Task-driven Satellite Cluster Self-organization Method Based on Linear Groups in Finite Fields
-
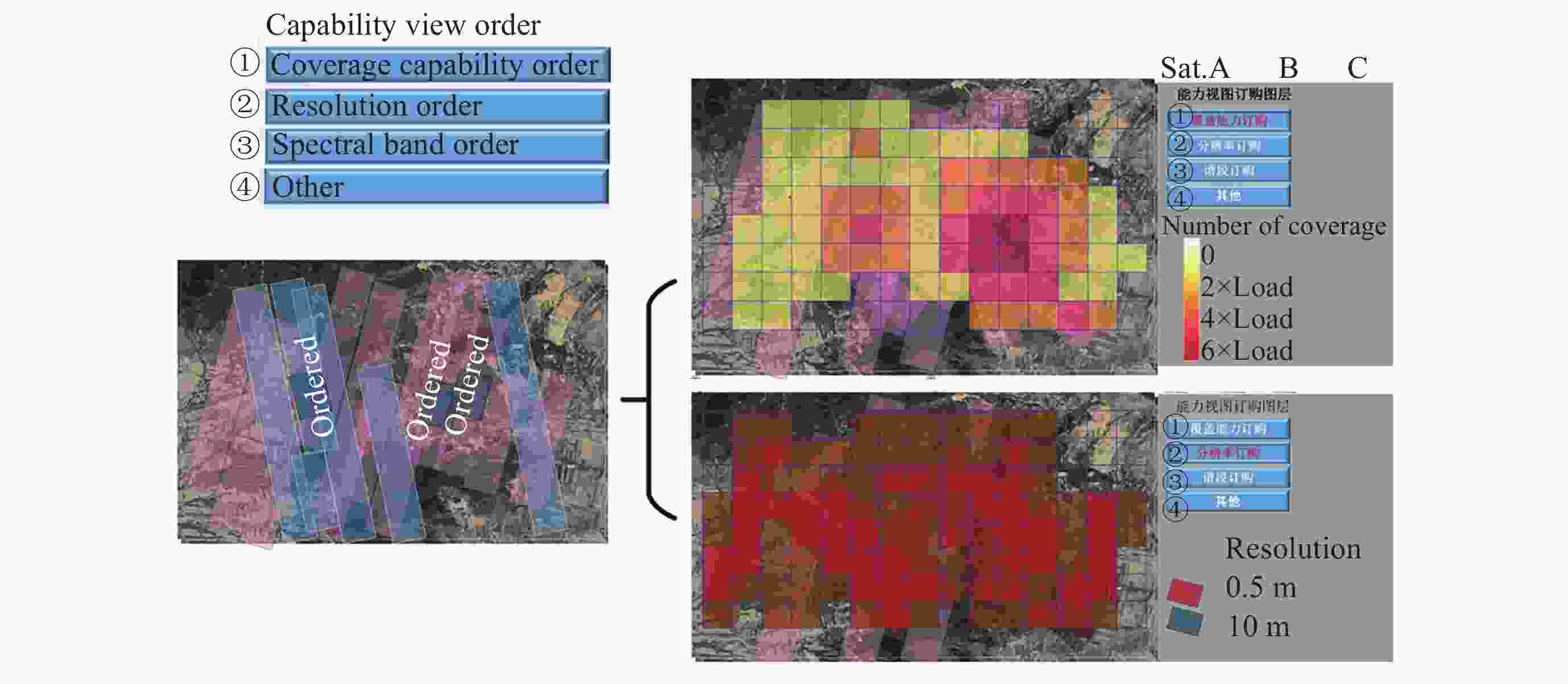
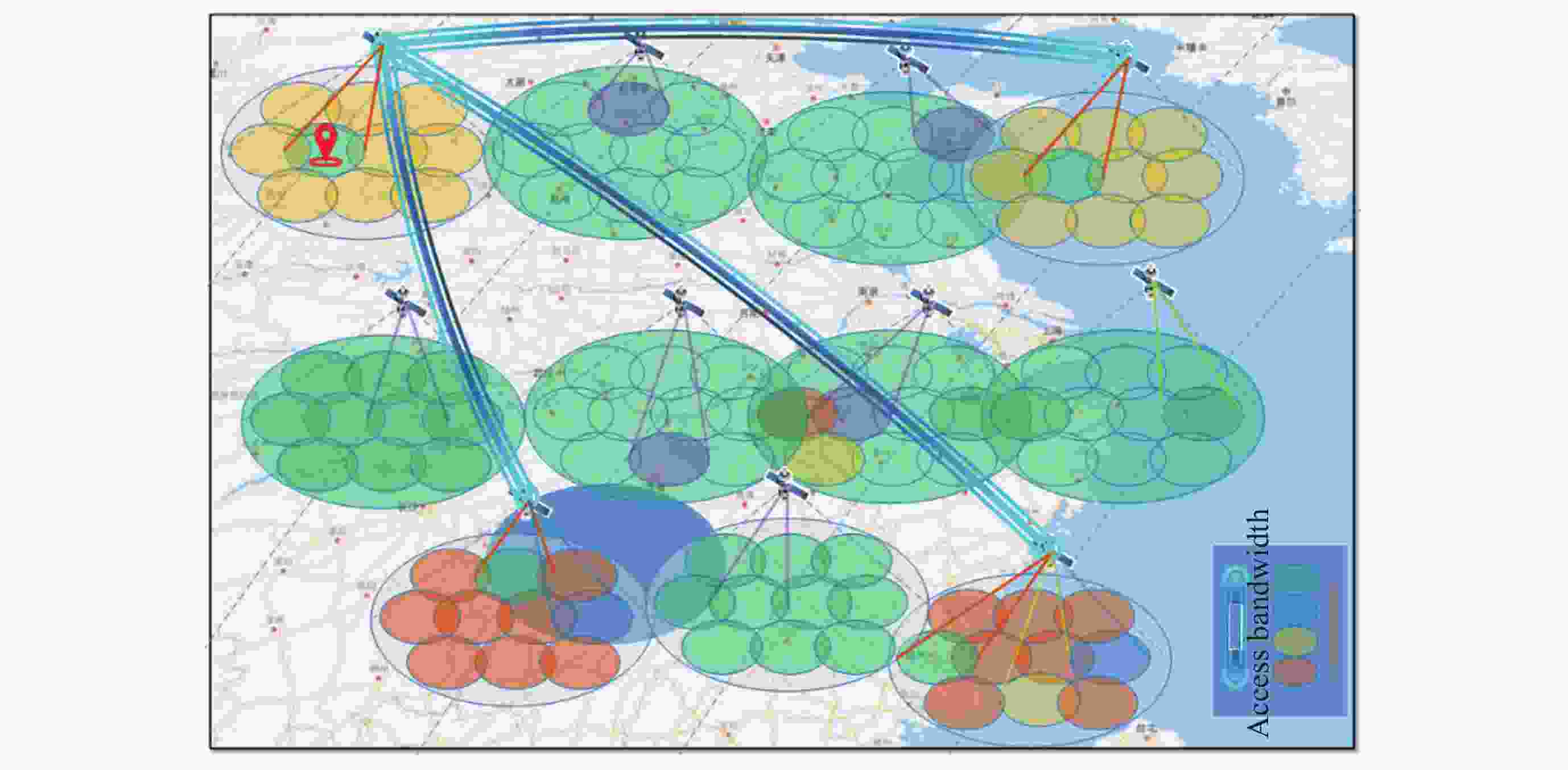
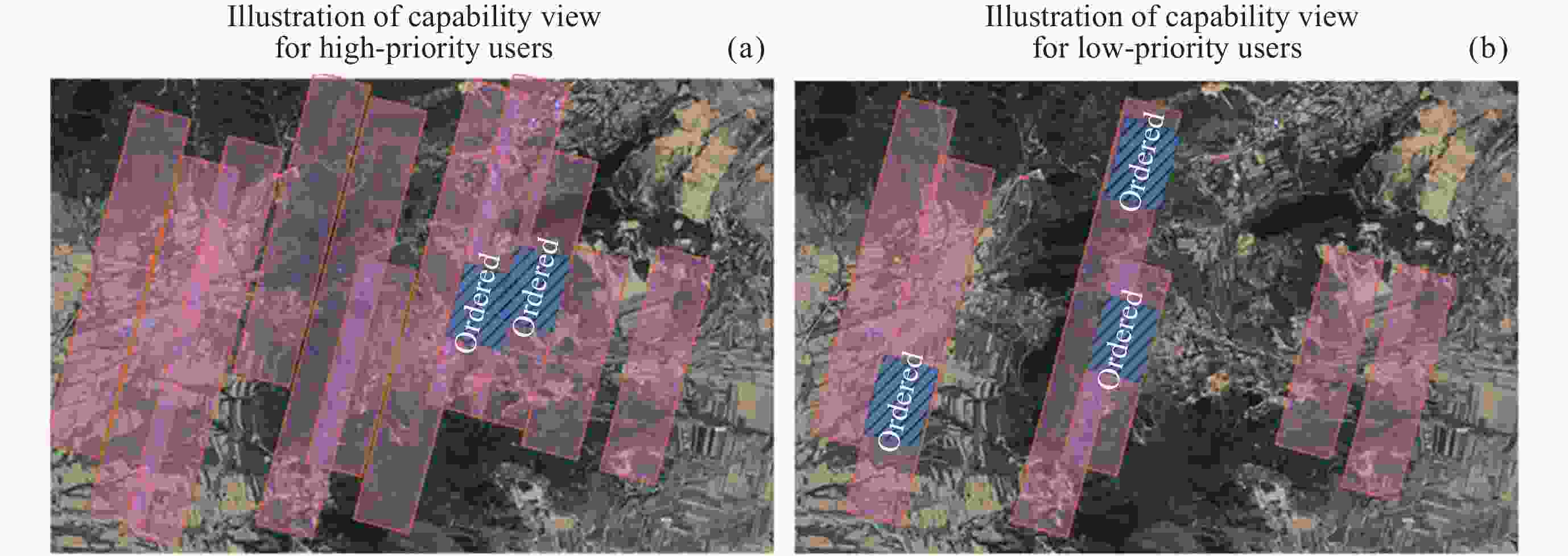
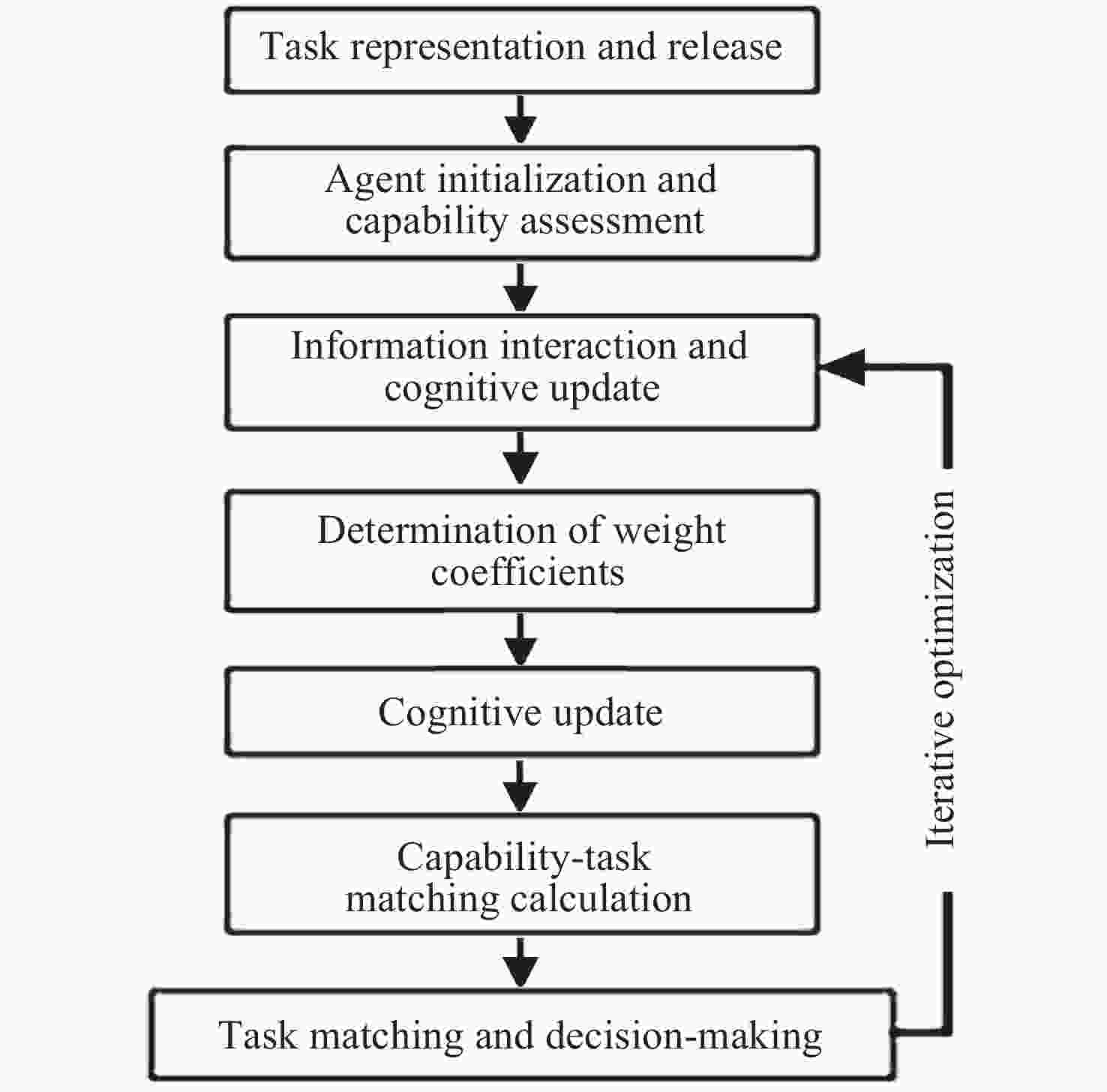
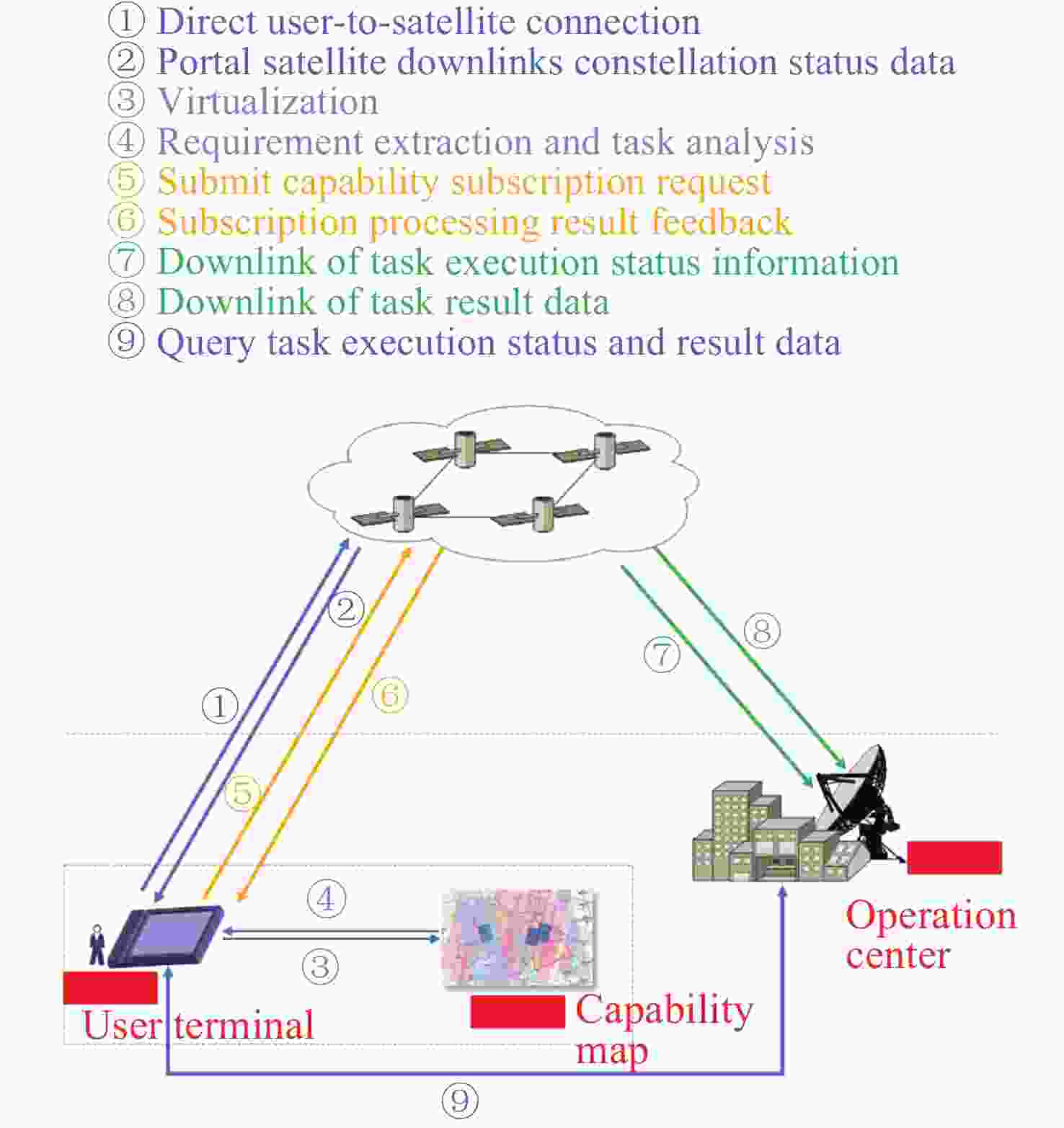
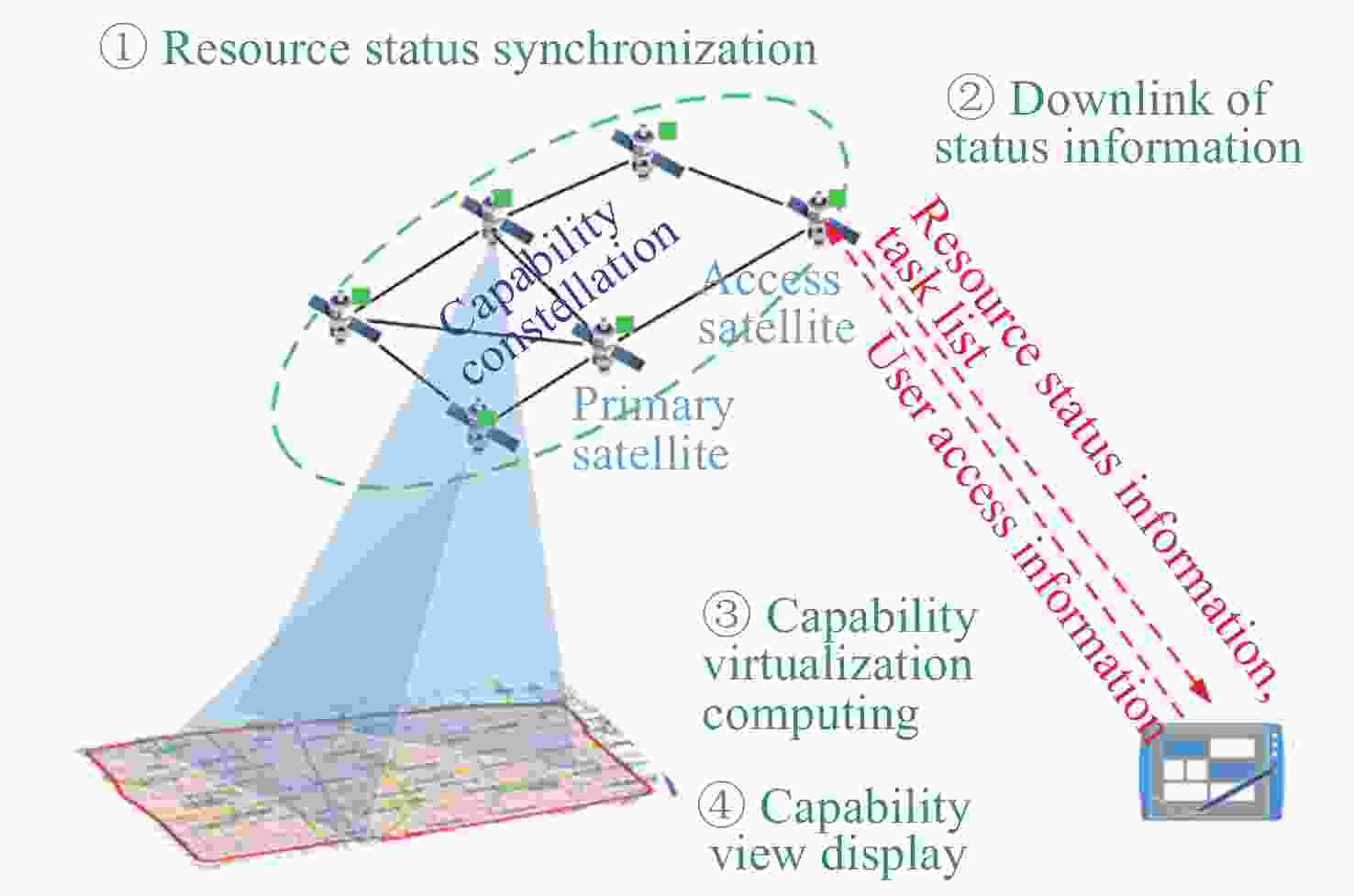
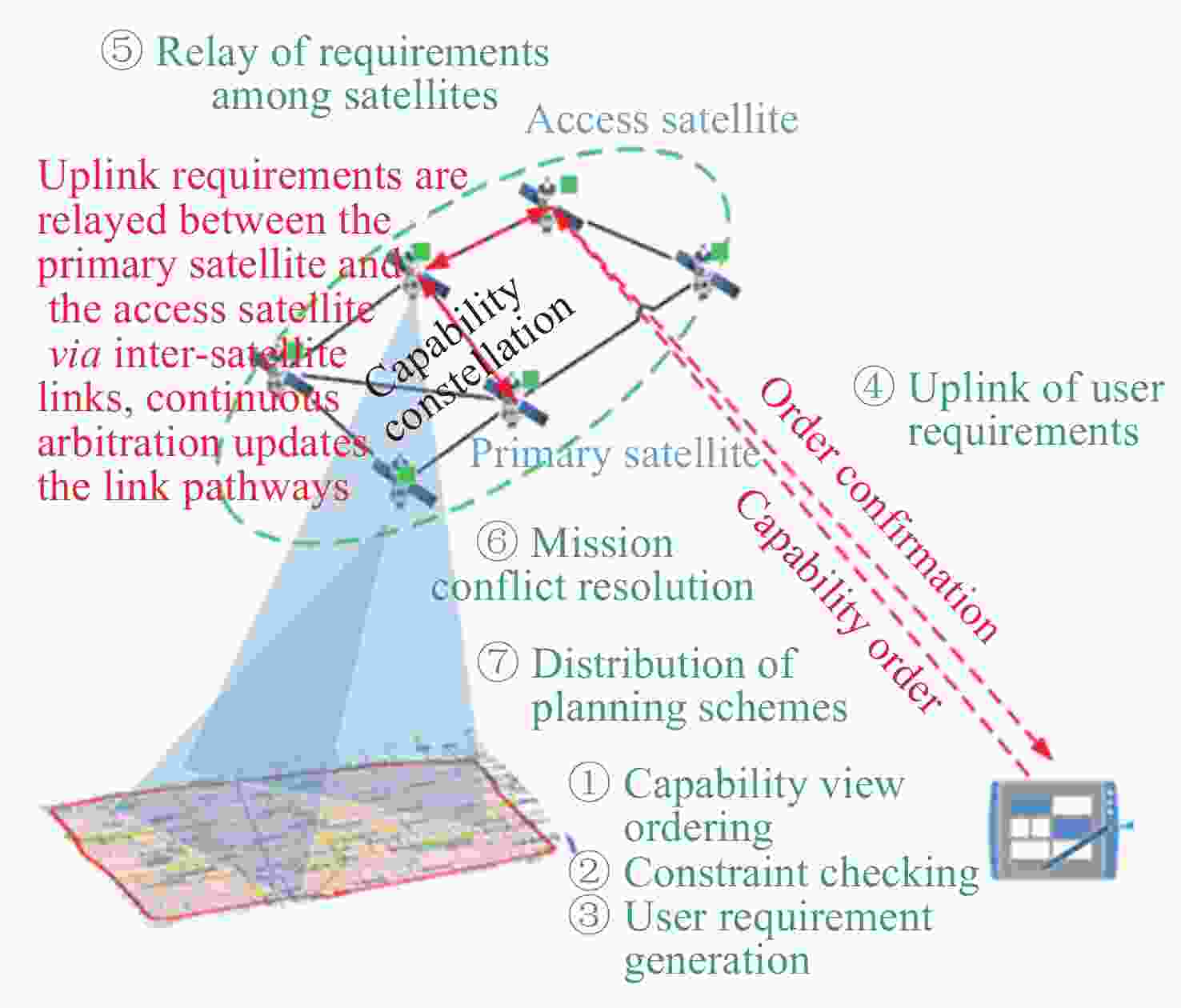
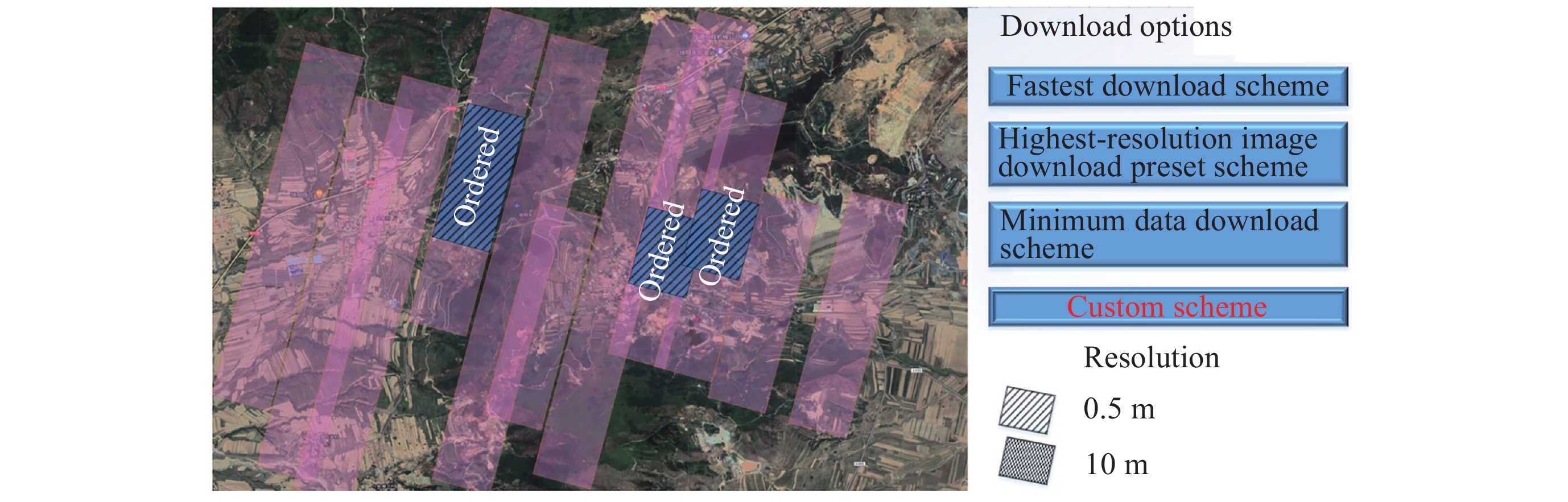
摘要: 提出一种基于有限域线性群的卫星集群能力与认知模型构建方法, 并基于该模型研究了能力视图、自主任务分配算法和发布订购机制, 进行在轨验证. 引入有限域与线性群的代数理论, 构建卫星智能体的能力模型, 为后续任务分配提供建模方法和逻辑依据, 基于能力与认知模型, 构建基于能力与认知模型的卫星集群能力视图, 为用户提供直观的能力显示和交互手段, 便于资源订购和管理; 设计基于能力与认知模型的卫星集群自主任务分配算法, 综合考虑智能体自身能力、邻居影响和任务驱动因素, 实现任务需求的自主匹配与决策, 确保卫星智能体能够合理分配卫星资源; 构建卫星集群发布订购机制, 实现卫星资源与用户需求的精准对接; 进行了卫星集群发布订购服务流程的在轨验证实验, 实现卫星资源能力构建、自主任务分配算法及能力视图发布订购服务流程, 星地即时能力订购响应时间(带天地链路通信时间)为 31s, 验证了能力及认知模型的可行性和有效性, 为其实际应用提供了依据.Abstract: This paper proposes a method for constructing the capability and cognitive model of satellite constellations based on the linear group over a finite field. Based on this model, the capability view, autonomous mission assignment algorithm, and publish-subscribe mechanism are studied, and an on-orbit verification is conducted. Firstly, by introducing the algebraic theory of the finite field and the linear group, the capability model of satellite agents is constructed. The capabilities of satellites are mapped into matrices over the finite field, and the cognitive state vector is established to accurately describe the capability structure and cognitive state of satellite agents, providing a modeling method and logical basis for subsequent mission assignment. Secondly, based on the capability and cognitive model, the capability view of the satellite constellation is constructed. By organizing and processing the capability data, the capability view is designed to provide users with an intuitive display and interaction means of capabilities, facilitating resource subscription and management. Then, an autonomous mission assignment algorithm for satellite constellations based on the capability and cognitive model is designed. By comprehensively considering the agents' own capabilities, neighbor influences, and mission-driven factors, the autonomous matching and decision-making of mission requirements are realized, ensuring that satellite agents can allocate satellite resources reasonably. Next, the publish-subscribe mechanism of satellite constellations is constructed to achieve the precise docking of satellite resources and user requirements. Finally, an on-orbit verification experiment of the publish-subscribe service process of satellite constellations is carried out. The construction of satellite resource capabilities, the autonomous mission assignment algorithm, and the publish-subscribe service process of the capability view are realized. The instantaneous capacity subscription response time between the satellite and the ground (including the communication time of the space-to-ground link) is 31 seconds, verifying the feasibility and effectiveness of the capability and cognitive model and providing a basis for its practical application.
-
表 1 能力数据结构层次
Table 1. Capability data structure hierarchy
数据层次 描述 设备属性层 描述单个卫星的基础属性, 如轨道状态和位置 卫星能力层 反映单个卫星的具体能力指标 集群能力层 综合多个卫星的能力, 提供整体能力视图 表 2 在轨实验硬件环境
Table 2. On orbit experiment hardware environment
类别 参数 CPU Cortex-A9双核, 主频800 MHz QSPI FLASH 2片, 单片64 MB PS DDR3 512 MB, 16 bit SD 4 GB SATA 1路, 单SSD容量 1 TByte 表 3 在轨实验软件环境
Table 3. On orbit experiment software environment
类别 参数 芯片型号 Xilinx-zynq 7045 操作系统 PetaLinux v2015.4 中间件 zmq (ZeroMQ 4.2.1), czmq 数据库 sqlite3 SDK SDK: Xilinx SDK 2015.4 日志库 log4 cplus, 1.2.1-rc1 开发语言 C++ 开发环境 Xilinx Software Development Kit
Release Version: 2015.4表 4 在轨实验时间指标
Table 4. On orbit experiment time evaluation index
类别 参数 基础计算时间 78.995 s 能力发布时间 单颗卫星, 4个覆盖条带, <1 s 能力视图约束检查时间 <1 s 在轨冲突决策时间 单星两个任务(观测、处理) 9 ms 规划方案数据帧生成时间 <3 s 能力订购响应时间
(带天地链路通信时间)31 s 表 5 在轨试验遥测参数
Table 5. On orbit experiment telemetry parameters
英文名 中文名 物理量 源码(16进制) RW10 当前任务状态 0000 0000 RW11 下一任务类型 1 a (Sar观测-处理) 1 a RW12 下一任务来源 Aa (星上) aa RW13 下一任务执行星 C2 (A星) C2 RW14 下一任务编号 11 000b RW15 下一任务起始时间 2021-06-22 15:26:12.0000 11d25f14 RW16 下一任务时长 11 0000000b RW17 当前任务编号 0 00000000 -
[1] ZOU Run, LIU Yang, ZANG Qing, et al. A review of the development of foreign space-based space target surveillance systems[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2023, 32(05): 110-118 (邹润, 刘阳, 臧晴, 魏斌斌, 刘春恒, 侯进永, 周宇翔. 国外天基空间目标监视系统发展综述[J]. 航天器工程, 2023, 32(05): 110-118ZOU Run, LIU Yang, ZANG Qing, et al. A review of the development of foreign space-based space target surveillance systems[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2023, 32(05): 110-118 [2] WEI Wenting, FU Liying, WANG Kun, et al. A review of satellite Internet routing technologies[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 1-15 (魏雯婷, 伏丽莹, 王琨, 卢雪玉, 周兆军. 卫星互联网路由技术综述[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 1-15WEI Wenting, FU Liying, WANG Kun, et al. A review of satellite Internet routing technologies[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 1-15 [3] WANG Zhenlang, HE Huiqun, ZHOU Jun, et al. Multi-satellite observation task allocation method based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. Shanghai Aerospace, 2024, 41(01): 108-115 (in Chinese and English) (王桢朗, 何慧群, 周军, 金云飞. 基于多智能体深度强化学习的多星观测任务分配方法[J]. 上海航天(中英文), 2024, 41(01): 108-115 doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.2096-8655.2024.01.014WANG Zhenlang, HE Huiqun, ZHOU Jun, et al. Multi-satellite observation task allocation method based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. Shanghai Aerospace, 2024, 41(01): 108-115 (in Chinese and English) doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.2096-8655.2024.01.014 [4] LEI Yonggang, ZHANG Ruoyu, MA Jianan. Application of artificial intelligence technology in the field of satellite mission control[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2022, 62(09): 1377-1382 (雷永刚, 张若禹, 马佳楠. 人工智能技术在卫星任务管控领域的应用[J]. 电讯技术, 2022, 62(09): 1377-1382LEI Yonggang, ZHANG Ruoyu, MA Jianan. Application of artificial intelligence technology in the field of satellite mission control[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2022, 62(09): 1377-1382 [5] ZHANG Xudong, LI Shaobo, LI Chuanjiang, et al. A review of unmanned aerial vehicle swarms: technologies, challenges and the future[J]. Radio Engineering, 2023, 53(07): 1487-1501 (张旭东, 李少波, 李传江, 张安思, 杨磊. 无人机集群综述: 技术、挑战与未来[J]. 无线电工程, 2023, 53(07): 1487-1501ZHANG Xudong, LI Shaobo, LI Chuanjiang, et al. A review of unmanned aerial vehicle swarms: technologies, challenges and the future[J]. Radio Engineering, 2023, 53(07): 1487-1501 [6] LI Huan. Research on task-driven unmanned aerial vehicle ad hoc network[D]. University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2023 (李欢. 面向任务驱动的无人机自组织网络研究[D]. 电子科技大学, 2023LI Huan. Research on task-driven unmanned aerial vehicle ad hoc network[D]. University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2023 [7] ZHAI Sheping, CAO Yongqiang, YANG Rui, et al. Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus algorithm supporting dynamic feedback decision-making[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 1-16 (翟社平, 曹永强, 杨锐, 张瑞婷. 支持动态反馈决策的拜占庭容错共识算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 1-16ZHAI Sheping, CAO Yongqiang, YANG Rui, et al. Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus algorithm supporting dynamic feedback decision-making[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 1-16 [8] TAN Shaolin, GU Haibo, LIU Kexin. Distributed learning in multi-agent games: principles and algorithms[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2024, 10(02): 127-136 (谭少林, 谷海波, 刘克新. 多智能体博弈中的分布式学习: 原理与算法[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2024, 10(02): 127-136TAN Shaolin, GU Haibo, LIU Kexin. Distributed learning in multi-agent games: principles and algorithms[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2024, 10(02): 127-136 [9] BIAN Yujing. Research on satellite time-domain resource allocation scheme for multi-tasks[D]. Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2023 (卞雨靖. 面向多任务的卫星时域资源分配方案研究[D]. 南京信息工程大学, 2023.BIAN Yujing. Research on satellite time-domain resource allocation scheme for multi-tasks[D]. Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2023 [10] CHEN Xu, HE Ping, LUO Meng, WU Han. Consistency of multi-agent systems with state constraints under event triggering[J]. Journal of Yibin University, 1-12 (陈旭, 何平, 罗萌, 吴汉. 事件触发下状态约束的多智能体系统一致性[J]. 宜宾学院学报, 1-12CHEN Xu, HE Ping, LUO Meng, WU Han. Consistency of multi-agent systems with state constraints under event triggering[J]. Journal of Yibin University, 1-12 [11] CHEN Yu, ZHANG Yong, CHEN Shi. Adaptive weighted clustering algorithm for large-scale satellite cluster networks[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021, 41(11): 1188-1192 (陈宇, 张勇, 陈实. 大规模卫星集群网络自适应加权分簇算法[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2021, 41(11): 1188-1192 doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.072CHEN Yu, ZHANG Yong, CHEN Shi. Adaptive weighted clustering algorithm for large-scale satellite cluster networks[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021, 41(11): 1188-1192 doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.072 [12] ZHU Zhengyuan. A property of linear groups and the orders of their subgroups[J]. Journal of Beijing Union University, 1995(03): 27-30 (朱正元. 线性群及其子群阶的一种性质[J]. 北京联合大学学报, 1995(03): 27-30 doi: 10.16255/j.cnki.ldxbz.1995.03.005ZHU Zhengyuan. A property of linear groups and the orders of their subgroups[J]. Journal of Beijing Union University, 1995(03): 27-30 doi: 10.16255/j.cnki.ldxbz.1995.03.005 -
-




 李英玉 女, 1976年11月出生于河北省迁安市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心副研究员, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为空间信息组织、复杂系统仿真等. E-mail:
李英玉 女, 1976年11月出生于河北省迁安市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心副研究员, 硕士生导师, 主要研究方向为空间信息组织、复杂系统仿真等. E-mail: 
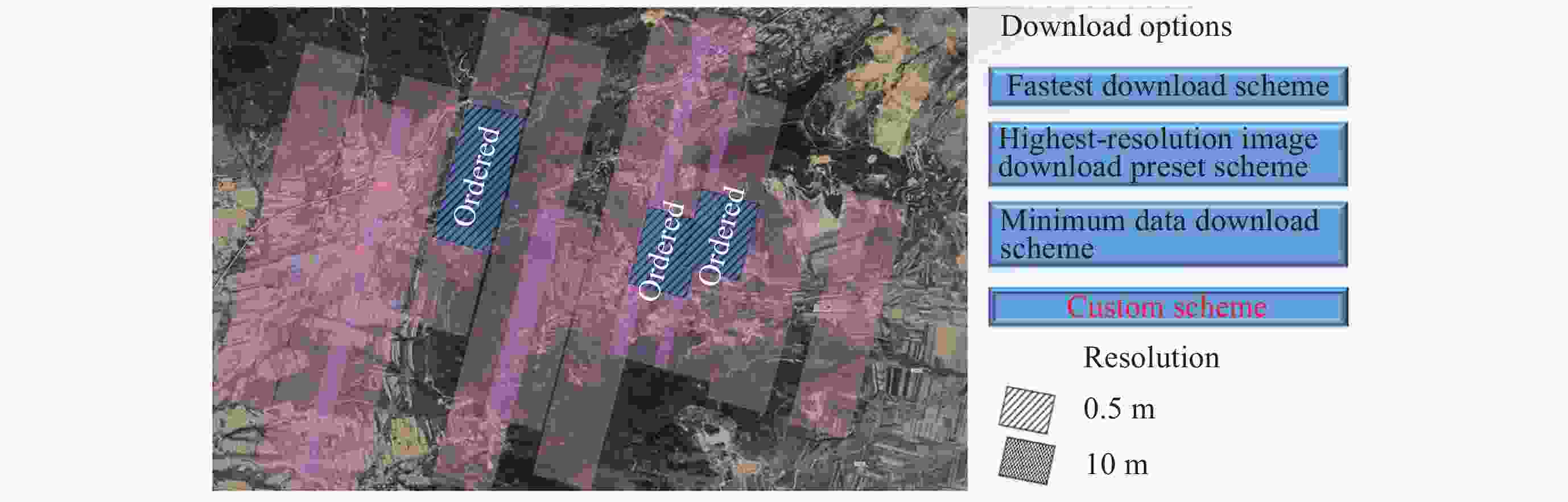
 下载:
下载: