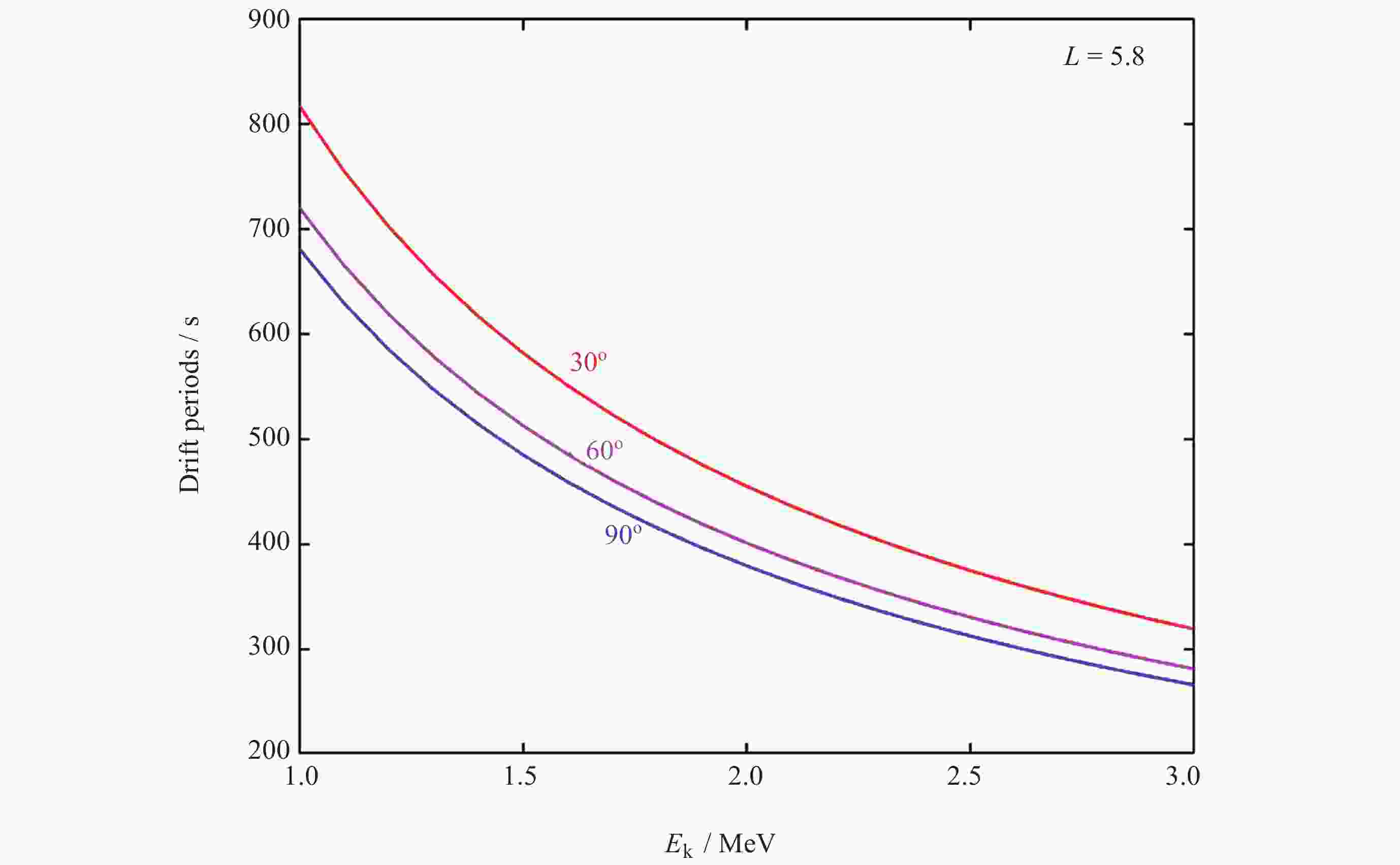
Rapid Evolution of the Relativistic Electron Pitch Angle Distributions Caused by Chorus in the Earth’s Outer Radiation Belt
-
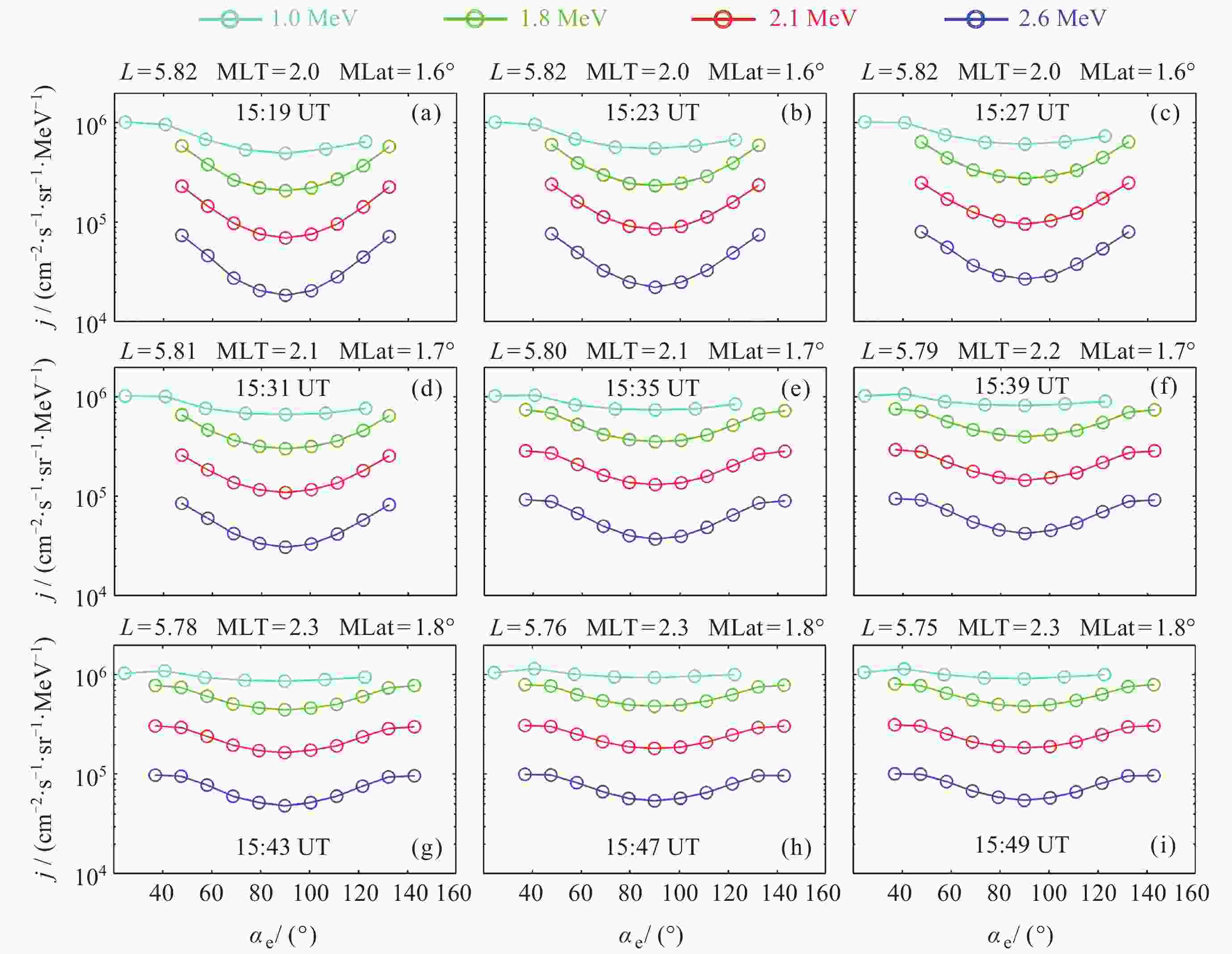
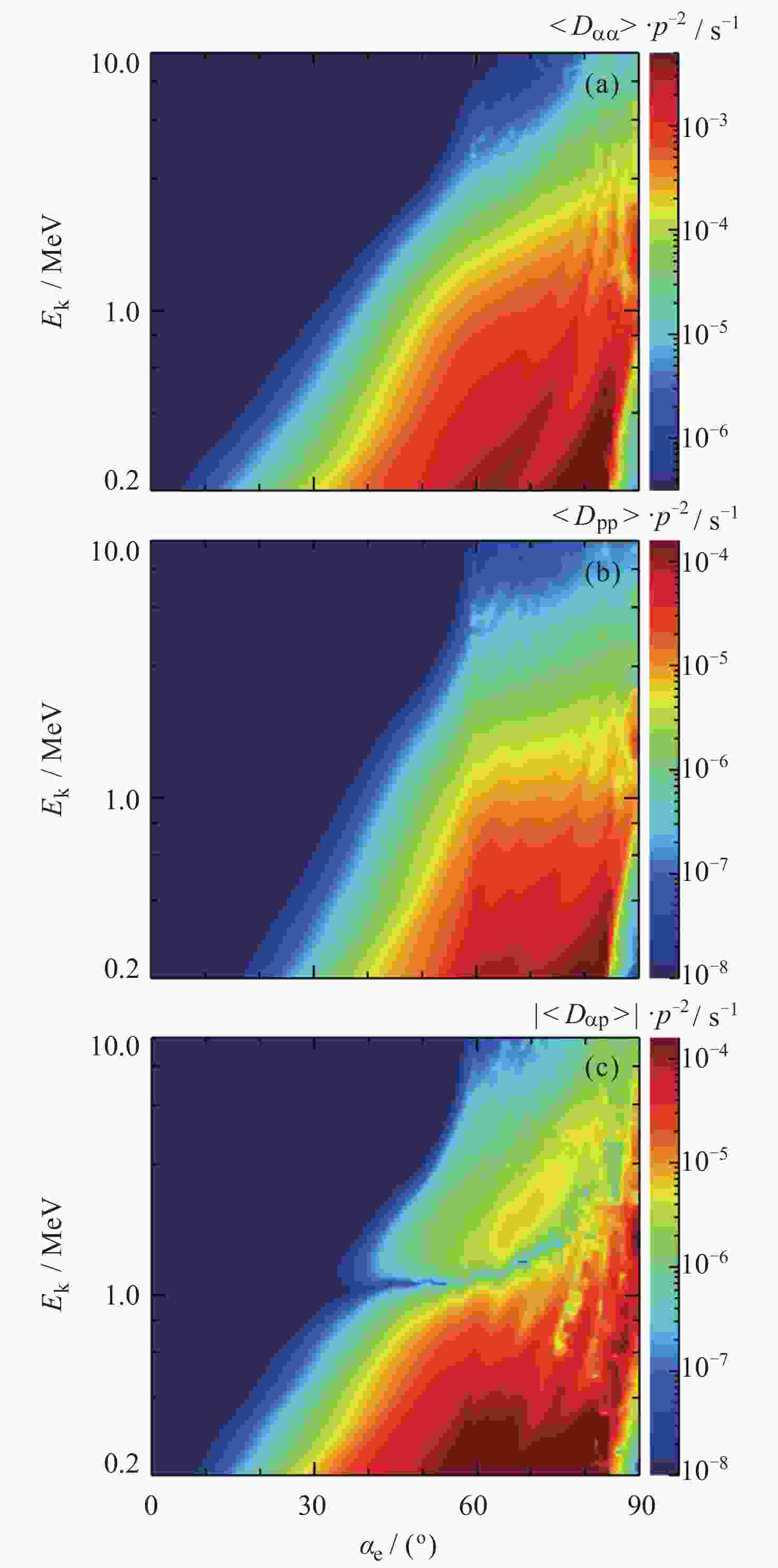
摘要: 投掷角是带电粒子运动方向与背景磁场的夹角, 研究电子投掷角分布对于理解地球辐射带动力学演化具有重要意义. 本文利用范艾伦探针数据, 对2016年9月7日15:19-15:49 UT期间发生的一次外辐射带相对论电子投掷角分布演化事例进行了详细分析. 卫星在此期间运行于远地点附近, 轨道速度较慢, 空间位置变化很小, 基本保持在L≈5.8, MLT≈2, Mlat≈1.7° 附近, 因此可以忽略位置变化对观测结果的影响. 卫星数据显示相对论电子的投掷角分布在30 min内从蝴蝶型分布逐步转变为平顶型分布, 且该区域存在强的哨声模合声波. 数值模拟结果表明哨声模合声波对高能电子的扩散作用是导致该事件中电子投掷角分布转变的主要物理机制. 本文研究进一步证明了合声波对于辐射带演化的重要意义.Abstract: The pitch angle, defined as the angle between a charged particle’s velocity vector and the ambient magnetic field, is a key parameter that governs the particle’s motion within the magnetic field. In Earth’s outer radiation belt, energetic electrons display diverse Pitch Angle Distribution (PAD) patterns. These patterns are influenced by various factors and frequently undergo changes, typically occurring over timescales ranging from several hours to several days. Investigating electron PAD variations and uncovering the underlying physical mechanisms are of significant importance for understanding the dynamic evolution of the Earth’s outer radiation belt. This paper utilizes Van Allen Probe-B data to conduct a detailed analysis of the evolution of relativistic electron PADs in the outer radiation belt during an event that occurred from 15:19 UT to 15:49 UT on 7 September 2016. During this period, the satellite was operating near its apogee, with a slow orbital speed and minimal changes in spatial position, remaining approximately at the location L≈5.8, MLT≈2 and Mlat≈1.7°. As a result, the impact of positional changes on the observational results can be considered negligible. Satellite observations revealed that relativistic (Ek ≥ 1 MeV) electron PADs transitioned from butterfly patterns to flat-top patterns during this period, within a timescale of only 30 minutes, which is significantly shorter than previously reported cases. Concurrently, intense whistler-mode chorus waves were detected in this region. Based on observational data, we calculated the chorus-driven diffusion coefficients of relativistic electrons. We then simulated the evolution of electron PADs by solving a Fokker-Planck equation. The simulation results indicate that the diffusion driven by whistler-mode chorus waves is the primary physical mechanism responsible for the transformation of the electron PADs during this event. The research presented in this paper further demonstrates the significant role of chorus waves in the evolution of the radiation belts.
-
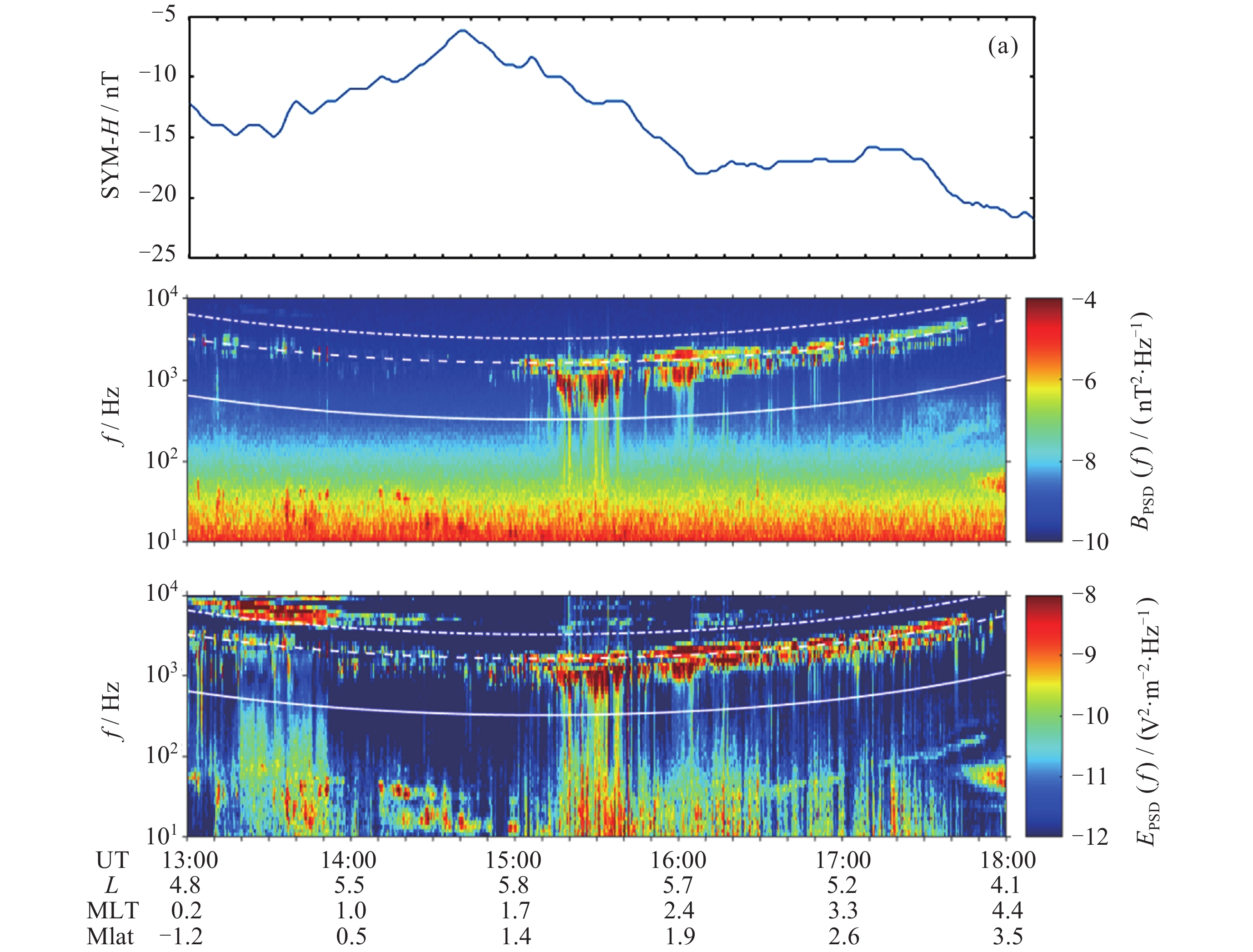
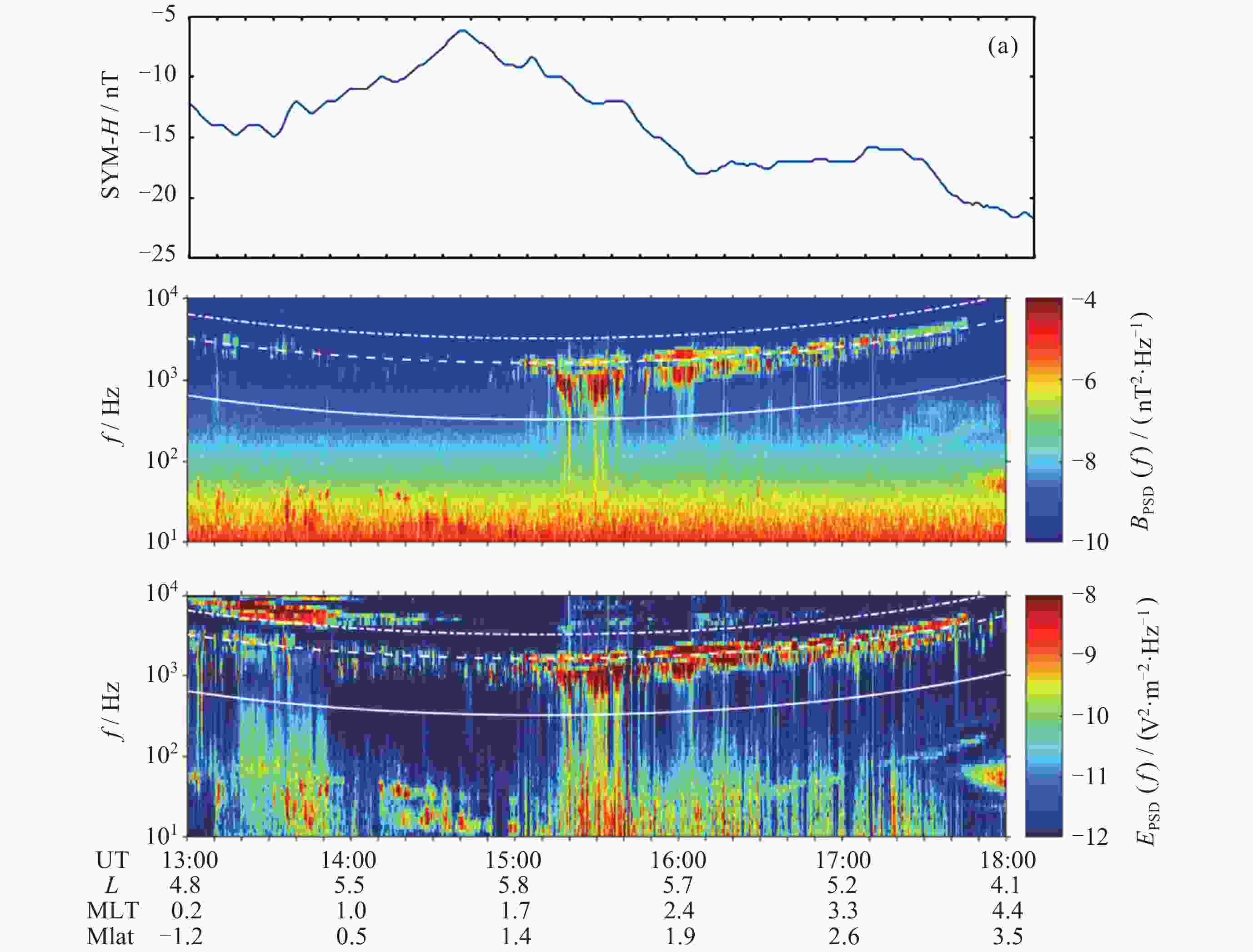
图 1 地磁活动指数SYM-H (a), 2016年9月7日由Probe-B上的EMFISIS测量的磁场谱(b)和电场谱(c). (b)(c)中的点划线、虚线和白色实线分别表示电子回旋频率1.0 fce, 0.5 fce和0.1 fce
Figure 1. Geomagnetic activity index SYM-H (a). The magnetic field spectrum (b) and electric field spectrum (c), where the dot-dashed, dashed and solid white lines in both panels represent 1.0 fce, 0.5 fce and 0.1 fce respectively
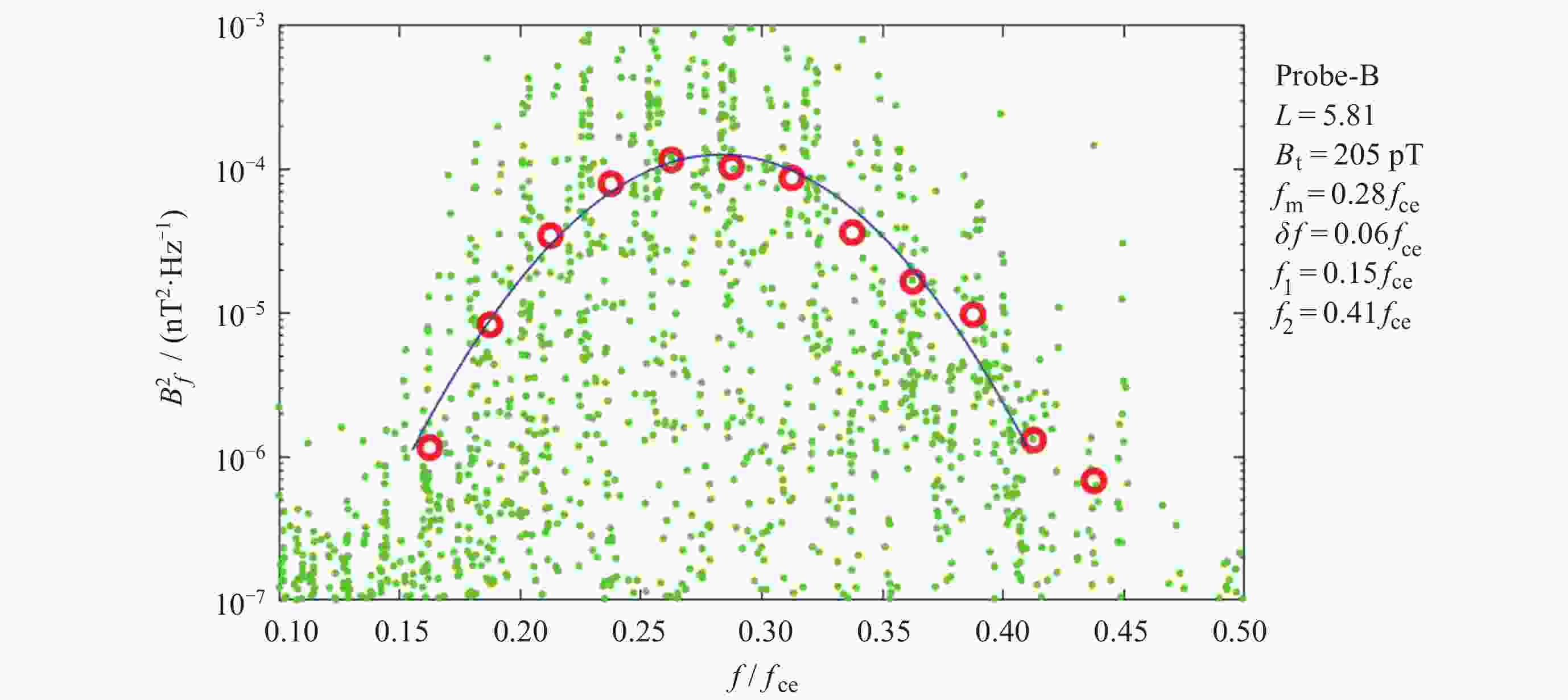
图 3 2016年9月7日15:19-15:49 UT期间观测波磁场谱的高斯拟合 (绿色点表示观测到的波谱, 红色圆圈表示这个频率区间内波谱密度的平均值, 蓝线表示高斯拟合结果)
Figure 3. Gaussian fitting of the magnetic field spectrum of the observed waves during 15:19-15:39 UT on 7 September 2016 (The green dots represent the observed wave spectra, the red circles denote the averaged spectra over each period and the blue lines show the fitting results)
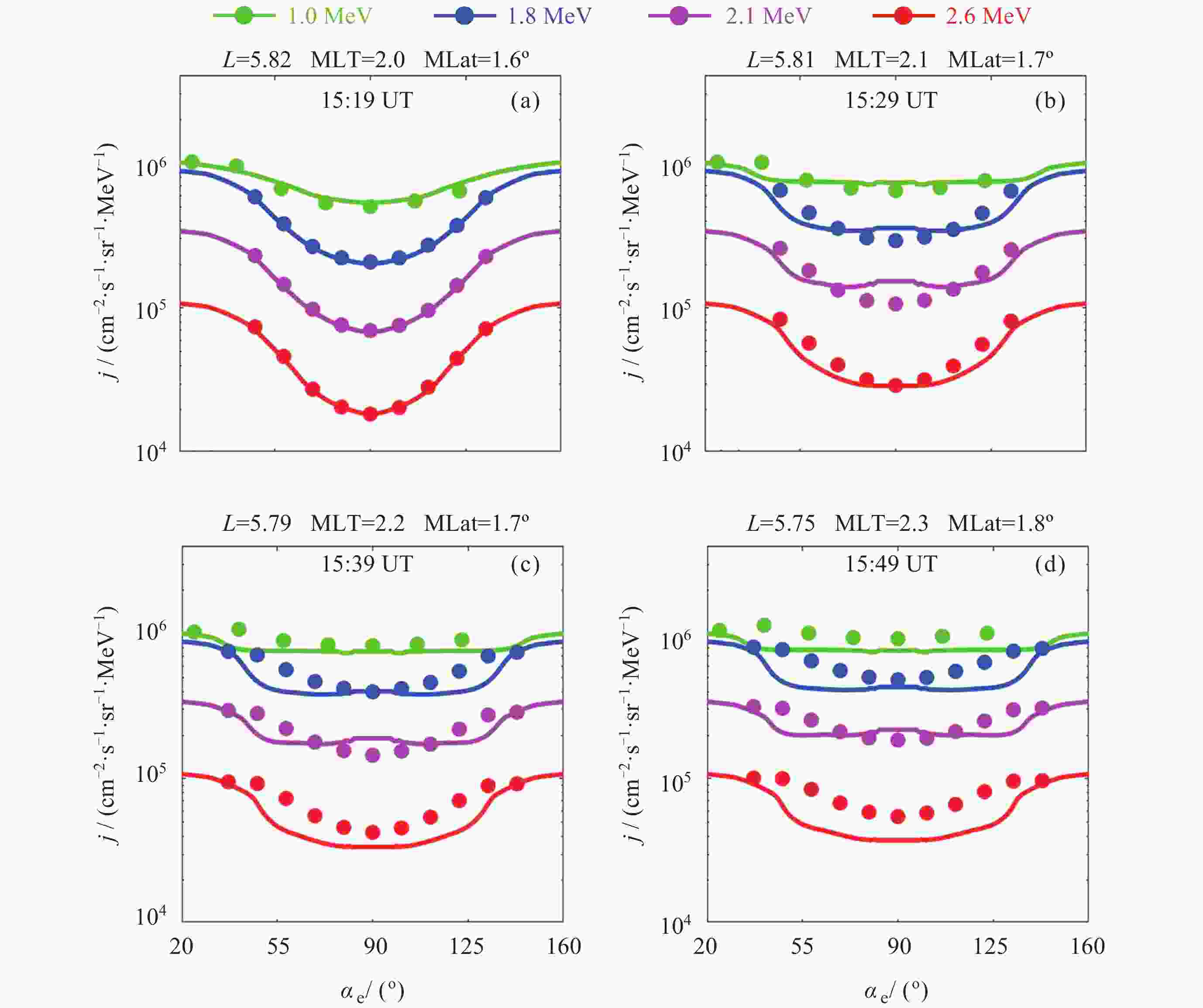
图 5 观测与模拟得到的微分通量j的比较. (a) 为初始状态, (b)~(d)为每10 min后的观测结果 与模拟结果, 实线表示计算得到的演化结果(实际观测数据已在2 min时间尺度内进行了滑动平均处理)
Figure 5. Comparisons between the observed (dots) and simulated (lines) differential flux j. (a) Initial state, (b)~(d) comparison between the observed and simulated differential flux j at 10 min intervals. The green, blue, purple, and red circles represent the observed electron flux values at 1.0, 1.8, 2.1, and 2.6 MeV, respectively, while the solid lines show the calculated evolution results (The observed data have been smoothed using a 2-minute time window)
-
[1] LI L Y, YANG S S, CAO J B, et al. Effects of solar wind plasma flow and interplanetary magnetic field on the spatial structure of earth's radiation belts[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2019, 124(12): 10332-10344 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027284 [2] LI L Y, CAO J B, ZHOU G C, et al. Statistical roles of storms and substorms in changing the entire outer zone relativistic electron population[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2009, 114(A12): A12214 [3] YU J, LI L Y, CAO J B, et al. Multiple loss processes of relativistic electrons outside the heart of outer radiation belt during a storm sudden commencement[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2015, 120(12): 10275-10288 [4] SU Z P, GAO Z L, ZHU H, et al. Nonstorm time dropout of radiation belt electron fluxes on 24 September 2013[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2016, 121(7): 6400-6416 doi: 10.1002/2016JA022546 [5] SU Z P, ZHU H, XIAO F L, et al. Ultra-low-frequency wave-driven diffusion of radiation belt relativistic electrons[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 10096 doi: 10.1038/ncomms10096 [6] OZEKE L G, MANN I R, OLIFER L, et al. Statistical characteristics of energetic electron pitch angle distributions in the Van Allen Probe era: 1. Butterfly distributions with flux peaks at preferred pitch angles[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2022, 127(3): e2021JA029907 doi: 10.1029/2021JA029907 [7] LUO Qiong, NI Binbin, CAO Xing, et al. An optimized identification method for radiation belt electron butterfly pitch angle distributions based on the chi-square distribution function[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(3): 809-818 (罗琼, 倪彬彬, 曹兴, 等. 基于卡方分布函数的辐射带电子蝴蝶状投掷角分布的优化判别方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(3): 809-818LUO Qiong, NI Binbin, CAO Xing, et al. An optimized identification method for radiation belt electron butterfly pitch angle distributions based on the chi-square distribution function[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(3): 809-818 [8] YU J, LI L Y, CAO J B, et al. The influences of solar wind pressure and interplanetary magnetic field on global magnetic field and outer radiation belt electrons[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(14): 7319-7327 doi: 10.1002/2016GL069029 [9] SIBECK D G, MCENTIRE R W, LUI A T Y, et al. Magnetic field drift shell splitting: cause of unusual dayside particle pitch angle distributions during storms and substorms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1987, 92(A12): 13485-13497 doi: 10.1029/JA092iA12p13485 [10] LI L Y, YU J, CAO J B, et al. Effects of ULF waves on local and global energetic particles: particle energy and species dependences[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2016, 121(11): 11007-11020 [11] BRAUTIGAM D H, ALBERT J M. Radial diffusion analysis of outer radiation belt electrons during the October 9, 1990, magnetic storm[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2000, 105(A1): 291-309 doi: 10.1029/1999JA900344 [12] YUAN H C, LI L Y, YANG L, et al. Competing influences of earthward convection and azimuthal drift loss on the pitch angle distribution of energetic electrons[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2024, 129(7): e2024JA032534 doi: 10.1029/2024JA032534 [13] XIAO F L, YANG C, SU Z P, et al. Wave-driven butterfly distribution of Van Allen belt relativistic electrons[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 8590 doi: 10.1038/ncomms9590 [14] LI L Y, YU J, CAO J B, et al. Roles of whistler mode waves and magnetosonic waves in changing the outer radiation belt and the slot region[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2017, 122(5): 5431-5448 doi: 10.1002/2016JA023634 [15] LI L Y, YU J, CAO J B, et al. Competitive influences of different plasma waves on the pitch angle distribution of energetic electrons inside and outside plasmasphere[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(1): e2021GL096062 doi: 10.1029/2021GL096062 [16] YANG Lixian, LIU Si, GAO Zhonglei, et al. Statistical study on propagation characteristics of chorus in the earth’s magnetosphere[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2024, 44(6): 998-1005 (杨立贤, 刘斯, 高中磊, 等. 地球磁层中合声波的频率与传播角分布特征[J]. 空间科学学报, 2024, 44(6): 998-1005 doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.06.2024-yg27YANG Lixian, LIU Si, GAO Zhonglei, et al. Statistical study on propagation characteristics of chorus in the earth’s magnetosphere[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2024, 44(6): 998-1005 doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.06.2024-yg27 [17] XIAO F L, LIU S, TAO X, et al. Generation of extremely low frequency chorus in Van Allen radiation belts[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2017, 122(3): 3201-3211 doi: 10.1002/2016JA023561 [18] SANTOLÍK O, GURNETT D A, PICKETT J S, et al. Spatio‐temporal structure of storm‐time chorus[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2003, 108(A7): 1278 [19] LI W, THORNE R M, ANGELOPOULOS V, et al. Global distribution of whistler‐mode chorus waves observed on the THEMIS spacecraft[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009, 36(9): L09104 [20] SU Z P, ZHU H, XIAO F L, et al. Quantifying the relative contributions of substorm injections and chorus waves to the rapid outward extension of electron radiation belt[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2014, 119(12): 10023-10040 [21] SU Z P, ZHU H, XIAO F L, et al. Intense duskside lower band chorus waves observed by Van Allen Probes: generation and potential acceleration effect on radiation belt electrons[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2014, 119(6): 4266-4273 doi: 10.1002/2014JA019919 [22] HU Xiong, ZHANG Xunxie. Interaction between whistler mode wave and the electrons in the magnetosphere[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 1992, 12(4): 279-286 (胡雄, 张训械. 磁层中哨声波与电子的相互作用[J]. 空间科学学报, 1992, 12(4): 279-286 doi: 10.11728/cjss1992.04.279HU Xiong, ZHANG Xunxie. Interaction between whistler mode wave and the electrons in the magnetosphere[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 1992, 12(4): 279-286 doi: 10.11728/cjss1992.04.279 [23] HE Tian, LIU Siqing, ZHENG Jinlei, et al. Study on high energy electron flux enhancement events and whistler chorus wave[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2013, 33(2): 170-175 (何甜, 刘四清, 郑金磊, 等. 哨声模合声波与地球同步轨道高能电子通量增强事件事例研究[J]. 空间科学学报, 2013, 33(2): 170-175 doi: 10.11728/cjss2013.02.170HE Tian, LIU Siqing, ZHENG Jinlei, et al. Study on high energy electron flux enhancement events and whistler chorus wave[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2013, 33(2): 170-175 doi: 10.11728/cjss2013.02.170 [24] XIAO F L, SU Z P, ZHENG H N, et al. Three‐dimensional simulations of outer radiation belt electron dynamics including cross‐diffusion terms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2010, 115(A5): A05216 [25] HE J B, JIN Y Y, XIAO F L, et al. The influence of various frequency chorus waves on electron dynamics in radiation belts[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2021, 64(4): 890-897 doi: 10.1007/s11431-020-1750-6 [26] YANG C, SU Z P, XIAO F L, et al. Rapid flattening of butterfly pitch angle distributions of radiation belt electrons by whistler‐mode chorus[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(16): 8339-8347 doi: 10.1002/2016GL070194 [27] YANG C, XIAO F L, HE Y H, et al. Storm time evolution of outer radiation belt relativistic electrons by a nearly continuous distribution of chorus[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(5): 2159-2167 doi: 10.1002/2017GL075894 [28] JIN Y Y, YANG C, HE Y H, et al. Butterfly distribution of Earth’s radiation belt relativistic electrons induced by dayside chorus[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2018, 61(2): 212-218 doi: 10.1007/s11431-017-9067-y [29] KLETZING C A, BORTNIK J, HOSPODARSKY G, et al. The Electric and Magnetic Fields Instrument Suite and Integrated Science (EMFISIS): science, data, and usage best practices[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2023, 219(4): 28 doi: 10.1007/s11214-023-00973-z [30] BLAKE J B, CARRANZA P A, CLAUDEPIERRE S G, et al. The Magnetic Electron Ion Spectrometer (MagEIS) instruments aboard the Radiation Belt Storm Probes (RBSP) spacecraft[J]. Space Science Reviews 2013, 179(1): 383-421 [31] BAKER D N, KANEKAL S G, HOXIE V, et al. The Relativistic Electron-Proton Telescope (REPT) investigation: design, operational properties, and science highlights[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2021, 217(5): 68 doi: 10.1007/s11214-021-00838-3 [32] MAUK B H, FOX N J, KANEKAL S G, et al. Science objectives and rationale for the radiation belt storm probes mission[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2013, 179(1): 3-27 [33] XIAO F L, SU Z P, ZHENG H N, et al. Modeling of outer radiation belt electrons by multidimensional diffusion process[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2009, 114(A3): A03201 [34] SUMMERS D. Quasi‐linear diffusion coefficients for field‐aligned electromagnetic waves with applications to the magnetosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2005, 110(A8): A08213 [35] KURTH W S, DE PASCUALE S, FADEN J B, et al. Electron densities inferred from plasma wave spectra obtained by the waves instrument on Van Allen Probes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2015, 120(2): 904-914 doi: 10.1002/2014JA020857 -
-




 岳佳旭 男, 2001年1月出生于河北省秦皇岛市, 现为长沙理工大学物理与电子科学学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为辐射带波–粒相互作用等. E-mail:
岳佳旭 男, 2001年1月出生于河北省秦皇岛市, 现为长沙理工大学物理与电子科学学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为辐射带波–粒相互作用等. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: