Orbit Determination of Asteroid 2016HO3 and Analysis of Detection of Yarkovsky Effect Force
-
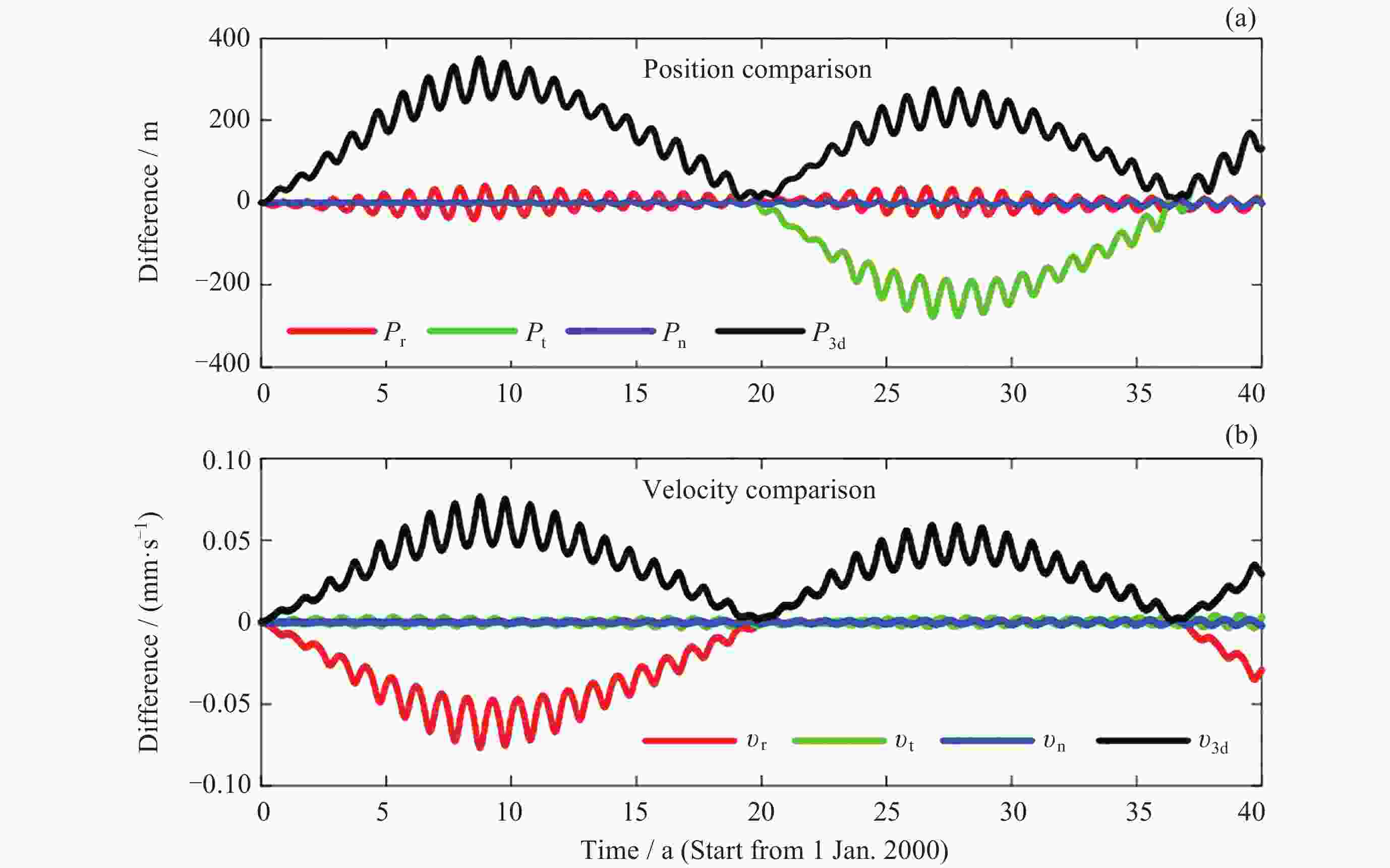
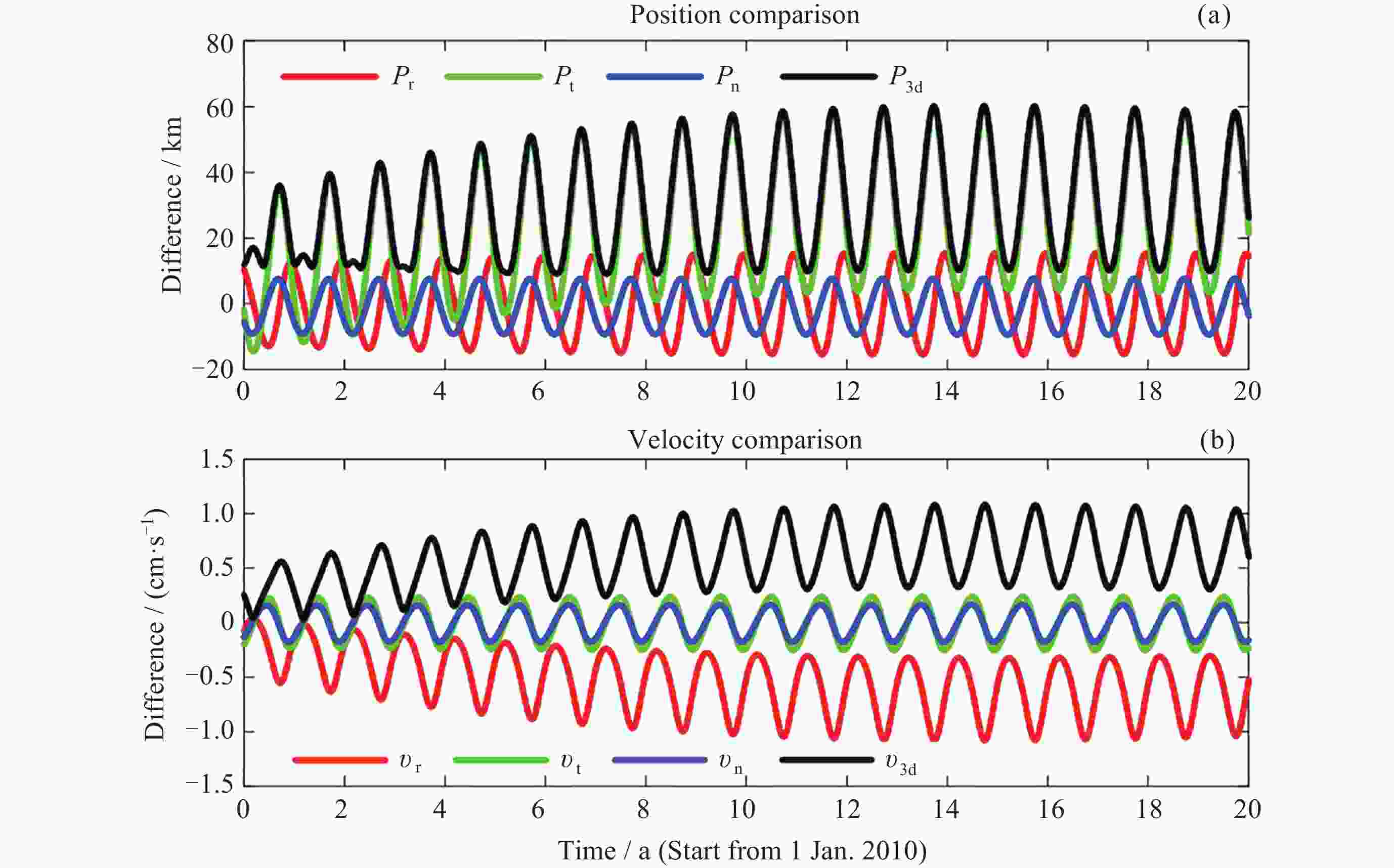
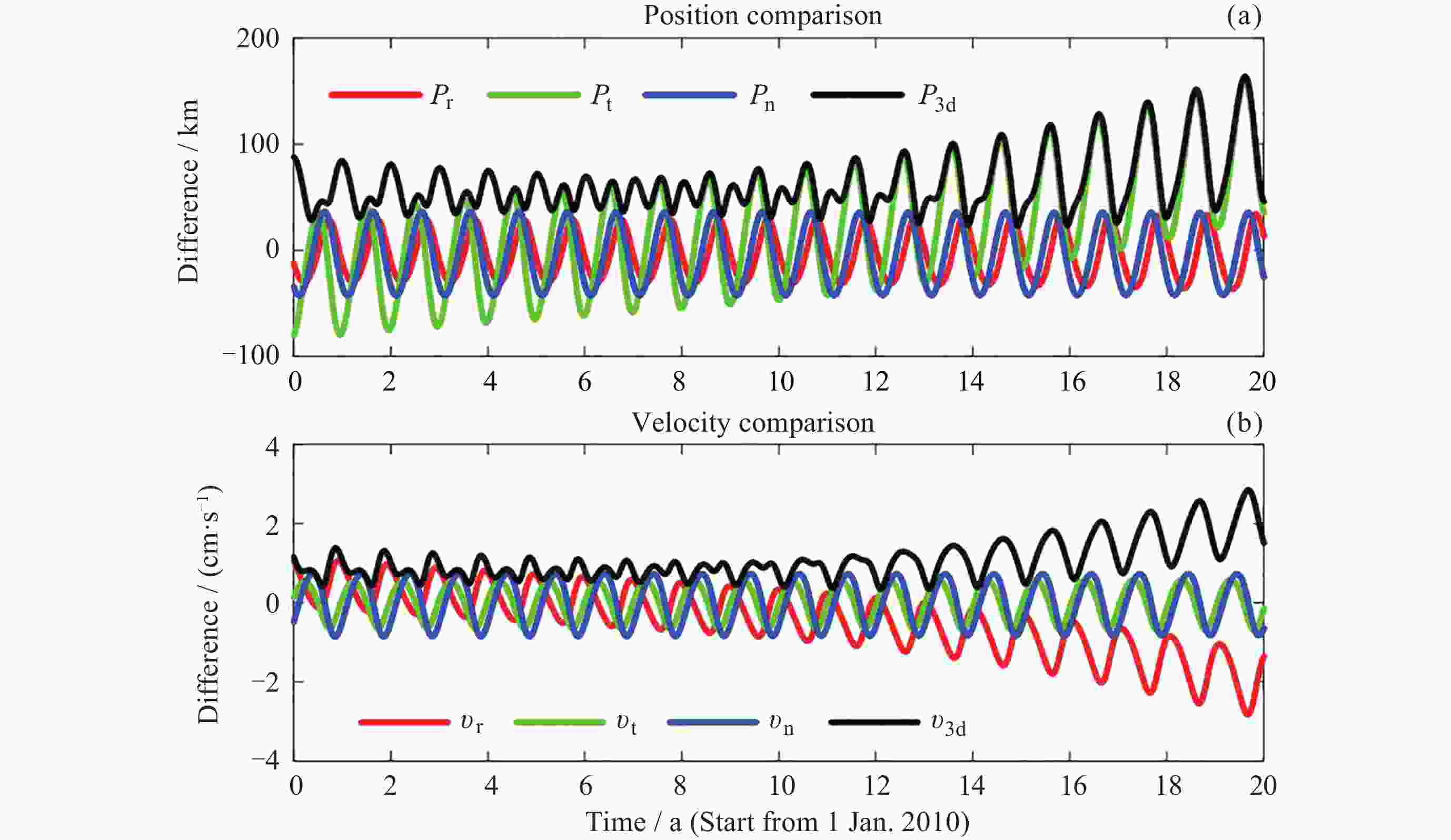
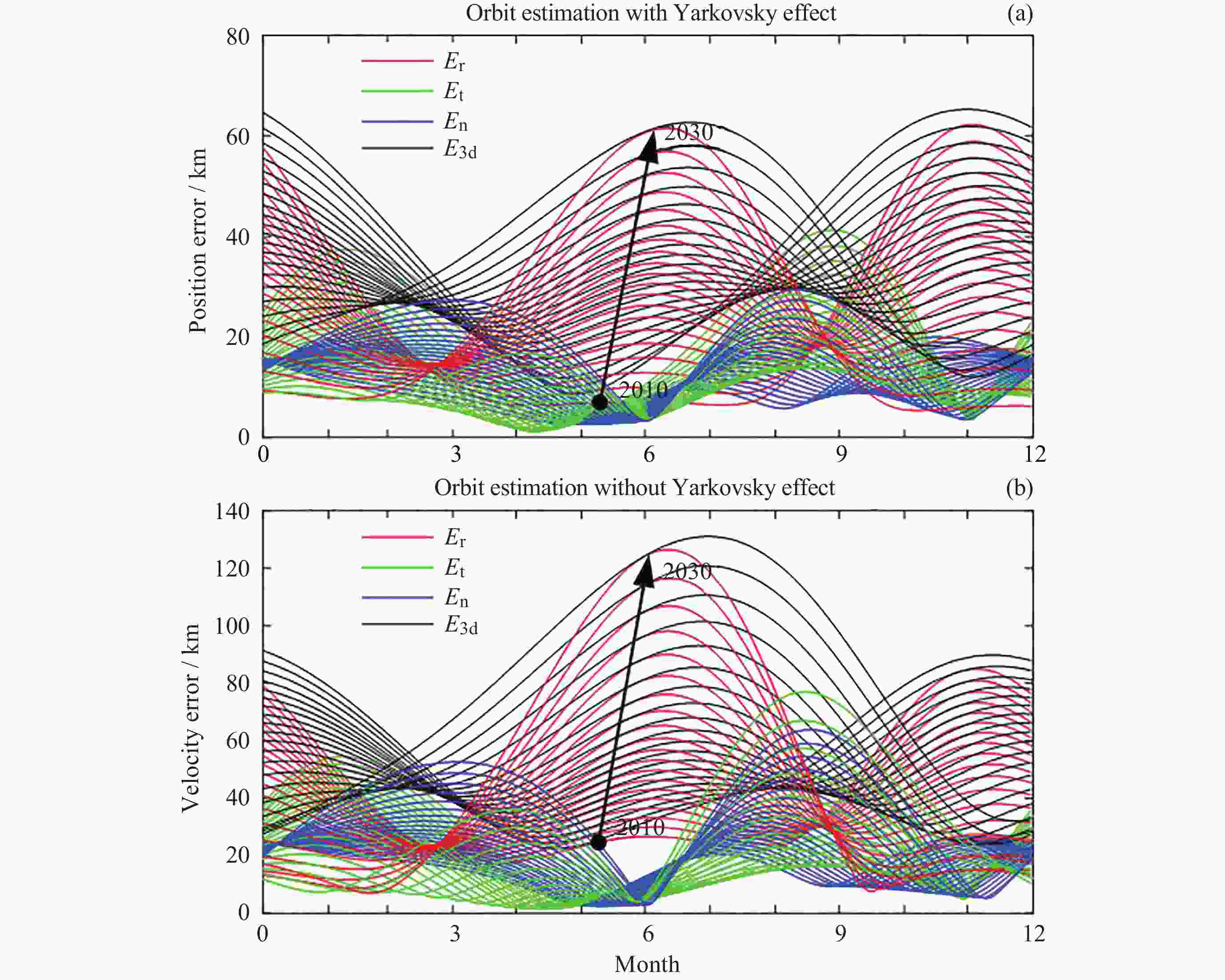
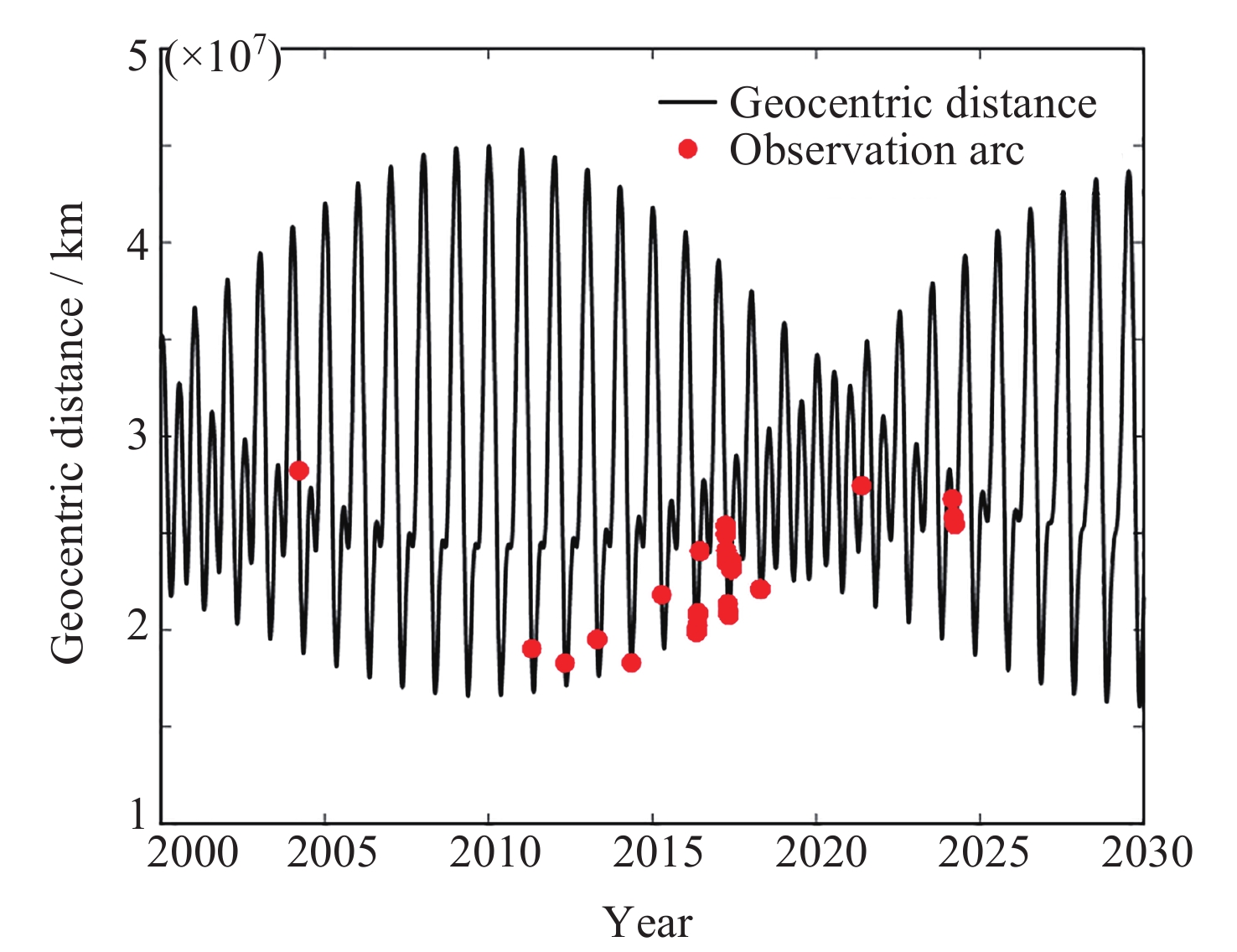
摘要: 针对自主小行星探测任务中对历表的高精度需求, 对小行星2016HO3进行数据处理与深入分析. 构建了小行星2016HO3的高精度动力学模型, 该模型在40年积分周期后与Horizons星历的偏差保持在400 m以内. 利用MPC发布的观测数据进行了定轨计算, 并对两种不同加权策略下的定轨结果进行了对比分析. 同时, 在轨道解算过程中, 还尝试进行了雅科夫斯基效应力的探测. 结果表明, 两种加权策略下的残差表现出高度一致性, 但轨道偏差却接近100 km. 此外, 通过轨道解算成功探测到了雅科夫斯基效应, 并验证了该检测方法的有效性. 轨道演化分析进一步揭示, 当地面设备在每年固定月份观测小行星时, 该月份的轨道偏差最为稳定, 而其他月份的轨道则呈现出显著的发散趋势. 本研究为自主小行星探测任务后续的测量数据处理提供了有益的参考和理论方法支持, 有助于提升探测任务的精度和可靠性.Abstract: To address the requirement for high-precision ephemerides in autonomous asteroid exploration missions, data processing and analysis were conducted on asteroid 2016HO3. Initially, a high-precision dynamical model for the asteroid was established. After a 40-year integration, the resulting ephemerides exhibited a deviation of less than 400 m compared to those from the JPL Horizons system. Subsequently, orbit determination calculations were performed using observational data released by the Minor Planet Center (MPC). The impact of two weighting strategies on the orbit determination results was analyzed, revealing that, despite highly consistent residuals, the orbital deviation approached 100 km. Furthermore, an attempt was made to detect the Yarkovsky effect through orbital solutions, which verified the effectiveness of the detection method. The orbital evolution analysis demonstrated that, due to the fixed-month observations of the asteroid by ground-based facilities, the orbital deviation was most stable during that specific month, whereas the orbital evolution diverged significantly in other months. This study provides references and theoretical support for subsequent data processing in autonomous asteroid exploration missions.
-
Key words:
- Asteroid exploration /
- Ephemeris construction /
- Yarkovsky effect /
- Orbital evolution
-
表 1 轨道计算的摄动力模型
Table 1. Perturbation force models for orbit calculation
表 2 小天体引力常数
Table 2. Gravitational constants for small celestial bodies
小行星名称 引力常数/(m3·s–2) Ceres 62809392663.751 Pallas 13923011068.771 Juno 1622414767.576 Vesta 17288009363.646 Hebe 372800244.326 Hygiea 5542391735.244 Eunomia 2098154705.595 Psyche 1530048436.930 Euphrosyne 2844871570.964 Europa 1110804430.899 Cybele 1426480699.967 Sylvia 986352777.786 Thisbe 1155799234.540 Camilla 749743219.400 Davida 2331286426.251 Interamnia 2357317307.308 表 3 NEODyS权重设置策略
Table 3. Weighting strategies for NEODyS
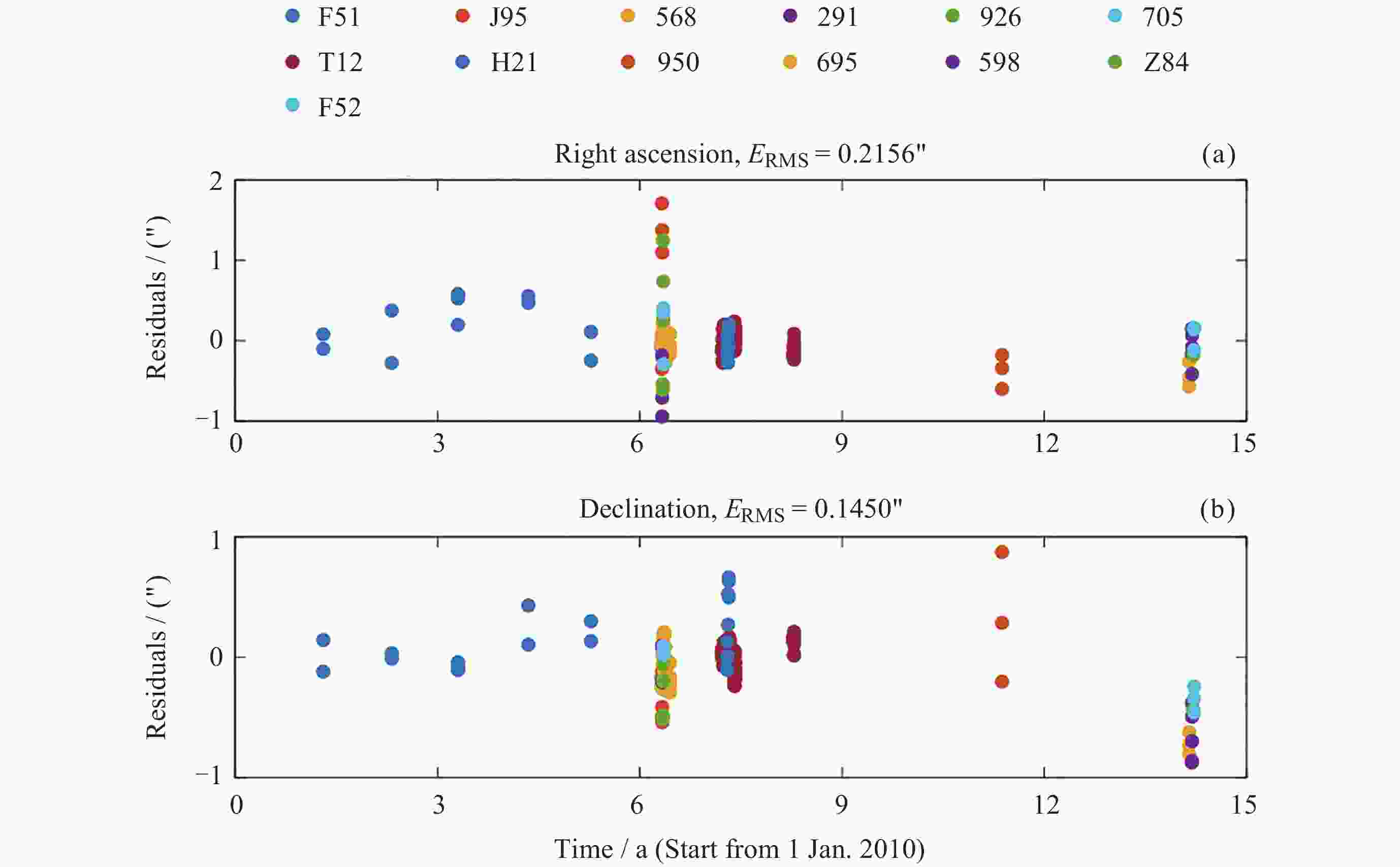
测站代号 NEODyS/(″ ) F51 0.2 F52 0.2 645 0.3 695 0.6 568 0.2 291 0.5 926 1.0 705 1.0 T12 0.158 H21 1.0 950 1.0 J95 1.0 598 0.6 Z84 0.4 表 4 定轨残差统计
Table 4. Statistics of orbit determination residuals
定轨策略 数据类型 数据个数 使用个数 残差${E_{{\text{RMS}}}}$/(″ ) 等权处理 赤经 320 318 0.2156 赤纬 320 319 0.1450 NEODyS权重 赤经 320 320 0.2163 赤纬 320 319 0.1495 -
[1] 魏思佳, 何雨旸, 刘天宇, 等. 小行星探测历史及启示[J]. 空间科学学报, 2024, 44(1): 19-50 doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.01.2024-yg02WEI Sijia, HE Yuyang, LIU Tianyu, et al. History and implications of asteroid exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2024, 44(1): 19-50 doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.01.2024-yg02 [2] DE LA FUENTE MARCOS C, DE LA FUENTE MARCOS R. Asteroid (469219) 2016 HO3, the smallest and closest Earth quasi-satellite[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2016, 462(4): 3441-3456 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stw1972 [3] GUR'YANOV S A, GALUSHINA T Y. Study of the dynamics of the asteroid Kamo’oalewa[J]. Russian Physics Journal, 2021, 63(11): 1989-1996 doi: 10.1007/s11182-021-02261-1 [4] REDDY V, KUHN O, THIROUIN A, et al. Ground-based characterization of Earth Quasi Satellite (469219) 2016HO3[C]//Proceedings of American Astronomical Society. DPS Meeting: USA: AIAA, 2017: 204-207 [5] 贾晓宇, 杨晨, 王彤, 等. 近地小行星2016HO3表面温度建模研究[J]. 深空探测学报, 2019, 6(5): 470-480JIA Xiaoyu, YANG Chen, WANG Tong, et al. Modeling of surface temperature for near-Earth asteroid 2016HO3[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2019, 6(5): 470-480 [6] LI X Y, SCHEERES D J. The shape and surface environment of 2016 HO3[J]. Icarus, 2021, 357: 114249 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2020.114249 [7] FENUCCI M, NOVAKOVIĆ B. The role of the Yarkovsky effect in the Long-term dynamics of asteroid (469219) Kamo’oalewa[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 2021, 162(6): 227 doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/ac2902 [8] REZKY M, SOEGIARTINI E. The orbital dynamics of asteroid 469219 Kamo’Oalewa[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1523(1): 012019 doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1523/1/012019 [9] LIU L, YAN J G, YE M, et al. Yarkovsky effect detection from ground-based astrometric data for near-Earth asteroid (469219) Kamo’oalewa[J]. Astronomy :Times New Roman;">& Astrophysics, 2022, 667: A150 [10] HUI M T, JEWITT D. Non-gravitational acceleration of the active asteroids[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 2017, 153(2): 80 doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/153/2/80 [11] VOKROUHLICKÝ D, MILANI A, CHESLEY S R. Yarkovsky effect on small Near-Earth asteroids: mathematical formulation and examples[J]. Icarus, 2000, 148(1): 118-138 doi: 10.1006/icar.2000.6469 [12] HU S C, BIN L, JIANG H X, et al. Peculiar orbital characteristics of Earth Quasi-Satellite 469219 Kamo‘oalewa: implications for the yarkovsky detection and orbital uncertainty propagation[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 2023, 166(4): 178 doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/acf8cc [13] TIAN W. Orbit determination of the asteroid (469219) Kamo’oalewa and its error analysis[J]. Chinese Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2021, 45(3): 402-411 doi: 10.1016/j.chinastron.2021.08.007 [14] 黄皓, 刘山洪, 曹建峰, 等. 2016HO3探测任务星载光学观测量建模及定轨[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(3): 521-530 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.03.2022-0026HUANG Hao, LIU Shanhong, CAO Jianfeng, et al. Optical observations and its application on orbit determination for 2016HO3 exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(3): 521-530 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.03.2022-0026 [15] PETIT G, LUZUM B. IERS Conventions (2010), IERS technical note No. 36[R]. Paderborn: Bonifatius GmbH, 2010: 1-179 [16] FOLKNER W M, WILLIAMS J G, BOGGS D H, et al. The Planetary and Lunar Ephemerides DE430 and DE431[R]. 2014: 1-81 [17] DEL VIGNA A, FAGGIOLI L, MILANI A, et al. Detecting the Yarkovsky effect among near-Earth asteroids from astrometric data[J]. Astronomy :Times New Roman;">& Astrophysics, 2018, 617: A61 [18] 姜浩轩, 季江徽. 小行星热物理及Yarkovsky效应和YORP效应的研究进展[J]. 天文学进展, 2018, 36(3): 213-231 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8349.2018.03.01JIANG Haoxuan, JI Jianghui. The review of thermophysics, Yarkovsky and YORP effects for asteroids[J]. Progress in Astronomy, 2018, 36(3): 213-231 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8349.2018.03.01 [19] 曹建峰, 李勰, 鞠冰, 等. 太阳系多星精密定轨软件[J]. 深空探测学报, 2022, 9(5): 532-541CAO Jianfeng, LI Xie, JU Bing, et al. Multi-satellite precision orbit determination and data analysis software in solar system[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2022, 9(5): 532-541 [20] VEREŠ P, FARNOCCHIA D, CHESLEY S R, et al. Statistical analysis of astrometric errors for the most productive asteroid surveys[J]. Icarus, 2017, 296: 139-149 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2017.05.021 [21] FARNOCCHIA D, CHESLEY S R, VOKROUHLICKÝ D, et al. Near earth asteroids with measurable Yarkovsky effect[J]. Icarus, 2013, 224(1): 1-13 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2013.02.004 -
-




 曹建峰 男, 1982年8月出生于江苏省如皋市, 现为北京航天飞行控制中心副研究员, 主要研究方向为航天器精密定轨及其科学应用. E-mail:
曹建峰 男, 1982年8月出生于江苏省如皋市, 现为北京航天飞行控制中心副研究员, 主要研究方向为航天器精密定轨及其科学应用. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: