Dst Index Prediction Method Based on LSTM Neural Network
-
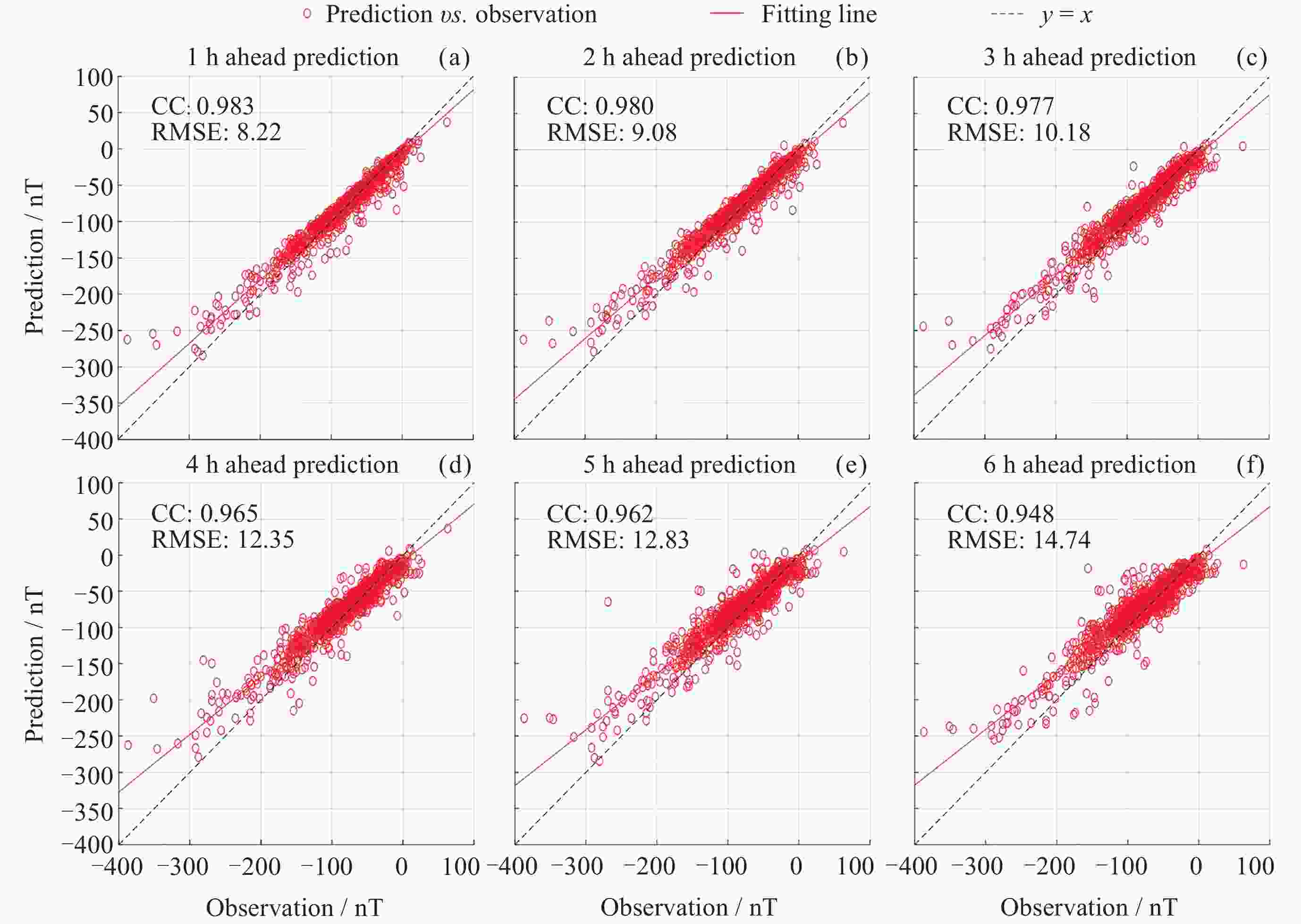
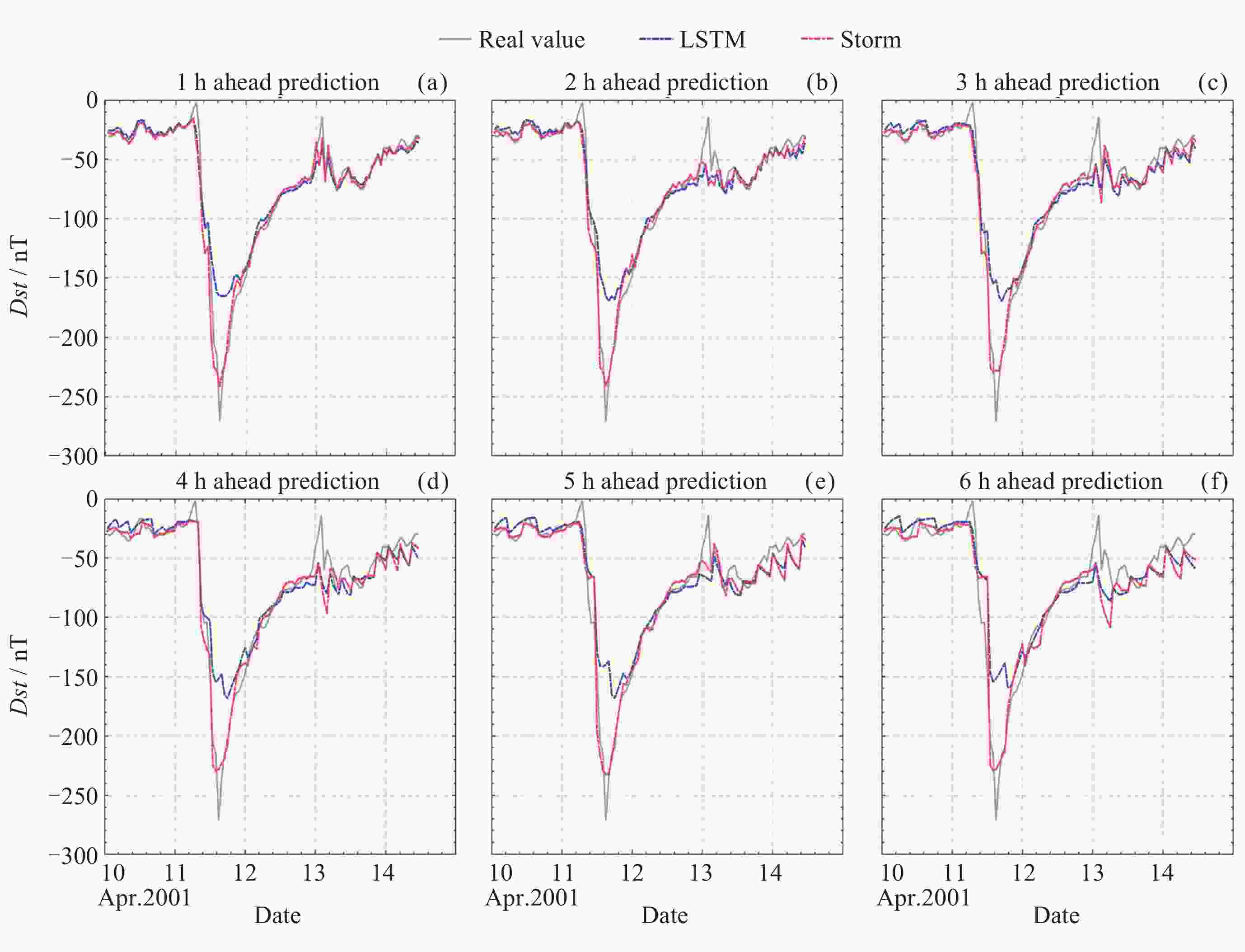
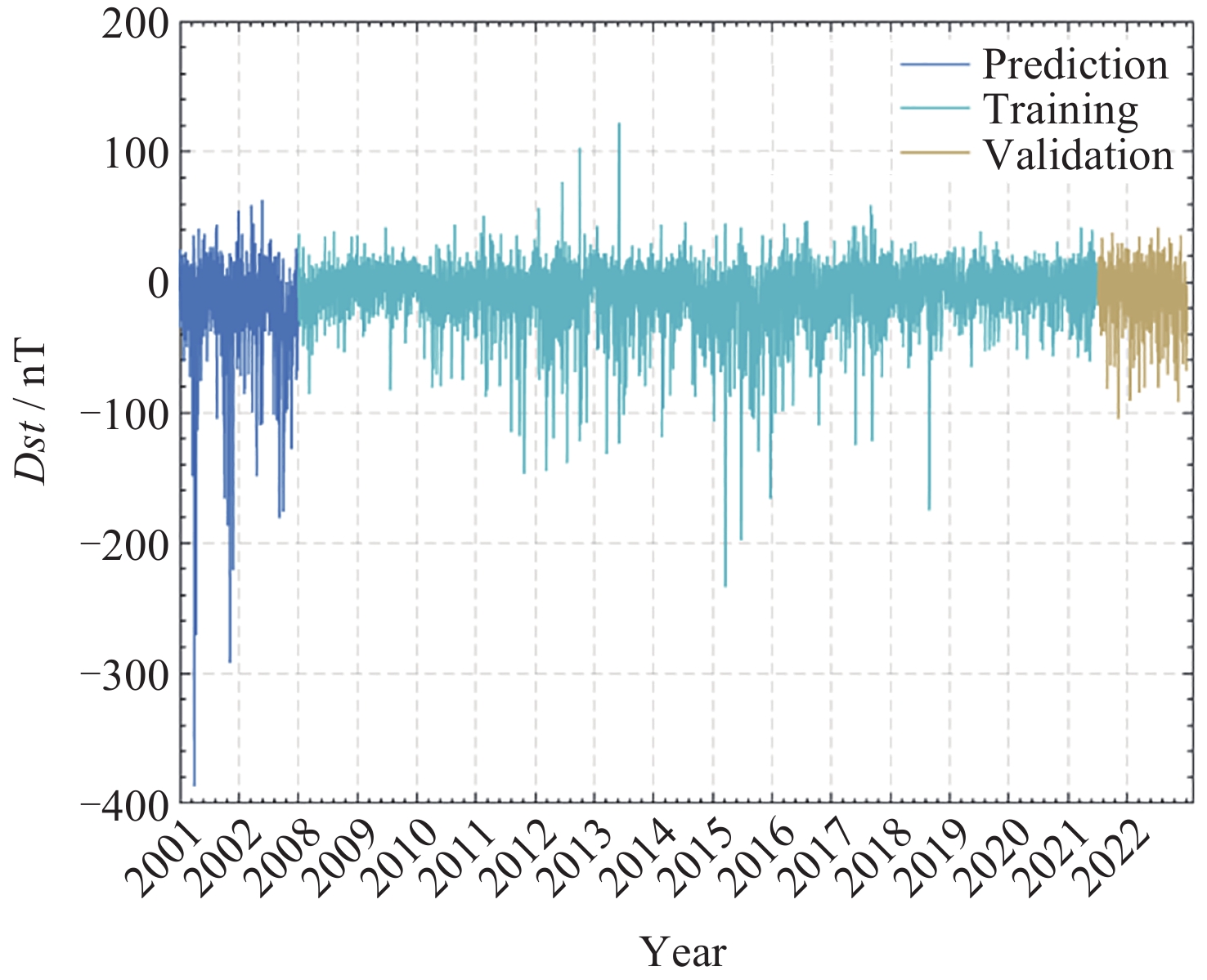
摘要: Dst指数是当前使用较广泛的用于反映磁暴过程的小时地磁指数, 对Dst指数的预报是现代空间天气学主要研究内容之一. 基于LSTM神经网络方法, 利用2008-2022年的太阳风参数和Dst指数建立Dst指数预报模型, 分别为使用全时域数据建模的LSTM模型和仅使用磁暴期间数据建模的Storm模型. 使用LSTM模型对2001-2002年间的Dst指数进行滚动预报, 预报结果显示该模型对提前1~6 h的Dst指数预报相关系数达到0.94以上, 均方根误差在11 nT以内. Storm模型能够较好地解决LSTM模型在磁暴(尤其是强磁暴, Dst< –100 nT)主相期间预报误差较大的问题, 对2001-2002年期间的23次强磁暴事件预报结果表明, Storm模型对磁暴期间提前6 h的预报结果相关系数较LSTM模型由0.902提升至0.948. 综合两个预报模型组成的LSTM-Storm模型对Dst指数的预报结果相关系数在0.95以上, 均方根误差在9 nT以内, 相比单LSTM模型的预报精度有显著提升.
-
关键词:
- Dst指数预报 /
- LSTM神经网络 /
- 预报模型 /
- LSTM-Storm模型
Abstract: The Dst index is one of the widely used hourly geomagnetic indices to reflect geomagnetic storm processes, and forecasting the Dst index constitutes a primary concern in modern space weather studies. This study leverages Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network methodology alongside solar wind parameters and Dst index data spanning from 2008 to 2022 to construct a predictive model for the Dst index. Two models are established: the LSTM model, modeling the entire temporal domain, and the Storm model, modeling solely data from storm periods. Employing the LSTM model for rolling forecasts of Dst index during 2001 to 2002 yields a correlation coefficient exceeding 0.94 and a root mean square error within 11 nT for forecasts ranging from 1 to 6 hours in advance. The Storm model effectively addresses the issue of pronounced forecast errors during storm periods, particularly during the main phase of intense storms (Dst < –100 nT), showcasing improved forecast accuracy. Forecasting experiments conducted on 23 strong storm events occurring during 2001―2002 demonstrate an enhancement in the correlation coefficient for forecasts made 6 hours in advance during storm periods, increasing from 0.902 with the LSTM model to 0.948 with the Storm model. Integration of both forecasting models into the LSTM-Storm model yields correlation coefficients above 0.95 and root mean square errors within 9 nT for Dst index forecasts, presenting a marked improvement in forecasting accuracy compared to the standalone LSTM model.-
Key words:
- Dst index prediction /
- LSTM neural network /
- Forecasting model /
- LSTM-Storm model
-
表 1 2001-2002年强磁暴事件参数
Table 1. Parameters of severe magnetic storm events in 2001-2002
Start date Start time (UT) End date End time (UT) Min. Dst /nT 2001-03-19 12:00 2001-03-22 15:00 –149 2001-03-31 00:00 2001-04-04 11:00 –387 2001-04-10 10:00 2001-04-14 10:00 –271 2001-04-18 01:00 2001-04-19 19:00 –114 2001-04-22 02:00 2001-04-24 17:00 –102 2001-08-17 07:00 2001-08-19 07:00 –105 2001-09-30 22:00 2001-10-06 16:00 –166 2001-10-19 11:00 2001-10-25 12:00 –187 2001-10-27 05:00 2001-10-31 16:00 –157 2001-10-31 17:00 2001-11-03 09:00 –106 2001-11-05 20:00 2001-11-12 11:00 –292 2001-11-22 19:00 2001-11-28 10:00 –221 2002-03-23 14:00 2002-03-25 05:00 –100 2002-04-17 09:00 2002-04-19 02:00 –127 2002-04-19 09:00 2002-04-26 06:00 –149 2002-05-11 12:00 2002-05-13 16:00 –110 2002-05-23 09:00 2002-05-26 07:00 –109 2002-08-01 23:00 2002-08-03 23:00 –102 2002-08-18 23:00 2002-08-22 22:00 –106 2002-09-04 01:00 2002-09-06 04:00 –109 2002-09-07 01:00 2002-09-14 08:00 –181 2002-09-30 09:00 2002-10-12 20:00 –176 2002-11-20 16:00 2002-11-26 22:00 –128 表 2 LSTM模型对2001-2002年Dst指数的预报结果
Table 2. Dst index prediction results of the LSTM model during 2001-2002
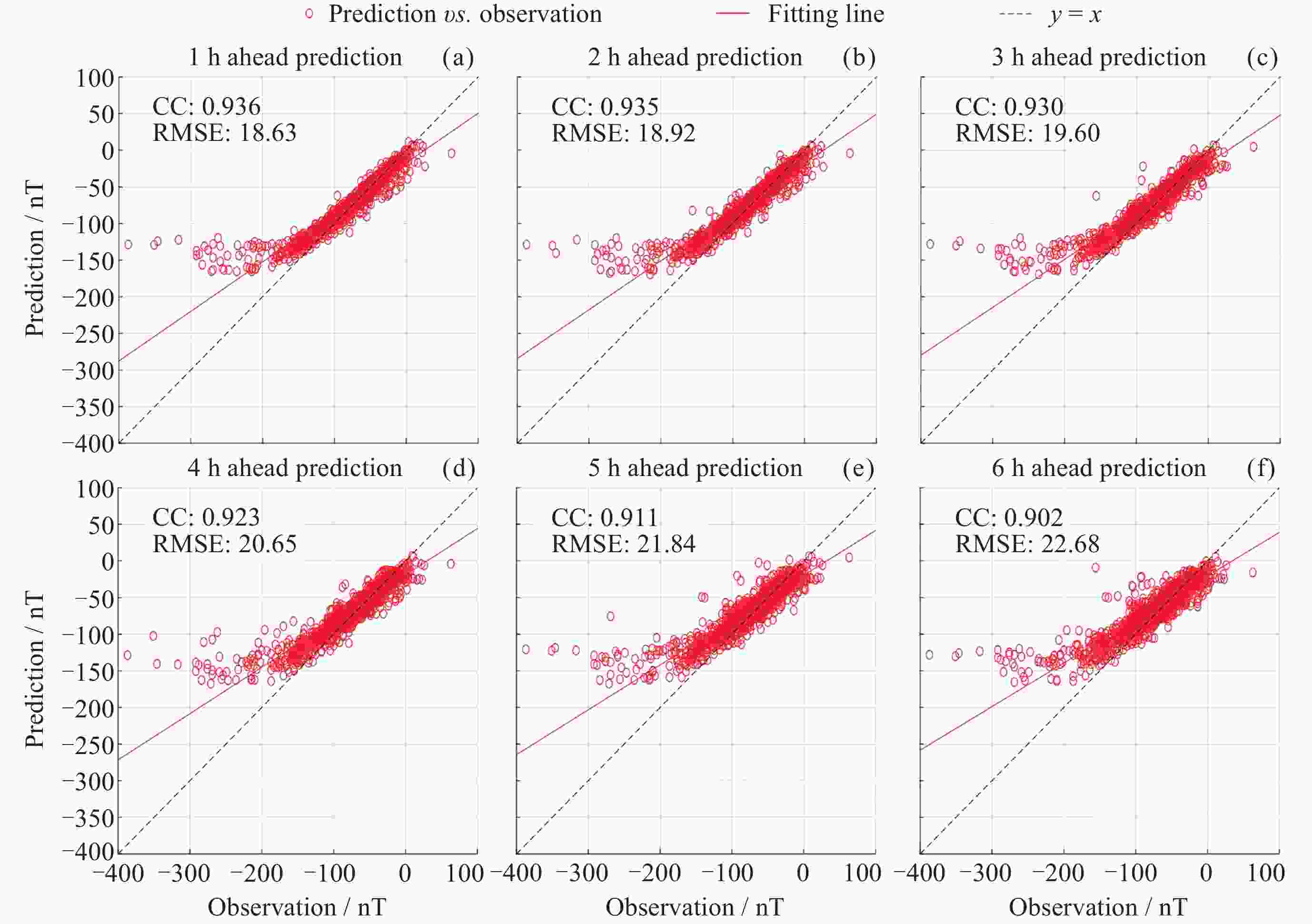
提前时间/h t+1 t+2 t+3 t+4 t+5 t+6 CC 0.971 0.968 0.962 0.955 0.947 0.940 RMSE/ nT 7.44 7.92 8.53 9.26 9.96 10.64 表 3 LSTM-Storm模型提前1~6 h预报结果与已有研究的比较
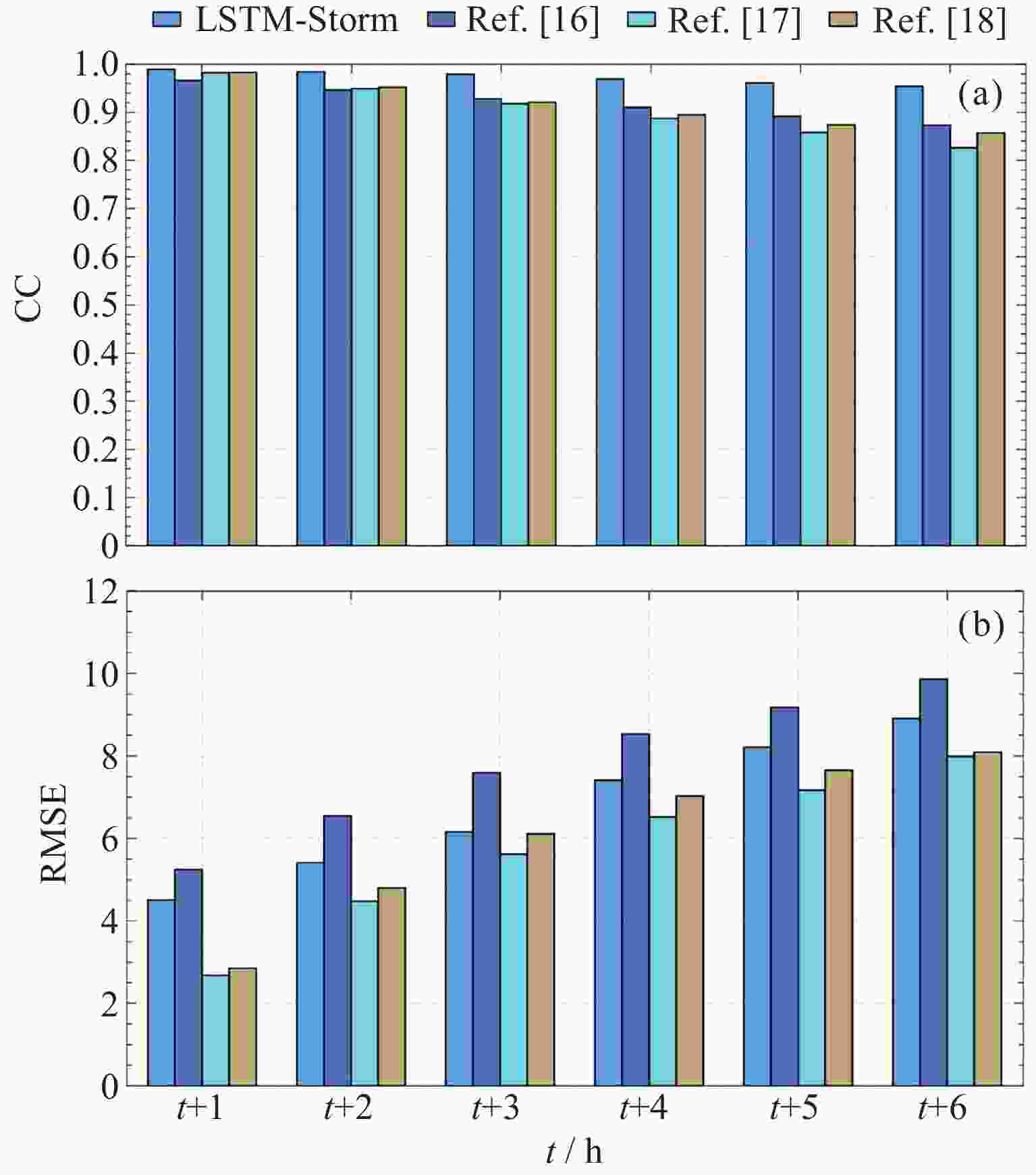
Table 3. Comparison of LSTM-Storm model forecast results 1~6 h in advance with past studies
提前时间/h LSTM-Storm Ref. [16] Ref. [17] Ref. [18] CC RMSE/nT CC RMSE/nT CC RMSE/nT CC RMSE/nT t+1 0.989 4.51 0.966 5.25 0.982 2.68 0.983 2.85 t+2 0.984 5.41 0.946 6.55 0.949 4.48 0.952 4.80 t+3 0.980 6.16 0.928 7.59 0.918 5.62 0.921 6.11 t+4 0.970 7.41 0.910 8.53 0.887 6.52 0.895 7.03 t+5 0.963 8.21 0.892 9.18 0.858 7.17 0.874 7.65 t+6 0.957 8.91 0.873 9.86 0.826 7.99 0.857 8.09 -
[1] BURTON R K, MCPHERRON R L, RUSSELL C T. An empirical relationship between interplanetary conditions and Dst[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1975, 80(31): 4204-4214 doi: 10.1029/JA080i031p04204 [2] IYEMORI T, MAEDA H, KAMEI T. Impulse response of geomagnetic indices to interplanetary magnetic field[J]. Journal of Geomagnetism and Geoelectricity, 1979, 31(1): 1-9 doi: 10.5636/jgg.31.1 [3] 彭宇翔, 吕建永, 顾赛菊. 利用支持向量机预测大磁暴期间Dst指数的变化[J]. 空间科学学报, 2016, 36(6): 866-874 doi: 10.11728/cjss2016.06.866PENG Yuxiang, LÜ Jianyong, GU Saiju. Application of support vector machine to the forecasting of Dst index during geomagnetic storm[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2016, 36(6): 866-874 doi: 10.11728/cjss2016.06.866 [4] YATSENKO V O, IVANOV S M, PARNOWSKI A, et al. Guaranteed narmax model for the prediction of geomagnetic Dst index[J]. Journal of Physical Studies, 2019, 23(1): 1901 doi: 10.30970/jps.23.1901 [5] MYAGKOVA I N, SHIROKII V R, VLADIMIROV R D, et al. Prediction of the Dst geomagnetic index using adaptive methods[J]. Russian Meteorology and Hydrology, 2021, 46(3): 157-162 doi: 10.3103/S1068373921030031 [6] BEJ A, BANERJEE A, CHATTERJEE T N, et al. One-hour ahead prediction of the Dst index based on the optimum state space reconstruction and pattern recognition[J]. The European Physical Journal Plus, 2022, 137(4): 479 doi: 10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02687-7 [7] NILAM B, RAM S T. Forecasting geomagnetic activity (Dst Index) using the ensemble Kalman filter[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2022, 511(1): 723-731 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stac099 [8] 吴洪钟, 都亨. 行星际参量和地磁指数相关关系之比较[J]. 空间科学学报, 1986, 6(3): 196-202 doi: 10.11728/cjss1986.03.196WU Hongzhong, DU Heng. Comparison of the correlations between the interplanetary parameters and geomagnetic indexes[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 1986, 6(3): 196-202 doi: 10.11728/cjss1986.03.196 [9] LUNDSTEDT H, WINTOFT P. Prediction of geomagnetic storms from solar wind data with the use of a neural network[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 1994, 12(1): 19-24 doi: 10.1007/s00585-994-0019-2 [10] WU J G, LUNDSTEDT H. Geomagnetic storm predictions from solar wind data with the use of dynamic neural networks[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1997, 102(A7): 14255-14268 doi: 10.1029/97JA00975 [11] LUNDSTEDT H, GLEISNER H, WINTOFT P. Operational forecasts of the geomagnetic DstDst index[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(24): 2181 [12] 陈春, 孙树计, 许正文, 等. 利用神经网络技术提前一小时预报Dst指数[J]. 空间科学学报, 2011, 31(2): 182-186 doi: 10.11728/cjss2011.02.182CHEN Chun, SUN Shuji, XU Zhengwen, et al. Short-term Dst index forecasting method based on neural network techniques[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2011, 31(2): 182-186 doi: 10.11728/cjss2011.02.182 [13] BALA R, REIFF P. Improvements in short-term forecasting of geomagnetic activity[J]. Space Weather, 2012, 10(6): S06001 [14] REVALLO M, VALACH F, HEJDA P, et al. A neural network Dst index model driven by input time histories of the solar wind–magnetosphere interaction[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2014, 110-111: 9-14 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2014.01.011 [15] LAZZÚS J A, VEGA P, ROJAS P, et al. Forecasting the Dst index using a swarm-optimized neural network[J]. Space Weather, 2017, 15(8): 1068-1089 doi: 10.1002/2017SW001608 [16] GRUET M A, CHANDORKAR M, SICARD A, et al. Multiple-hour-ahead forecast of the Dst index using a combination of long short-term memory neural network and Gaussian process[J]. Space Weather, 2018, 16(11): 1882-1896 doi: 10.1029/2018SW001898 [17] LAZZÚS J A, VEGA-JORQUERA P, PALMA-CHILLA L, et al. Dst index forecast based on ground-level data aided by bio-inspired algorithms[J]. Space Weather, 2019, 17(10): 1487-1506 [18] XU S B, HUANG S Y, YUAN Z G, et al. Prediction of the Dst index with Bagging ensemble-learning algorithm[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2020, 248(1): 14 doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ab880e [19] PARK W, LEE J, KIM K C, et al. Operational Dst index prediction model based on combination of artificial neural network and empirical model[J]. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2021, 11(38): 38 [20] NURAENI F, RUHIMAT M, ARIS M A, et al. Development of 24 hours Dst index prediction from solar wind data and IMF Bz using NARX[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022, 2214: 012024 doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2214/1/012024 [21] XU W W, ZHU Y M, ZHU L, et al. A class of Bayesian machine learning model for forecasting Dst during intense geomagnetic storms[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 72(9): 3882-3889 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2023.07.009 [22] ZHANG J Y, FENG Y, ZHANG J X, et al. The short time prediction of the Dst index based on the long-short time memory and empirical mode decomposition-long-short time memory models[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(21): 11824 doi: 10.3390/app132111824 [23] HU A, CAMPOREALE E, SWIGER B. Multi-hour-ahead Dst index prediction using multi-fidelity boosted neural networks[J]. Space Weather, 2023, 21(4): e2022SW003286 doi: 10.1029/2022SW003286 [24] NAIR M, REDMON R, YOUNG L Y, et al. MagNet—a data-science competition to predict disturbance storm-time index (Dst) from solar wind data[J]. Space Weather, 2023, 21(10): e2023SW003514 doi: 10.1029/2023SW003514 [25] CIANCHINI G, PISCINI A, DE SANTIS A, et al. Fast Dst computation by applying deep learning to Swarm satellite magnetic data[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 69(2): 837-855 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.10.051 [26] RUHIMAT M, NURAENI F, YATINI C Y, et al. Prediction of Dst index by using artificial neural network NARX[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2023, 2941(1): 040006 [27] LU J Y, PENG Y X, WANG M, et al. Support vector machine combined with distance correlation learning for Dst forecasting during intense geomagnetic storms[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2016, 120: 48-55 doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2015.11.004 [28] LI Y Y, HUANG S Y, XU S B, et al. Selection of the main control parameters for the Dst index prediction model based on a layer-wise relevance propagation method[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2022, 260(1): 6 doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ac616c [29] HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780 doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 -
-




 李绍文 男, 2003年5月出生于四川省凉山州, 现为国防科技大学气象海洋学院在读本科生, 主要研究方向为电离层物理、空间天气建模预报. E-mail:
李绍文 男, 2003年5月出生于四川省凉山州, 现为国防科技大学气象海洋学院在读本科生, 主要研究方向为电离层物理、空间天气建模预报. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: