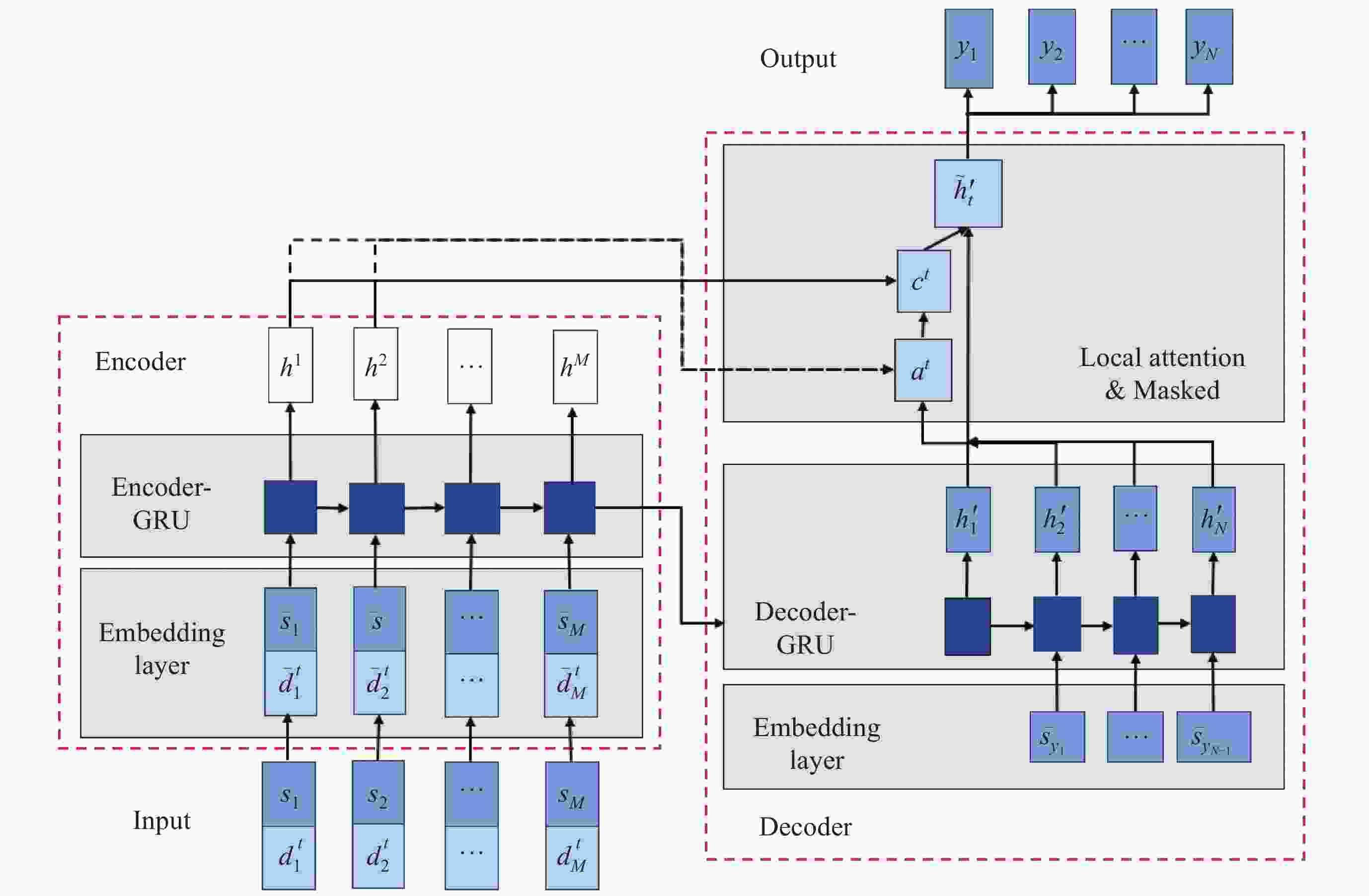
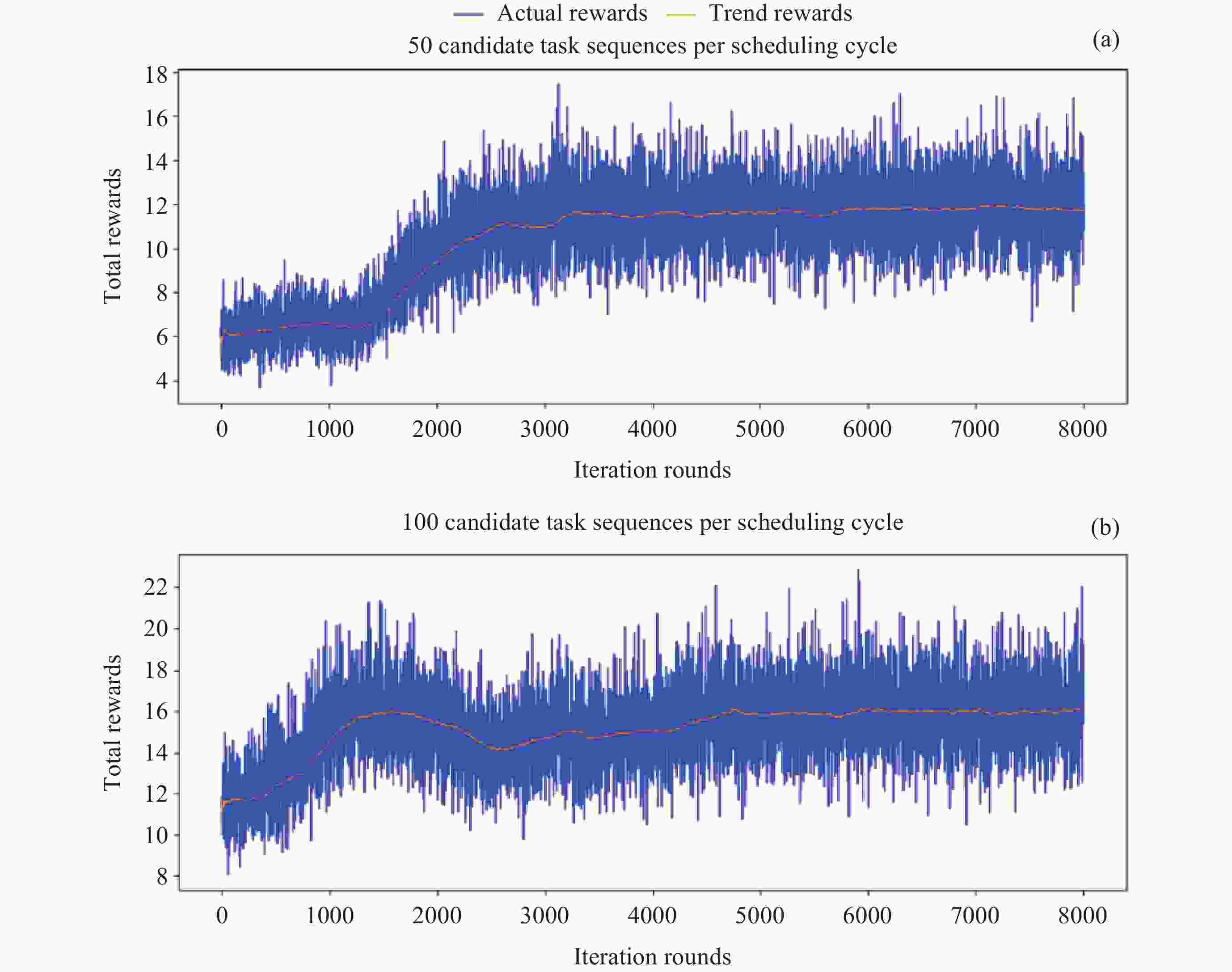
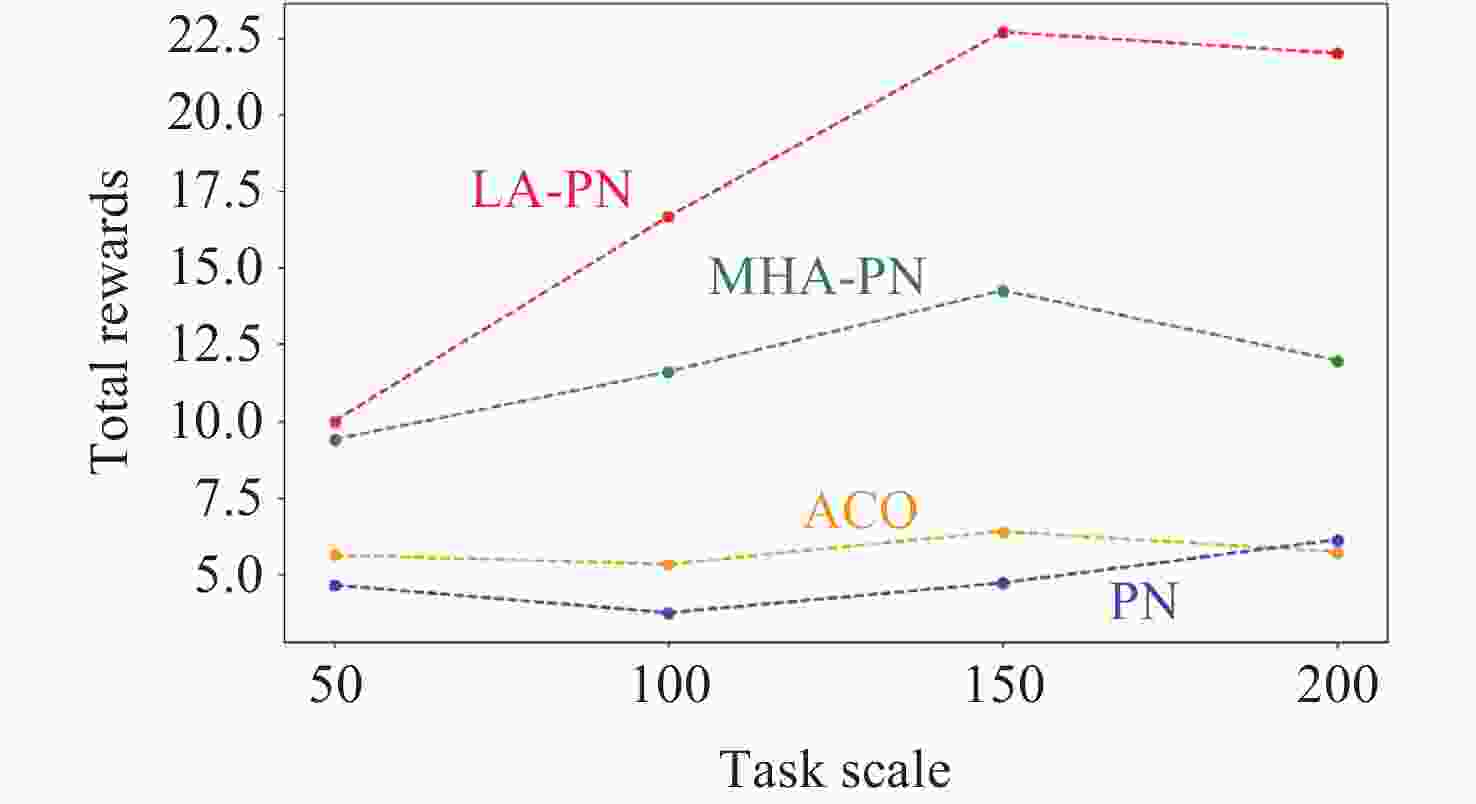
Scheduling Methods for Astronomical Satellite Target of Opportunity Tasks with High-frequency Dynamic Arrivals
-
摘要: 以巡天设备每天将探测到数以万计的变源天体以及对变源天体的观测需求增长为背景, 形成了由高频动态到达的机遇目标(ToO)及其后随观测任务组成的长序列任务规划问题. 该问题具有观测事件随机性、数据获取高时效性、可选择性多和约束复杂的特点, 常被视为NP (非确定性多项式)难题, 因此获取监督学习的标签数据不易. 而针对采用无监督学习的深度强化学习(DRL)方法求解长序列任务规划问题时, 卫星作为智能体难以快速收敛至全局最优策略. 为此本文借鉴局部注意力(LA)机制的思想对指针网络(PN)进行改进, 提出局部注意力指针网络(LA-PN)算法. 该算法通过引入时间窗口的方式, 使模型专注于对当前决策有重要影响的序列部分, 减少了无效探索. 通过仿真结果对比分析, 验证算法的收益性、实时性和泛化性.Abstract: Based on the background where sky survey equipment detects tens of thousands of variable sources daily and the demand for observing these variable sources increases, a long-sequence task planning problem is formed. This problem comprises dynamically arriving high-frequency Targets of Opportunity (ToO) and their subsequent follow-up observation tasks. This type of problem is classified as an NP hard problem due to the randomness of observation events, strong timeliness of data acquisition, high selectivity of decision paths, and the coupling effect of complex constraints such as Earth occlusion and observation time windows. Traditional supervised learning methods are difficult to apply due to the difficulty in obtaining high-quality labeled data, while Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) combines the perceptual ability of deep learning with the sequential decision optimization mechanism of reinforcement learning to construct end-to-end autonomous decision-making agents, demonstrating the universal advantage of handling complex planning problems. This article is based on the DRL framework and constructs a Markov Decision Process (MDP) model for long sequence task planning problems. State space encoding, action space encoding, and reward functions are defined in the task planning problem to guide reinforcement learning algorithms to converge towards optimizing the target set. However, classical DRL methods have significant limitations in unsupervised learning mode - when faced with long sequence dynamic task flows, agents have difficulty quickly converging to the global optimal strategy due to the large exploration space, and lack sensitivity to local key tasks. Therefore, this paper improves the Pointer Network (PN) by drawing on the concept of the Local Attention (LA) mechanism, proposing the Local Attention Pointer Network (LA-PN) algorithm. This algorithm innovatively introduces a sliding time window constraint on the attention range, allowing the model to dynamically focus on task subsequences related to the current decision, and filter high-value targets through local context awareness to reduce redundant computation. By comparing and analyzing simulation results, verify the profitability, real-time performance, and generalization of the algorithm.
-
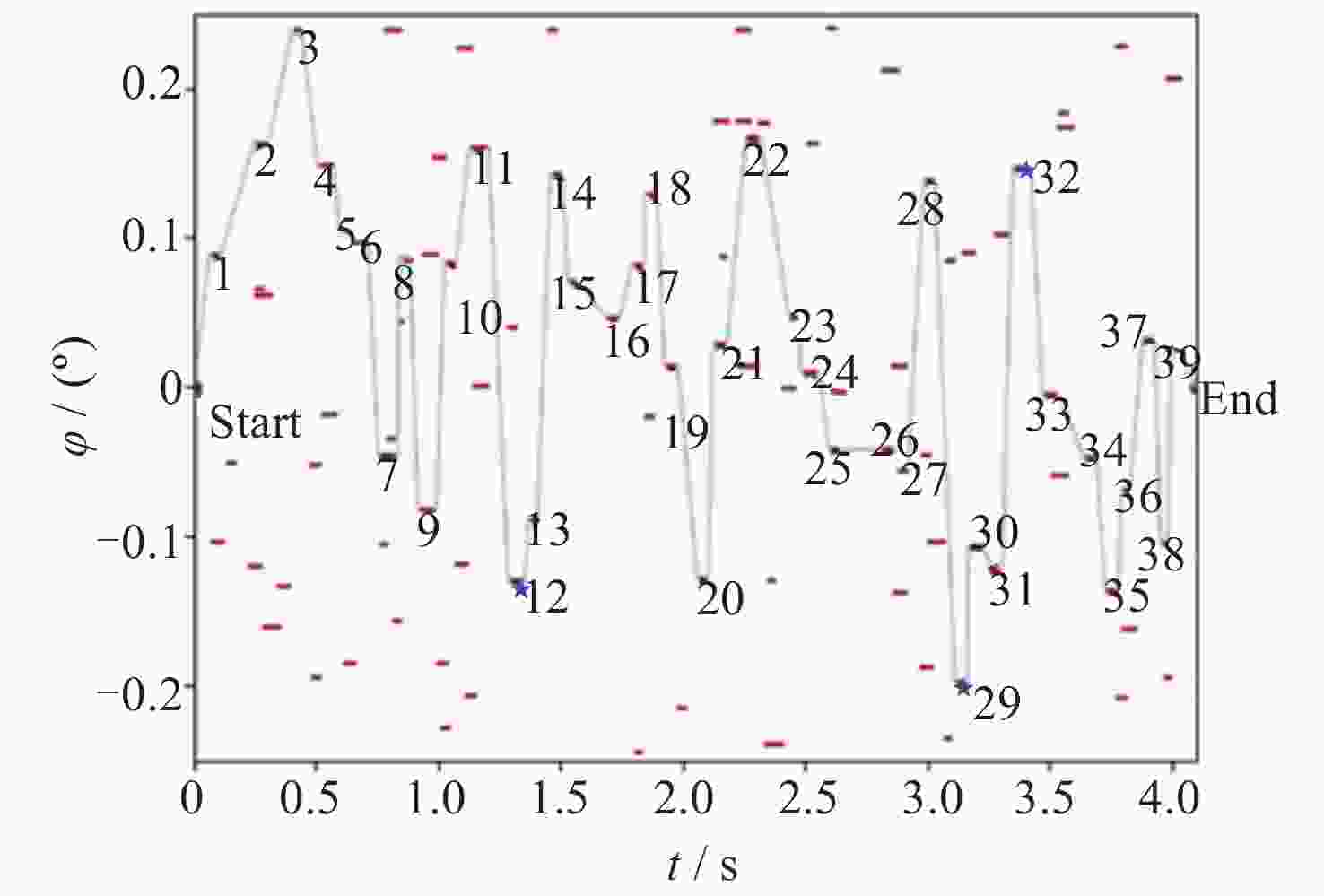
图 4 模型的推理结果 (红色点表示观测任务时间窗口, 编号表示规划结果任务执行顺序, 蓝色五星表示执行任务前需要调姿)
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of the inference results of the model (Red dots represent the time window of observation tasks, numbers represent the sequence of planned result tasks execution, and blue stars represent the need for attitude adjustment before task execution)
表 1 卫星轨道参数
Table 1. Satellite orbit parameters
参数 取值 轨道高度/km 7012.2172 偏心率 0.0002961 轨道倾角/(°) 28.863529 升交点赤经/(°) 287.41907 近地点幅角/(°) 299.01349 平近点角/(°) 292.49033 表 2 LA-PN算法训练参数设定
Table 2. LA-PN algorithm training parameter settings
参数名 参数值 含义 Batch_size 128 批样本数量 D 5 滑动窗口大小 lr_actor $ 1\times {10}^{-5} $ Actor网络的学习率 lr_critic $ 5\times {10}^{-4} $ Critic网络的学习率 hidden_size 512 隐含层维度 表 3 数据集中每个任务的元素设定
Table 3. Element settings for each task in dataset
元素 设定 $ {T}^{\mathrm{w}\mathrm{s}} $ [0 s, 4000 s] D [600 s, 700 s] $ {T}^{\mathrm{w}\mathrm{e}} $ [$ {T}^{\mathrm{w}\mathrm{s}} $+700 s, $ {T}^{\mathrm{w}\mathrm{s}} $+800 s] A [$ -{5}^\circ ,{5}^\circ $] P [0.1, 0.9] 表 4 周期内算法平均执行时间对比
Table 4. Comparison of average execution time of algorithms within a cycle
算法 $ T/(\mathrm{s} \cdot {\mathrm{e}\mathrm{p}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{h}}^{-1}) $ $ {R}_{\mathrm{r}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{e}}/(\mathrm{\%}) $ LA-PN 0.396318 — PN 0.308217 273.83 MHA-PN 0.297375 37.21 ACO 13.027278 192.80 -
[1] LI Dalin. Research on Observation Scheduling Model and Method of Astronomy Satellite[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020 (李大林. 天文观测卫星任务规划模型与方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020LI Dalin. Research on Observation Scheduling Model and Method of Astronomy Satellite[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020 [2] XU Ziling, LIU Yurong, FENG Zhun. Mission planning for astronomical satellite based on genetic algorithm under tiling coverage strategy[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(2): 321-328 (徐子羚, 刘玉荣, 冯准. 基于遗传算法的Tiling覆盖策略天文卫星任务规划[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(2): 321-328 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.02.210112006XU Ziling, LIU Yurong, FENG Zhun. Mission planning for astronomical satellite based on genetic algorithm under tiling coverage strategy[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(2): 321-328 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.02.210112006 [3] XIANG Shang, CHEN Yinguo, LI Guoliang, et al. Review on satellite autonomous and collaborative task scheduling planning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(2): 252-264 (向尚, 陈盈果, 李国梁, 等. 卫星自主与协同任务调度规划综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(2): 252-264XIANG Shang, CHEN Yinguo, LI Guoliang, et al. Review on satellite autonomous and collaborative task scheduling planning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(2): 252-264 [4] WU Haiyan, MENG Xin, ZHANG Yuzhu, et al. Research on the planning method for astronomy observation mission[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2013, 33(5): 561-568 (吴海燕, 孟新, 张玉珠, 等. 面向天文观测的空间科学卫星任务规划方法研究[J]. 空间科学学报, 2013, 33(5): 561-568 doi: 10.11728/cjss2013.05.561WU Haiyan, MENG Xin, ZHANG Yuzhu, et al. Research on the planning method for astronomy observation mission[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2013, 33(5): 561-568 doi: 10.11728/cjss2013.05.561 [5] HUANG Yue, QU Jinlu, JIA Shumei, et al. Long-term planning algorithm for the HXMT mission[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2017, 37(6): 766-772 (黄跃, 屈进禄, 贾淑梅, 等. HXMT卫星长期任务规划算法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2017, 37(6): 766-772 doi: 10.11728/cjss2017.06.766HUANG Yue, QU Jinlu, JIA Shumei, et al. Long-term planning algorithm for the HXMT mission[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2017, 37(6): 766-772 doi: 10.11728/cjss2017.06.766 [6] YIN Xiaodan, BAI Meng, LI Zhuoheng. Clustering-scheduling methods for oversubscribed short-term tasks of astronomical satellites[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 40(3): 307-322 (尹晓丹, 白萌, 李卓恒. 超额订购下天文卫星短期任务的聚类规划方法[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报(英文版), 2023, 40(3): 307-322YIN Xiaodan, BAI Meng, LI Zhuoheng. Clustering-scheduling methods for oversubscribed short-term tasks of astronomical satellites[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 40(3): 307-322 [7] WANG Haijiao. Massive Scheduling Method Under Online Situation for Satellites Based on Reinforcement Learning[D]. Beijing: National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018 (王海蛟. 基于强化学习的卫星规模化在线调度方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院国家空间科学中心), 2018WANG Haijiao. Massive Scheduling Method Under Online Situation for Satellites Based on Reinforcement Learning[D]. Beijing: National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018 [8] MA Yifan. Agile Imaging Satellite Task Planning Method Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2021 (马一凡. 基于深度强化学习的敏捷成像卫星任务规划方法[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2021MA Yifan. Agile Imaging Satellite Task Planning Method Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2021 [9] ZHAO Shijie. Research and Implementation of Satellite Autonomous Task Planning Method Based on Reinforcement Learning[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2024 (赵世杰. 基于强化学习的卫星自主任务规划方法研究与实现[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2024ZHAO Shijie. Research and Implementation of Satellite Autonomous Task Planning Method Based on Reinforcement Learning[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2024 [10] LIU Xiaolu, XU Yingjie, HE Renjie, et al. Satellite-oriented on-orbit service mission planning method[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2020, 42(5): 143-150 (刘晓路, 许英杰, 贺仁杰, 等. 面向卫星的在轨服务任务规划方法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2020, 42(5): 143-150 doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202005020LIU Xiaolu, XU Yingjie, HE Renjie, et al. Satellite-oriented on-orbit service mission planning method[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2020, 42(5): 143-150 doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202005020 [11] ZENG Erkang, WU Haiyan, FENG Zhun. Sky area target of opportunity mission planning method[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(2): 361-368 (曾而康, 吴海燕, 冯准. 天区机遇目标空间探测任务规划算法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(2): 361-368 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.02.220225020ZENG Erkang, WU Haiyan, FENG Zhun. Sky area target of opportunity mission planning method[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(2): 361-368 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.02.220225020 [12] CHUNG J, GULCEHRE C, CHO K, et al. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.3555, 2014 [13] LUONG T, PHAM H, MANNING C D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Lisbon: ACL, 2015 [14] BELLO I, PHAM H, LE Q V, et al. Neural combinatorial optimization with reinforcement learning[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon: OpenReview. net, 2017 [15] ZHAO Fanyu. Mission Scheduling and Planning of Multi-Target Observations for Spacecraft[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015 (赵凡宇. 航天器多目标观测任务调度与规划方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2015ZHAO Fanyu. Mission Scheduling and Planning of Multi-Target Observations for Spacecraft[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015 -
-





 王旭航 女, 1999年2月出生于河北省石家庄市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心研究生, 主要从事卫星智能运控等方面的研究. E-mail:
王旭航 女, 1999年2月出生于河北省石家庄市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心研究生, 主要从事卫星智能运控等方面的研究. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: