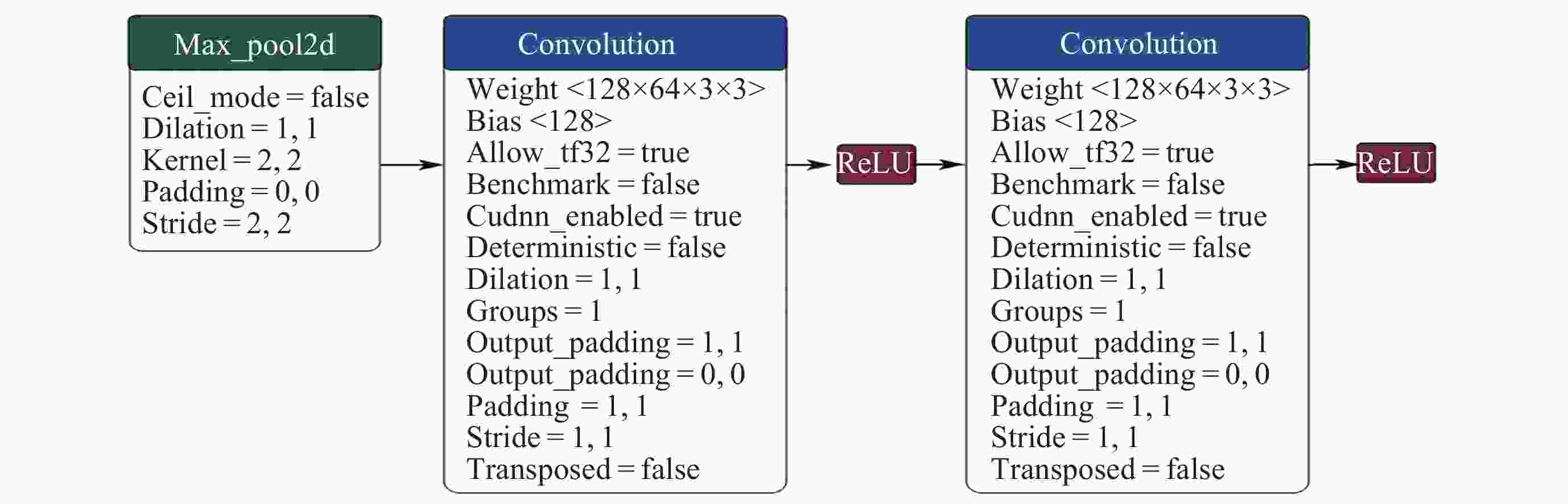
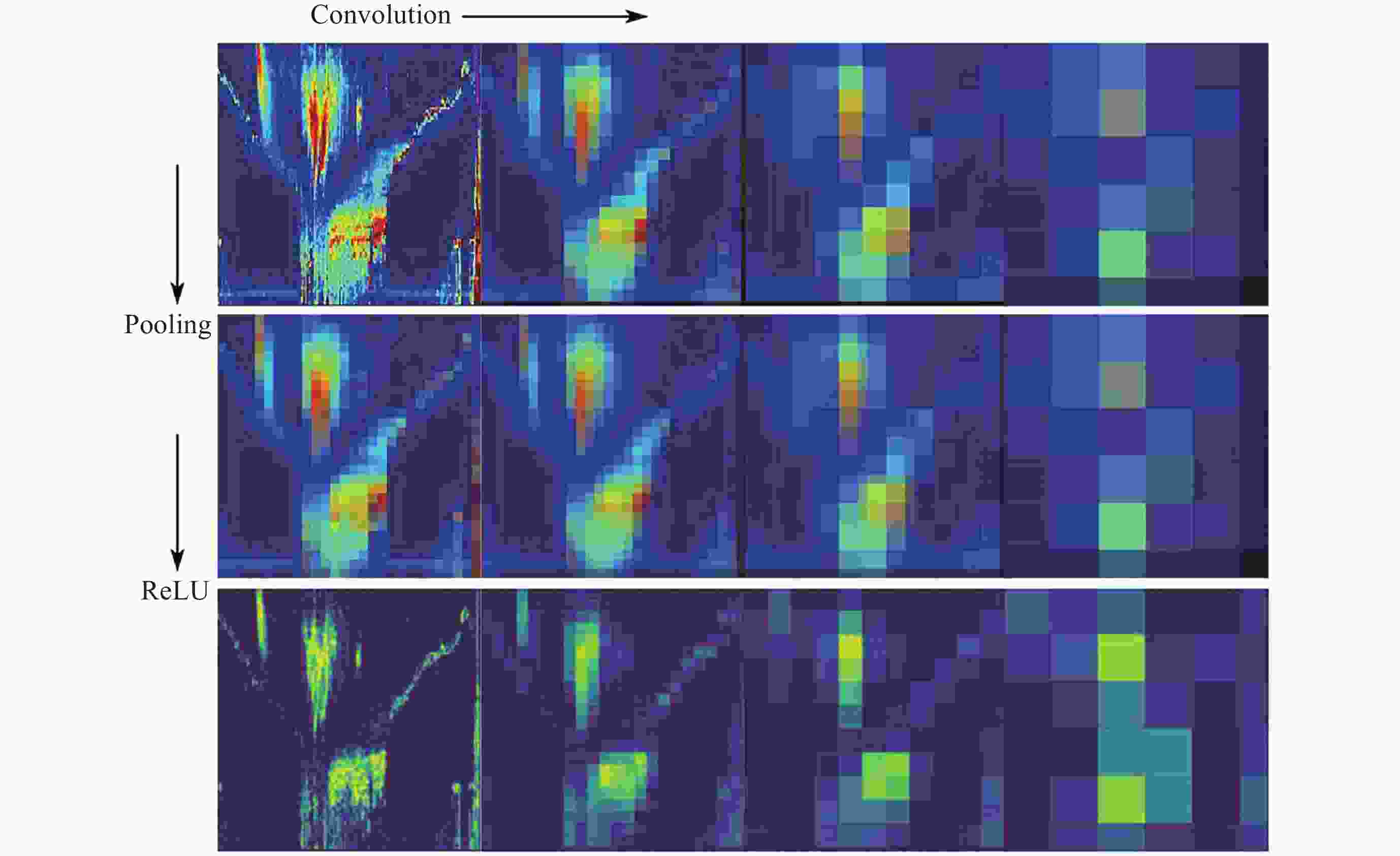
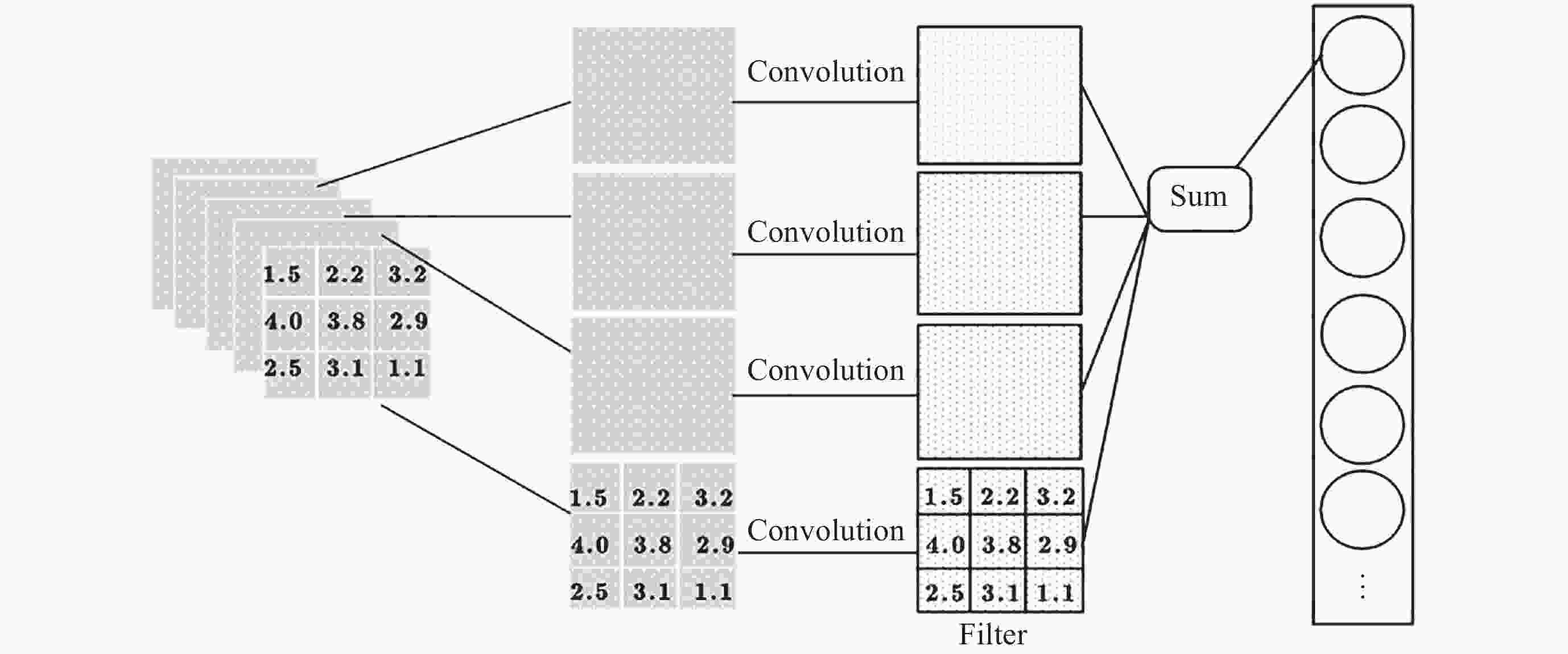
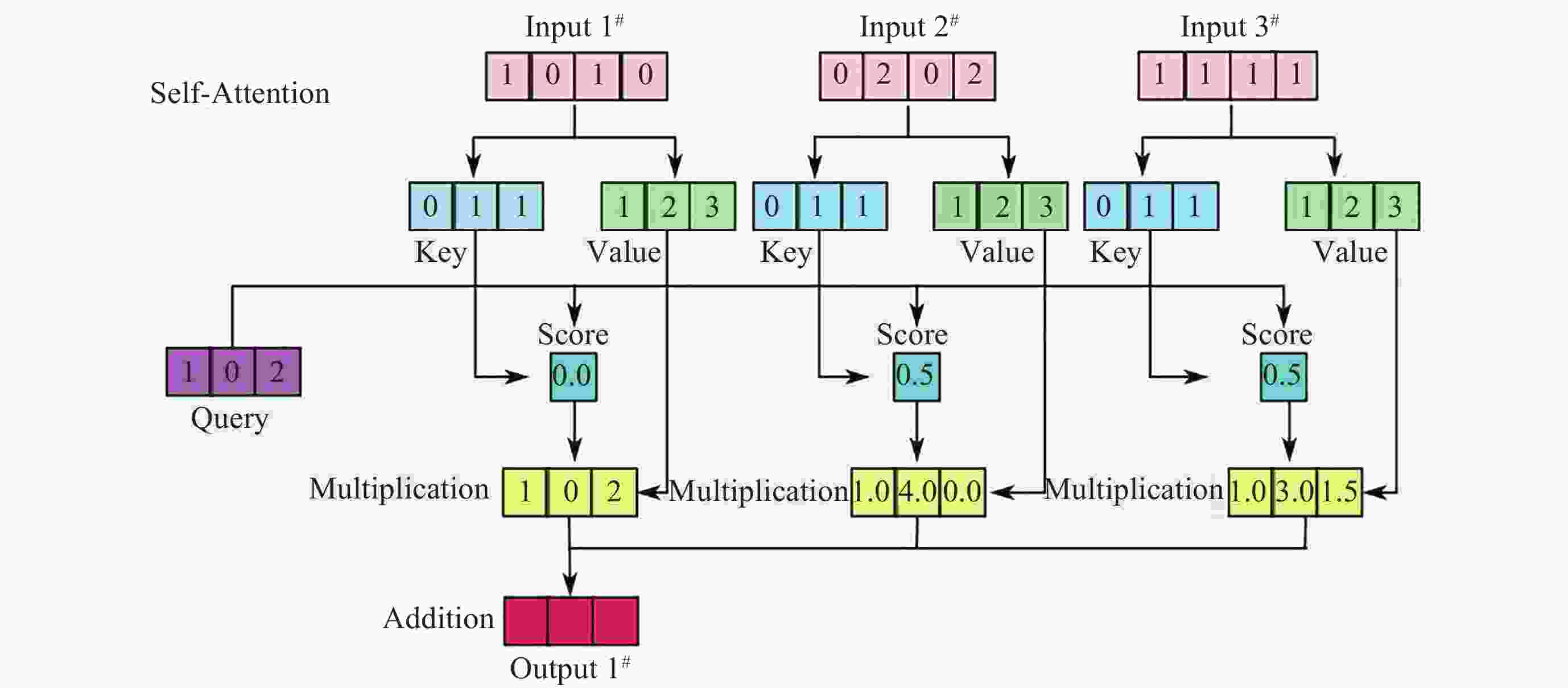
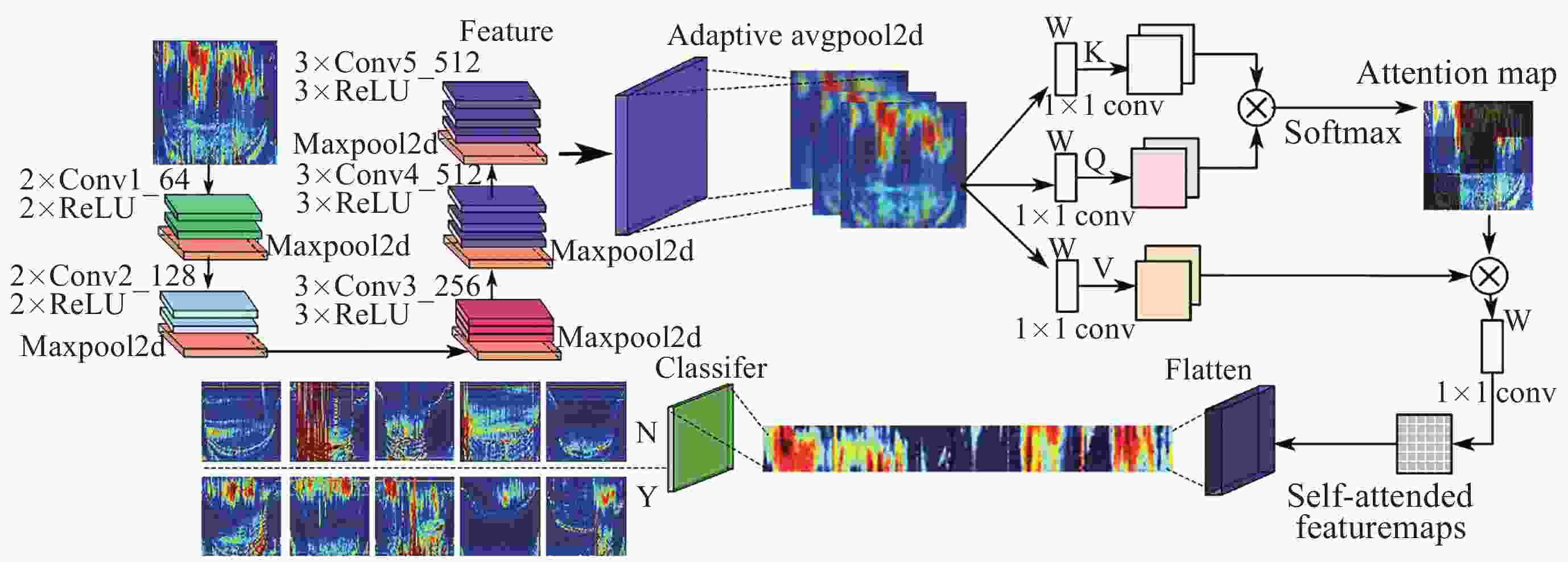
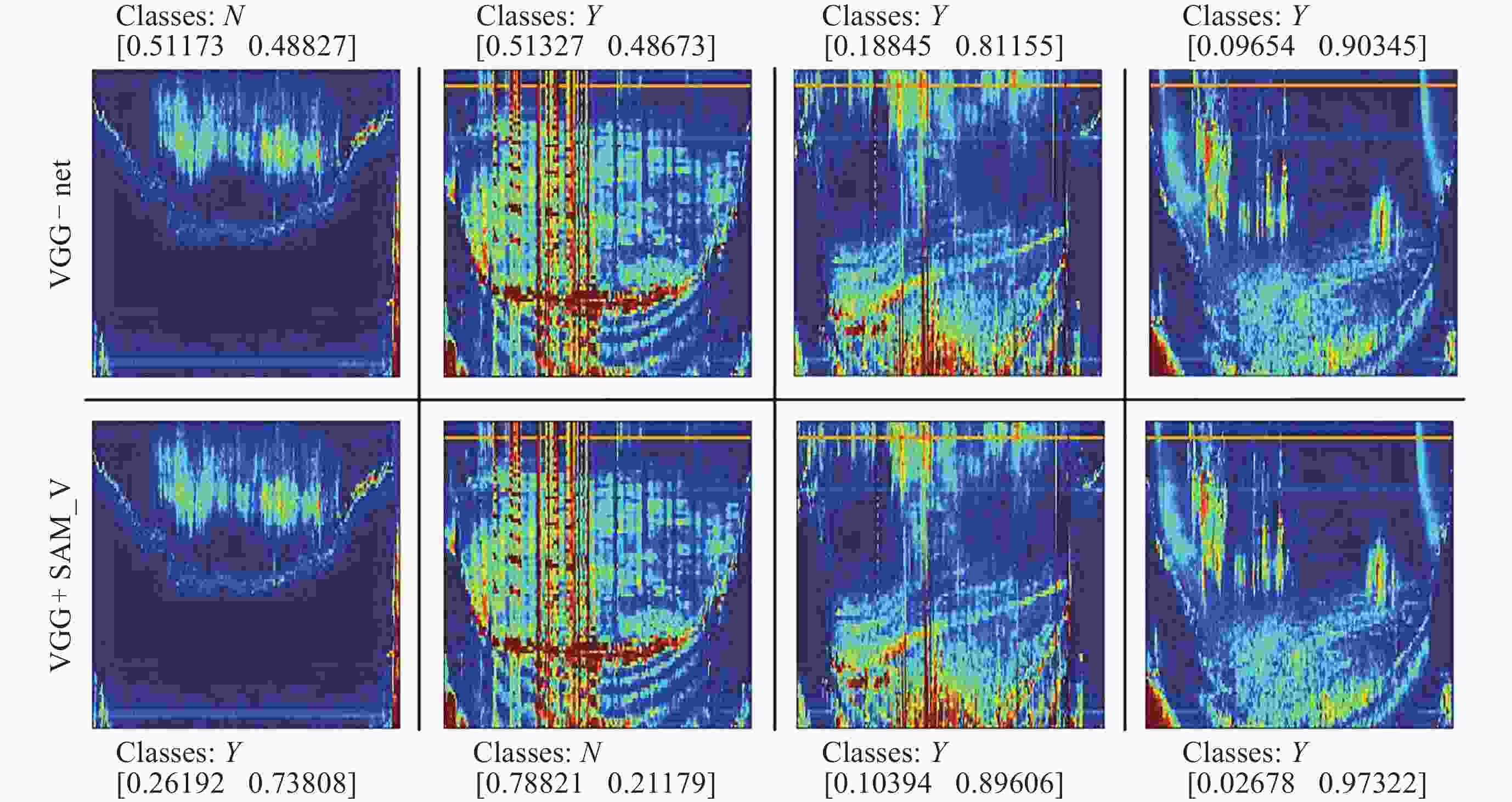
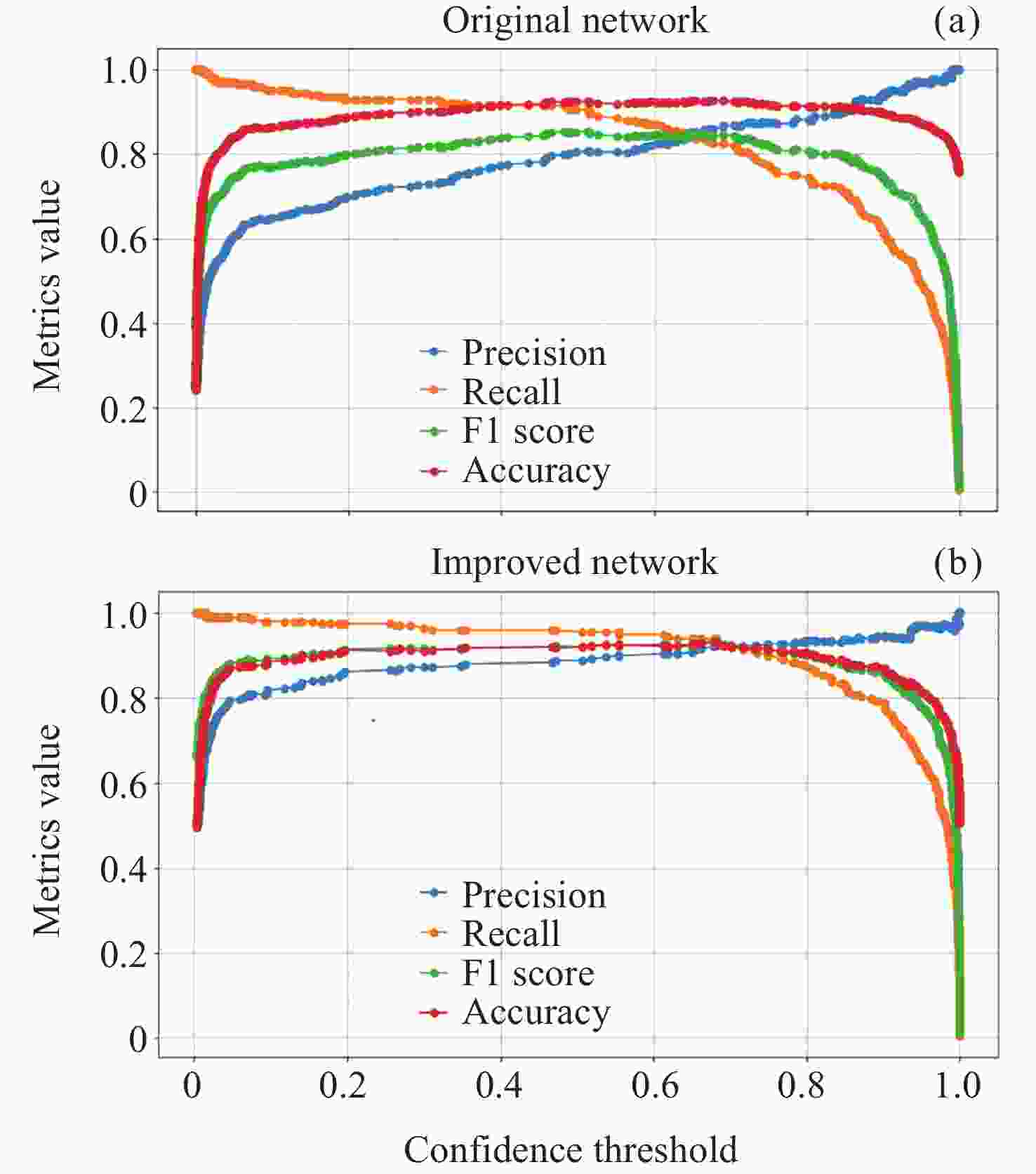
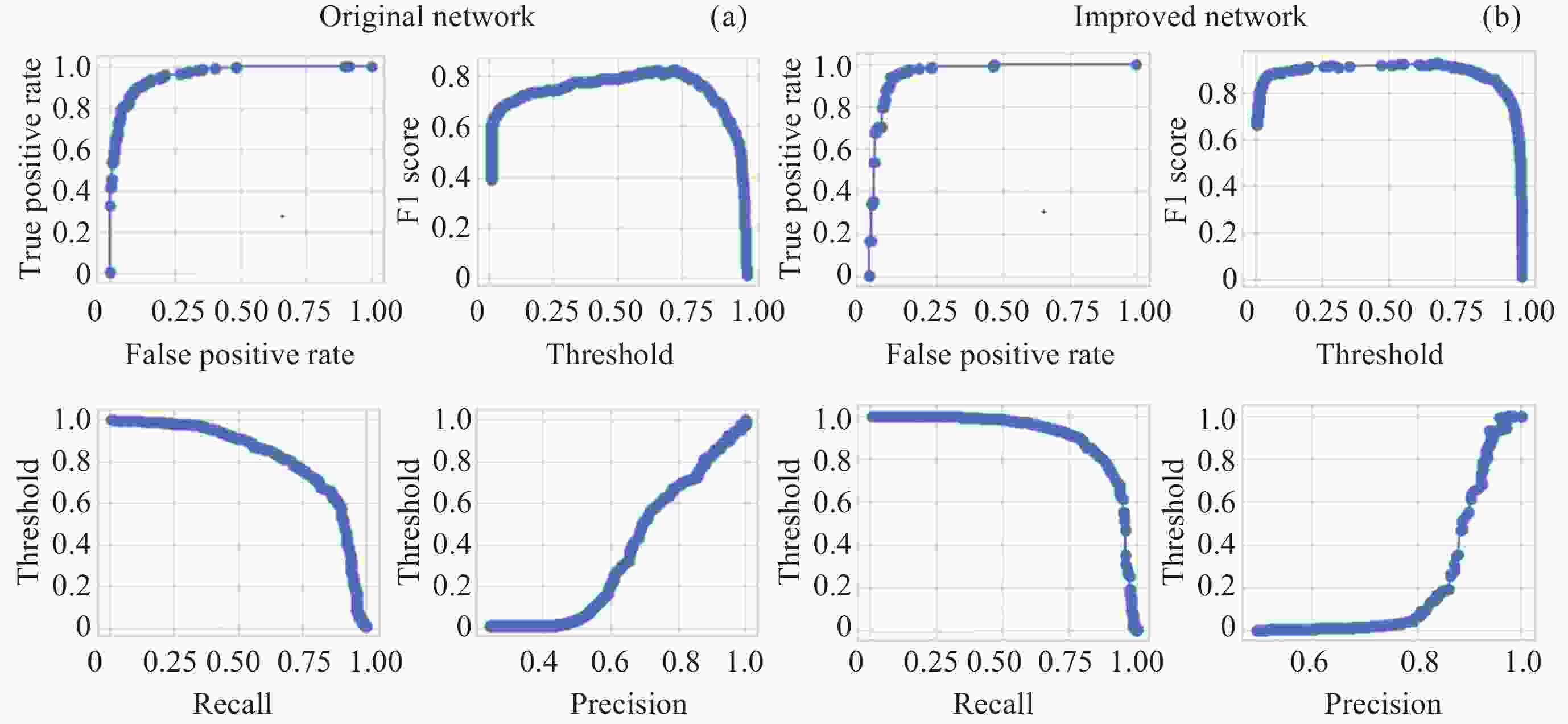
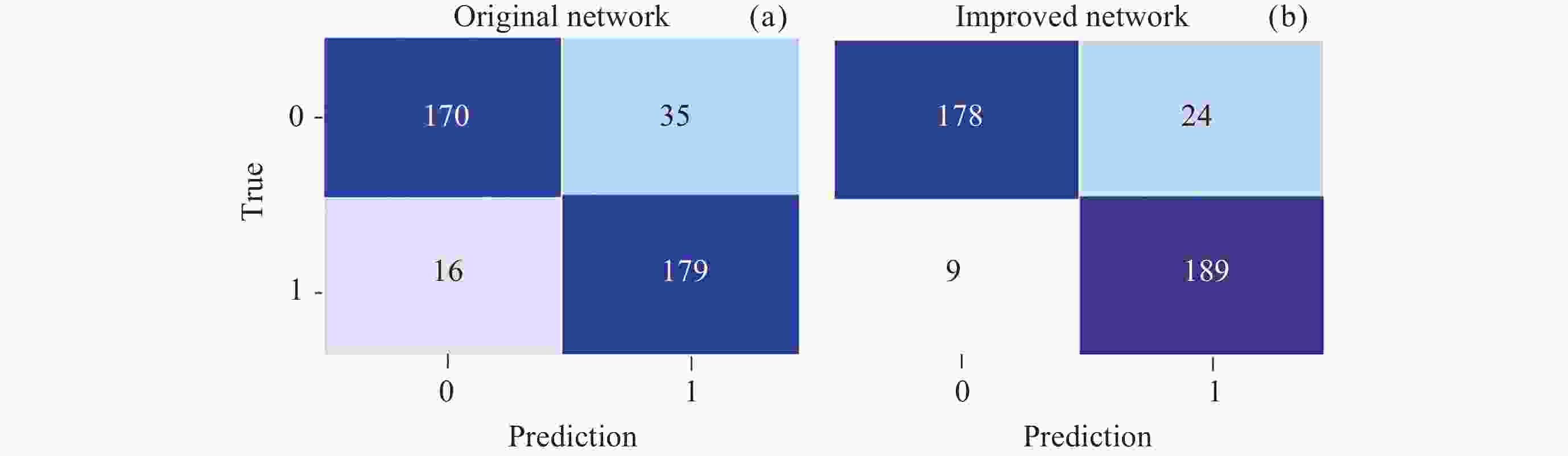
Recognition Method of Auroral Kilometric Radiation Based on Fusion of VGG16 and Self-attention Mechanism
-
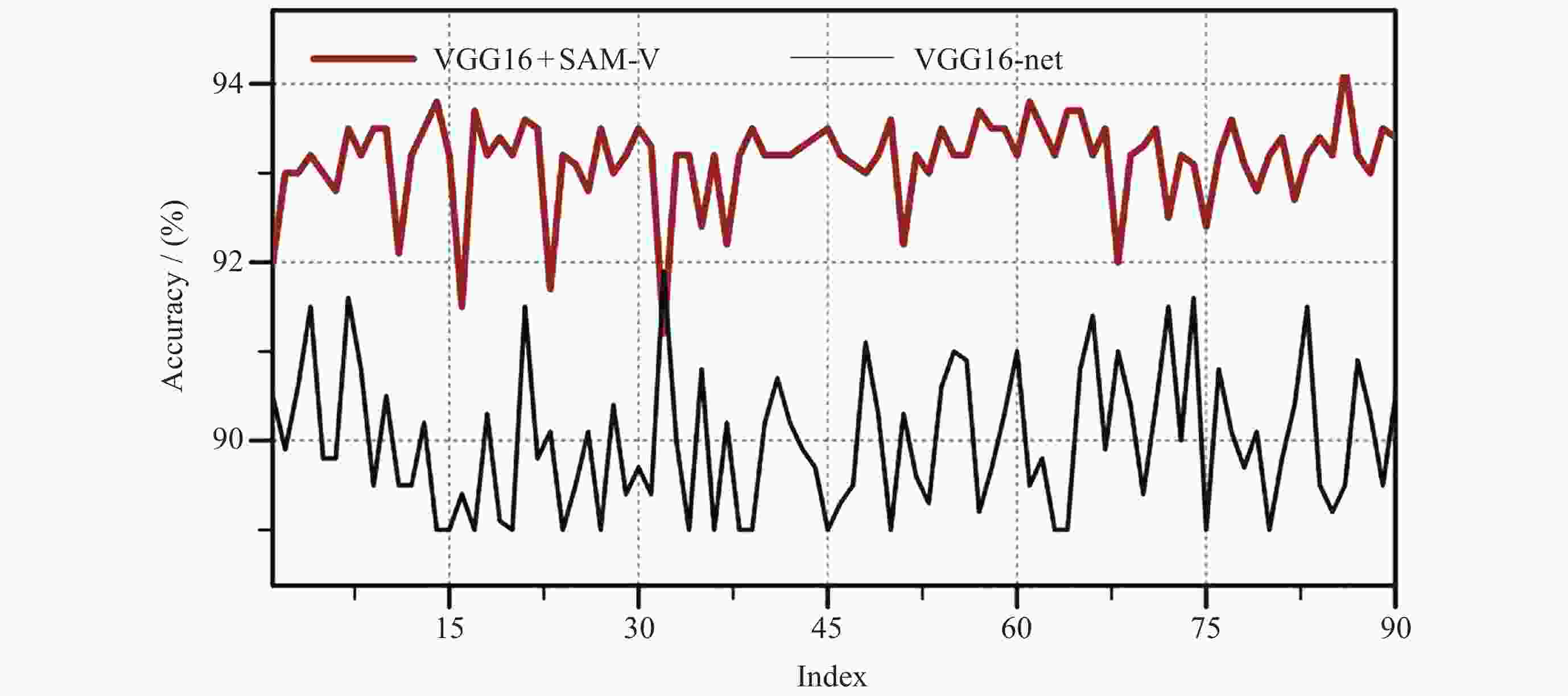
摘要: 提出了一种能准确识别极光千米波(Auroral Kilometric Radiation, AKR)的方法, 为进一步研究极光千米波在地球辐射带能量粒子剧烈变化过程中的作用提供支撑. 首先采用VGG16卷积神经网络作为基础模型, 从原始数据中提取出有助于识别AKR的局部特征. 之后引入嵌入VGG16网络的定制化自注意力机制(Self-Attention Mechanism embedded in VGG network, SAM-V), 该机制有助于捕捉功率谱图中不同时间点或频率上的信号可能存在的关联, 减小其他杂波的影响, 提高识别准确性. 同时, 采用线性学习率预热和动态衰减策略使模型更快地收敛并提高泛化能力. 实验结果表明, 改进后的模型平均识别准确率在93%左右, 比原始VGG16平均提高约3.3%, 并且召回率和精确度等指标均有所改善.
-
关键词:
- VGG16卷积神经网络 /
- 自注意力机制 /
- 极光千米波 /
- 学习率策略
Abstract: An enhanced image recognition algorithm for Auroral Kilometric Radiation (AKR) detection is presented by integrating a self-attention mechanism into the VGG16 Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture. The primary goal is to improve the flexibility and detection accuracy of AKR identification, which is crucial for understanding the dynamic changes in Earth’s radiation belts and the associated energetic particle variations. The methodology begins with employing the VGG16 CNN as the foundational model to extract local features from raw data that are instrumental in AKR recognition. Subsequently, a custom Self-Attention Mechanism (SAM-V) is embedded in the VGG network. The Self-Attention Mechanism (SAM), originally designed for sequential data processing, is adapted to work with the VGG16 network. Traditional integration of SAM with VGG16 could potentially increase the model’s complexity and computational cost, leading to potential feature sparsity issues. However, the proposed custom SAM-V generates queries, keys, and values through defined convolutional layers, offering more control over feature input and output. This customization implies shared parameters, reducing the number of model parameters, thereby mitigating the risk of overfitting and enhancing the model’s generalization capabilities. This approach is particularly adept at capturing correlations in power spectral density across different time points or frequencies, minimizing the impact of noise and improving recognition accuracy. Additionally, a linear learning rate warm-up and dynamic decay strategy are employed to accelerate model convergence and enhance generalization. The experimental results demonstrate that the improved model achieves an average recognition accuracy of approximately 93%, which represents a 3.3% increase compared to the original VGG16 model. Furthermore, other performance metrics such as recall rate and precision have also seen significant improvements. In conclusion, the integration of a custom self-attention mechanism into the VGG16 network has yielded a more efficient and accurate model for AKR detection. This advancement not only bolsters the study of auroral kilometric radiation but also has broader implications for the analysis of Earth’s radiation belt dynamics and energetic particle behavior. The model’s enhanced generalization capabilities and improved accuracy underscore the potential for applying similar techniques to other image recognition tasks within the field of space physics and beyond. -
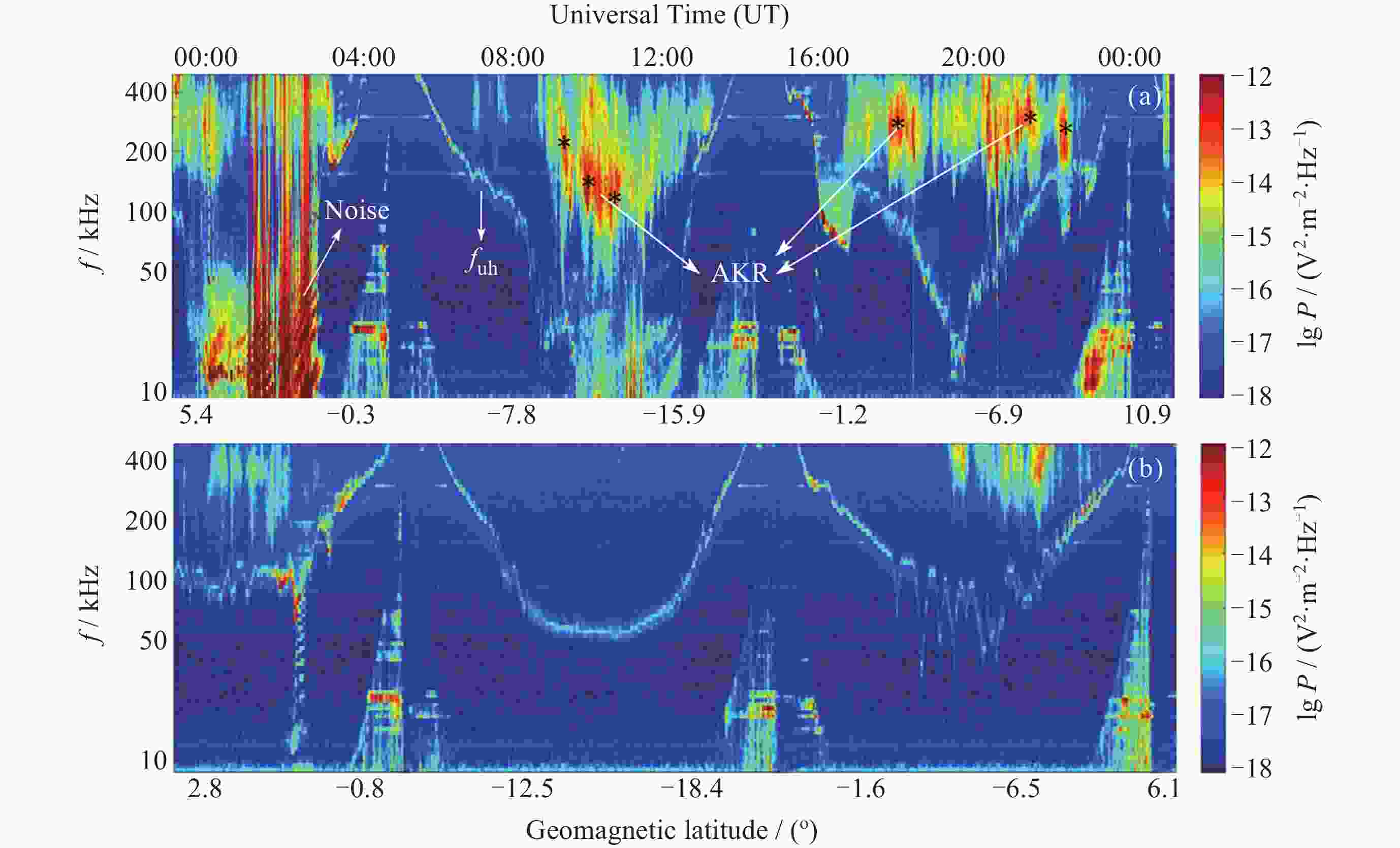
表 1 AKR频率中心点的部分信息
Table 1. Partial information about the AKR frequency center
1* 2* 3* 4* 5* 6* UT 09:30 10:00 11:10 18:20 21:30 22:00 lgP/
$ (\mathrm{V}^2\cdot\mathrm{m}^{-2}\cdot\text{Hz}^{-1}) $–12.55 –12.05 –12.75 –13.05 –12.65 –12.90 表 2 实验环境配置
Table 2. Configuration of the experimental environment
GPU CPU 架构 环境 RTX AMD PyTorch Python3.8 3090 EPYC 1.7.0 Cuda11.0 表 3 模型参数的数据对比
Table 3. Comparison of model parameters and other data
NET Parameters FLOPs Model_size/Byte VGG16-net 134268738 15466226688.0 539190670 VGG16+SAM-V 134794051 15491916800.0 553441679 -
[1] 赵万里. 地球辐射带区域极光千米波的全球分布特征研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2019ZHAO Wanli. The Global Distribution Characteristics of Auroral Kilometric Radiations in the Radiation Belt[D]. Changsha: Changsha University of Science & Technology, 2019 [2] GURNETT D A. The Earth as a radio source: terrestrial kilometric radiation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1974, 79(28): 4227-4238 doi: 10.1029/JA079i028p04227 [3] KURTH W S, BAUMBACK M M, GURNETT D A. Direction-finding measurements of auroral kilometric radiation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1975, 80(19): 2764-2770 doi: 10.1029/JA080i019p02764 [4] PRITCHETT P L, WINGLEE R M. Generation and propagation of kilometric radiation in the auroral plasma cavity[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1989, 94(A1): 129-143 doi: 10.1029/JA094iA01p00129 [5] BENEDIKTOV E A, GETMANTSEV G G, SAZONOV Y A, et al. Preliminary results of measurements of the intensity of distributed extraterrestrial radio-frequency emission at 725 and 1525-kHz frequencies by the satellite electron-2[J]. Kosmicheskie Issledovaniya, 1965, 3(6): 791-794 [6] CALVERT W. The auroral plasma cavity[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1981, 8(8): 919-921 doi: 10.1029/GL008i008p00919 [7] 李文涛. 极光千米波对外辐射带高能电子动力学演化过程的影响研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2021LI Wentao. Research on the Influence of Outer Radiation Belt Electron Dynamic Evolution by Auroral Kilometric Radiation[D]. Changsha: Changsha University of Science & Technology, 2021 [8] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego: ICLR, 2015 [9] 王菲, 杨秋菊. 基于卷积神经网络的极光图像分类[J]. 极地研究, 2018, 30(2): 123-131WANG Fei, YANG Qiuju. Classification of auroral images based on convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2018, 30(2): 123-131 [10] 李彦枝, 陈昌红, 谢晓芳. 基于改进卷积神经网络的极光图像分类算法研究[J]. 南京邮电大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 39(6): 86-93LI Yanzhi, CHEN Changhong, XIE Xiaofang. Aurora image classification algorithm based on improved convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications: Natural Science, 2019, 39(6): 86-93 [11] 牛闯. 基于深度学习的极光局部结构识别与定位[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2020NIU Chuang. Deep Learning Based Method for Auroral Local Structure Recognition and Localization[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2020 [12] 任杰. 基于深度学习的极光事件自动识别与检测[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2022REN Jie. Automatic Recognition and Detection of Aurora Events Based on Deep Leaning[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2022 [13] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach: Curran Associates Inc. , 2017: 6000-6010 [14] 岳泓光, 韩龙玫, 王正勇, 等. 基于多通道自注意力网络的遥感图像场景分类[J]. 四川大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 60(2): 023002YUE Hongguang, HAN Longmei, WANG Zhengyong, et al. Remote sensing image scene classification based on multi-channel self-attention network[J]. Journal of Sichuan University: Natural Science Edition, 2023, 60(2): 023002 [15] 常禧龙, 梁琨, 李文涛. 深度学习优化器进展综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(7): 1-12 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2307-0370CHANG Xilong, LIANG Kun, LI Wentao. Review of development of deep learning optimizer[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(7): 1-12 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2307-0370 [16] 潘美艳, 蔡兴雨, 薛健. 基于时频谱图和CNN的雷达空中目标识别方法[J]. 火控雷达技术, 2023, 52(4): 16-22PAN Meiyan, CAI Xingyu, XUE Jian. An aerial target recognition method for radar based on time-frequency spectrogram and CNN[J]. Fire Control Radar Technology, 2023, 52(4): 16-22 [17] HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO. , LTD. A Channel Prediction Method and Related Equipment: CN201811054284.7[P]. 2018-09-08 (华为技术有限公司. 一种信道预测方法及相关设备: CN 201811054284.7[P]. 2018-09-08 [18] 张良. AdamX优化器: 基于梯度和动量协调控制学习率的一种新型优化器[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2022ZHANG Liang. AdamX Optimizer: A New Optimizer Based on Gradient and Momentum Coodination of Learning Pate[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2022 [19] 朱圣伟, 邓小江, 张广智. 基于深度神经网络的地震岩性分类[C]//2018年中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国地球物理学会, 中国地震学会, 全国岩石学与地球动力学研讨会组委会, 中国地质学会构造地质学与地球动力学专业委员会, 中国地质学会区域地质与成矿专业委员会, 国家自然科学基金委员会地球科学部, 2018ZHU Shengwei, DENG Xiaojiang, ZHANG Guangzhi. Lithology Classification of Earthquakes Based on Deep Neural Networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 Joint Academic Annual Meeting of Chinese Earth Sciences. Beijing: Chinese Geophysical Society, China Seismological Society, Organizing Committee of the National Symposium on Petrology and Geodynamics, Professional Committee on Tectonic Geology and Geodynamics of the Chinese Geological Society, Professional Committee on Regional Geology and Mineralization of the Chinese Geological Society, Earth Sciences Division of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2018 [20] 蒋锐, 孙刘婷, 王小明, 等. 基于AE和Transformer的运动想象脑电信号分类研究[J]. 物联网学报, 2023, 7(1): 118-128 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2023.00310JIANG Rui, SUN Liuting, WANG Xiaoming, et al. Research on EEG signal classification of motor imagery based on AE and transformer[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2023, 7(1): 118-128 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2023.00310 [21] 马路宽. 基于数据增强和属性辅助的行人重识别研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2021MA Lukuan. Research on Pedestrian Reidentification Based on Data Enhancement and Attribute Assist[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2021 [22] XIAO F L, TANG J W, ZHANG S, et al. Asymmetric distributions of auroral kilometric radiation in earth’s northern and southern hemispheres observed by the Arase satellite[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(13): e2022GL099571 doi: 10.1029/2022GL099571 [23] 汪华健, 许丽, 刁志程, 等. 音频处理方法、装置、电子设备和存储介质: CN202310997762.2[P]. 2023-08-07WANG Huajian, XU Li, DIAO Zhicheng, et al. Audio processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium: CN202310997762.2[P]. 2023-08-07 [24] ZHANG S, LIU S, LI W T, et al. A concise empirical formula for the field-aligned distribution of auroral kilometeric radiation based on Arase satellite and van Allen probes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(8): e2021GL092805 doi: 10.1029/2021GL092805 [25] ZHANG S, SHANG X J, HE Y H, et al. Dominant roles of high harmonics on interactions between AKR and radiation belt relativistic electrons[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(16): e2020GL088421 doi: 10.1029/2020GL088421 [26] ZHANG S, YIN Q P, YANG H M, et al. Direct observation of l-x mode of auroral kilometric radiation in the lower latitude magnetosphere by the Arase satellite[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2024, 51(5): e2023GL105694 doi: 10.1029/2023GL105694 [27] 严孝宸. 基于改进残差神经网络的化工过程故障诊断方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2023YAN Xiaochen. Research on Chemical Process Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Improved Resnet[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2023 [28] 赵雪娇, 江湧, 苏露情. 基于深度学习算法的图像识别技术研究[J]. 建模与仿真, 2023, 12(3): 3024-3034 doi: 10.12677/MOS.2023.123278ZHAO Xuejiao, JIANG Yong, SU Luqing. Research on image recognition technology based on deep learning algorithm[J]. Modeling and Simulation, 2023, 12(3): 3024-3034 doi: 10.12677/MOS.2023.123278 -
-





 王鹤野 女, 2003年4月出生于山东省滨州市, 现为长沙理工大学物理与电子科学学院大四学生, 主要参与机器人运控, 机器视觉CV等应用与研究. E-mail:
王鹤野 女, 2003年4月出生于山东省滨州市, 现为长沙理工大学物理与电子科学学院大四学生, 主要参与机器人运控, 机器视觉CV等应用与研究. E-mail:  张赛 男, 1986年10月出生于山西省运城市, 现为长沙理工大学物理与电子科学学院副教授, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为空间等离子体物理和人工智能应用等. E-mail:
张赛 男, 1986年10月出生于山西省运城市, 现为长沙理工大学物理与电子科学学院副教授, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为空间等离子体物理和人工智能应用等. E-mail: 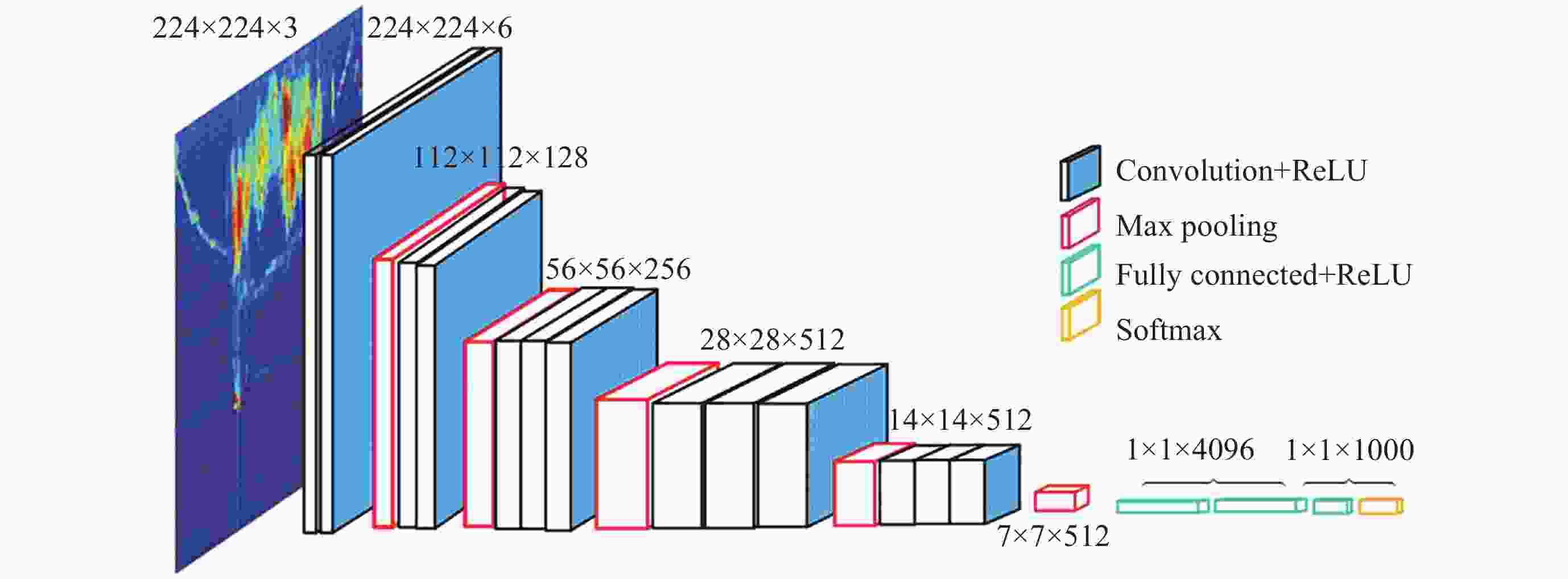
 下载:
下载: