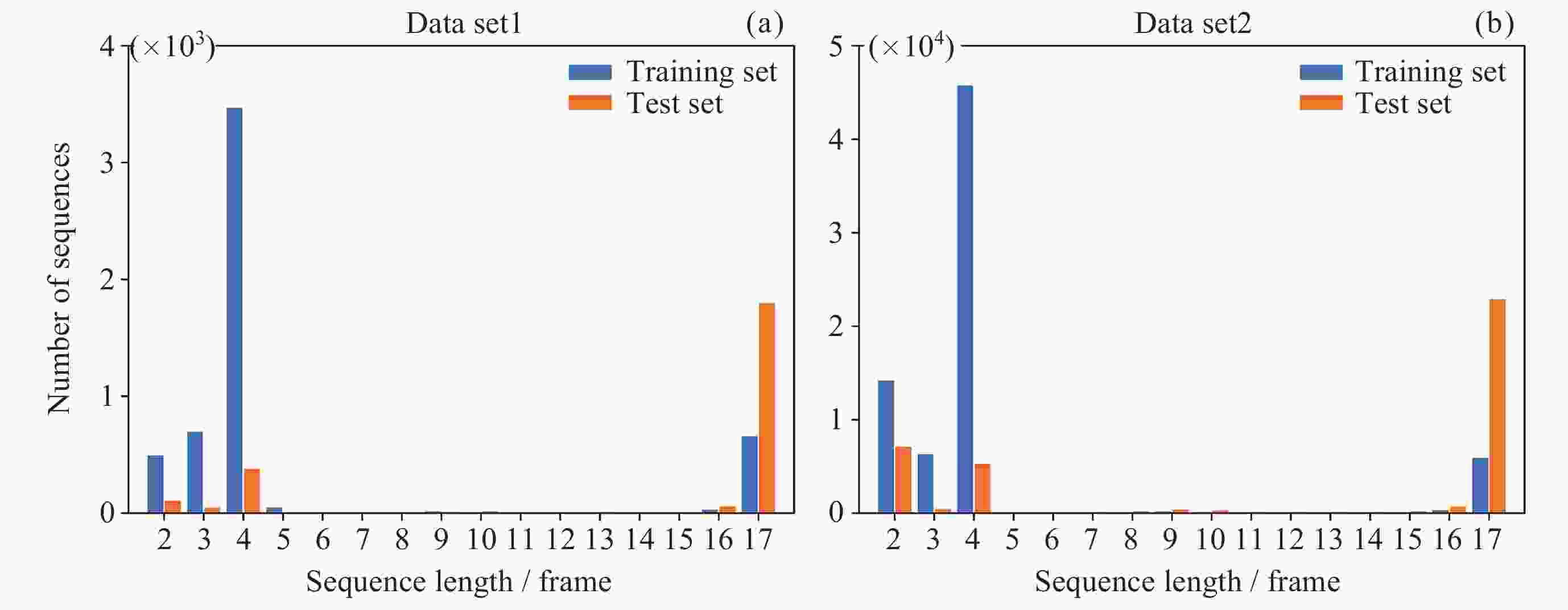
表 1 两组数据集的序列与图像数量
Table 1. Number of sequences and images in two datasets
训练集1 测试集1 训练集2 测试集2 暴时序列数量 1367 615 1367 615 非暴时序列数量 3740 1772 72028 37666 暴时图像数量 7382 8545 7382 8545 非暴时图像数量 17926 23712 337442 447926 表 2 CBAM-EfficientNet组成架构
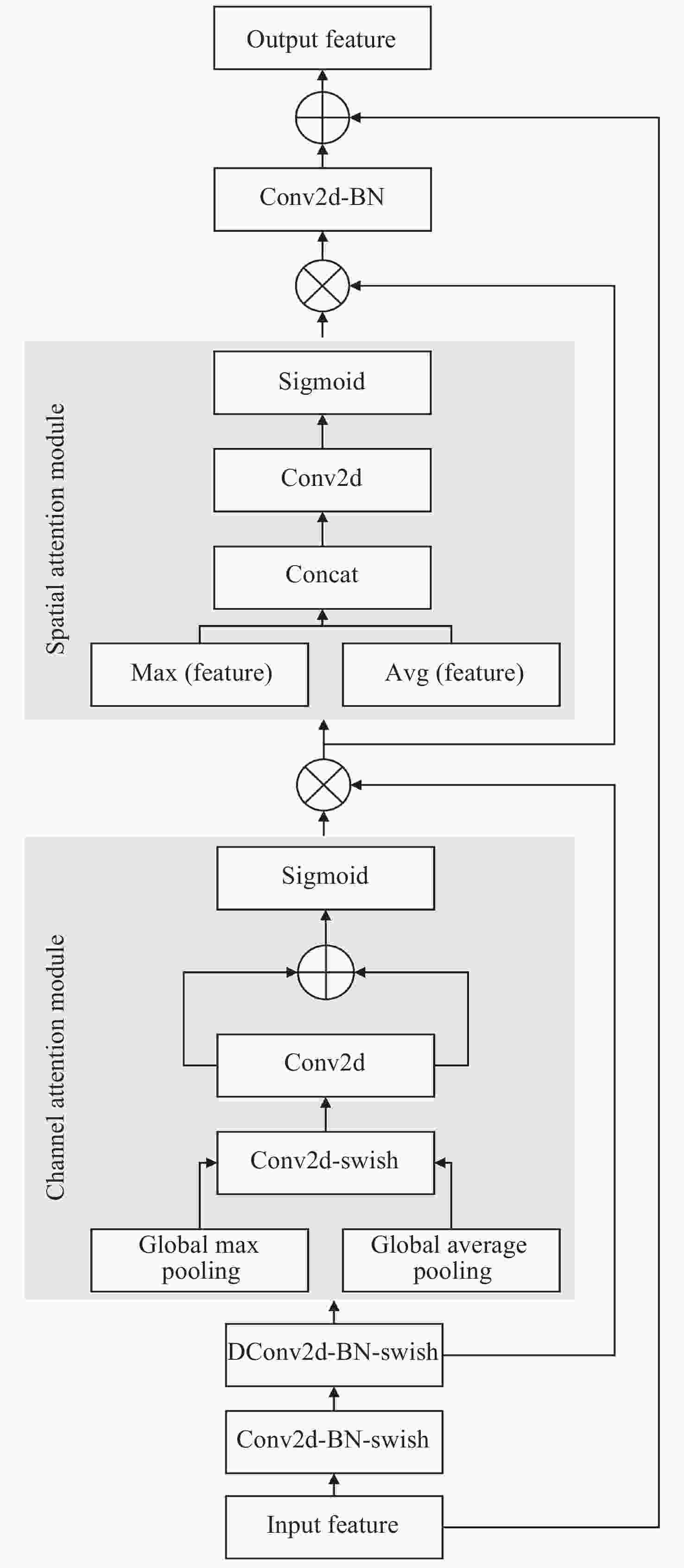
Table 2. Architecture of CBAM-EfficientNet
阶段 模块 卷积核大小 通道数 步长 模块数量 1 Conv2d-BN-Swish 3×3 32 2 1 2 CBAM 7×7 32 1 1 3 CBAM-MB 3×3 16 1 1 4 CBAM-MB 3×3 24 2 2 5 CBAM-MB 5×5 40 2 2 6 CBAM-MB 3×3 80 2 3 7 CBAM-MB 5×5 112 1 4 8 CBAM-MB 5×5 192 2 5 9 CBAM-MB 3×3 320 1 1 10 Conv2d-BN-Swish 1×1 1280 1 1 11 Global Average Pooling - - - 1 表 3 以不同网络结构为主干网络的模型在测试集上的识别准确性评估结果
Table 3. Identification accuracy evaluation results of the models with different networks as backbone
模型 测试集1 测试集2 P R F1 P R F1 InceptionV3-CFS 0.98 0.90 0.94 0.96 0.87 0.91 ViT-CFS 0.98 0.93 0.96 0.93 0.88 0.90 CBAM-EfficientNet-CFS 0.99 0.91 0.95 0.98 0.87 0.92 InceptionV3-SMS 0.91 0.87 0.89 0.82 0.88 0.85 ViT-SMS 0.93 0.90 0.91 0.86 0.88 0.87 CBAM-EfficientNet-SMS 0.94 0.94 0.94 0.84 0.89 0.86 -
[1] 涂传诒, 宗秋刚, 周煦之. 日地空间物理学: 下册·磁层物理[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020TU Chuanzhi, ZONG Qiugang, ZHOU Xuzhi. Solar-Terrestrial Physics: Volume 2 - Magnetospheric Physics[M]. 2nd edit. Beijing: Science Press, 2020 [2] AKASOFU S I. Dynamic morphology of auroras[J]. Space Science Reviews, 1965, 4(4): 498-540 [3] JUUSOLA L, ØSTGAARD N, TANSKANEN E, et al. Earthward plasma sheet flows during substorm phases[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2011, 116(A10): A10228 [4] PARTAMIES N, JUUSOLA L, TANSKANEN E, et al. Statistical properties of substorms during different storm and solar cycle phases[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2013, 31(2): 349-358 doi: 10.5194/angeo-31-349-2013 [5] OHTANI S, GJERLOEV J W. Is the substorm current wedge an ensemble of wedgelets: revisit to midlatitude positive bays[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(9): e2020JA027902 doi: 10.1029/2020JA027902 [6] FREY H U, MENDE S B, ANGELOPOULOS V, et al. Substorm onset observations by IMAGE-FUV[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2004, 109(A10): A10304 [7] LIOU K. Polar ultraviolet imager observation of auroral breakup[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2010, 115(A12): A12219 [8] 杨秋菊, 梁继民, 刘俊明, 等. 一种基于紫外极光图像的亚暴膨胀期起始时刻的自动检测方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(5): 1435-1447YANG Qiuju, LIANG Jimin, LIU Junming, et al. A method for automatic identification of substorm expansion phase onset from UVI images[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56(5): 1435-1447 [9] YANG X, GAO X B, TAO D C, et al. Shape-constrained sparse and low-rank decomposition for auroral substorm detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(1): 32-46 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2411613 [10] 韩怡园, 韩冰, 高新波. 结合眼动信息和序列指纹的亚暴事件识别方法[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2023, 17(1): 187-197HAN Yiyuan, HAN Bing, GAO Xinbo. Auroral Substorm event recognition method combining eye movement Information and sequence fingerprint[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2023, 17(1): 187-197 [11] 杨秋菊, 任杰, 向晗. 基于深度学习的极光亚暴时-空自动检测[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(3): 898-907YANG Qiuju, REN Jie, XIANG Han. Spatio-temporal detection of auroral substorm based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(3): 898-907 [12] TORR M R, TORR D G, ZUKIC M, et al. A far ultraviolet imager for the international solar-terrestrial physics mission[J]. Space Science Reviews, 1995, 71(1): 329-383 [13] LUMMERZHEIM D, LILENSTEN J. Electron transport and energy degradation in the ionosphere: evaluation of the numerical solution, comparison with laboratory experiments and auroral observations[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 1994, 12(10): 1039-1051 doi: 10.1007/s005850050127 [14] RICHMOND A D. Ionospheric electrodynamics using magnetic apex coordinates[J]. Journal of Geomagnetism and Geoelectricity, 1995, 47(2): 191-212 doi: 10.5636/jgg.47.191 [15] JIANG J N, ZOU Z M, LU Y. A ConvLSTM-based prediction model of aurora evolution during the substorm expansion phase[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2023, 10(4): e2022EA002721 doi: 10.1029/2022EA002721 [16] TAN M X, LE Q V. EfficientNetV2: Smaller models and faster training[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2104.00298, 2021 [17] 付国栋, 黄进, 杨涛, 等. 改进CBAM的轻量级注意力模型[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(20): 150-156FU Guodong, HUANG Jin, YANG Tao, et al. Improved lightweight attention model based on CBAM[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(20): 150-156 [18] 卫雅娜, 王志彬, 乔晓军, 等. 基于注意力机制与EfficientNet的轻量化水稻病害识别方法[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2022, 43(11): 172-181WEI Ya’na, WANG Zhibin, QIAO Xiaojun, et al. Lightweight rice disease identification method based on attention mechanism and EfficientNet[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2022, 43(11): 172-181 [19] RAMACHANDRAN P, ZOPH B, LE Q V. Searching for activation functions[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1710.05941, 2017 [20] CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017: 1800-1807 [21] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6980, 2017 [22] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016: 2818-2826 [23] ARNAB A, DEHGHANI M, HEIGOLD G, et al. ViViT: A video vision transformer[C]//2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, QC, Canada: IEEE, 2021 [24] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[OL]. arXiv: 2010.11929, 2021 [25] CHEN X H, ZHOU Y C, WU D Y, et al. Imagine by reasoning: A reasoning-based implicit semantic data augmentation for long-tailed classification[C]//Thirty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto, CA, USA: AAAI, 2022 [26] ZHANG S Y, LI Z M, YAN S P, et al. Distribution alignment: A unified framework for long-tail visual recognition[C]//2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, TN, USA: IEEE, 2021 [27] 刘晓红, 王咏梅, 王天放. 基于包应用标准的紫外极光成像仪通信控制系统的设计与实现[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(6): 1204-1209 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.06.211108112LIU Xiaohong, WANG Yongmei, WANG Tianfang. Design and realization of the ultra-violet imager communication and control system based on packet utilization standard[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(6): 1204-1209 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.06.211108112 -
-




 蒋家楠 女, 1996年5月出生, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心在读博士生, 主要研究方向为机器学习在极光科学领域的应用. E-mail:
蒋家楠 女, 1996年5月出生, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心在读博士生, 主要研究方向为机器学习在极光科学领域的应用. E-mail:  邹自明 男, 1971年5月出生, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心研究员, 博士生导师, 主要研究方向为日地空间信息系统技术、机器学习在空间物理的应用等. E-mail:
邹自明 男, 1971年5月出生, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心研究员, 博士生导师, 主要研究方向为日地空间信息系统技术、机器学习在空间物理的应用等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: