Local Temperature Gradient Laser Pulse Triggered Nucleation Experimental Technology under Electrostatic Levitation
-
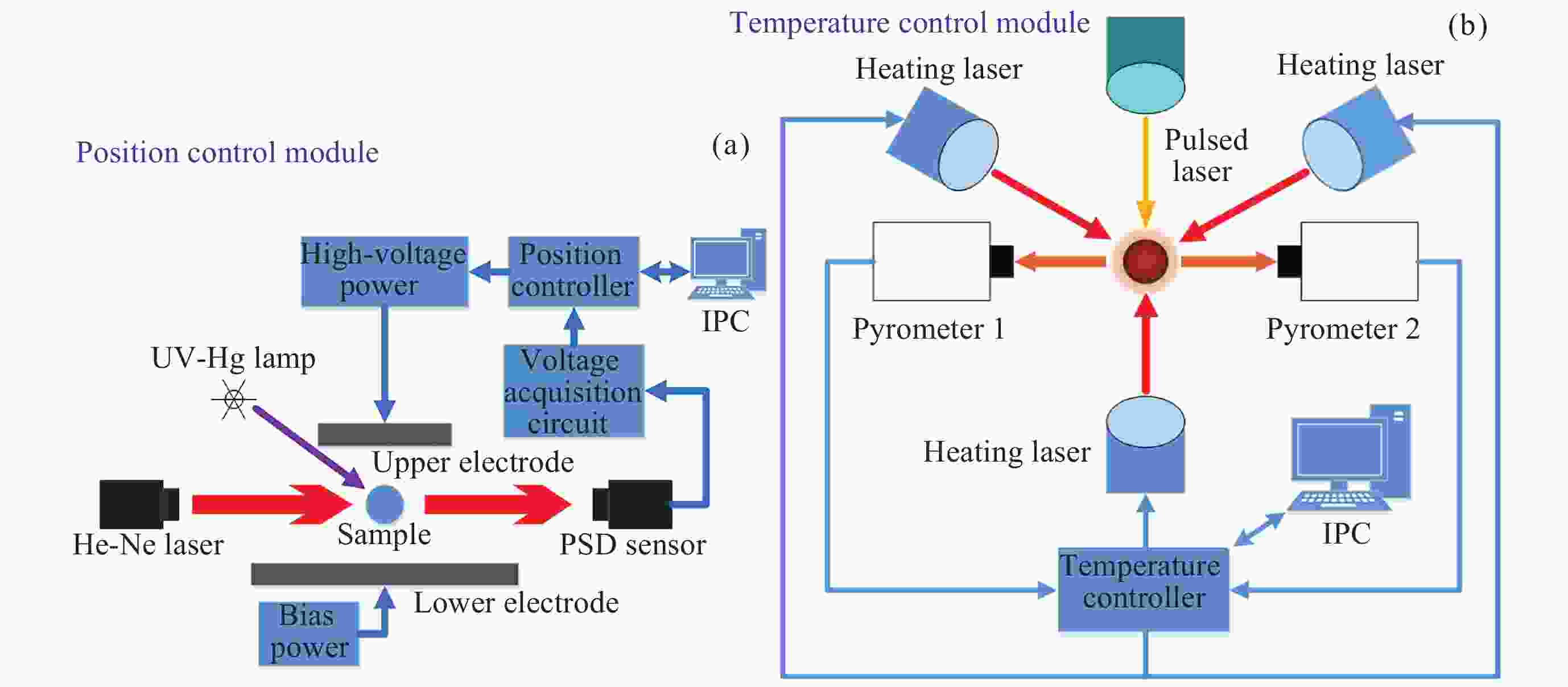
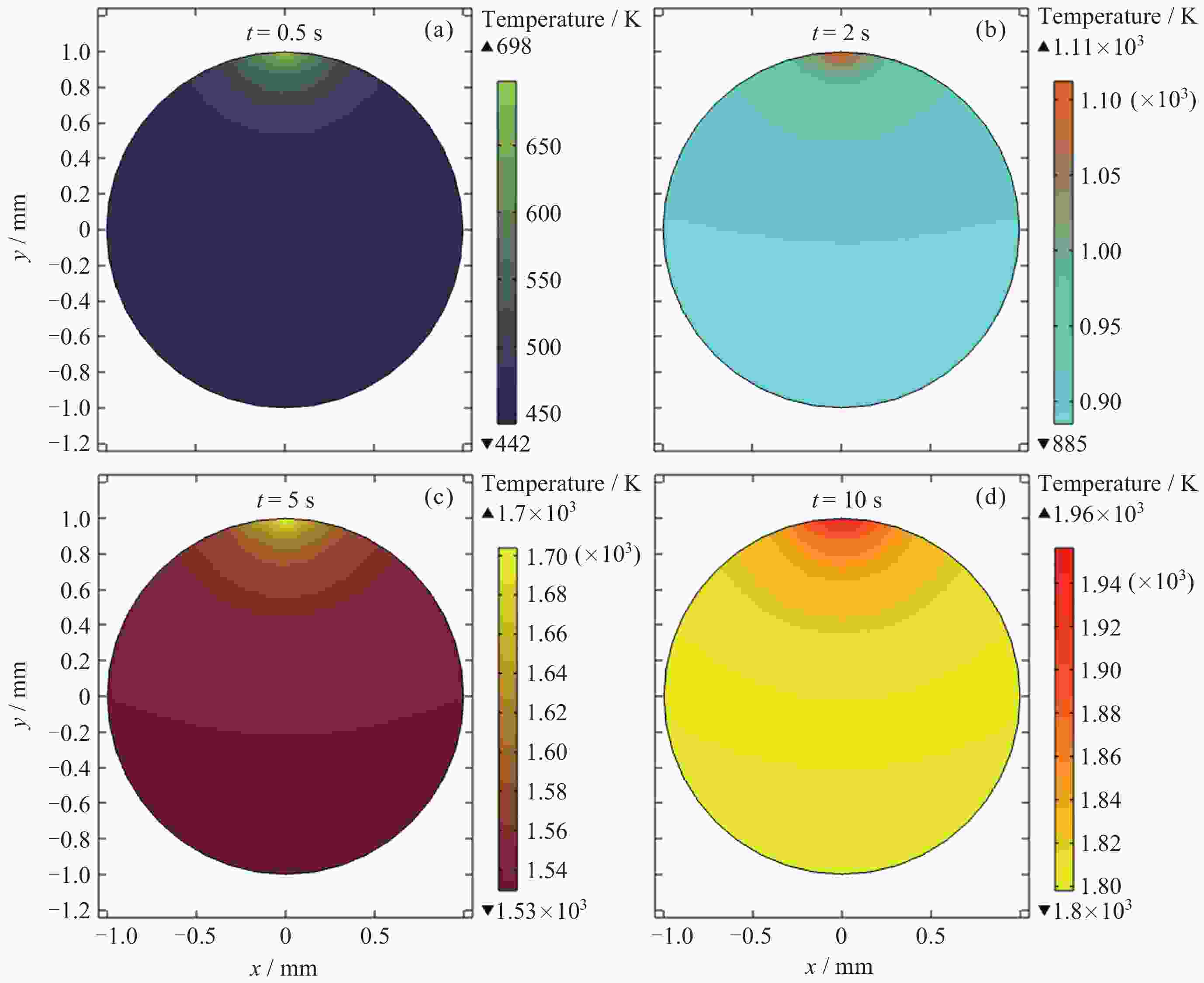
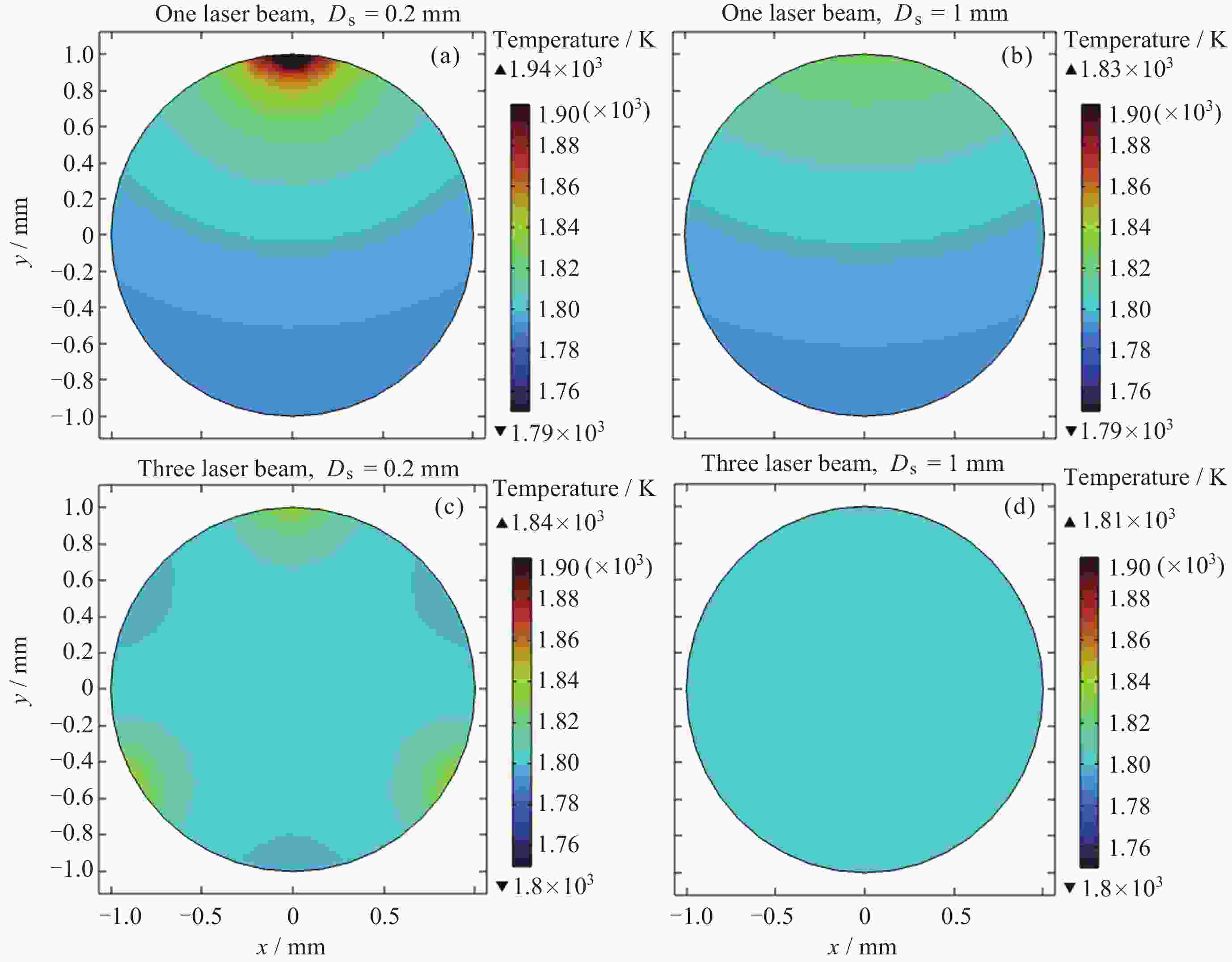
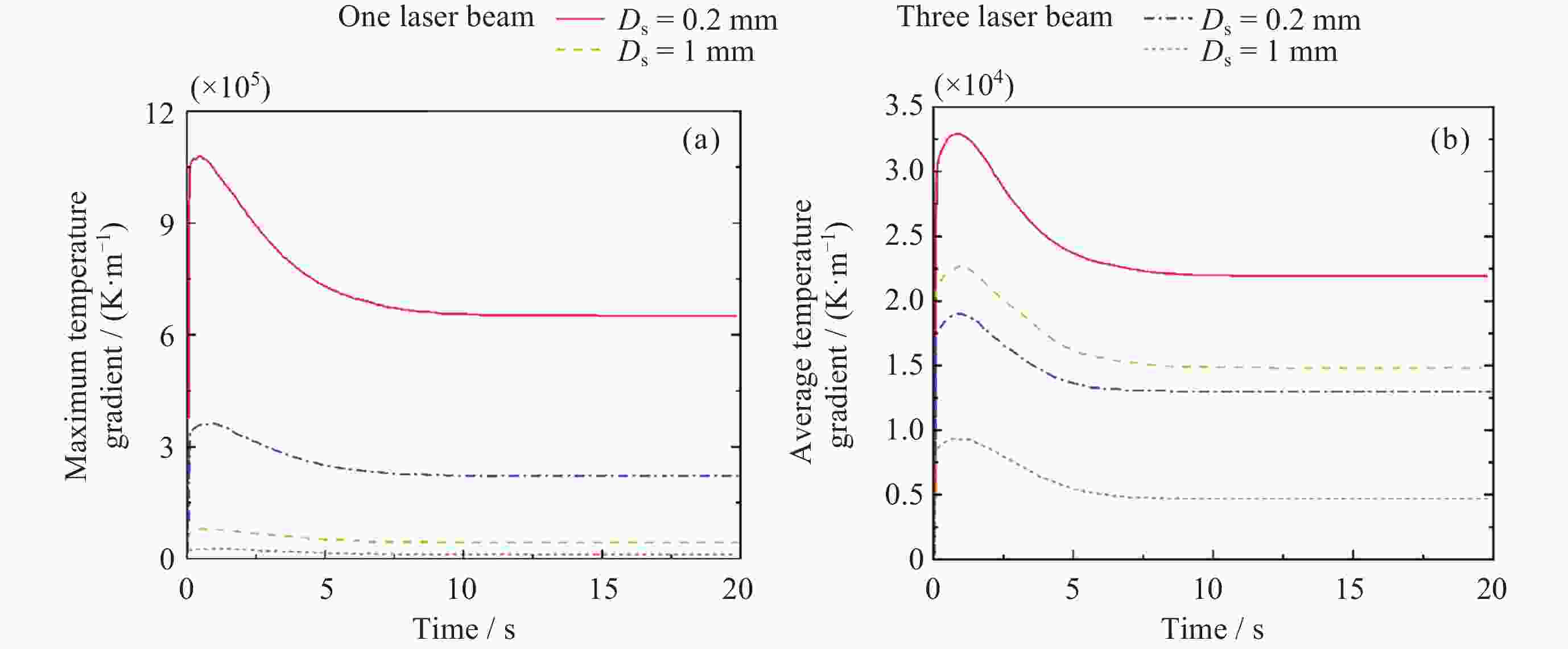
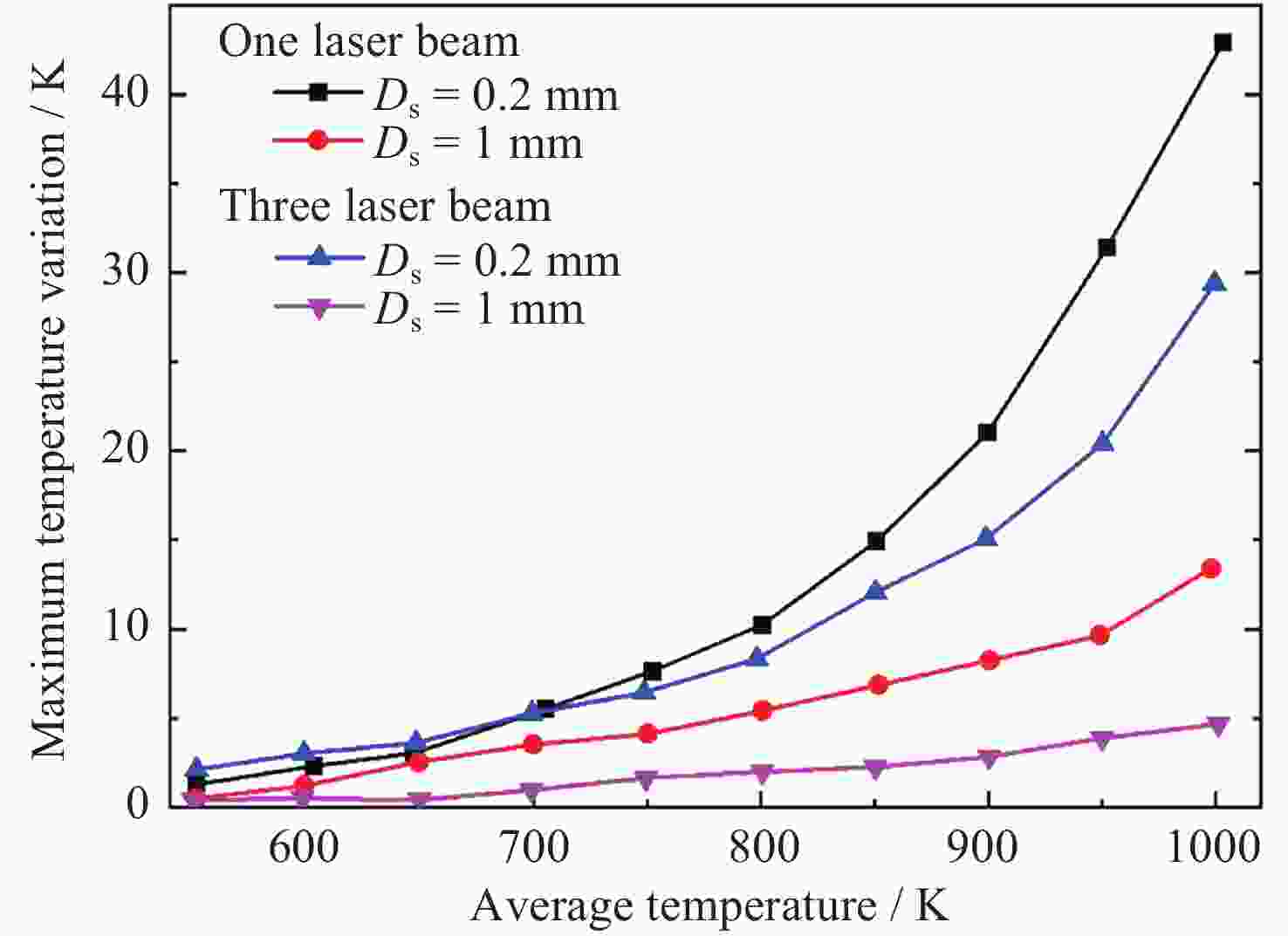
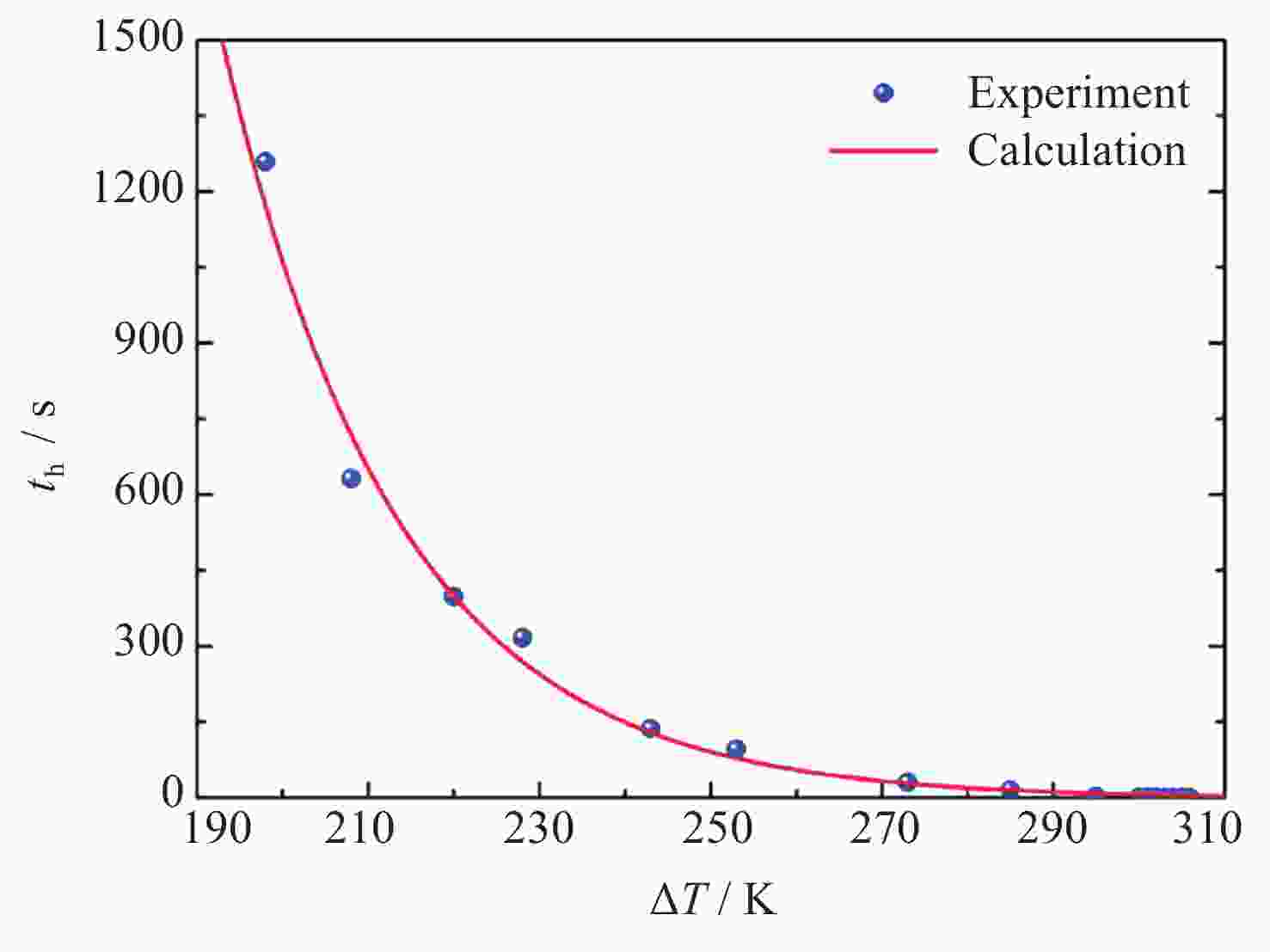
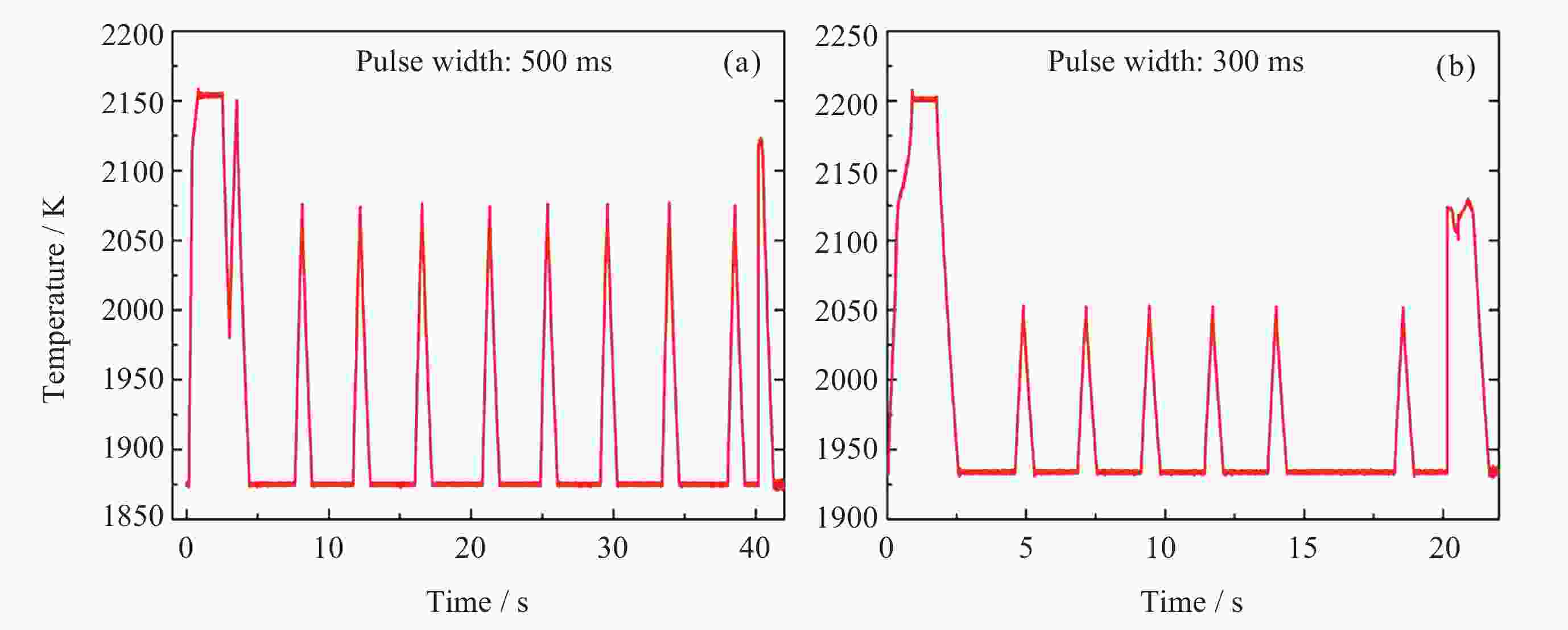
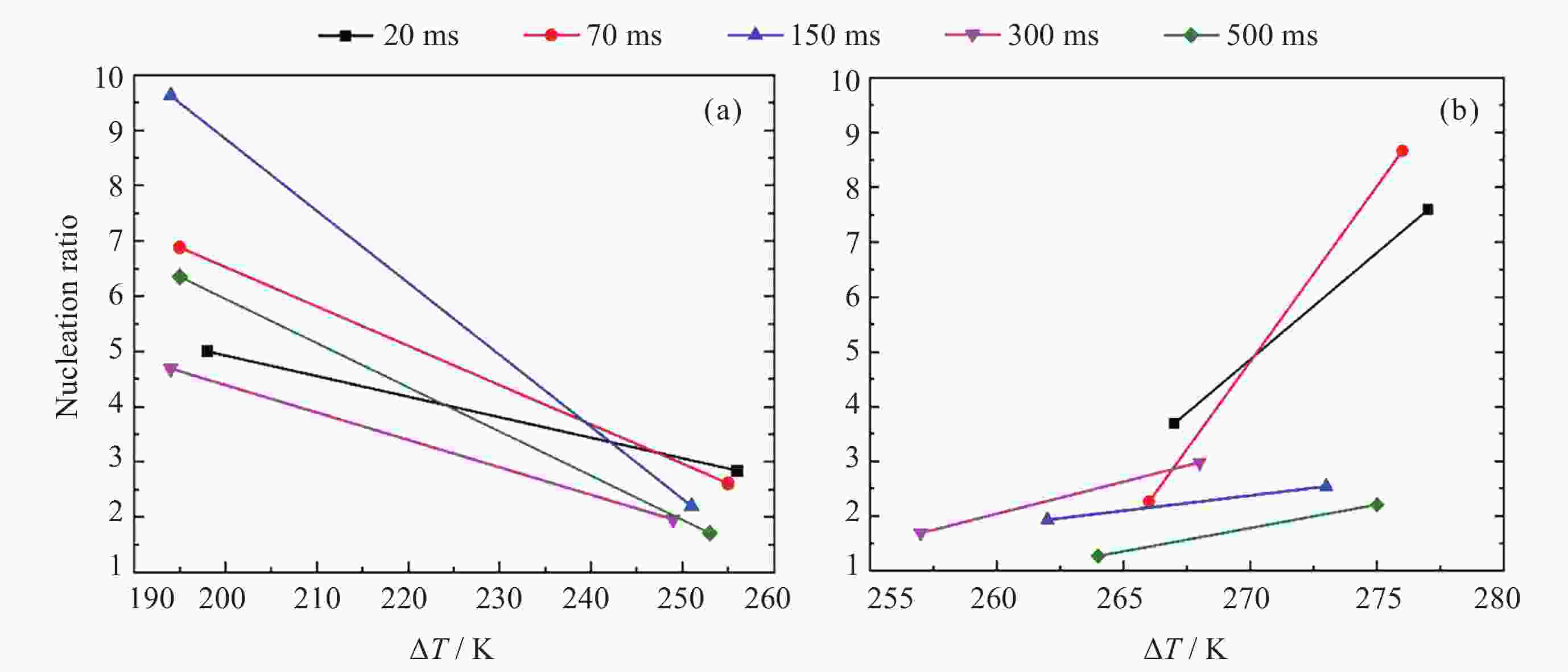
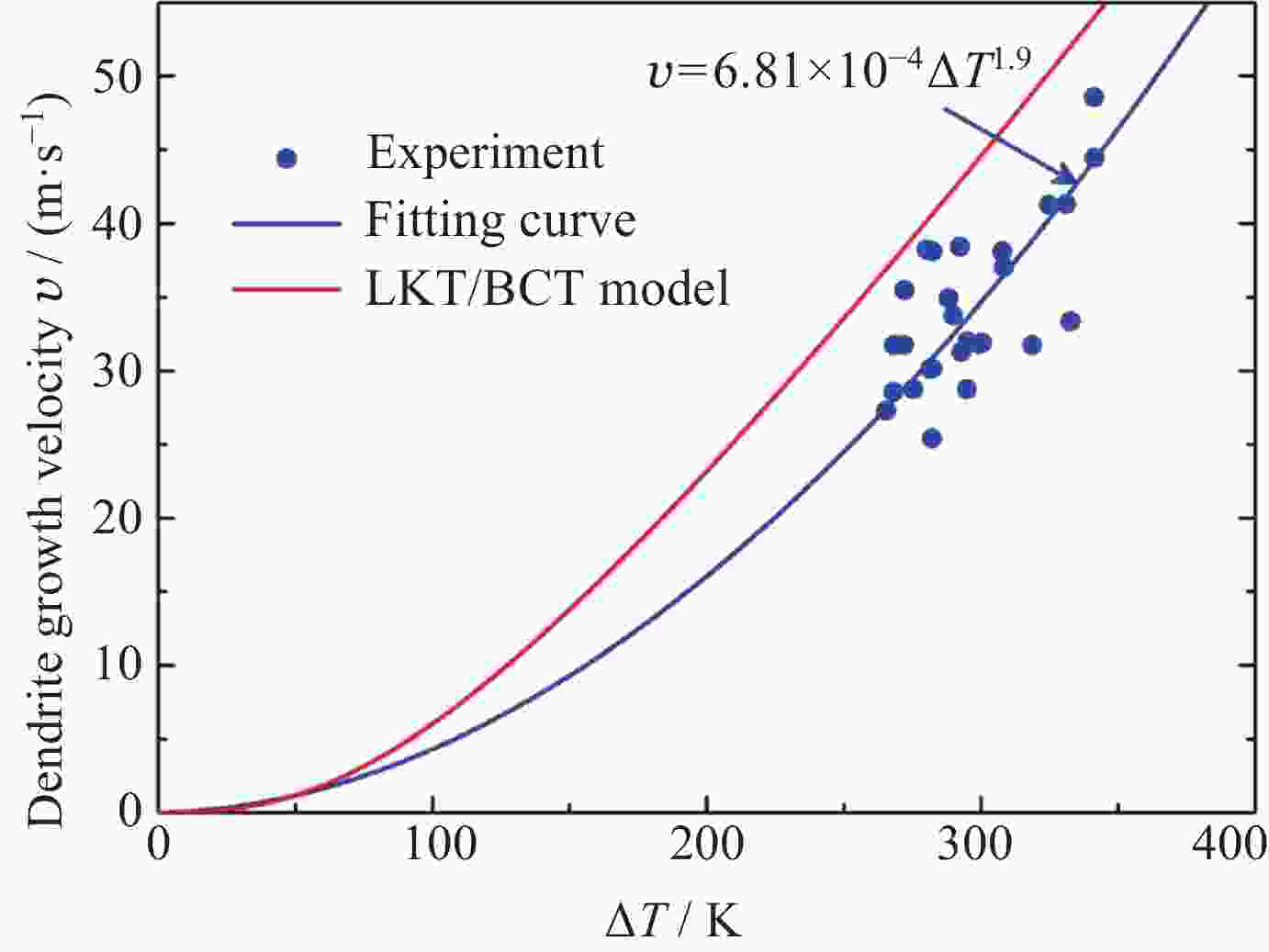
摘要: 通过激光脉冲在样品表面局部区域形成温度梯度, 引起实验样品内部结构起伏和能量起伏概率加大, 程度加深, 使晶体从熔融的液相亚稳态相变为固相, 实现静电悬浮下高质量可控深过冷激光脉冲触发形核. 通过有限元模拟仿真方法研究不同加热激光束斑直径, 功率为9 W, 功率密度为$ 2.86\times {10}^{8}\;\mathrm{W} \cdot {\mathrm{m}}^{-2} $和$ 1.146\times {10}^{7}\;\mathrm{W} \cdot {\mathrm{m}}^{-2} $的激光对温度梯度场的影响, 得到不同激光束斑直径下熔融样品局部温度梯度场分布结果. 采用直径为2 mm锆材料样品, 研究在较小激光束斑直径下, 不同的激光脉冲宽度与过冷度熔融材料样品触发形核时间尺度变化. 基于经典形核理论, 通过16组不同过冷度, 每组20次自发形核的数据统计分析, 得到锆材料样品在不同过冷度下从母相熔体的亚稳态向固相移动所需时间的变化关系. 在此基础上, 开展激光脉冲束斑直径为0.2 mm的波长为936 nm, 样品为锆材料激光脉冲触发形核实验研究. 实验结果表明, 锆材料在过冷度为195 K ± 3 K, 样品形核凝固过程中所需的时间比自发形核所需时间降低3/4, 高质量可控地使熔融样品在不同过冷度下触发形核.Abstract: The containerless and solidification method of electrostatically suspended deep subcooled samples is of great significance for materials science research and materials preparation, and this paper proposes to realize the experimental study of triggered nucleation and solidification and measurement of materials under deep subcooling based on the local temperature gradient field of the laser pulse. By triggering the laser pulse to generate a local temperature, a temperature gradient is formed around the sample, and the temperature gradient triggers convection to increase the probability of structural and energy undulation inside the experimental sample and deepen the degree, so that the crystals change from a molten liquid phase to a solid phase, realizing high-quality and controllable deep-subcooling laser pulse-triggered nucleation under electrostatic levitation. By means of finite element simulation methods, the effect of laser heating with different spot diameters and a power of 9 W, a power density of $ 2.86\times {10}^{8}\;\mathrm{W} \cdot {\mathrm{m}}^{-2} $ and $ 1.146\times {10}^{7}\;\mathrm{W} \cdot {\mathrm{m}}^{-2} $ on the temperature gradient field was investigated. The distribution results of the local temperature gradient field in the molten sample under different laser spot diameters were obtained. A zirconium sample with a diameter of 2 mm was used in the experiment to study the time scale of triggered nucleation of molten samples with different laser pulse widths and subcooling degrees under smaller laser beam spot diameters. Based on the classical nucleation theory, the time required for the zirconium samples to move from the substable state of the mother phase melt to the solid phase under different supercooling degrees was obtained by statistically analyzing the data from 16 groups of 20 spontaneous nucleations at different supercooling degrees. On this basis, the experimental study of laser pulse triggered nucleation was carried out at a wavelength of 936 nm with a laser pulse spot diameter of 0.2 mm and a sample of zirconium material. The experimental results show that the time required for nucleation and solidification of zirconium material at a low subcooling of 195 K ± 3 K is 3/4 times lower than that required for spontaneous nucleation, and that high quality and controllable nucleation can be triggered for molten samples at different subcooling levels.
-
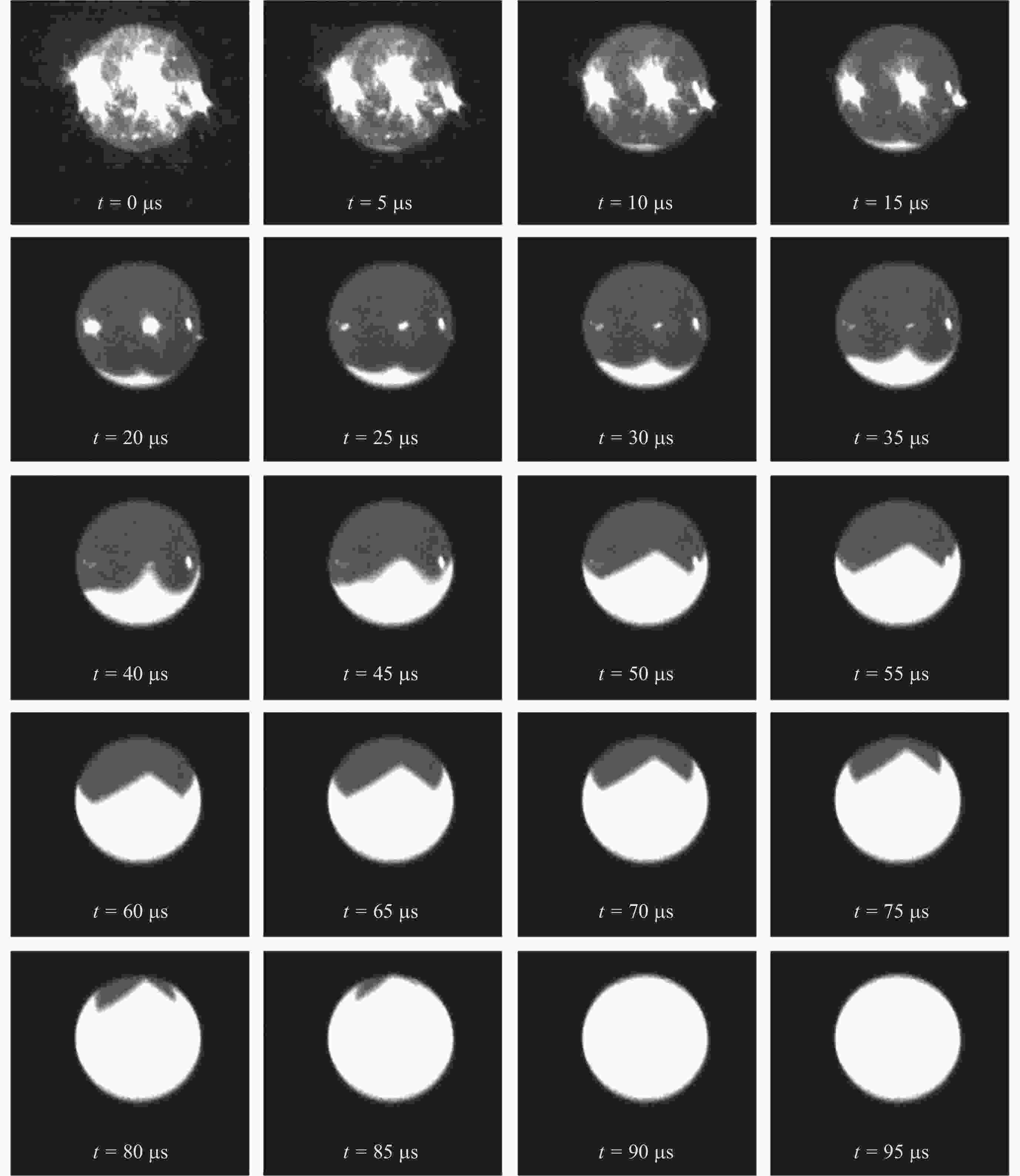
图 13 样品锆在245 K过冷度下凝固时的表面固液界面迁移情况 (暗色部分为过冷的液态锆, 明亮色部分为再辉凝固后的固态锆. 高速相机拍摄速率为2×105 frame·s–1)
Figure 13. Surface solid-liquid interface migration situation of zirconium under 245 K undercooling (The dark parts of the picture are liquid zirconium that is supercooled, and the bright white parts are solid zirconium that has recized. Shooting rate of high-speed camera is 2×105 frame·s–1)
-
[1] WANG F L, DAI B, LIU X F, et al. Containerless heating process of a deeply undercooled metal droplet by electrostatic levitation[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2015, 32(11): 114101 doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/32/11/114101 [2] YU J D, PARADIS P F, YODA S, et al. Dielectric properties of BaTiO3 synthesized by containerless processing technique[J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2005, 46(1): 15-18 [3] ISHIKAWA T, KOYAMA C, PARADIS P F, et al. Densities of liquid Re, Os, and Ir, and their temperature dependence measured by an electrostatic levitator[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2020, 92: 105305 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2020.105305 [4] ZHAO D D, YANG F, HOLLAND-MORITZ D, et al. In situ studies of liquid-liquid phase separation, solidification sequence and dendrite growth kinetics in electrostatically levitated Ti–Y alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2021, 213: 116962 [5] LI D M, WANG W L, JIA Y, et al. Structural optimization of radial containment ultrasonic suspension bearing[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(10): 2375-2385 (李东明, 王万雷, 贾颖, 等. 径向包容式超声悬浮轴承结构优化[J]. 光学精密工程, 2021, 29(10): 2375-2385 doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212910.2375LI D M, WANG W L, JIA Y, et al. Structural optimization of radial containment ultrasonic suspension bearing[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(10): 2375-2385 doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212910.2375 [6] GREFFRATH F, PRIELER R, TELLE R. A new method for the estimation of high temperature radiant heat emittance by means of aero-acoustic levitation[J]. Infrared Physics :Times New Roman;">& Technology, 2014, 67: 333-337 [7] LIU H, YANG Z P, WU D Y. Estimation of rotor speed using displacement signals in magnetic suspended flywheel[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(5): 1116-1123 (刘虎, 杨振鹏, 武登云. 基于位移信号的磁悬浮飞轮转速估计[J]. 光学精密工程, 2020, 28(5): 1116-1123LIU H, YANG Z P, WU D Y. Estimation of rotor speed using displacement signals in magnetic suspended flywheel[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(5): 1116-1123 [8] MOHR M, WUNDERLICH R K, KOCH S, et al. Surface tension and viscosity of Cu50Zr50 measured by the oscillating drop technique on board the international space station[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2019, 31(2): 177-184 doi: 10.1007/s12217-019-9678-1 [9] JEON S, SANSOUCIE M P, MATSON D M. Hyper-cooling limit, heat of fusion, and temperature-dependent specific heat of Fe-Cr-Ni melts[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2019, 138: 51-58 doi: 10.1016/j.jct.2019.06.001 [10] LEE J, SANSOUCIE M P. Experiments using a ground-based electrostatic levitator and numerical modeling of melt convection for the iron-cobalt system in support of space experiments[J]. Jom, 2017, 69(8): 1298-1302 doi: 10.1007/s11837-017-2387-6 [11] TAMARU H, KOYAMA C, SARUWATARI H, et al. Status of the Electrostatic Levitation Furnace (ELF) in the ISS-KIBO[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2018, 30(5): 643-651 doi: 10.1007/s12217-018-9631-8 [12] HERLACH D M, KOBOLD R, KLEIN S. Crystal nucleation and growth in undercooled melts of pure Zr, binary Zr-based and ternary Zr-Ni-Cu glass-forming alloys[J]. Jom, 2018, 70(5): 726-732 doi: 10.1007/s11837-018-2782-7 [13] LEE G W, JEON S, PARK C, et al. Crystal–liquid interfacial free energy and thermophysical properties of pure liquid Ti using electrostatic levitation: hypercooling limit, specific heat, total hemispherical emissivity, density, and interfacial free energy[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2013, 63: 1-6 doi: 10.1016/j.jct.2013.03.012 [14] KOSTANOVSKII A V, KOSTANOVSKAYA M E. Thermophysical properties of stable and supercooled liquid carbon[J]. Measurement Techniques, 2019, 62(2): 532-539 [15] HU L, JIN Y J, LIN M J, et al. Temperature dependence of thermophysical properties for liquid Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe alloy measured at electrostatic levitation state[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2021, 776: 138667 doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2021.138667 [16] SUN Y N, WANG F L, YU Q, et al. Thermophysical property measurements by electrostatic levitation in material science[J]. Materials Reports, 2016, 30(S2): 253-258 (孙一宁, 王飞龙, 于强, 等. 静电悬浮条件下的材料典型热物理性质测量[J]. 材料导报, 2016, 30(S2): 253-258SUN Y N, WANG F L, YU Q, et al. Thermophysical property measurements by electrostatic levitation in material science[J]. Materials Reports, 2016, 30(S2): 253-258 [17] CHEN D Y, GUO Q Y, DONG W B, et al. Control system of electrostatic levitation based on high-speed vision[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(11): 2343-2353 (陈东阳, 郭清远, 董文博, 等. 基于高速视觉的静电悬浮控制系统[J]. 光学精密工程, 2019, 27(11): 2343-2353 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192711.2343CHEN D Y, GUO Q Y, DONG W B, et al. Control system of electrostatic levitation based on high-speed vision[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(11): 2343-2353 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192711.2343 [18] XUE S Q, DONG W B, CHEN D Y, et al. Analysis of electrostatic levitation control system and oscillation method for material properties measurement[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92(6): 065111 doi: 10.1063/5.0026974 [19] RATHZ T J, ROBINSON M B, HYERS R W, et al. Triggered nucleation in Ni60Nb40 using an electrostatic levitator[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2002, 21(4): 301-303 doi: 10.1023/A:1017928022508 [20] HERLACH D M. Non-equilibrium solidification of undercooled metallic melts[J]. Metals, 2014, 4(2): 196-234 doi: 10.3390/met4020196 [21] AOYAMA T, PARADIS P F, ISHIKAWA T, et al. Observation of rapid solidification of deeply undercooled Si melts using electrostatic levitation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004, 375/376/377: 460-463 [22] YANG S J. Electrostatic Levitation Processing and Rapid Solidification Mechanism of Refractory Metallic Materials[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2018 (杨尚京. 难熔金属材料的静电悬浮过程与快速凝固机理研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2018YANG S J. Electrostatic Levitation Processing and Rapid Solidification Mechanism of Refractory Metallic Materials[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2018 [23] CHEN H M, ZHAO X Y. Principles and Applications of Laser[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2009 (陈鹤鸣, 赵新彦. 激光原理及应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2009CHEN H M, ZHAO X Y. Principles and Applications of Laser[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2009 [24] ANTONY K, ARIVAZHAGAN N, SENTHILKUMARAN K. Numerical and experimental investigations on laser melting of stainless steel 316 L metal powders[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2014, 16(3): 345-355 doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2014.04.001 [25] PARADIS P F, ISHIKAWA T, YODA S. Non-contact measurements of thermophysical properties of niobium at high temperature[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2001, 36(21): 5125-5130 doi: 10.1023/A:1012477308332 [26] PARADIS P F, ISHIKAWA T, SAITA Y, et al. Containerless property measurements of liquid palladium[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 2004, 25(6): 1905-1912 doi: 10.1007/s10765-004-7744-3 [27] WANG L, HU L, ZHAO J F, et al. Ultrafast growth kinetics of titanium dendrites investigated by electrostatic levitation experiments and molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2020, 742: 137141 doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2020.137141 [28] LIU F. Design of nanostructured materials by thermos-kinetic couple[J/OL]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, (2023-04-10). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/43.1238.TG.20230410.1325.001.html (刘峰. 基于热力学-动力学耦合的纳米晶结构材料设计[J/OL]. 中国有色金属学报, 1-15[2025-06-27]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/43.1238.TG.20230410.1325.001.htmlLIU F. Design of nanostructured materials by thermos-kinetic couple[J/OL]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, (2023-04-10). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/43.1238.TG.20230410.1325.001.html [29] VINET B, MAGNUSSON L, FREDRIKSSON H, et al. Correlations between surface and interface energies with respect to crystal nucleation[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2002, 255(2): 363-374 doi: 10.1006/jcis.2002.8627 [30] TURNBULL D. Formation of crystal nuclei in liquid metals[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1950, 21(10): 1022-1028 doi: 10.1063/1.1699435 [31] WU H M. Research on Laser Heating System Based on Spot Detection[D]. Taiyuan: North Central University, 2019 (武慧敏. 基于光斑检测的激光加热系统研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2019WU H M. Research on Laser Heating System Based on Spot Detection[D]. Taiyuan: North Central University, 2019 [32] YU K, HUANG D X, YIN J J, et al. Reflected-intensity distribution of a thin-film filter with oblique incidence of a Gaussian beam under-parallel case[J]. Chinese Journal of Laser, 2012, 39(8): 0807003 (俞侃, 黄德修, 尹娟娟, 等. 高斯光束斜入射非平行薄膜滤光片的反射光强分布[J]. 中国激光, 2012, 39(8): 0807003 doi: 10.3788/CJL201239.0807003YU K, HUANG D X, YIN J J, et al. Reflected-intensity distribution of a thin-film filter with oblique incidence of a Gaussian beam under-parallel case[J]. Chinese Journal of Laser, 2012, 39(8): 0807003 doi: 10.3788/CJL201239.0807003 [33] YOU K M. Research on the Propagation and Focusing Properties of Broadband Laser Pulses[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2009 (游开明. 宽带脉冲激光的传输和聚焦特性研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2009YOU K M. Research on the Propagation and Focusing Properties of Broadband Laser Pulses[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2009 [34] WANG L, HU L, YANG S J, et al. Thermophysical properties and rapid dendritic growth of liquid zirconium under electrostatic levitation condition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(9): 1816-1823 (王磊, 胡亮, 杨尚京, 等. 静电悬浮条件下液态锆的热物理性质与快速枝晶生长[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(9): 1816-1823WANG L, HU L, YANG S J, et al. Thermophysical properties and rapid dendritic growth of liquid zirconium under electrostatic levitation condition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(9): 1816-1823 [35] LU X X, ZHANG M H, LIU X K, et al. Nucleation and solidification measurement of deep-undercooling molten zirconium under electrostatic levitation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2023, 33(3): 804-816 (陆潇晓, 张明辉, 刘晓珂, 等. 静电悬浮深过冷熔融锆形核凝固测量[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2023, 33(3): 804-816LU X X, ZHANG M H, LIU X K, et al. Nucleation and solidification measurement of deep-undercooling molten zirconium under electrostatic levitation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2023, 33(3): 804-816 [36] YU J C, YAN J F, LI X, et al. Progress in ultrafast laser-induced nucleation and crystal growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48(2): 0202020 (俞嘉晨, 闫剑锋, 李欣, 等. 超快激光调控晶体形核与生长过程研究进展[J]. 中国激光, 2021, 48(2): 0202020 doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.0202020YU J C, YAN J F, LI X, et al. Progress in ultrafast laser-induced nucleation and crystal growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48(2): 0202020 doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.0202020 [37] LU X X, LIU X K, LI H, et al. RBF neural network in electrostatic levitation position control[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(5): 952-960 (陆潇晓, 刘晓珂, 李虎, 等. RBF神经网络在静电悬浮位置控制中的应用[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(5): 952-960 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.05.210927103LU X X, LIU X K, LI H, et al. RBF neural network in electrostatic levitation position control[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(5): 952-960 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.05.210927103 -
-





 王艳秋 1987年7月出生于河北省承德市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心高级工程师, 博士研究生, 主要研究方向为静电悬浮无容器实验技术研究、空间科学实验技术研究及仪器研制. E-mail:
王艳秋 1987年7月出生于河北省承德市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心高级工程师, 博士研究生, 主要研究方向为静电悬浮无容器实验技术研究、空间科学实验技术研究及仪器研制. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: