Regional GNSS Elevation Anomaly Fitting Method Based on IHHO-LSSVM
-
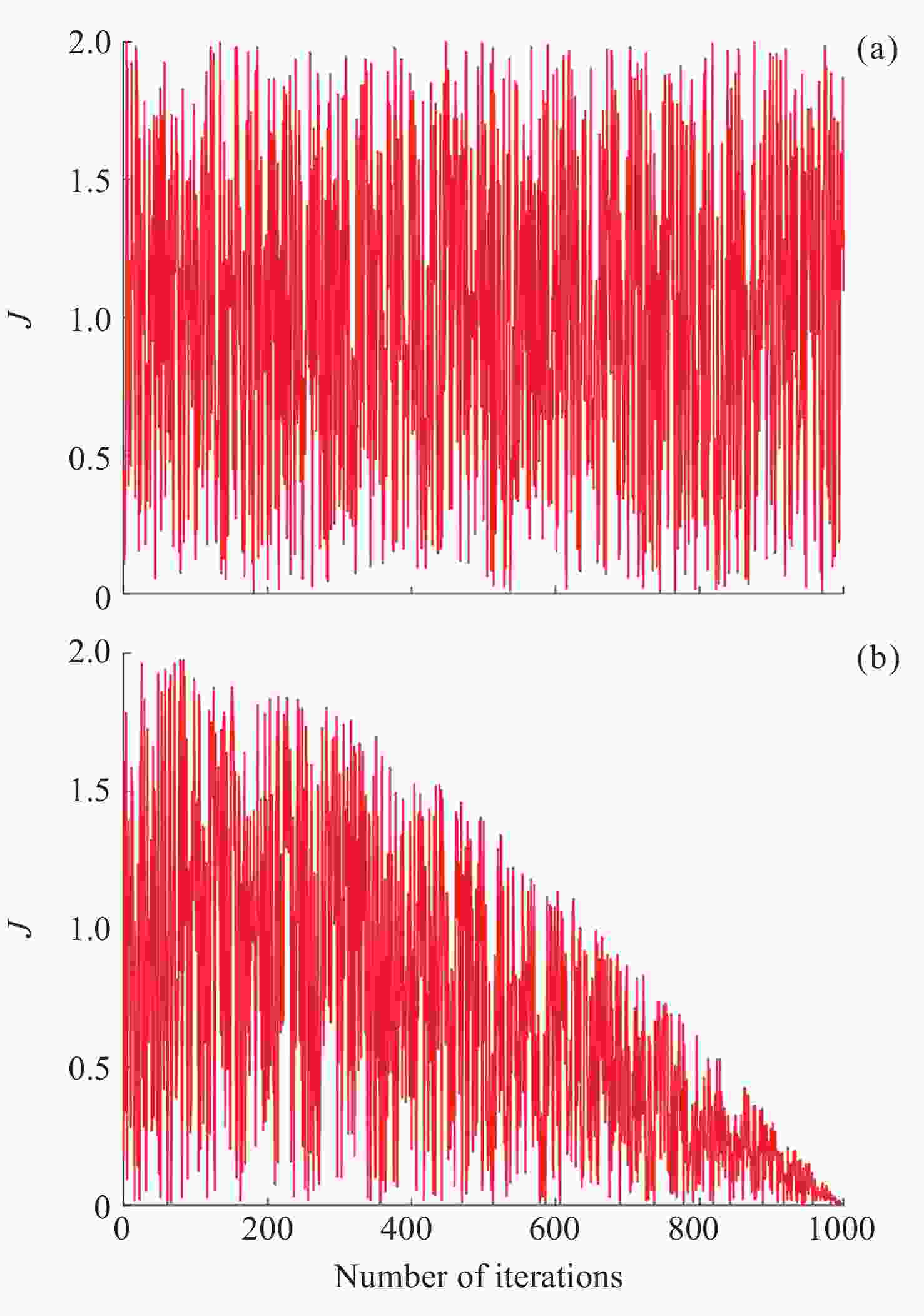
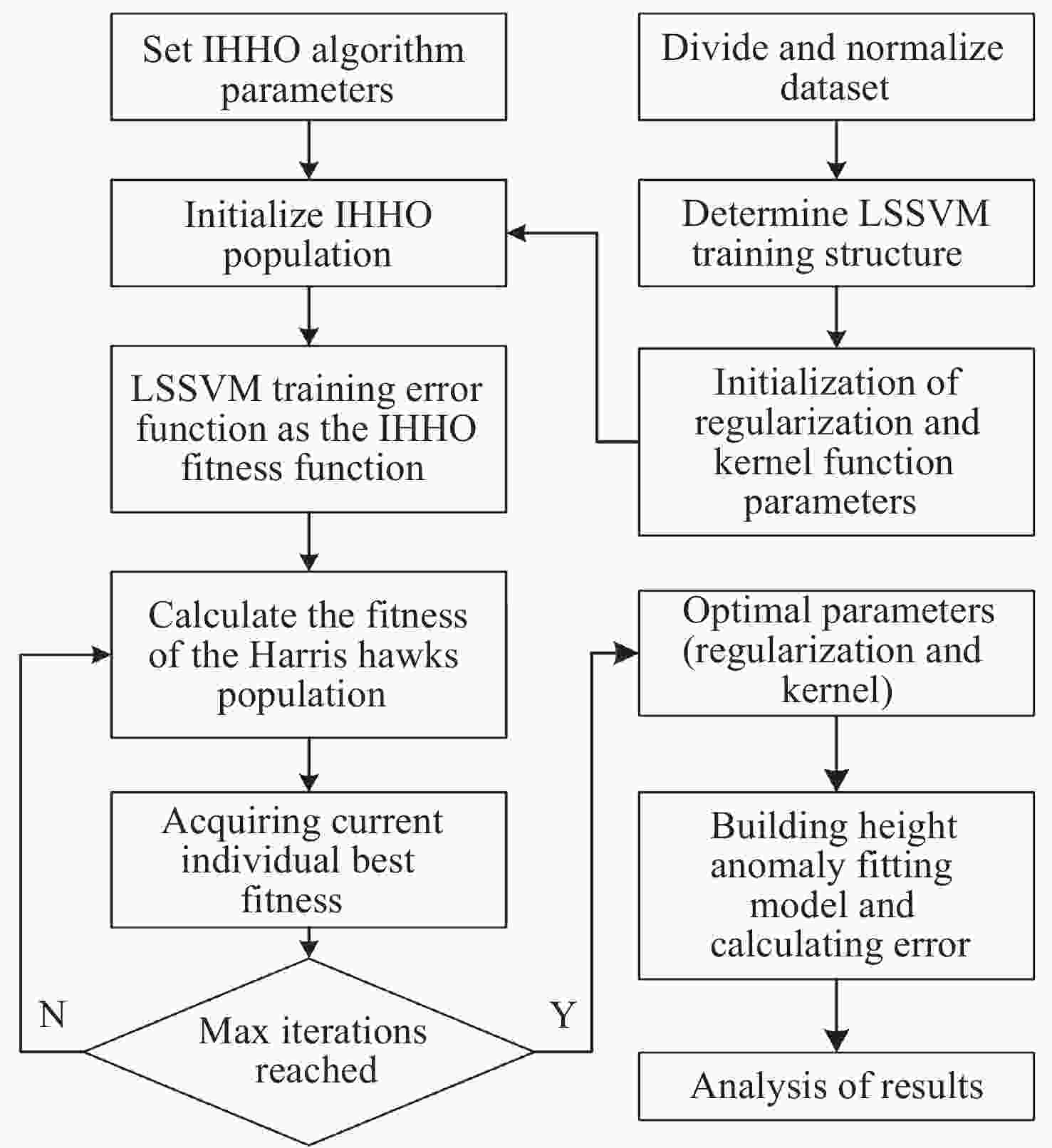
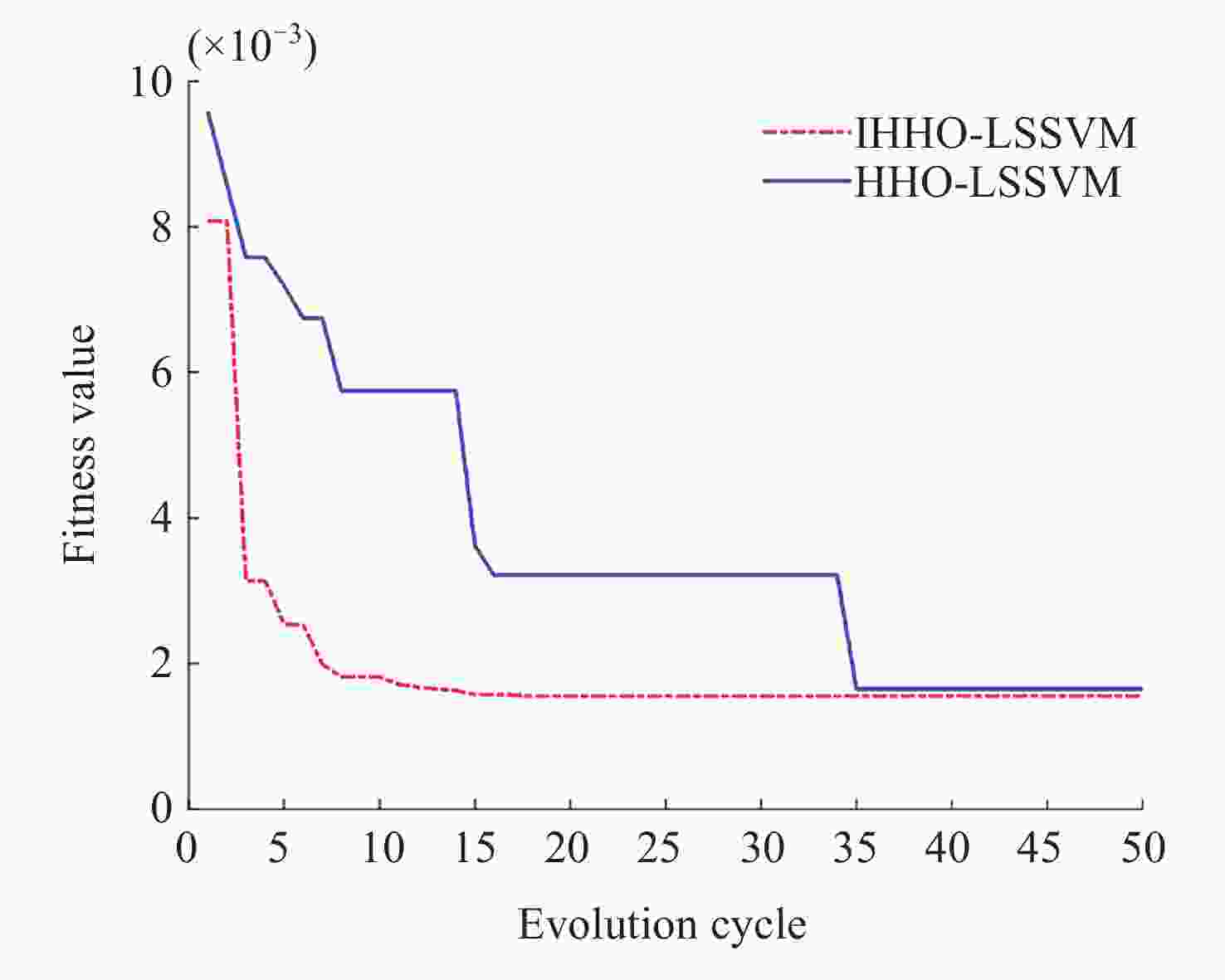
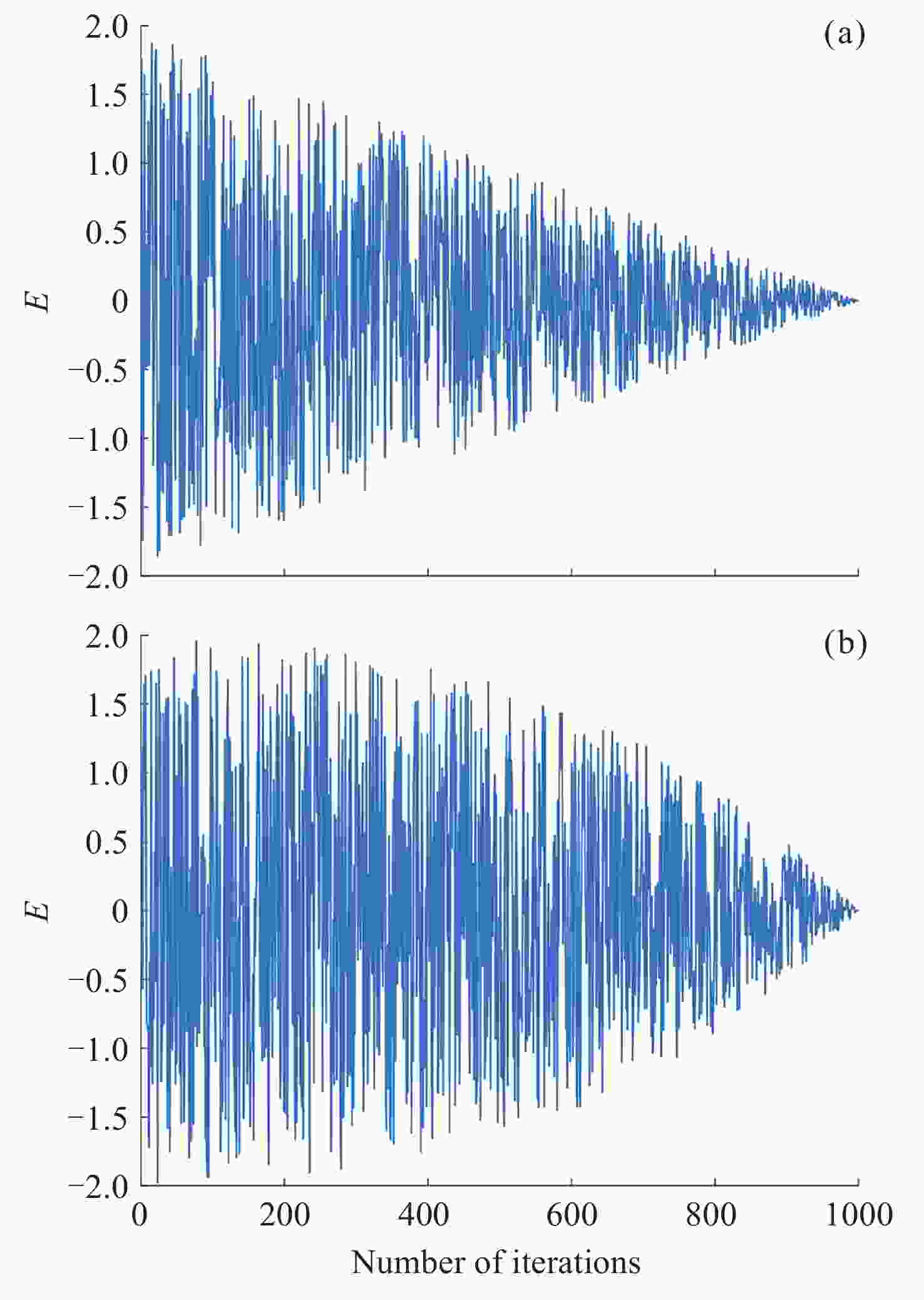
摘要: 针对当前复杂区域难以获取较高精度的高程异常值问题, 提出一种基于IHHO-LSSVM的高程异常拟合方法. 采用具有非线性的收敛因子、跳跃距离和自适应权重对哈里斯鹰优化算法(Harris Hawk Optimization, HHO)进行改进; 利用改进后的HHO算法为最小二乘向量机(Least Squares Support Vector Machine, LSSVM)高程异常拟合模型提供更为精确的正则化参数和核函数; 为验证高程异常组合模型在复杂地形中的适应性, 以高程异常值的均方根误差作为评判依据, 并结合两组不同地形的工程实例数据进行试验. 结果表明, 在桥梁带状区域和喀斯特面状区域, 相比于HHO-LSSVM法和LSSVM法, IHHO-LSSVM拟合模型的外符合精度更高、稳定性更强、适应性更广, 其中桥梁带状区域精度达到0.0101 m, 喀斯特面状区域达到0.0125 m, 可为GNSS高程异常拟合模型的建立提供一定的参考价值.Abstract: In order to effectively address the challenge of obtaining high-precision elevation outliers in complex geographical areas, this paper proposes an innovative elevation anomaly fitting method based on IHHO-LSSVM. The study begins with an improved Harris Hawk Optimization (HHO) algorithm through the implementation of nonlinear convergence factors, optimized jump distances, and adaptive weights. These improvements significantly enhance the algorithm’s ability to escape local optima and improve convergence efficiency, thereby providing a more robust optimization framework for subsequent model parameter tuning. Subsequently, the improved HHO algorithm is employed to determine more accurate regularization parameters and kernel functions for the Least Squares Support Vector Machine (LSSVM) elevation anomaly fitting model. This optimization process ensures that the LSSVM model achieves higher precision and better generalization capabilities in elevation anomaly fitting tasks. To thoroughly validate the adaptability and robustness of the proposed elevation anomaly combination model in complex terrains, extensive experiments were conducted using engineering case data from two distinct geographical regions: a bridge strip area and a karst surface area. The evaluation was based on the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of the elevation anomaly values as the primary metric, with additional consideration given to computational efficiency and model stability. The experimental results demonstrate that in both the bridge strip area and karst surface area, the IHHO-LSSVM method outperforms the conventional HHO-LSSVM and standard LSSVM methods in terms of external conformity accuracy, stability, and adaptability. Specifically, the IHHO-LSSVM method achieves remarkable accuracy levels of 0.0101 meters in the bridge strip area and 0.0125 meters in the karst surface area, representing significant improvements over traditional methods. Furthermore, the proposed method exhibits superior stability across different terrain types, with reduced variance in prediction errors. These findings not only highlight the superior performance of the proposed method but also provide valuable insights and a reliable reference for the establishment of GNSS elevation anomaly fitting models in various complex terrains. The study contributes to the field of geodetic surveying by offering a more precise and robust solution for elevation anomaly fitting, particularly in challenging geographical conditions.
-
表 1 组合模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of the combined model
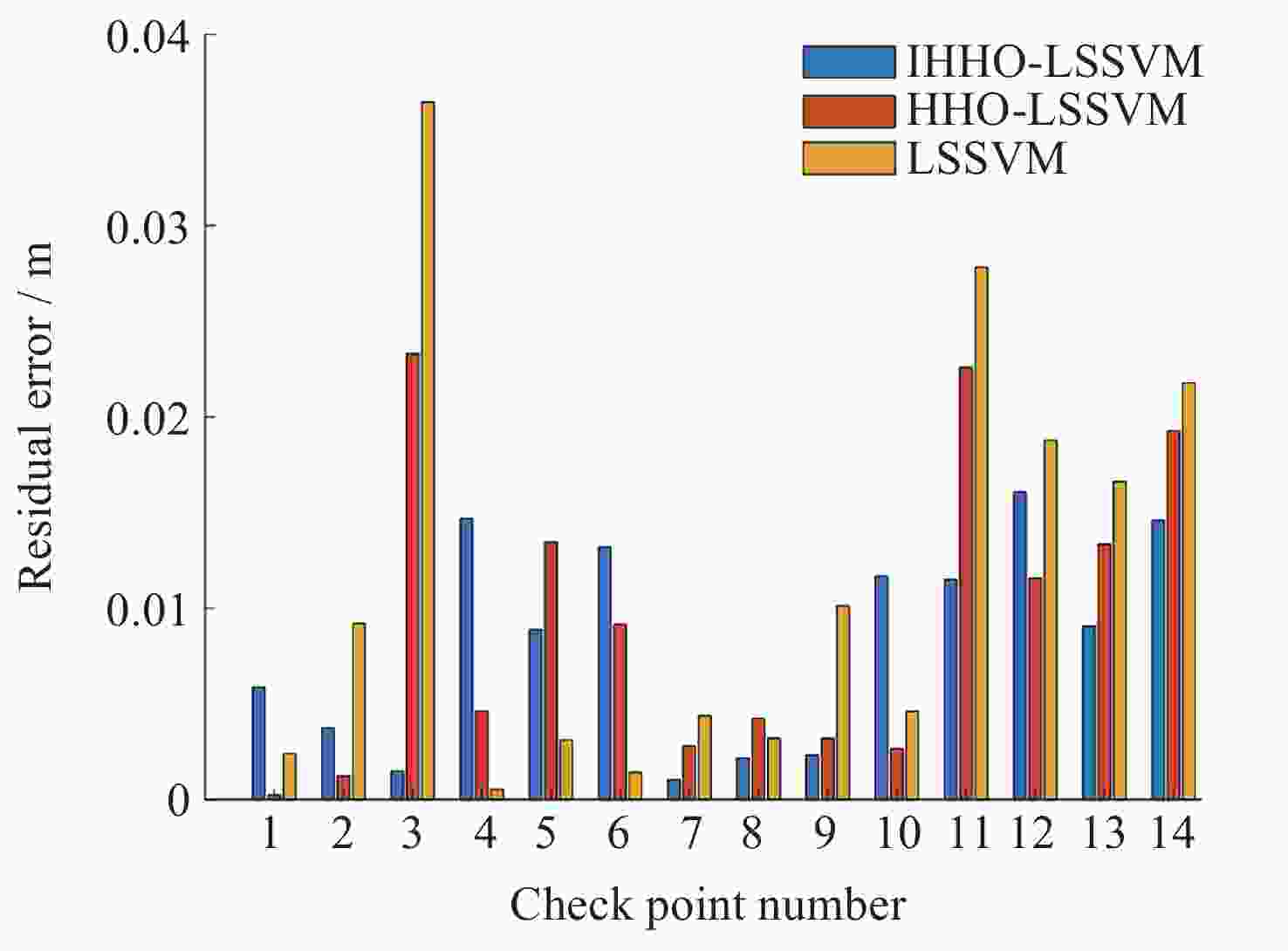
参数名 含义 数值 sizepop 种群规模 50 T 最大迭代次数 50 bu 模型参数上界 10000 bl 模型参数下界 0.01 dim 优化参数个数 2 表 2 三种方法的外符合精度统计
Table 2. Statistics of external coincidence accuracy for three methods
Comp.
orderIHHO-LSSVM HHO-LSSVM LSSVM c σ Acc/m c σ Acc/m c σ Acc/m 1 9.4563 0.0627 0.0101 48.3160 0.3132 0.0120 242.7275 0.3364 0.0159 2 9.2120 0.0467 0.0101 46.3075 0.4095 0.0126 902.8057 1.0192 0.0153 3 8.6297 0.0454 0.0101 6.3957 0.2001 0.0125 667.4809 0.8753 0.0157 4 6.5542 0.0673 0.0099 5.3087 0.2064 0.0126 834.2785 0.9877 0.0160 5 5.0345 0.0939 0.0103 3.1908 0.1504 0.0125 518.1796 0.7436 0.0157 6 4.7826 0.0836 0.0103 4.1458 0.1677 0.0122 641.3714 0.8620 0.0155 7 6.3225 0.0759 0.0100 19.8899 0.3015 0.0125 746.0421 0.3305 0.0154 8 9.9653 0.0475 0.0102 99.9546 0.5915 0.0129 254.1818 0.3484 0.0155 9 10.9717 0.0592 0.0103 25.6355 0.3020 0.0123 571.8598 0.8055 0.0162 10 7.3621 0.0492 0.0099 46.7021 0.3757 0.0124 946.7136 1.0382 0.0161 $\bar A_{\mathrm{cc}} $ ― ― 0.0101 ― ― 0.0125 ― ― 0.0157 注 Acc为精度. 表 3 检查点的预测结果及精度分析
Table 3. Prediction results and accuracy analysis of check points
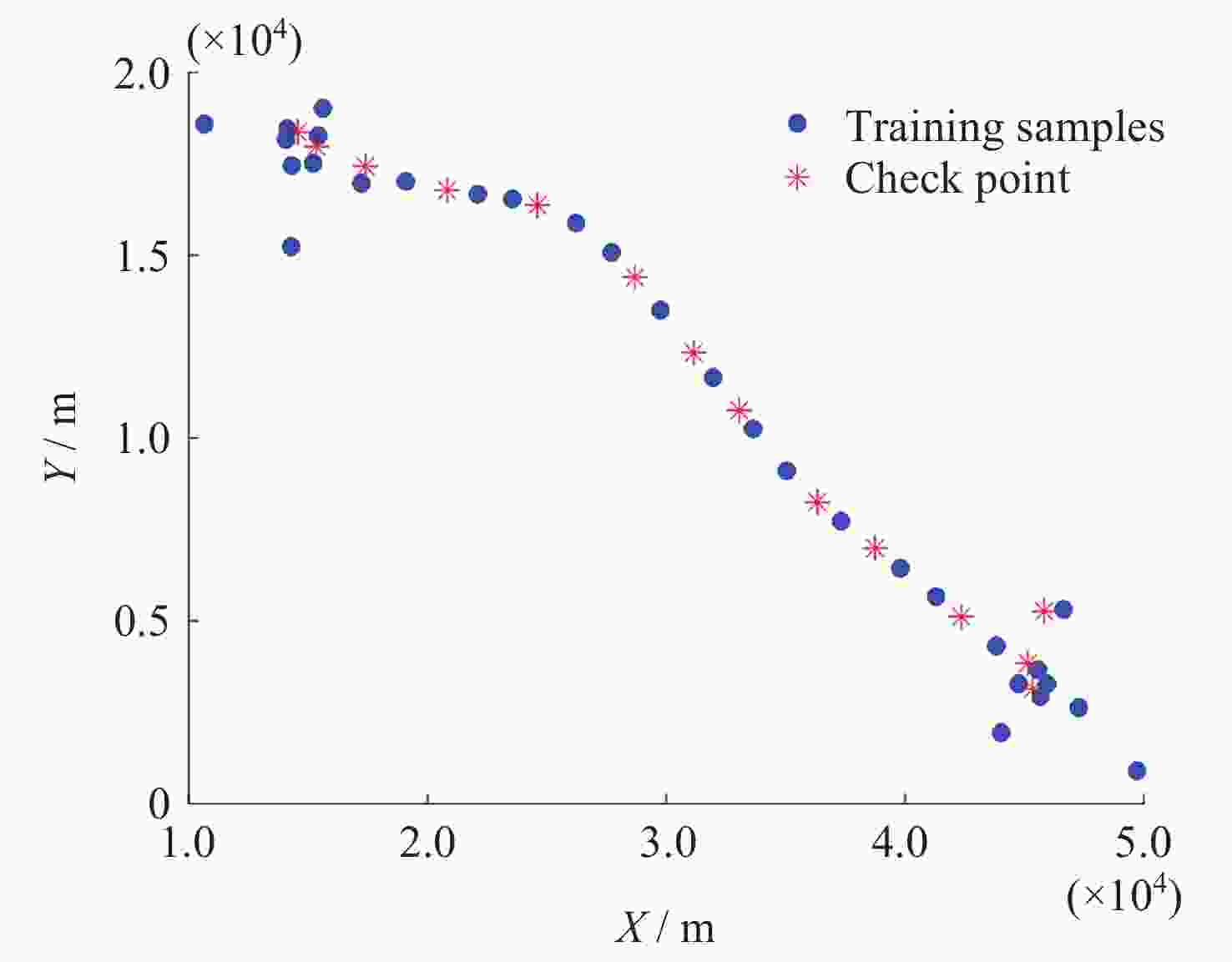
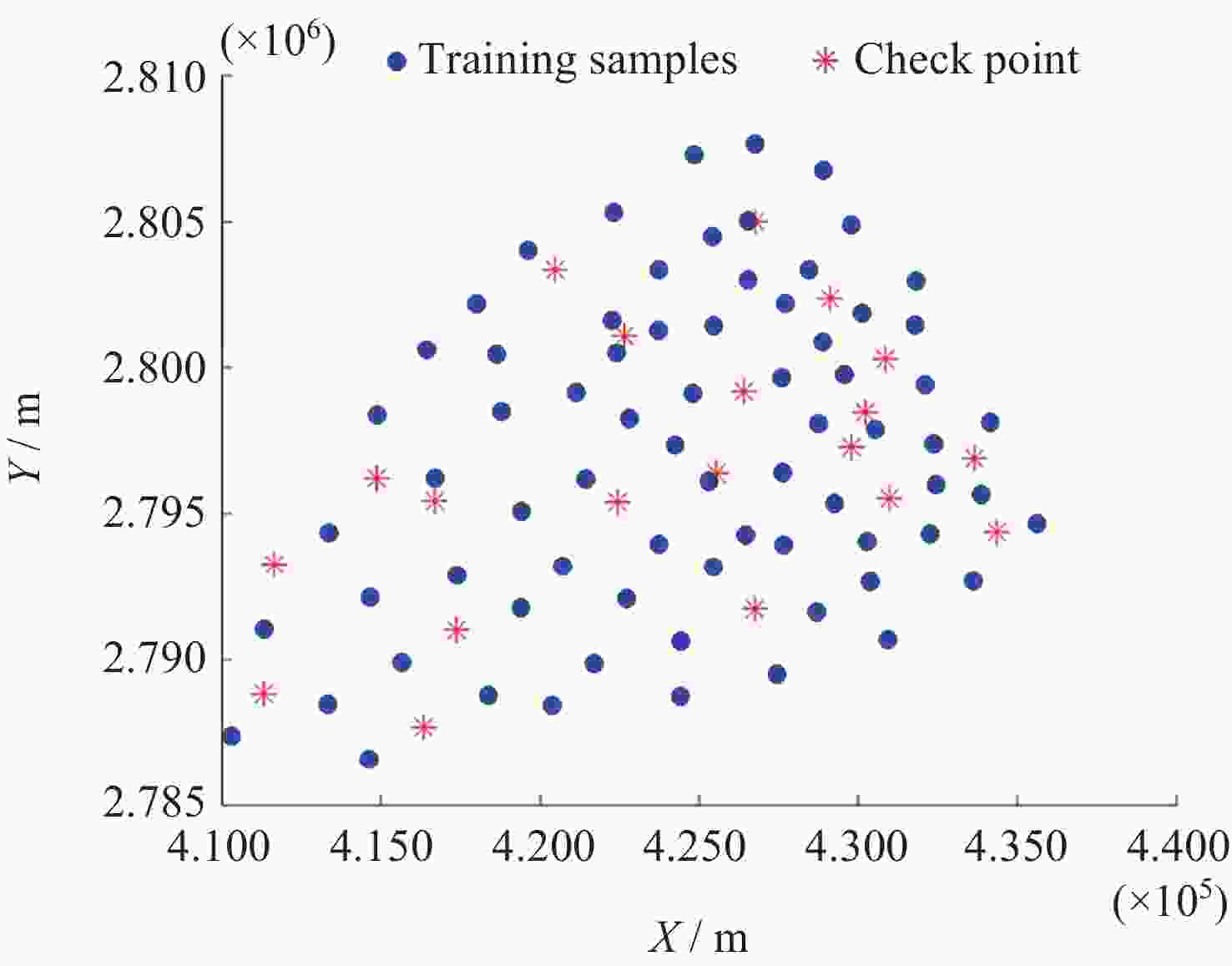
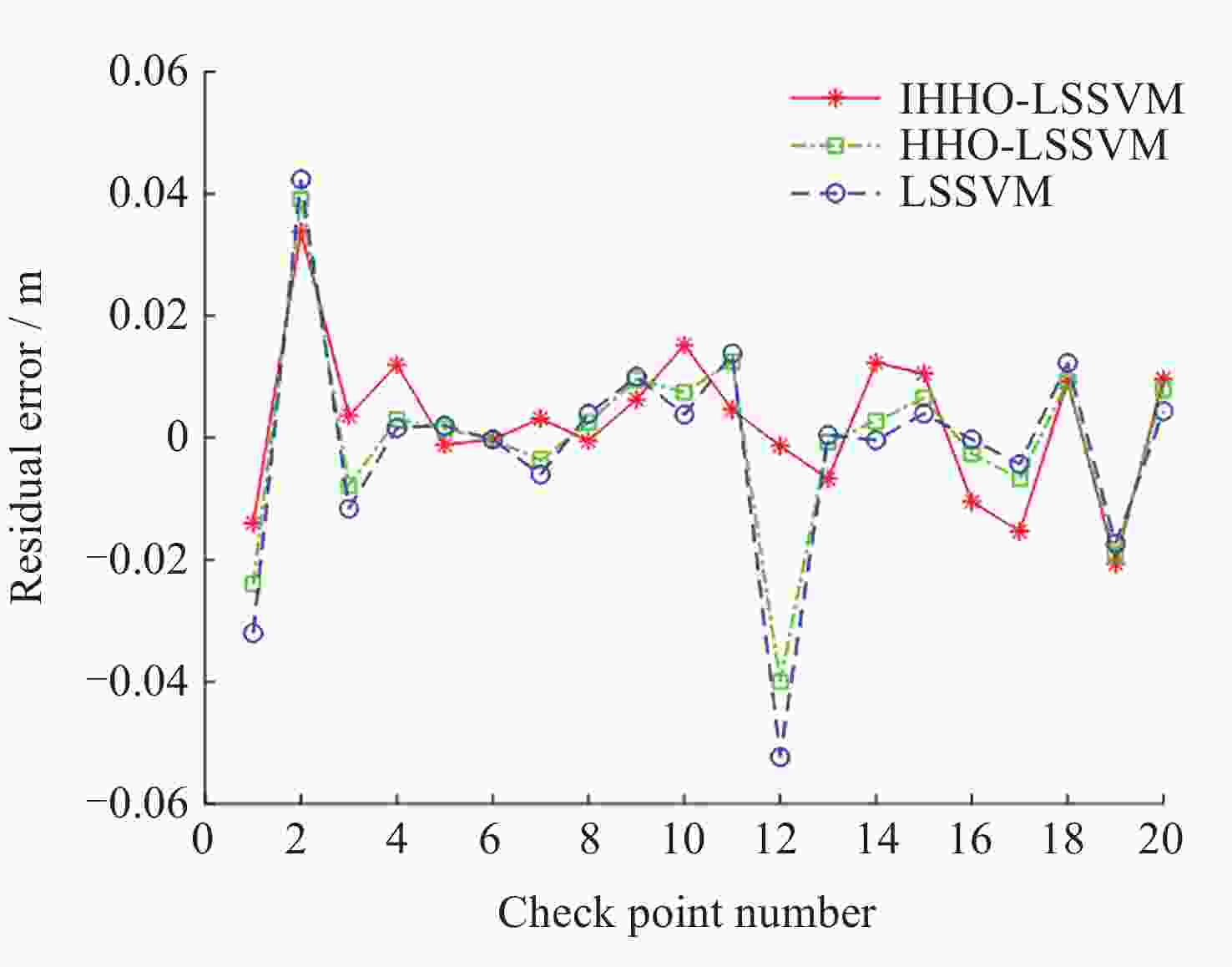
Check points Given height
anomaly/mResidual error/m IHHO HHO LSSVM 1 –20.7172 –0.0140 –0.0240 –0.0320 2 –20.6537 0.0338 0.0391 0.0423 3 –20.5230 0.0036 –0.0078 –0.0116 4 –20.0759 0.0120 0.0030 0.0016 5 –20.0170 –0.0011 0.0015 0.0020 6 –19.9065 –0.0002 –0.0003 –0.0003 7 –20.4448 0.0031 –0.0036 –0.0060 8 –19.8739 –0.0005 0.0025 0.0039 9 –19.9360 0.0063 0.0095 0.0100 10 –20.1365 0.0152 0.0075 0.0038 11 –20.4328 0.0046 0.0124 0.0139 12 –20.4832 –0.0013 –0.0400 –0.0523 13 –19.9431 –0.0067 –0.0007 0.0004 14 –19.9499 0.0123 0.0027 –0.0004 15 –20.0201 0.0105 0.0065 0.0039 16 –20.0453 –0.0105 –0.0026 –0.0003 17 –19.8213 –0.0154 –0.0067 –0.0043 18 –19.7091 0.0123 0.0092 0.0092 19 –20.0251 –0.0206 –0.0191 –0.0174 20 –19.6036 0.0096 0.0078 0.0043 -
[1] 金俐君, 陈必焰, 王晓嫚, 等. 基于2021年GNSS TEC的电离层模型IRI-Plas 2020与IRI-2020的全球精度评估[J]. 空间科学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1031-1046 doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.06.2023-0075JIN Lijun, CHEN Biyan, WANG Xiaoman, et al. Global accuracy assessment and analysis of the ionospheric model IRI-Plas 2020 and IRI-2020 based on GNSS observations[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2024, 44(6): 1031-1046 doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.06.2023-0075 [2] 王冬伟, 孙越强, 王先毅, 等. 一种基于北斗三号系统的GNSS-R海面干涉测高技术[J]. 空间科学学报, 2022, 42(3): 492-499 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210315029WANG Dongwei, SUN Yueqiang, WANG Xianyi, et al. A new GNSS-R interferometric ocean altimetry using Beidou-3 signal[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(3): 492-499 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.03.210315029 [3] 王国权, 鲍艳. 基于区域参考框架的GNSS滑坡监测[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(10): 2107-2116WANG Guoquan, BAO Yan. GNSS landslide monitoring based on regional reference frame[J]. Journal of Surveying and Mapping, 2022, 51(10): 2107-2116 [4] 魏德宏, 禤键毫, 杨嘉伟, 等. 基于深度BP/ELMAN神经网络的山区GNSS高程转换精度分析[J]. 测绘通报, 2023(09): 113-116+143 doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2023.0244WEI Dehong, XUAN Jianhao, YANG Jiawei, et al. GNSS elevation conversion accuracy analysis in mountainous areas based on deep BP/ELMAN neural network[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2023(09): 113-116+143 doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2023.0244 [5] 段文义, 许烨璋, 王灵锋, 等. 一种基于CGC-S2000框架的单椭球七参数转换法[J]. 测绘科学, 2017, 42(06): 50-54 doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2017.06.010DUAN Wenyi, XU Yezhang, WANG Lingfeng, et al. A Seven-parameter transformation method for single ellipsoid based on CGC-S2000 framework[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, 42(06): 50-54 doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2017.06.010 [6] 张炎, 刘立龙, 蒙金龙, 等. 一种IGrubbs-LWLR的区域高程异常拟合方法[J]. 无线电工程, 2023, 53(10): 2345-2351 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2023.10.015ZHANG Yan, LIU Lilong, MENG Jinlong, et al. A regional elevation anomaly fitting method for IGrubbs-LWLR[J]. Radio Engineering, 2023, 53(10): 2345-2351 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2023.10.015 [7] 钱建国, 樊意广. 基于改进小波神经网络的GPS高程拟合研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2022, 42(03): 253-257 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2022.03.007QIAN Jianguo, FAN Yiguang. Research on GPS elevation fitting based on improved wavelet neural network[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 42(03): 253-257 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2022.03.007 [8] 张怀亮, 李晓莉, 朱赛虎. 改进多面函数拟合跨带区域高程异常的研究[J]. 测绘科学, 2016, 41(03): 132-137 doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2016.03.027ZHANG Huailiang, LI Xiaoli, ZHU Saihu. Study on Improved multi-faceted function fitting of regional elevation anomalies across zones[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2016, 41(03): 132-137 doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2016.03.027 [9] 周飞, 张炎, 唐诗华, 等. 利用蜂群算法优化的区域高程拟合精度分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(16): 6330-6335 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.16.003ZHOU Fei, ZHANG Yan, TANG Shihua, et al. Analysis of area elevation fitting accuracy optimized by Bee Colony Algorithm[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(16): 6330-6335 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.16.003 [10] 谢洋洋, 付超, 解琨, 等. 灰色最小支持向量机模型在高程拟合中的应用[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(03): 55-60 doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2021.03.009XIE Yangyang, FU Chao, XIE Kun, et al. Application of grey minimum support vector machine model in elevation fitting[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(03): 55-60 doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2021.03.009 [11] 吴艳敏, 刘家旗, 王璐, 等. 基于改进哈里斯鹰优化算法的配电网动态重构[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24(08): 3251-3259WU Yanmin, LIU Jiaqi, WANG Lu, et al. Dynamic reconstruction of distribution network based on improved Harris Eagle Optimization algorithm[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24(08): 3251-3259 [12] 何广焕. 基于IHHO-LSSVM的地面匹配点云孔洞修补应用研究[D]. 广西桂林: 桂林理工大学, 2023HE Guanghuan. Research on the Application of Ground Matching Point Cloud Hole Repair Based on IHHO-LSSVM[D]. Guilin, Guangxi: Guilin University of Technology, 2023 [13] 钱建国, 徐志文, 赵玉国, 等. 基于改进鲸鱼算法优化神经网络的GPS高程拟合方法[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2024, 44(02): 122-127 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2023.04.188QIAN Jianguo, XU Zhiwen, ZHAO Yuguo, et al. GPS elevation fitting method based on improved Whale algorithm Optimization neural network[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2024, 44(02): 122-127 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2023.04.188 [14] 张燕. 改进的哈里斯鹰算法及其在空压机智能调度中的应用研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆理工大学, 2024ZHANG Yan. Research on Improved Harris Eagle Algorithm and its Application in Intelligent Scheduling of Air Compressors[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University of Technology, 2024 [15] 张晓莉, 王秦飞, 冀汶莉. 一种改进的自适应惯性权重的粒子群算法[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2019, 36(03): 72-76 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2012.12.067ZHANG Xiaoli, WANG Qinfei, JI Wenli. An improved particle swarm optimization based on adaptive inertia weighting[J]. Microelectronics & Computer, 2019, 36(03): 72-76 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2012.12.067 [16] 何广焕, 唐诗华, 王文贯, 等. 一种基于CSF-WOA-LSSVM的匹配点云土石方量计算方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(30): 13194-13201 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.30.006HE Guanghuan, TANG Shihua, WANG Wenguan, et al. A method for calculating matching point cloud soil and stone quantities based on CSF-WOA-LSSVM[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(30): 13194-13201 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.30.006 [17] 李明飞, 吴军超, 张一驰. 基于最小二乘支持向量机的组合模型在区域似大地水准面拟合中的应用[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2022, 42(09): 971-974 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2022.09.016LI Mingfei, WU Junchao, ZHANG Yichi. Application of combinatorial model based on least squares support vector machine in region-similar geoid fitting[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 42(09): 971-974 doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2022.09.016 [18] 李耸. 基于机器学习的GNSS对流层延迟建模与预报[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2022LI Cong. TropospheriC Delay Modeling and Prediction of GNSS Based on Machine Learning[D]. Xi’an, Shaanxi: Chang’an University, 2022 [19] 杨天宇. 基于BP神经网络的GPS高程拟合及其在杭州湾跨海大桥中的应用[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2006YANG Tianyu. GPS Elevation Fitting Based on BP Neural Network and its Application in Hangzhou Bay Bridge[D]. Chengdu, Sichuan: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2006 -
-





 何广焕 男, 1997年3月出生于广西梧州市, 现为广西建设职业技术学院市政与交通学院专任教师, 硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为GNSS数据处理及应用、无人机数据处理与应用. E-mail:
何广焕 男, 1997年3月出生于广西梧州市, 现为广西建设职业技术学院市政与交通学院专任教师, 硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为GNSS数据处理及应用、无人机数据处理与应用. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: