Dataset of Geomagnetic Ultra-low Frequency Waves Based on Meridian Project Observation Data
-
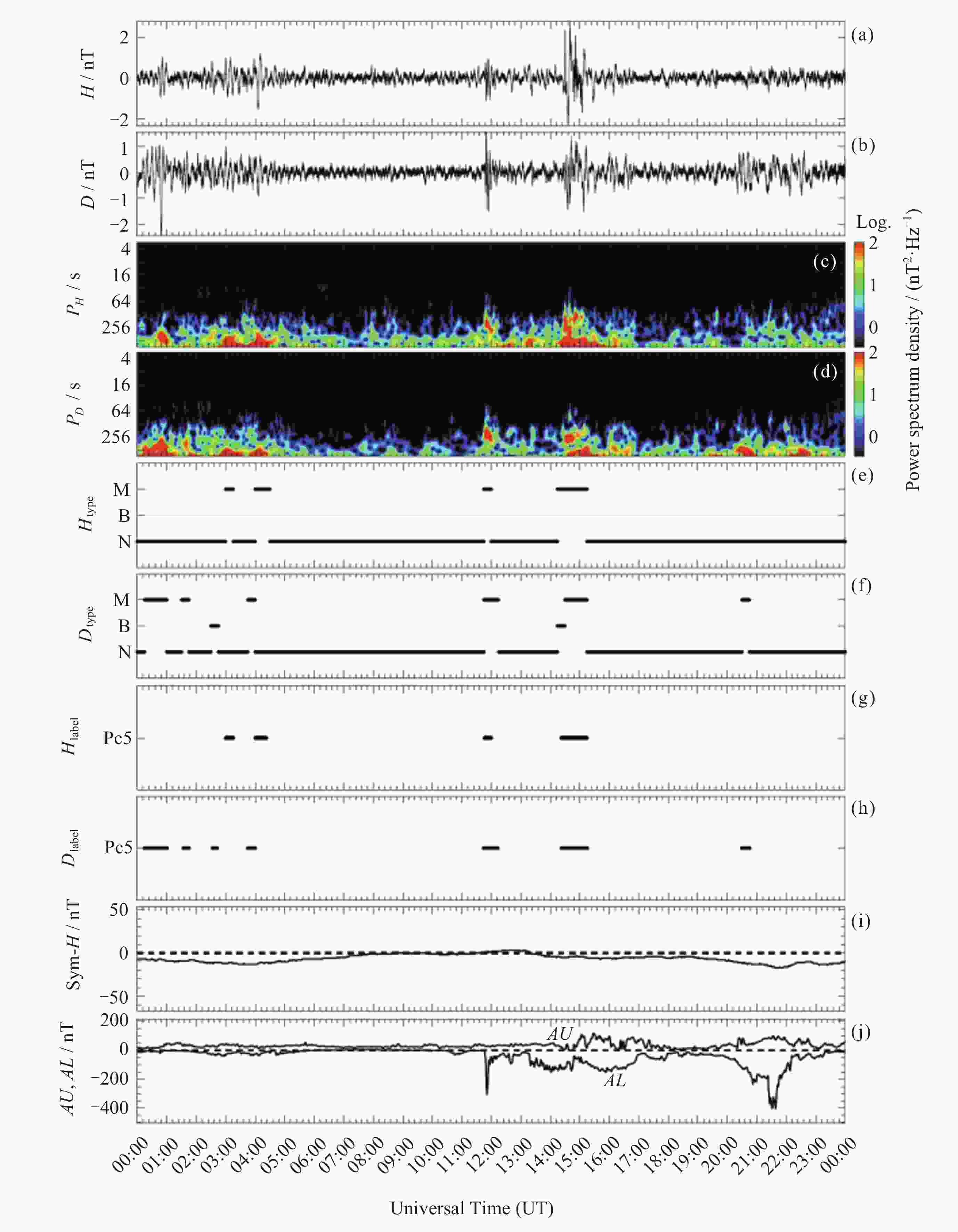
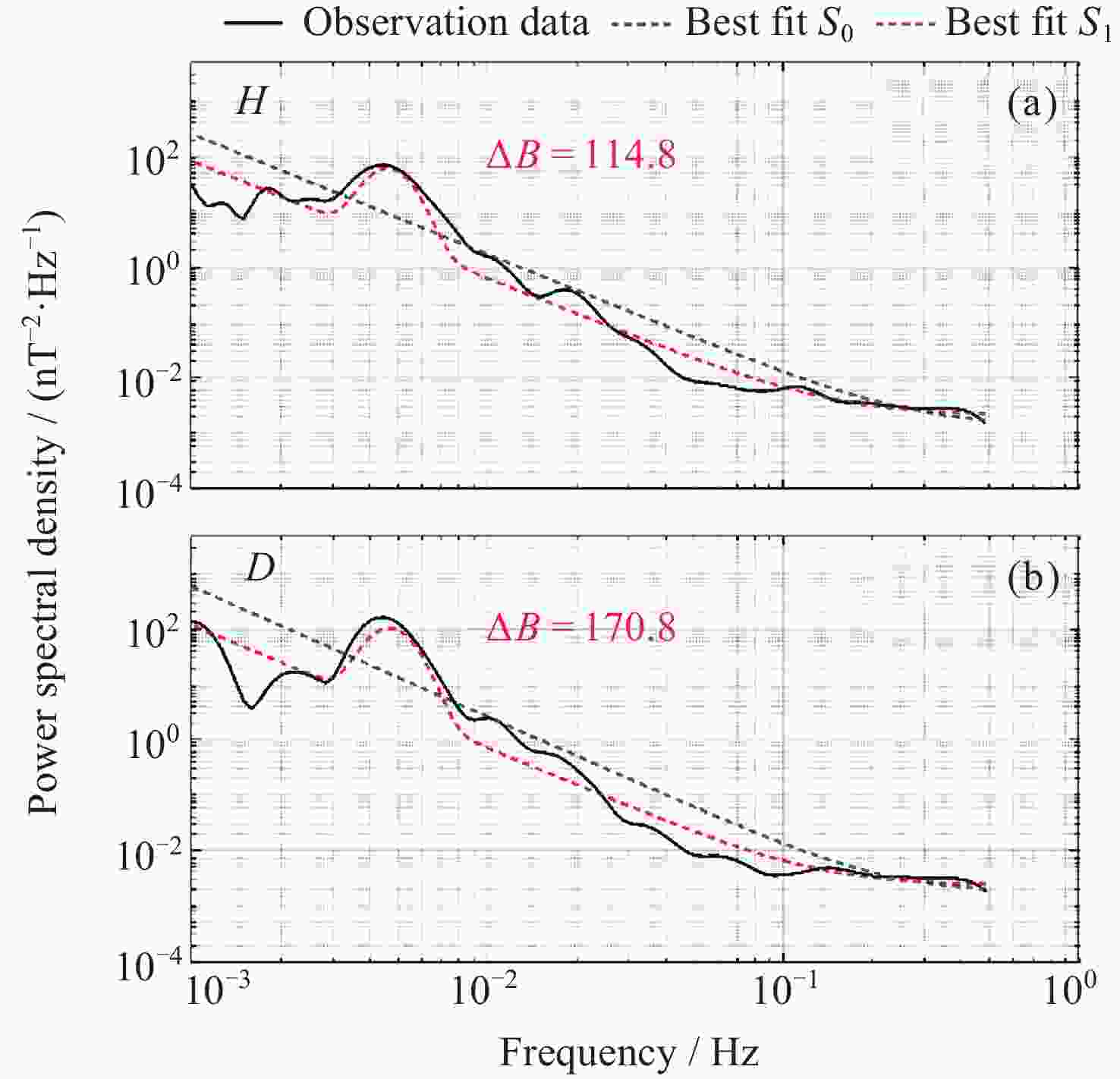
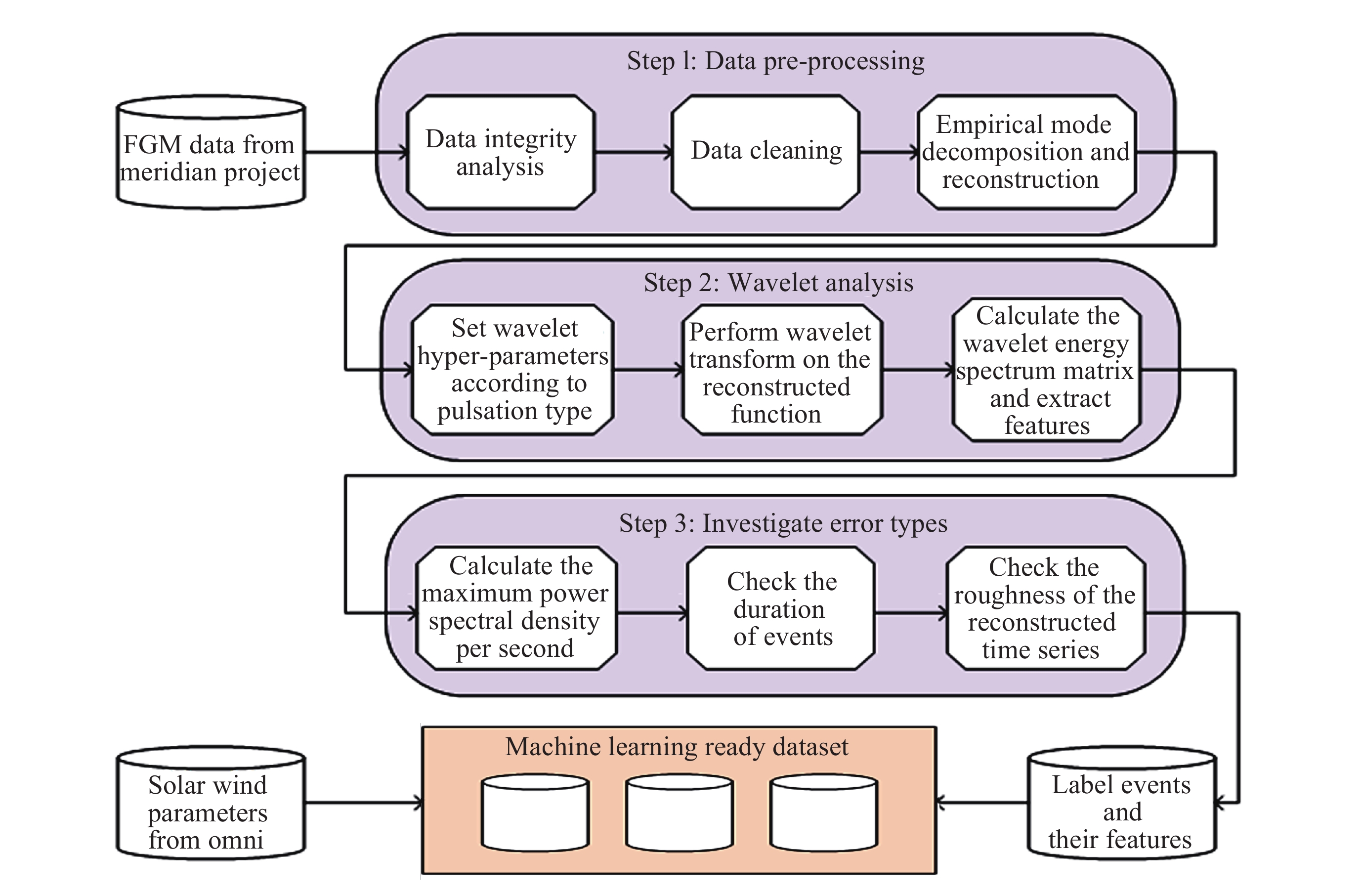
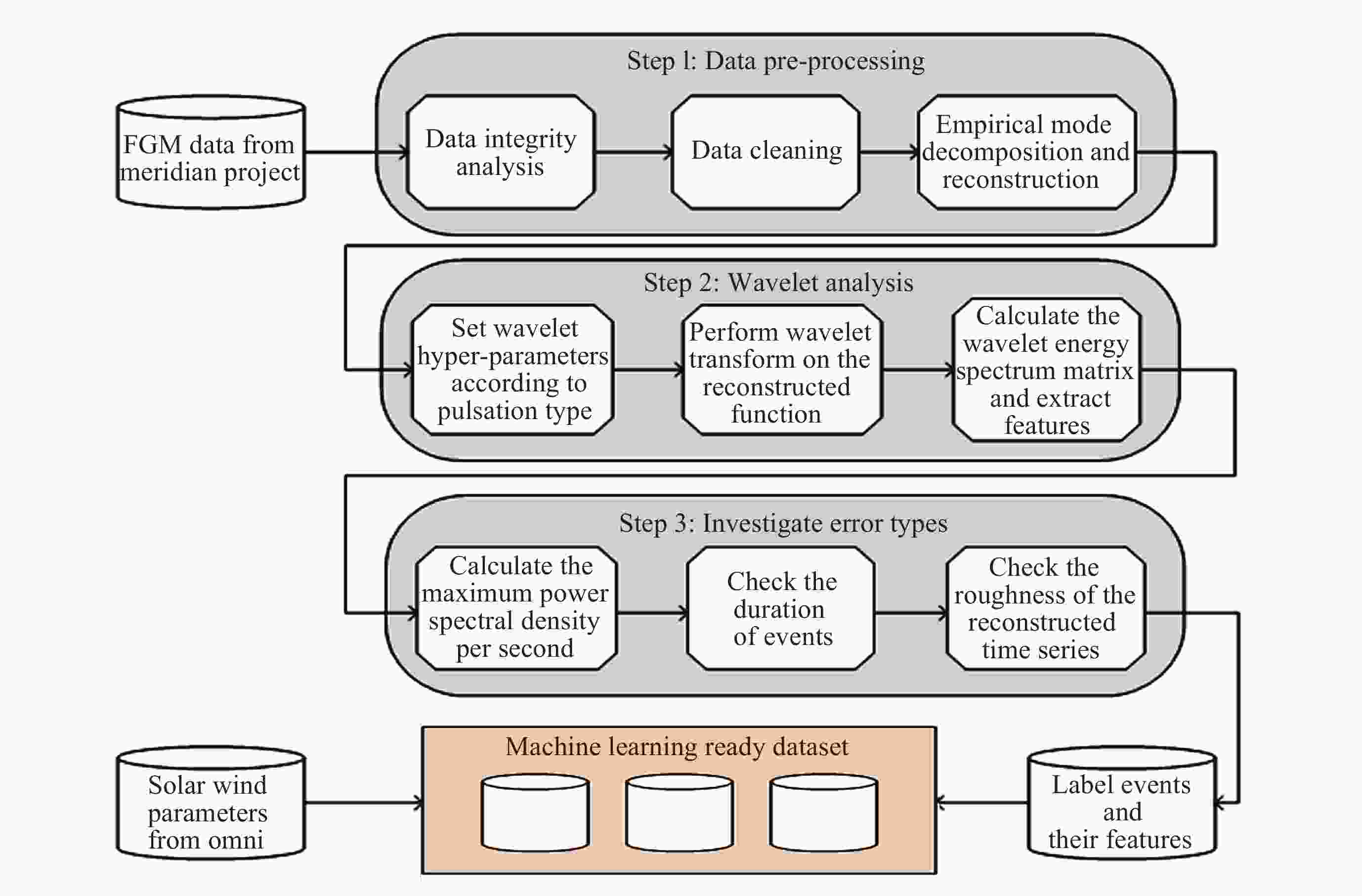
摘要: 子午工程作为中国重要的空间环境监测基础设施, 在空间物理研究中意义重大, 尤其为超低频(ULF)波观测提供了关键支撑. 本研究基于2011-2021年子午工程多站点磁通门磁力仪采集的地磁场水平分量(H)与磁偏角分量(D)秒采样数据, 经数据清洗、降噪预处理后, 结合时频分析(Morlet小波变换)与统计方法, 构建了高质量、长时序的地磁超低频波数据集. 数据集覆盖高、中、低纬五个台站, 包含Pc3~Pc5 规则脉动事件标注及原始序列, 以jsonl格式存储, 支持主流科研软件读取. 该数据集填补区域观测空白, 为磁层波动、空间天气建模等研究提供了基础数据, 助力提升中国空间环境监测能力, 可用于ULF波自动识别及耦合机制研究.Abstract: The Meridian Project, as an important space environment monitoring infrastructure in China, is of great significance in space physics research, especially providing key support for the observation of Ultra-Low-Frequency (ULF) waves. Based on the second-sampled data of the horizontal component (H) and declination component (D) of the geomagnetic field collected by multi-station fluxgate magnetometers of the Meridian Project from 2011 to 2021, this paper constructs a high-quality and long-time-series dataset of geomagnetic ULF waves through data cleaning, noise reduction preprocessing, and combined with time-frequency analysis (Morlet wavelet transform) and statistical methods. The dataset covers 5 stations at high, middle and low latitudes, includes event annotations and original sequences of Pc3~Pc5 regular pulsations, and is stored in jsonl format, supporting reading by mainstream scientific research software. This dataset fills the gap in regional ULF wave observations, provides basic data for research such as magnetospheric fluctuations and space weather modeling, helps improve China’s space environment monitoring capabilities, and can be used for automatic ULF wave identification and coupling mechanism research.
-
表 1 台站名称与位置
Table 1. Stations and their locations
台站名称 地理经度 (E) 地理纬度 (N) 地磁经度 (W) 地磁纬度 (N) 黑龙江漠河站 (MHT) 122°20′ 53°30′ 167.6° 43.9° 武汉九峰站 (JFT) 114°29′ 30°30′ 173.5° 20.7° 海南三亚站 (SYS) 109°35′ 19°30′ 177.9° 9.7° 内蒙古满洲里站 (MZL) 117°25′ 49°32′ 171.5° 39.8° 山东马陵山站 (MLS) 118°27′ 34°42′ 170.0° 25.0° 表 2 地磁超低频波数据集关键字信息
Table 2. Keywords information of geomagnetic ultra-low-frequency wave dataset
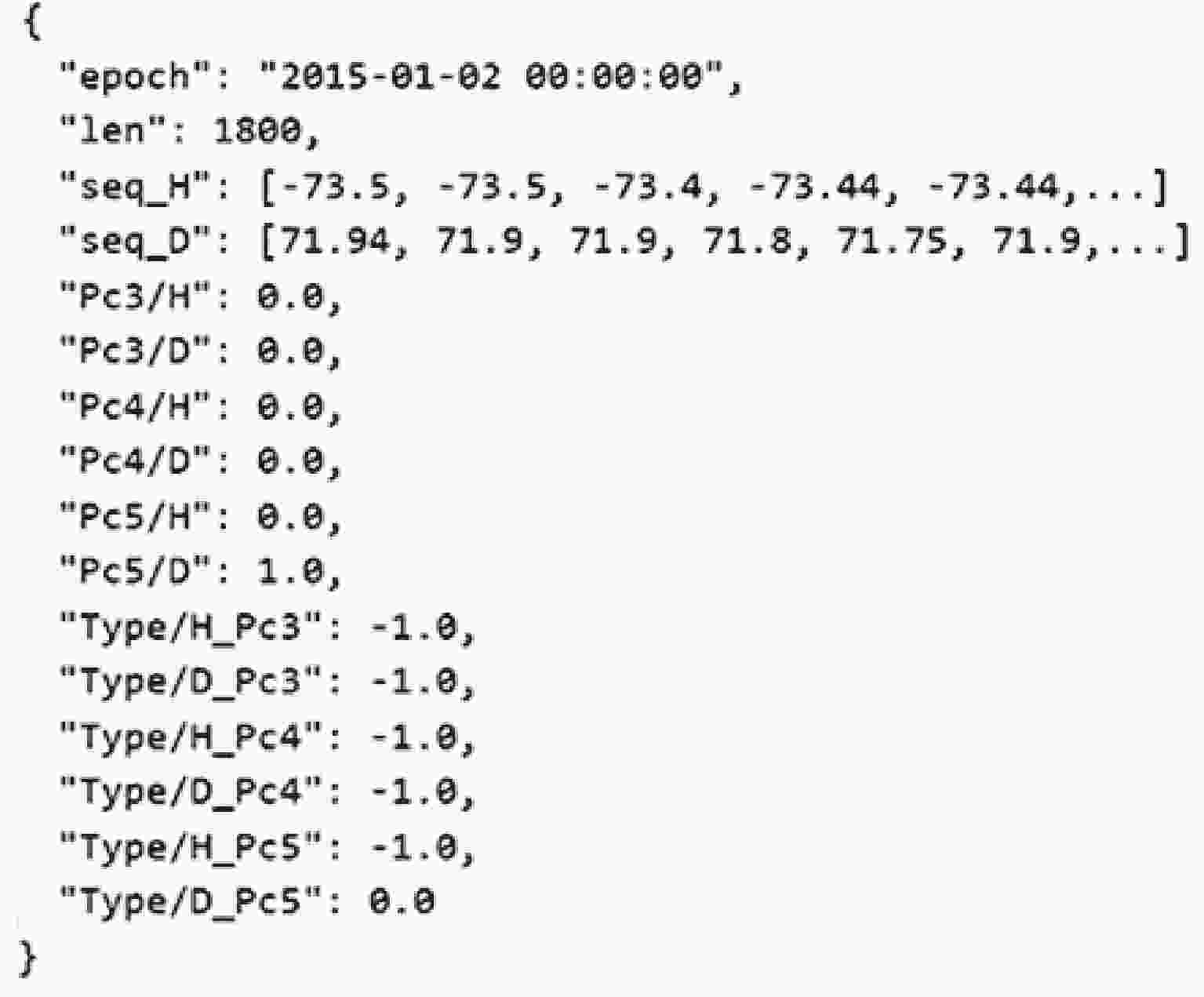
序号 关键字 描述 1 epoch 观测时间 2 seq_H H分量观测原始序列 3 seq_D D分量观测原始序列 4 Pc3/H H分量Pc3事件标注 5 Pc3/H_type H分量Pc3事件单色波标注 6 Pc4/H H分量Pc4事件标注 7 Pc4/H_type H分量Pc4事件单色波标注 8 Pc5/H H分量Pc5事件标注 9 Pc5/H_type H分量Pc5事件单色波标注 10 Pc3/D D分量Pc3事件标注 11 Pc3/D_type D分量Pc3事件单色波标注 12 Pc4/D D分量Pc4事件标注 13 Pc4/D_type D分量Pc4事件单色波标注 14 Pc5/D D分量Pc5事件标注 15 Pc5/D_type D分量Pc5事件单色波标注 -
[1] PULKKINEN T I, PALMROTH M, TANSKANEN E I, et al. Solar wind—magnetosphere coupling: a review of recent results[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2007, 69(3): 256-264 doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2006.05.029 [2] JACOBS J A, KATO Y, MATSUSHITA S, et al. Classification of geomagnetic micropulsations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1964, 69(1): 180-181 doi: 10.1029/JZ069i001p00180 [3] QIN Jiamei, ZHONG Dingkun, FENG Xueshang, et al. A summary of data resources produced by the Meridian Project[J]. China Scientific Data, 2021, 6(2): 1-23 (秦佳媚, 钟鼎坤, 冯学尚, 等. 子午工程数据资源概述[J]. 中国科学数据 (中英文网络版), 2021, 6(2): 1-23QIN Jiamei, ZHONG Dingkun, FENG Xueshang, et al. A summary of data resources produced by the Meridian Project[J]. China Scientific Data, 2021, 6(2): 1-23 [4] ZHANG Qingmei, WANG Chi, LI Hui, et al. Characters of the Pc3-4 magnetic pulsations at middle and low latitudes: preliminary geomagnetic results from Chinese meridian project[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2013, 33(6): 608-616 (张青梅, 王赤, 李晖, 等. 中低纬度Pc3-4地磁脉动特性研究——子午工程数据分析初步结果[J]. 空间科学学报, 2013, 33(6): 608-616 doi: 10.11728/cjss2013.06.608ZHANG Qingmei, WANG Chi, LI Hui, et al. Characters of the Pc3-4 magnetic pulsations at middle and low latitudes: preliminary geomagnetic results from Chinese meridian project[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2013, 33(6): 608-616 doi: 10.11728/cjss2013.06.608 [5] LI Hui, LIU Ziqian. A dataset of Dst indexes in China (2010-2022)[J]. China Scientific Data, 2023, 8(4): 322-328 (李晖, 刘子谦. 中国区域Dst指数数据集(2010-2022)[J]. 中国科学数据(中英文网络版), 2023, 8(4): 322-328LI Hui, LIU Ziqian. A dataset of Dst indexes in China (2010-2022)[J]. China Scientific Data, 2023, 8(4): 322-328 [6] ZHANG Min. Study on Characteristic of Geomagnetic Pulsation and Geomagnetic Storm in Meridian Region[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, 2012 (张敏. 子午圈地磁脉动和磁暴特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所, 2012ZHANG Min. Study on Characteristic of Geomagnetic Pulsation and Geomagnetic Storm in Meridian Region[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, 2012 [7] BALASIS G, AMINALRAGIA-GIAMINI S, PAPADIMITRIOU C, et al. A machine learning approach for automated ULF wave recognition[J]. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2019, 9: A13 doi: 10.1051/swsc/2019010 [8] OMONDI S, YOSHIKAWA A, ZAHRA W K, et al. Automatic detection of auroral Pc5 geomagnetic pulsation using machine learning approach guided with discrete wavelet transform[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 72(3): 866-883 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.06.063 [9] ANTONOPOULOU A, BALASIS G, PAPADIMITRIOU C, et al. Convolutional neural networks for automated ULF wave classification in swarm time series[J]. Atmosphere, 2022, 13(9): 1488 doi: 10.3390/atmos13091488 [10] OSMANE A, SAVOLA M, KILPUA E, et al. Quantifying the non-linear dependence of energetic electron fluxes in the Earth's radiation belts with radial diffusion drivers[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2022, 40(1): 37-53 doi: 10.5194/angeo-40-37-2022 [11] HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995 doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193 [12] BALASIS G, DAGLIS I A, GEORGIOU M, et al. Magnetospheric ULF wave studies in the frame of Swarm mission: a time-frequency analysis tool for automated detection of pulsations in magnetic and electric field observations[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2013, 65(11): 1385-1398 doi: 10.5047/eps.2013.10.003 [13] BALASIS G, PAPADIMITRIOU C, DAGLIS I A, et al. ULF wave power features in the topside ionosphere revealed by Swarm observations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(17): 6922-6930 doi: 10.1002/2015GL065424 [14] ZENG Zhengjun, ZHANG Ying, DU Aimin, et al. Characteristics of Pc3 compressional waves in the topside ionosphere[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(3): 918-924 (曾正君, 张莹, 杜爱民, 等. 顶部电离层Pc3压缩波的波动特征[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(3): 918-924ZENG Zhengjun, ZHANG Ying, DU Aimin, et al. Characteristics of Pc3 compressional waves in the topside ionosphere[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(3): 918-924 [15] INGLIS A R, IRELAND J, DOMINIQUE M. Quasi-periodic pulsations in solar and stellar flares: re-evaluating their nature in the context of power-law flare Fourier spectra[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2014, 798(2): 108 [16] INGLIS A R, IRELAND J, DENNIS B R, et al. A large-scale search for evidence of quasi-periodic pulsations in solar flares[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2016, 833(2): 284 doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/833/2/284 [17] PAPADIMITRIOU C, BALASIS G, DAGLIS I A, et al. An initial ULF wave index derived from 2 years of Swarm observations[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2018, 36(2): 287-299 doi: 10.5194/angeo-36-287-2018 -
-





 方少峰 男, 博士, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心高级工程师, 中国科学院青年创新促进会成员, 主要研究方向为数据挖掘与空间天气学的交叉融合研究. E-mail:
方少峰 男, 博士, 中国科学院国家空间科学中心高级工程师, 中国科学院青年创新促进会成员, 主要研究方向为数据挖掘与空间天气学的交叉融合研究. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: