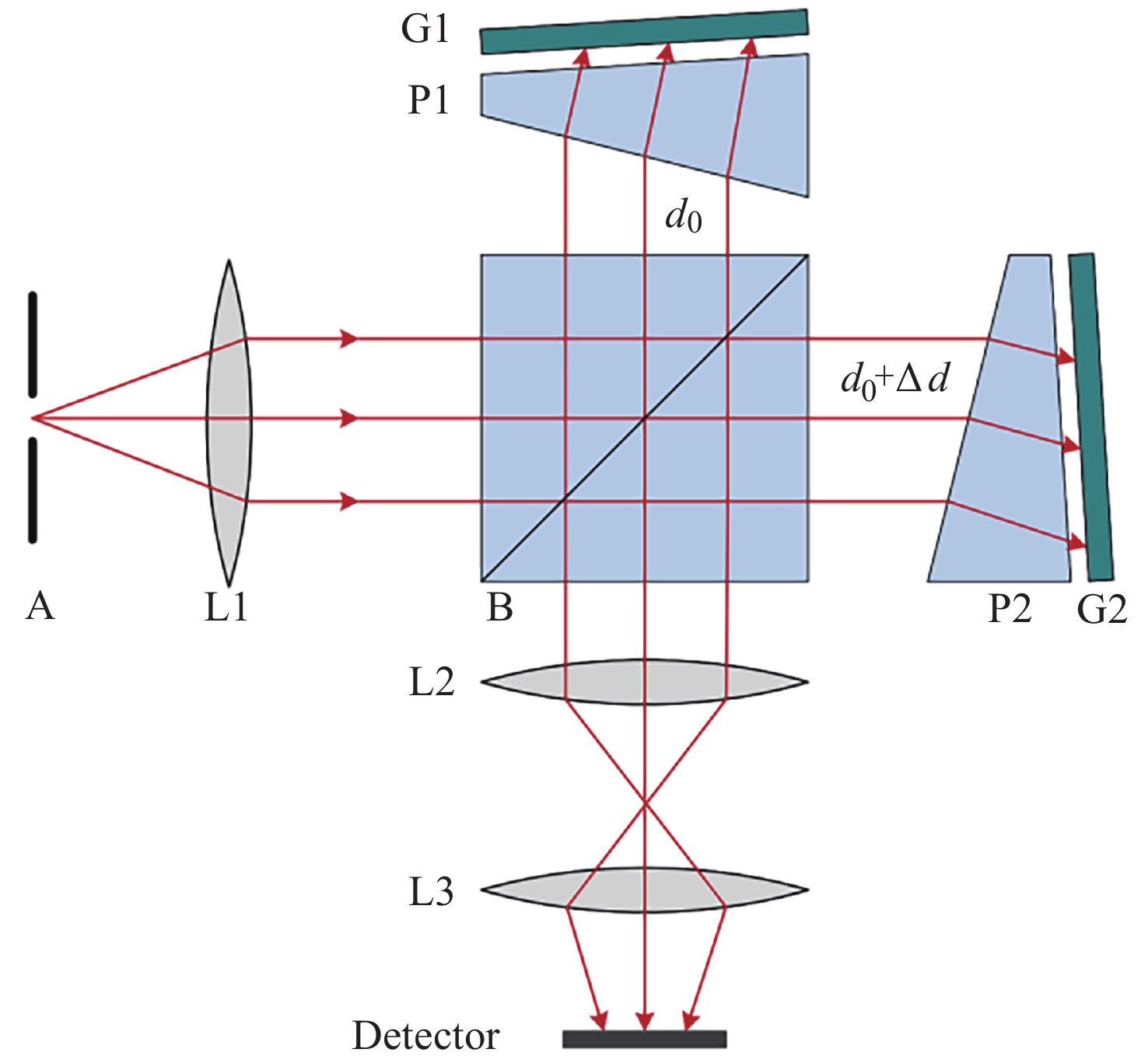
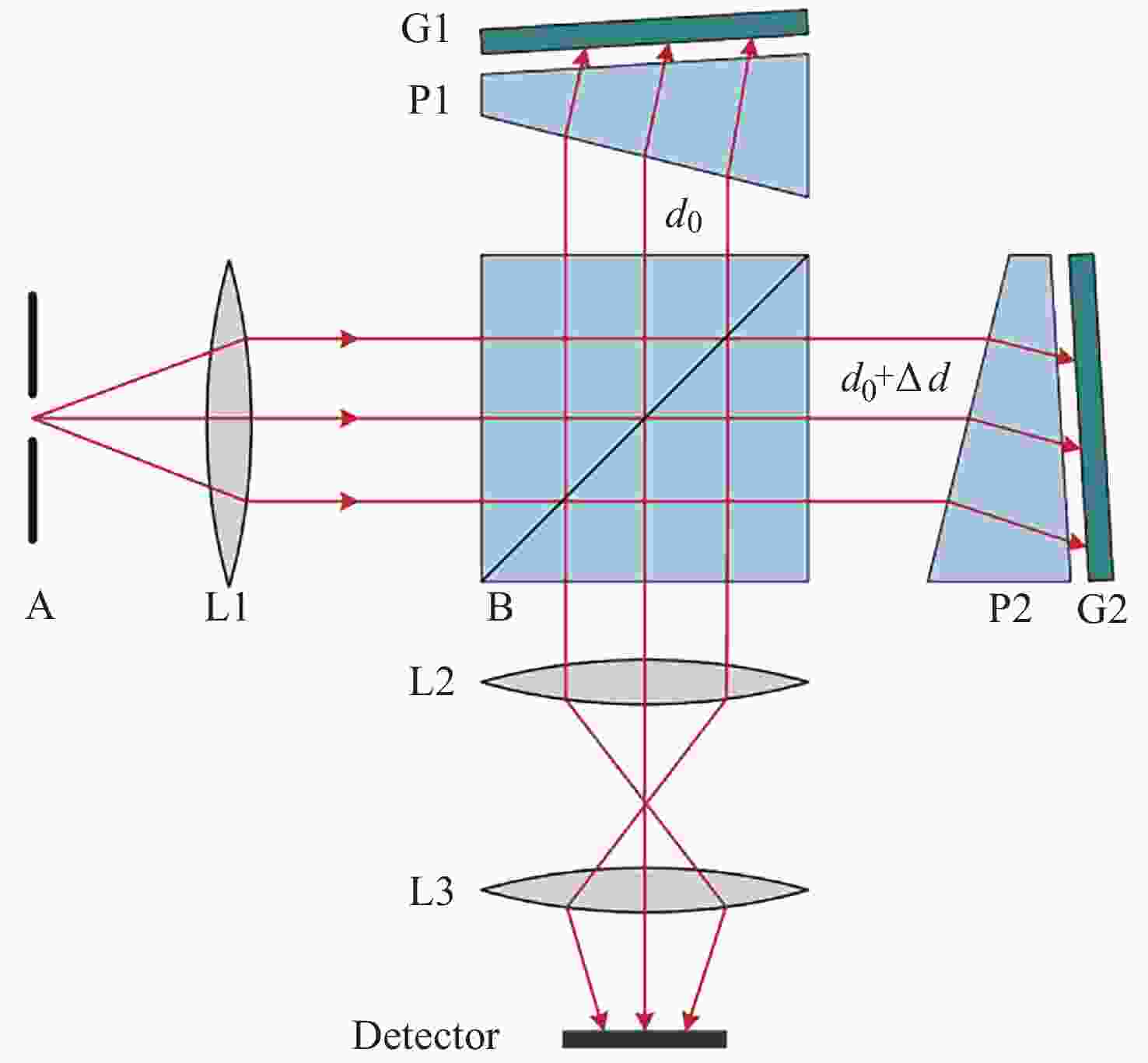
Calibration Techniques for Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne Interferometers
-
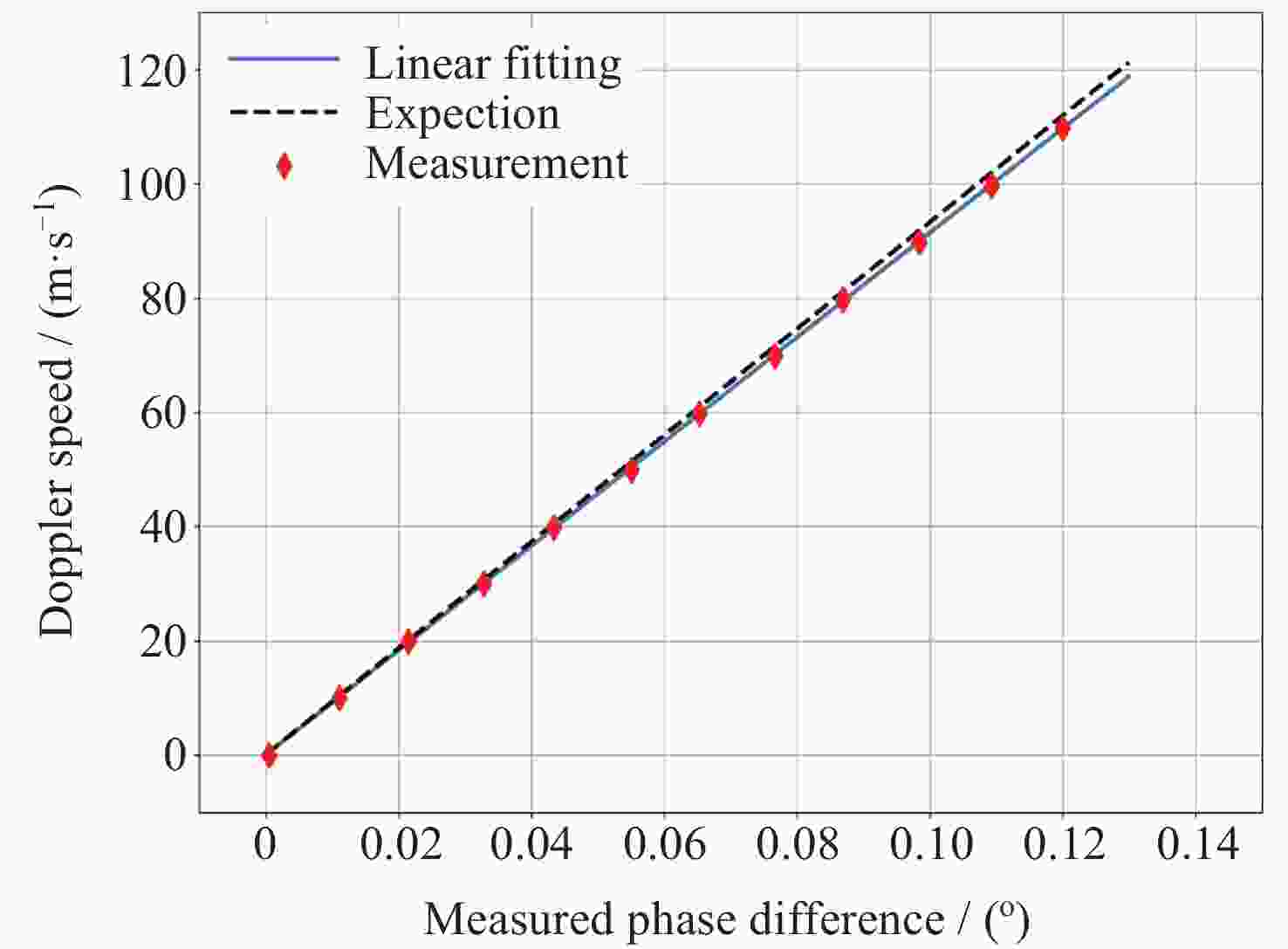
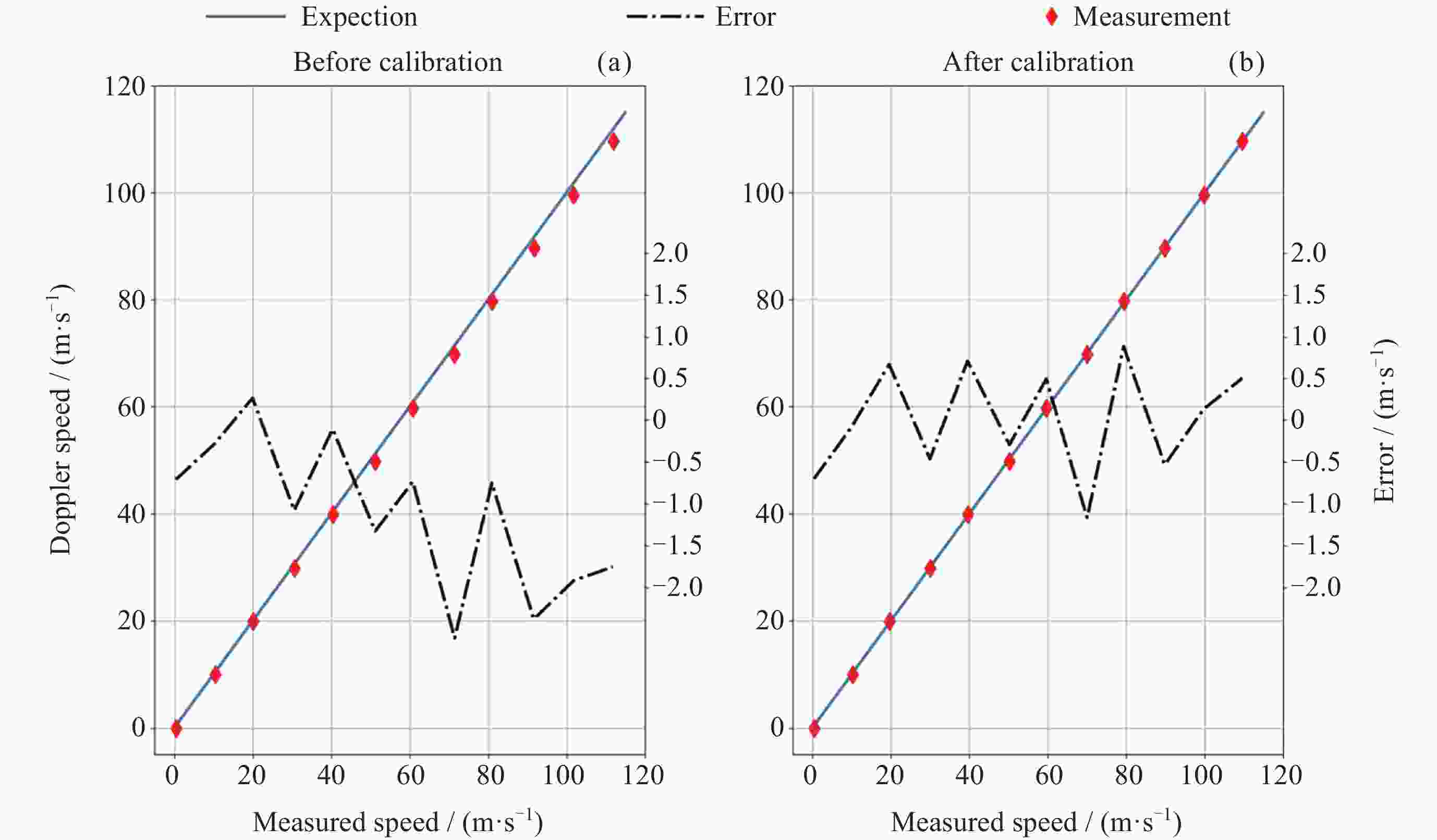
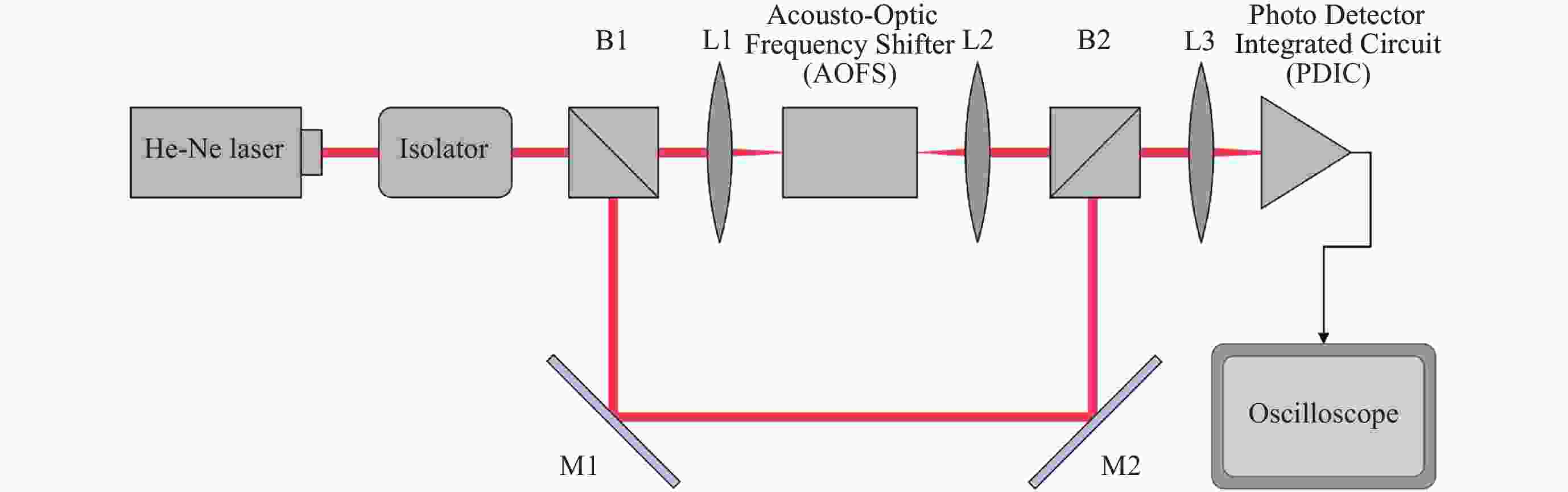
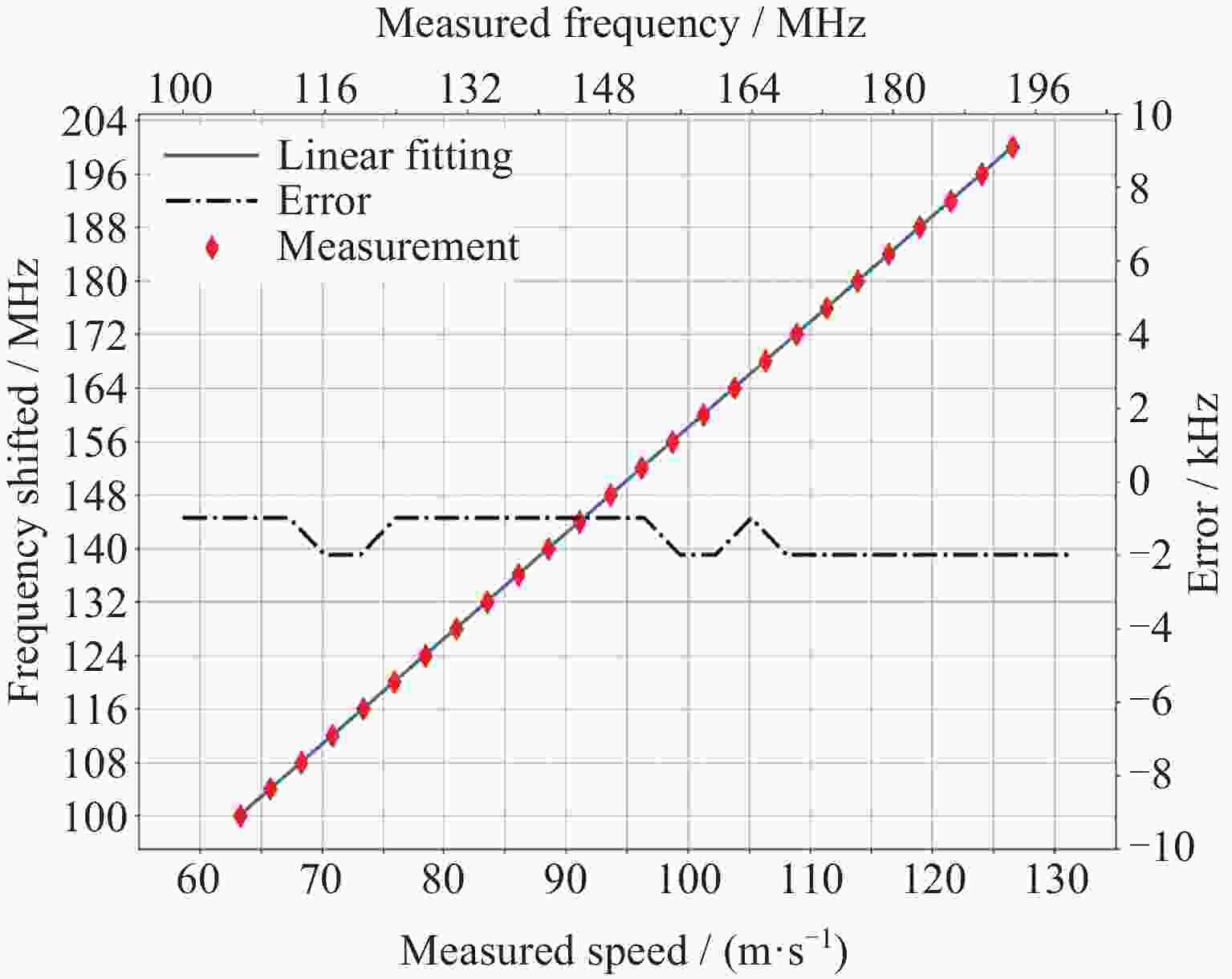
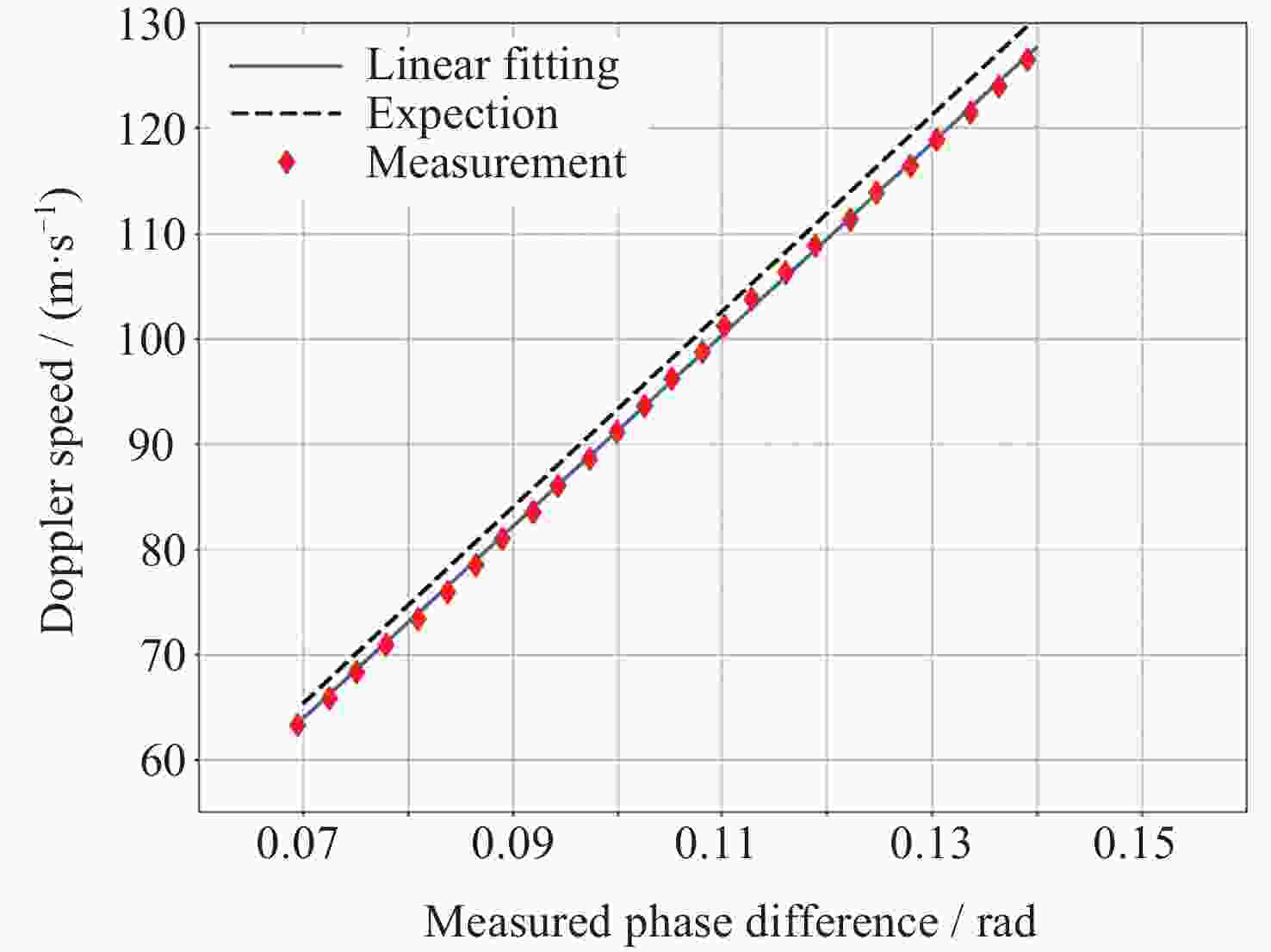
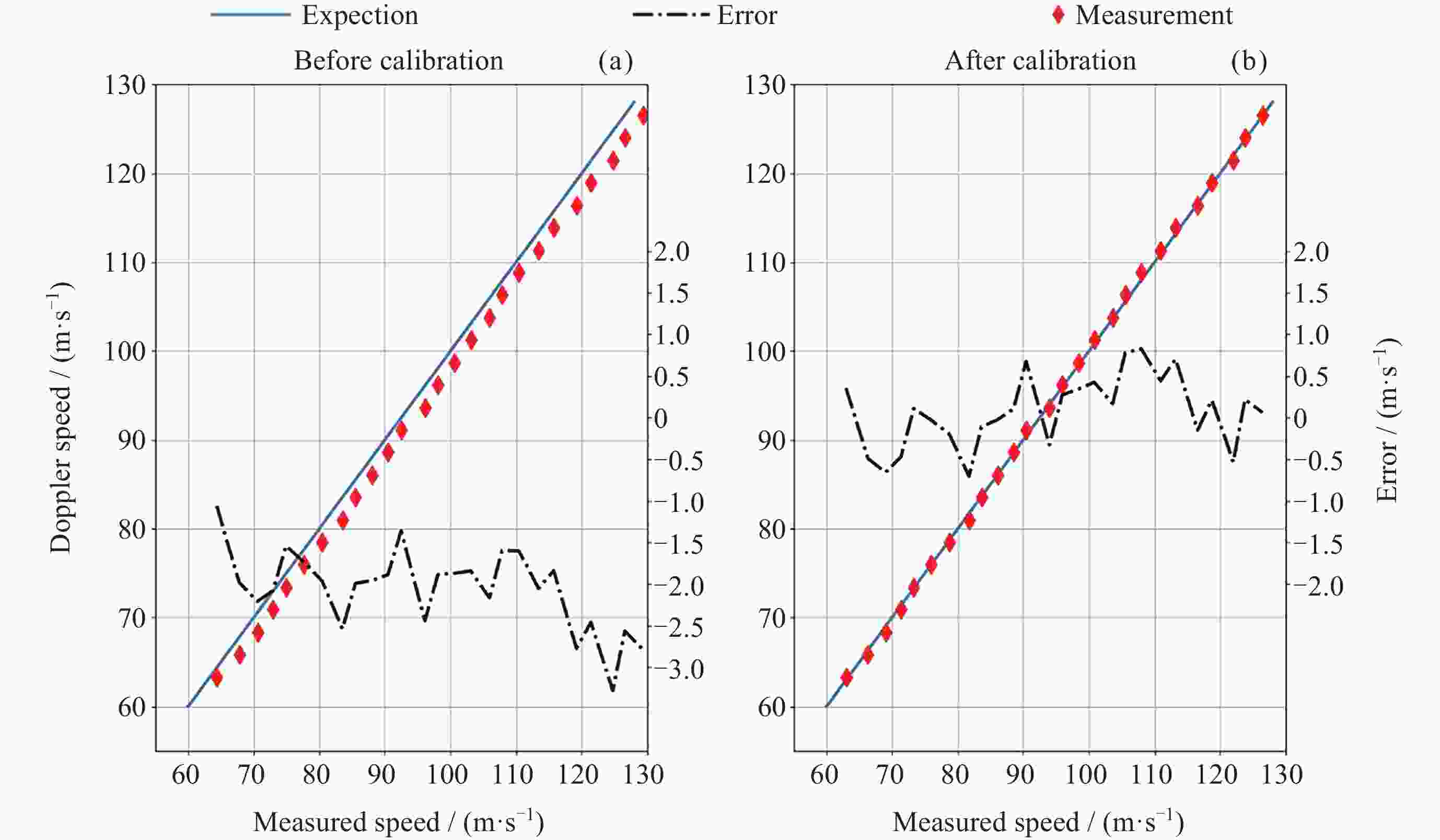
摘要: 中高层大气风场探测对于大气模型构建、卫星轨道预测、通信导航保障和空间天气灾害预测具有重要的科学和应用价值. 光学干涉仪获取气辉辐射的多普勒频移是大气风场遥感最重要的方法之一. 标定光学干涉仪的测风性能对于确保探测精确度有重要意义. 通过研究非对称空间外差干涉仪的测风原理, 提出测风敏感系数的概念, 为仪器标定提供理论依据. 设计并实施了两种典型的标定系统, 用以对非对称空间外差干涉仪进行测风标定实验. 结合标定过程与结果对这两种标定系统的不确定度以及适用性进行综合评估. 声光移频测风标定系统具有优于±1 m·s–1的不确定度, 并且结构紧凑、易于集成, 可作为传递标准, 用于地面测风网络的内部校准, 反射转盘式测风标定系统具有广泛的光源适用性. 该结果可为测风光学干涉仪的实验室和常规现场标定提供参考.
-
关键词:
- 非对称空间外差干涉仪 /
- 中高层大气风场 /
- 被动光学探测 /
- 标定技术
Abstract: The detection of wind in the middle and upper atmosphere has important scientific and practical value for the construction of atmospheric models, satellite orbit prediction, communication and navigation support, and space weather disaster prediction. The Doppler shift of airglow radiation obtained by optical interferometer is one of the most important methods for remote sensing of atmosphere wind. Ensuring the accuracy of these measurements necessitates the calibration of the wind measurement performance of optical interferometers. In this paper, we propose the concept of wind measurement sensitivity coefficient through studying the wind measurement principle of asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometer, providing a solid theoretical foundation for instrument calibration. Two typical calibration systems are designed and implemented to calibrate an asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometer. By examining both the calibration process and results, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the uncertainty and applicability of these two systems. The acousto-optic frequency shift calibration system boasts an uncertainty of less than ±1 m·s–1, coupled with its compact design and ease of integration, making it an ideal transfer standard for internal calibration within ground wind measurement networks. On the other hand, the reflective wheel calibration system demonstrates wide applicability across various light sources. The findings presented in this paper can serve as a valuable reference for both laboratory and routine field calibration of wind-measuring optical interferometers. -
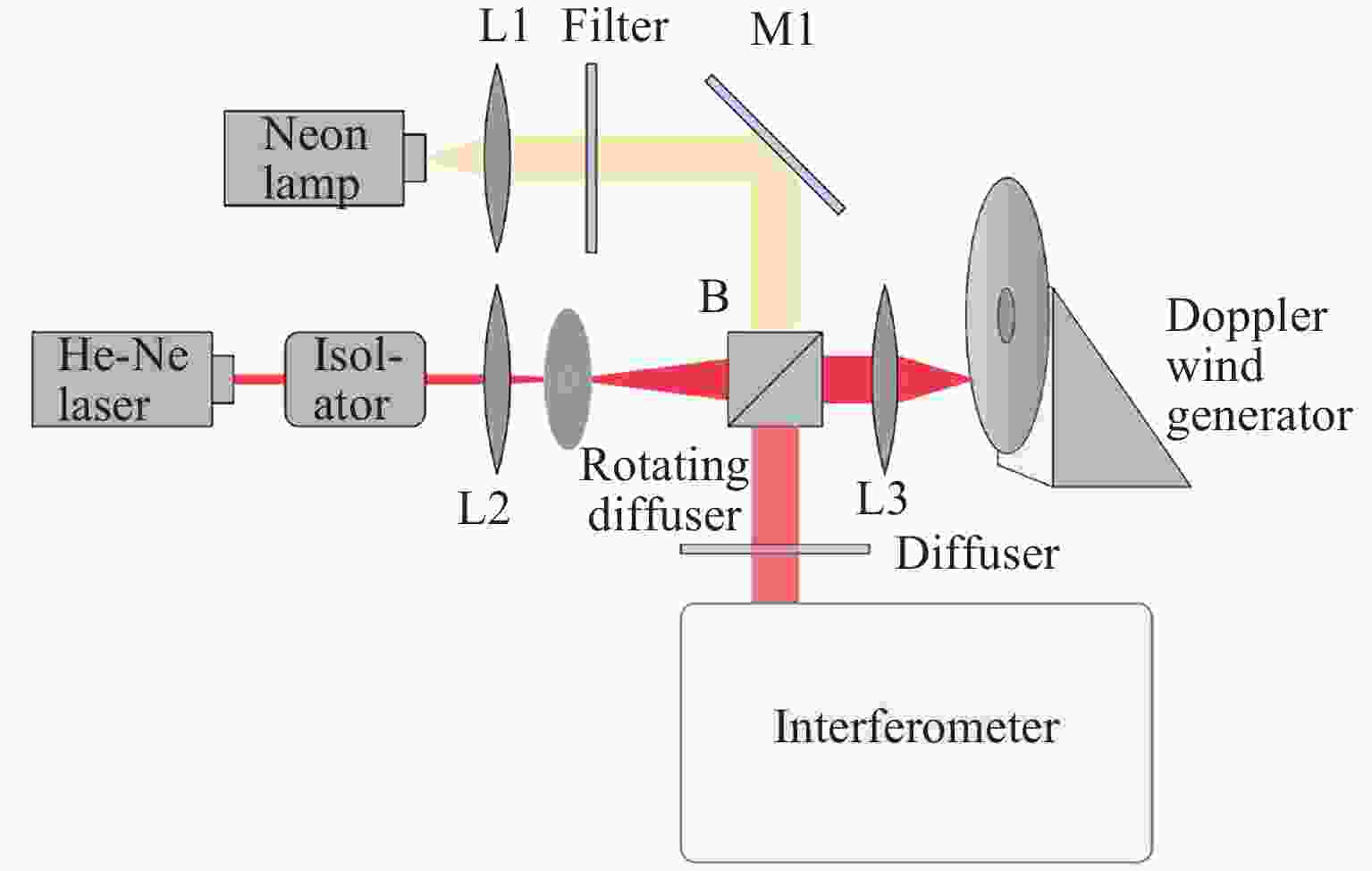
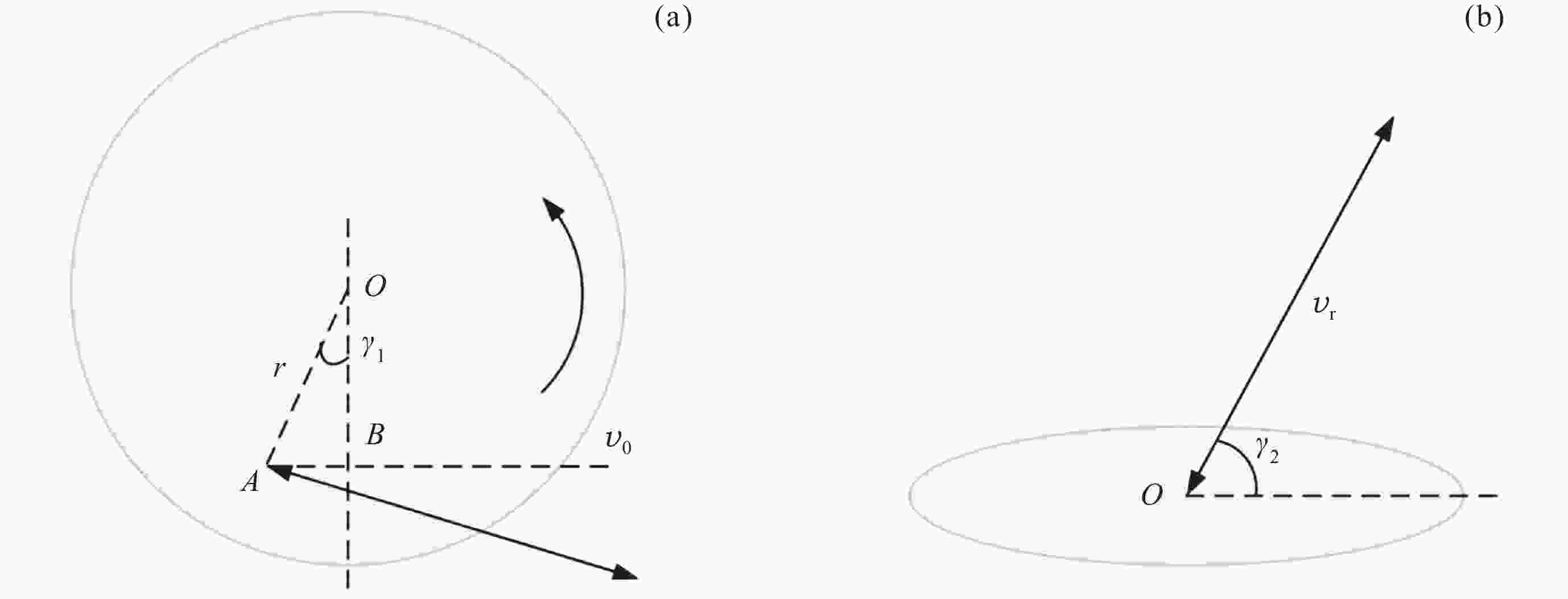
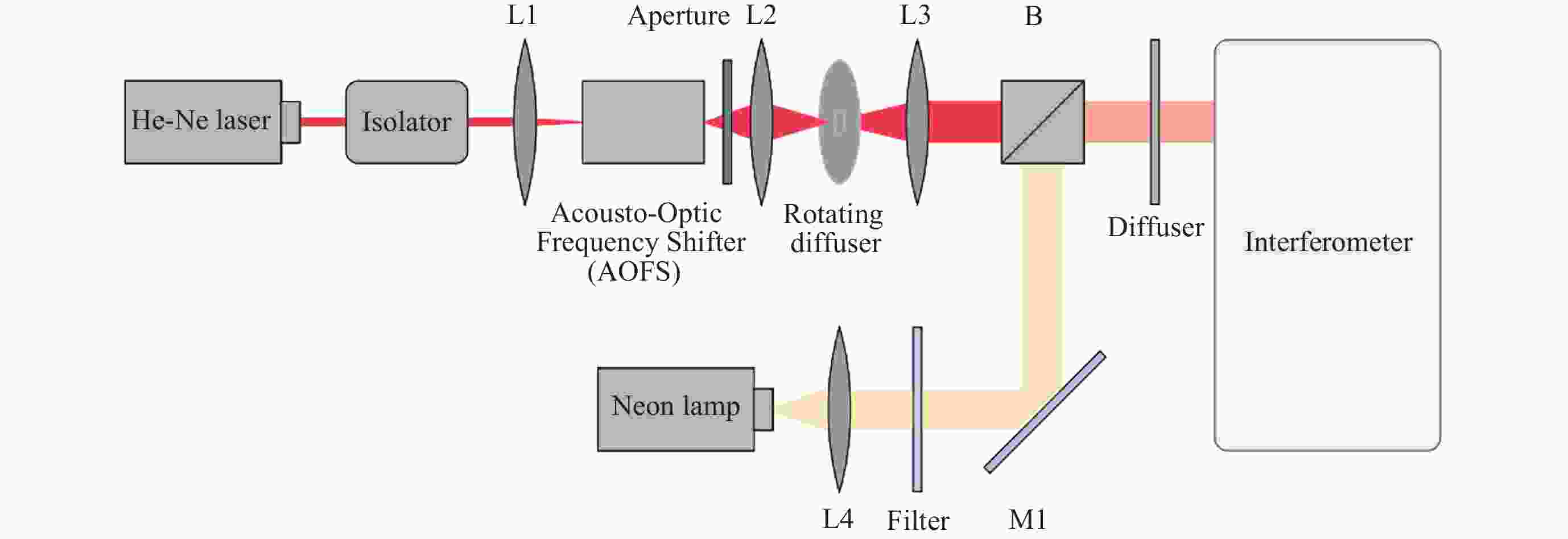
表 1 反射转盘式多普勒风速模拟器参数
Table 1. Parameters of Doppler wind generation system of reflection wheel
$ {{N}}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $ 0~6000 r·min–1 r 13.8 cm $ \cos {{\gamma }}_{1} $ 0.9629 $ \cos {{\gamma }}_{2} $ 0.6691 $ {{v}}_{\rm{r}} $ 0~119.6 m·s–1 表 2 反射转盘式多普勒风速模拟器不确定度分析
Table 2. Uncertainty of Doppler wind generation system of reflection wheel
$ {{N}}_{\rm{s}}=4000\; $r·min–1时
不确定度来源测量不确定度 $ {v} $r = 79.76 m·s–1时
引起的速度不确定度/(m·s–1)$ {{N}}_{\rm{s}} $ ±10 r·min–1 ±0.19 $ {r} $ ±0.2 cm ±1.08 $ \cos {{\gamma }}_{1} $ ±0.020 ±1.55 $ \cos {{\gamma }}_{2} $ ±0.036 ±0.08 光源频率 ±1 MHz ±0.63 $ {v} $r的不确定度 – ±2.00 -
[1] EMMERT J T. Thermospheric mass density: a review[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2015, 56(5): 773-824 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2015.05.038 [2] IMMEL T J, ENGLAND S L, MENDE S B, et al. The ionospheric connection explorer mission: mission goals and design[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2018, 214(1): 13 doi: 10.1007/s11214-017-0449-2 [3] LIU Weining, BLANC M, WANG Chi, et al. Scientific challenges and instrumentation for the International Meridian Circle Program[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2021, 64(12): 2090-2097 (刘维宁, BLANC M, 王赤, 等. 国际子午圈计划的科学挑战和观测系统[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2021, 51(12): 2056-2062LIU Weining, BLANC M, WANG Chi, et al. Scientific challenges and instrumentation for the International Meridian Circle Program[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2021, 64(12): 2090-2097 [4] DHADLY M, SASSI F, EMMERT J, et al. Neutral winds from mesosphere to thermosphere—past, present, and future outlook[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2023, 9: 1050586 doi: 10.3389/fspas.2022.1050586 [5] WANG Chi, WANG Yuming, TIAN Hui, et al. Strategic study for the development of space physics[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(1): 9-42 (王赤, 汪毓明, 田晖, 等. 空间物理学科发展战略研究[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(1): 9-42WANG Chi, WANG Yuming, TIAN Hui, et al. Strategic study for the development of space physics[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(1): 9-42 [6] SHEPHERD G G, THUILLIER G, GAULT W A, et al. WINDII, the wind imaging interferometer on the upper atmosphere research satellite[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1993, 98(D6): 10725-10750 doi: 10.1029/93JD00227 [7] KILLEEN T L, WU Q, SOLOMON S C, et al. TIMED Doppler interferometer: overview and recent results[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2006, 111(A10): A10S01 [8] MERIWETHER J W. Studies of thermospheric dynamics with a Fabry–Perot interferometer network: a review[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2006, 68(13): 1576-1589 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2005.11.014 [9] ZHANG C M, WU Q M, MU T K. Influences of pyramid prism deflection on inversion of wind velocity and temperature in a novel static polarization wind imaging interferometer[J]. Applied Optics, 2011, 50(32): 6134-6139 doi: 10.1364/AO.50.006134 [10] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, BROWN C M, et al. Michelson Interferometer for Global High-resolution Thermospheric Imaging (MIGHTI): instrument design and calibration[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2017, 212(1/2): 553-584 [11] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, EMMERT J T, et al. Initial ground-based thermospheric wind measurements using Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne spectroscopy (DASH)[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(26): 27416-27430 doi: 10.1364/OE.18.027416 [12] WEI D K, GONG Q C, CHEN Q Y, et al. Modeling and correction of fringe patterns in Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometry[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(35): 10528-10537 doi: 10.1364/AO.473147 [13] HARLANDER J M, ENGLERT C R. Laboratory demonstration of mini-MIGHTI: a prototype sensor for thermospheric red-line (630 nm) neutral wind measurements from a 6U CubeSat[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2020, 207: 105363 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2020.105363 [14] ZHU G Y, ZHU Y J, KAUFMANN M, et al. An efficient calibration system of optical interferometer for measuring middle and upper atmospheric wind[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(7): 1898 doi: 10.3390/rs15071898 [15] WEI D G. Development of an Optical Instrument for the Observation of Neutral Winds in Earth’s Upper Atmosphere[D]. Wuppertal: Bergische Universität Wuppertal, 2020 [16] LIU J L, WEI D K, ZHU Y J, et al. Effective wind and temperature retrieval from Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectrometer interferograms[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(30): 8829-8835 doi: 10.1364/AO.57.008829 [17] BABCOCK D D. Development of a Space Flight Prototype Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne (DASH) Spectrometer for the Measurement of Upper Atmospheric Winds[R]. Ohio: Air Force Research Laboratory, 2011 [18] SHEN Jing. Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne Technique for Wind Detection in the Upper Atmosphere[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2017 (沈静. 中高层大气风场探测多普勒非对称空间外差技术研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2017SHEN Jing. Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne Technique for Wind Detection in the Upper Atmosphere[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2017 [19] DÖTZER F. Calibration of a Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne Interferometer for Atmospheric Wind Measurements[D]. Freistaat Bayern: Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nuernberg, 2019 [20] KUANG Yinli. Research on Radial Velocity Measurement Technology Based on Doppler Asymmetric Space Heterodyne Interferometer[D]. Chengdu: Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020 (况银丽. 基于非对称空间外差干涉仪的多普勒测速技术研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院光电技术研究所), 2020KUANG Yinli. Research on Radial Velocity Measurement Technology Based on Doppler Asymmetric Space Heterodyne Interferometer[D]. Chengdu: Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020 -
-





 朱光逸 男, 1995年11月出生于黑龙江省哈尔滨市, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心在读博士研究生, 主要研究方向为中高层大气风场探测与反演. E-mail:
朱光逸 男, 1995年11月出生于黑龙江省哈尔滨市, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心在读博士研究生, 主要研究方向为中高层大气风场探测与反演. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: