南极中山站长期(1993-2023年)再分析臭氧总量地基观测验证及趋势
doi: 10.11728/cjss2026.01.2025-0009 cstr: 32142.14.cjss.2025-0009
Validation of the Long-term (1993-2023) Reanalysis of Total Ozone Column and Their Trends at Zhongshan Station in Antarctica
-
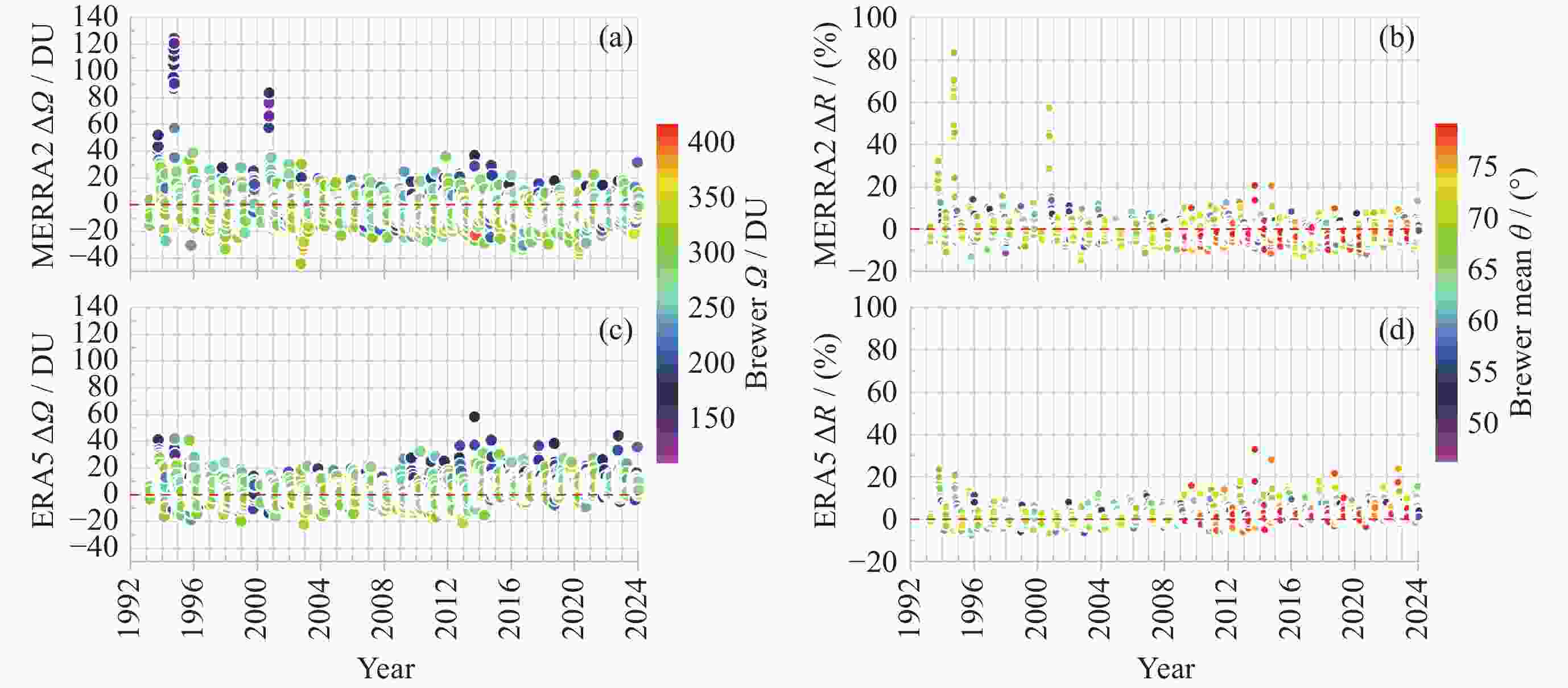
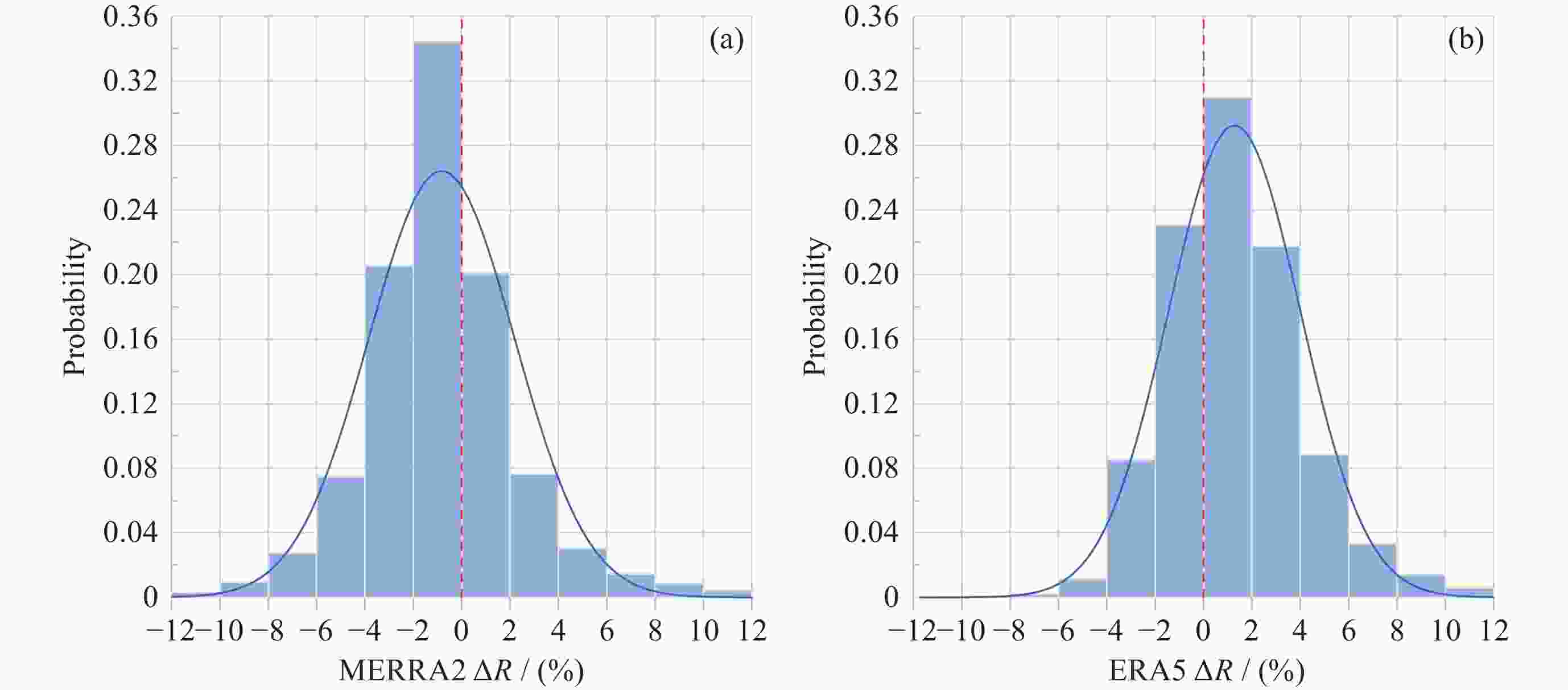
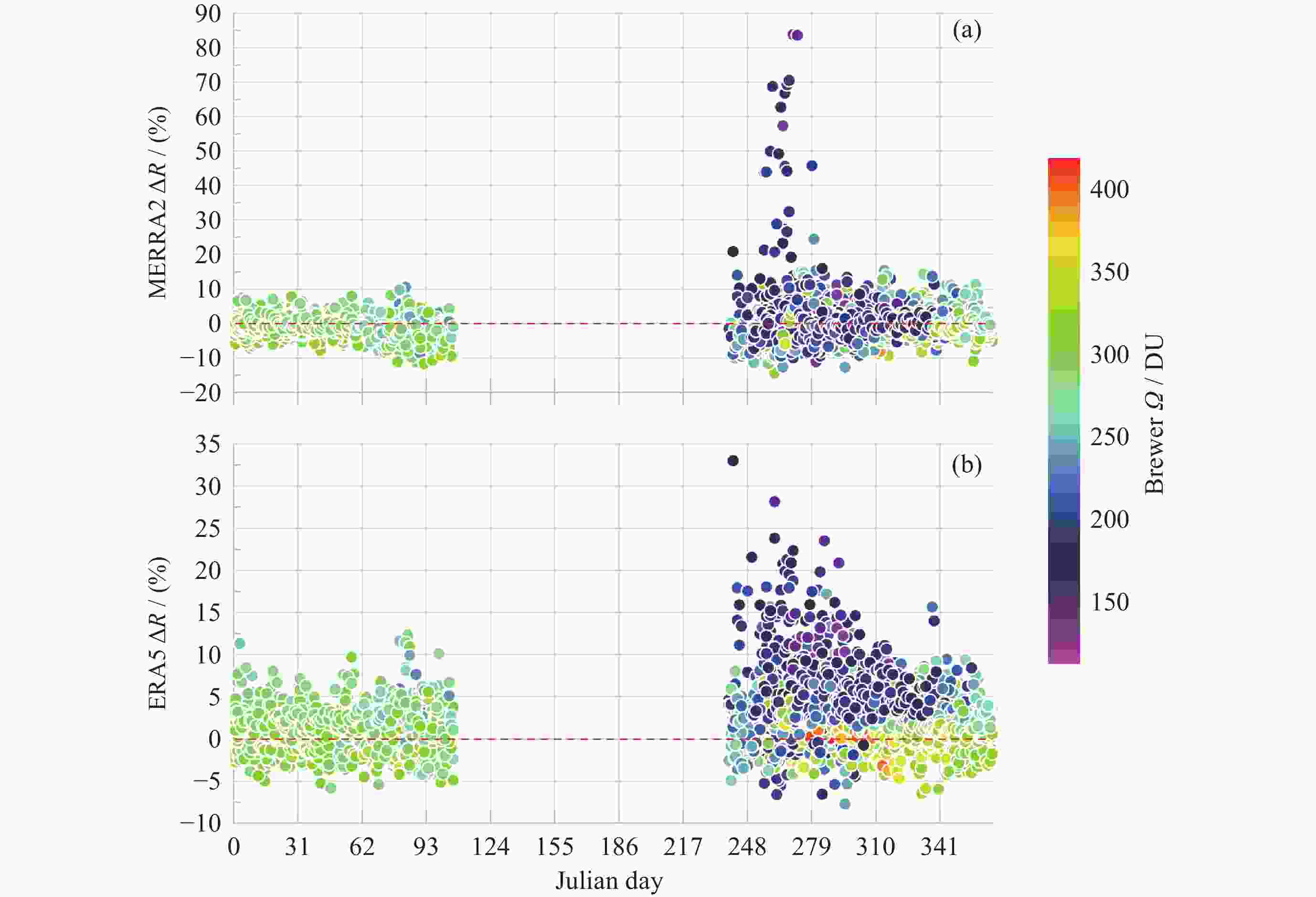
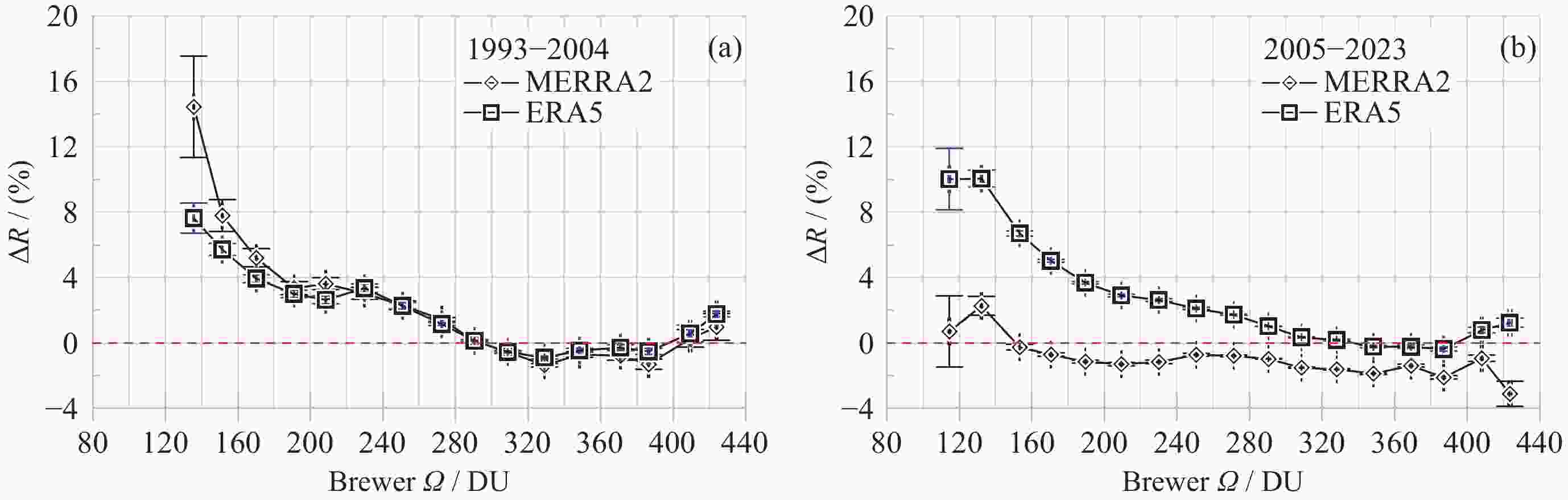
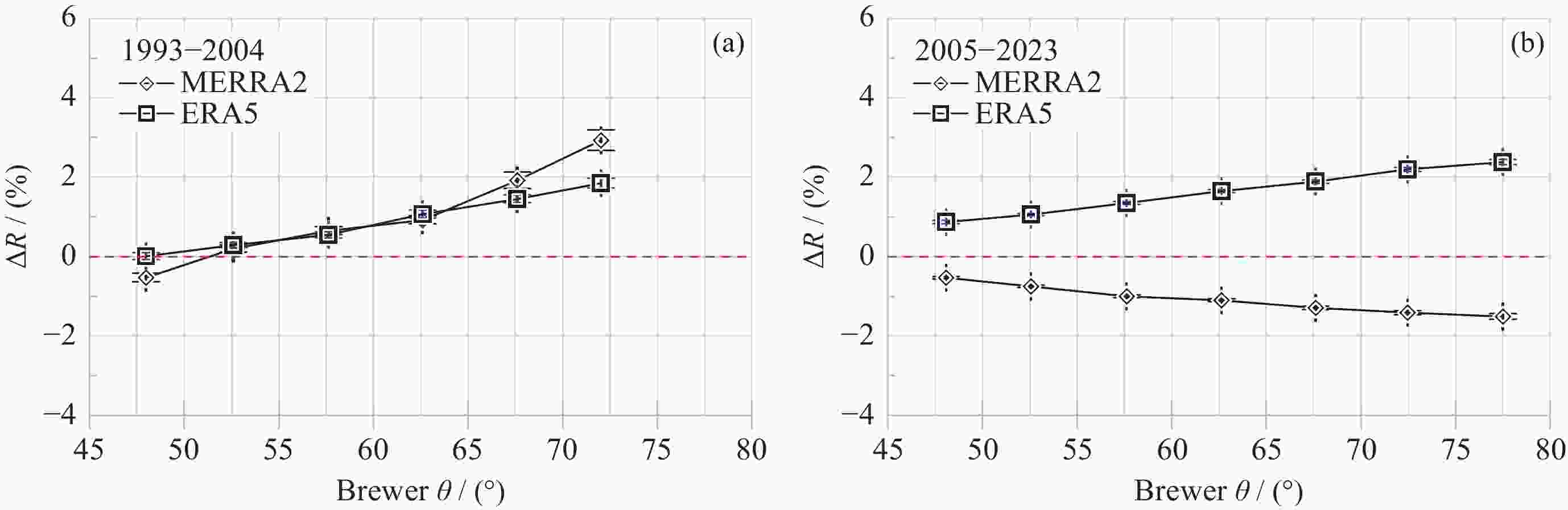
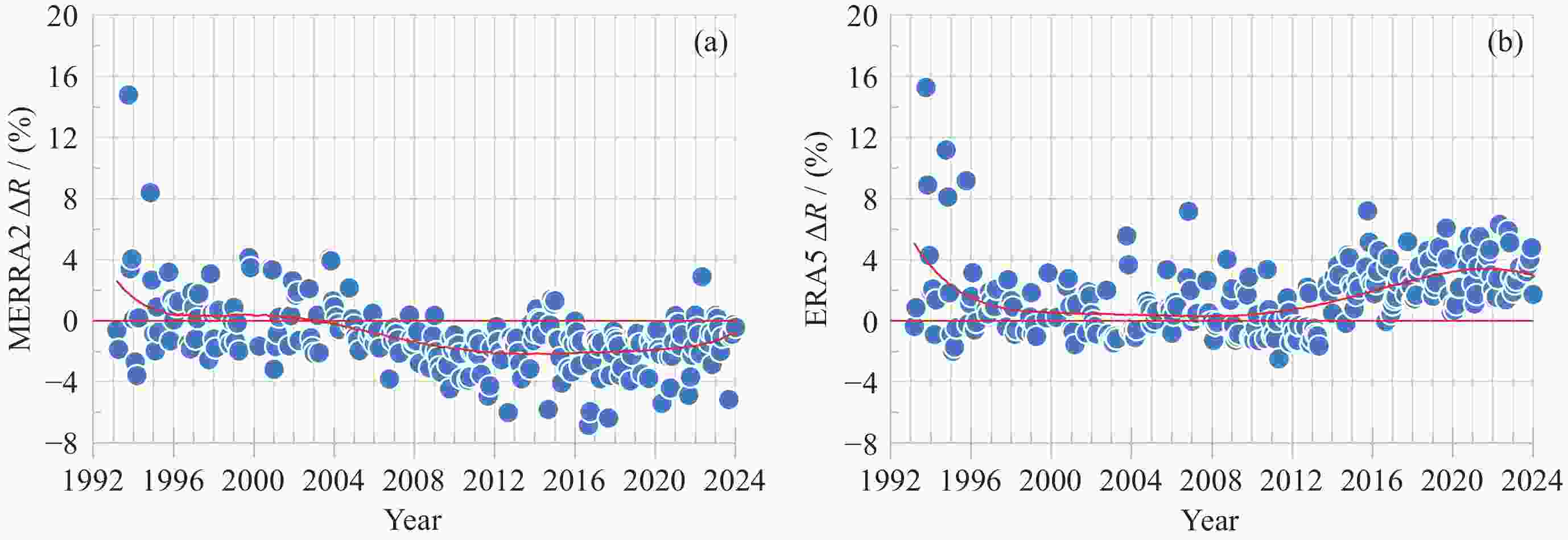
摘要: 基于南极中山站1993-2023年Brewer光谱仪地基观测大气臭氧总量(Ω), 对再分析数据MERRA2和ERA5的臭氧总量进行验证、评估和趋势分析. 研究发现, 再分析数据与地基测值在反映南极臭氧洞及臭氧总量季节变化方面是一致的. 日均 MERRA2和ERA5的臭氧总量差异浓度值(ΔΩ)分别为–2.0±9.6 DU和3.2±7.8 DU, 相对差异分布均呈随机特征. 1993-2004年和2005-2023年两个时段的臭氧洞(地基Ω ≤220 DU)期间, MERRA2的相对差异百分比 ΔR 均值分别为6.9%±4.6%和–0.4%±2.3%, 而ERA5则分别为4.6%±2.0%和6.4%±3.1%; 随着太阳天顶角θ 的上升, MERRA2 与ERA5的 ΔR 在1993-2004年分别呈现总体幅度为3%和2%的上升, 而在2005-2023年则分别呈–2%下降和2%上升; 2005-2023年的再分析臭氧总量数据质量优于1993-2004年. 经Brewer光谱仪测值订正后的再分析数据均表现出Ω 的恢复态势, 其中ERA5的恢复速率每10年为 1.3 DU. 再分析数据在被地基验证和订正之前应慎用于评估南极大气臭氧总量长期趋势变化. 地基臭氧总量观测时数虽然受太阳天顶角或天气影响而远低于再分析数据, 但对再分析数据的验证是评估臭氧总量长期变化的关键依据.Abstract: Based on the Brewer ozone spectrophotometer long-term (1993-2023) observations at Zhongshan Station, Antarctica, the atmospheric Total Ozone Column (TOC) of the MERRA2 and ERA5 reanalysis are compared, evaluated, and their trends are analyzed. The results show that the reanalysis is generally in good agreement with the ground-based data in the context of occurrence of the ozone hole and the TOC seasonality. The TOC bias (ΔΩ) on the daily mean scale is –2.0±9.6 DU and 3.2±7.8 DU for MERRA2 and ERA, respectively. Both the probability distributions of the reanalysis ΔΩ exhibit normal random processes and their large variations occurred at the end of March and during the ozone hole period. The reanalysis data were divided into two periods, 1993-2004 and 2005-2023, based on the changes of satellites to which the reanalysis data were assimilated, but the ΔΩ values (including ERA5) during the ozone hole increases with decreasing of the TOC in the both periods, and the ΔR values for MERRA2/ERA5 were 6.9%±4.6%/4.6%±2.0% and –0.4%~2.3%/6.4%±3.1%, respectively. The ΔR of MERRA2 and ERA5 show an increasing trend with the Solar Zenith Angle (SZA) during 1993-2004, with each magnitude of 3% and 2%, while the opposite trend is observed from 2005 to 2023, with magnitudes of –2% and 2% for MERRA2 and ERA5, respectively. The quality of reanalysis TOC data from 2005 to 2023 is superior to that from 1993 to 2004. Both the reanalysis TOC data validated by Brewer show their consistent recovery trends of TOC, and the linearly fitted recovery rate of ERA5 is 1.3 DU per decade. The study suggests that raw reanalysis TOC data should be used with much caution before evaluating the long-term trends of the ozone layer, and the data from the ground-based observations, although the number of the data is much less than that of reanalysis outputs due to seasonal SZA or weather conditions, is critical for the reanalysis TOC validation and conclusions of the TOC trend.
-
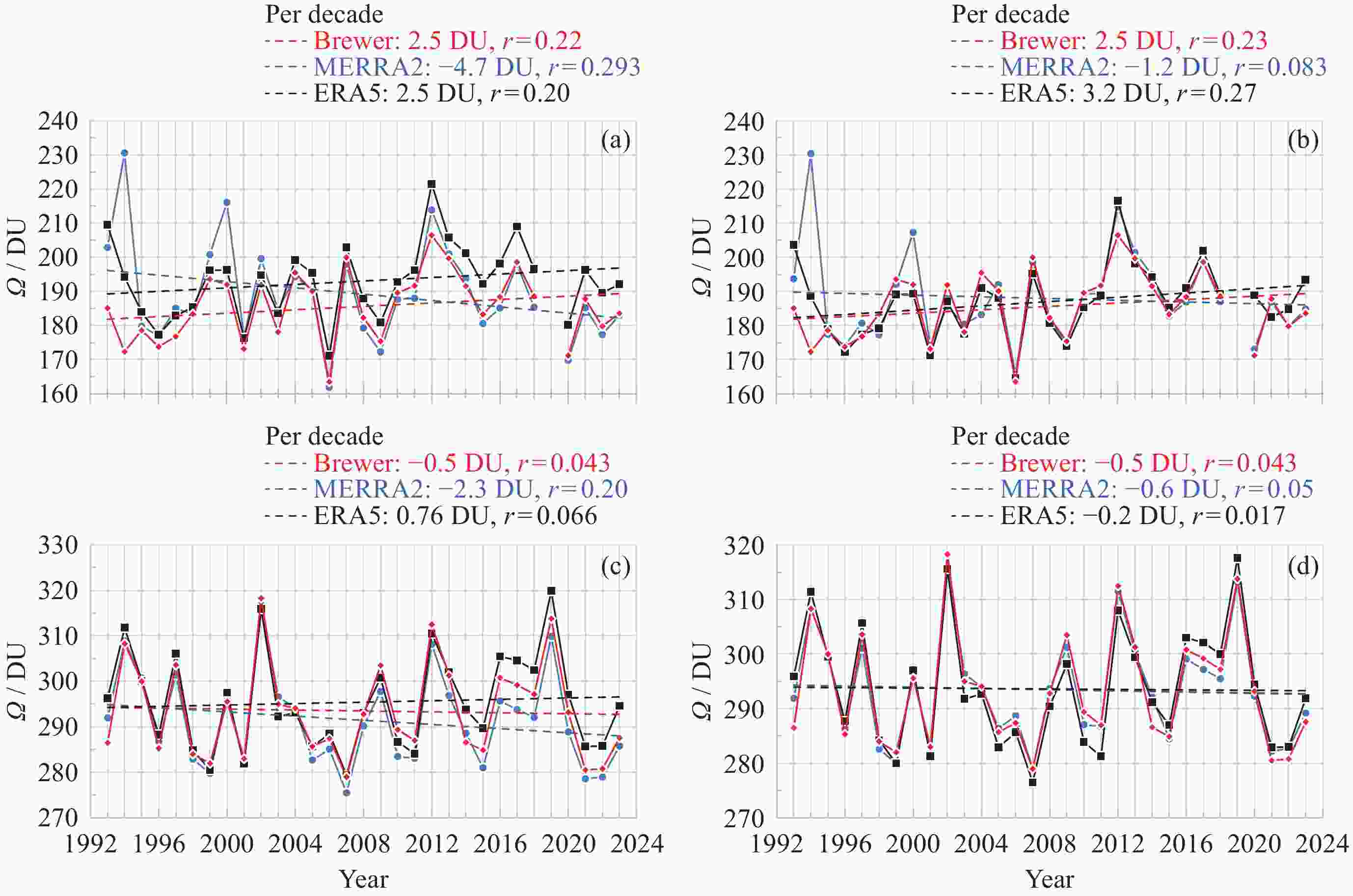
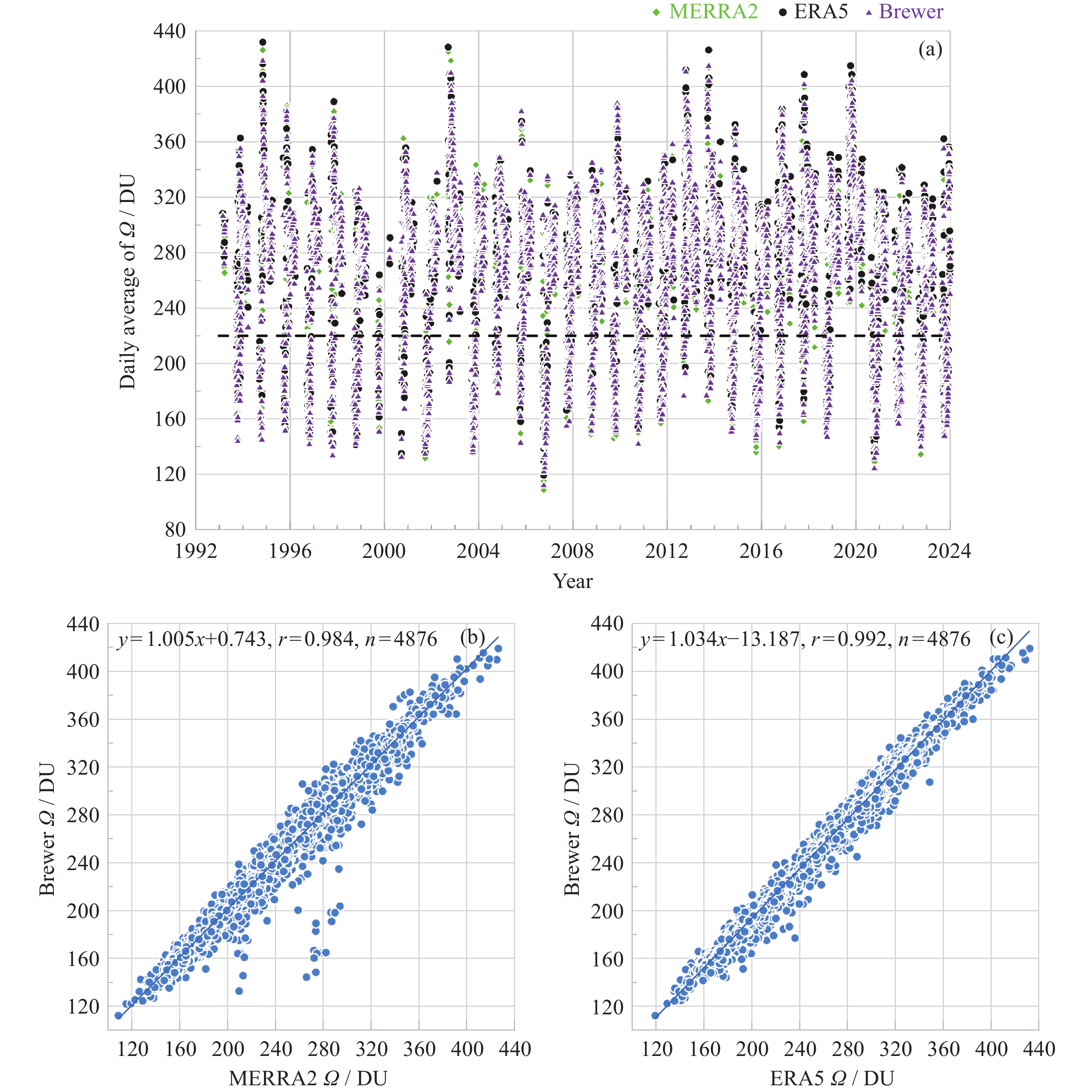
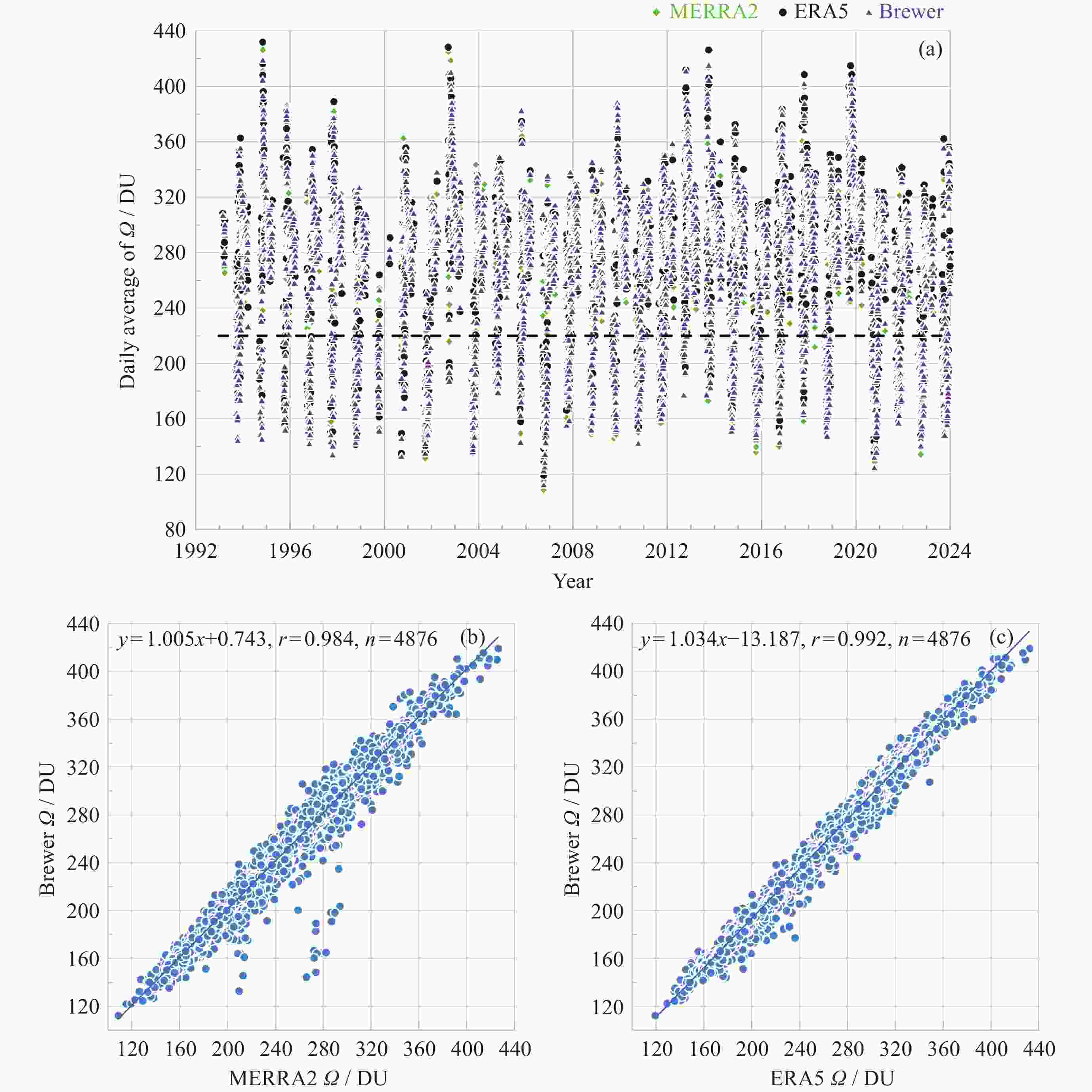
图 1 (a) 1993-2023年中山站臭氧总量日均值变化, (b) MERRA2与Brewer光谱仪的臭氧总量散点图及线性拟合结果, (c) ERA5与Brewer光谱仪的臭氧总量散点图及线性拟合结果
Figure 1. (a) Variations of daily mean TOC at Zhongshan station from 1993 to 2023. (b) Scatter plot and linear fitting results of MERRA2 and Brewer’s TOC. (c) Scatter plot linear fitting results of ERA5 and Brewer’s TOC
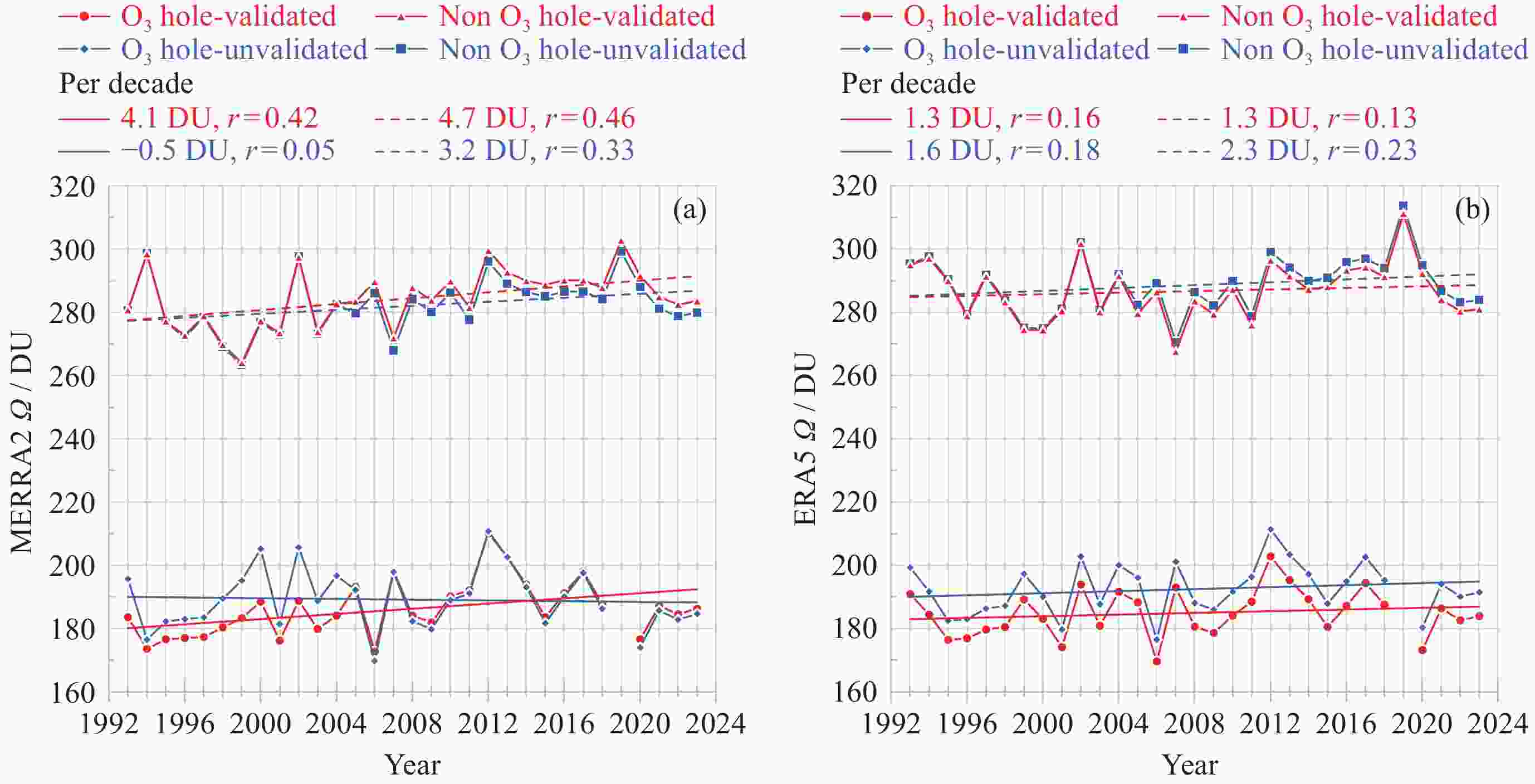
图 8 1993-2023 年南极中山站Brewer光谱仪, MERRA2和ERA5年均臭氧总量的变化及线性拟合趋势比较. (a) 原始臭氧总量数据呈现的臭氧洞趋势, (b) Brewer观测数据及订正再分析臭氧总量数据呈现臭氧洞趋势, (c) 同(a)但为非臭氧洞趋势, (d)同(c) 但为非臭氧洞趋势
Figure 8. Comparison of yearly mean TOC variations and their linearly fitted trends of Brewer, MERRA2 and ERA5 at Zhongshan Station, Antarctica from 1993 to 2023. (a) Ozone hole trends with raw TOC data, (b) ozone hole trends with validated reanalyzed and TOC data of Brewer, (c) as same as (a) but for non-ozone hole trends, (d) as same as (b) but for non-ozone hole trends
-
[1] CHUBACHI S. Preliminary result of ozone observations at Syowa station from February 1982 to January 1983[J]. Memoirs of National Institute of Polar Research, 1984, 34: 13-19 [2] FARMAN J C, GARDINER B G, SHANKLIN J D. Large losses of total ozone in Antarctica reveal seasonal ClOx/NOx interaction[J]. Nature, 1985, 315(6016): 207-210 doi: 10.1038/315207a0 [3] KESSENICH H E, SEPPäLä A, RODGER C J. Potential drivers of the recent large Antarctic ozone holes[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 7259 doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42637-0 [4] OHNEISER K, ANSMANN A, KAIFLER B, et al. Australian wildfire smoke in the stratosphere: the decay phase in 2020/2021 and impact on ozone depletion[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 22(11): 7417-7442 doi: 10.5194/acp-22-7417-2022 [5] EVAN S, BRIOUDE J, ROSENLOF K H, et al. Rapid ozone depletion after humidification of the stratosphere by the Hunga Tonga Eruption[J]. Science, 2023, 382(6669): eadg2551 doi: 10.1126/science.adg2551 [6] FERREIRA J P, HUANG Z Y, NOMURA K I, et al. Potential ozone depletion from satellite demise during atmospheric reentry in the era of mega-constellations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2024, 51(11): e2024GL109280 doi: 10.1029/2024GL109280 [7] DHOMSE S S, KINNISON D, CHIPPERFIELD M P, et al. Estimates of ozone return dates from Chemistry-Climate Model initiative simulations[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 18(11): 8409-8438 doi: 10.5194/acp-18-8409-2018 [8] 毛节泰. 南极长城站大气臭氧和NO2的观测研究[J]. 气象, 1989, 15(12): 3-7MAO Jietai. Measurement of the O3 and NO2 column abundance at the Great Wall Station Antarctica[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 1989, 15(12): 3-7 [9] 周秀骥, 郑向东, 陆龙骅, 等. 1993年中山站地区“臭氧洞”和UV-B的特征分析[J]. 南极研究, 1994, 6(4): 17-25ZHOU Xiuji, ZHENG Xiangdong, LU Longhua, et al. Ground based measurements of column amounts of ozone and UV-B over Zhongshan station, Antarctica, in the 93 “ozone hole”[J]. Antarctic Research, 1994, 6(4): 14-22 [10] ZHENG Xiangdong, ZHOU Xiuji, LU Longhua, et al. Observational study on the Antarctic "ozone hole" at Zhongshan station in 1993[J], Chinese Science Bulletin, 1994, 40(6): 533-535 (郑向东, 周秀骥, 陆龙骅, 等. 1993年中山站南极“臭氧洞”的观测研究[J]. 科学通报, 1994, 40(6): 533-535 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.06.016 [11] 郑向东, 陆龙骅, 周秀骥. 近六年中山站春季臭氧低值的观测结果分析[J]. 极地研究, 1999, 11(4): 265-274ZHENG Xiangdong, LU Longhua, ZHOU Xiuji. A study on the 6-year observation of the spring ozone depletion at Zhongshan station, Antarctica[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 1999, 11(4): 265-274 [12] ZHANG Lei, ZHENG Xiangdong, BIAN Lingen. Comparison of long-term total ozone observations from space- and ground-based methods at Zhongshan Station, Antarctica[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 47(11): 2013-2024. (张雷, 郑向东, 卞林根. 南极中山站卫星臭氧总量与地基长期测值的对比分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 47(11): 1371-1382. DOI: 10.1360/N072017-00054 [13] 孔琴心, 刘广仁, 王庚辰. 1993年春季南极中山站上空大气臭氧的观测分析[J]. 大气科学, 1996, 20(4): 395-400 doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1996.04.0KONG Qinxin, LIU Guangren, WANG Gengchen. Observations and analyses of atmospheric ozone over antarctic Zhongshan station in the spring of 1993[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 1996, 20(4): 395-400 doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1996.04.0 [14] 卞林根, 林忠, 张东启, 等. 南极大气臭氧和温度垂直结构及其季节变化的研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41(12): 262-270BIAN Lingen, LIN Zhong, ZHANG Dongqi, et al. The vertical structure and seasonal changes of atmosphere ozone and temperature at Zhongshan station over east Antarctica[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(12): 262-270 [15] ZHAO X Y, BOGNAR K, FIOLETOV V, et al. Assessing the impact of clouds on ground-based UV–visible total column ozone measurements in the high Arctic[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2019, 12(4): 2463-2483 doi: 10.5194/amt-12-2463-2019 [16] SCARNATO B, STAEHELIN J, STÜBI R, et al. Long-term total ozone observations at Arosa (Switzerland) with Dobson and Brewer instruments (1988-2007)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2010, 115(D13): D13306 doi: 10.1029/2009JD011908 [17] ZHAO X Y, FIOLETOV V, CEDE A, et al. Accuracy, precision, and temperature dependence of Pandora total ozone measurements estimated from a comparison with the Brewer triad in Toronto[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2016, 9(12): 5747-5761 doi: 10.5194/amt-9-5747-2016 [18] WARGAN K, LABOW G, FRITH S, et al. Evaluation of the ozone fields in NASA’s MERRA-2 reanalysis[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017, 30(8): 2961-2988 doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0699.1 [19] ZHAO X Y, FIOLETOV V, BROHART M, et al. The world Brewer reference triad – updated performance assessment and new double triad[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2021, 14(3): 2261-2283 doi: 10.5194/amt-14-2261-2021 [20] WANG M C, FU Q. Stratosphere-troposphere exchange of air masses and ozone concentrations based on reanalyses and observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2021, 126(18): e2021JD035159 doi: 10.1029/2021JD035159 [21] WANG M C, FU Q, HALL A, et al. Stratosphere-troposphere exchanges of air mass and ozone concentrations from ERA5 and MERRA2: annual-mean climatology, seasonal cycle, and interannual variability[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2023, 128(24): e2023JD039270 doi: 10.1029/2023JD039270 [22] HERSBACH H, BELL B, BERRISFORD P, et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2020, 146(730): 1999-2049 doi: 10.1002/qj.3803 [23] HERSBACH H, DE ROSNAY P, BELL B, et al. Operational Global Reanalysis: Progress, Future Directions and Synergies with NWP[R]. ERA Report Series No.27. Reading: ECMWF, 2018. DOI: 10.21957/tkic6g3wm [24] YAMAZAKI Y, MATTHIAS V, MIYOSHI Y, et al. September 2019 Antarctic sudden stratospheric warming: quasi-6-day wave burst and ionospheric effects[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(1): e2019GL086577 doi: 10.1029/2019GL086577 [25] BHARTIA P K, MCPETERS R D, FLYNN L E, et al. Solar Backscatter UV (SBUV) total ozone and profile algorithm[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2013, 6(10): 2533-2548 doi: 10.5194/amt-6-2533-2013 [26] 胡筱欣, 陆龙骅, 张凤英, 等. 南极春季臭氧的TOVS反演及其与Brewer观测的比较[J]. 应用气象学报, 1996, 7(4): 437-442HU Xiaoxin, LU Longhua, ZHANG Fengying, et al. Retrieval of total ozone from TOVS data and its comparison with brewer observations in Antarctic spring[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 1996, 7(4): 437-442 [27] MCPETERS R D, LABOW G J. An assessment of the accuracy of 14.5 years of Nimbus 7 TOMS version 7 ozone data by comparison with the Dobson network[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1996, 23(25): 3695-3698 doi: 10.1029/96GL03539 [28] 郑向东, 韦小丽. 中国4个地点地基与卫星臭氧总量长期观测比较[J]. 应用气象学报, 2010, 21(1): 1-10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2010.01.001ZHENG Xiangdong, WEI Xiaoli. Long term total ozone comparisons between space based and ground based observations at 4 sites in China[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2010, 21(1): 1-10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2010.01.001 [29] HASSLER B, DANIEL J S, JOHNSON B J, et al. An assessment of changing ozone loss rates at South Pole: twenty‐five years of ozonesonde measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2011, 116(D22): D22301 doi: 10.1029/2011JD016353 [30] CHIPPERFIELD M P, BEKKI S, DHOMSE S, et al. Detecting recovery of the stratospheric ozone layer[J]. Nature, 2017, 549(7671): 211-218 doi: 10.1038/nature23681 [31] STONE K A, SOLOMON S, KINNISON D E, et al. On recent large Antarctic ozone holes and ozone recovery metrics[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(22): e2021GL095232 doi: 10.1029/2021GL095232 [32] 郑广惠, 巨天珍, 丁明虎, 等. 南极高太阳天顶角下地基臭氧总量观测比较分析[J]. 气象学报, 2025ZHENG Guanghui, JU Tianzhen, DING Minghu, et al. Comparison analysis of ground-based total ozone observations under high solar zenith angle at Zhongshan Station, Antarctica[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica (in press), 2025 -
-




 郑广惠 1997年4月出生, 理学硕士, 西北师范大学地理与环境科学学院, 主要从事大气探测研究. E-mail:
郑广惠 1997年4月出生, 理学硕士, 西北师范大学地理与环境科学学院, 主要从事大气探测研究. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: