Observation and Analysis of Plasma Bubbles in Hainan during the Magnetic Storm in March 2015
-
摘要: 利用子午工程富克站(19.5°N, 109.1°E) 630 nm气辉成像仪、电离层测高仪、VHF雷达回波强度数据和Dalat地磁台站(11.9°N, 108.5°E; GL:2.5°)、PHU Thuy地磁台站(21.0°N, 105.9°E; GL:11.5°)地磁水平分量数据及ACE卫星的行星际磁场、太阳风速度观测数据, 针对2015年3月特大磁暴期间海南上空电离层等离子体泡进行了研究. 结果显示, 磁暴前后均观测到午夜前等离子体泡和日落后电离层底部虚高的抬升现象; 磁暴期间电离层底部虚高抬升受到明显抑制, 富克站未观测到等离子体泡. 对行星际电/磁场及地磁水平分量的变化情况的分析表明, 磁暴期间电离层翻转前增强(Pre-Reversal Enhancement, PRE)电场可能先后被西极性过屏蔽穿透电场和扰动发电机电场抑制, 导致瑞利–泰勒不稳定性降低, 不利于等离子体泡/电离层不规则体结构的发育.Abstract: This study utilizes the optical observation data from the 630 nm all-sky airglow imager, the data from the ionospheric digital ionosonde, and the data of the echo intensity of the Very High Frequency (VHF) coherent scatter radar at the Fuke Station in Hainan of the Meridian Project (19.5°N, 109.1°E). In combination with the geomagnetic horizontal component data from the Dalat Geomagnetic Station (11.9°N, 108.5°E; GL:2.5°) and the PHU Thuy Geomagnetic Station (21.0°N, 105.9°E; GL:11.5°), as well as the observations of the interplanetary magnetic field and solar wind speed from the ACE satellite, the study is carried out on the variations of the ionospheric plasma bubbles/irregularity structures over Hainan during the super geomagnetic storm in March 2015. The results show that the appearance of pre-midnight plasma bubbles and the uplift of the virtual height at the bottom of the ionosphere after sunset were observed both before and after the geomagnetic storm. However, the plasma bubbles observed after the end of the geomagnetic storm were of a fossil structure, which may be due to the fact that the ionospheric electric field during the occurrence period of the plasma bubbles on that day showed a westward polarity, which was not conducive to the development of the plasma bubbles. The uplift of the virtual height at the bottom of the ionosphere during the geomagnetic storm was significantly suppressed, and no plasma bubbles were observed at the Fuke station. The analysis of the variations of the interplanetary electric/magnetic field and the geomagnetic horizontal component shows that the Pre-Reversal Enhancement (PRE) electric field before the ionospheric reversal during the geomagnetic storm may have been successively suppressed by the over-shielding penetrating electric field with a westward polarity and the Disturbance Dynamo Electric Field (DDEF), resulting in a decrease in the Rayleigh-Taylor instability, which is not conducive to the development of the plasma bubble/ionospheric irregularity structures.
-
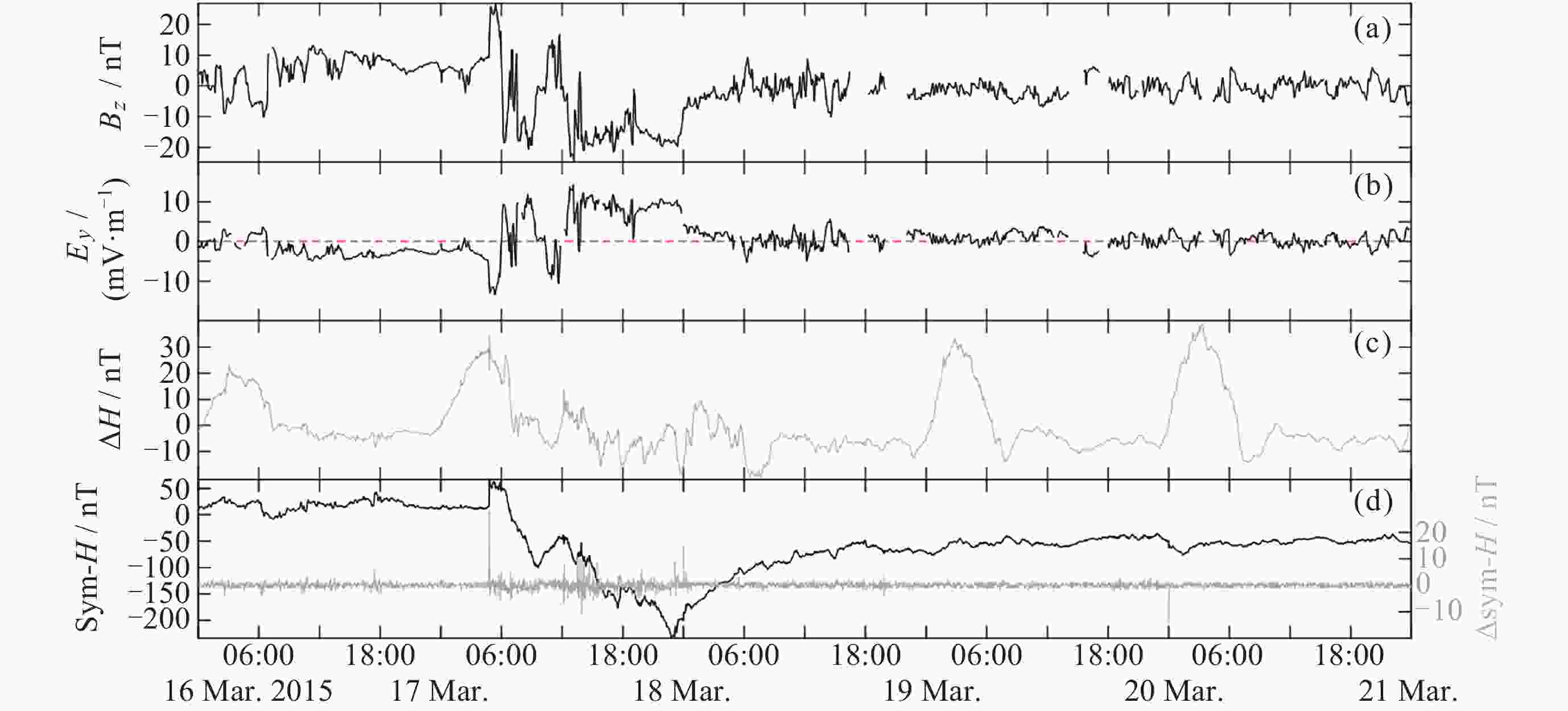
图 2 2015年3月16-20日行星际磁场/电场参量和地磁参量的变化情况. (a)行星际磁场Bz分量, 北向为正方向; (b)由太阳风速和行星际磁场Bz分量计算得到的行星际电场Ey; (c)地磁ΔH由Dalat和PHU Thuy地磁台站的地磁水平分量计算得到; (d) sym-H即1 min分辨率的地磁Dst指数数据
Figure 2. Variations in interplanetary magnetic/electric field and geomagnetic parameters from 16-20 March 2015. (a) Bz component of IMF with northward positive direction. (b) Interplanetary electric field Ey, calculated from solar wind speed and Bz component of IMF. (c) Geomagnetic ΔH, calculated from the horizontal component of geomagnetism at Dalat geomagnetic station and PHU Thuy geomagnetic station. (d) sym-H, i.e. geomagnetic Dst index data at 1 min resolution
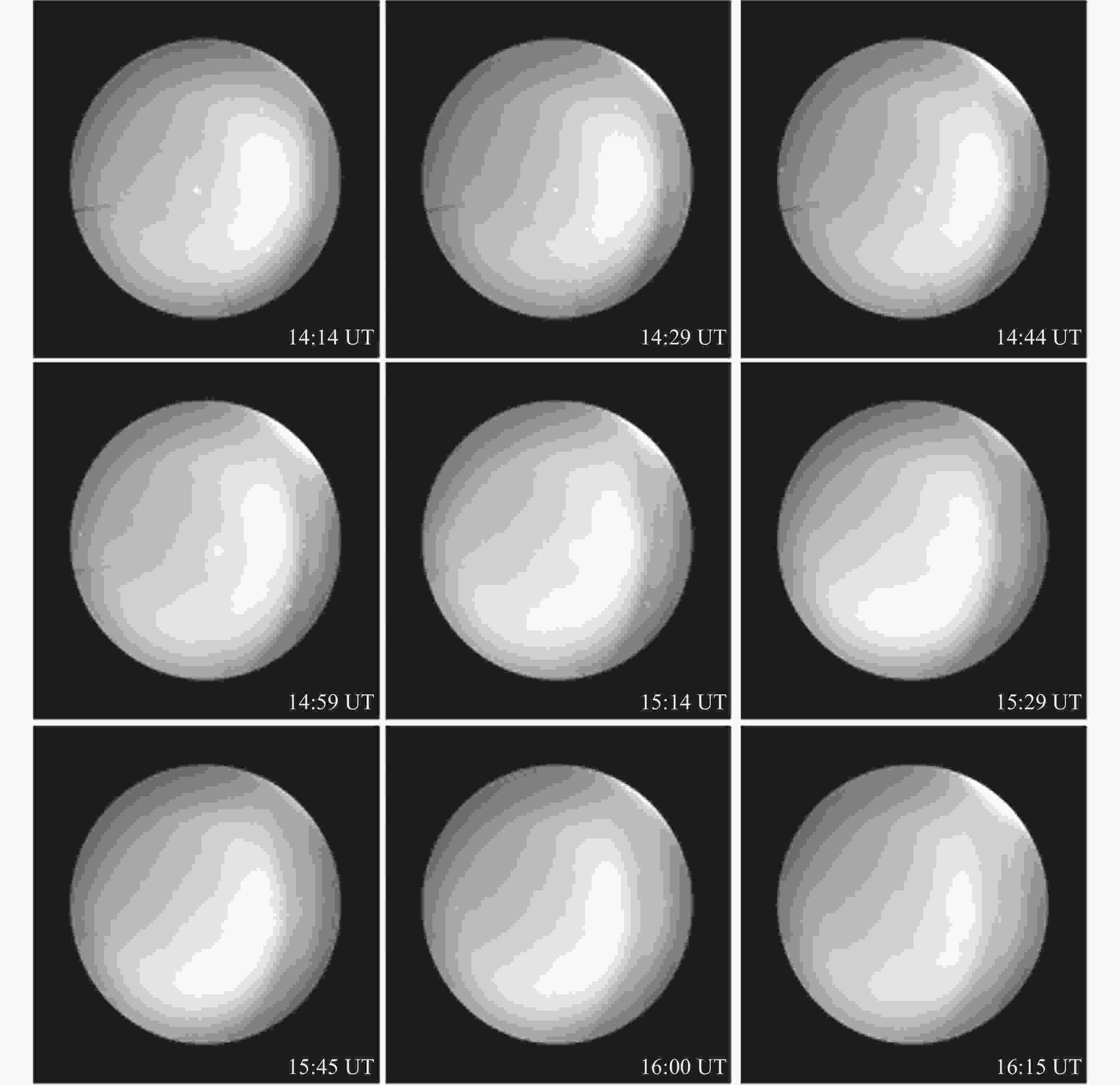
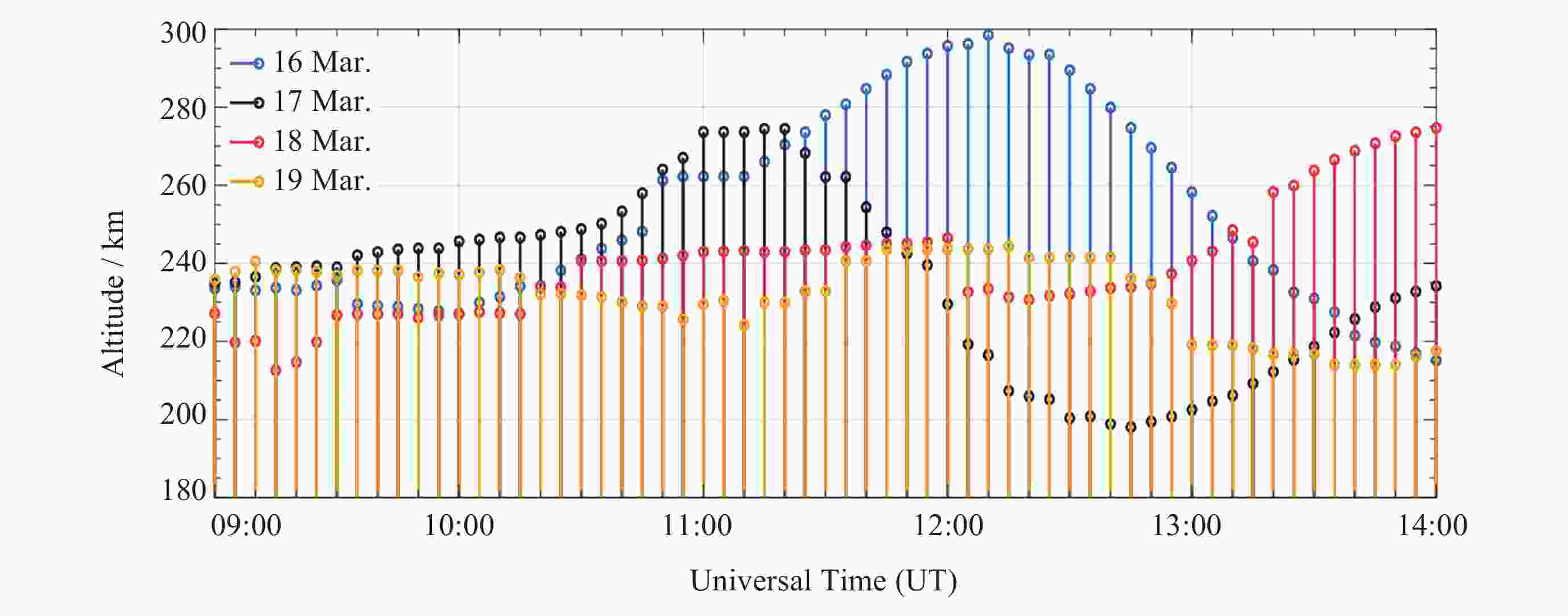
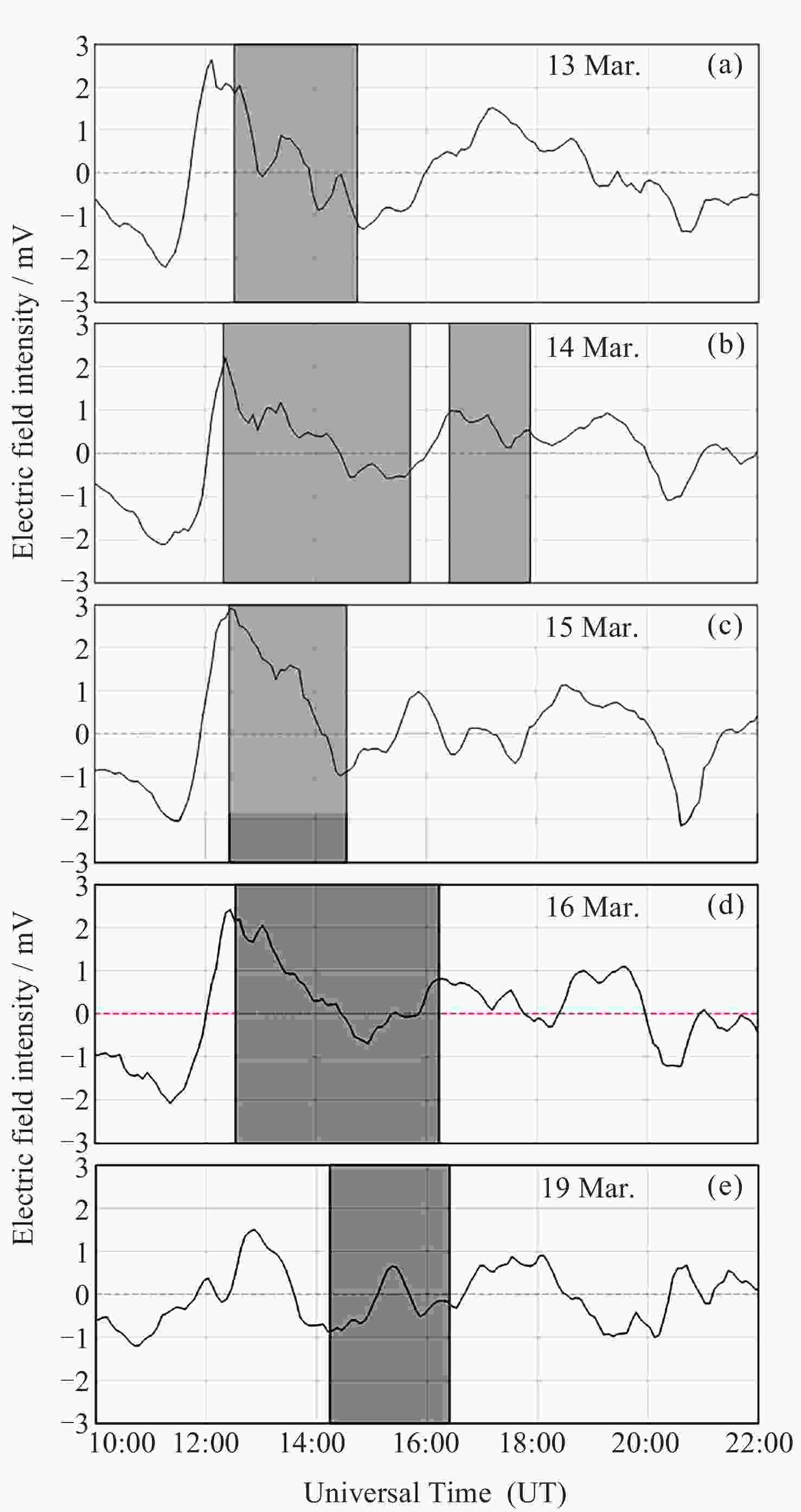
图 10 2015年3月13-16日及3月19日日落前后电离层电场的变化情况 (灰色区域表示当日630 nm气辉成像仪观测到等离子体泡的时段)
Figure 10. Variation of the ionospheric electric field around sunset on 13-16 and 19 March 2015 (The grey shaded areas indicate the time periods during which plasma bubbles were observed by the 630 nm airglow imager on that day)
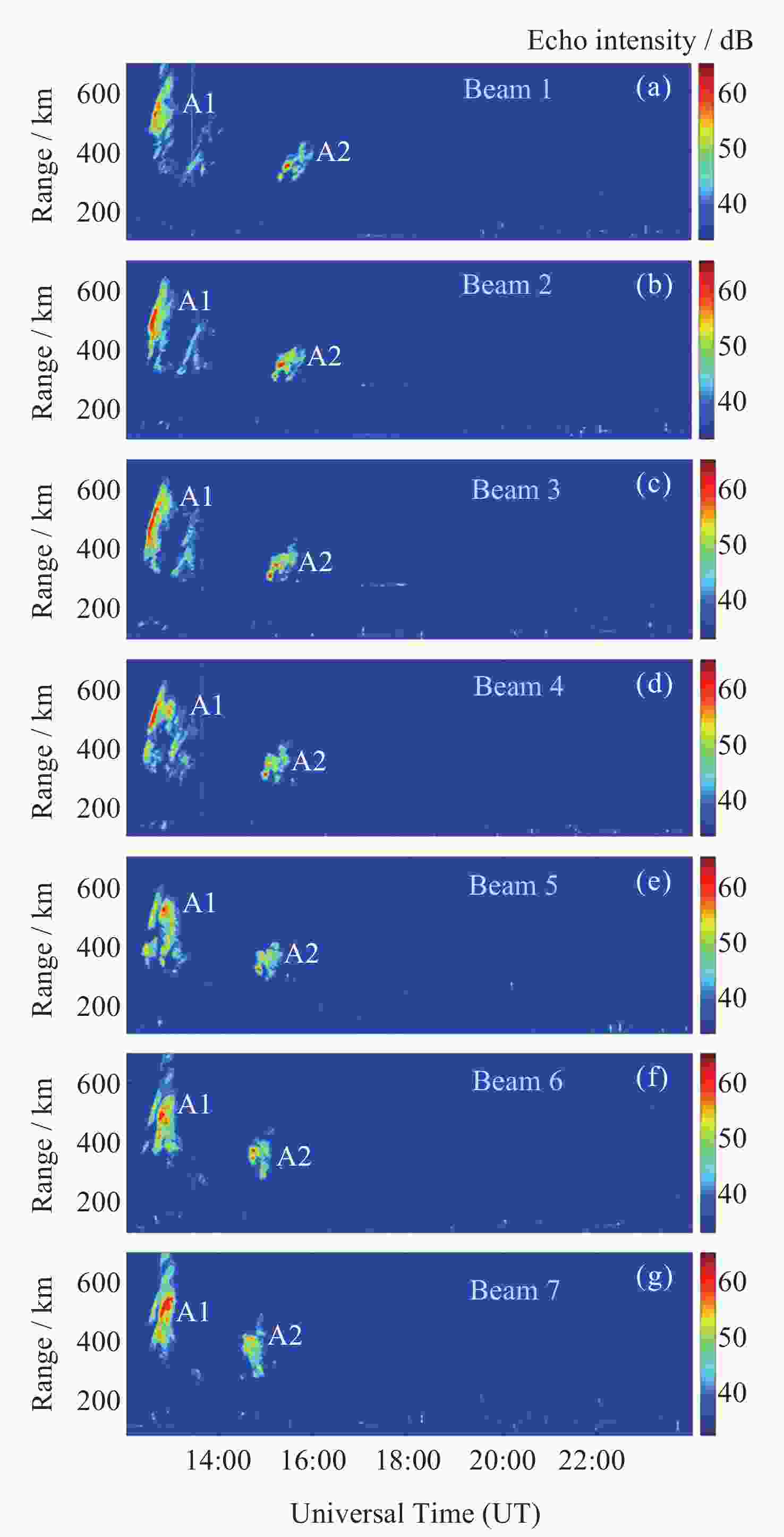
表 1 2015年3月13-16日和3月19日气辉成像仪视场中出现等离子体泡的时间统计结果
Table 1. Statistical result on the appearance time of plasma bubbles in the field of view of the airglow imager on 13-16 and 19 March 2015
日期 等离子体泡出现时间 (UT) 2015年3月13日 12:31-14:44 2015年3月14日 12:19-15:42, 16:25-17:53 2015年3月15日 12:26-14:33 2015年3月16日 12:32-16:14 2015年3月19日 14:14-16:24 表 2 2015年3月13-16日不规则体结构出现时间统计结果
Table 2. Statistical results of the occurrence time of structures of irregularities on 13-16 March 2015
日期 电离层不规则体出现时间 (UT) 2015年3月13日 12:13 -13:23, 14:27-15:23 2015年3月14日 12:00-12:20, 13:18-15:16 2015年3月15日 12:26-12:46, 14:57-17:59 2015年3月16日 12:20-13:23, 14:49-15:29 -
[1] BOOKER H G, WELLS H W. Scattering of radio waves by the F‐region of the ionosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheric, 1938, 43(3): 249-256 [2] WOODMAN R F, LA HOZ C. Radar observations of F region equatorial irregularities[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1976, 81(31): 5447-5466 doi: 10.1029/JA081i031p05447 [3] HAERENDEL G. Theory of Equatorial Spread F[R]. Munich: Max-Planck-institute für Physik und Astrophysik, Federal Republic of Germany, 1973 [4] KELLEY M C. The Earth’s Ionosphere[M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 1989 [5] CHOU M Y, YUE J, SASSI F, et al. Modeling the day-to-day variability of midnight equatorial plasma bubbles with SAMI3/SD-WACCM-X[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2023, 128(5): e2023JA031585 [6] HUANG F Q, LEI J H, XIONG C, et al. Observations of equatorial plasma bubbles during the geomagnetic storm of October 2016[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2021, 5(5): 416-426 [7] ABDU M A. Equatorial spread F/plasma bubble irregularities under storm time disturbance electric fields[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2012, 75-76: 44-56 [8] GONZÁLEZ G, WU Y J, GASQUE L C, et al. Effects of storm-time winds on ionospheric pre-midnight equatorial plasma bubbles over South America as observed by ICON and GOLD[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2024, 129(10): e2024JA033111 [9] MARTNIS C R, MENDILLO M J, AARONS J. Toward a synthesis of equatorial spread F onset and suppression during geomagnetic storms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2005, 110(A7): A07306 doi: 10.1029/2003ja010362 [10] BASU S, BASU S, GROVES K M, et al. Response of the equatorial ionosphere in the South Atlantic region to the great magnetic storm of July 15, 2000[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(18): 3577-3580 doi: 10.1029/2001GL013259 [11] CHAKRABARTY D, SEKAR R, NARAYANAN R, et al. Effects of interplanetary electric field on the development of an equatorial spread F event[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2006, 111(A12): A12316 doi: 10.1029/2006ja011884 [12] KELLEY M C, FEJER B G, GONZALES C A. An explanation for anomalous equatorial ionospheric electric fields associated with a northward turning of the interplanetary magnetic field[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1979, 6(4): 301-304 doi: 10.1029/GL006i004p00301 [13] BLANC M, RICHMOND A D. The ionospheric disturbance dynamo[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1980, 85(A4): 1669-1686 doi: 10.1029/JA085iA04p01669 [14] ABDU M A, BATISTA I S, BERTONI F, et al. Equatorial ionosphere responses to two magnetic storms of moderate intensity from conjugate point observations in Brazil[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2012, 117(A5): A05321 doi: 10.1029/2011JA017174 [15] TAHIR A, WU F L, SHAH M, et al. Multi-instrument observation of the ionospheric irregularities and disturbances during the 23‒24 March 2023 geomagnetic storm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(9): 1594 doi: 10.3390/rs16091594 [16] ABDU M A, BATISTA I S, TAKAHASHI H, et al. Magnetospheric disturbance induced equatorial plasma bubble development and dynamics: a case study in Brazilian sector[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2003, 108(A12): 1449 doi: 10.1029/2002ja009721 [17] ABDU M A, KHERANI E A, BATISTA I S, et al. Equatorial evening prereversal vertical drift and spread F suppression by disturbance penetration electric fields[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009, 36(19): L19103 doi: 10.1029/2009gl039919 [18] WAN X, XIONG C, WANG H, et al. A statistical study on the climatology of the equatorial plasma depletions occurrence at topside ionosphere during geomagnetic disturbed periods[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2019, 124(10): 8023-8038 doi: 10.1029/2019JA026926 [19] LI G Z, NING B Q, WANG C, et al. Storm‐enhanced development of postsunset equatorial plasma bubbles around the meridian 120°E/60°W on 7‒8 September 2017[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2018, 123(9): 7985-7998 doi: 10.1029/2018JA025871 [20] DABAS R S, LAKSHMI D R, REDDY B M. Effect of geomagnetic disturbances on the VHF nighttime scintillation activity at equatorial and low latitudes[J]. Radio Science, 1989, 24(4): 563-573 doi: 10.1029/RS024i004p00563 [21] WANG G J, SHI J K, WANG X, et al. Seasonal variation of spread-F observed in Hainan[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2008, 41(4): 639-644 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2007.04.077 [22] 吴祺, 余涛, 林兆祥, 等. 海南电离层F区不规则体的气辉观测[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(1): 17-27 doi: 10.6038/cjg20160103WU Qi, YU Tao, LIN Zhaoxiang, et al. Night airglow observations to irregularities in the ionospheric F region over Hainan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(1): 17-27 doi: 10.6038/cjg20160103 [23] JIN H, ZOU S S, CHEN G, et al. Formation and evolution of low‐latitude F region field‐aligned irregularities during the 7-8 September 2017 storm: Hainan coherent scatter phased array radar and digisonde observations[J]. Space Weather, 2018, 16(6): 648-659 doi: 10.1029/2018SW001865 [24] PIMENTA A A, FAGUNDES P R, BITTENCOURT J A, et al. Ionospheric plasma bubble zonal drift: a methodology using OI 630 nm all-sky imaging systems[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2001, 27(6/7): 1219-1224 doi: 10.1016/s0273-1177(01)00201-0 [25] SARUDIN I, HAMID N S A, ABDULLAH M, et al. Equatorial plasma bubble zonal drift velocity variations in response to season, local time, and solar activity across Southeast Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2020, 125(3): e2019JA027521 doi: 10.1029/2019JA027521 [26] 赵秀宽, 李国主, 胡连欢, 等. 基于GNSS观测的全球赤道等离子体泡对太阳和地磁活动及季节依赖特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2023, 66(7): 2703-2712 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0771ZHAO Xiukuan, LI Guozhu, HU Lianhuan, et al. Solar and geomagnetic activity and seasonal dependence of global equatorial plasma bubbles based on GNSS observations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2023, 66(7): 2703-2712 doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0771 [27] KELLEY M C. The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics[M]. 2nd ed. San Diego: Academic Press, 2009 [28] KIKUCHI T, HASHIMOTO K K, NOZAKI K. Penetration of magnetospheric electric fields to the equator during a geomagnetic storm[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2008, 113(A6): A06214 doi: 10.1029/2007ja012628 [29] SULTAN P J. Linear theory and modeling of the Rayleigh-Taylor instability leading to the occurrence of equatorial spread F[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1996, 101(A12): 26875-26891 doi: 10.1029/96JA00682 [30] SIDOROVA L N. Equatorial plasma bubbles: the influence of the meridional thermospheric winds[J]. Geomagnetism and Aeronomy, 2022, 62(3): 246-254 doi: 10.1134/S0016793222030161 [31] SEKAR R, CHAKRABARTY D, SARKHEL S, et al. Identification of active fossil bubbles based on coordinated VHF radar and airglow measurements[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2007, 25(10): 2099-2102 doi: 10.5194/angeo-25-2099-2007 -
-




 林郁莎 女, 2000年11月出生于重庆市, 现为长安大学地质工程与测绘学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为电离层物理. E-mail:
林郁莎 女, 2000年11月出生于重庆市, 现为长安大学地质工程与测绘学院硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为电离层物理. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: