Geomagnetic Storm Image Recognition Based on Spectrogram and Convolutional Neural Network
-
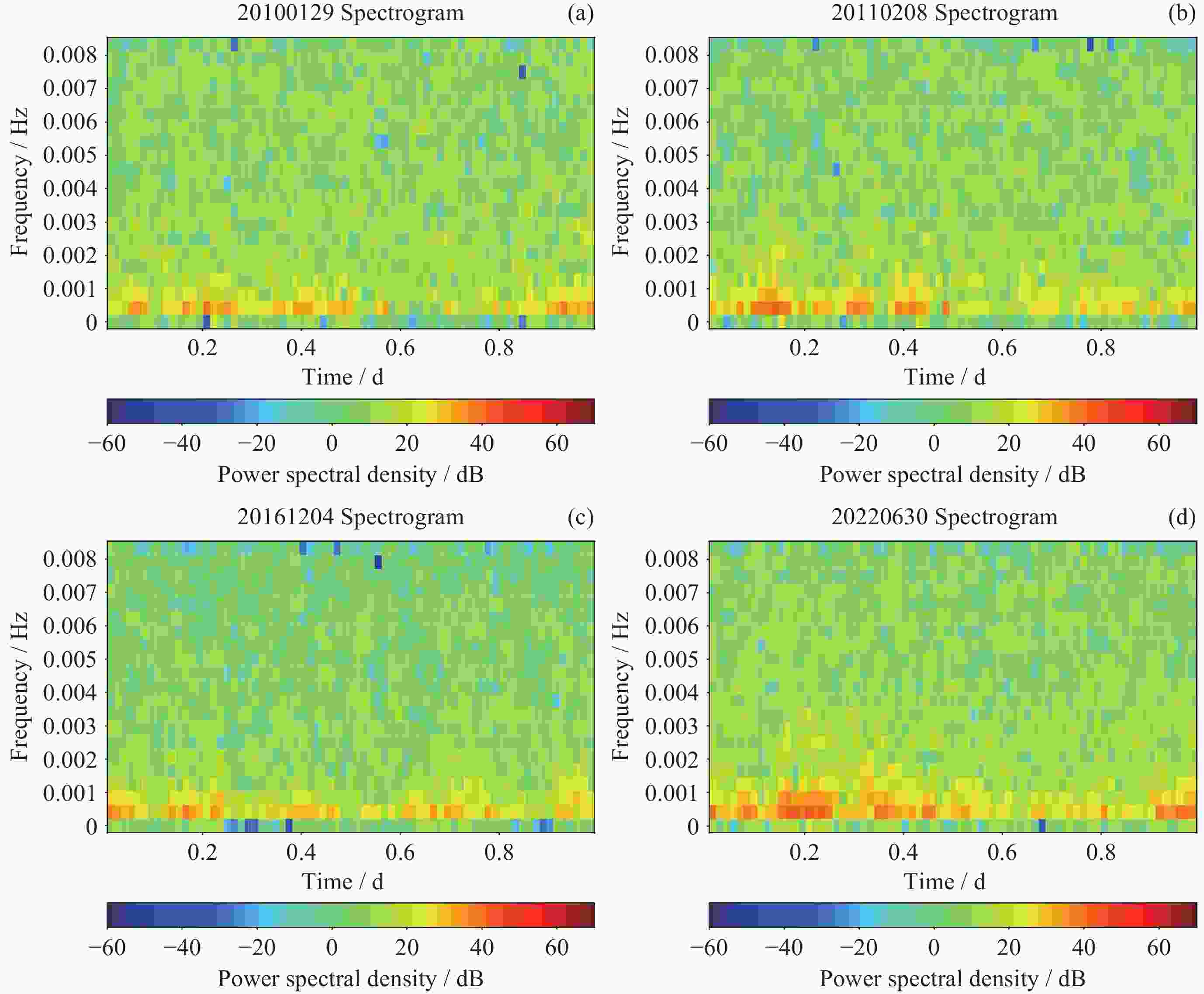
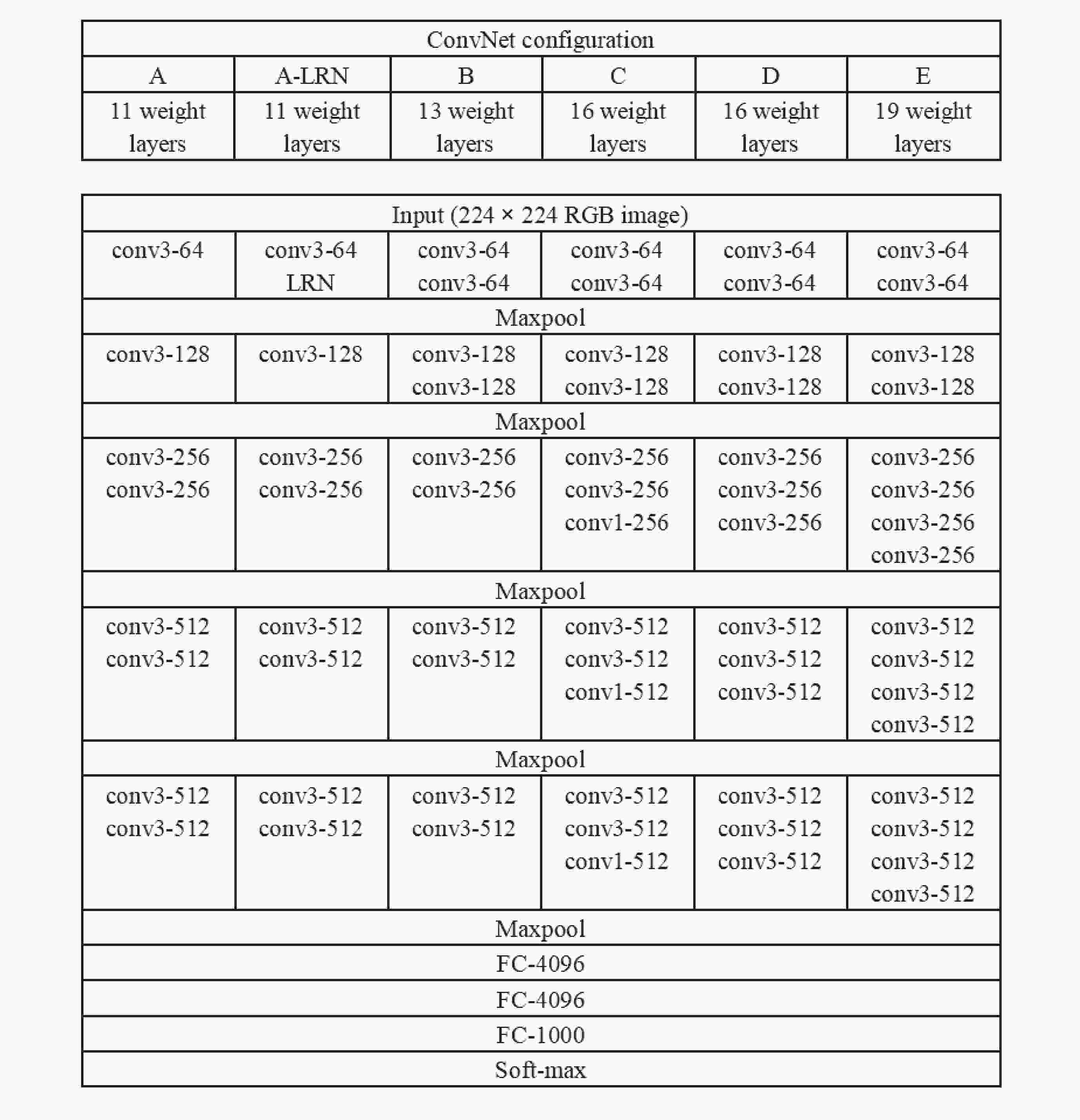
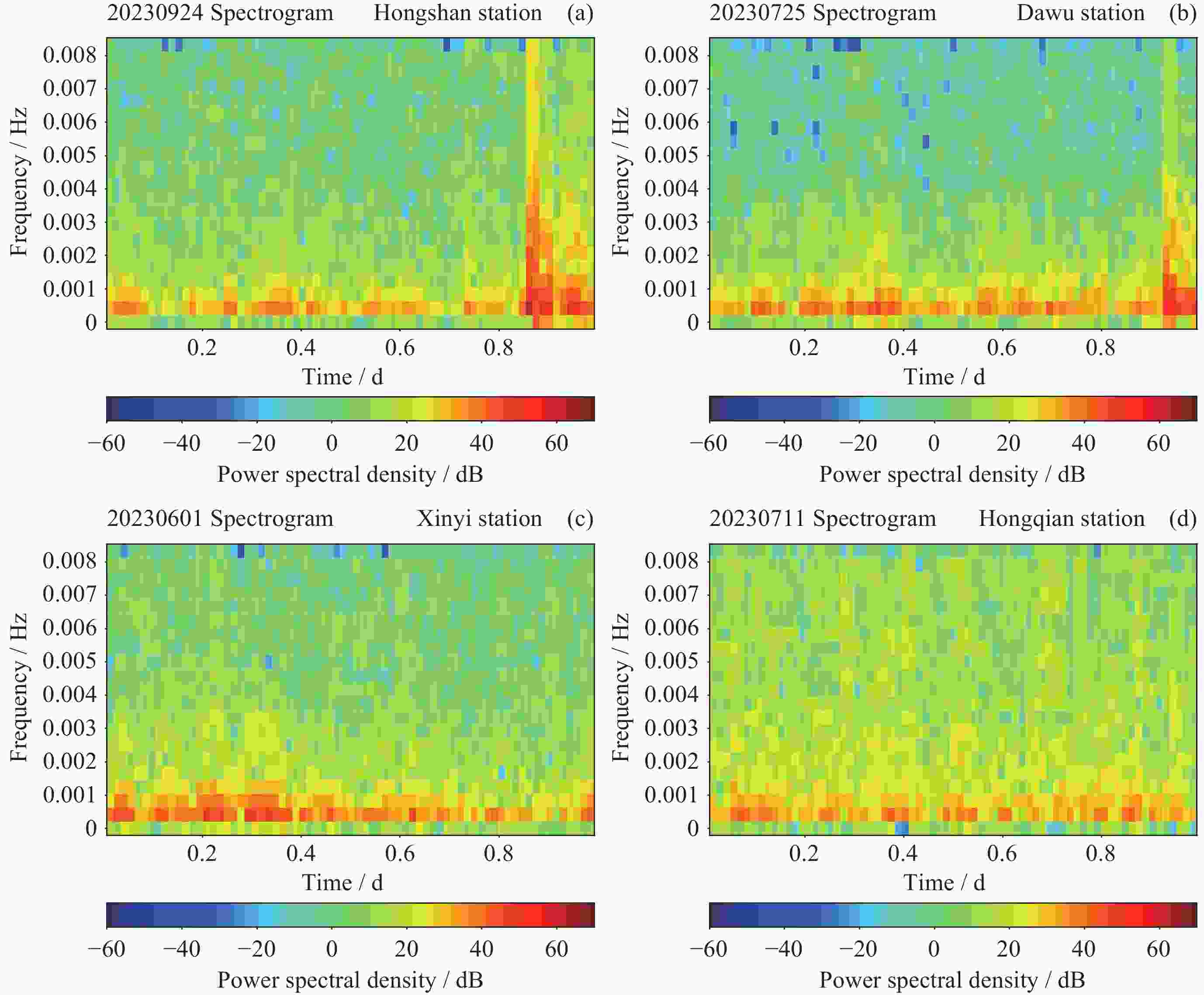
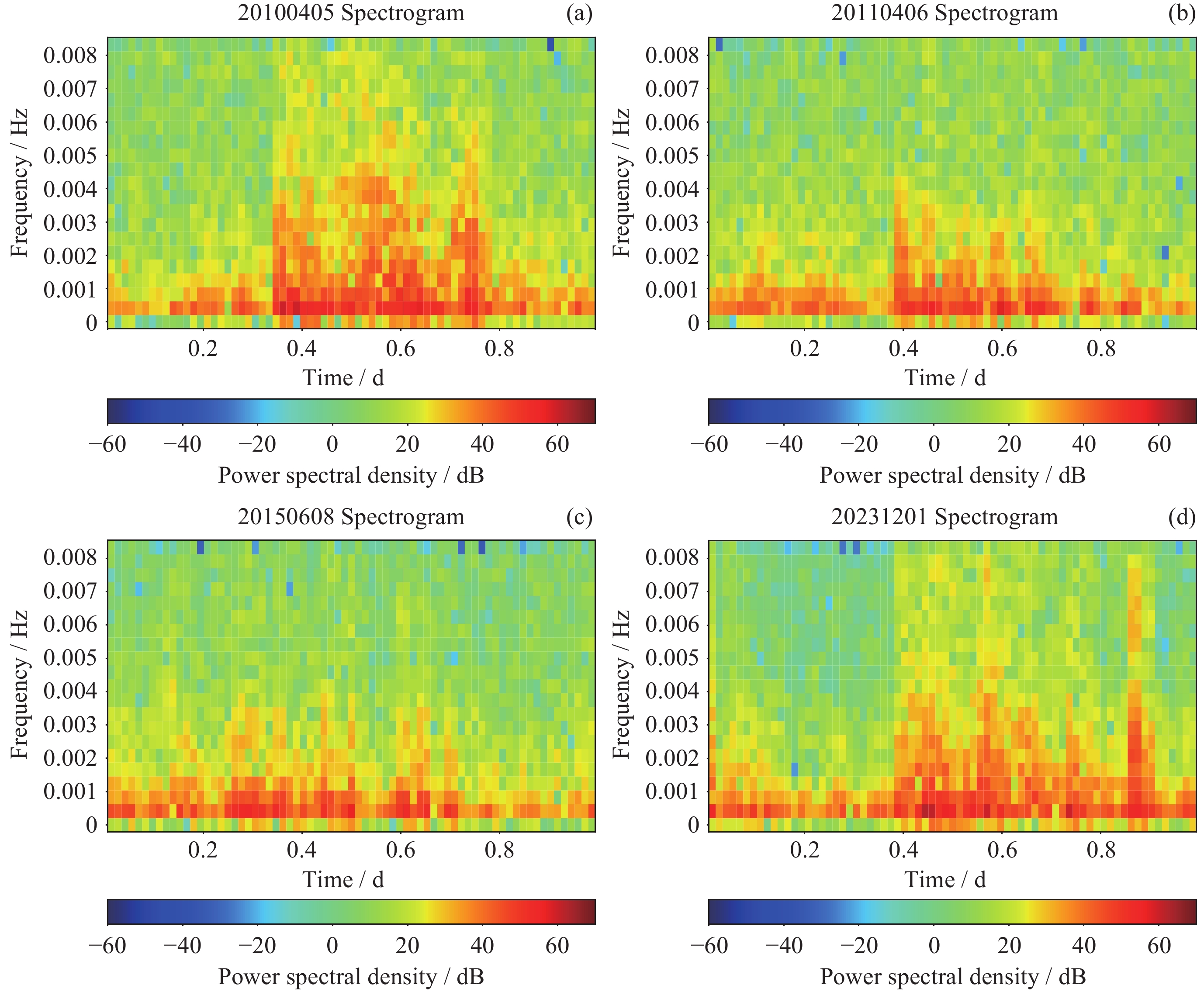
摘要: 磁暴是一种重要的地磁场扰动类型, 影响着通信、电力和航空航天等领域, 因此对磁暴识别技术进行研究与创新有助于磁暴信息的应用. 基于2010-2023年12个定点地磁观测水平分量分钟值数据, 采用声谱图成像技术, 运用VGG19卷积神经网络模型开展磁暴日和磁静日人工智能图像分类研究. 实验结果显示, 模型的准确率为97.41%, 精确率为98.00%, 召回率为96.80%, 模型的预测能力较好, 这表明声谱图成像技术在图像识别分类问题中具有较高的实用性, 且VGG19卷积神经网络模型用于磁暴日和磁静日地磁分类的可行性较高, 研究结果为磁暴预警与监测提供了新的思路.Abstract: Geomagnetic storms represent an important type of geomagnetic field disturbance that can cause interference and damage to fields such as communication, power supply, and aerospace technology. Therefore, the advancement and innovation of geomagnetic storm recognition technology have good development prospects for strengthening the application of geomagnetic storm data in related fields. In this study, we leveraged an extensive dataset comprising minute value recordings of horizontal components sourced from 12 permanent geomagnetic observation stations from 2010 to 2023. Employing spectral imaging technology, we conducted a comprehensive artificial intelligence-based image classification analysis to differentiate between geomagnetic storm days and geomagnetic quiet days, utilizing the VGG19 convolutional neural network model. We have obtained good experimental results. This experiment uses accuracy, precision, and recall as evaluation metrics. The experimental model demonstrated the accuracy rate of 97.41%, with a precision value of 98.00% and a recall rate standing at 96.80%. These indicators collectively emphasize the reliable predictive ability of our model. Furthermore, the application of spectrograms within the context of image recognition and classification has demonstrated significant feasibility. Notably, the VGG19 convolutional neural network model exhibited remarkable feasibility when tasked with categorizing geomagnetic storm days and geomagnetic quiet days. The recognition accuracy of this model for geomagnetic storm days is relatively high and the model itself is relatively stable. However, there is some fluctuation in the recognition of geomagnetic quiet days, which also means that the model still has room for further improvement, especially by increasing the number of training sets and improving the learning accuracy of the model for map information. In summary, our research findings contribute to the improvement of geomagnetic storm identification methods, providing a promising approach to enhance geomagnetic storm prediction and monitoring capabilities, and ultimately promoting the wider application of geomagnetic storm information in related fields.
-
Key words:
- Geomagnetism /
- Geomagnetic storm /
- Spectrograms /
- Convolutional neural networks /
- Image classification
-
表 1 测试集实验结果的混淆矩阵
Table 1. Confusion matrix of test set experimental results
预测情况 正例(磁暴日) 反例(磁静日) 真实情况 正例(磁暴日) 393 (TP) 13 (FN) 反例(磁静日) 8 (FP) 398 (TN) 表 2 10组测试集实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of 10 test sets
1组 2组 3组 4组 5组 6组 7组 8组 9组 10组 磁暴日 正 (TP) 393 392 393 393 394 395 393 392 392 393 反 (FN) 13 14 13 13 12 11 13 14 14 13 磁静日 正 (TN) 399 388 398 394 377 354 378 405 374 387 反 (FP) 7 18 8 12 29 52 28 1 32 19 -
[1] XU Wenyao. Geomagnetism[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 2003 (徐文耀. 地磁学[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 2003) [2] BARTELS J, HECK N H, JOHNSTON H F. The three-hour-range index measuring geomagnetic activity[J]. Terrestrial Magnetism and Atmospheric Electricity, 1939, 44(4): 411-454 doi: 10.1029/TE044i004p00411 [3] 王建军, 李琪, 杨冬梅, 等. 地磁活动K指数自动计算FMI方法的改进[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(7): 2534-2544 doi: 10.6038/cjg20170703WANG Jianjun, LI Qi, YANG Dongmei, et al. An improved FMI method of deriving K indices[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(7): 2534-2544 doi: 10.6038/cjg20170703 [4] 高永国, 尹欣欣, 李少华. 基于深度学习的地震与爆破事件自动识别研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2022, 42(4): 426-430GAO Yongguo, YIN Xinxin, LI Shaohua. Automatic recognition of earthquake and blasting events based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 42(4): 426-430 [5] 赵明, 陈石, YUEN D. 基于深度学习卷积神经网络的地震波形自动分类与识别[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(1): 374-382 doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0151ZHAO Ming, CHEN Shi, YUEN D. Waveform classification and seismic recognition by convolution neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(1): 374-382 doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0151 [6] 杜晓冬, 滕光辉, TOMAS N, 等. 基于声谱图纹理特征的蛋鸡发声分类识别[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(9): 215-220 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.09.025DU Xiaodong, TENG Guanghui, TOMAS N, et al. Classification and recognition of laying hens’ vocalization based on texture features of spectrogram[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(9): 215-220 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.09.025 [7] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Banff, Morocco: the Core Research Group Led by Yoshua Bengio and Yann LeCun, 2014 [8] 朱明哲, 姬红兵, 金艳. 基于自适应抽取STFT的混合DS/FH扩频信号参数估计[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2010, 32(3): 454-457,462ZHU Mingzhe, JI Hongbing, JIN Yan. Parameter estimation of hybrid DS/FH spread spectrum signals based on adaptive decimating STFT[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(3): 454-457,462 [9] 刘建伯. 基于卷积神经网络图像分类方法研究及应用[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2018LIU Jianbo. Research and Application of Image Classification Method Based on Convolutional Neural Network[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2018 -
-




 李鸿宇 男, 1982年4月出生于吉林省梅河口市, 现为江苏省地震局电磁研究中心预测研究室主任, 高级工程师, 主要研究方向为地震电磁分析预报方法和电磁大数据分析. E-mail:
李鸿宇 男, 1982年4月出生于吉林省梅河口市, 现为江苏省地震局电磁研究中心预测研究室主任, 高级工程师, 主要研究方向为地震电磁分析预报方法和电磁大数据分析. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: