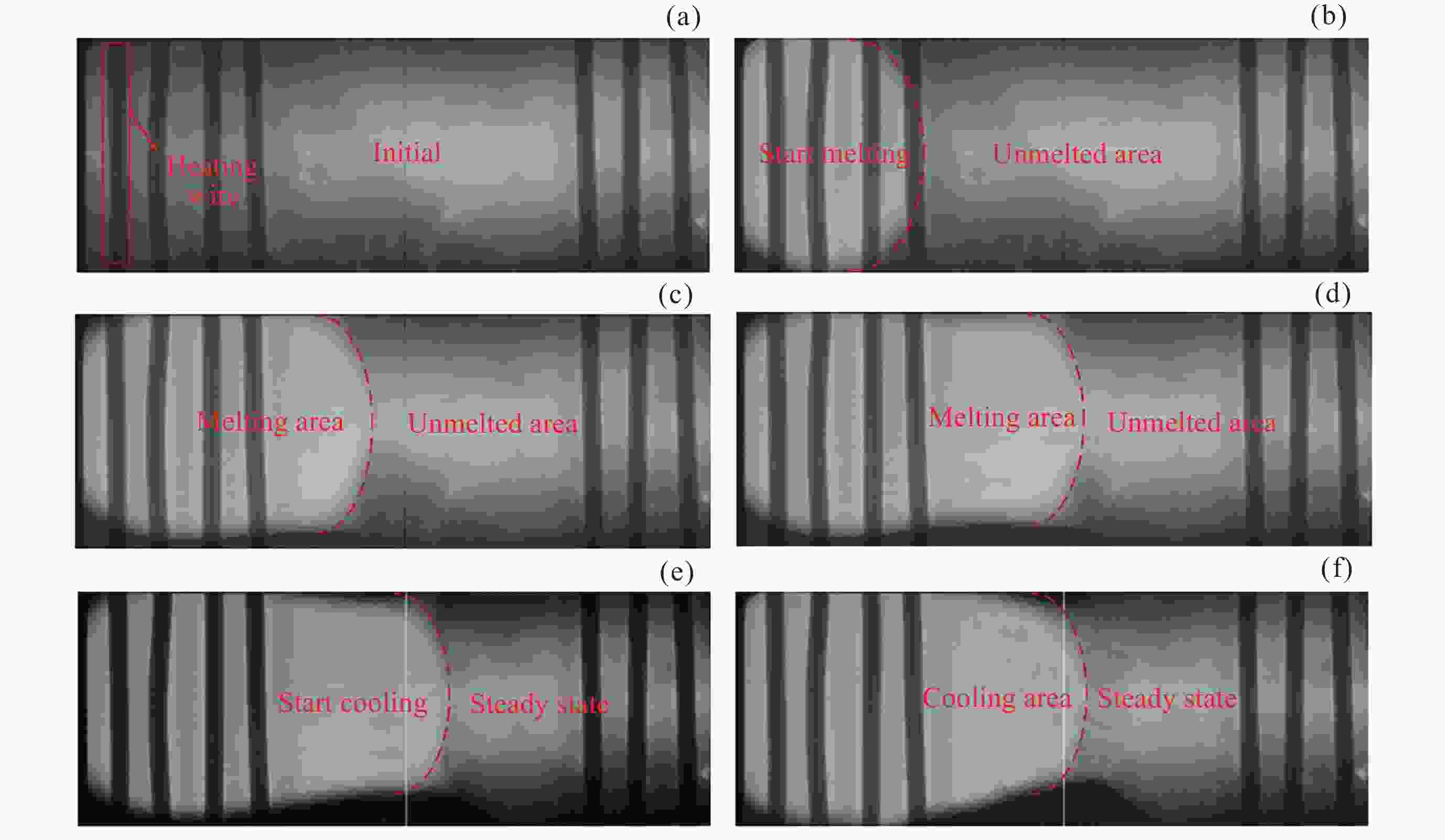
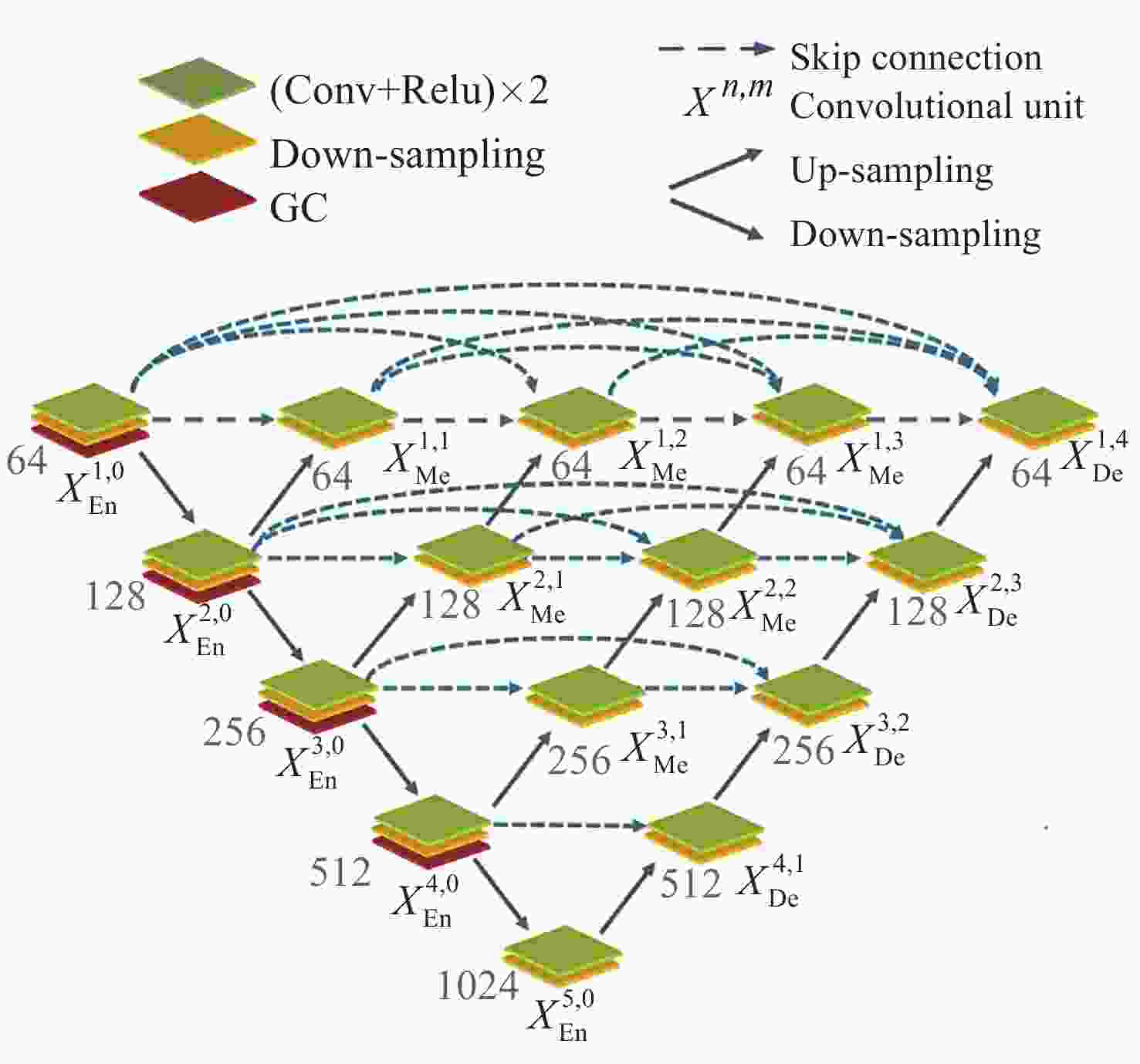
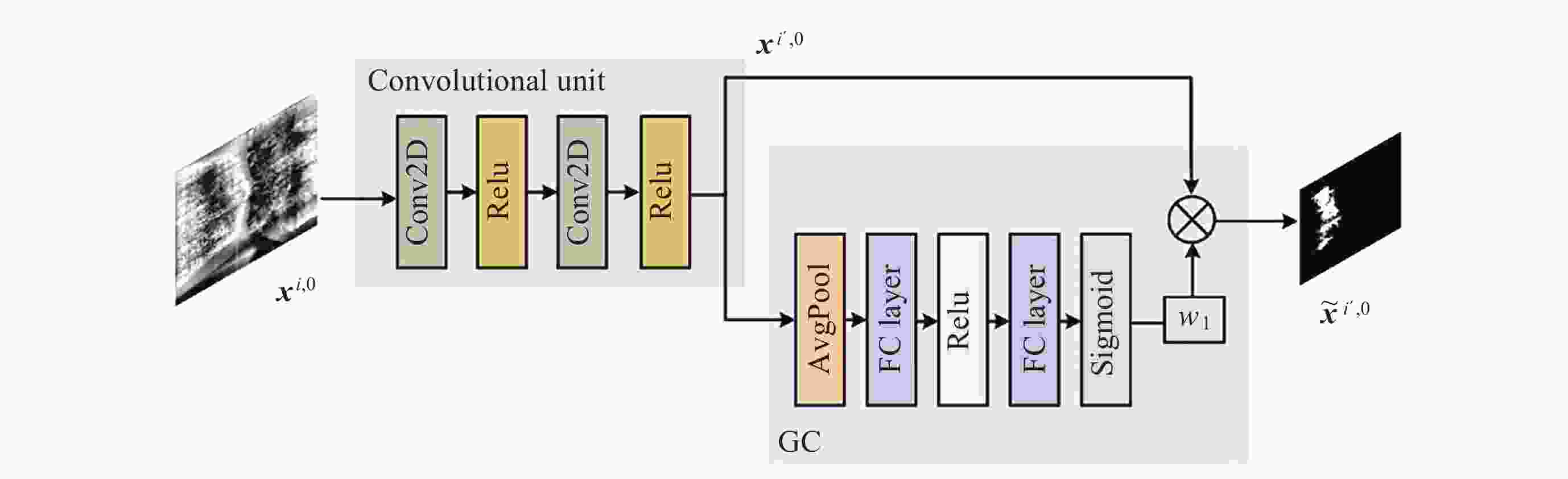
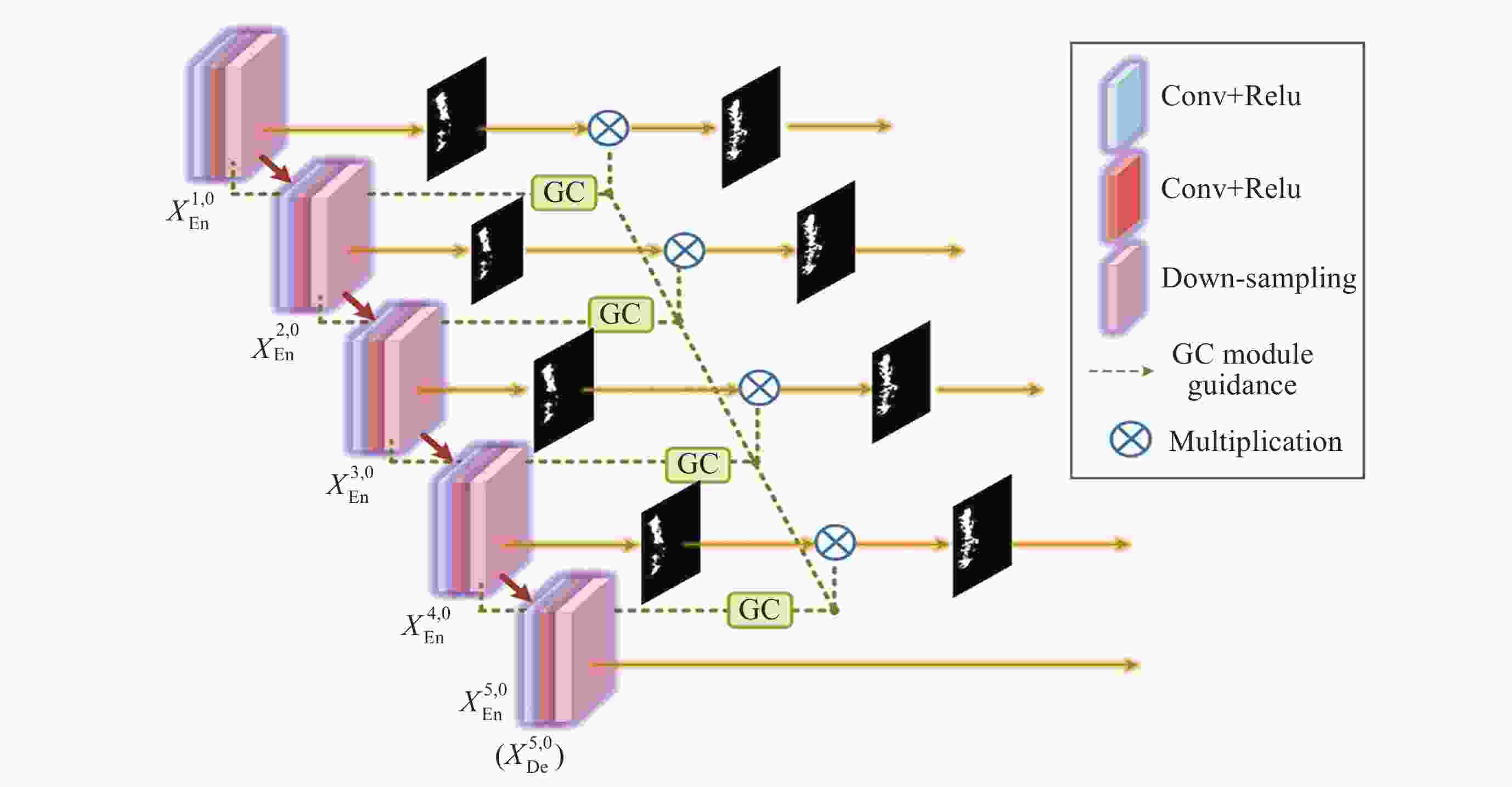
Segmentation Algorithm of X-ray Microstructure Image of Na6Mo11O36 Material
-
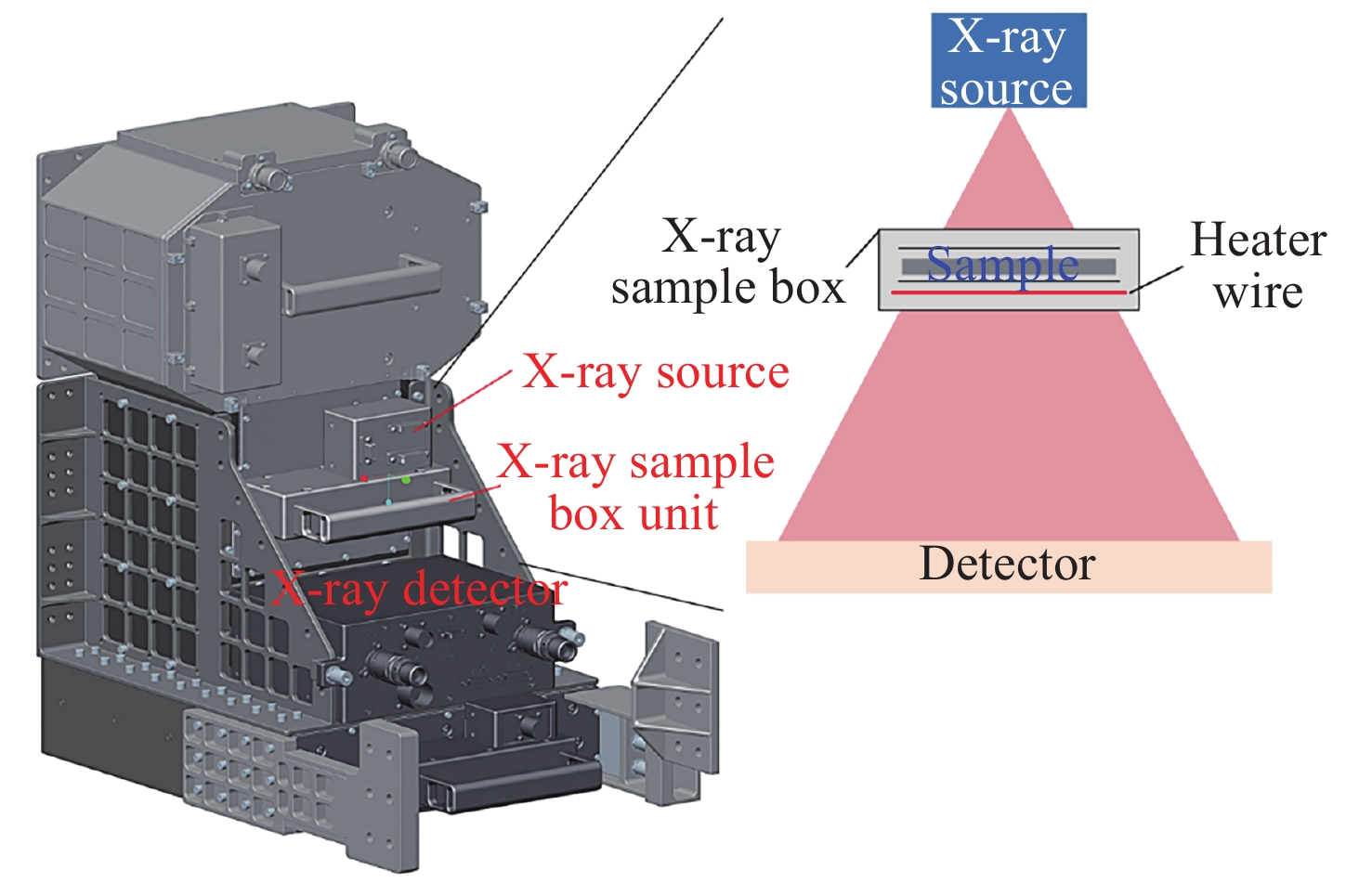
摘要: 在微重力环境下进行材料科学实验可以消除重力对材料实验过程的干扰, 揭示材料生长过程的本征规律, 获得具有更高性能的材料. 中国空间站高温材料科学实验柜配备了X射线透射成像模块, 能够实现在微重力条件下对材料凝固过程的实时成像和观察. 受空间站实验条件等因素的限制, X射线透射成像模块拍摄到的材料X射线图像模糊不清, 图像中的微观结构难以直接观察. 本文提出了一种专门针对 Na6Mo11O36材料凝固过程中生成的微观结构图像而设计的分割算法GFF-UNet++, 并从图像分割性能及材料科学两个方面对GFF-UNet++算法进行全面评估. 实验结果表明, 相比UNet, UNet++, DC-UNet, UNet3+, Pretrained-Microscopy-Models等图像分割算法, GFF-UNet++在图像分割任务中的各项图像分割指标上均有明显提升, 能够更准确分割出Na6Mo11O36材料在生长过程中形成的微观结构. 这为材料的微观结构分割研究提供了新的思路和方法, 具有重要应用价值.Abstract: Conducting materials science experiments in a microgravity environment mitigates the influence of gravity, enabling the study of intrinsic material growth mechanisms and the fabrication of materials with enhanced properties. The high-temperature materials research rack aboard the Chinese Space Station is equipped with an X-ray transmission imaging module, facilitating real-time imaging and observation of material solidification processes under microgravity. However, due to the constraints of the space station’s experimental conditions, the X-ray images acquired by this module often exhibit blurriness, making direct observation of microstructures challenging. To address this issue, the GFF-UNet++ image segmentation algorithm is proposed, specifically tailored for analyzing the microstructures formed during the solidification of Na6Mo11O36 material. The algorithm’s effectiveness is rigorously evaluated in terms of both image segmentation performance and its relevance to materials science applications. The experimental results demonstrate that in the image segmentation task, GFF-UNet++ outperforms established algorithms such as UNet, UNet++, DC-UNet, UNet3+ and Pretrained-Microscopy-Models, achieving notable improvements across various image segmentation metrics. Furthermore, the microstructures formed during the growth of the Na6Mo11O36 can be segmented more accurately. This provides new ideas and methods for the study of the microstructure segmentation of materials, and has important application value.
-
表 1 本实验中混淆矩阵的构建方法
Table 1. Construction method of the confusion matrix in this experiment
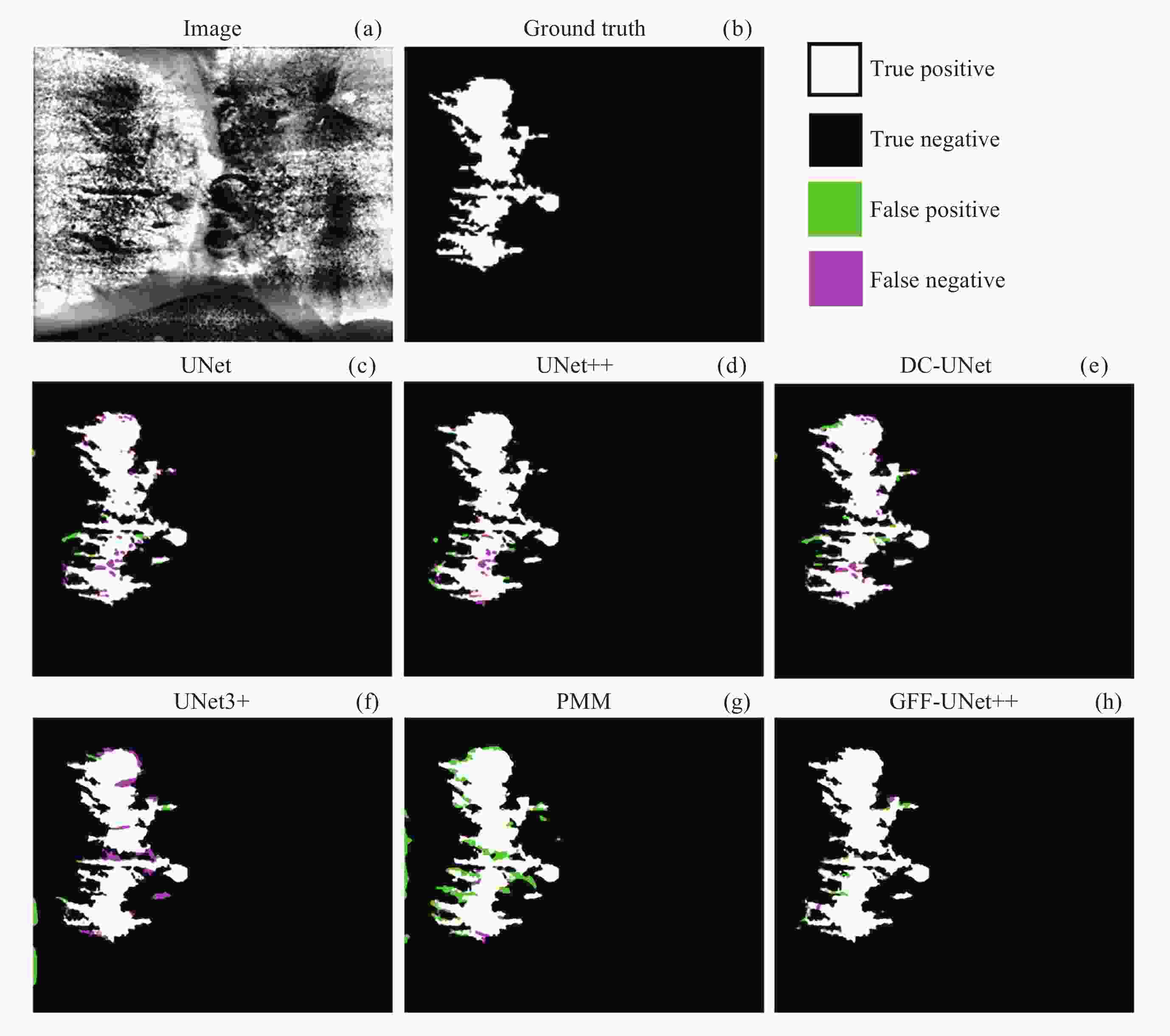
混淆矩阵 预测结果 条状微观结构 背景 真实标签 条状微观结构 TP FN 背景 FP TN 表 2 图像分割评价指标
Table 2. Image segmentation evaluation index
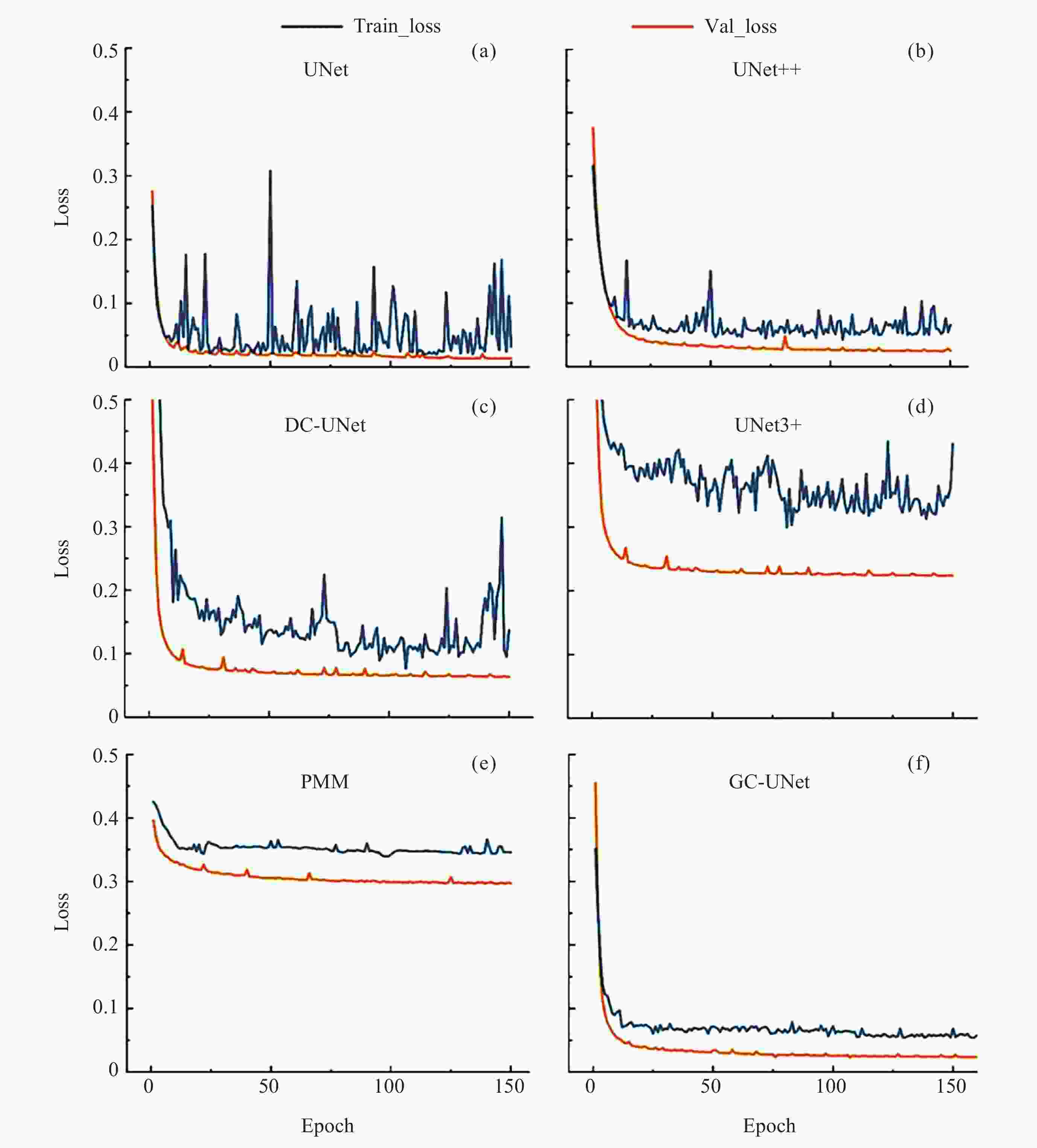
Architecture Evaluation index Accuracy Recall Precision Dice IOU UNet 0.822 0.790 0.982 0.868 0.835 UNet++ 0.813 0.788 0.988 0.834 0.822 DC-UNet 0.850 0.776 0.978 0.842 0.849 UNet3+ 0.867 0.851 0.990 0.877 0.882 PMM 0.880 0.833 0.983 0.906 0.870 GFF-UNet++ 0.898 0.885 0.993 0.894 0.901 注 粗体数值表示每列在所述指标下的最优结果. -
[1] WANG Y, LI S, LIU Z, et al. Anisotropy-dependent seaweed growth during directional solidification of Al-4.5%Cu single crystal[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2020, 186: 121-126 doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.05.006 [2] AGHALARI M, AGHAGOLZADEH A, EZOJI M. Brain tumor image segmentation via asymmetric/symmetric UNet based on two-pathway-residual blocks[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 69(6): 102841 [3] WANG E K, CHEN C-M, HASSAN M M, et al. A deep learning based medical image segmentation technique in Internet-of-Medical-Things domain[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 108: 135-144 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2020.02.054 [4] HUANG H, LIN L, TONG R, et al. UNet 3+: a full-scale connected UNet for medical image segmentation[C]// 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2020: 1055-1059 [5] SONG Y, QU Z, LIAO H, et al. Material twins generation of woven polymer composites based on ResL-U-Net convolutional neural networks[J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 307: 116672 doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2023.116672 [6] GUAN Y, PANG Z, SUN H, et al. Material strain image segmentation algorithm based on improved UNET network[C/OL]//Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Test Automation & Instrumentation (ISTAI 2022), 2022 [7] SHI P, DUAN M M, YANG L F, et al. An improved U-Net image segmentation method and its application for metallic grain size statistics[J]. MATERIALS, 2022, 15(13) [8] STUCKNER J, HARDER B, SMITH T M. Microstructure segmentation with deep learning encoders pre-trained on a large microscopy dataset[J]. NPJ Computational Materials, 2022, 8(1): 200 doi: 10.1038/s41524-022-00878-5 [9] IBTEHAZ N, RAHMAN M S. MultiResUNet : Rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation[J]. Neural Networks, 2019, 121: 74-87 [10] GAO WEIZE, CHEN SHANXIONG, MO BOFENG, et al. R-UNet++: a local segmentation network for the classification of oracle bone materials[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design :Times New Roman;">& Computer Graphics, 2022, 34(3): 415-424 [11] HIRABAYASHI Y, IGA H, OGAWA H, et al. Deep learning for three-dimensional segmentation of electron microscopy images of complex ceramic materials[J]. NPJ Computational Materials, 2024, 10(1): 46 doi: 10.1038/s41524-024-01226-5 [12] HORWATH J P, ZAKHAROV D N, MéGRET R, et al. Understanding important features of deep learning models for segmentation of high-resolution transmission electron microscopy images[J]. NPJ Computational Materials, 2020, 6(1): 108 doi: 10.1038/s41524-020-00363-x [13] YANG B, WU M, TEIZER W. Modified UNet++ with attention gate for graphene identification by optical microscopy[J]. Carbon: An International Journal Sponsored by the American Carbon Society, 2022, 195: 246-252 [14] LIU P, SONG Y, CHAI M, et al. Swin–UNet++: a nested swin transformer architecture for location identification and morphology segmentation of dimples on 2.25Cr1Mo0.25V fractured surface[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(24): 7504 doi: 10.3390/ma14247504 [15] SHU K Y, CHEN Z X, ZHU B, et al. Unsupervised Segmentation for Microstructure Identification of High Strength Steel with Superpixel Segmentation and Texture Feature Clustering[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on the Technology of Plasticity - Current Trends in the Technology of Plasticity, 2024. Switzerland: Springer [16] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[J]. Springer, Cham, 2015. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-662-54345-0_3 [17] ZHOU Z, RAHMAN SIDDIQUEE M M, TAJBAKHSH N, et al. Unet++: a nested U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation[J]. 2018. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_1 [18] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation; proceedings of the medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention[C]//MICCAI 2015: 18th international conference, 2015. Munich: Springer [19] ZHOU Z, RAHMAN SIDDIQUEE M M, TAJBAKHSH N, et al. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support, 2018. Springer International Publishing. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_1 [20] LOU A, GUAN S, LOEW M H. DC-UNet: rethinking the U-Net architecture with dual channel efficient CNN for medical image segmentation[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2021, 11596(000). DOI: 10.1117/12.2582338 [21] HUANG H, LIN L, TONG R, et al. UNet 3+: a full-scale connected UNet for medical image segmentation[J]. arXiv, 2020. DOI: 10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9053405 [22] ISENSEE F, JAEGER P F, KOHL S A A, et al. nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(2): 203-211 doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-01008-z [23] LOU A, GUAN S, LOEW M. DC-UNet: rethinking the U-Net architecture with dual channel efficient CNN for medical image segmentation[C]//Image Processing. SPIE, 2021. DOI: 10.1117/12.2582338 -
-




 李欣泽 女, 2000年8月出生于广西南宁市, 现为中国科学院大学硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为图像对比度增强、图像分割. E-mail:
李欣泽 女, 2000年8月出生于广西南宁市, 现为中国科学院大学硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为图像对比度增强、图像分割. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: