Imaging Method of Synthetic Aperture Radio Telescope Based on Minimax Concave Penalty
-
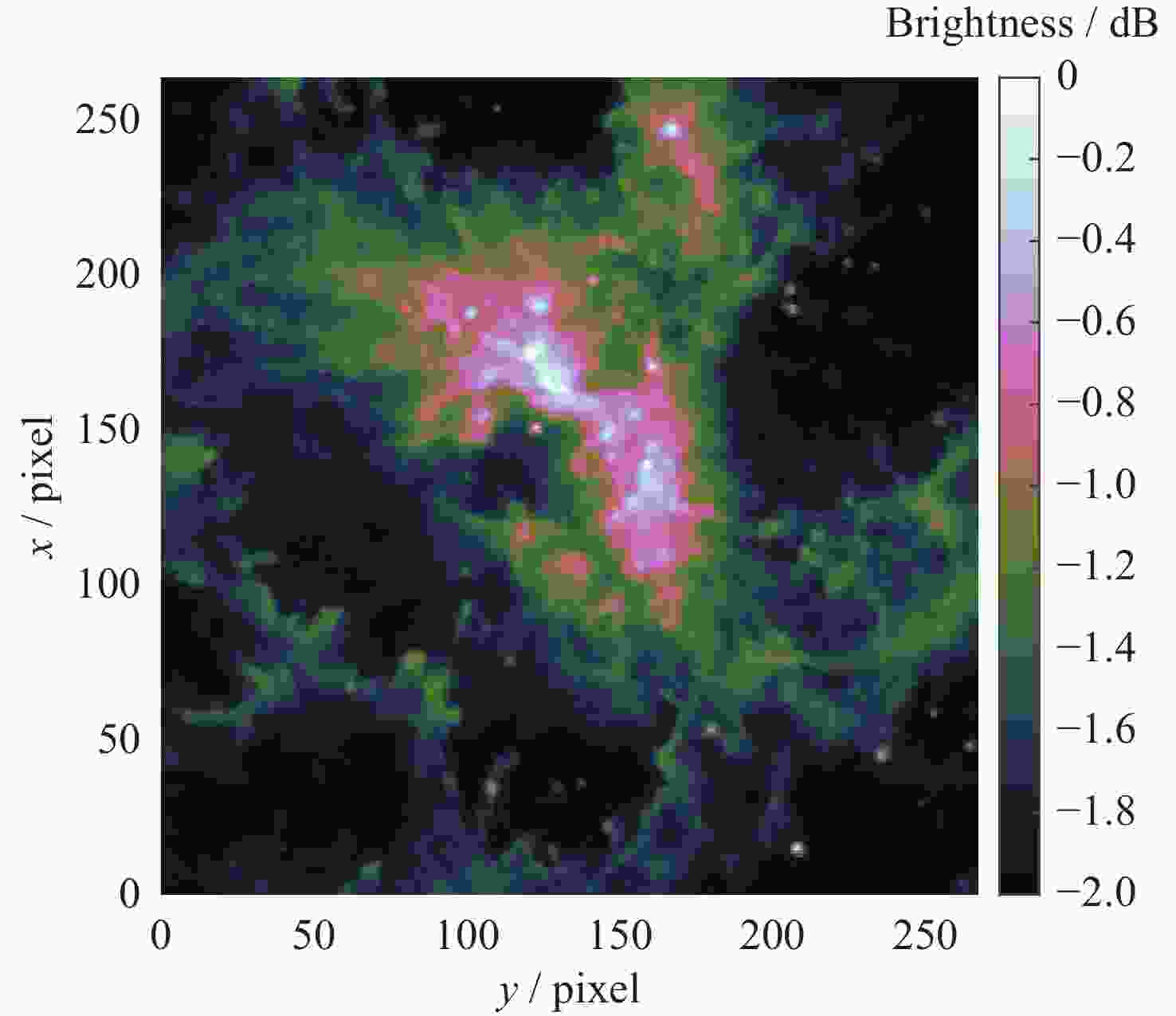
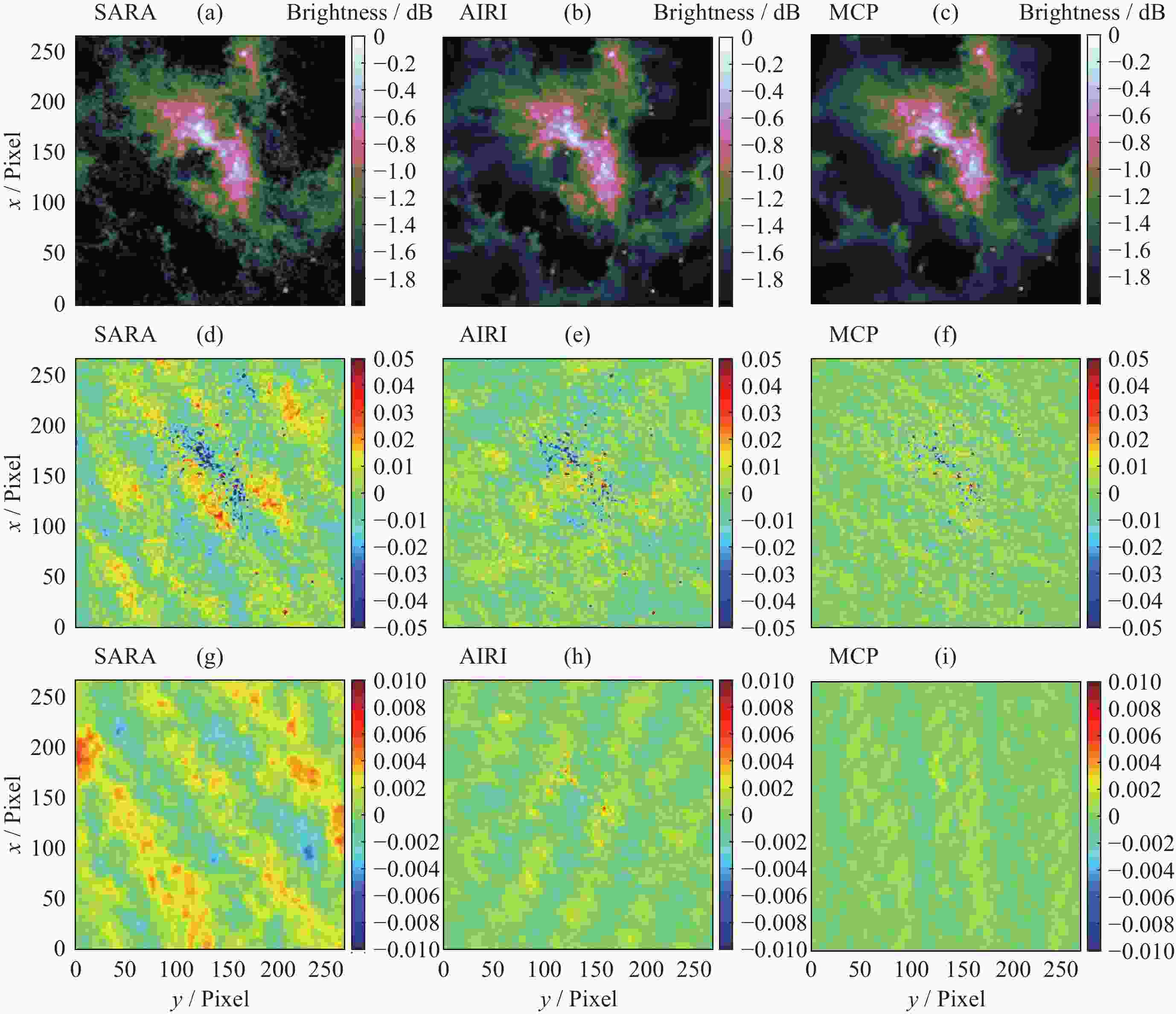
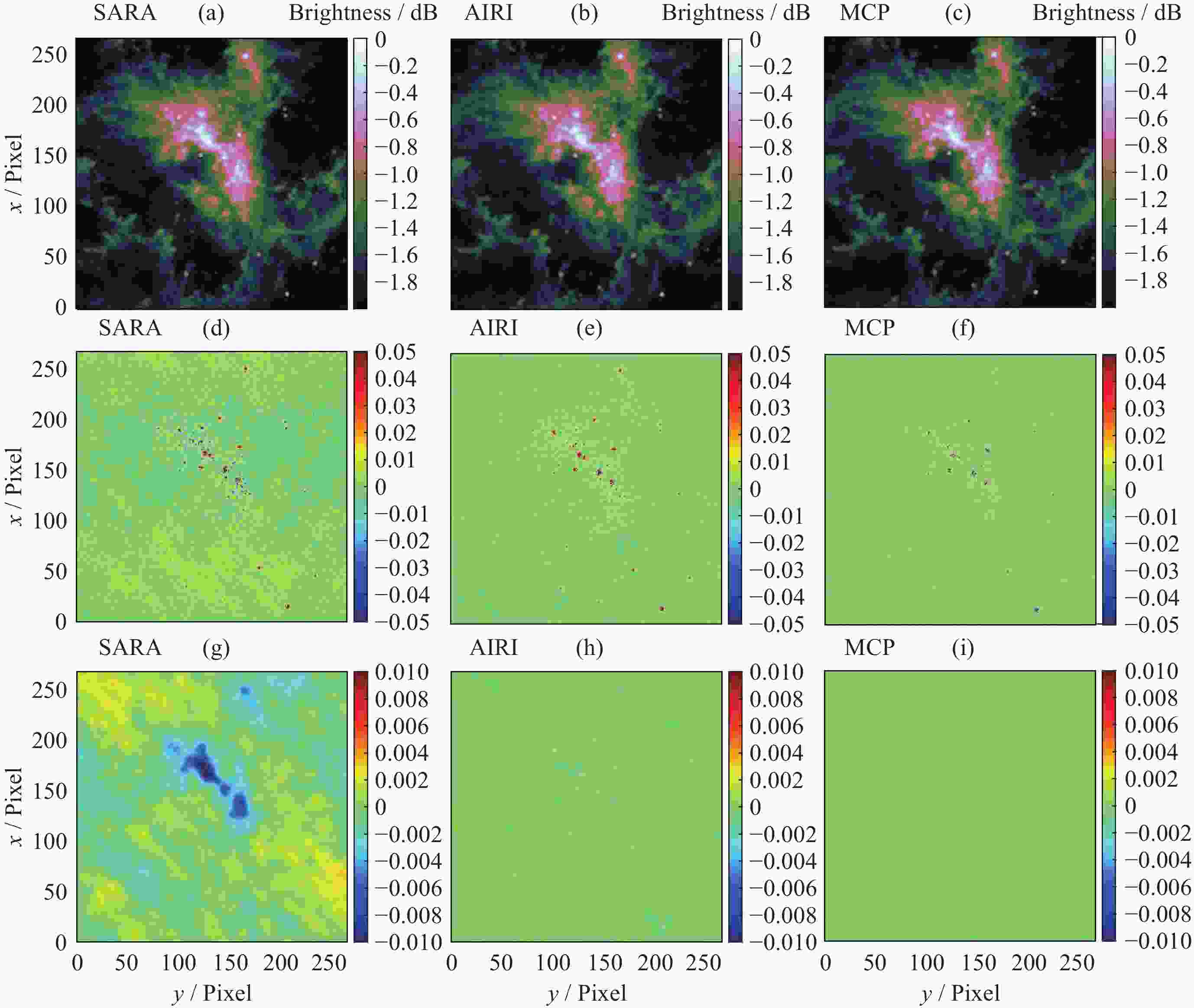
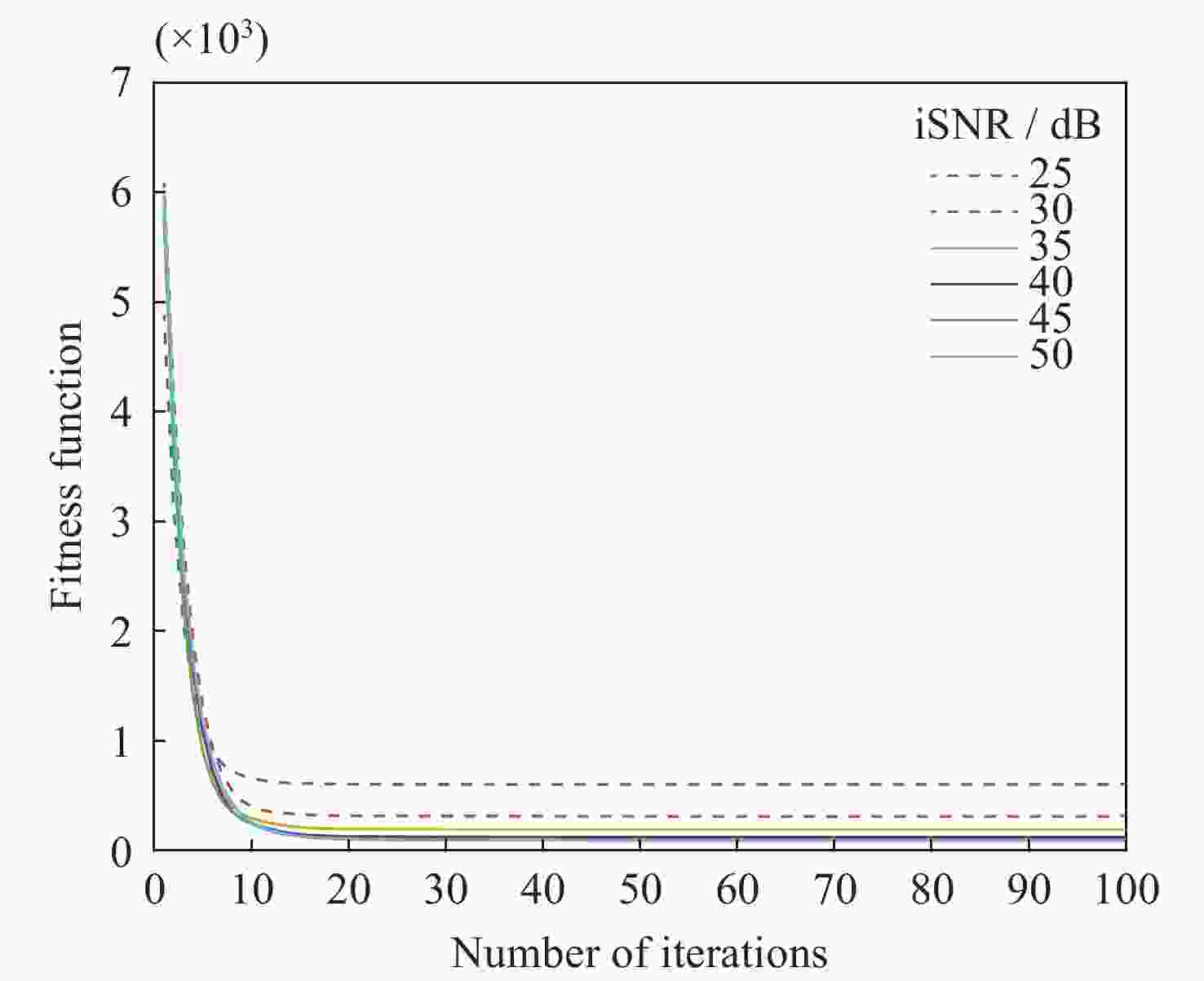
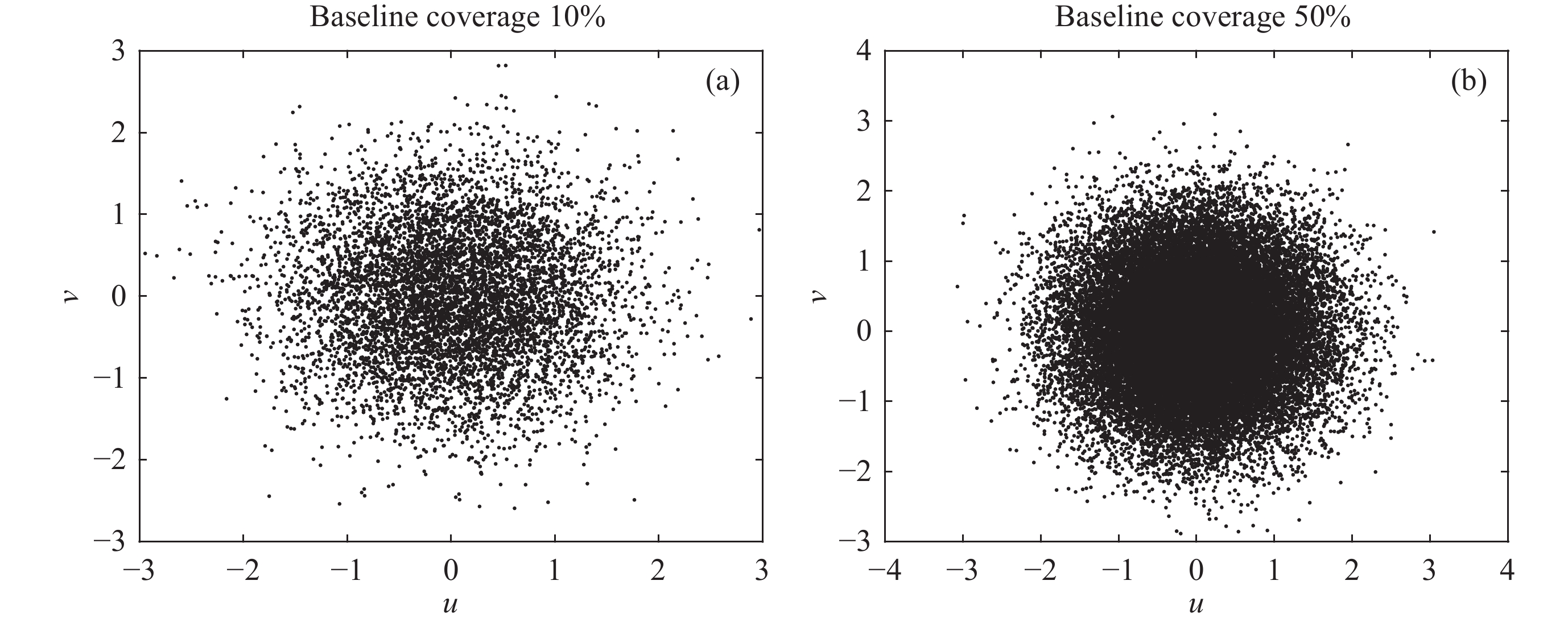
摘要: 在综合孔径射电望远镜中, 从测量的可见度函数重构出图像是一个病态的反问题. 虽然压缩感知技术已成功地应用于综合孔径射电望远镜成像中, 但是传统的压缩感知算法利用L1范数最小化, 近似取代L0范数最小化, 带来了一定的偏差. 针对此问题, 本文提出了一种基于最小最大凹惩罚的综合孔径射电望远镜成像方法. 该方法利用最小最大凹惩罚来近似L0范数, 并利用近端梯度算法求解最小化模型. 在求解过程中, 采用最大似然估计来自适应选取正则化参数, 提高重构结果的准确性. 并采用重启和自适应策略, 以避免迭代过程中的振荡, 并提高算法的收敛速度. 实验结果表明, 该方法在重建精度和对噪声鲁棒性方面优于目前典型的压缩感知算法, 证明了其有效性.Abstract: In the synthetic aperture radio telescope, the reconstruction of an image from the measured visibility function is an ill-posed inverse problem on account of limitations in the visibility sampling scheme. Although compressed sensing technology has been successfully applied in interferometric imaging of a synthetic aperture radio telescope, the traditional compressed sensing algorithms make use of L1 norm minimization to approximately replace L0 norm minimization, which brings a certain deviation. To address this issue, a new imaging method of a synthetic aperture radio telescope based on a minimax concave penalty is proposed in this paper. This method approximates the L0 norm by the minimax concave penalty, and efficiently solves the non-convex minimization model by the proximal gradient algorithm. Compared with the L1 norm, the minimax concave penalty is a closer approximation of the L0 norm. In the iterative process, the maximum likelihood estimation is employed to adaptively select the regularization parameter, thereby enhancing the accuracy of the reconstruction results. In addition, the restart and adaptive strategies are adopted to avoid the oscillations during the iteration process and improve the convergence speed of the algorithm. Based on a simulated general array using a random sampling pattern of variable density and the Square Kilometer Array, numerical simulation experiments have been conducted to compare the performance of the proposed method in terms of reconstruction quality and computation speed with respect to classical imaging methods such as the Sparsity Averaging Reweighted Analysis (SARA) and Artificial Intelligence for Regularization in radio-interferometric Imaging (AIRI). The numerical experiment results indicate that compared with the SARA and AIRI approaches, the proposed approach can effectively reduce the reconstruction error and improve the reconstruction quality. The computation speed of the proposed approach is markedly faster than the SARA and slightly slower than the AIRI. Furthermore, the proposed approach exhibits superior robustness to noise interference than the SARA and AIRI approaches.
-
Key words:
- Radio telescope /
- Aperture synthesis /
- Compressed sensing /
- Minimax concave penalty
-
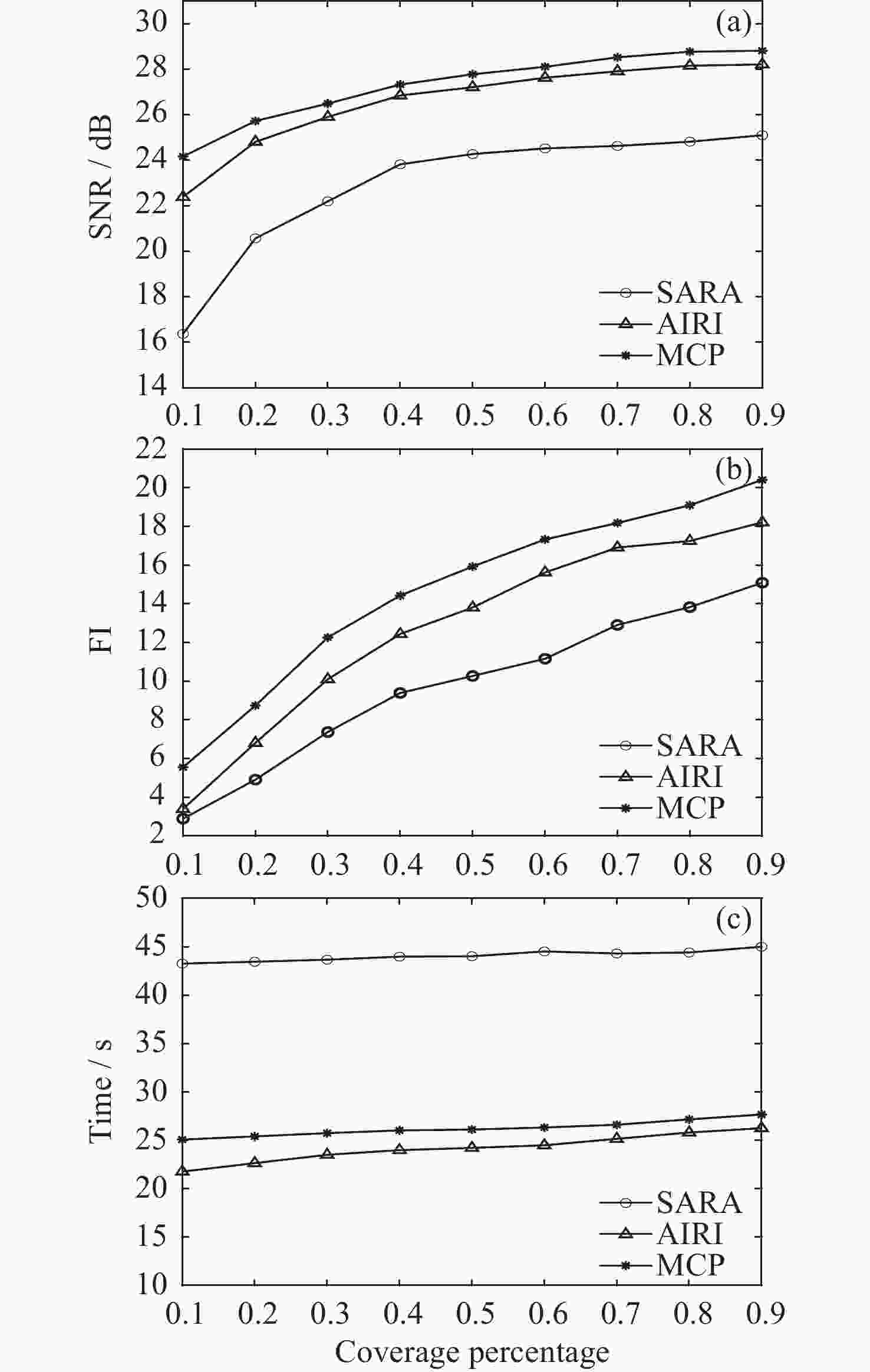
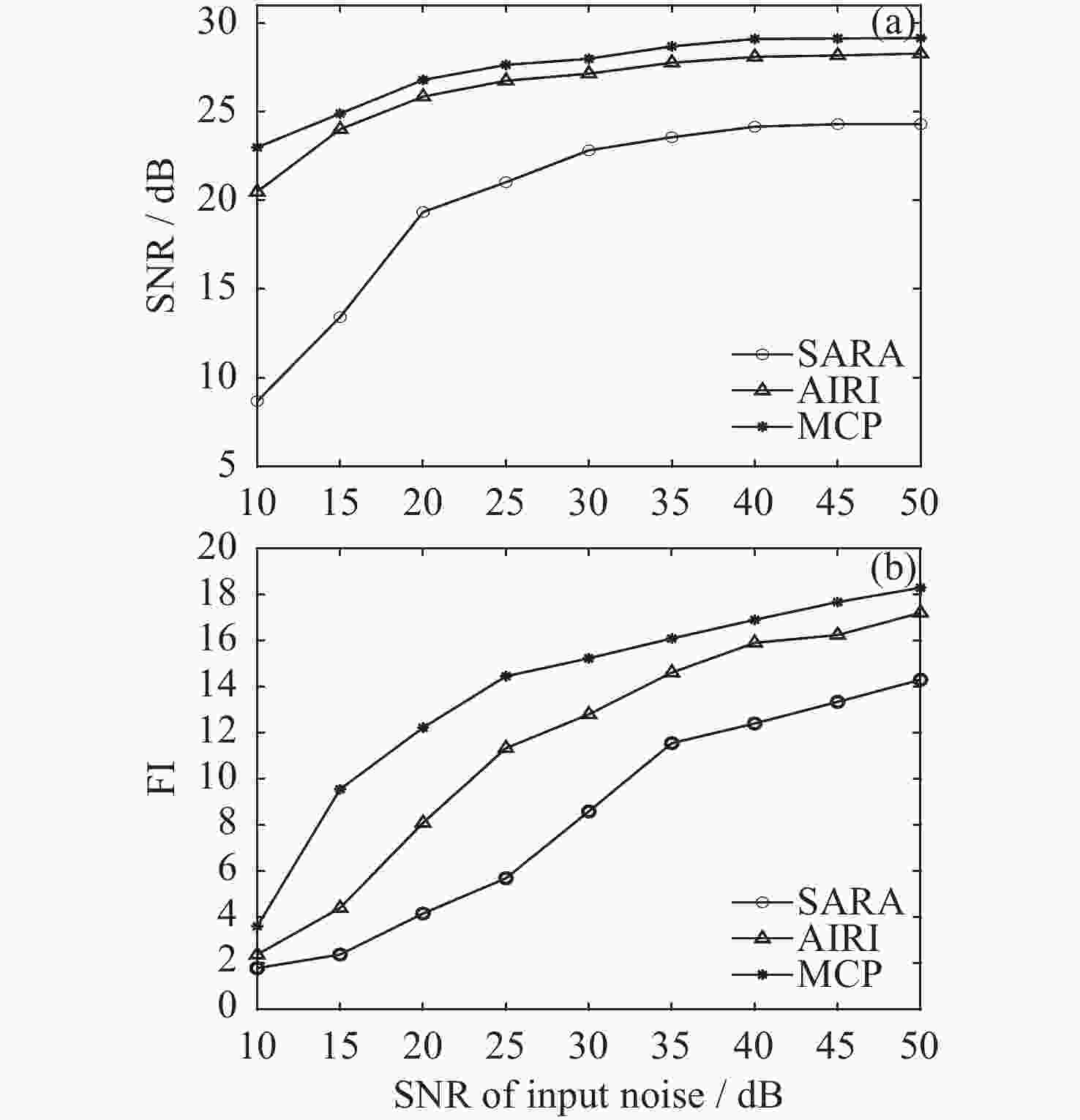
表 1 重构结果的性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of reconstruction results
Undersampling rates Algorithms SNR/dB FI Time/s 10% SARA 16.37 2.89 43.27 AIRI 22.39 3.39 21.76 MCP 24.16 5.55 25.07 50% SARA 24.27 10.27 44.03 AIRI 27.21 13.81 24.21 MCP 27.78 15.93 26.11 表 2 重构结果的性能对比
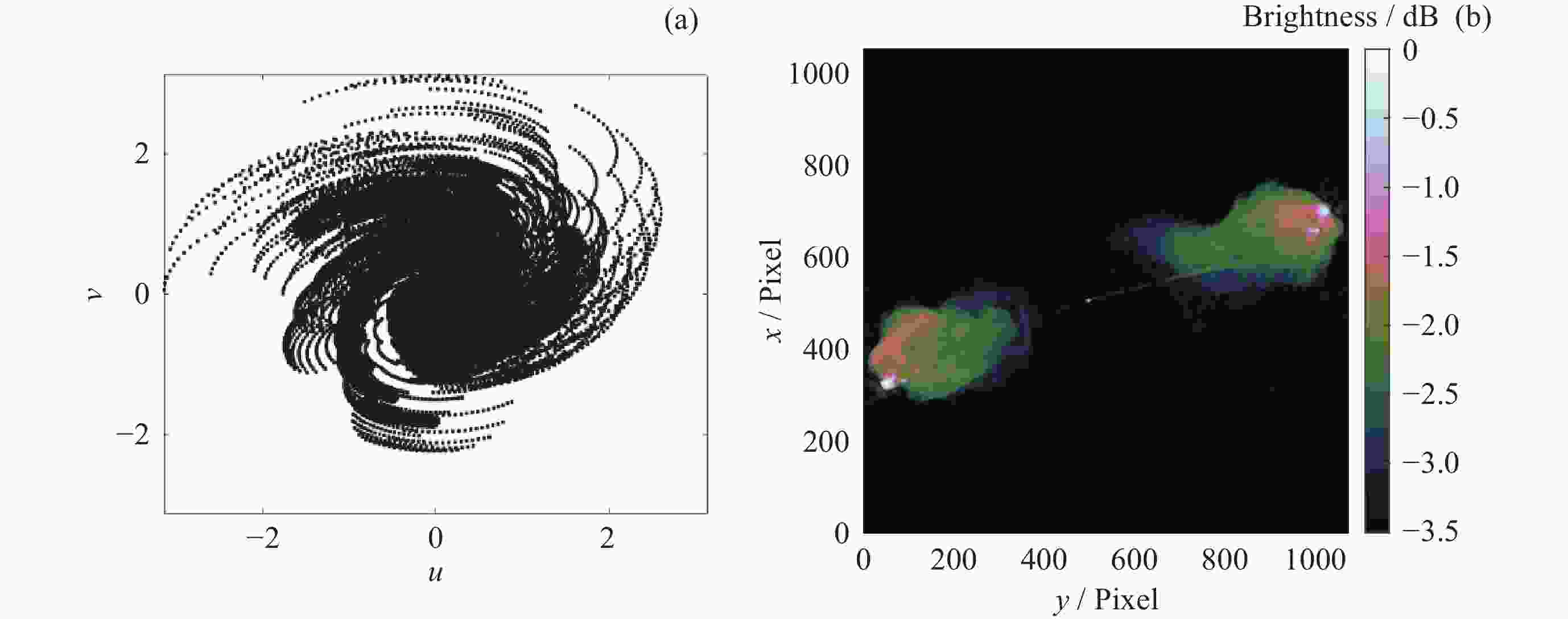
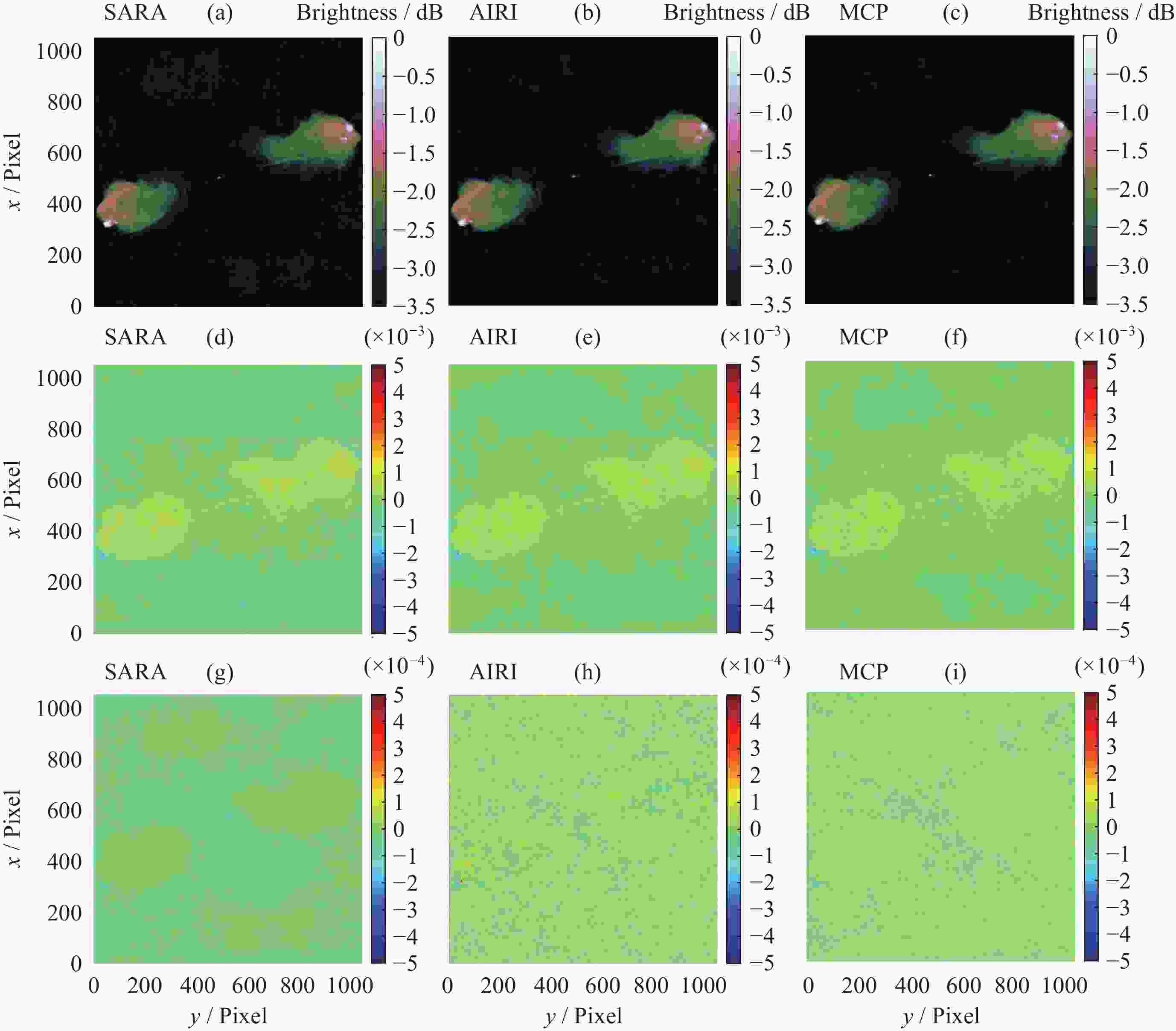
Table 2. Performance comparison of reconstruction results
Algorithms SNR/dB FI Time/s SARA 32.83 0.85 342.75 AIRI 34.52 0.97 175.32 MCP 35.73 1.09 189.62 -
[1] XUE Yanjie, XUE Suijian, ZHU Ming, et al. Overview of current status and development strategies in China’s astronomical facilities and related technologies[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014, 29(3): 368-375 [2] PERLEY R A, CHANDLER C J, BUTLER B J, et al. The expanded very large array: a new telescope for new science[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2011, 739(1): L1 doi: 10.1088/2041-8205/739/1/L1 [3] PADUANO A, BAHRAMIAN A, MILLER-JONES J C A, et al. Ultradeep ATCA imaging of 47 Tucanae reveals a central compact radio source[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2024, 961(1): 54 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad0e68 [4] WOOD A G, DORRIAN G D, BOYDE B, et al. Quasi-stationary substructure within a sporadic E layer observed by the Low-Frequency Array (LOFAR)[J]. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2024, 14: 27 doi: 10.1051/swsc/2024024 [5] ZHAO B X, ZHENG Q, SHAN H Y, et al. North celestial region observed with 21 CentiMeter Array[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2022, 22(1): 015012 doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/ac37b3 [6] SU Cang, WANG Wei, YAN Yihua, et al. Measuring and analysis of the phase pattern of MUSER[J]. Astronomical Research and Technology, 2016, 13(3): 293-299 [7] YAN J Y, WU J, WU L, et al. A super radio camera with a one-kilometre lens[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2023, 7(6): 750 doi: 10.1038/s41550-023-01932-y [8] HÖGBOM J A. Aperture synthesis with a non-regular distribution of interferometer baselines[J]. Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement, 1974, 15: 417-426 [9] ZHANG Li, XU Long, MI Ligong, et al. Study on deconvolution algorithm of radio astronomical images[J]. Acta Astronomica Sinica, 2018, 59(6): 117-124 [10] CORNWELL T J. Multiscale CLEAN deconvolution of radio synthesis images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2008, 2(5): 793-801 doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2008.2006388 [11] ZHANG L. Fused CLEAN deconvolution for compact and diffuse emission[J]. Astronomy :Times New Roman;">& Astrophysics, 2018, 618: A117 [12] ZHANG L, BHATNAGAR S, RAU U, et al. Efficient implementation of the adaptive scale pixel decomposition algorithm[J]. Astronomy :Times New Roman;">& Astrophysics, 2016, 592: A128 [13] REN Yuemei, ZHANG Yanning, LI Ying. Advances and perspective on compressed sensing and application on image processing[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(8): 1563-1575 [14] LI F, CORNWELL T J, DE HOOG F. The application of compressive sampling to radio astronomy I. deconvolution[J]. Astronomy :Times New Roman;">& Astrophysics, 2011, 528: 1265-1279 [15] ZHANG Xun, GUO Shaoguang, ZHU Renjie, et al. A radio astronomy image restoration algorithm based on compressed sensing framework[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica :Times New Roman;">& Astronomica, 2024, 54(8): 84-99 [16] CARRILLO R E, MCEWEN J D, WIAUX Y. Sparsity Averaging Reweighted Analysis (SARA): a novel algorithm for radio-interferometric imaging[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2012, 426(2): 1223-1234 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21605.x [17] ONOSE A, CARRILLO R E, REPETTI A, et al. Scalable splitting algorithms for big-data interferometric imaging in the SKA era[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2016, 462(4): 4314-4335 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stw1859 [18] ONOSE A, DABBECH A, WIAUX Y. An accelerated splitting algorithm for radio-interferometric imaging: when natural and uniform weighting meet[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2017, 469(1): 938-949 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stx755 [19] YANG Xiaocheng, YOU Xiang, WU Lin, et al. Imaging algorithm of synthetic aperture radio telescope based on improved SARA[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica :Times New Roman;">& Astronomica, 2024, 54(8): 289514 [20] GHELLER C, VAZZA F. Convolutional deep denoising autoencoders for radio astronomical images [J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 2021, 509(1): 990–1009 [21] AGHABIGLOU A, CHU C S, DABBECH A, et al. The R2D2 deep neural network series paradigm for fast precision imaging in radio astronomy[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2024, 273(1): 3 doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ad46f5 [22] TERRIS M, DABBECH A, TANG C, et al. Image reconstruction algorithms in radio interferometry: from handcrafted to learned regularization denoisers[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2022, 518(1): 604-622 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stac2672 [23] WILBER A G, DABBECH A, TERRIS M, et al. Scalable precision wide-field imaging in radio interferometry–II. AIRI validated on ASKAP data[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 522(4): 5576-5587 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad1353 [24] ROTH J, ARRAS P, REINECKE M, et al. Bayesian radio interferometric imaging with direction-dependent calibration[J]. Astronomy :Times New Roman;">& Astrophysics, 2023, 678: A177 [25] LIAUDAT T I, MARS M, PRICE M A, et al. Scalable Bayesian uncertainty quantification with data-driven priors for radio interferometric imaging[J]. RAS Techniques and Instruments, 2024, 3(1): 505-534 doi: 10.1093/rasti/rzae030 [26] WEN F, CHU L, LIU P, et al. A survey on nonconvex regularization-based sparse and low-rank recovery in signal processing, statistics, and machine learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 69883-69906 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2880454 [27] DONG Liang, ZHANG Ming, XIE Huanhuan, et al. The key technology analyses and researches of the sparse array in VHF band in radio astronomy[J]. Astronomical Research :Times New Roman;">& Technology, 2023, 20(5): 421-437 [28] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289-1306 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [29] CANDÈS E J, ELDAR Y C, NEEDELL D, et al. Compressed sensing with coherent and redundant dictionaries[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2011, 31(1): 59-73 doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2010.10.002 [30] FAN J, LI R. Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties[J]. Journal of the American statistical Association, 2001, 96(456): 1348-1360 doi: 10.1198/016214501753382273 [31] SHEN X, GU Y. Nonconvex sparse logistic regression with weakly convex regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(12): 3199-3211 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2824289 [32] AUJOL J F, CALATRONI L, DOSSAL C, et al. Parameter-free FISTA by adaptive restart and backtracking[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2024, 34(4): 3259-3285 doi: 10.1137/23M158961X [33] YU L, ZHANG X W, CHU Y. Super-resolution reconstruction algorithm for infrared image with double regular items based on sub-pixel convolution[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(3): 1109 doi: 10.3390/app10031109 [34] ABDULAZIZ A, DABBECH A, WIAUX Y. Wideband super-resolution imaging in radio interferometry via low rankness and joint average sparsity models (HyperSARA)[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2018, 489(1): 1230-1248 [35] VIJAY KARTIK S, CARRILLO R E, THIRAN J P, et al. A Fourier dimensionality reduction model for big data interferometric imaging[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2017, 468(2): 2382-2400 doi: 10.1093/mnras/stx531 -
-




 范小艺 女, 2000年5月出生于浙江杭州, 浙江理工大学信息科学与工程学院(网络空间安全学院)硕士研究生. 主要研究方向为综合孔径射电望远镜成像算法. E-mail:
范小艺 女, 2000年5月出生于浙江杭州, 浙江理工大学信息科学与工程学院(网络空间安全学院)硕士研究生. 主要研究方向为综合孔径射电望远镜成像算法. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: