Spatio-temporal Characteristics Analysis of Ozone Valley on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau Based on Satellite Data
-
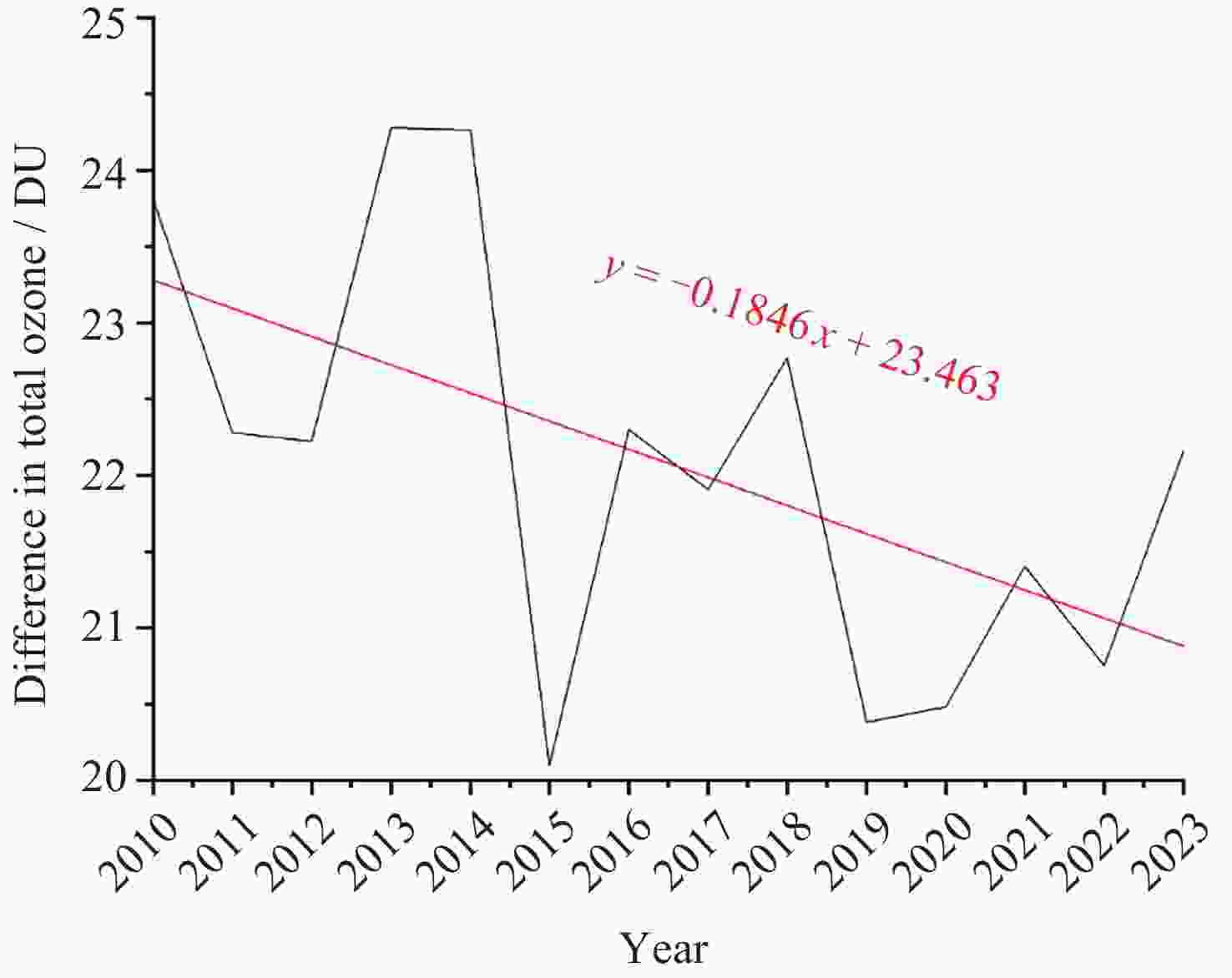
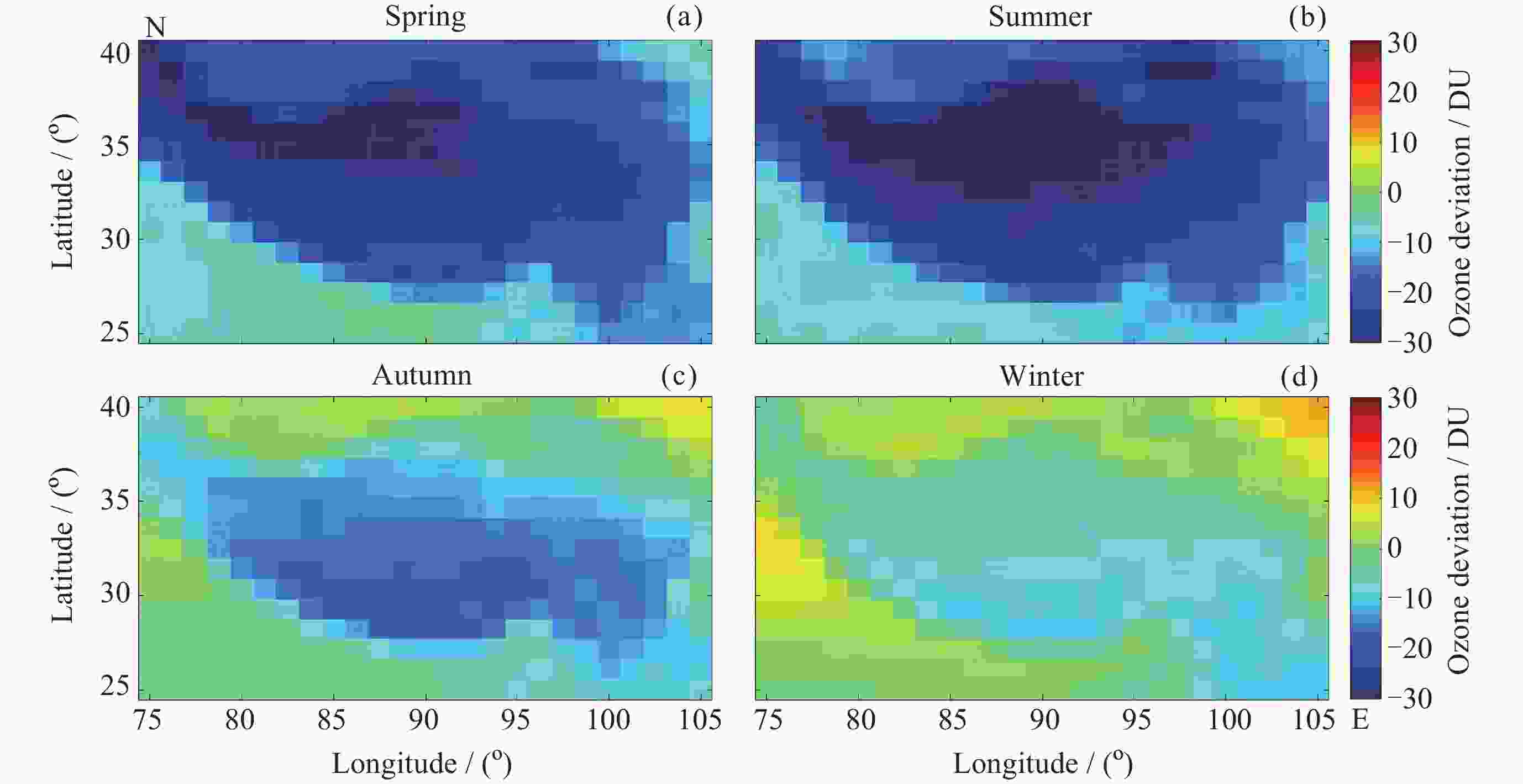
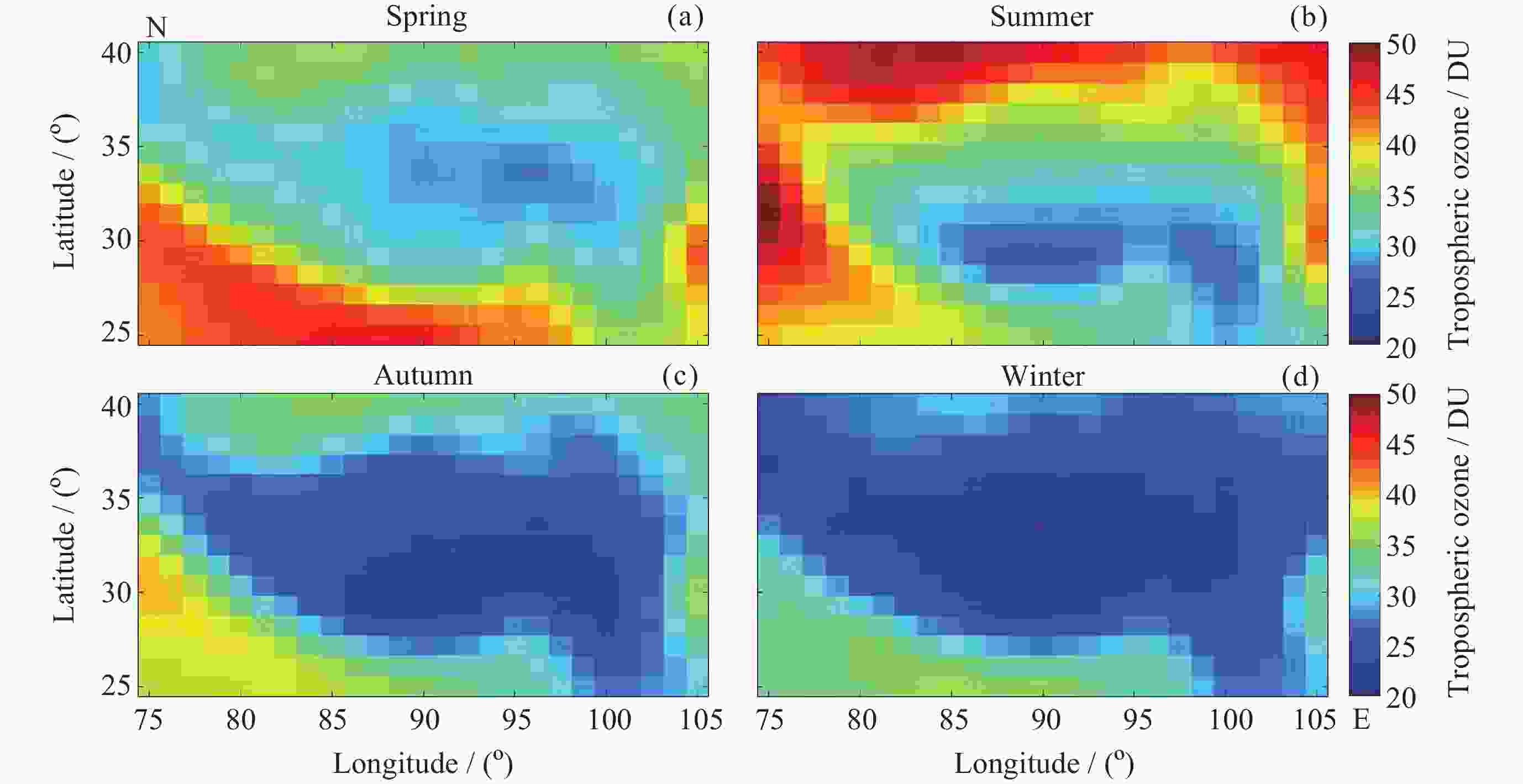
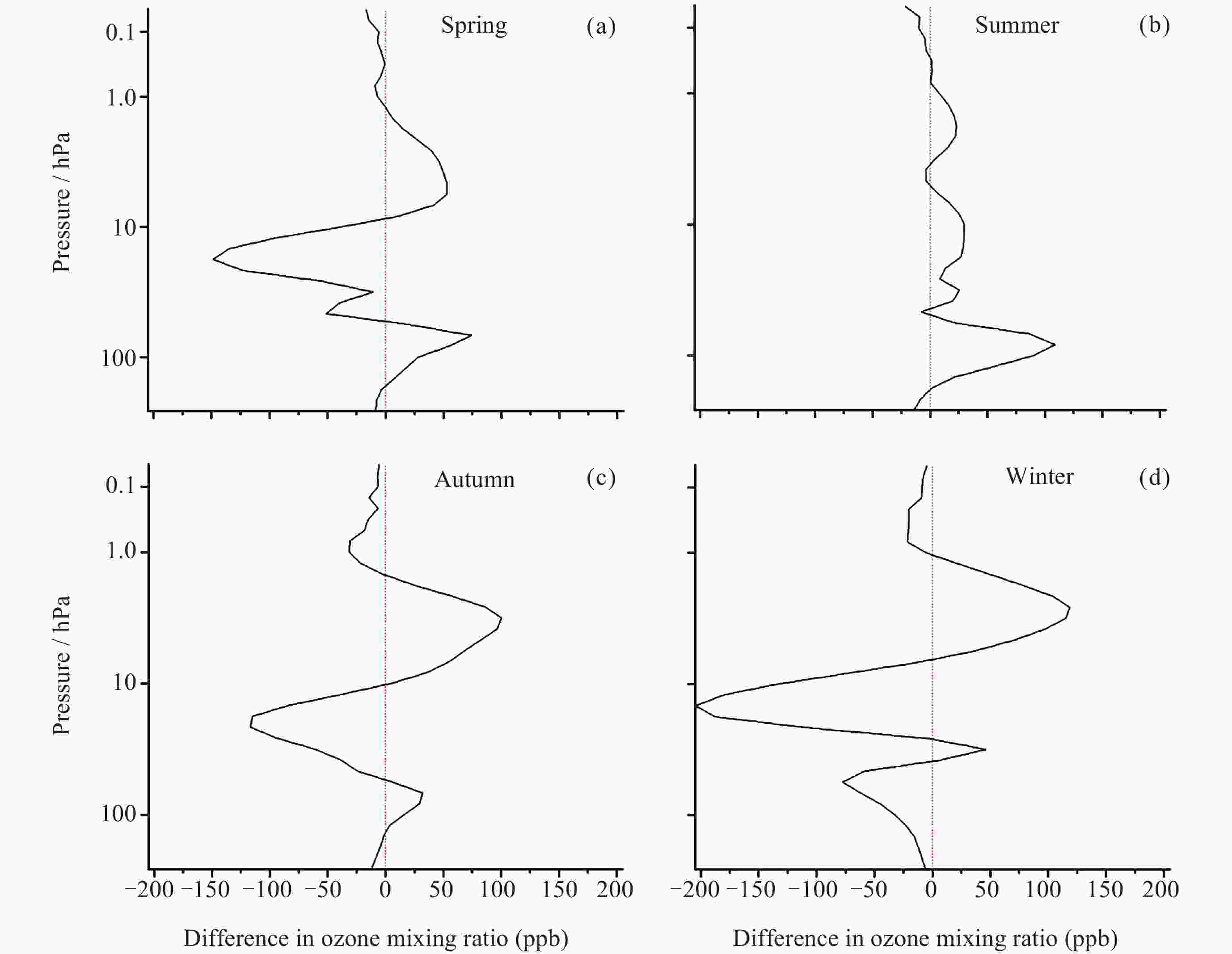
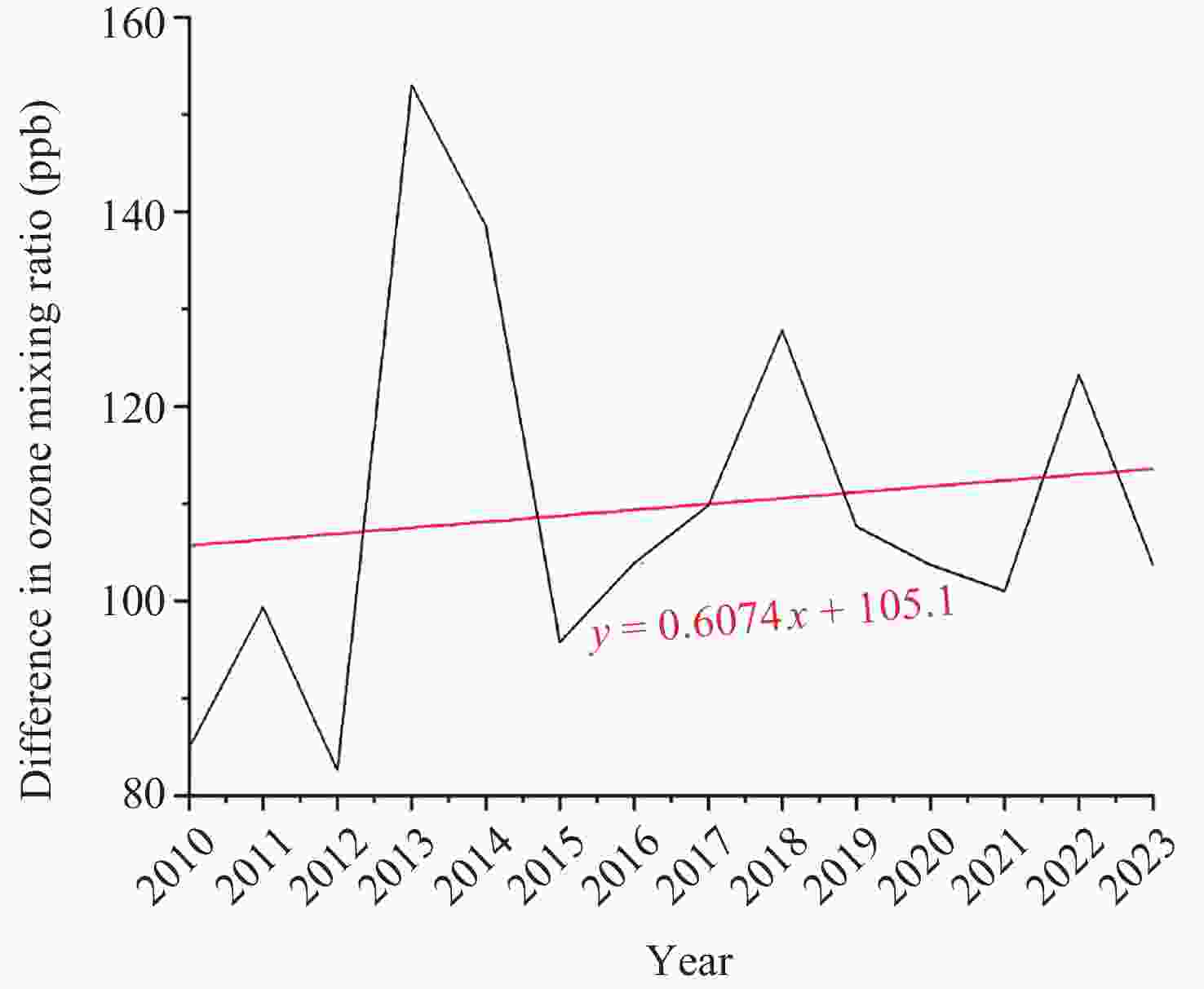
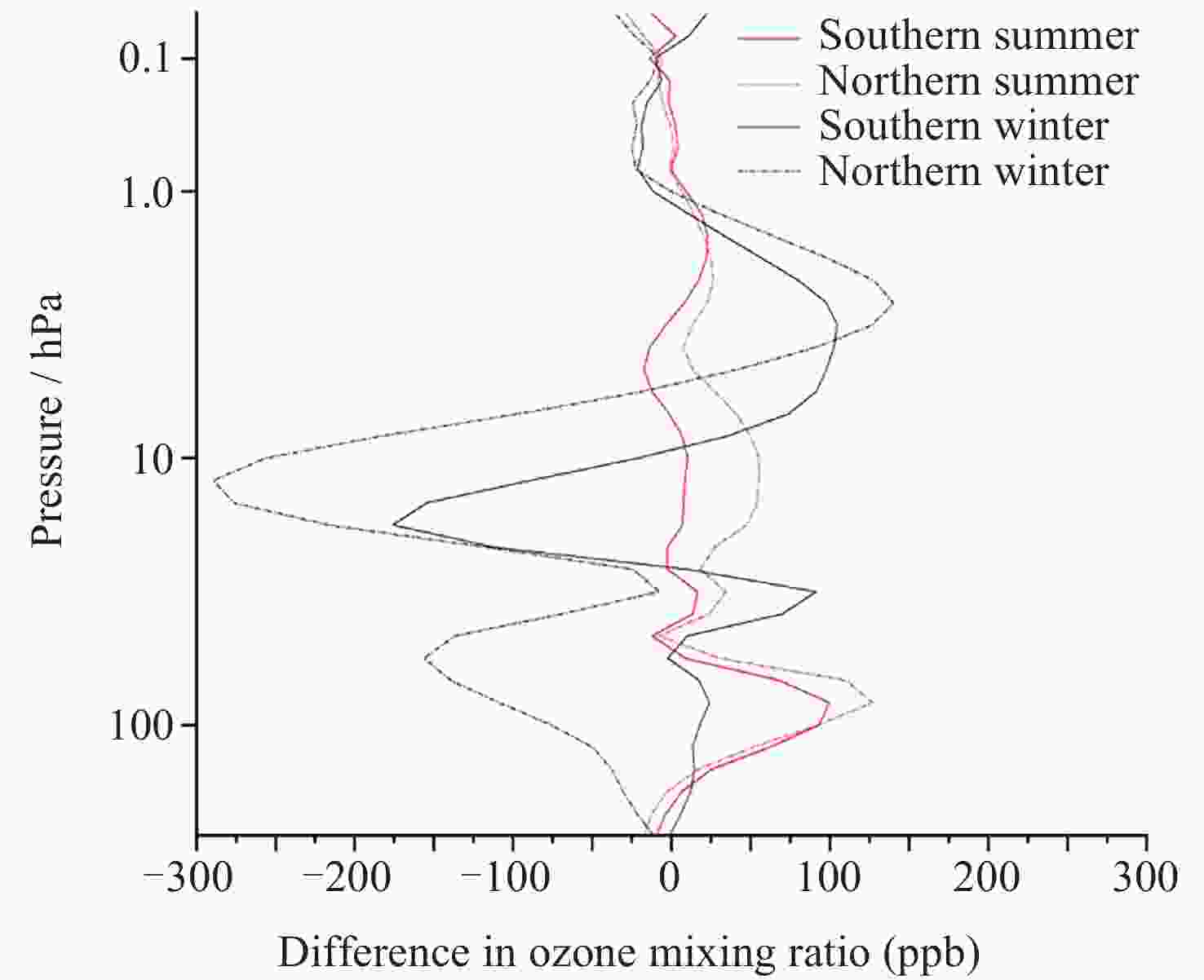
摘要: 青藏高原臭氧谷对全球气候具有重要影响, 为探索臭氧谷具体时空特征, 本文主要利用臭氧监测仪(OMI)和微波临边探测器(MLS)提供的2010-2023年青藏高原和同纬度地区臭氧总量日观测数据、对流层臭氧月均值数据和臭氧廓线数据, 对青藏高原上空臭氧低值中心的时空分布特征进行相应分析, 并简要讨论总结了该现象产生的可能原因. 研究结果表明, 青藏高原和全球同纬度地区相比, 夏季存在明显的臭氧低值现象; 青藏高原垂直方向臭氧低值主要发生在15~20 km范围内, 其中最低值对应高度为16.8 km, 大致位于对流层顶; 青藏高原内部臭氧低值现象存在明显的地域差异, 冬季南部和北部规律相反.Abstract: The ozone valley over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau has a significant impact on global climate. To explore the specific temporal and spatial characteristics of the ozone valley, this study primarily utilizes daily total ozone columns, monthly average tropospheric ozone columns, and ozone profiles derived from OMI and MLS over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau from 2010 to 2023. The study analyzes the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of the ozone low-value center over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and briefly discusses the possible causes of this phenomenon. Additionally, we employ spatial interpolation and precision-controlled data screening to minimize uncertainties in satellite retrievals, ensuring robust conclusions. The results are indicated below. Compared to other regions at the same latitude globally, the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau exhibits a distinct low-ozone phenomenon during the summer, with a maximum deficit of 36 DU (Dobson Unit), located in the northwestern part of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Notably, this seasonal anomaly extends to tropospheric ozone, where the plateau shows a deficit of 15 DU relative to regions at the same latitude globally. Vertically, there are multiple peaks of the ozone deficit over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in summer. The low ozone values over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau are mainly concentrated within the 15~20 km range, with the lowest value corresponding to an altitude of 16.8 km, roughly at the tropopause. There are significant regional differences in the low-ozone phenomenon within the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, with opposite patterns observed between the southern and northern parts during the winter, where northern regions show ozone surpluses (+156.2 ppb) within the 15~20 km range, contrasting southern deficits. Based on the current study, future research will utilize high-resolution, multi-source data and relevant climate models to analyze further and validate the formation mechanisms of the ozone valley and its impacts on climate.
-
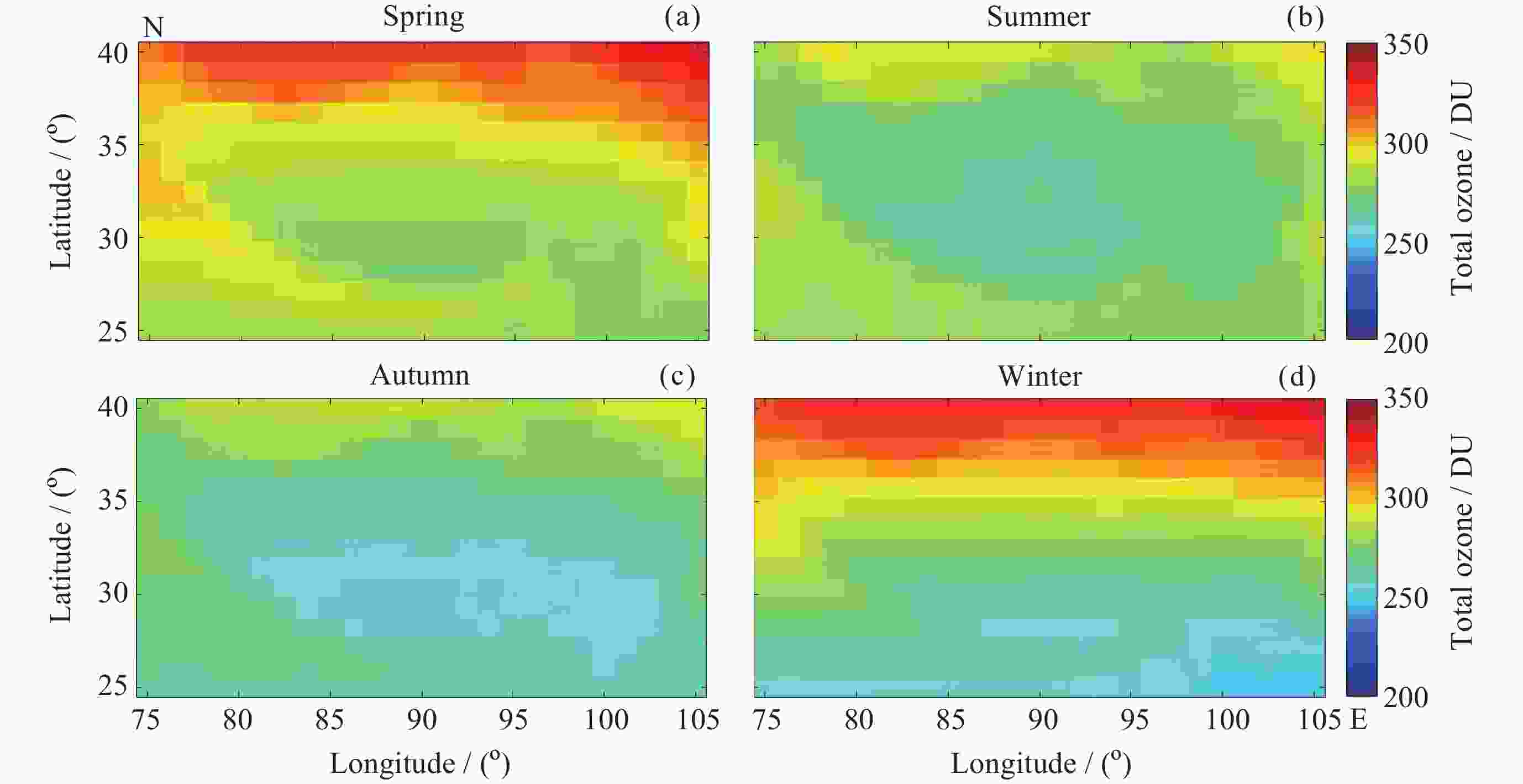
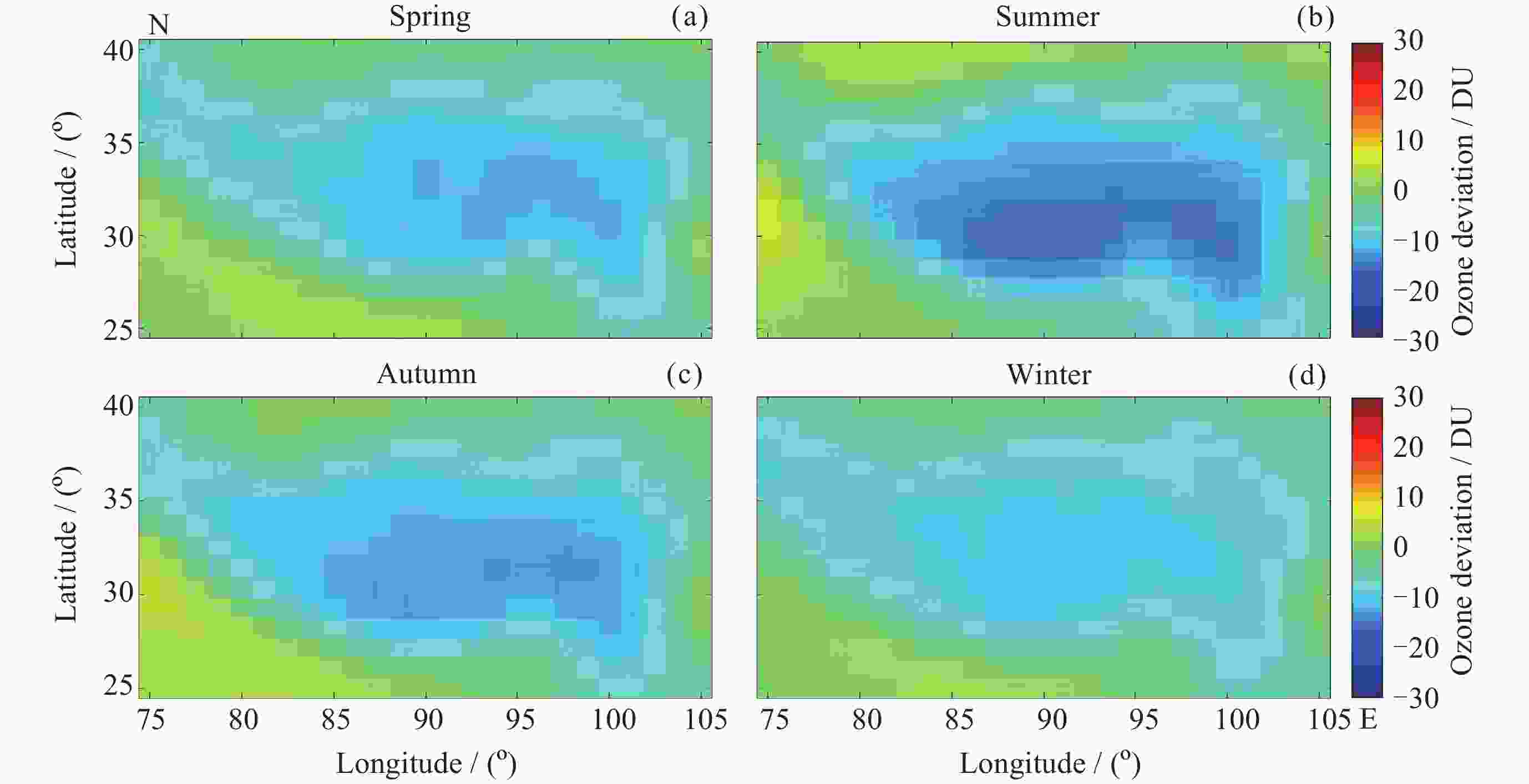
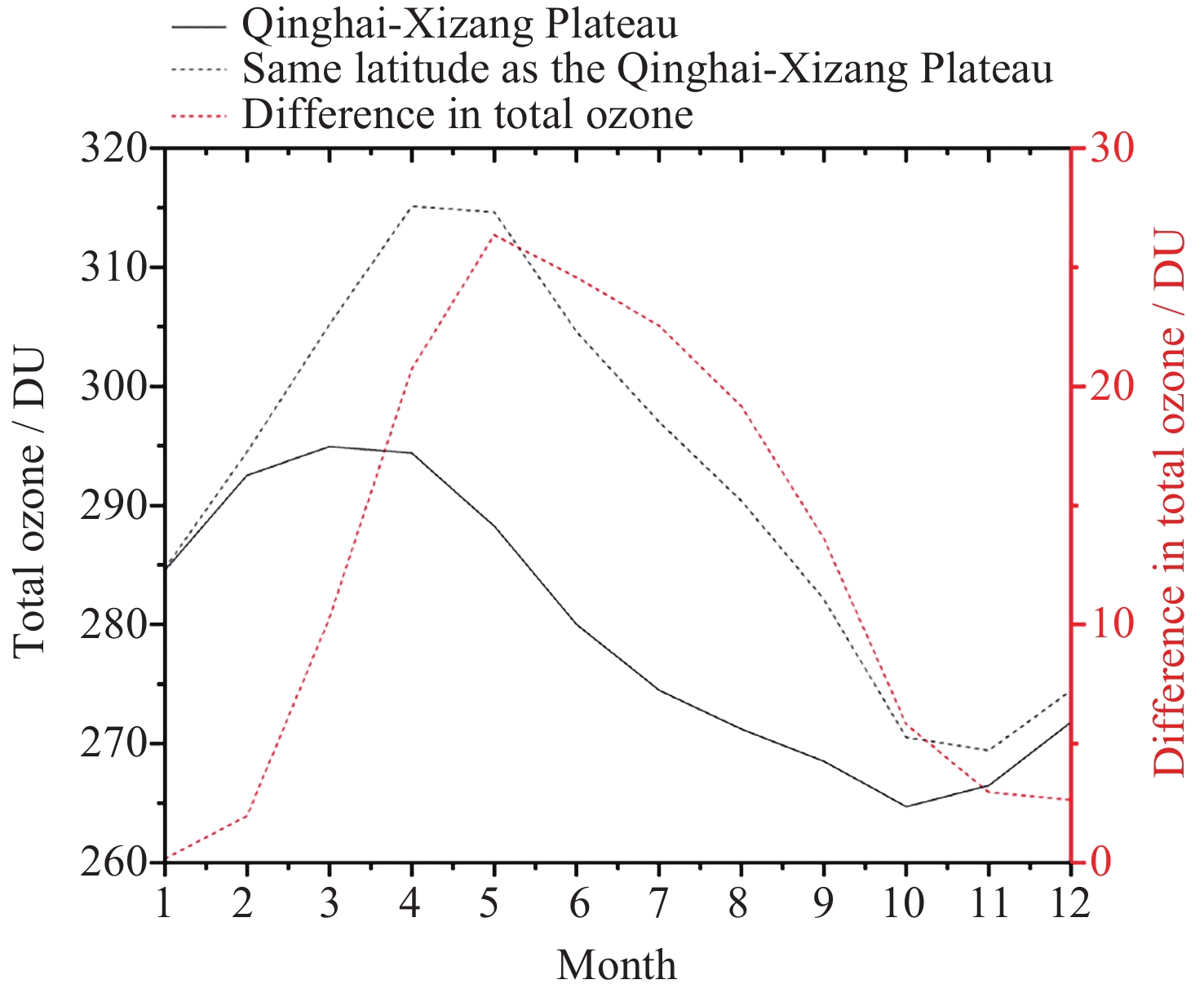
图 4 2010-2023年青藏高原四季臭氧总量纬向偏差(3-5月均值代表春季, 6-8月均值代表夏季, 9-11月均值代表秋季, 12月至次年2月代表冬季)
Figure 4. Latitudinal deviation of total ozone in four seasons on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau between 2010 and 2023 (March to May averages represent spring, June to August averages represent summer, September to November averages represent autumn, and December to February averages represent winter)
-
[1] ZHANG Ying, GAO Yang, ZHU Shanyou, et al. Variation of total ozone over China for 30 years analyzed by multi-source satellite remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2014, 16(6): 971-978 (张莹, 高玚, 祝善友, 等. 近30a中国上空臭氧总量时空变化遥感监测分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2014, 16(6): 971-978ZHANG Ying, GAO Yang, ZHU Shanyou, et al. Variation of total ozone over China for 30 years analyzed by multi-source satellite remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2014, 16(6): 971-978 [2] XIE Jinghan, LI Sa, XIAO Zhongyong. Investigating the temporal and spatial variabilities of total ozone over China for the past 50 years[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(7): 2977-2987 (谢静晗, 李飒, 肖钟湧. 50年来中国臭氧总量时空变化特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(7): 2977-2987 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.07.001XIE Jinghan, LI Sa, XIAO Zhongyong. Investigating the temporal and spatial variabilities of total ozone over China for the past 50 years[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(7): 2977-2987 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.07.001 [3] CHI Yulei, ZHAO Chuanfeng. Progress and challenges of ozone satellite remote sensing inversion[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2023, 43(18): 1899905 (迟雨蕾, 赵传峰. 臭氧卫星遥感反演进展及挑战[J]. 光学学报, 2023, 43(18): 1899905 doi: 10.3788/AOS230583CHI Yulei, ZHAO Chuanfeng. Progress and challenges of ozone satellite remote sensing inversion[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2023, 43(18): 1899905 doi: 10.3788/AOS230583 [4] XU J, ZHANG Z, RAO L L, et al. Remote sensing of tropospheric ozone from space: progress and challenges[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0178 doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0178 [5] FARMAN J C, GARDINER B G, SHANKLIN J D. Large losses of total ozone in antarctica reveal seasonal ClOx/NOx interaction[J]. Nature, 1985, 315(6016): 207-210 doi: 10.1038/315207a0 [6] NEWMAN P A, GLEASON J F, MCPETERS R D, et al. Anomalously low ozone over the Arctic[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1997, 24(22): 2689-2692 doi: 10.1029/97GL52831 [7] BOJKOV R D, BISHOP L, FIOLETOV V E. Total ozone trends from quality-controlled ground-based data (1964-1994)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1995, 100(D12): 25867-25876 doi: 10.1029/95JD02907 [8] POLVANI L M, WAUGH D W, CORREA G J P, et al. Stratospheric ozone depletion: the main driver of twentieth-century atmospheric circulation changes in the southern hemisphere[J]. Journal of Climate, 2011, 24(3): 795-812 doi: 10.1175/2010JCLI3772.1 [9] MCLANDRESS C, SHEPHERD T G, SCINOCCA J F, et al. Separating the dynamical effects of climate change and ozone depletion. Part II: southern hemisphere troposphere[J]. Journal of Climate, 2011, 24(6): 1850-1868 doi: 10.1175/2010JCLI3958.1 [10] CHANG S J, HE H T, HUANG D. The effects of gravity waves on ozone over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2024, 299: 107204 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2023.107204 [11] SHEN L, RAO J, GUO D, et al. Comparison of the climatic characteristics of ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau and the Rocky Mountains[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2024, 11(4): e2023EA003379 doi: 10.1029/2023EA003379 [12] LIN P, MING Y. Enhanced climate response to ozone depletion from ozone-circulation coupling[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2021, 126(7): e2020JD034286 doi: 10.1029/2020JD034286 [13] HU Yongyun. Possible impact of stratospheric polar ozone depletion on tropospheric climate[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2006, 42(5): 561-568 (胡永云. 平流层极地臭氧损耗影响对流层气候的研究进展[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 42(5): 561-568HU Yongyun. Possible impact of stratospheric polar ozone depletion on tropospheric climate[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2006, 42(5): 561-568 [14] ZHU L G N, Wu Z W. Climatic influence of the Antarctic ozone hole on the East Asian winter precipitation[J]. Climate and Atmospheric Science, 2024, 7(1): 184 doi: 10.1038/s41612-024-00732-z [15] ZHOU X J, LUO C. Ozone valley over Tibetan Plateau[J]. Annual Report of CAMS, 1995, 8(4): 505-506 [16] ZOU Han, GAO Yongqi, ZHOU Libo. Ozone low and surface heating over large scale topography[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 1998, 3(3): 209-217 (邹捍, 郜永祺, 周立波. 大尺度山地上空的臭氧低值及地面加热[J]. 气候与环境研究, 1998, 3(3): 209-217 doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9585.1998.03.03ZOU Han, GAO Yongqi, ZHOU Libo. Ozone low and surface heating over large scale topography[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 1998, 3(3): 209-217 doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9585.1998.03.03 [17] ZHOU X J, LI W L, CHEN L X, et al. Study on ozone change over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2006, 20(2): 129-143 [18] ZHOU Xiuji, LUO Chao, LI Weiliang, et al. Total ozone changes in China and low center of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(15): 1396-1398 (周秀骥, 罗超, 李维亮, 等. 中国地区臭氧总量变化与青藏高原低值中心[J]. 科学通报, 1995, 40(15): 1396-1398 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.15.016ZHOU Xiuji, LUO Chao, LI Weiliang, et al. Total ozone changes in China and low center of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(15): 1396-1398 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.15.016 [19] GUO D, WANG P X, ZHOU X J, et al. Dynamic effects of the South Asian high on the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2012, 26(2): 216-228 doi: 10.1007/s13351-012-0207-2 [20] ZHOU Renjun, CHEN Yuejuan. Ozone variations over the Tibetan and Iranian Plateaus and their relationship with the South Asia High pressure[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology of China, 2005, 35(6): 899-908 (周任君, 陈月娟. 青藏高原和伊朗高原上空臭氧变化特征及其与南亚高压的关系[J]. 中国科学技术大学学报, 2005, 35(6): 899-908ZHOU Renjun, CHEN Yuejuan. Ozone variations over the Tibetan and Iranian Plateaus and their relationship with the South Asia High pressure[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology of China, 2005, 35(6): 899-908 [21] ZHANG K Q, DUAN J K, ZHAO S Y, et al. Evaluating the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau in CMIP6 models[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2022, 39(7): 1167-1183 doi: 10.1007/s00376-021-0442-2 [22] WANG Qilu, XU Wenwen, TU Jingyi, et al. Comparison of the dynamic transport characteristics of low ozone regions over the Arctic and the Tibetan Plateau from 1979 to 2020[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2023, 47(3): 866-880 (王启璐, 徐雯雯, 涂静怡, 等. 1979~2020年北极和青藏高原臭氧低值区的动力输送特征比较[J]. 大气科学, 2023, 47(3): 866-880WANG Qilu, XU Wenwen, TU Jingyi, et al. Comparison of the dynamic transport characteristics of low ozone regions over the Arctic and the Tibetan Plateau from 1979 to 2020[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2023, 47(3): 866-880 [23] WANG Xiuying, TIAN Mengkun, CHEN Yan, et al. Characteristics and causes of the ozone low value center over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Ecology and Environmental Monitoring of Three Gorges, 2019, 4(1): 47-55 (王秀英, 田孟坤, 陈艳, 等. 青藏高原臭氧低值中心特征及成因分析[J]. 三峡生态环境监测, 2019, 4(1): 47-55WANG Xiuying, TIAN Mengkun, CHEN Yan, et al. Characteristics and causes of the ozone low value center over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Ecology and Environmental Monitoring of Three Gorges, 2019, 4(1): 47-55 [24] QIU Yongyan, WEI Min, JIANG Ailiang, et al. General characteristics of the ozone low center above the Tibetan Plateau and (low) trough above the Rocky Mountains—on the cause of static deficit/depletion above the High Mountains[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2008, 13(5): 617-628 (仇永炎, 魏民, 江爱良, 等. 青藏高原臭氧总量低中心与落基山臭氧低槽的基本特征——兼论高山静力亏损的成因[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2008, 13(5): 617-628QIU Yongyan, WEI Min, JIANG Ailiang, et al. General characteristics of the ozone low center above the Tibetan Plateau and (low) trough above the Rocky Mountains—on the cause of static deficit/depletion above the High Mountains[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2008, 13(5): 617-628 [25] LIU Yu, GUO Caili, LI Weiliang, et al. Trends of stratospheric ozone and aerosols over Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2007, 65(6): 938-945 (刘煜, 郭彩丽, 李维亮, 等. 青藏高原平流层臭氧和气溶胶的变化趋势研究[J]. 气象学报, 2007, 65(6): 938-945LIU Yu, GUO Caili, LI Weiliang, et al. Trends of stratospheric ozone and aerosols over Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2007, 65(6): 938-945 [26] LIU Yu, LI Weiliang, ZHOU Xiuji. A possible effect of heterogeneous reactions on the formation of the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2010, 68(6): 836-846 (刘煜, 李维亮, 周秀骥. 非均相化学过程在青藏高原臭氧低谷形成中的作用[J]. 气象学报, 2010, 68(6): 836-846LIU Yu, LI Weiliang, ZHOU Xiuji. A possible effect of heterogeneous reactions on the formation of the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2010, 68(6): 836-846 [27] LIU Y, LI W L, ZHOU X J, et al. Mechanism of formation of the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau in summer—transport and chemical process of ozone[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2003, 20(1): 103-109 doi: 10.1007/BF03342054 [28] WAN Lingfeng, GUO Dong, LIU Renqiang, et al. Evaluation of the WACCM3 performance on simulation of the double core of ozone valley over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in summer[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2017, 36(1): 57-66 (万凌峰, 郭栋, 刘仁强, 等. WACCM3对夏季青藏高原臭氧谷双心结构的模拟性能评估[J]. 高原气象, 2017, 36(1): 57-66 doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2016.00004WAN Lingfeng, GUO Dong, LIU Renqiang, et al. Evaluation of the WACCM3 performance on simulation of the double core of ozone valley over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in summer[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2017, 36(1): 57-66 doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2016.00004 [29] YAN J J, WANG G L, YANG P C, et al. Influence of NOX, Cl, and Br on the upper core of the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau during summer: simulations with a box model[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 817: 152776 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152776 [30] BIAN Jianchun, WANG Gengchen, CHEN Hongbin, et al. Ozone mini-holes appeared over the Tibetan Plateau in December 2003[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(5): 606-609 (卞建春, 王庚辰, 陈洪滨, 等. 2003年12月青藏高原上空出现微型臭氧洞[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(5): 606-609 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.05.017BIAN Jianchun, WANG Gengchen, CHEN Hongbin, et al. Ozone mini-holes appeared over the Tibetan Plateau in December 2003[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(5): 606-609 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.05.017 [31] BIAN J C. Features of ozone mini-hole events over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2009, 26(2): 305-311 doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-0305-8 [32] ZHOU Shunwu, YANG Shuangyan, ZHANG Renhe, et al. Possible causes of total ozone depletion over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and its relation to tropopause height in recent 30 years[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2012, 31(6): 1471-1478 (周顺武, 杨双艳, 张人禾, 等. 近30年青藏高原臭氧总量亏损的可能原因及其与对流层顶高度的联系[J]. 高原气象, 2012, 31(6): 1471-1478ZHOU Shunwu, YANG Shuangyan, ZHANG Renhe, et al. Possible causes of total ozone depletion over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and its relation to tropopause height in recent 30 years[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2012, 31(6): 1471-1478 [33] ZHOU Renjun, Chen Yuejuan. Anomaly of the ozone low center over the Tibetan Plateau in 1998 and the surrounding flow field[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2006, 11(2): 169-174 (周任君, 陈月娟. 1998年青藏高原臭氧低值中心异常及其背景环流场的分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2006, 11(2): 169-174 doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9585.2006.02.04ZHOU Renjun, Chen Yuejuan. Anomaly of the ozone low center over the Tibetan Plateau in 1998 and the surrounding flow field[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2006, 11(2): 169-174 doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9585.2006.02.04 [34] GUO Fengxia, MU Yijun, LI Yang, et al. Effects of nitrogen oxides produced from lightning on the formation of the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2019, 43(2): 266-276 (郭凤霞, 穆奕君, 李扬, 等. 闪电产生氮氧化物对青藏高原臭氧低谷形成的影响[J]. 大气科学, 2019, 43(2): 266-276GUO Fengxia, MU Yijun, LI Yang, et al. Effects of nitrogen oxides produced from lightning on the formation of the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2019, 43(2): 266-276 [35] LIU Z, GUO F X, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Impact of lightning-induced nitrogen oxides over and around the Tibetan Plateau on the Tibetan Plateau ozone valley[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2024, 129(1): e2023JD039575 doi: 10.1029/2023JD039575 [36] ZOU H, JI C P, ZHOU L B, et al. ENSO signal in total ozone over Tibet[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2001, 18(2): 231-238 doi: 10.1007/s00376-001-0016-2 [37] LI Y C, XU F, WAN L F, et al. Effect of ENSO on the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau based on the WACCM4 model[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(2): 525 doi: 10.3390/rs15020525 [38] CHANG S J, LI Y C, SHI C H, et al. Combined effects of the ENSO and the QBO on the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(19): 4935 doi: 10.3390/rs14194935 [39] CHEN Peng, LI Yongchi, JING Guole, et al. Analysis of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau ozone valley of stratospheric formation mechanism[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2023, 42(5): 1182-1193 (陈鹏, 李永炽, 景国乐, 等. 青藏高原平流层臭氧谷形成机制分析[J]. 高原气象, 2023, 42(5): 1182-1193CHEN Peng, LI Yongchi, JING Guole, et al. Analysis of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau ozone valley of stratospheric formation mechanism[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2023, 42(5): 1182-1193 [40] YAN J J, WANG G L, YANG P C. Study on the sensitivity of summer ozone density to the enhanced aerosol loading over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Atmosphere, 2020, 11(2): 138 doi: 10.3390/atmos11020138 [41] XIA Y, HU Y Y, HUANG Y, et al. Stratospheric ozone loss enhances summer precipitation over the southern slope of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2023, 50(15): e2023GL103742 doi: 10.1029/2023GL103742 [42] ZHOU Renjun, CHEN Yuejuan. Effects of variation of low ozone center over the Tibetan Plateau on climate in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2007, 31(3): 479-485 (周任君, 陈月娟. 青藏高原臭氧低值中心的变化与我国气候的关系[J]. 大气科学, 2007, 31(3): 479-485ZHOU Renjun, CHEN Yuejuan. Effects of variation of low ozone center over the Tibetan Plateau on climate in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2007, 31(3): 479-485 [43] LI Yong, WANG Shifeng, CHEN Tianlu, et al. Research status of solar ultraviolet radiation and its biological effects on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(4): 1321-1328 (李勇, 王世锋, 陈天禄, 等. 青藏高原太阳紫外线辐射及其生物学效应研究现状[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(4): 1321-1328 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.04.003LI Yong, WANG Shifeng, CHEN Tianlu, et al. Research status of solar ultraviolet radiation and its biological effects on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(4): 1321-1328 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.04.003 [44] SU Yucheng, Guo Dong, Guo Shengli, et al. Ozone trends over the Tibetan Plateau in the next 100 years and their possible mechanism[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2016, 39(3): 309-317 (苏昱丞, 郭栋, 郭胜利, 等. 未来百年夏季青藏高原臭氧变化趋势及可能机制[J]. 大气科学学报, 2016, 39(3): 309-317SU Yucheng, Guo Dong, Guo Shengli, et al. Ozone trends over the Tibetan Plateau in the next 100 years and their possible mechanism[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2016, 39(3): 309-317 [45] WANG Ke, LI Zhengqiang, LI Kaitao, et al. Accuracy verification of OMI global ozone products based on Pandora observations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2022, 17(6): 640-654 (汪可, 李正强, 李凯涛, 等. 基于Pandora观测的OMI全球臭氧产品精度验证[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2022, 17(6): 640-654WANG Ke, LI Zhengqiang, LI Kaitao, et al. Accuracy verification of OMI global ozone products based on Pandora observations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2022, 17(6): 640-654 [46] HU Yueming, YAN Huanhuan, ZHANG Xingying, et al. Comparing OMI-TOMS and OMI-DOAS total ozone column in China[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2019, 45(3): 362-370 (胡玥明, 闫欢欢, 张兴赢, 等. OMI-TOMS与OMI-DOAS臭氧柱总量产品在中国地区的比较[J]. 气象, 2019, 45(3): 362-370HU Yueming, YAN Huanhuan, ZHANG Xingying, et al. Comparing OMI-TOMS and OMI-DOAS total ozone column in China[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2019, 45(3): 362-370 [47] VEEFKIND J P, DE HAAN J F, BRINKSMA E J, et al. Total ozone from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) using the DOAS technique[J]. IEEE Transactions On Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(5): 1239-1244 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.871204 [48] GUO Dong, XU Jianjun, SU Yucheng, et al. Comparison of vertical structure and formation mechanism of summer ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau and North America[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2017, 40(3): 412-417 (郭栋, 徐建军, 苏昱丞, 等. 青藏高原和北美夏季臭氧谷垂直结构和形成机制的比较[J]. 大气科学学报, 2017, 40(3): 412-417GUO Dong, XU Jianjun, SU Yucheng, et al. Comparison of vertical structure and formation mechanism of summer ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau and North America[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2017, 40(3): 412-417 [49] LIVESEY N J, FILIPIAK M J, FROIDEVAUX L, et al. Validation of Aura Microwave Limb Sounder O3 and CO observations in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2008, 113(D15): D15S02 [50] TANG Zhou. The Impact of the Chlorine Element on the Ozone Valley in the Upper Stratosphere Over the Tibetan Plateau[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2019 (唐舟. 氯元素对青藏高原上平流层臭氧谷的作用[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2019TANG Zhou. The Impact of the Chlorine Element on the Ozone Valley in the Upper Stratosphere Over the Tibetan Plateau[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2019 [51] WATERS J W, FROIDEVAUX L, HARWOOD R S, et al. The Earth Observing System Microwave Limb Sounder (EOSMLS) on the aura Satellite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(5): 1075-1092 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.873771 [52] ZHANG Chenxin. Validation of Ozone, Temperature and Water Vapor Between Ballon Sounding and Satellite Observation for the Center of the South Asian High[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2019 (张晨昕. 南亚高压核心区臭氧、温度、水汽的气球探空与卫星观测的比较验证[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2019ZHANG Chenxin. Validation of Ozone, Temperature and Water Vapor Between Ballon Sounding and Satellite Observation for the Center of the South Asian High[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2019 [53] YAN Xiaolu, ZHENG Xiangdong, ZHOU Xiuji, et al. Validation of Aura Microwave Limb Sounder water vapor and ozone profiles over the Tibetan Plateau and its adjacent region during boreal summer[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(4): 589-603 (颜晓露, 郑向东, 周秀骥, 等. 夏季青藏高原及其周边地区卫星MLS水汽、臭氧产品的探空检验分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 45(3): 335-350YAN Xiaolu, ZHENG Xiangdong, ZHOU Xiuji, et al. Validation of Aura Microwave Limb Sounder water vapor and ozone profiles over the Tibetan Plateau and its adjacent region during boreal summer[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(4): 589-603 [54] CAO Xiaoyun, QI Donglin, XIAO Jianshe, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of tropospheric ozone in Qinghai Plateau based on satellite observations[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(5): 1640-1648 (曹晓云, 祁栋林, 肖建设, 等. 基于卫星观测的青海高原对流层臭氧时空分布特征研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(5): 1640-1648CAO Xiaoyun, QI Donglin, XIAO Jianshe, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of tropospheric ozone in Qinghai Plateau based on satellite observations[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(5): 1640-1648 [55] WANG Guiqin, XIAO Wenjun. Research on the relations between changes of total amount of atmospheric ozone and general circulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 1987, 11(3): 337-340 (王贵勤, 肖文俊. 大气臭氧总量变化与大气环流关系的研究[J]. 大气科学, 1987, 11(3): 337-340WANG Guiqin, XIAO Wenjun. Research on the relations between changes of total amount of atmospheric ozone and general circulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 1987, 11(3): 337-340 [56] MA J Z, ZHOU X J, Xu X D, et al. Chapter 15 - Ozone and Aerosols Over the Tibetan Plateau[M]//Singh R P. Asian Atmospheric Pollution. Amsterdam Elsevier, 2022: 287-302 [57] ZHU L G N, WU Z W. To what extent can the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau influence the East Asian summer precipitation?[J]. Climate and Atmospheric Science, 2023, 6(1): 177 doi: 10.1038/s41612-023-00508-x [58] LI Y J, CHIPPERFIFIELD M P, FENG W H, et al. Analysis and attribution of total column ozone changes over the Tibetan Plateau during 1979-2017[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 20(14): 8627-8639 doi: 10.5194/acp-20-8627-2020 [59] YIN X F, RUPAKHETI D, ZHANG G S, et al. Surface ozone over the Tibetan Plateau controlled by stratospheric intrusion[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2023, 23(17): 10137-10143 doi: 10.5194/acp-23-10137-2023 [60] ZHANG J Q, LI D, BIAN J C, et al. Deep stratospheric intrusion and Russian wildfire induce enhanced tropospheric ozone pollution over the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2021, 259: 105662 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105662 [61] LIANG T, LUO J L, ZHANG C Y, et al. The impact of tropopause fold event on surface ozone concentration over Tibetan Plateau in July[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2024, 298: 107156 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2023.107156 [62] ZHAO Shaohua, YANG Xiaoyu, LI Zhengqiang, et al. Advances of ozone satellite remote sensing in 60 years[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2022, 26(5): 817-833 (赵少华, 杨晓钰, 李正强, 等. 臭氧卫星遥感六十年进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2022, 26(5): 817-833 doi: 10.11834/j.issn.1007-4619.2022.5.ygxb202205003ZHAO Shaohua, YANG Xiaoyu, LI Zhengqiang, et al. Advances of ozone satellite remote sensing in 60 years[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2022, 26(5): 817-833 doi: 10.11834/j.issn.1007-4619.2022.5.ygxb202205003 [63] YIN X F, KANG S C, DE FOY B, et al. Surface ozone at Nam Co in the inland Tibetan Plateau: variation, synthesis comparison and regional representativeness[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2017, 17(18): 11293-11311 doi: 10.5194/acp-17-11293-2017 [64] ZHENG Xiangdong, TANG Jie, LI Weiliang, et al. Observational study on total ozone amount and its vertical profile over lhasa in the summer of 1998[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2000, 11(2): 173-179 (郑向东, 汤洁, 李维亮, 等. 拉萨地区1998年夏季臭氧总量及垂直廓线的观测研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 2000, 11(2): 173-179 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2000.02.006ZHENG Xiangdong, TANG Jie, LI Weiliang, et al. Observational study on total ozone amount and its vertical profile over lhasa in the summer of 1998[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2000, 11(2): 173-179 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2000.02.006 [65] SUN Yuting, ZHENG Xiangdong, BIAN Jianchun, et al. Vertical distribution of summer tropospheric ozone over the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 806-818 (孙宇婷, 郑向东, 卞建春, 等. 夏季青藏高原北部对流层臭氧垂直分布的观测研究[J]. 气象学报, 2022, 80(5): 806-818 doi: 10.11676/qxxb2022.054SUN Yuting, ZHENG Xiangdong, BIAN Jianchun, et al. Vertical distribution of summer tropospheric ozone over the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 806-818 doi: 10.11676/qxxb2022.054 [66] GUO D, SU Y C, SHI C H, et al. Double core of ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau and its possible mechanisms[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2015, 130/131: 127-131 [67] JIAO Boyang, SU Yucheng, GUO Shengli, et al. Distribution of ozone valley and its relationship with solar radiation over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2017, 36(5): 1201-1208 (焦铂洋, 苏昱丞, 郭胜利, 等. 青藏高原臭氧谷的分布及其与太阳辐射的关系[J]. 高原气象, 2017, 36(5): 1201-1208JIAO Boyang, SU Yucheng, GUO Shengli, et al. Distribution of ozone valley and its relationship with solar radiation over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2017, 36(5): 1201-1208 [68] ZOU H, GAO Y Q. Vertical ozone profile over Tibet using sage I and II data[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 1997, 14(4): 505-512 doi: 10.1007/s00376-997-0068-z [69] LIN Weili, YAO Bo. Analysis on the vertical ozone profiles over Tibetan Plateau using SAGE Ⅱ data[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2005, 18(4): 102-105,128 (林伟立, 姚波. 利用SAGEⅡ卫星资料分析青藏高原上空臭氧垂直廓线[J]. 环境科学研究, 2005, 18(4): 102-105,128LIN Weili, YAO Bo. Analysis on the vertical ozone profiles over Tibetan Plateau using SAGE Ⅱ data[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2005, 18(4): 102-105,128 [70] CHEN Quanliang, GAO Guolu, LI Yang. Advances in studies of deep convection over the Tibetan Plateau and its effect on stratospheric—tropospheric material transport[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2022, 46(5): 1198-1208 (陈权亮, 高国路, 李扬. 青藏高原深对流及其在对流层—平流层物质输送中作用的研究进展[J]. 大气科学, 2022, 46(5): 1198-1208CHEN Quanliang, GAO Guolu, LI Yang. Advances in studies of deep convection over the Tibetan Plateau and its effect on stratospheric—tropospheric material transport[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2022, 46(5): 1198-1208 [71] BIAN Jianchun, YAN Renchang, CHEN Hongbin. Tropospheric pollutant transport to the stratosphere by Asian summer monsoon[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2011, 35(5): 897-902 (卞建春, 严仁嫦, 陈洪滨. 亚洲夏季风是低层污染物进入平流层的重要途径[J]. 大气科学, 2011, 35(5): 897-902BIAN Jianchun, YAN Renchang, CHEN Hongbin. Tropospheric pollutant transport to the stratosphere by Asian summer monsoon[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2011, 35(5): 897-902 -
-





 马湘君 女, 2001年4月出生于山东省烟台市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心硕士研究生, 主要从事基于卫星遥感的地球多圈层耦合机制研究. E-mail:
马湘君 女, 2001年4月出生于山东省烟台市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心硕士研究生, 主要从事基于卫星遥感的地球多圈层耦合机制研究. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: