Analysis and Evaluation of Data from Near Space Meteorological Rocket Detection over Northwest Area in 2023
-
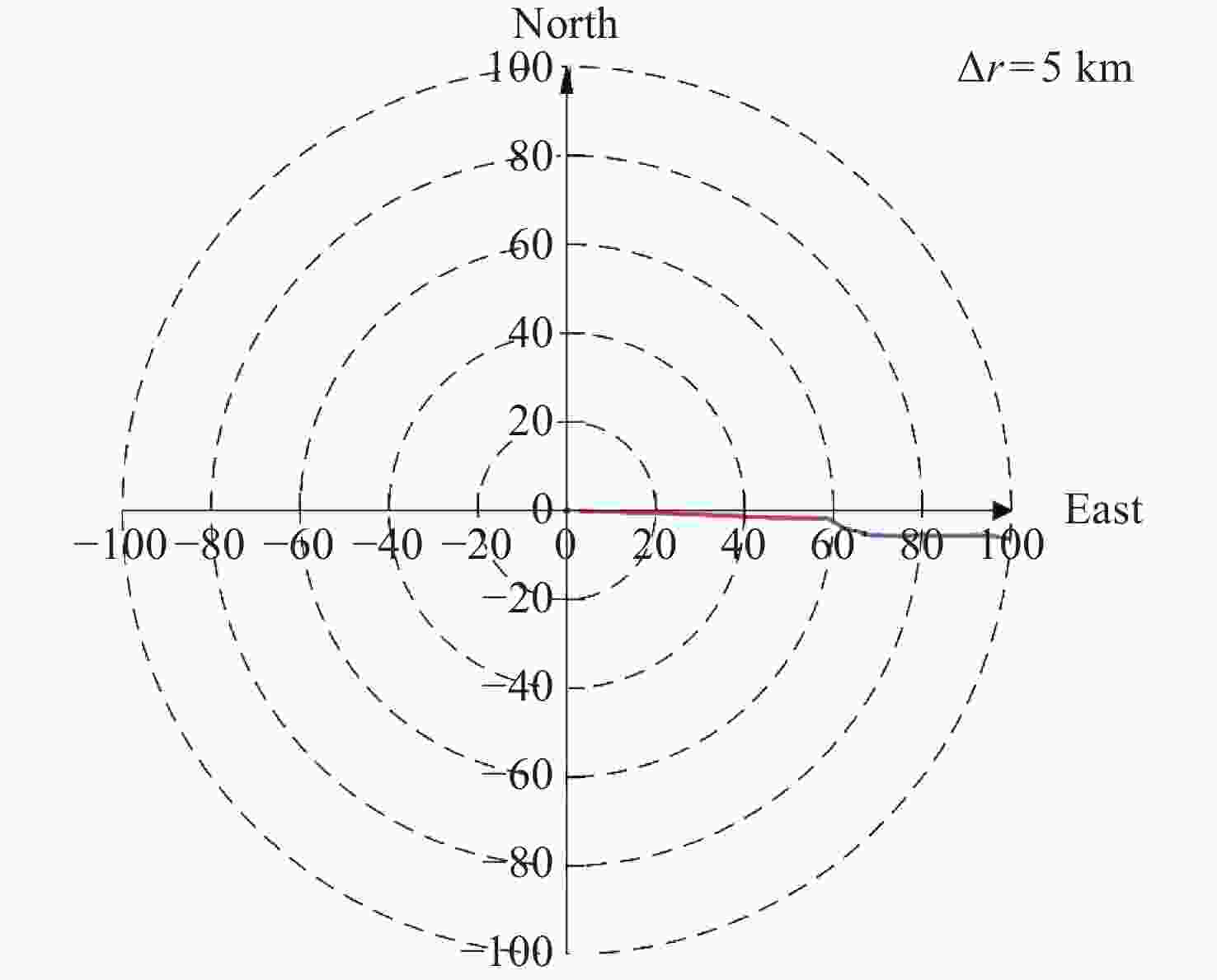
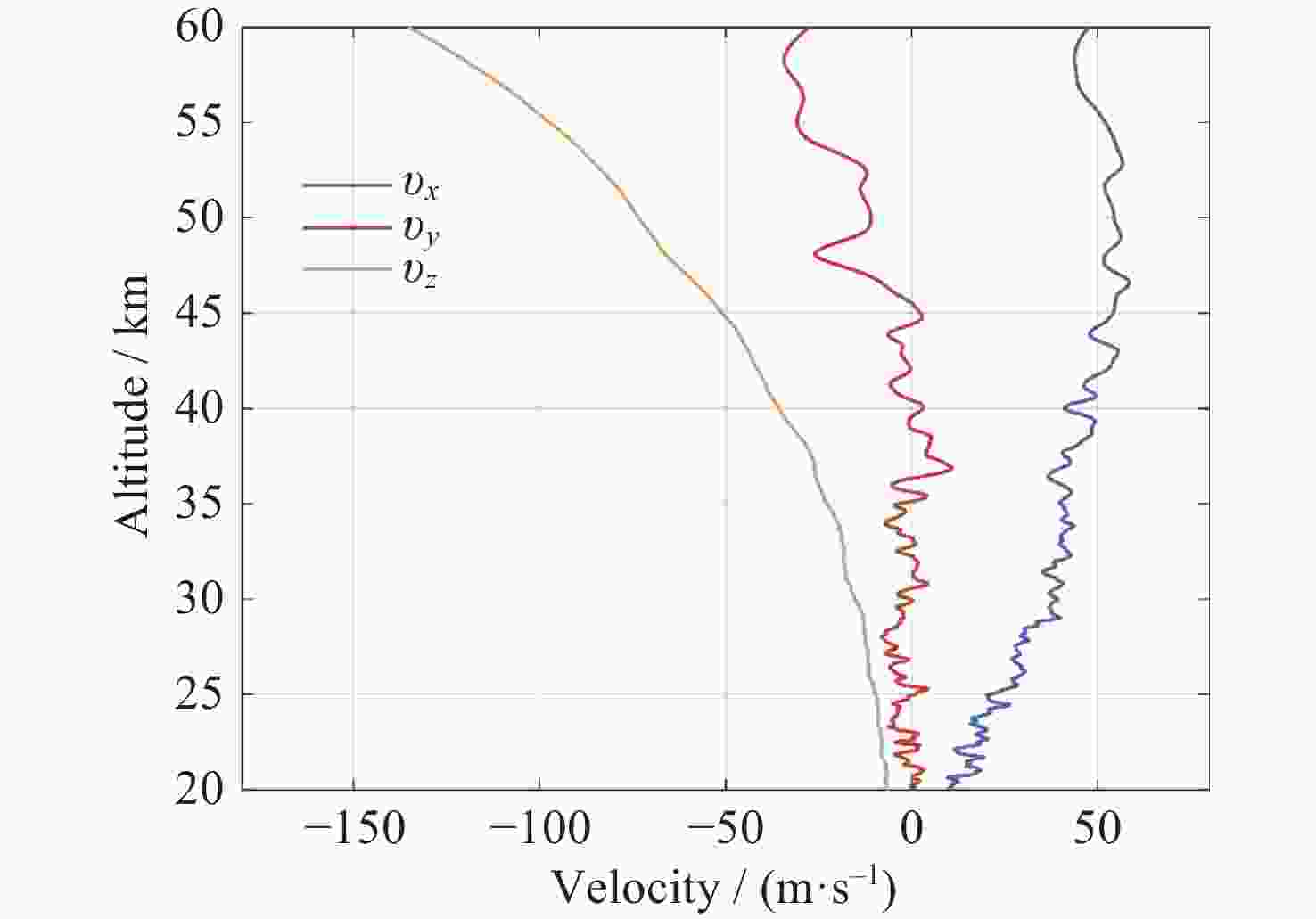
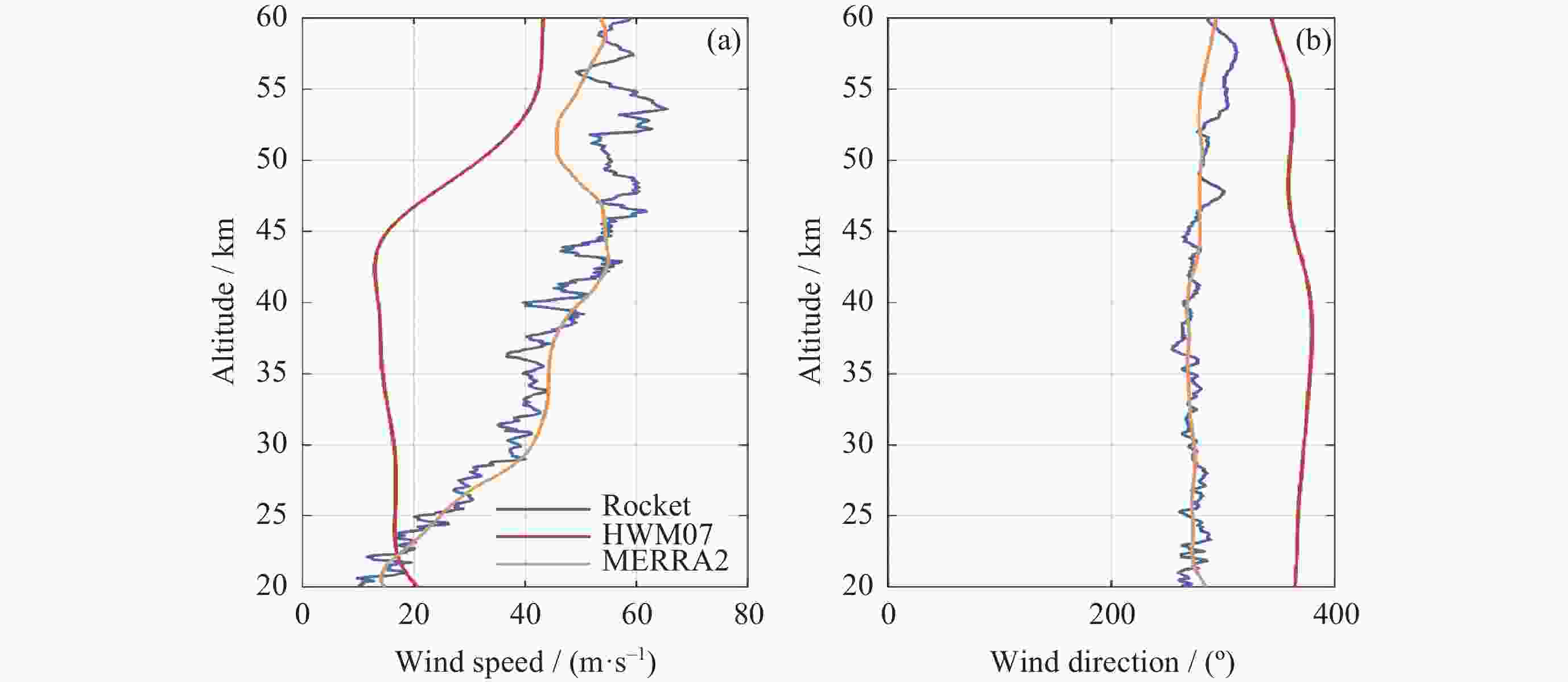
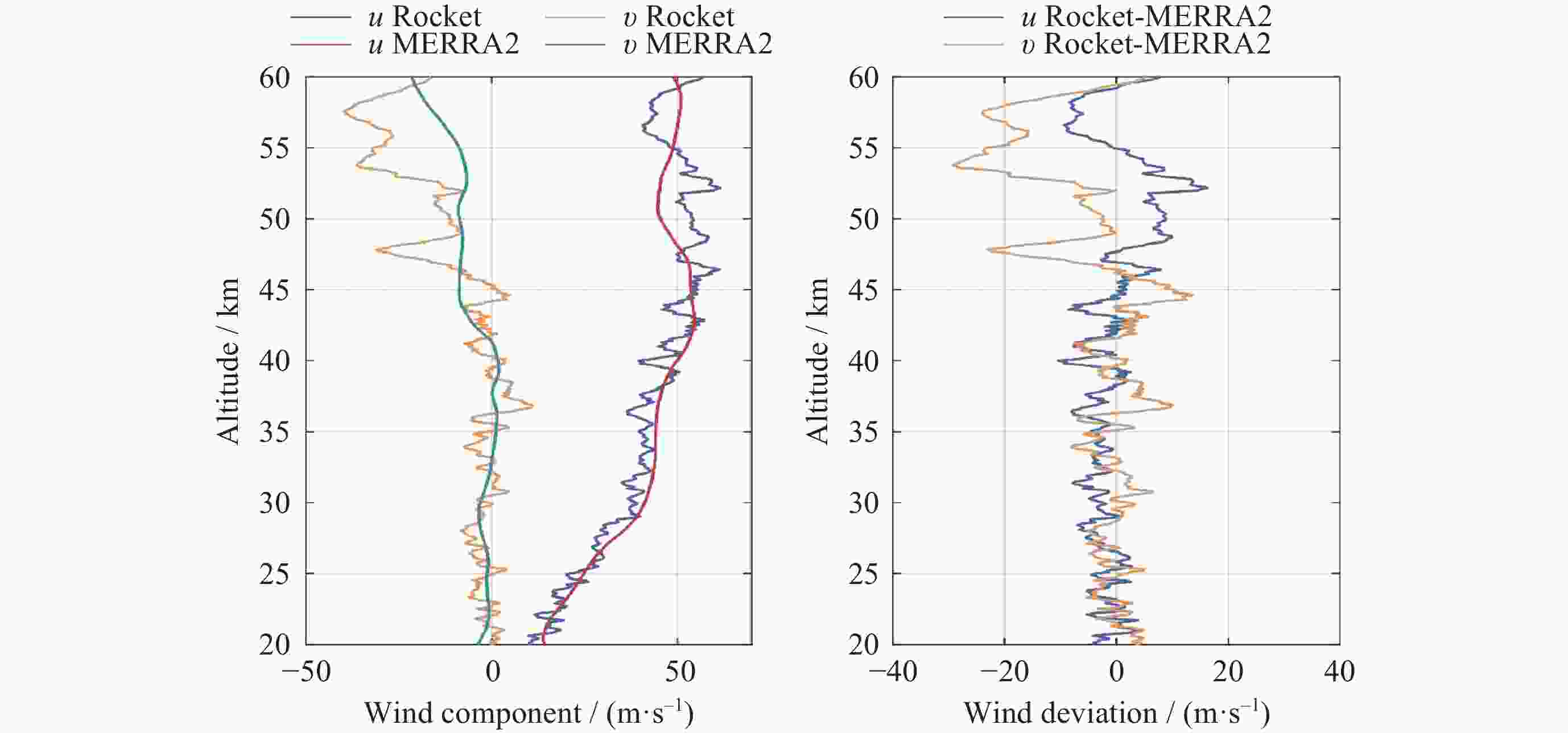
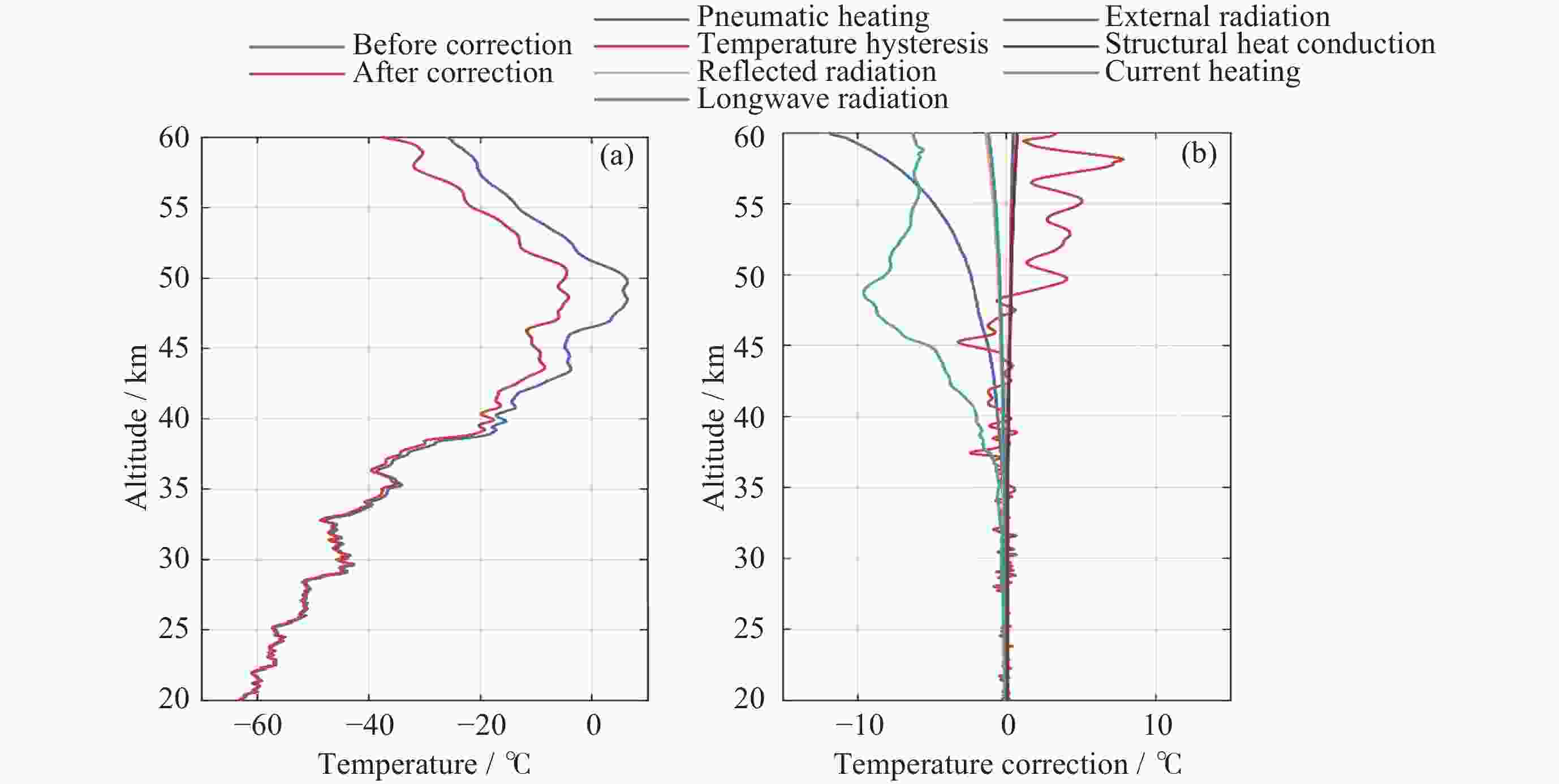
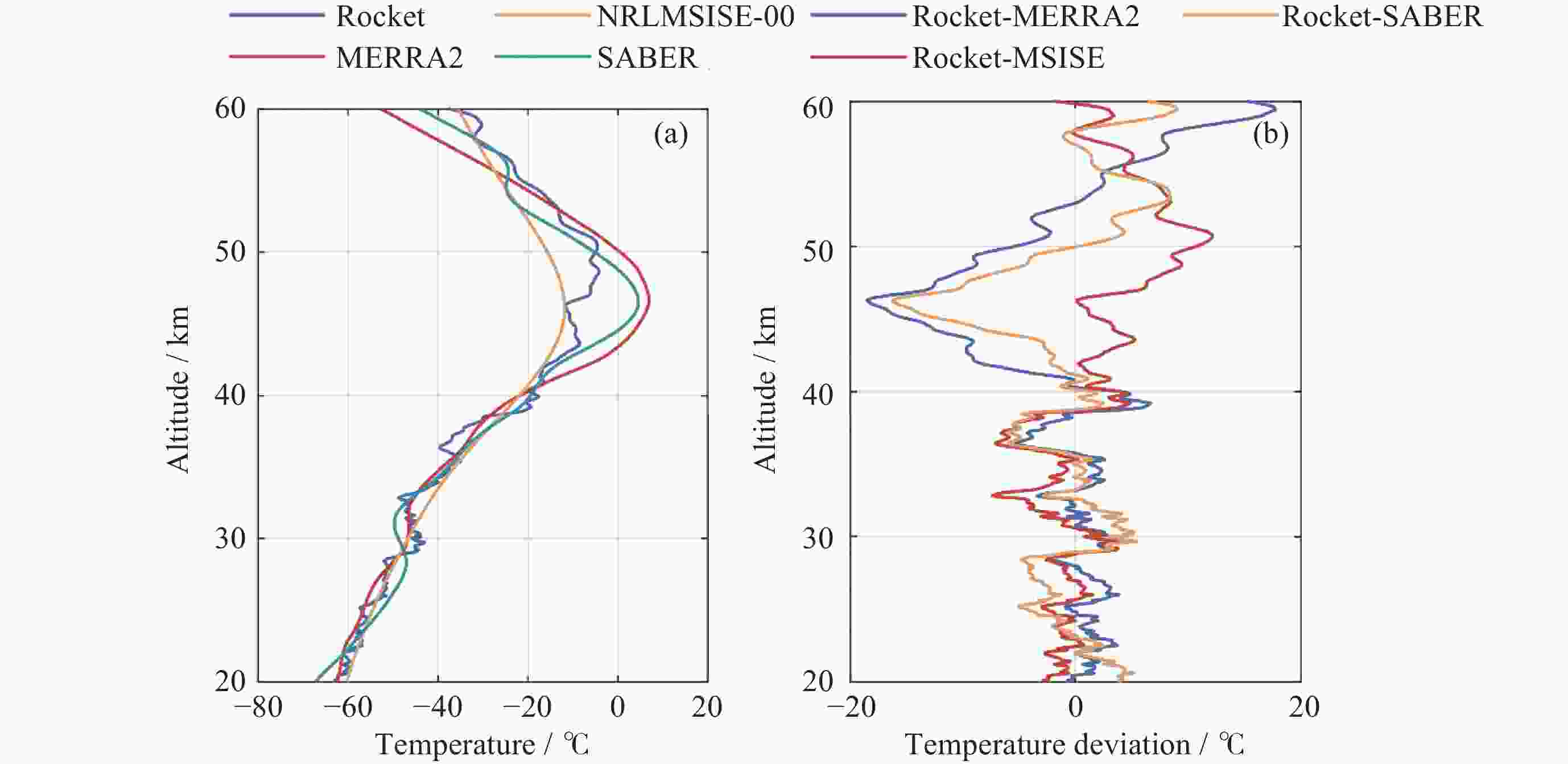
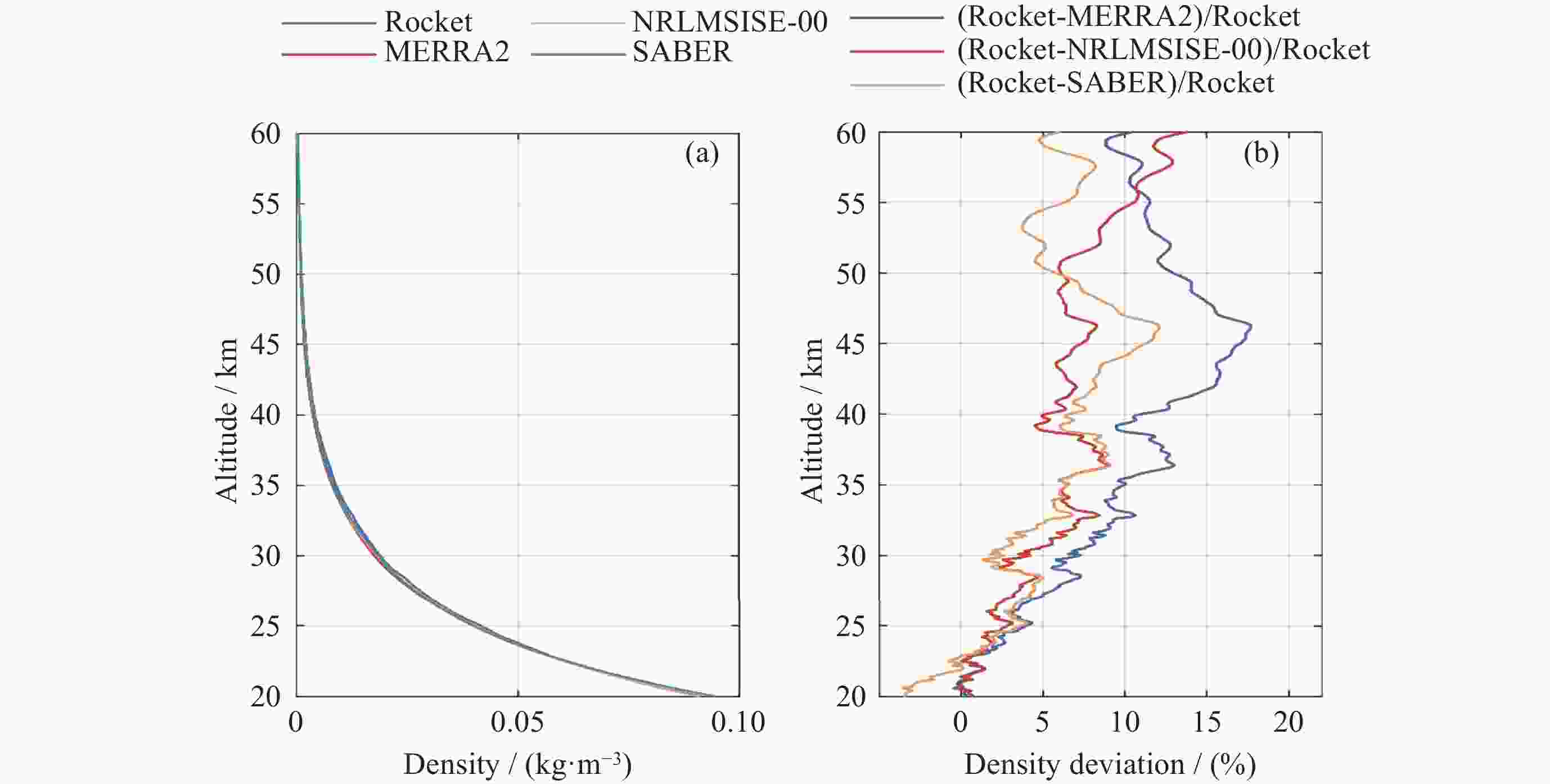
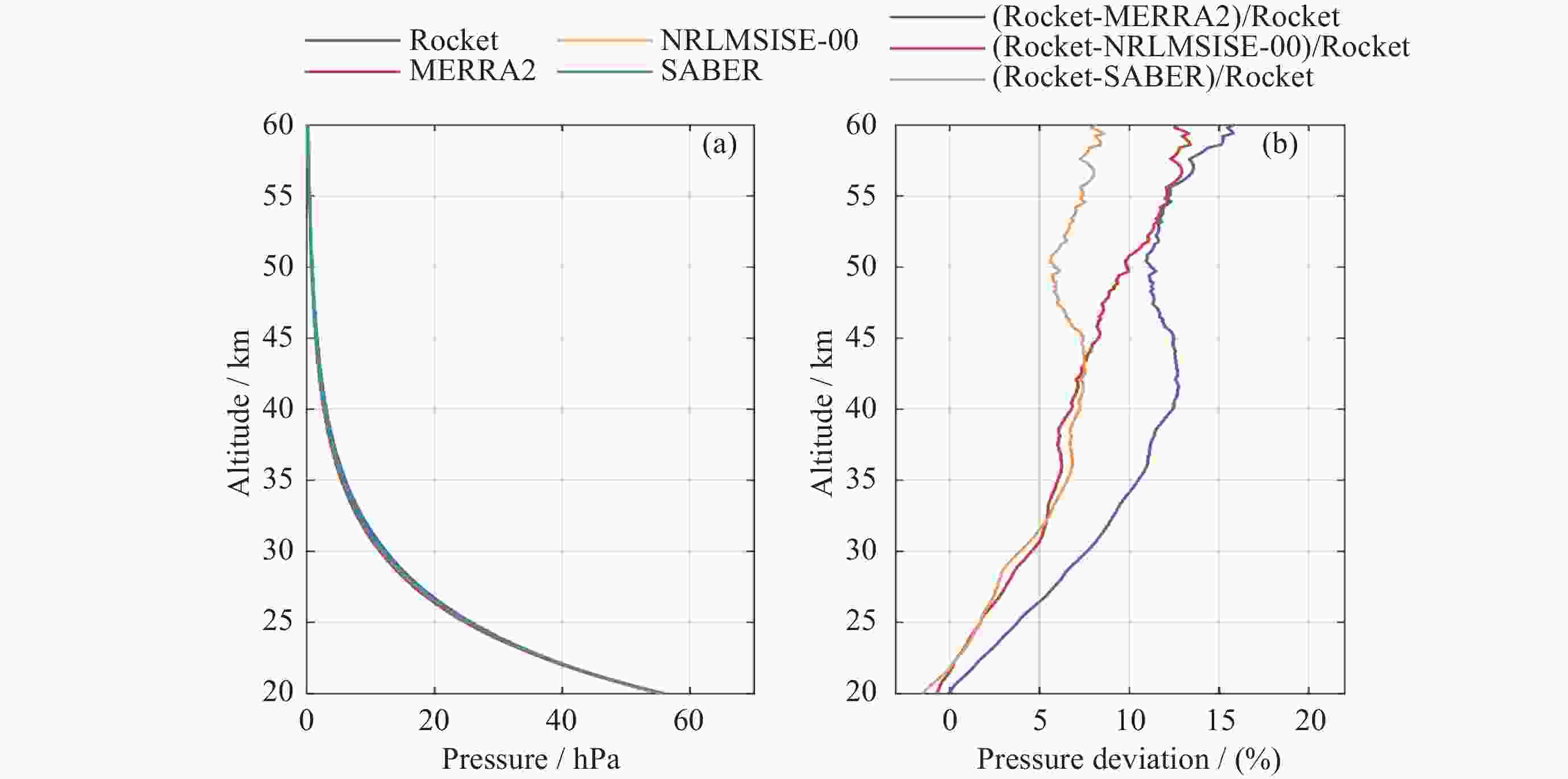
摘要: 气象火箭是一种获取临近空间大气环境垂直分布精细结构的重要原位探测手段, 其探测结果具有比地基和天基遥感探测更高的精度, 客观评估其数据质量是各部门有效使用该探测数据的重要前提. 利用2023年冬季在西北地区进行的一次气象火箭探测, 获取了20~60 km高度区间内的气温、风场、密度和气压数据, 对热敏电阻测得的温度进行了偏差修正, 并将探测结果与遥感探测、经验预报模式以及再分析资料等数据进行了比对评估. 结果表明: 火箭探测风场结果与再分析数据吻合得较好, 并且能够更加准确地描述对应区域的精细大气环境; 火箭实测气温偏差在40 km以上逐渐凸显, 主要偏差项为电流加热项、温度滞后项以及气动加热项, 修正后的气温与参考数据吻合性较好, 不同来源的气温数据主要差异是平流层顶气温拐点出现的高度不同; 气压和密度结果的偏差随着高度的上升而增加. 分析认为, 本次火箭的探测数据质量较好, 精度较高, 通过对数据的分析评估验证了大气要素反演数学模型有效可靠.Abstract: Meteorological rocket is an important in-situ detection method to obtain the fine structure of vertical distribution of atmospheric environment in near space, the detection results should have higher accuracy than ground-based or space-based remote sensing detection. Objective evaluation of the data quality is an important prerequisite for the effective use of the data. In this paper, the atmospheric temperature, wind field, density, and pressure in the altitude range of 20~60 km are obtained by using a meteorological sounding rocket launched in Qinghai in winter of 2023. The error correction of the temperature measured by thermistors is carried out. The detection results are compared with the data of remote sensing detection, empirical prediction model and reanalysis data. The results show that the rocket wind field results are in good agreement with the MERRA2 data, and the HWM empirical forecast model cannot accurately describe the atmospheric environment in the corresponding region. The measured temperature error of the rocket is gradually prominent when it is over 40 km, and the main error terms are current heating term, temperature hysteresis term and pneumatic heating term. The corrected temperature is in good agreement with the reference data, and the main difference of temperature data from different sources is that the height of the temperature inflection point in the stratosphere is different. The deviation of pressure and density results increases with altitude. The analysis believes that the quality of the rocket’s detection data is good and the accuracy is high. Through the analysis and evaluation of the data, the effectiveness and reliability of the mathematical model of atmospheric element inversion are verified.
-
Key words:
- Near space /
- Meteorological rocket /
- Temperature correction /
- Multi-source data
-
表 1 原始探测数据不同高度区间的获取率
Table 1. Acquisition rate of the original detection data in different height intervals
探测区段/km 60~50 50~40 40~30 30~20 数据获取率/(%) 99.5 99.6 99.6 99.6 -
[1] 邓小龙, 杨希祥, 朱炳杰, 等. 智能平流层浮空器Loon关键技术分析与仿真[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(8): 127412DENG Xiaolong, YANG Xixiang, ZHU Bingjie, et al. Simulation research and key technologies analysis of intelligent stratospheric aerostat Loon[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(8): 127412 [2] 王梓皓, 姜毅, 黄宛宁, 等. 基于气球平台的临近空间环境原位探测技术研究[J]. 空天技术, 2023(4): 70-79WANG Zihao, JIANG Yi, HUANG Wanning, et al. Research on in-situ detection technology of near space environment[J]. Aerospace Technology, 2023(4): 70-79 [3] 黄宛宁, 张晓军, 李智斌, 等. 临近空间科学技术的发展现状及应用前景[J]. 科技导报, 2019, 37(21): 46-62HUANG Wanning, ZHANG Xiaojun, LI Zhibin, et al. Development status and application prospect of near space science and technology[J]. Science :Times New Roman;">& Technology Review, 2019, 37(21): 46-62 [4] 熊俊辉, 李克勇, 刘燚, 等. 临近空间防御技术发展态势及突防策略[J]. 空天防御, 2021, 4(2): 82-86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4641.2021.02.013XIONG Junhui, LI Keyong, LIU Yi, et al. Study on near space defense technology development and penetration strategy[J]. Air :Times New Roman;">& Space Defense, 2021, 4(2): 82-86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4641.2021.02.013 [5] 顾逸东, 吴季, 陈虎, 等. 中国空间探测领域40年发展[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(1): 10-21 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.01.010GU Yidong, WU Ji, CHEN Hu, et al. Review of the 40-year development of China’s space exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(1): 10-21 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.01.010 [6] 耿丹, 赵增亮, 万黎, 等. 冬季西北地区临近空间气象火箭探测数据分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(3): 396-402 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210527065GENG Dan, ZHAO Zengliang, WAN Li, et al. Analysis of data from near space meteorological rocket sounding in northwest China in winter[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(3): 396-402 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210527065 [7] 史东波, 胡雄, 涂翠, 等. 临近空间环境探空火箭膨胀落球探测技术[J]. 装备环境工程, 2018, 15(7): 89-92SHI Dongbo, HU Xiong, TU Cui, et al. Near space environment detection technology—sounding rocket falling sphere[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2018, 15(7): 89-92 [8] 范志强, 盛峥, 万黎, 等. 临近空间气象火箭探测资料精度的综合评估[J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62(19): 199601 doi: 10.7498/aps.62.199601FANG Zhiqiang, SHENG Zheng, WAN Li, et al. Comprehensive assessment of the accuracy of the data from near space meteorological rocket sounding[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(19): 199601 doi: 10.7498/aps.62.199601 [9] 范志强, 盛峥, 赵增亮, 等. 临近空间大气环境落球探测中的科氏力影响[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(1): 103-116 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.01.201203104FAN Zhiqiang, SHENG Zheng, ZHAO Zengliang, et al. Impact of Coriolis force in the falling-sphere detection of near-space atmospheric environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(1): 103-116 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.01.201203104 [10] GE W, SHENG Z, ZHANG Y Y, et al. The study of in situ wind and gravity wave determination by the first passive falling-sphere experiment in China’s northwest region[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2019, 182: 130-137 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2018.11.015 [11] ZHOU L S, SHENG Z, FAN Z Q, et al. Data analysis of the TK-1G sounding rocket installed with a satellite navigation system[J]. Atmosphere, 2017, 8(10): 199 doi: 10.3390/atmos8100199 [12] SONG Y Y, HE Y, LENG H Z. Analysis of atmospheric elements in near space based on meteorological-rocket soundings over the East China Sea[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(2): 402 doi: 10.3390/rs16020402 [13] KRÄUCHI A, PHILIPONA R, ROMANENS G, et al. Controlled weather balloon ascents and descents for atmospheric research and climate monitoring[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2016, 9(3): 929-938 doi: 10.5194/amt-9-929-2016 [14] 程旋. 临近空间大气建模及其应用研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院国家空间科学中心, 2020CHENG Xuan. Researches on Atmospheric Modeling and Applications in Near Space[D]. Beijing: National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020 [15] PICONE J M, HEDIN A E, DROB D P, et al. NRLMSISE-00 empirical model of the atmosphere: statistical comparisons and scientific issues[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2002, 107(A12): SIA15 [16] DROB D P, EMMERT J T, CROWLEY G, et al. An empirical model of the Earth’s horizontal wind fields: HWM07[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2008, 113(A12): A12304 [17] ERN M, PREUSSE P, GILLE J C, et al. Implications for atmospheric dynamics derived from global observations of gravity wave momentum flux in stratosphere and mesosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2011, 116(D19): D19107 doi: 10.1029/2011JD015821 -
-




 何阳 男, 1996年生, 四川成都人, 北京航空气象研究所工程师, 主要研究方向为临近空间和电离层大气环境. E-mail:
何阳 男, 1996年生, 四川成都人, 北京航空气象研究所工程师, 主要研究方向为临近空间和电离层大气环境. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: