A Multiplicative Model with Frequency-domain Features Superimposed on Time-domain Mutations for Predicting Ionospheric TEC Methods
-
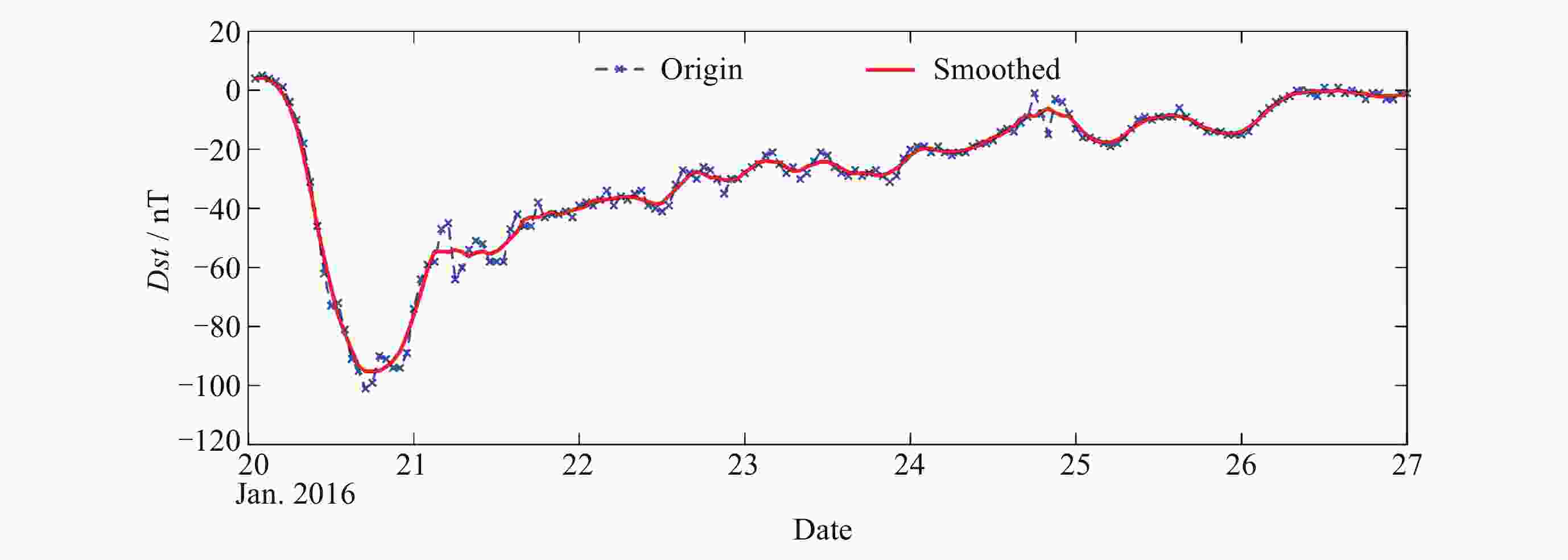
摘要: 电离层总电子含量(TEC)是电离层的重要特征参数, 对导航误差修正等应用有较大影响, 但是目前的电离层TEC预报精度无法完全满足需求, 尤其在太阳风暴期间的精度和提前量方面存在不足. 针对区域电离层TEC预报需要, 综合考虑电离层TEC的频域和时域特性, 根据电离层TEC的变化受太阳活动影响存在趋势性、周期性和突发性的特征, 在分析太阳活动高低年趋势的基础上, 在频域用多个周期长度解析电离层TEC变化, 在时域上考虑地磁暴等因素对电离层TEC的突发性影响, 将扰动暴时(Dst)指数、经纬度作为输入参数, 对各个区域磁层–电离层耦合情况进行特异性建模. 实验结果表明, 在地磁平静时期中纬度地区, 本文方法在太阳活动低年7天预报值的均方根误差(RMSE)优于1.262总电子含量单位(TECU), 1天预报值的RMSE优于1.094 TECU, 在太阳活动高年7天预报值的RMSE优于2.771 TECU. 在地磁活跃时期, 7天预报值的RMSE优于4.186 TECU, 1天预报值的RMSE优于4.115 TECU. 本文建立了具备7天提前量的预报模型, 方法在预报精度和时效方面表现良好.Abstract: Total Electronic Content (TEC) is an important characteristic parameter of the ionosphere, which has a great influence on the navigation error correction and other applications, but the current ionospheric TEC prediction accuracy cannot fully meet the demand, and there are deficiencies in the accuracy and lead time. The paper focuses on the needs of regional ionospheric TEC forecasting, comprehensively considers the characteristics of ionospheric TEC in both frequency and time domains, analyzes the ionospheric TEC changes in multiple cycle lengths in the frequency domain according to the characteristics of trend, periodicity, and suddenness of the changes in the ionospheric TEC affected by solar activities, considers the suddenness of the geomagnetic storms and other factors on the ionospheric TEC in the time domain, and considers the Dst index and latitude/longitude as the input parameters for forecasting. Forecast input parameters, and train the specificity of the magnetosphere-ionosphere coupling in each region. The experimental results show that the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of the proposed method is better than 1.262 Total Electronic Content Unit (TECU) in the middle latitude region during the geomagnetic lull period. The RMSE of 1-day forecast value is better than 1.094 TECU, and the RMSE of 7-day forecast value is better than 2.771 TECU during high solar activity years. The RMSE of the 7-day forecast value is better than 4.186 TECU and the RMSE of the 1-day forecast value is better than 4.115 TECU during the geomagnetic active period. In this paper, a prediction model with a 7-day lead is established, and the method shows good performance in forecasting accuracy and timeliness.
-
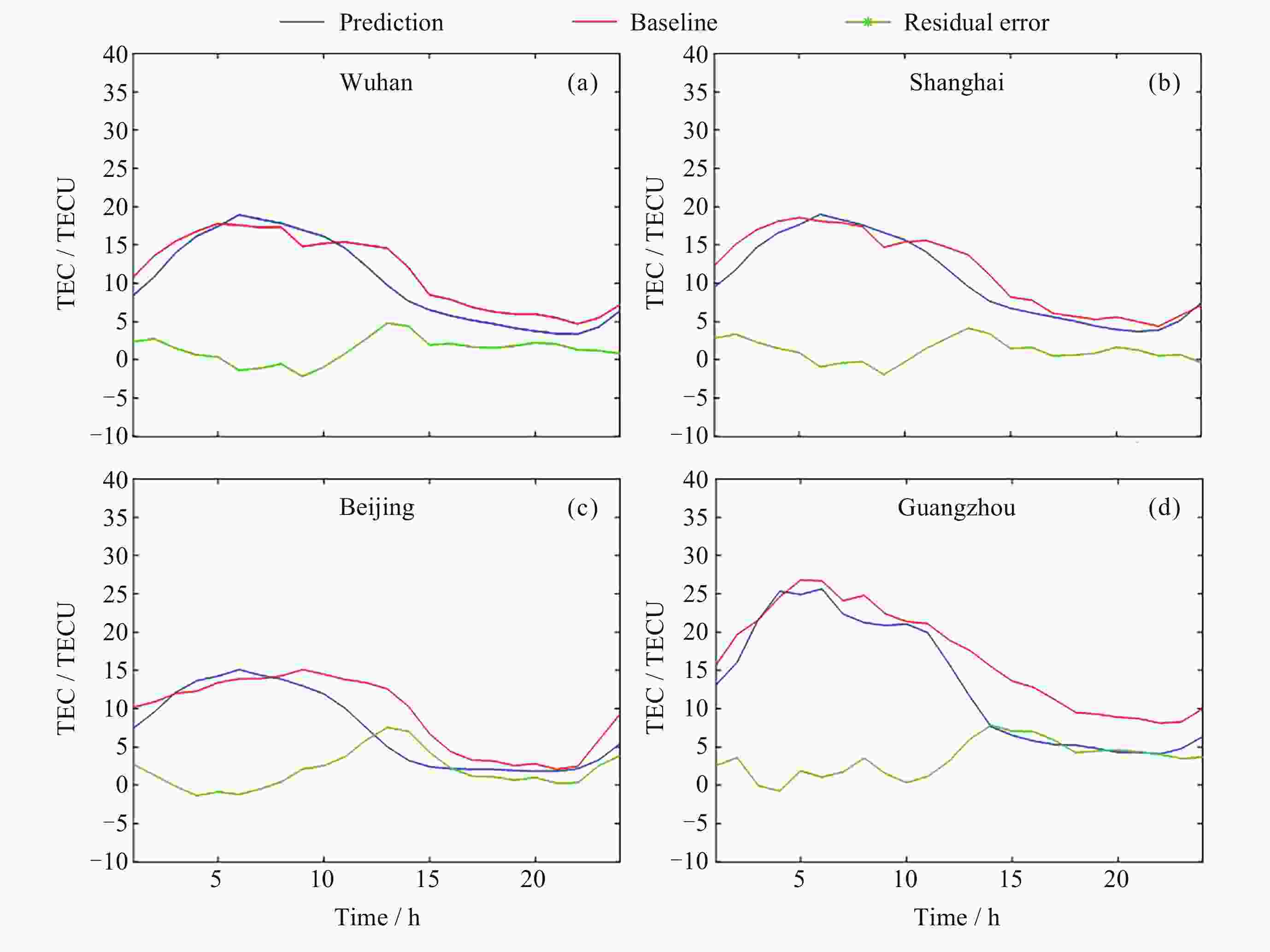
表 1 对武汉等4地TEC的各种预测方法结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of various prediction methods for TEC in Wuhan and other four regions
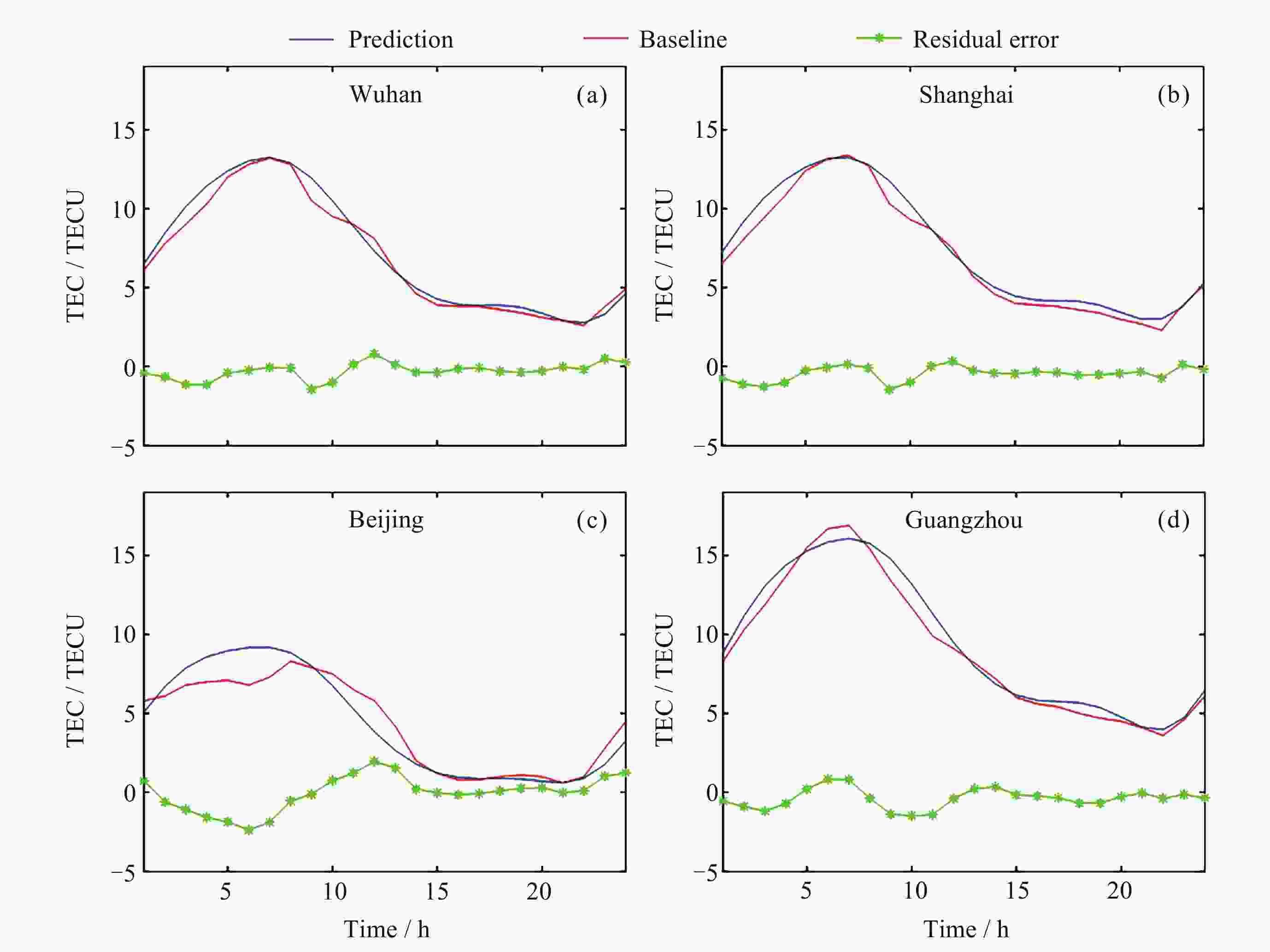
地区 方法 ρ RMSE/TECU MAE/TECU R2 武汉 本文算法 0.971 0.942 0.711 0.926 LSTM 0.843 1.936 1.458 0.724 IRI 2016 0.899 3.074 2.610 0.207 IGS预测 0.957 1.341 1.027 0.849 上海 本文算法 0.973 0.907 0.699 0.932 LSTM 0.710 2.906 1.999 0.302 IRI 2016 0.891 3.224 2.739 0.141 IGS预测 0.961 1.291 1.019 0.862 北京 本文算法 0.949 1.058 0.788 0.871 LSTM 0.968 1.243 1.082 0.820 IRI 2016 0.673 2.380 1.891 0.343 IGS预测 0.964 0.999 0.800 0.884 广州 本文算法 0.958 1.262 0.945 0.915 LSTM 0.919 2.801 2.331 0.578 IRI 2016 0.922 4.545 4.101 0 IGS预测 0.957 1.586 1.215 0.865 表 2 对武汉等4地TEC的各种预测方法结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of various prediction methods for TEC in Wuhan and other four regions
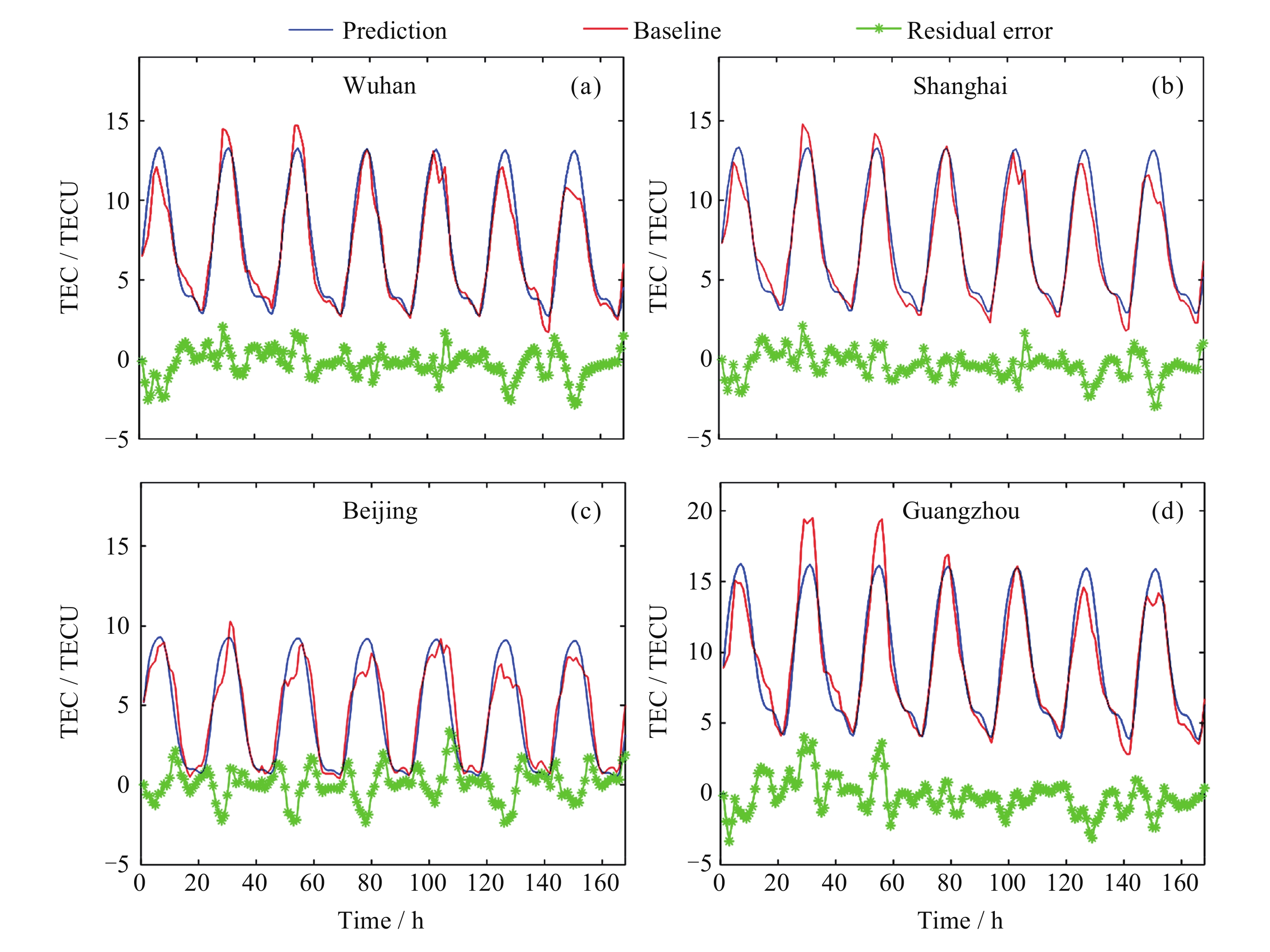
地区 方法 ρ RMSE/TECU MAE/TECU R2 武汉 本文算法 0.992 0.560 0.434 0.973 LSTM 0.758 2.096 1.724 0.419 IRI 2016 0.904 3.002 2.433 0.274 IGS预测 0.988 1.006 0.871 0.918 上海 本文算法 0.992 0.638 0.504 0.969 LSTM 0.906 1.717 1.266 0.618 IRI 2016 0.901 3.048 2.512 0.283 IGS预测 0.988 1.074 0.942 0.911 北京 本文算法 0.948 1.094 0.825 0.846 LSTM 0.876 2.278 1.862 0.370 IRI 2016 0.641 2.393 1.975 0.263 IGS预测 0.980 1.011 0.888 0.868 广州 本文算法 0.990 0.721 0.588 0.972 LSTM 0.895 3.106 2.349 0.174 IRI 2016 0.963 4.149 3.796 0.057 IGS预测 0.992 1.029 0.863 0.941 表 3 对武汉、上海、北京、广州四个地区TEC的各种预测方法结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of various prediction methods for TEC in Wuhan Shanghai Beijing and Guangzhou four regions
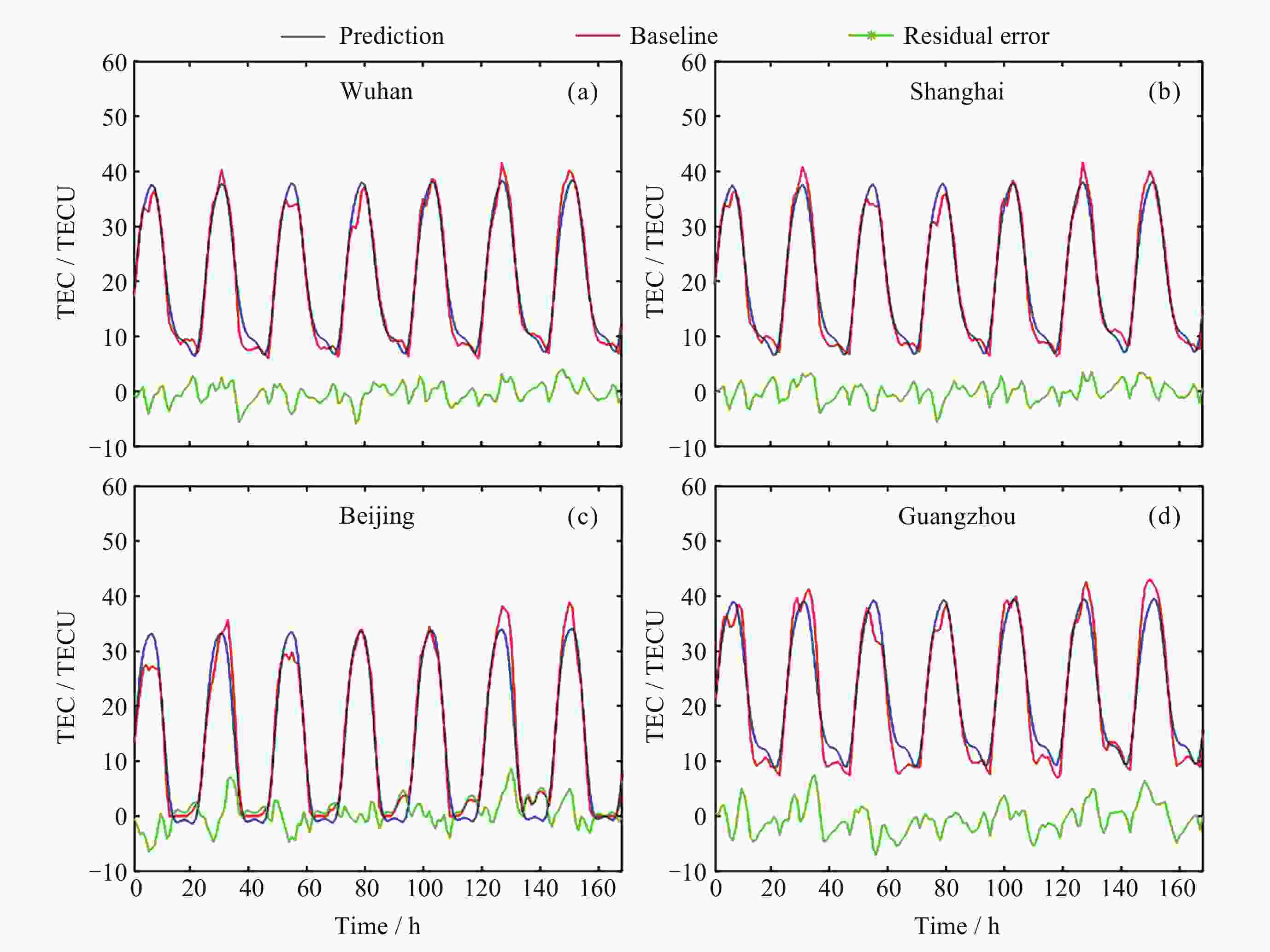
地区 方法 ρ RMSE/TECU MAE/TECU R2 武汉 本文算法 0.988 1.822 1.442 0.981 LSTM 0.899 5.466 3.803 0.779 IRI 2016 0.968 3.103 2.502 0.929 IGS预测 0.984 2.145 1.690 0.966 上海 本文算法 0.988 1.744 1.395 0.983 LSTM 0.808 7.603 5.458 0.558 IRI 2016 0.966 3.187 2.584 0.922 IGS预测 0.983 2.181 1.643 0.964 北京 本文算法 0.982 2.636 1.957 0.964 LSTM 0.837 9.957 6.761 0.434 IRI 2016 0.964 4.335 3.673 0.893 IGS预测 0.980 2.904 1.951 0.952 广州 本文算法 0.980 2.771 2.208 0.951 LSTM 0.913 7.718 6.972 0.660 IRI 2016 0.849 7.916 5.823 0.582 IGS预测 0.971 3.128 2.324 0.935 表 4 对武汉、上海、北京、广州四个地区TEC的各种预测方法结果对比
Table 4. Comparison of various prediction methods for TEC in Wuhan Shanghai Beijing and Guangzhou four regions
地区 方法 ρ RMSE/TECU MAE/TECU R2 武汉 本文算法 0.923 2.944 2.216 0.804 LSTM 0.793 4.816 3.921 0.473 IRI 2016 0.785 6.293 5.181 0.101 IGS预测 0.835 4.092 2.961 0.620 上海 本文算法 0.941 3.183 2.425 0.751 LSTM 0.673 5.612 4.221 0.113 IRI 2016 0.798 6.393 5.396 0 IGS预测 0.838 3.982 2.895 0.611 北京 本文算法 0.879 3.700 2.924 0.491 LSTM 0.820 4.773 3.852 0 IRI 2016 0.721 4.690 3.644 0.182 IGS预测 0.884 2.531 1.863 0.761 广州 本文算法 0.912 4.186 3.448 0.751 LSTM 0.529 16.553 14.937 0 IRI 2016 0.835 8.043 6.772 0.078 IGS预测 0.884 2.530 1.863 0.884 表 5 对武汉、上海、北京、广州四个地区TEC的各种预测方法结果对比
Table 5. Comparison of various prediction methods for TEC in Wuhan Shanghai Beijing and Guangzhou four regions
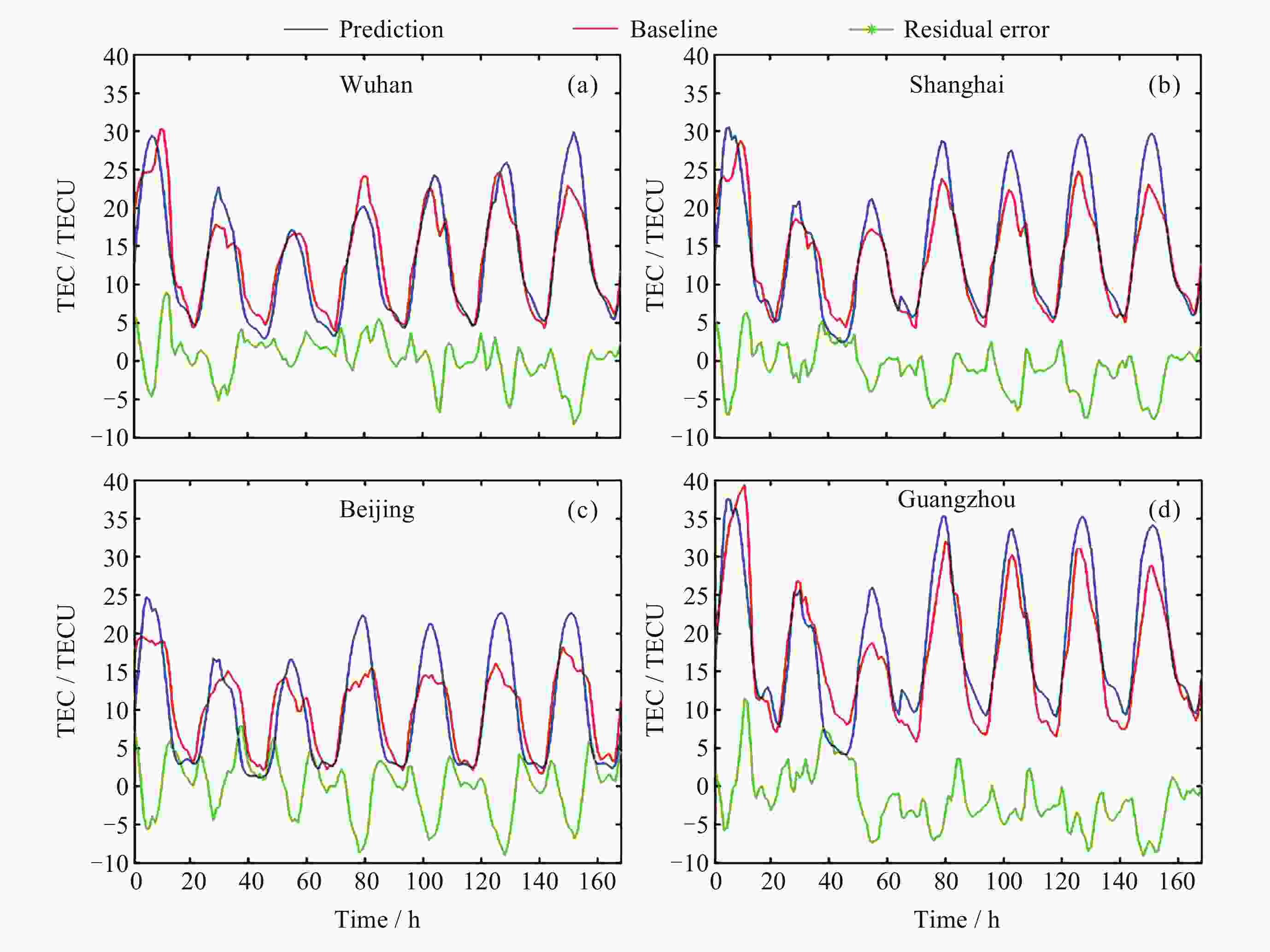
地区 方法 ρ RMSE/TECU MAE/TECU R2 武汉 本文算法 0.966 1.911 1.610 0.832 LSTM 0.034 9.125 6.970 0 IRI 2016 0.887 6.761 5.533 0 IGS预测 0.966 5.408 4.538 0 上海 本文算法 0.962 1.861 1.507 0.866 LSTM 0.134 5.215 4.231 0.153 IRI 2016 0.899 6.768 5.413 0 IGS预测 0.945 5.337 4.592 0 北京 本文算法 0.878 3.091 2.292 0.554 LSTM 0.413 7.553 6.023 0 IRI 2016 0.688 4.926 4.038 0 IGS预测 0.981 2.256 1.850 0.762 广州 本文算法 0.975 4.115 3.506 0.583 LSTM 0.527 15.184 13.535 0 IRI 2016 0.957 8.480 7.354 0 IGS预测 0.980 2.255 1.85 0.762 -
[1] YUAN Tianjiao, CHEN Yanhong, LIU Siqing, et al. Prediction model for ionospheric total electron content based on deep learning recurrent neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(1): 48-57 (袁天娇, 陈艳红, 刘四清, 等. 基于深度学习递归神经网络的电离层总电子含量经验预报模型[J]. 空间科学学报, 2018, 38(1): 48-57 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.048YUAN Tianjiao, CHEN Yanhong, LIU Siqing, et al. Prediction model for ionospheric total electron content based on deep learning recurrent neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(1): 48-57 doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.048 [2] ZHAI Dulin, ZHANG Xuemin, XIONG Pan, et al. Detection of ionospheric TEC anomalies based on Prophet Time-series Forecasting Model[J]. Earthquake, 2019, 39(2): 46-62 (翟笃林, 张学民, 熊攀, 等. Prophet 时序预测模型在电离层TEC异常探测中的应用[J]. 地震, 2019, 39(2): 46-62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2019.02.006ZHAI Dulin, ZHANG Xuemin, XIONG Pan, et al. Detection of ionospheric TEC anomalies based on Prophet Time-series Forecasting Model[J]. Earthquake, 2019, 39(2): 46-62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2019.02.006 [3] CHEN Yanhong, WAN Weixing, LIU Libo, et al. A statistical tec model based on the observation at Wuhan ionospheric observatory[J]. Earthquake, 2002, 22(1): 27-35 (陈艳红, 万卫星, 刘立波, 等. 武汉地区电离层电子浓度总含量的统计经验模式研究[J]. 空间科学学报, 2002, 22(1): 27-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2002.01.005CHEN Yanhong, WAN Weixing, LIU Libo, et al. A statistical tec model based on the observation at Wuhan ionospheric observatory[J]. Earthquake, 2002, 22(1): 27-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6124.2002.01.005 [4] TANG Siyu, HUANG Zhi. Prediction of ionospheric total electron content based on causal convolutional and LSTM network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 (唐丝语, 黄智. 基于因果卷积与LSTM网络的电离层总电子含量预报[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210401042TANG Siyu, HUANG Zhi. Prediction of ionospheric total electron content based on causal convolutional and LSTM network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(3): 357-365 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210401042 [5] XIONG Bo, LI Xiaolin, WANG Yuqing, et al. Prediction of ionospheric TEC over China based on long and short-term memory neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(7): 2365-2377 (熊波, 李肖霖, 王宇晴, 等. 基于长短时记忆神经网络的中国地区电离层TEC预测[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(7): 2365-2377 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0557XIONG Bo, LI Xiaolin, WANG Yuqing, et al. Prediction of ionospheric TEC over China based on long and short-term memory neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(7): 2365-2377 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0557 [6] HUANG Z, YUAN H. Ionospheric single-station TEC short-term forecast using RBF neural network[J]. Radio Science, 2014, 49(4): 283-292 doi: 10.1002/2013RS005247 [7] TANG Jun, GAO Xin. Prediction models of ionospheric TEC by Elman neural network with Bayesian regularization[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2020, 40(8): 799-805 (汤俊, 高鑫. 贝叶斯正则化的Elman神经网络电离层TEC预报模型[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2020, 40(8): 799-805TANG Jun, GAO Xin. Prediction models of ionospheric TEC by Elman neural network with Bayesian regularization[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2020, 40(8): 799-805 [8] WEN Z C, LI S H, LI L H, et al. Ionospheric TEC prediction using Long Short-Term Memory deep learning network[J]. Astrophysics and Space Science, 2021, 366(1): 3 doi: 10.1007/s10509-020-03907-1 [9] RUWALI A, KUMAR A J S, PRAKASH K B, et al. Implementation of hybrid deep learning model (LSTM-CNN) for ionospheric TEC forecasting using GPS data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(6): 1004-1008 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2992633 [10] SRIVANI I, PRASAD G S V, RATNAM D V. A deep learning-based approach to forecast ionospheric delays for GPS signals[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(8): 1180-1184 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2895112 [11] Shaikh M M, Butt R A, Khawaja A. Forecasting Total Electron Content (TEC) using CEEMDAN LSTM model[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 71(10): 4361-4373 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.12.054 [12] KASELIMI M, VOULODIMOS A, DOULAMIS N, et al. A causal long short-term memory sequence to sequence model for TEC prediction using GNSS observations[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(9): 1354 doi: 10.3390/rs12091354 [13] LIU Lilong, CHEN Yutian, LI Junyu, et al. Short-term prediction and applicability analysis of regional ionospheric total electron content in active period[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(12): 1757-1764 (刘立龙, 陈雨田, 黎峻宇, 等. 活跃期区域电离层总电子短期预报及适用性分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(12): 1757-1764LIU Lilong, CHEN Yutian, LI Junyu, et al. Short-term prediction and applicability analysis of regional ionospheric total electron content in active period[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(12): 1757-1764 [14] SONG R, ZHANG X M, ZHOU C, et al. Predicting TEC in China based on the neural networks optimized by genetic algorithm[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2018, 62(4): 745-759 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2018.03.043 [15] PEREZ R O. Using tensor flow-based neural network to estimate GNSS single frequency ionospheric delay (IONONet)[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2019, 63(5): 1607-1618 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2018.11.011 [16] CHEN Z, JIN M W, DENG Y, et al. Improvement of a deep learning algorithm for total electron content maps: Image completion[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2019, 124(1): 790-800 doi: 10.1029/2018JA026167 [17] LIAO Zhanghui, WU Beiping, SHEN Xinglin, et al. Analysis of ionospheric VTEC temporal-spatial characteristics in Guangxi and surrounding[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2018, 43(9): 40-45,62 (廖章回, 吴北平, 申兴林, 等. 广西及周边地区电离层时空特性分析[J]. 测绘科学, 2018, 43(9): 40-45,62LIAO Zhanghui, WU Beiping, SHEN Xinglin, et al. Analysis of ionospheric VTEC temporal-spatial characteristics in Guangxi and surrounding[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2018, 43(9): 40-45,62 [18] JI Changdong, WANG Qiang, WANG Guipeng, et al. TEC prediction of ionosphere based on deep learning LSTM model[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2019, 7(3): 76-81 (吉长东, 王强, 王贵朋, 等. 深度学习 LSTM 模型的电离层总电子含量预报[J]. 导航定位学报, 2019, 7(3): 76-81 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2019.03.013JI Changdong, WANG Qiang, WANG Guipeng, et al. TEC prediction of ionosphere based on deep learning LSTM model[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2019, 7(3): 76-81 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2019.03.013 [19] TAYLOR S J, LETHAM B. Forecasting at scale[J]. The American Statistician, 2018, 72(1): 37-45 doi: 10.1080/00031305.2017.1380080 [20] QUAN Lin, XUE Junchen, HU Xiaogong, et al. Performance of GPS single frequency standard point positioning in China during the main phase of different classified geomagnetic storms[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(9): 3030-3047 (全林, 薛军琛, 胡小工, 等. 中国区域 GPS 单频点定位在不同类型磁暴主相期间定位性能分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(9): 3030-3047 doi: 10.6038/cjg2021P0331QUAN Lin, XUE Junchen, HU Xiaogong, et al. Performance of GPS single frequency standard point positioning in China during the main phase of different classified geomagnetic storms[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(9): 3030-3047 doi: 10.6038/cjg2021P0331 [21] HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780 doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 -
-




 王帅 男, 1991年出生于湖北省襄阳市, 现为航天工程大学航天信息学院讲师, 主要研究方向为电离层探测与分析预报、空间环境探测设备设计等. E-mail:
王帅 男, 1991年出生于湖北省襄阳市, 现为航天工程大学航天信息学院讲师, 主要研究方向为电离层探测与分析预报、空间环境探测设备设计等. E-mail: 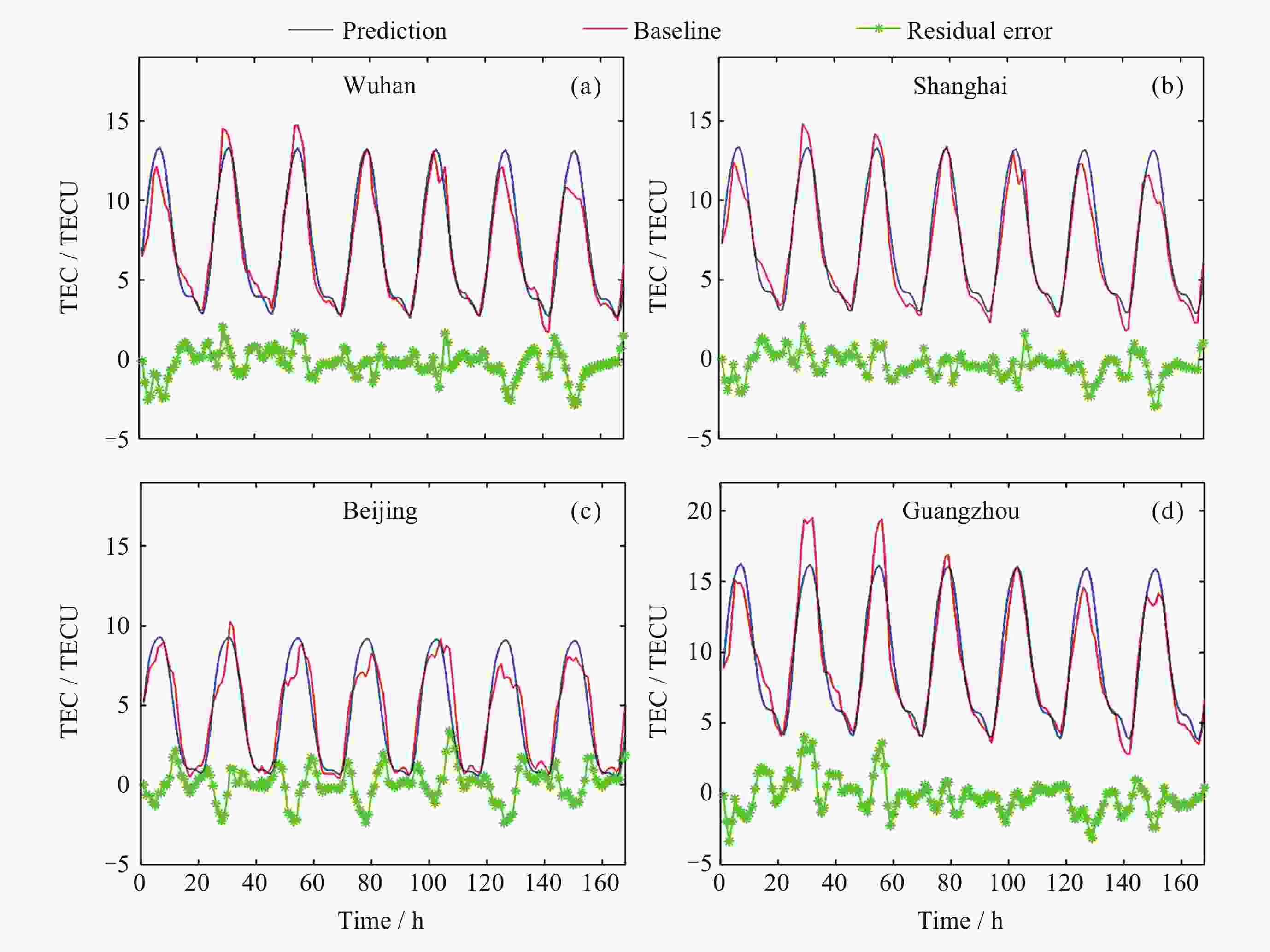
 下载:
下载: