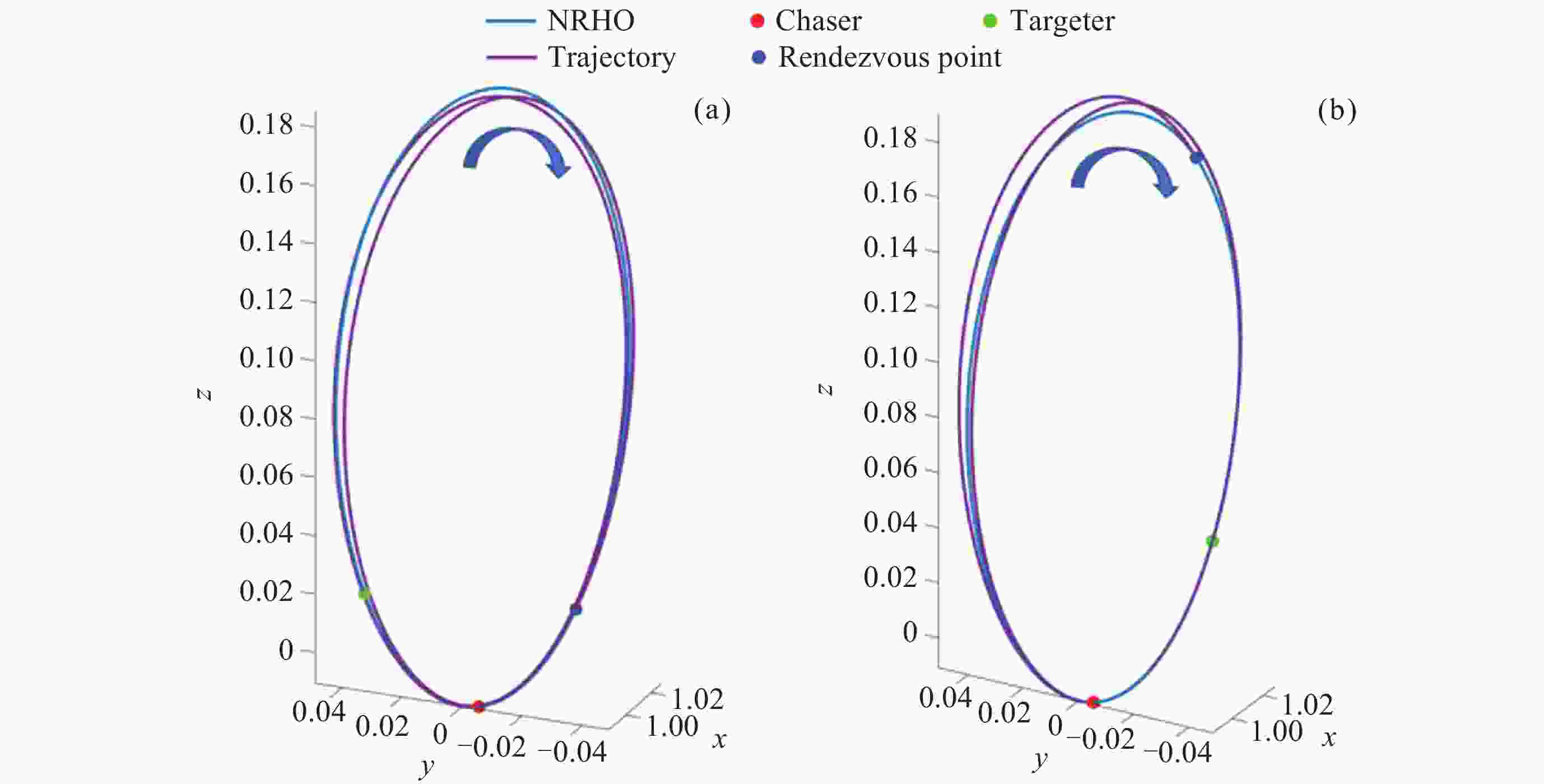
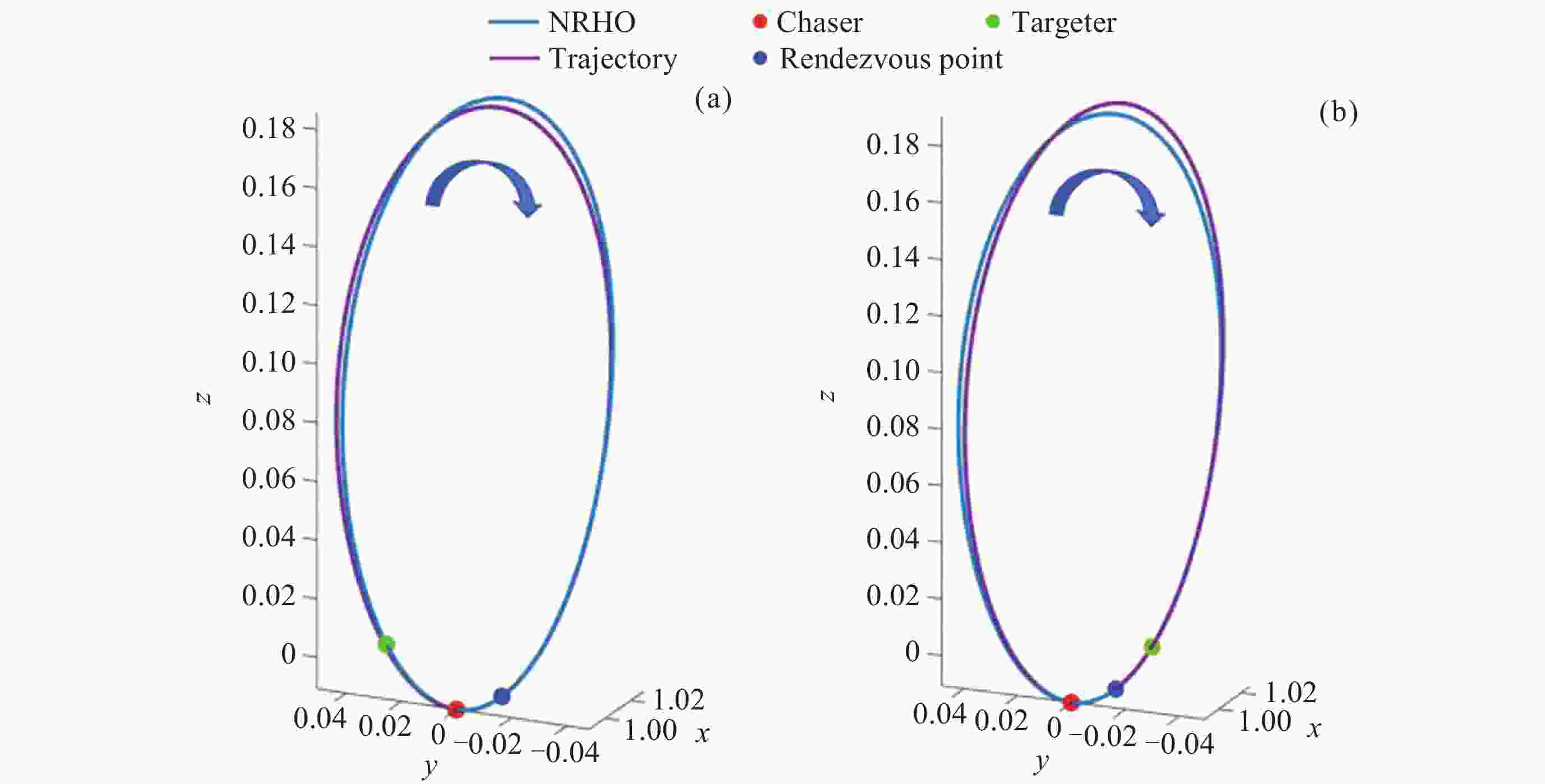
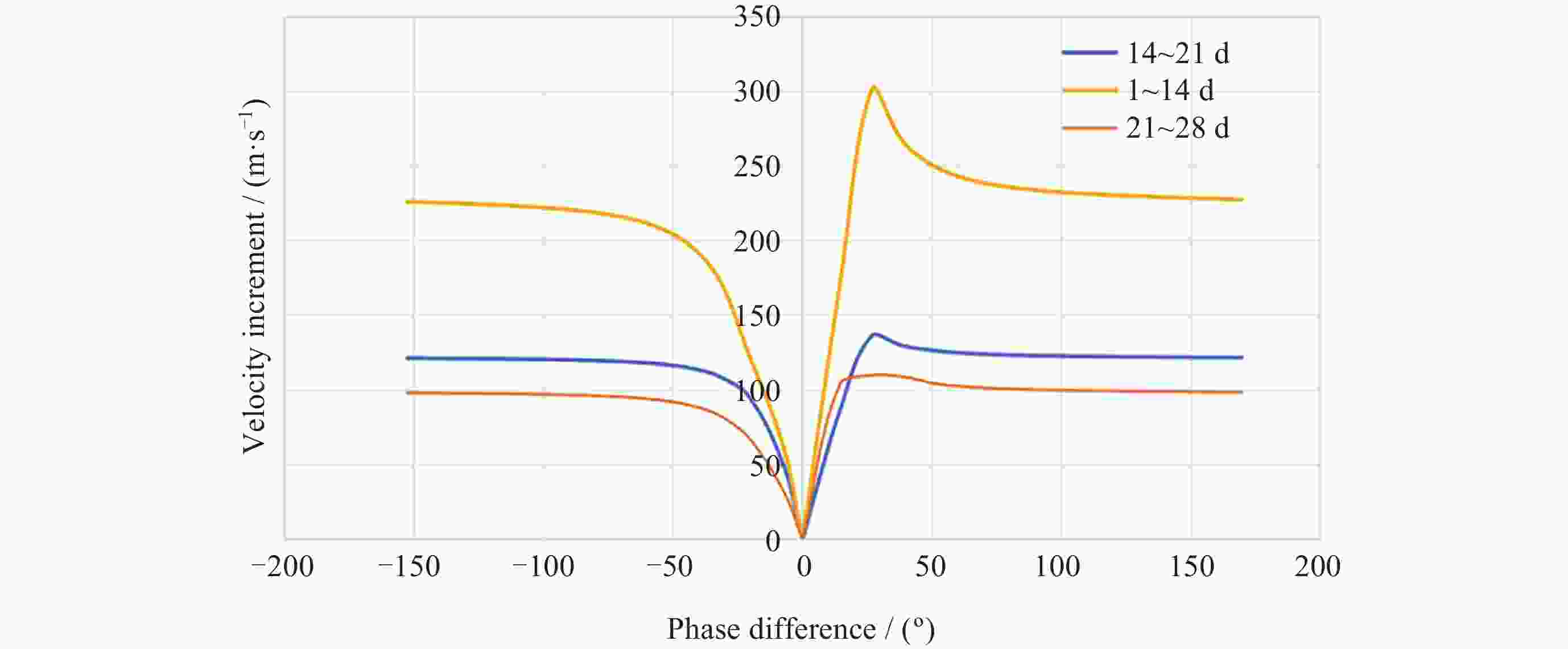
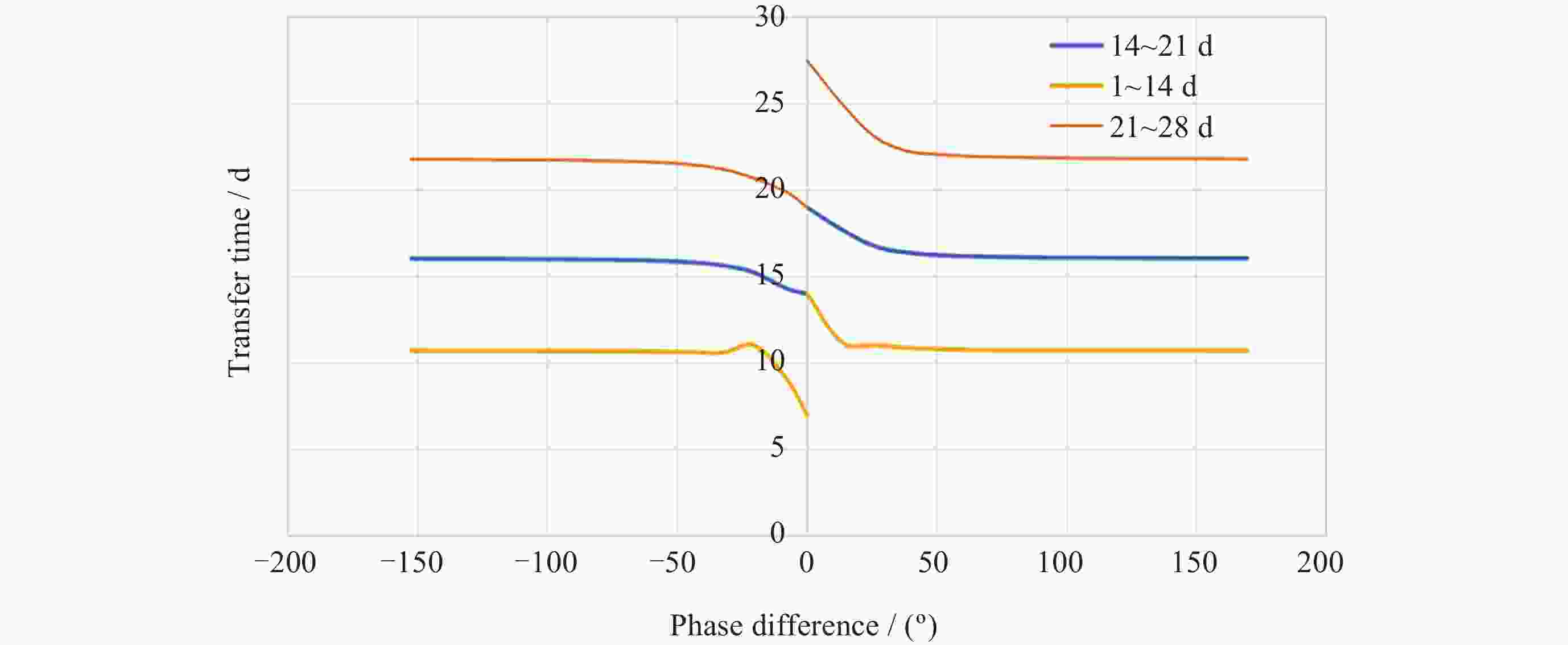
Optimization and Analysis of NRHO Two-impulsive Phasing Trajectory in Cislunar Space
-
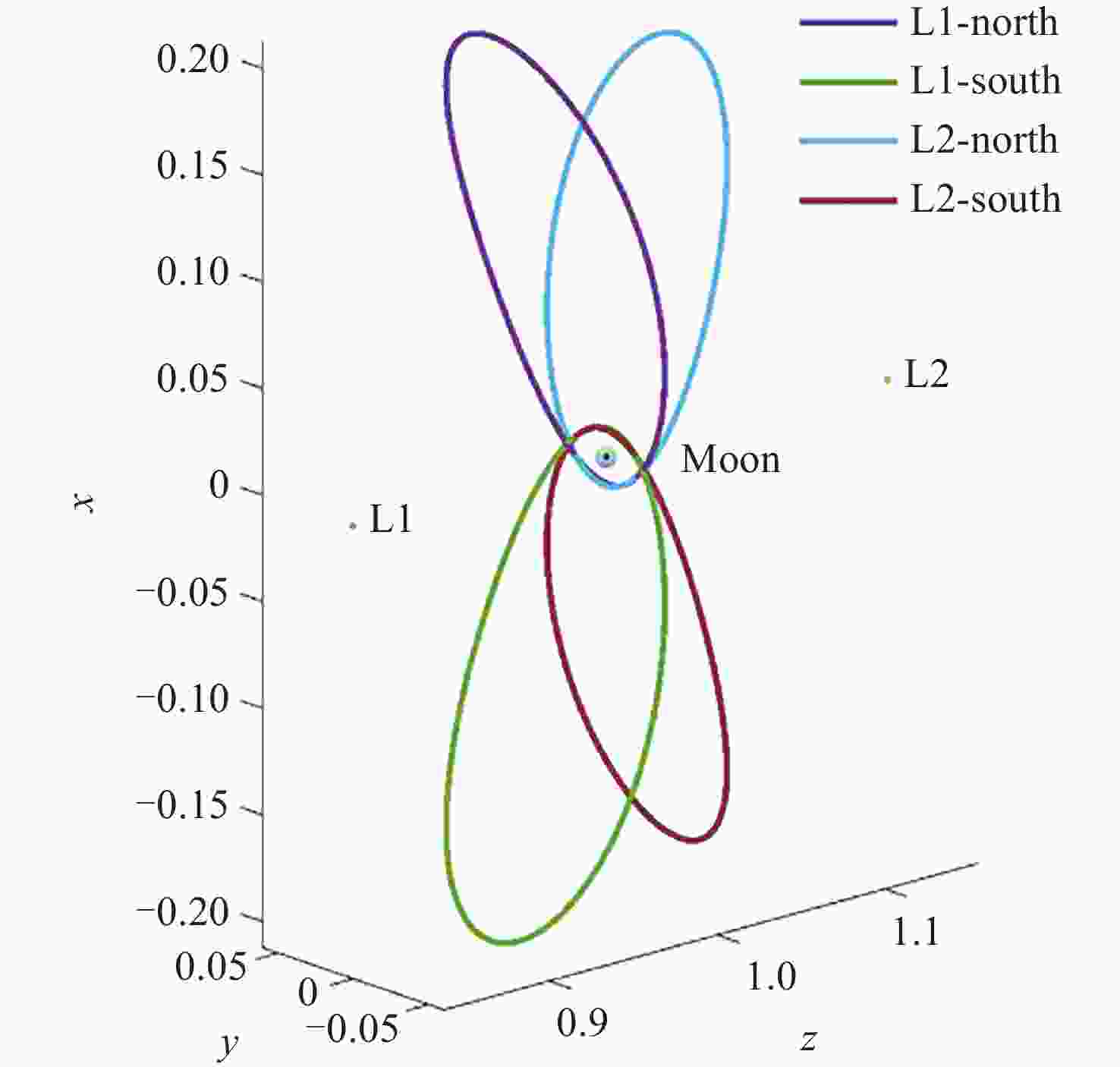
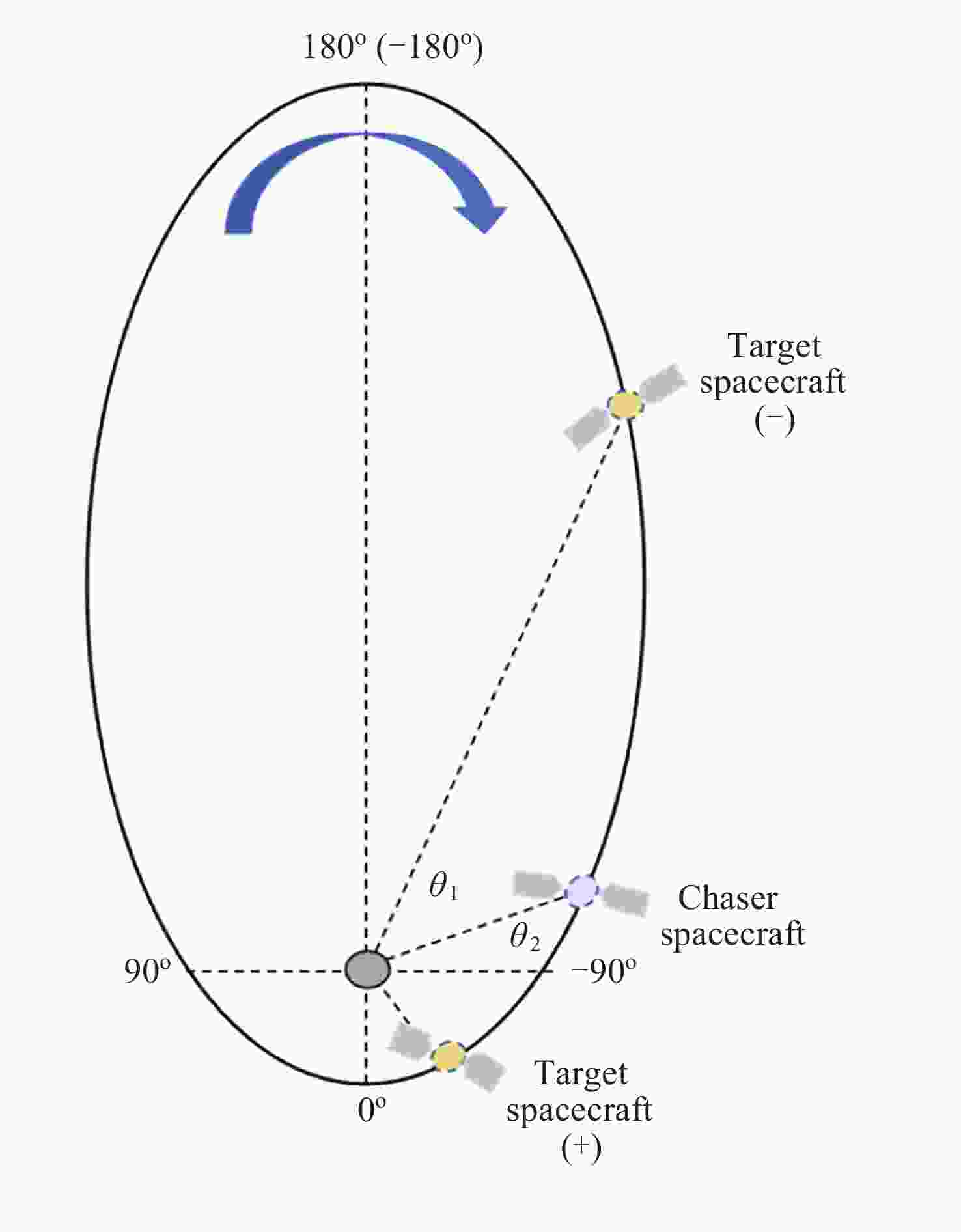
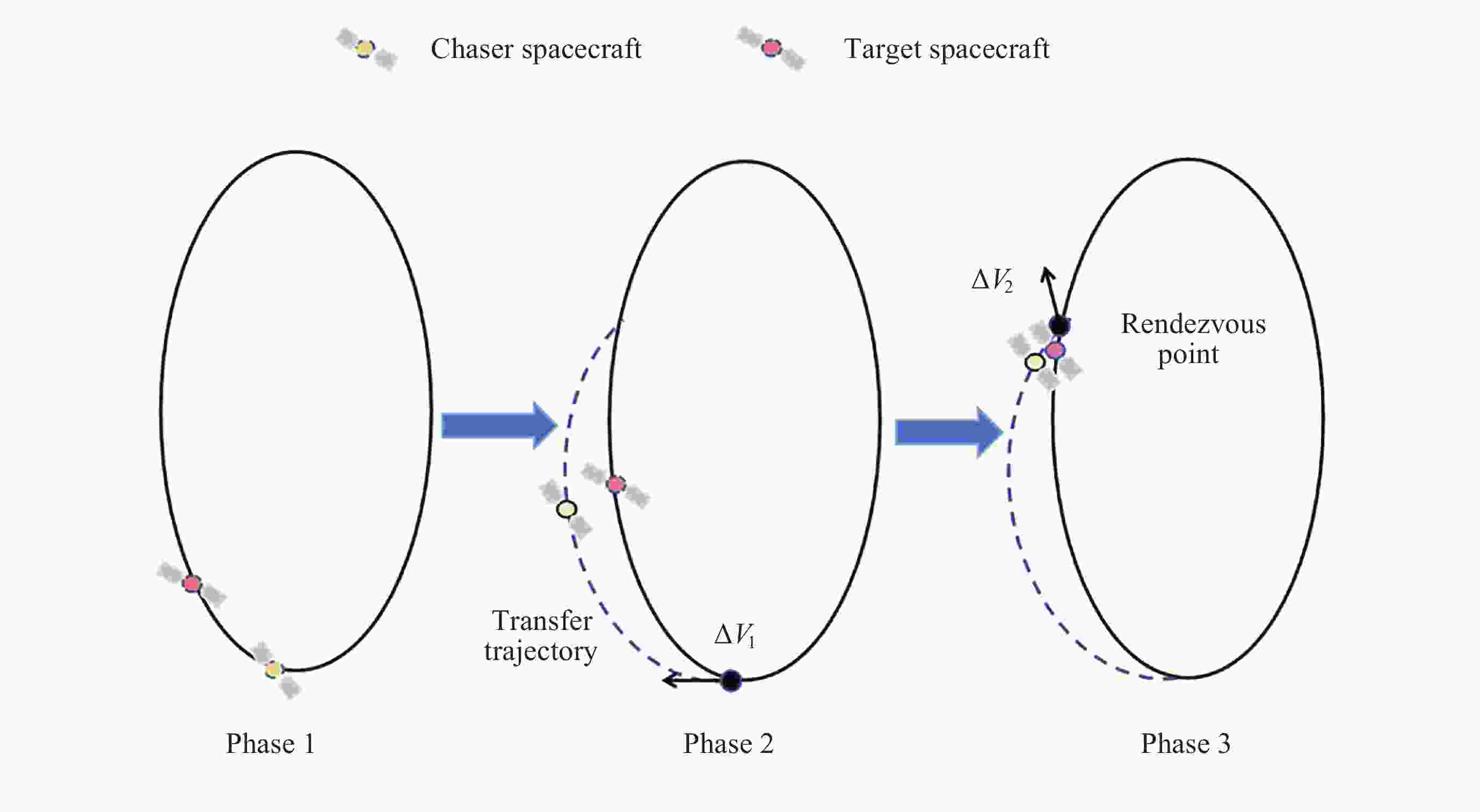
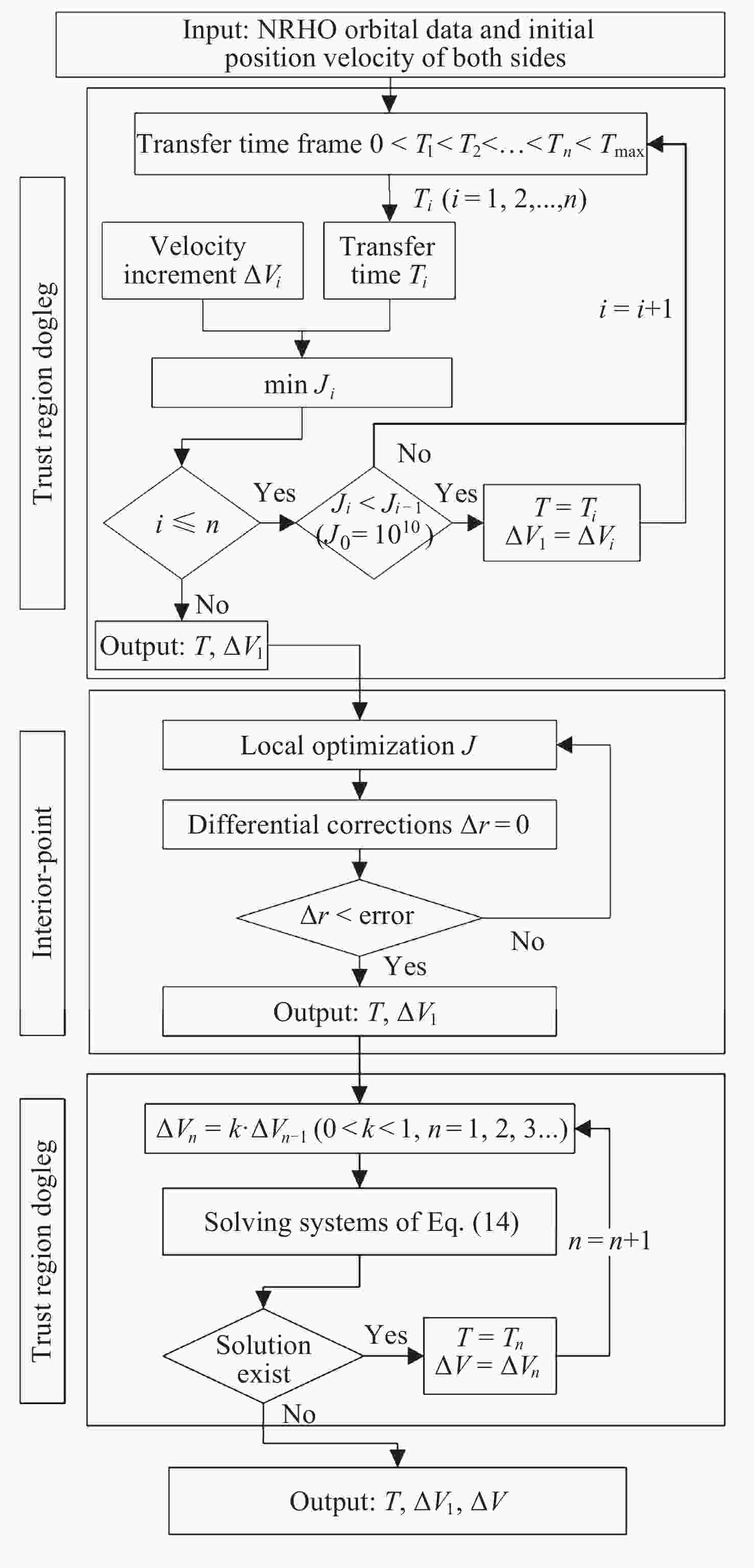
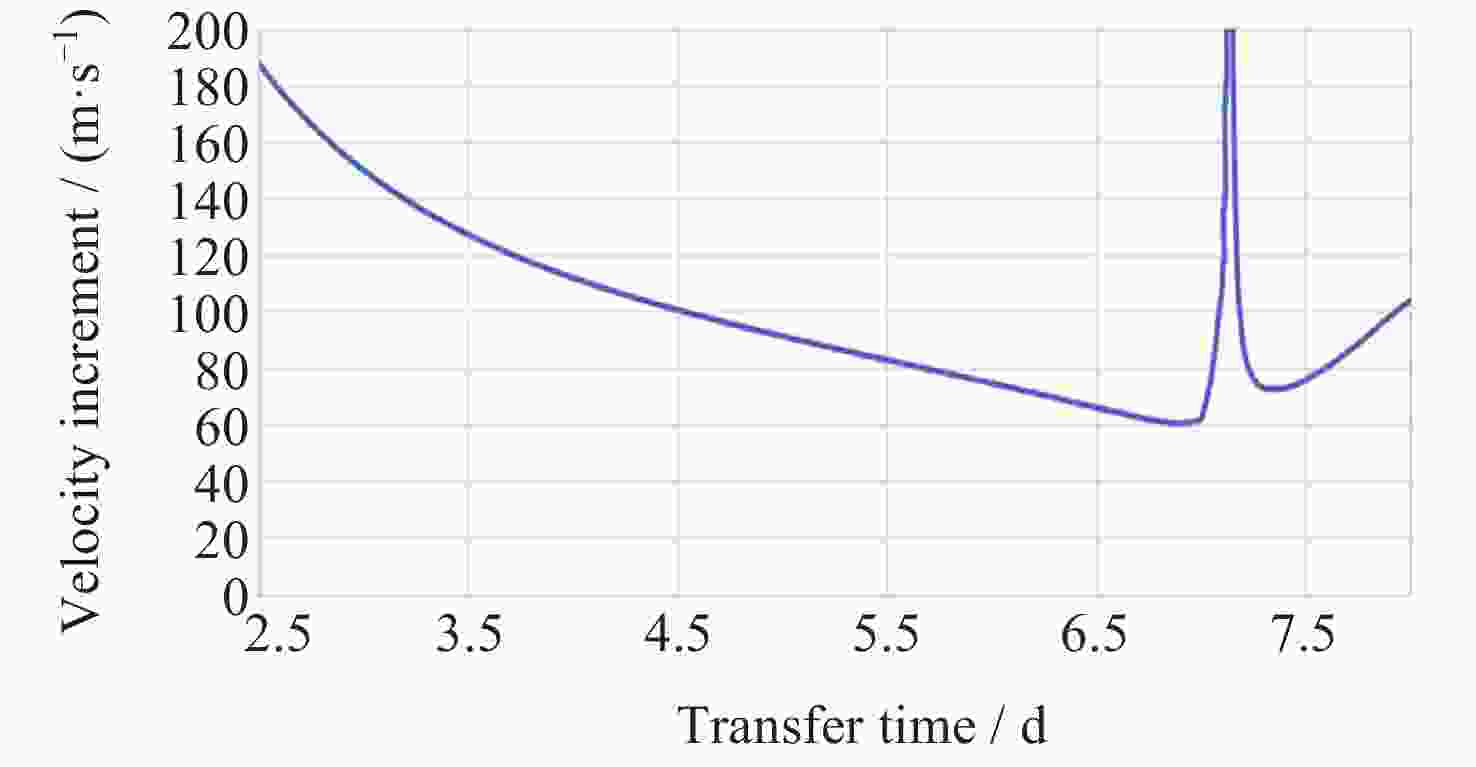
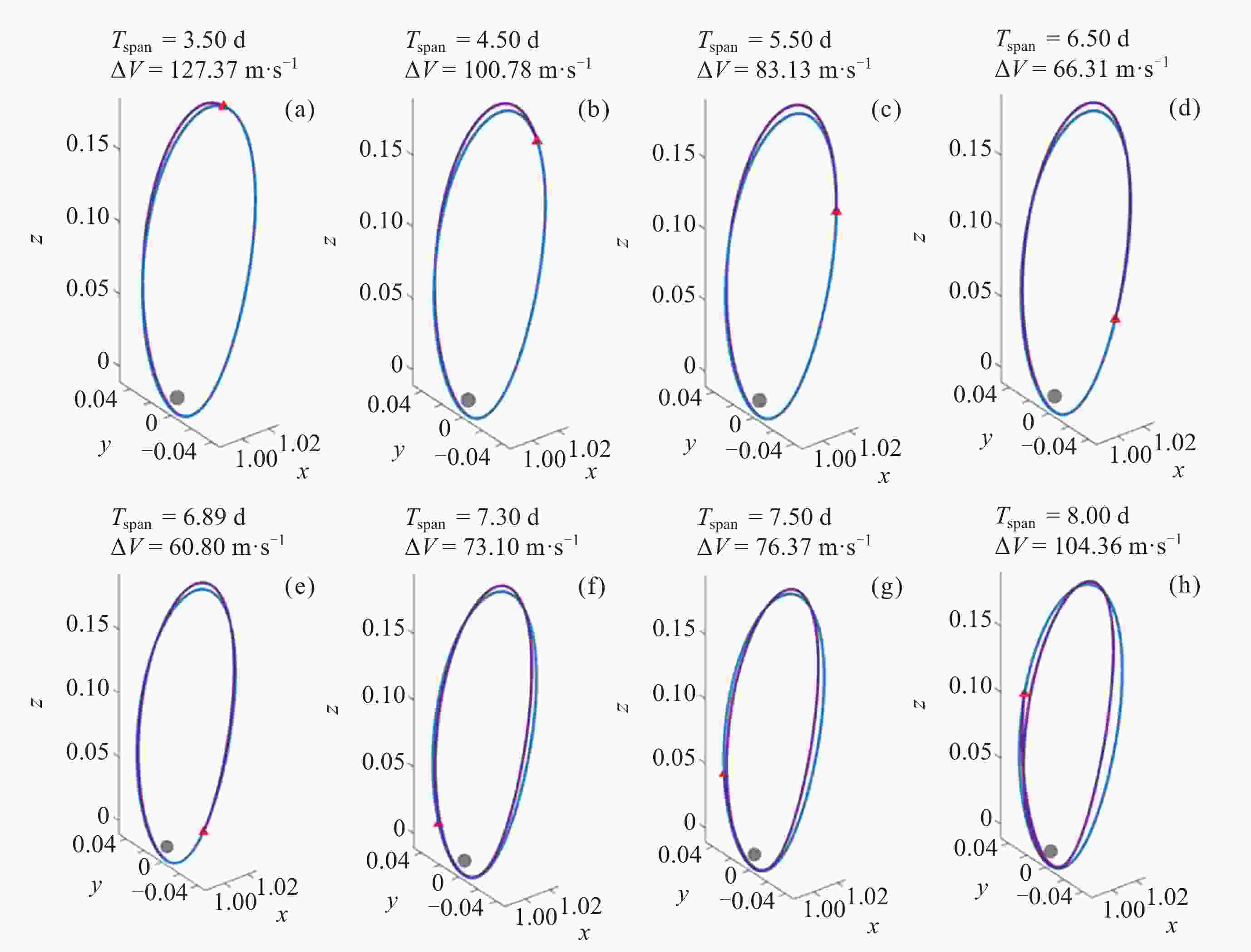
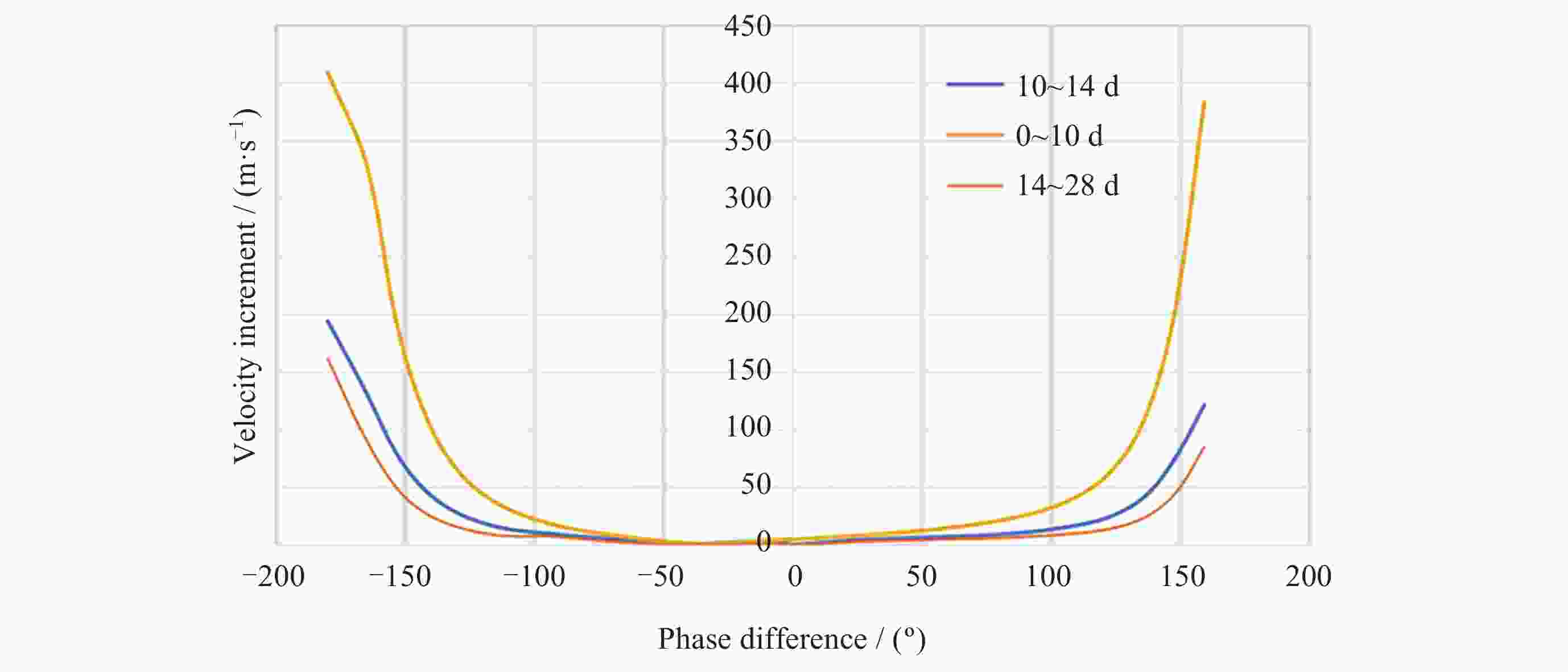
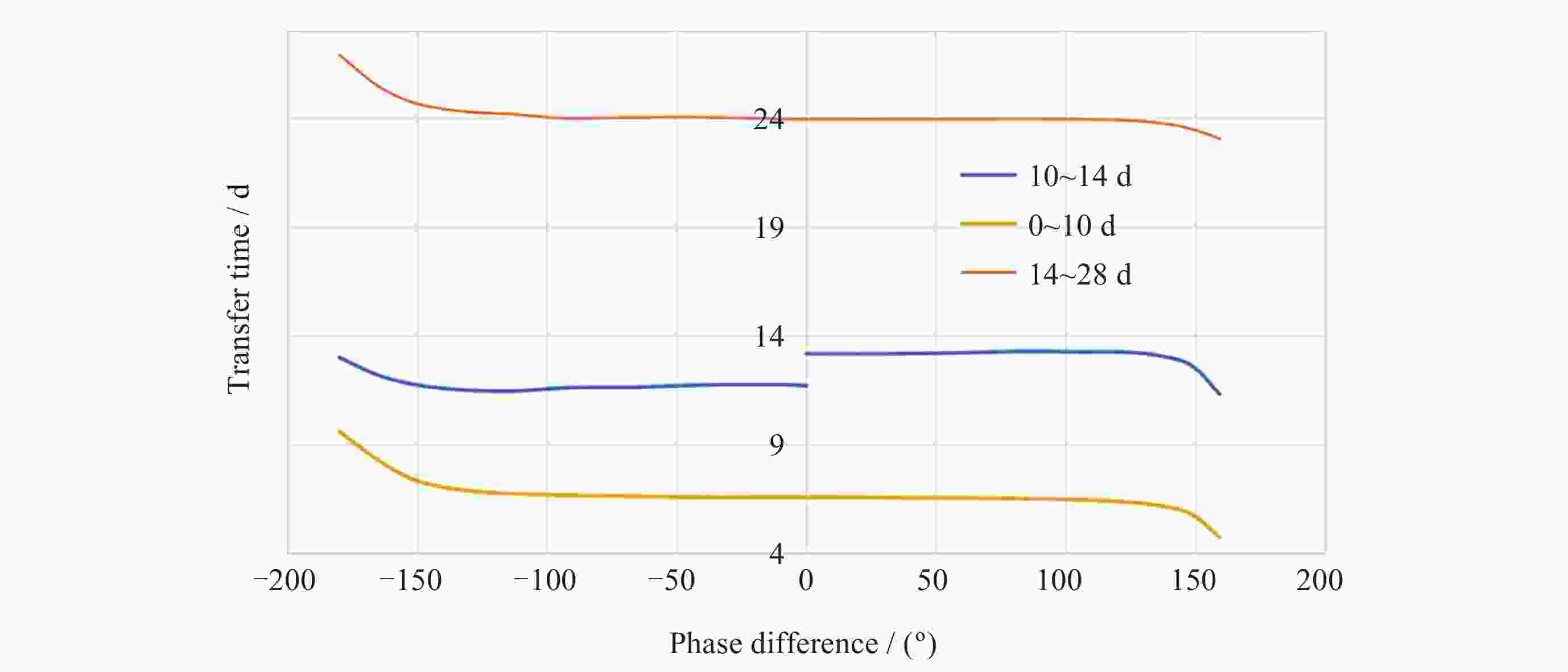
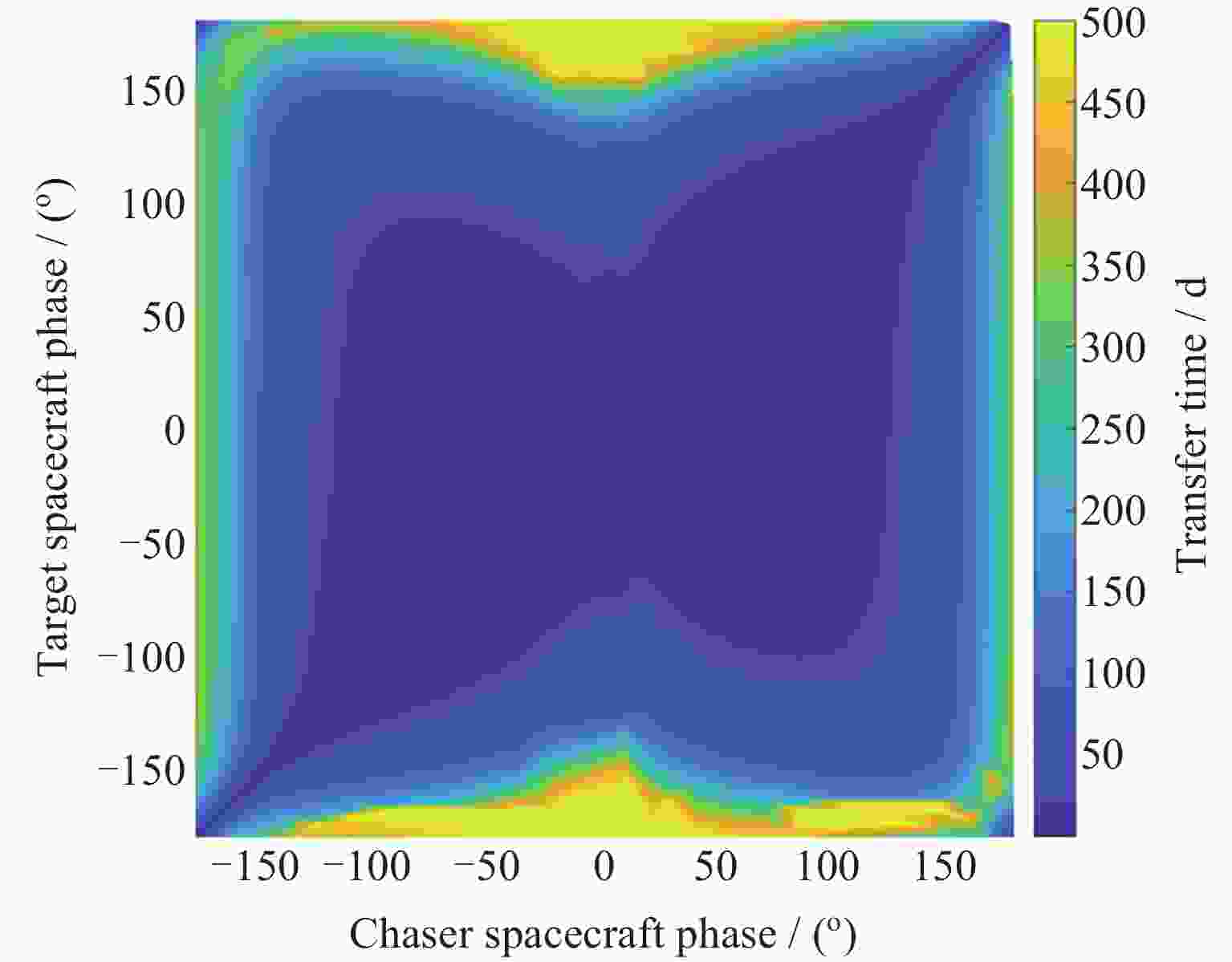
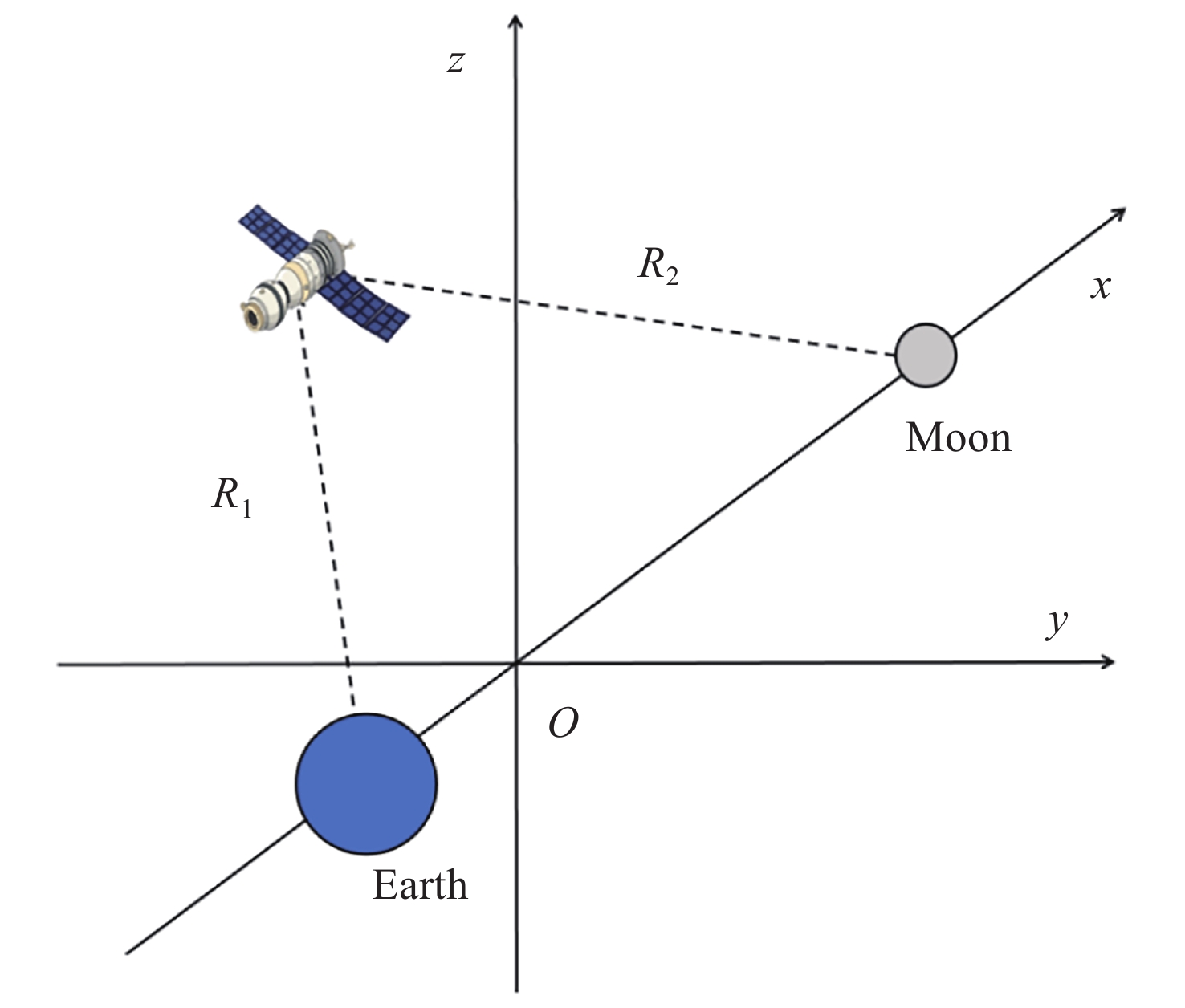
摘要: Artemis任务建造与运行月球轨道门户空间站期间, 将在近直线晕轨道(Near-Rectilinear Halo Orbit, NRHO)实施大量货运、载人飞行交会对接任务. 针对NRHO调相轨道优化问题, 基于圆型限制性三体问题模型, 通过信赖域算法对转移时间进行遍历, 采用非线性优化算法局部优化来修正位置误差, 进而迭代求解非线性方程组降低速度增量, 实现了低燃料消耗的NRHO调相优化; 针对调相代价问题, 对NRHO上不同转移时间和不同相位关系的调相进行了分析. 结果表明, 该算法计算效率较高, 相比遗传算法减少了53.2%的计算时间; 转移时间越长(转移轨道圈数越多), 消耗的速度增量越小; 目标航天器相位滞后时, 选择绕NRHO外圈的调相方式更省燃料, 反之, 相位超前则选择绕内圈更省燃料; 追踪航天器从近月点出发时燃料消耗更低.Abstract: During the construction and operation of the lunar gateway station under the U.S. Artemis program, numerous cargo and crew rendezvous and docking missions will be executed in the Near-Rectilinear Halo Orbit (NRHO). To address the phasing trajectory optimization problem in NRHO, a method based on the Circular Restricted Three-Body Problem (CRTBP) model is adopted. Initially, the transfer time is traversed using a trust-region algorithm. This step is critical to determining the transfer time that minimizes fuel consumption. Following the exploration of transfer times, a nonlinear optimization algorithm is applied to locally correct position errors along the trajectory. This local optimization fine-tunes the spacecraft’s path, ensuring precise alignment during the rendezvous. Finally, the nonlinear equations are solved iteratively to reduce the velocity increment required for the maneuver. This reduction in velocity increment is key to achieving low-fuel consumption during the NRHO phasing process. In addressing the phasing cost issue, this method is further utilized to analyze various scenarios on the NRHO, taking into account different transfer times and phase relationships. The analysis demonstrates that the algorithm boasts high computational efficiency, reducing computation time by 53.2% compared to a genetic algorithm. It is also observed that the longer the transfer time, indicating an increase in the number of transfer orbit revolutions, the smaller the velocity increment consumed during the maneuver becomes. Additionally, when the target spacecraft exhibits a phase lag, opting for a phasing maneuver along the outer loop of the NRHO results in fuel savings, whereas if the target spacecraft’s phase is advanced, choosing the inner loop proves to be more fuel-efficient. Finally, the study notes that when the tracking spacecraft departs from the perilune, the consumed velocity increment is comparatively lower. This approach, therefore, provides an effective and efficient solution for optimizing NRHO phasing, ensuring reliable rendezvous operations with reduced fuel consumption and enhanced computational performance.
-
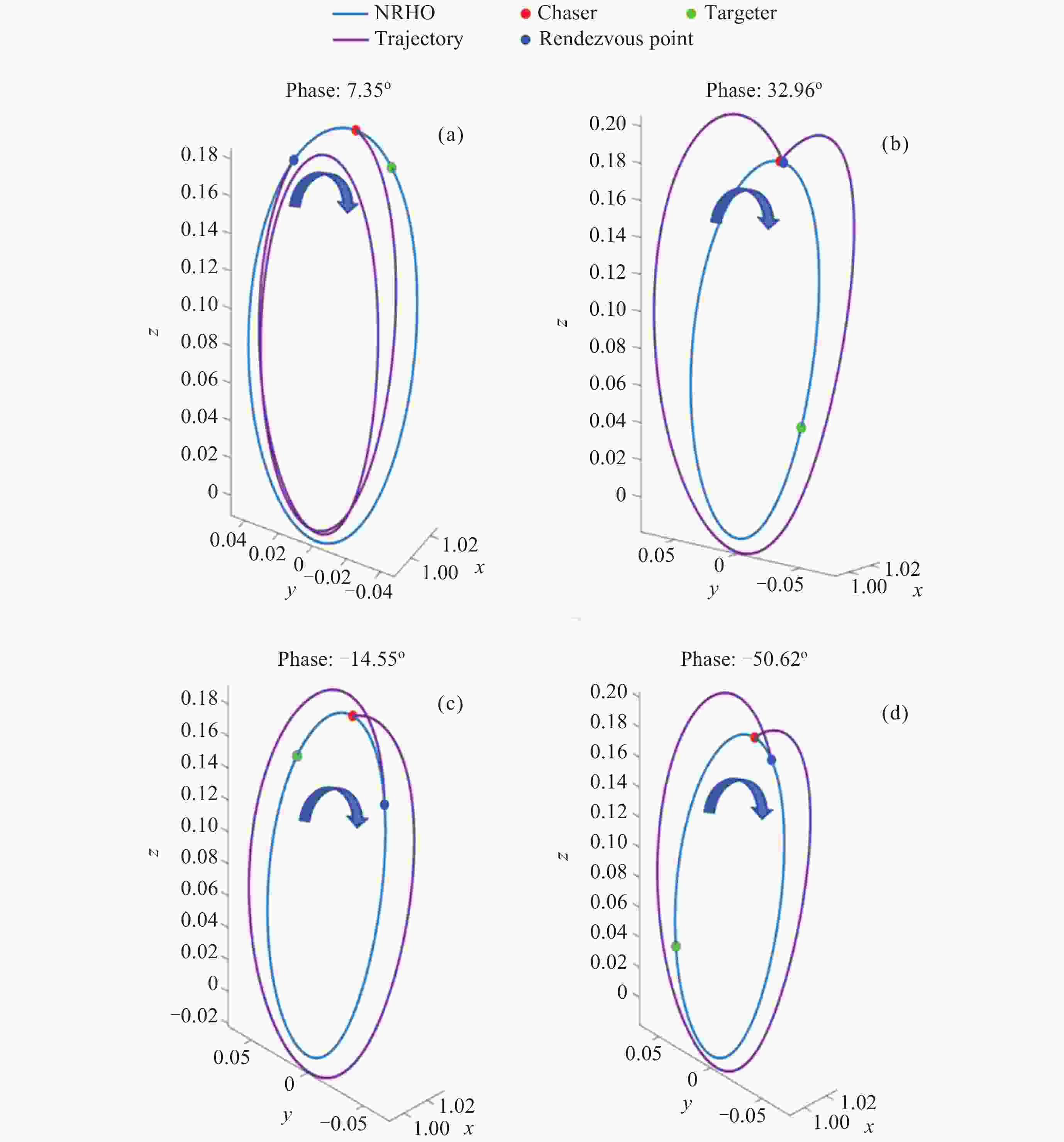
表 1 遍历时间的轨道调相优化结果
Table 1. Phasing optimization results for traversal time
目标
相位/(º)遍历时间优化初值 迭代优化结果
总计算时间/s转移时间/d 速度
增量/(m·s–1)计算
时间/s转移时间/d 速度
增量/(m·s–1)计算
时间/s–153.09 6.60 238.44 33.62 7.51 189.88 18.35 51.97 –128.25 6.02 74.45 36.45 6.89 60.80 36.99 73.44 –93.52 6.00 21.17 26.73 6.71 18.14 45.14 71.87 –39.07 5.99 1.64 10.71 6.60 1.43 52.27 62.98 27.46 5.93 9.52 18.22 6.60 8.28 57.79 76.01 84.60 6.00 25.71 21.06 6.54 23.10 59.83 80.89 121.99 6.03 65.16 28.22 6.40 61.22 62.50 90.71 147.59 4.97 216.77 41.97 5.87 199.72 59.43 101.4 表 2 遗传算法的轨道调相优化结果
Table 2. Phasing optimization results of GA
目标
相位/(º)遗传算法优化初值 迭代优化结果
总计算时间/s转移时间/d 速度
增量/(m·s–1)计算
时间/s转移时间/d 速度
增量/(m·s–1)计算
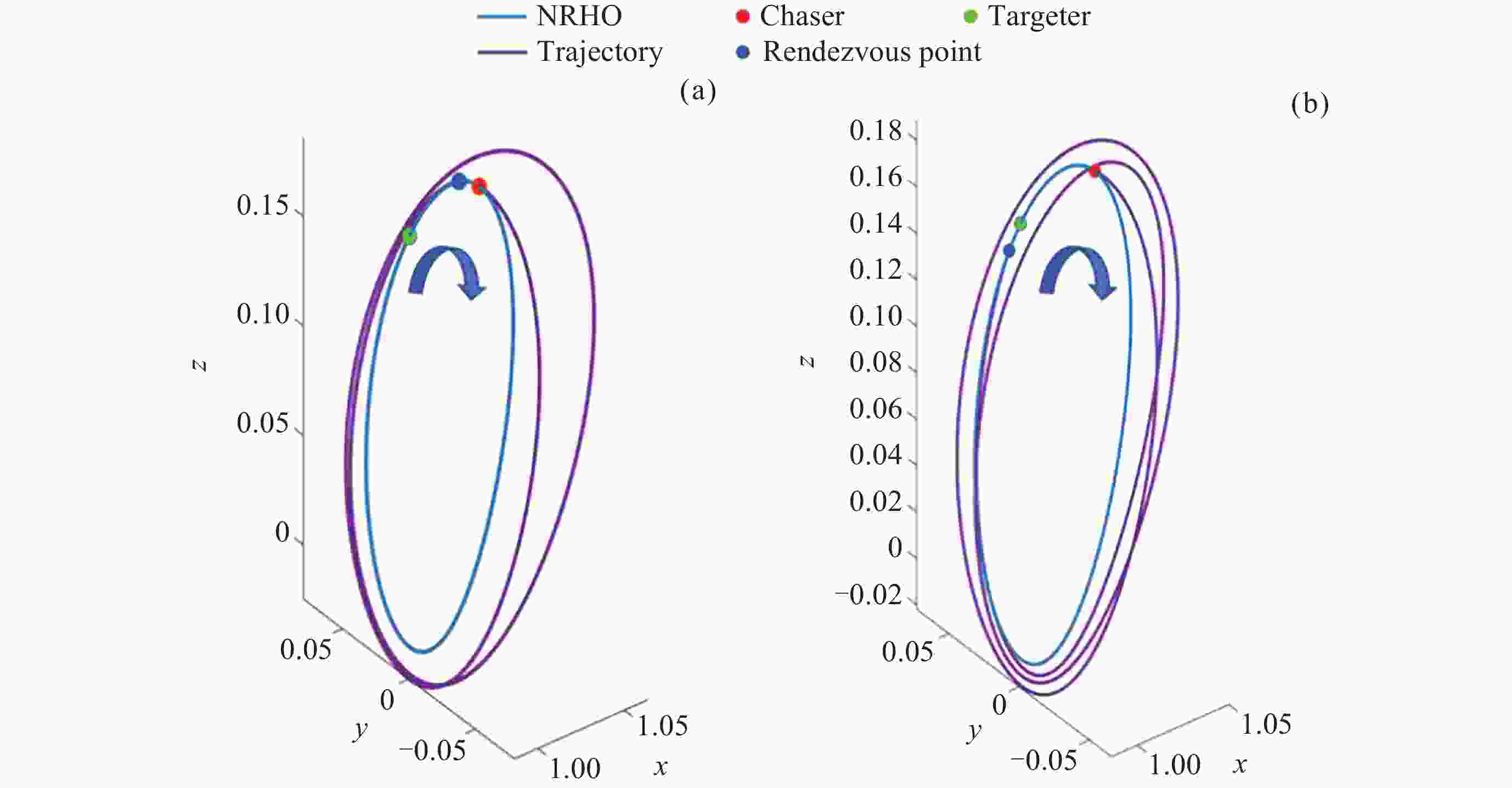
时间/s–153.09 6.87 221.15 173.07 7.51 189.88 31.26 204.33 128.25 6.20 71.44 143.13 6.89 60.80 21.74 164.87 –93.52 6.10 20.71 132.55 6.71 18.14 25.02 157.57 –39.07 6.27 1.54 125.64 6.60 1.43 29.31 154.94 27.46 2.43 21.38 121.75 3.37 15.40 4.54 126.29 84.60 2.46 56.64 120.94 3.45 40.84 3.43 124.37 121.99 5.45 72.29 123.05 6.40 61.19 21.69 144.74 147.59 5.32 209.35 145.13 5.87 199.78 79.87 225.00 表 3 不同圈数下总速度增量ΔV的对比
Table 3. Comparison of total velocity increment ΔV with different revolutions
相位差/(°) ΔV/(m·s–1) 最小ΔV对应
转移模式0~1圈 1~2圈 3~4圈 –180 409.32 194.00 161.00 绕外圈 –153 187.75 77.20 48.06 绕外圈 –128 60.11 25.82 14.37 绕外圈 –93 17.90 9.53 7.24 绕外圈 –38 1.32 1.07 0.37 绕外圈 59 14.48 6.95 4.69 绕内圈 106 37.43 15.41 9.28 绕内圈 136 107.95 41.36 23.47 绕内圈 159 383.55 121.31 84.52 绕内圈 -
[1] LEE D E. Gateway Destination Orbit Model: A continuous 15 Year NRHO Reference Trajectory[R]. Houston, Texas: NASA Johnson Space Center White Paper, 2019 [2] SMITH M, CRAIG D, HERRMANN N, et al. The Artemis program: an overview of NASA’s activities to return humans to the moon[C]//2020 IEEE Aerospace Conference. Big Sky: IEEE, 2020: 1-10 [3] GARDNER T, CHEETHAM B, PARKER J, et al. Capstone: a summary of a highly successful mission in the cislunar environment[C]//37th Annual Small Satellite Conference. Logan: Utah State University, 2023 [4] 秦理民, 杨洪伟, 李爽. 长期拟周期近直线晕轨道高效设计方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2024, 45(1): 43-51 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.01.005QIN Limin, YANG Hongwei, LI Shuang. An efficient design method for long-term quasi-periodic near rectilinear halo orbits[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2024, 45(1): 43-51 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.01.005 [5] BLAZQUEZ E, BEAUREGARD L, LIZY-DESTREZ S, et al. Rendezvous design in a cislunar near rectilinear Halo orbit[J]. The Aeronautical Journal, 2020, 124(1276): 821-837 doi: 10.1017/aer.2019.126 [6] BUCCHIONI G, INNOCENTI M. Rendezvous in cis-lunar space near rectilinear halo orbit: dynamics and control issues[J]. Aerospace, 2021, 8(3): 68 doi: 10.3390/aerospace8030068 [7] FOSSÀ A, BUCCHIONI G, BLAZQUEZ E, et al. Two and three impulses phasing strategy with a spacecraft orbiting on an Earth–Moon NRHO[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2022, 198: 669-679 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2022.06.042 [8] BUCCHIONI G, LIZY-DESTREZ S, VAUJOUR T, et al. Phasing with near rectilinear Halo orbits: design and comparison[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 71(5): 2449-2466 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.10.036 [9] XIE Y C, CHEN C Q, LI X Y, et al. A guidance strategy for rendezvous and docking to the space station in the Earth-Moon NRHO orbit[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2024, 44(4): 29-39 [10] 孙俞, 张进, 罗亚中. 基于三体Lambert算法的平动点交会轨道设计[J]. 载人航天, 2017, 23(5): 608-613 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2017.05.006SUN Yu, ZHANG Jin, LUO Yazhong. Rendezvous trajectory design of libration points based on three-body Lambert algorithm[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2017, 23(5): 608-613 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2017.05.006 [11] 周敬. 平动点航天器轨道交会动力学与控制研究[D]. 北京: 中国空间技术研究院, 2021ZHOU J. Studies on Dynamics and Control of Orbit Transfer of Spacecraft Near the Libration Points[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Space Technology, 2021 [12] FU H L, WANG M, ZHANG H. Phasing analysis on DRO with impulsive maneuver[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2023, 10: 1177573 doi: 10.3389/fspas.2023.1177573 [13] 董博文, 于锡峥, 李明涛, 等. 基于DRO的小行星往返飞越探测轨道设计优化方法[J]. 空间科学学报, 2023, 43(5): 864-874 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.05.2023-0011DONG Bowen, YU Xizheng, LI Mingtao, et al. Orbit design optimization method for an asteroid flyby mission from DRO[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(5): 864-874 doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.05.2023-0011 [14] WANG K D, WANG Y L, DONG B W, et al. Trajectory optimization of near-Earth asteroids exploration by using reusable probes from cislunar space[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2025, 38(3): 103234 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2024.09.010 [15] ESTY C C, LEE D, MARTINEZ R, et al. Assessment of Cislunar Staging Orbits to Support the Artemis III Lunar Surface Mission[C]//45th Annual AAS Guidance, Navigation and Control (GN&C) Conference. Springfield: American Astronautical Soc., 2023 [16] MORÉ J J, GARBOW B S, HILLSTROM K E. User Guide for MINPACK-1[R]. Argonne: Argonne National Lab, 1980 [17] BYRD R H, SCHNABEL R B, SHULTZ G A. Approximate solution of the trust region problem by minimization over two-dimensional subspaces[J]. Mathematical Programming, 1988, 40(1): 247-263 doi: 10.21236/ada176527 [18] WALTZ R A, MORALES J L, NOCEDAL J, et al. An interior algorithm for nonlinear optimization that combines line search and trust region steps[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2006, 107(3): 391-408 doi: 10.1007/s10107-004-0560-5 -
-




 李少峰 男, 1999年10月出生于山西省太原市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心硕士研究生. 主要研究方向为航天器轨道动力学与控制. E-mail:
李少峰 男, 1999年10月出生于山西省太原市, 现为中国科学院国家空间科学中心硕士研究生. 主要研究方向为航天器轨道动力学与控制. E-mail:  于锡峥 男, 硕士, 副研究员, 硕士研究生导师. 主要研究方向为航天器轨道动力学与控制. E-mail:
于锡峥 男, 硕士, 副研究员, 硕士研究生导师. 主要研究方向为航天器轨道动力学与控制. E-mail:  李明涛 男, 博士, 研究员, 博士研究生导师. 主要研究方向为航天器轨道动力学与控制、小行星防御与利用. E-mail:
李明涛 男, 博士, 研究员, 博士研究生导师. 主要研究方向为航天器轨道动力学与控制、小行星防御与利用. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: