Study on Ionospheric Absorption Variation Characteristics in the Northwest Corrido
-
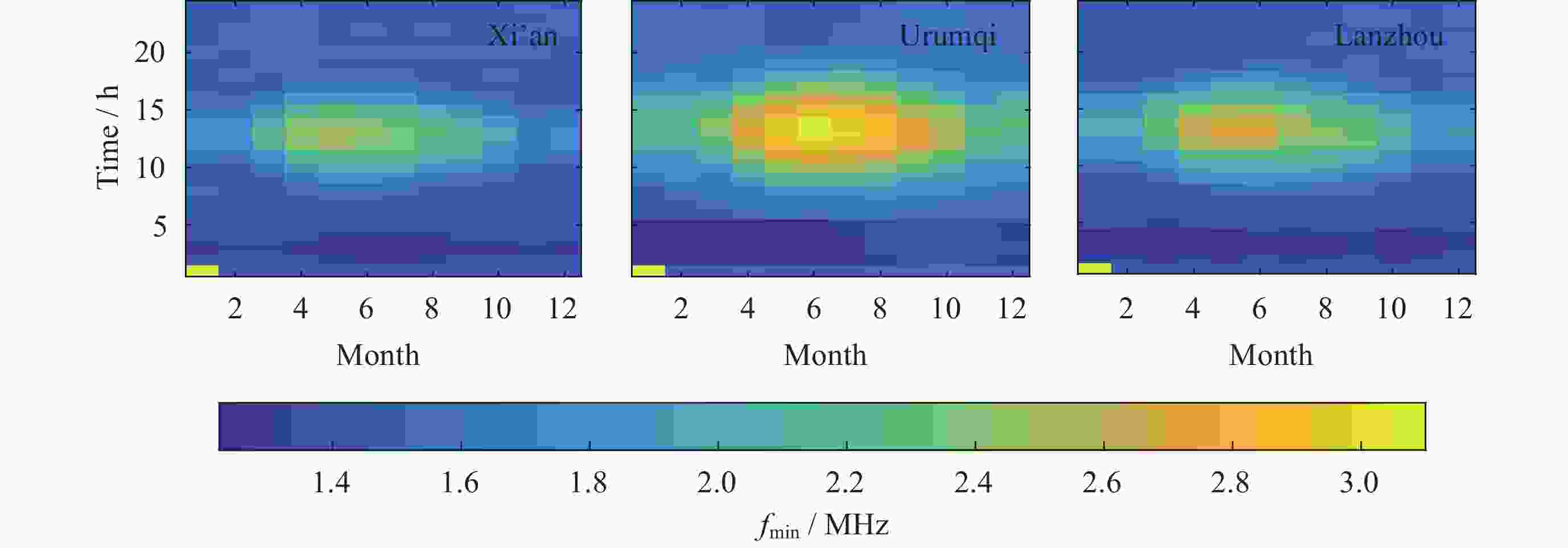
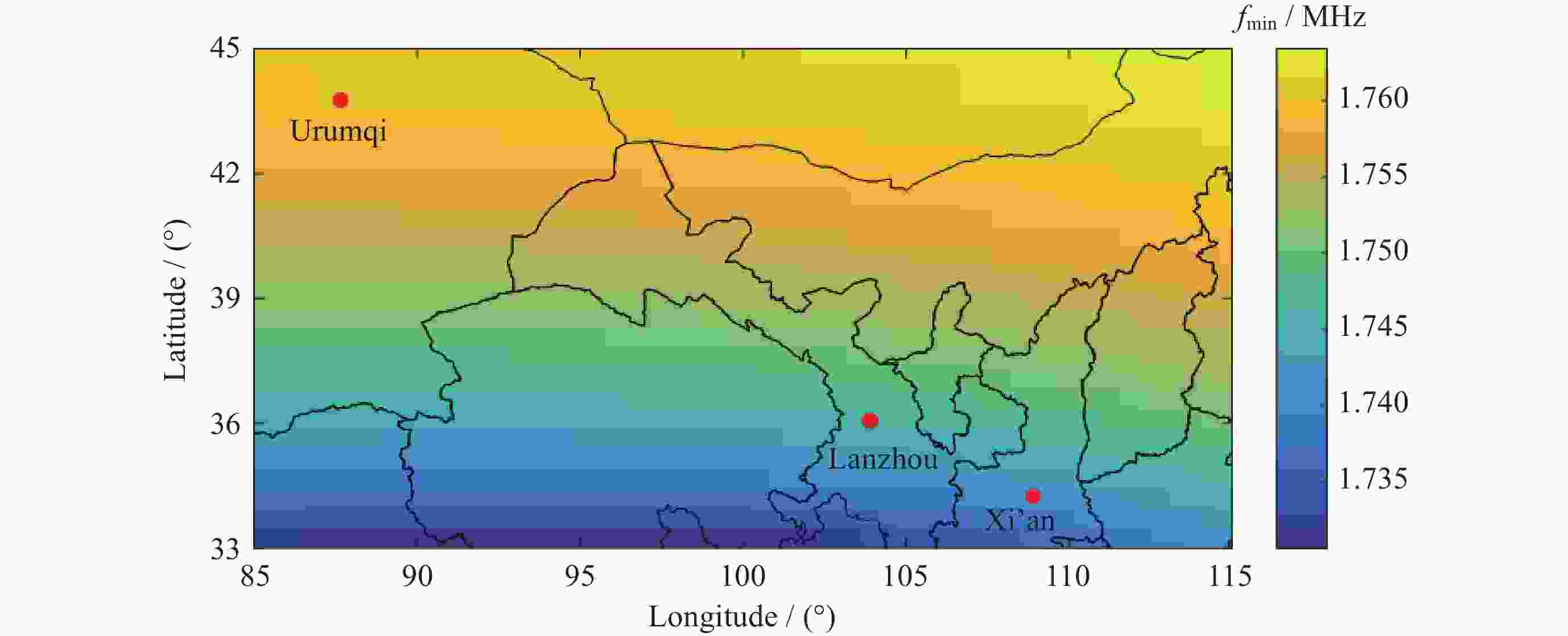
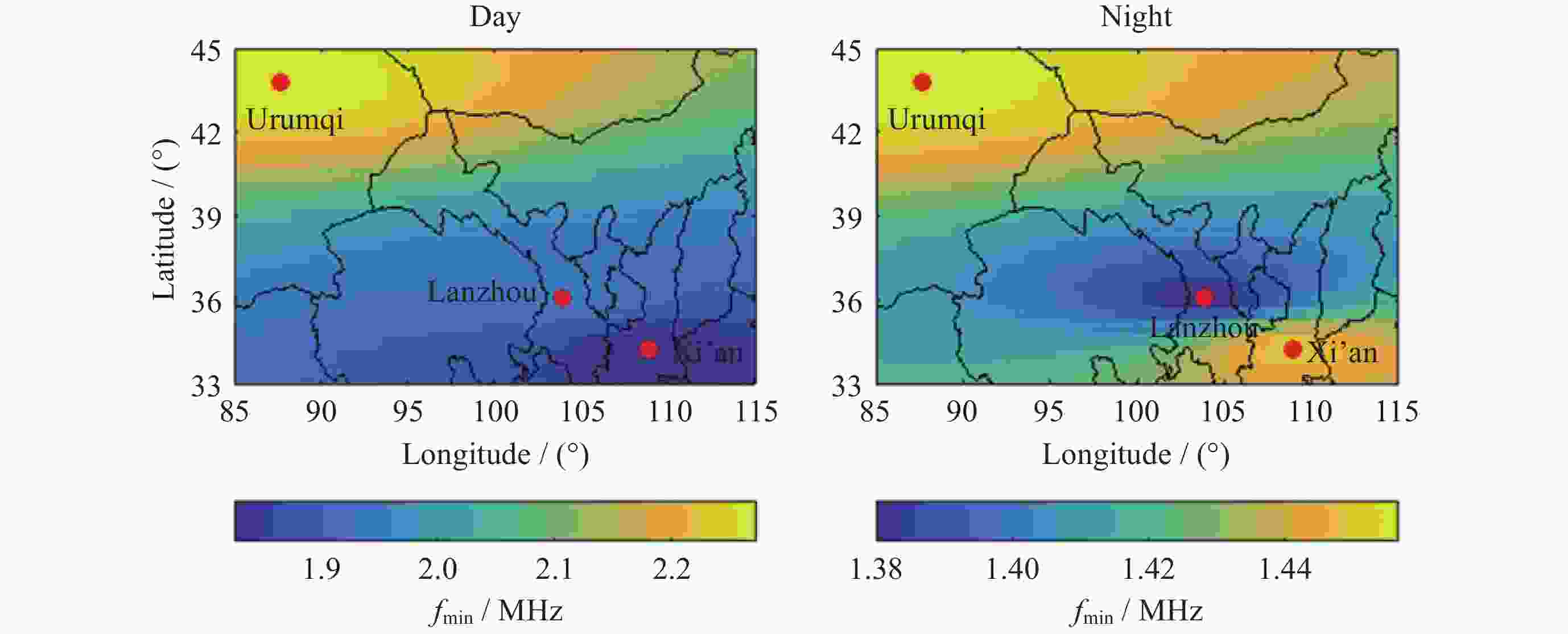
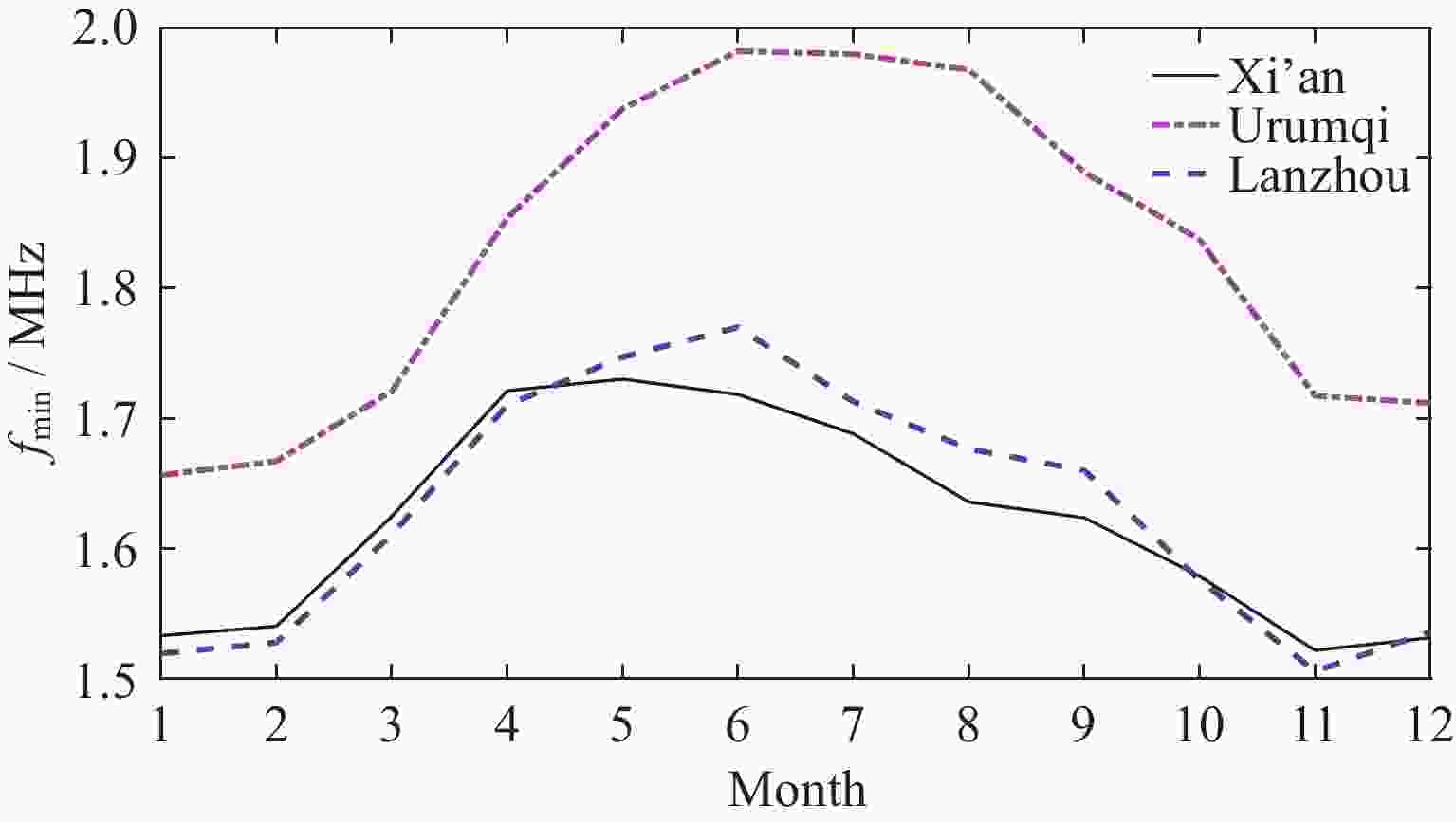
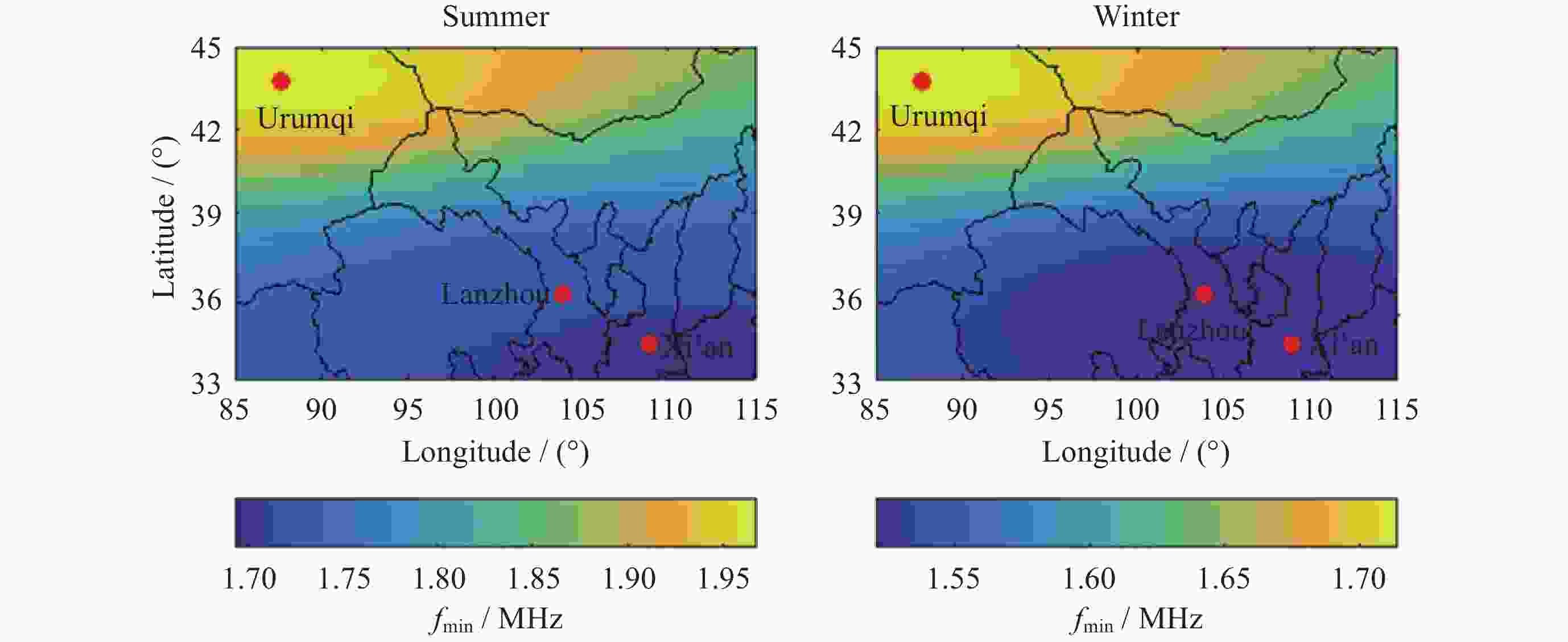
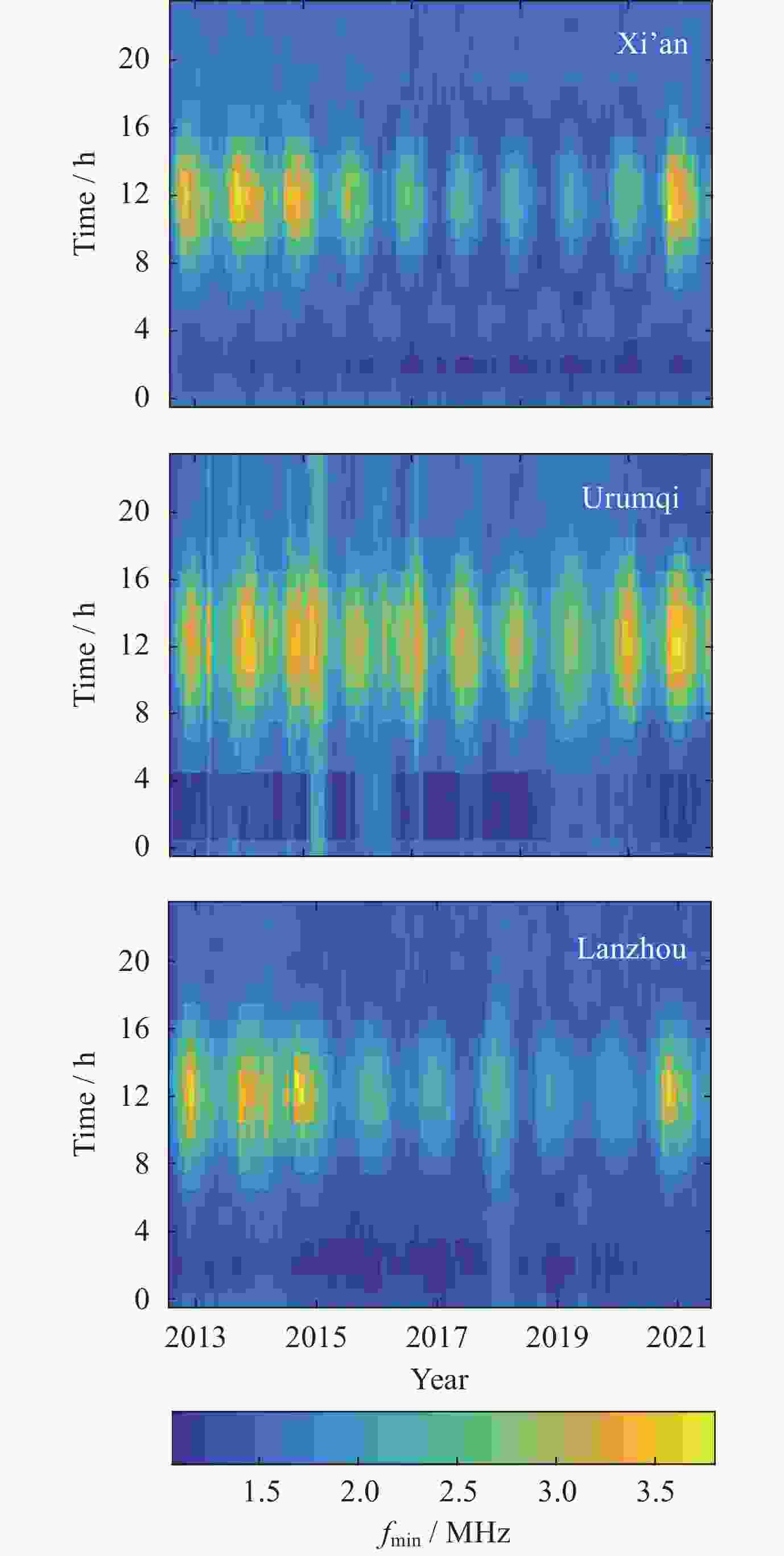
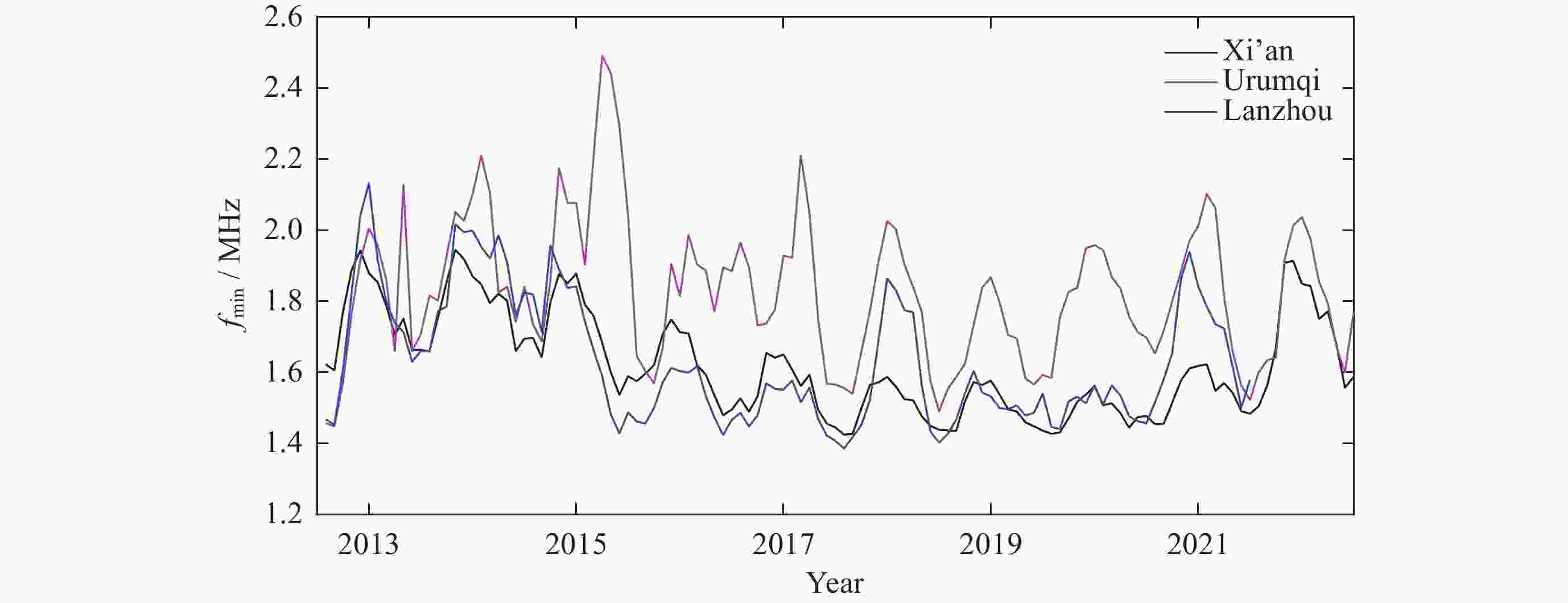
摘要: 电离层fmin是频高图上观测到的回波最低频率, 是电离层垂直探测仪性能的一个重要指标, 也是电离层D区吸收效应研究的重要指标. 本文利用中国电离层垂测站网位于西北走廊地区的西安、乌鲁木齐、兰州三个台站电离层fmin数据, 研究了西北走廊地区电离层吸收的强度特性、空间分布特性、日变化、季节变化及长期变化特性. 开展电离层吸收变化特性研究, 对研究短波通信最低频率选择、天波超视距雷达探测性能评估、甚低频(VLF)远程通信效能预测具有重要应用价值. 同时电离层吸收与D层电子密度关系紧密, 是D层电子密度强弱的重要指标, 开展电离层吸收特性研究, 对于研究D区电离层变化特性, 建立D区电子密度分布模型具有重要科学意义.Abstract: Ionospheric fmin is the lowest echo frequency observed on the frequency height map, which is an important index of the performance of the ionosonde and also an important index for the study of the absorption effect in the ionospheric D region. In this paper, the ionospheric absorption intensity, spatial distribution, diurnal variation, seasonal variation and long-term variation are studied by using ionospheric fmin data from Xi’an, Urumqi and Lanzhou stations of China ionospheric vertical survey network in the Northwest Corridor region. The study of ionospheric absorption variation is of great application value to the selection of the lowest frequency of shortwave communication, the evaluation of detection performance of sky-wave over-the-horizon radar and the prediction of VLF telecommunication efficiency. At the same time, ionospheric absorption is closely related to the electron density of the D layer, which is an important indicator of the intensity of the electron density of the D layer. To study the ionospheric absorption characteristics is of great scientific significance for the study of the ionospheric variation characteristics and the establishment of the electron density distribution model in the D region. The absorption effect of ionospheric region D in the Northwest Corridor mainly occurs in the daytime, with the highest absorption intensity at noon and the weakest in the early morning at night. Meanwhile, the absorption effect of ionospheric region D in the Northwest Corridor has significant seasonal variation characteristics, the strongest in summer and the weakest in other seasons. The ionospheric fmin value of Urumchi at higher latitude is obviously higher than that of Xi’an and Lanzhou at middle latitude, and the absorption effect center has obvious diurnal drift characteristics. The absorption of ionospheric region D in the Northwest Corridor is positively correlated with the intensity of solar activity. In particular, the absorption intensity of ionospheric region D in high solar activity years is significantly higher than that in low solar activity years.
-
Key words:
- Northwest corridor /
- Ionospheric fmin /
- Daily variation /
- Seasonal change /
- Long-term trend /
- Spatial distribution
-
表 1 电离层fmin观测站与数据年限
Table 1. Ionospheric observation stations and data duration of fmin
序号 站名 经度/(°)N 纬度/(°)E 数据年限 1 西安 34.23 108.92 2013-2022年 2 乌鲁木齐 43.75 87.63 2013-2022年 3 兰州 36.06 103.87 2013-2021年 -
[1] BELROSE J S. Radio wave probing of the ionosphere by the partial reflection of radio waves (from heights below 100km)[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, 1970, 32(4): 567-596 doi: 10.1016/0021-9169(70)90209-6 [2] BELROSE J S, BURKE M J. Study of the lower ionosphere using partial reflection: 1. Experimental technique and method of analysis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1964, 69(13): 2799-2818 doi: 10.1029/JZ069i013p02799 [3] BELROSE J S, BURKE M J, COYNE T N R, et al. D-region measurements with the differential-absorption, differential-phase partial-reflection experiments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1972, 77(25): 4829-4838 [4] CHAKRABARTY D K, CHAKRABARTY P, WITT G. A theoretical attempt to explain some observed features of the D region[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1978, 83(A12): 5763-5767 doi: 10.1029/JA083iA12p05763 [5] ISHISAKA K, OKADA T, HAWKINS J, et al. Investigation of electron density profile in the lower ionosphere by SRP-4 rocket experiment[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2005, 57(9): 879-884 doi: 10.1186/BF03351865 [6] MEIRA L G JR. Rocket measurements of upper atmospheric nitric oxide and their consequences to the lower ionosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1971, 76(1): 202-212 doi: 10.1029/JA076i001p00202 [7] THOMSON N R, CLILVERD M A, RODGER C J. Ionospheric D region: VLF-measured electron densities compared with rocket-based FIRI-2018 model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2022, 127(11): e2022JA030977 doi: 10.1029/2022JA030977 [8] MATHEWS J D. Incoherent scatter radar probing of the 60-100-km atmosphere and ionosphere[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1986, GE-24(5): 765-776 [9] MENDILLO M, EVANS J V. Incoherent scatter observations of the ionospheric response to a large solar flare[J]. Radio Science, 1974, 9(2): 197-203 doi: 10.1029/RS009i002p00197 [10] ŽIGMAN V, GRUBOR D, ŠULIĆ D. D-region electron density evaluated from VLF amplitude time delay during X-ray solar flares[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2007, 69(7): 775-792 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2007.01.012 [11] MCRAE W M, THOMSON N R. Solar flare induced ionospheric D-region enhancements from VLF phase and amplitude observations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2004, 66(1): 77-87 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2003.09.009 [12] THOMSON N R, CLILVERD M A. Solar flare induced ionospheric D-region enhancements from VLF amplitude observations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2001, 63(16): 1729-1737 doi: 10.1016/S1364-6826(01)00048-7 [13] PALIT S, BASAK T, MONDAL S K, et al. Modeling of Very Low Frequency (VLF) radio wave signal profile due to solar flares using the GEANT4 Monte Carlo simulation coupled with ionospheric chemistry[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2013, 13(18): 9159-9168 doi: 10.5194/acp-13-9159-2013 [14] SINGH A K, SINGH A K, SINGH R, et al. Solar flare induced D-region ionospheric perturbations evaluated from VLF measurements[J]. Astrophysics and Space Science, 2014, 350(1): 1-9 doi: 10.1007/s10509-013-1699-4 [15] TAN L M, THU N N, HA T Q, et al. Study of solar flare induced D-region ionosphere changes using VLF amplitude observations at a low-latitude site[J]. Indian Journal of Radio and Space Physics, 2014, 43(3): 197-204 [16] XIONG S P, LI J Y, WEI G C, et al. The northern and southern hemispheric asymmetries of mesospheric ozone at high latitudes during the January 2012 solar proton events[J]. Space Weather, 2023, 21(5): e2023SW003435 doi: 10.1029/2023SW003435 [17] THOMSON N R. Daytime tropical D region parameters from short path VLF phase and amplitude[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2010, 115(A9): A09313 doi: 10.1029/2010JA015355 [18] THOMSON N R, RODGER C J, CLILVERD M A. Daytime D region parameters from long-path VLF phase and amplitude[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2011, 116(A11): A11305 doi: 10.1029/2011JA016910 [19] HOLDSWORTH D A, VUTHALURU R, REID I M, et al. Differential absorption measurements of mesospheric and lower thermospheric electron densities using the Buckland Park MF radar[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2002, 64(18): 2029-2042 doi: 10.1016/S1364-6826(02)00232-8 [20] LI N, CHEN J S, DING Z H, et al. Mean winds observed by the Kunming MF radar in 2008-2010[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2015, 122: 58-65 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2014.10.011 [21] TANG Z M, LI N, WANG J Y, et al. Variation of electron density in the D-region using Kunming MF radar under low solar activity[J]. Atmosphere, 2023, 14(12): 1764 doi: 10.3390/atmos14121764 [22] LI N, LEI J, LUAN X, et al. Responses of the D region ionosphere to solar flares revealed by MF radar measurements[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2019, 182: 211-216 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2018.11.014 [23] 张东和, 萧佐, 吴健, 等. 利用MF雷达对耀斑期间电离层D区电子密度的观测研究[J]. 空间科学学报, 2003, 23(5): 334-342 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2003.05.003ZHANG Donghe, XIAO Zuo, WU Jian, et al. The study of the electron density in ionospheric d region using mf radar during flares period[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2003, 23(5): 334-342 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2003.05.003 [24] ZHU M Y, XU T, SUN S J, et al. Physical model of D-region ionosphere and preliminary comparison with IRI and data of MF radar at Kunming[J]. Atmosphere, 2023, 14(2): 235 doi: 10.3390/atmos14020235 [25] FEJER J A, VICE R W. An investigation of the ionospheric D-region[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, 1959, 16(3/4): 291-306 [26] ANANTHAKRISHNAN S, ABDU M A, PIAZZA L R. D-region recombination coefficients and the short wavelength X-ray flux during a solar flare[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 1973, 21(3): 367-375 doi: 10.1016/0032-0633(73)90035-4 [27] BARRINGTON R E, THRANE E. The determination of D-region electron densities from observations of cross modulations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, 1962, 24(1): 31-42 doi: 10.1016/0021-9169(62)90292-1 [28] RAULIN J P, TROTTET G, KRETZSCHMAR M, et al. Response of the low ionosphere to X-ray and Lyman-α solar flare emissions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2013, 118(1): 570-575 doi: 10.1029/2012JA017916 [29] VAMPOLA A L, GORNEY D J. Electron energy deposition in the middle atmosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1983, 88(A8): 6267-6274 doi: 10.1029/JA088iA08p06267 [30] NAGANO I, OKADA T. Electron density profiles in the ionospheric D-region estimated from MF radio wave absorption[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2000, 25(1): 33-42 doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(99)00894-7 [31] FERGUSON J A. Computer Programs for Assessment of Long-Wavelength Radio Communications, Version 2.0: User’s Guide and Source Files[R]. San Diego: Space and Naval Warfare Systems Center, 1998 [32] KUMAR A, KUMAR S. Solar flare effects on D‑region ionosphere using VLF measurements during low- and high-solar activity phases of solar cycle 24[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2018, 70(1): 29 doi: 10.1186/s40623-018-0794-8 [33] MAURYA A K, SINGH R, KUMAR S, et al. Waves-like signatures in the D-region ionosphere generated by solar flares[C]//Proceedings of 2014 XXXIth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium. Beijing: IEEE, 2014. DOI: 10.1109/URSIGASS.2014.6929796 [34] GRUBOR D, ŠULIĆ D, ŽIGMAN V. Influence of solar X-ray flares on the earth-ionosphere waveguide[J]. Serbian Astronomical Journal, 2005(171): 29-35 doi: 10.2298/SAJ0571029G [35] OSEPIAN A, KIRKWOOD S, DALIN P, et al. D-region electron density and effective recombination coefficients during twilight - experimental data and modelling during solar proton events[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2009, 27(10): 3713-3724 doi: 10.5194/angeo-27-3713-2009 [36] SELVAKUMARAN R, MAURYA A K, GOKANI S A, et al. Solar flares induced D-region ionospheric and geomagnetic perturbations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2015, 123: 102-112 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2014.12.009 [37] KUMAR A, KUMAR S. Space weather effects on the low latitude D-region ionosphere during solar minimum[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2014, 66(1): 76 doi: 10.1186/1880-5981-66-76 -
-




 辛浩 男, 1981年1月出生于河南省平顶山市, 现为平顶山工业职业技术学院讲师, 主要研究方向为无线电通信、网络安全技术、电离层电波传播等. E-mail:
辛浩 男, 1981年1月出生于河南省平顶山市, 现为平顶山工业职业技术学院讲师, 主要研究方向为无线电通信、网络安全技术、电离层电波传播等. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: