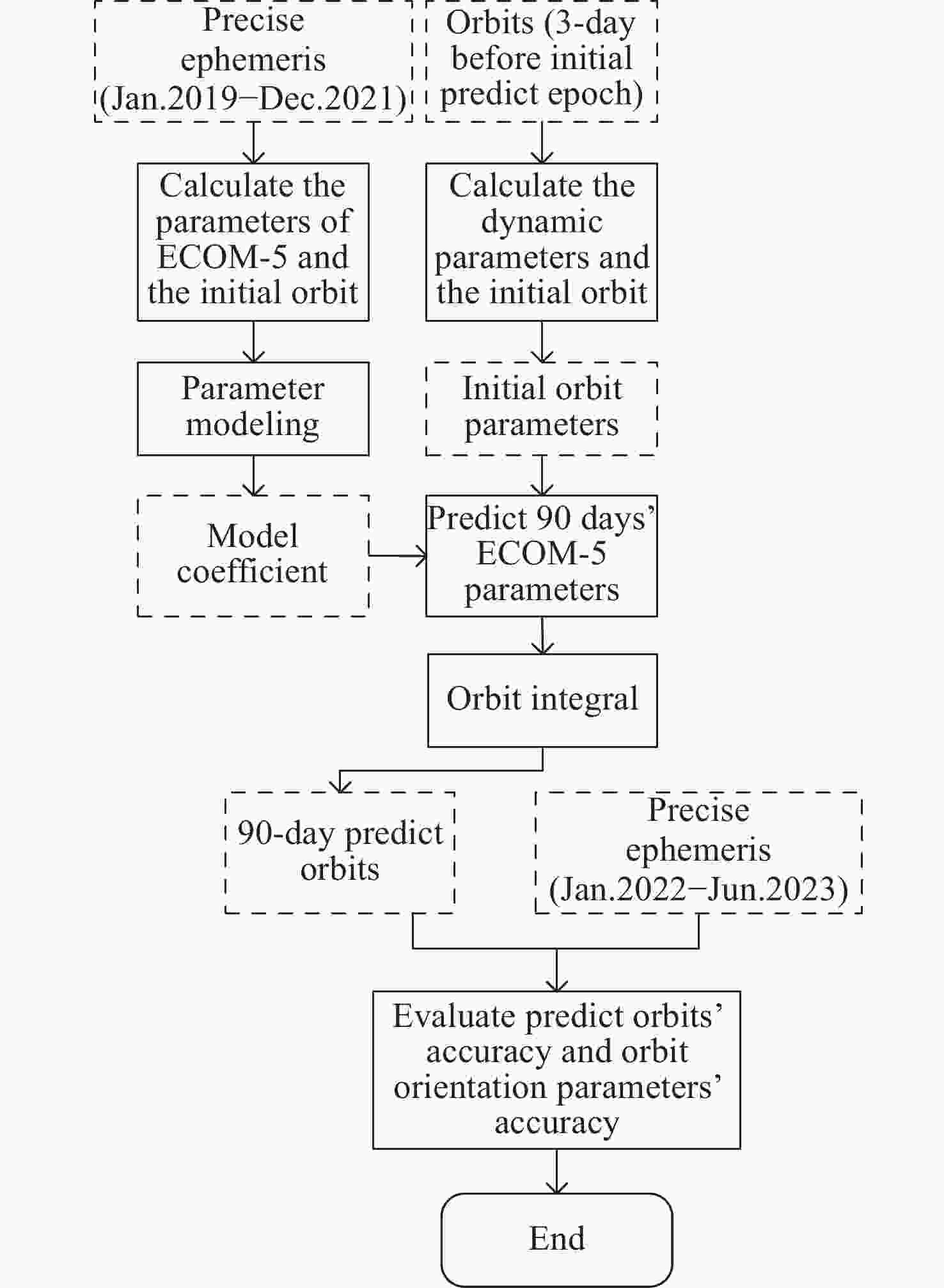
New Method and Accuracy Analysis for Medium and Long-term Orbit Prediction of BDS-3 Satellites
-
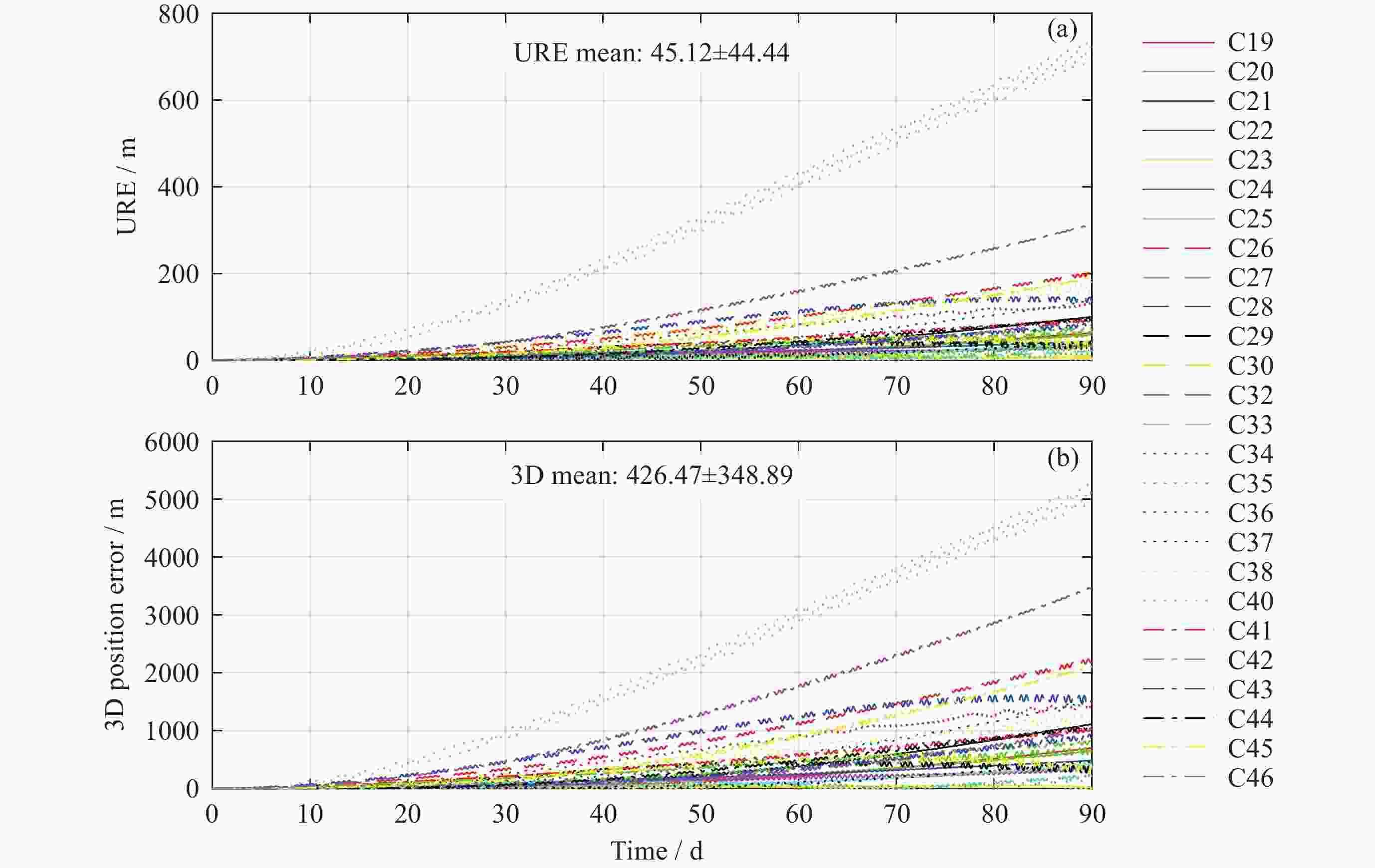
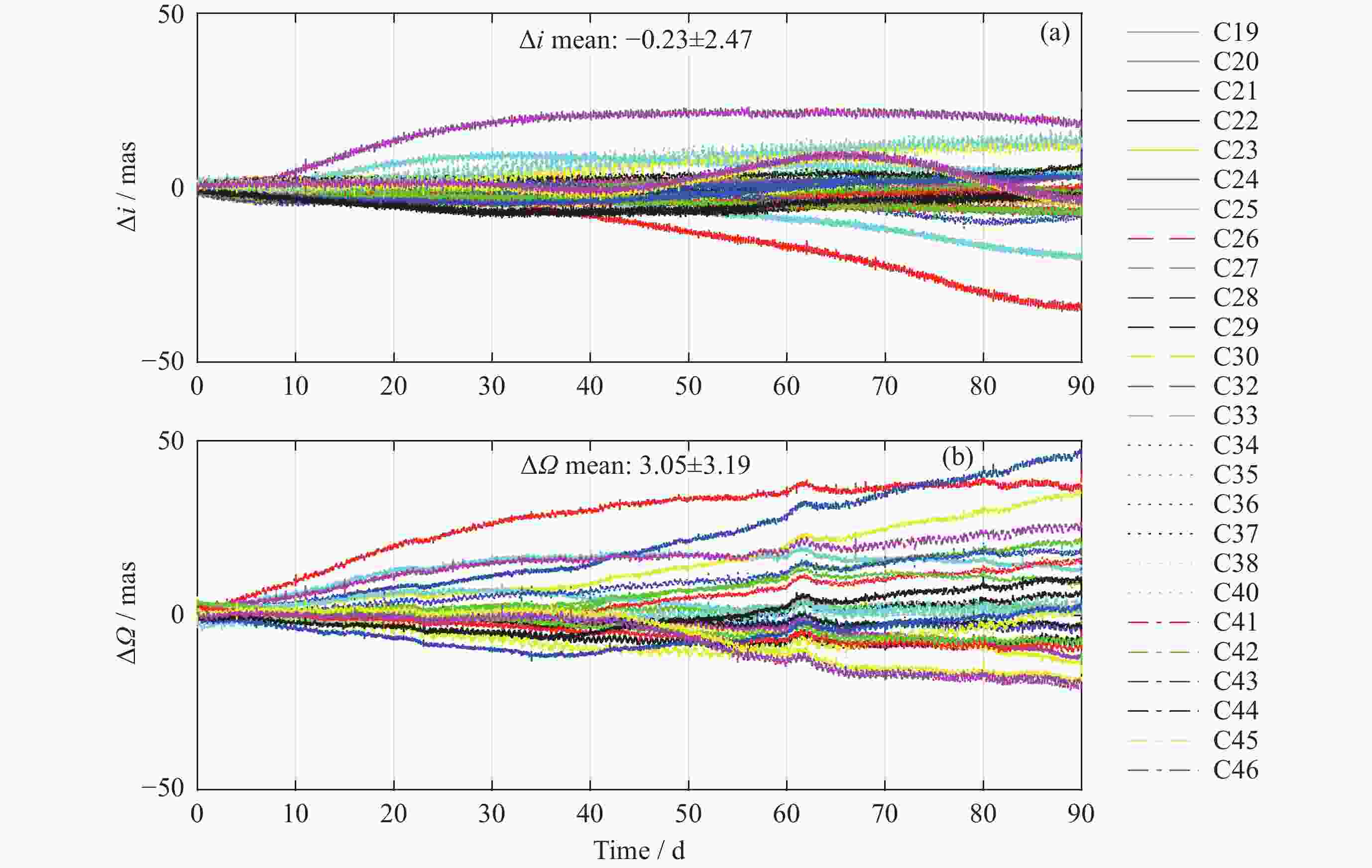
摘要: 利用光压系数与太阳高度角密切相关的特性, 提出对ECOM-5光压模型参数进行建模及预报更新的方法进行轨道长期预报, 并对该方法的轨道预报性能进行评估. 以北斗MEO/IGSO卫星为例, 对2022年1月1日至2023年6月1日内预报18组90天轨道, 以CODE北斗卫星精密星历作为参考轨道, 评估北斗卫星轨道长期预报的性能. 试验结果表明, 采用本文提出的轨道预报方法对导航卫星进行90天轨道预报: MEO卫星第30天、60天、90天预报轨道三维位置误差RMS均值分别约为180, 650, 1400 m, 轨道URE RMS的均值分别为18.79, 61.43, 124.00 m; 与精密星历轨道的倾角误差$\Delta i $的RMS均值分别为6.07, 9.76, 12.38 mas, 与精密星历轨道的升交点赤经误差$\Delta \varOmega $ RMS均值分别为6.47, 11.24, 14.88 mas; IGSO卫星预报轨道三维位置误差第30天、60天、90天RMS均值分别约为260, 1000, 2200 m, i和Ω预报误差与MEO卫星相当. 因此, 可以得出结论, 该方法获得的中长期预报轨道三维位置以及轨道定向参数i和Ω具有较高的精度.
-
关键词:
- 北斗三号导航卫星 /
- ECOM-5光压模型 /
- 轨道长期预报 /
- 轨道定向参数
Abstract: Long-term orbit prediction serves as an effective method to suppress the overall rotation of the inertial frame in autonomous navigation of satellite navigation systems, and the main factor influencing the accuracy of long-term orbit prediction is the uncertainty associated with the solar radiation pressure perturbation model. This paper proposes a method of modeling and updating the ECOM-5 solar radiation pressure model parameters for long-term orbit prediction, and evaluates its performance by fully utilizing the correlation between the solar radiation pressure coefficient and the solar altitude angle. Taking 24 Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites and 2 Inclined Geosynchronous Orbit (IGSO) satellites of the Beidou-3 Global Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3) as examples, 18 groups of 90-day orbits were predicted from 1 January 2022 to 1 June 2023. Then the precise ephemeris of the Center for Orbit Determination in Europe (CODE) was used as the reference orbit to evaluate the performance of long-term orbit prediction. The experimental results indicate that when adopting the new orbit prediction method proposed in this paper for 90-day orbit prediction of navigation satellites, for MEO satellites, the average Root Mean Square (RMS) of the three-dimensional position error on the 30th, 60th, and 90th day is approximately 180, 650, 1400 m, respectively, and that of the average URE RMS of the orbit is 18.79, 61.43, 124.00 m, respectively. The RMS mean values of the orbital inclination angle error $\Delta i $ are 6.07, 9.76, 12.38 mas, respectively, and those of the right ascension of the ascending node error $\Delta \varOmega $ are 6.47, 11.24, 14.88 mas, respectively. For IGSO satellites, the average RMS of the three-dimensional position error on the 30th, 60th, and 90th day is approximately 260, 1000, 2200 m, respectively, while the prediction errors of i and Ω are comparable to those of MEO satellites. Therefore, it can be concluded that the method in this paper exhibits high accuracy in long-term orbital predicting positions and orbital orientation parameters i and Ω, which is expected to provide essential support for mitigating the overall rotation of autonomous navigation of navigation satellite constellations. -
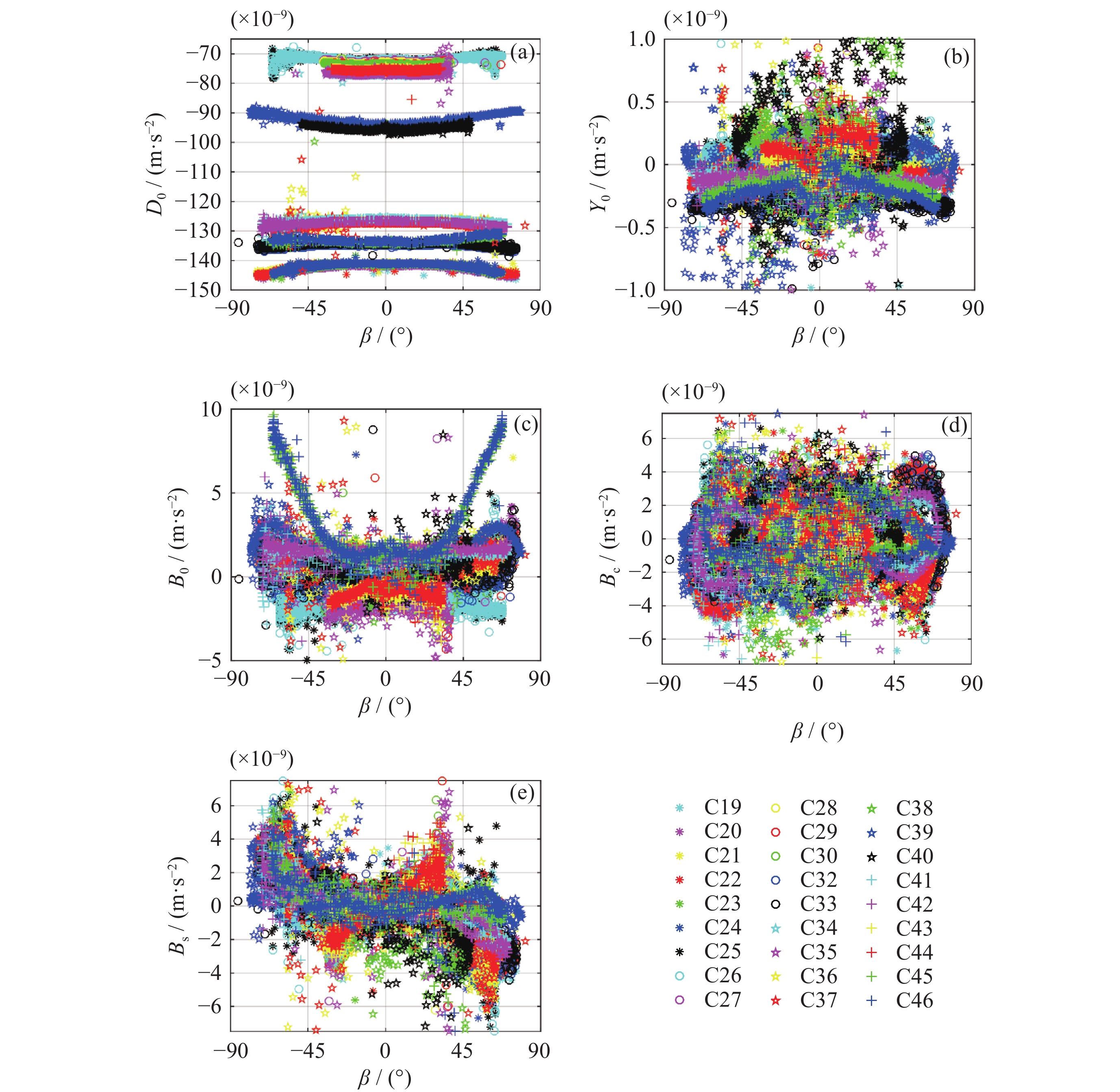
图 1 BDS-3卫星ECOM-5模型光压参数$ {{D}}_{{0}} $, $ {{Y}}_{{0}} $, $ {{B}}_{{0}} $, $ {{B}}_{\rm{c}} $, $ {{B}}_{\rm{s}} $随太阳高度角的变化
Figure 1. Variation of ECOM-5 parameters $ {{D}}_{\rm{0}} $, $ {{Y}}_{\rm{0}} $, $ {{B}}_{\rm{0}} $, $ {{B}}_{{\mathrm{c}}} $, $ {{B}}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $ with the solar altitude angle for BDS-3 satellites
表 1 C19卫星 ECOM-5模型与太阳高度角函数模型拟合系数
Table 1. Fitting coefficients of Satellite C19 ECOM-5 model with solar altitude angle function model
Coefficient A B C D $ {D}_{0} $ –0.144906×10–6 –0.525711×10–11 –0.722279×10–11 0.380356×10–8 $ {Y}_{0} $ –0.197577×10–9 –0.888765×10–11 0.353819×10–11 0.122991×10–9 $ {B}_{0} $ 0.164566×10–8 –0.147844×10–10 0.460865×10–11 –0.907190×10–9 $ {B}_{{\mathrm{c}}} $ –0.816728×10–9 0.101913×10–8 –0.343274×10–9 0.132983×10–8 $ {B}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $ –0.333089×10–9 –0.200095×10–8 0.347368×10–9 0.398325×10–9 表 2 北斗导航卫星长期预报第30天位置误差RMS值统计(单位: m)
Table 2. Position error RMS statistics on the 30th day of Beidou navigation satellites’ long-term orbit prediction (Unit: m)
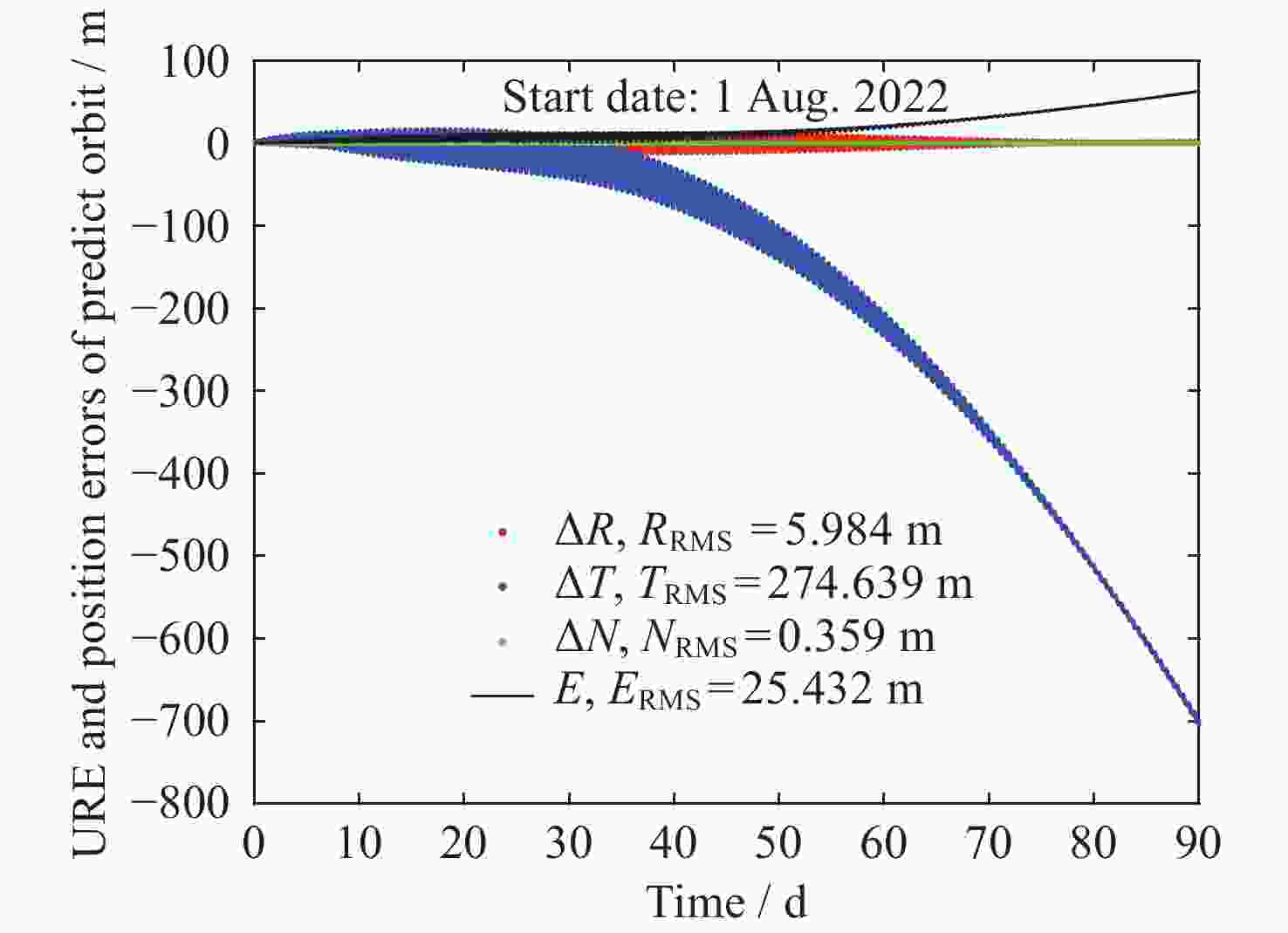
卫星类型 PRN ΔR ΔT ΔN 3D URE MEO C19 7.221 125.141 0.506 125.637 14.462 C20 6.697 113.495 0.534 114.007 13.337 C21 6.512 88.317 0.452 88.820 11.270 C22 6.907 176.129 0.578 176.362 17.933 C23 9.002 126.184 0.474 126.740 15.180 C24 8.659 99.984 0.613 100.610 13.392 C25 8.121 112.313 1.121 112.938 13.881 C26 8.882 225.326 1.788 225.854 23.715 C27 9.680 87.416 0.878 88.141 12.866 C28 10.054 440.936 1.407 441.099 41.312 C29 8.726 169.195 1.023 169.614 18.494 C30 9.665 341.254 1.438 341.553 32.786 C32 6.091 141.961 1.159 142.164 14.600 C33 5.988 266.652 0.946 266.874 25.760 C34 10.084 161.141 0.736 161.868 18.969 C35 10.267 272.558 0.845 272.859 27.235 C36 7.636 280.586 1.105 280.784 27.076 C37 7.544 114.962 0.401 115.594 13.996 MEO C41 5.181 169.843 0.475 170.019 16.847 C42 5.009 151.484 0.441 151.755 15.483 C43 6.026 67.942 0.782 68.393 9.174 C44 4.936 93.586 0.862 93.896 10.568 C45 8.000 180.254 0.871 180.683 19.258 C46 7.370 215.090 0.879 215.442 21.756 均值 7.659 176.844 0.857 177.258 18.793 IGSO C38 12.057 192.091 0.878 192.846 30.785 C40 23.006 325.491 1.085 326.832 52.814 均值 17.532 258.791 0.981 259.839 41.799 表 3 北斗导航卫星长期预报第60天位置误差RMS值统计(单位: m)
Table 3. Position error RMS statistics on the 60th day of Beidou navigation satellites’ long-term orbit prediction (Unit: m)
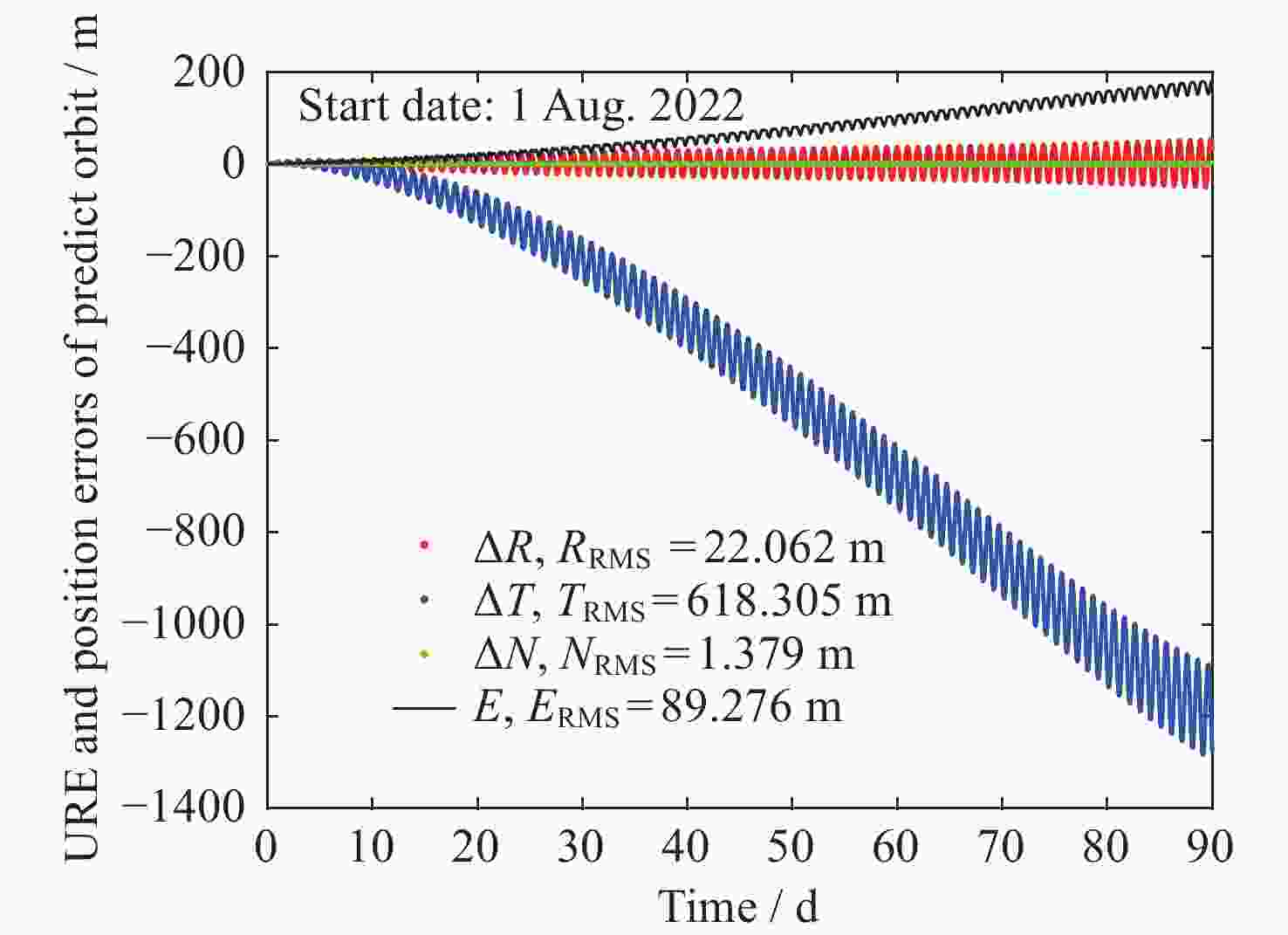
卫星类型 PRN ΔR ΔT ΔN 3D URE MEO C19 10.558 539.251 0.980 539.440 50.420 C20 9.817 429.150 0.992 429.411 40.718 C21 9.720 317.703 0.825 318.274 31.725 C22 9.783 621.583 1.098 621.850 57.573 C23 12.882 461.512 0.806 461.892 44.309 C24 11.532 307.503 1.191 308.034 31.434 C25 14.264 394.126 1.847 394.785 40.146 C26 15.182 881.259 3.000 881.824 83.382 C27 18.504 289.352 1.497 290.328 33.195 C28 19.363 1723.910 2.566 1724.206 157.273 C29 16.822 652.385 1.821 652.746 62.290 C30 18.813 1395.105 2.553 1395.270 127.309 C32 9.988 536.658 1.738 536.846 50.015 C33 9.478 730.198 1.307 730.376 67.442 C34 19.638 612.447 1.262 613.217 61.315 C35 19.704 1060.362 1.437 1060.868 98.816 C36 10.984 1053.330 1.851 1053.455 96.053 C37 9.747 418.462 0.735 418.670 39.664 C41 8.274 625.139 0.893 625.284 57.301 C42 8.115 547.748 0.840 547.864 50.460 C43 11.113 237.917 1.205 238.510 25.565 C44 8.739 340.791 1.395 341.224 33.294 C45 12.700 584.656 1.052 585.045 55.507 C46 11.773 771.800 1.042 772.098 71.669 均值 12.802 650.656 1.428 651.036 61.427 IGSO C38 25.337 937.171 1.709 937.753 135.005 C40 42.832 918.530 1.752 921.830 142.093 均值 34.084 927.850 1.731 929.791 138.549 表 4 北斗导航卫星长期预报第90天位置误差RMS值统计(单位: m)
Table 4. Position error RMS statistics on the 90th day of Beidou navigation satellites’ long-term orbit prediction (Unit: m)
卫星类型 PRN ΔR ΔT ΔN 3D URE MEO C19 13.774 1130.630 1.419 1130.760 103.159 C20 12.360 868.655 1.384 868.910 79.848 C21 12.813 658.330 1.178 658.804 62.193 C22 12.113 1227.798 1.585 1227.956 111.967 C23 16.362 945.159 1.133 945.396 87.274 C24 14.361 599.986 1.782 600.476 57.334 C25 20.457 842.590 2.223 843.037 80.217 C26 21.152 1987.638 3.560 1988.325 182.968 C27 26.139 560.860 1.872 561.901 59.152 C28 27.326 3723.320 3.372 3723.472 336.733 C29 23.719 1317.467 2.401 1318.364 124.208 C30 26.832 3035.307 3.374 3035.498 275.189 C32 12.985 1072.854 2.121 1073.049 98.388 C33 11.810 1285.367 1.759 1285.750 118.126 C34 27.967 1270.683 1.658 1271.980 122.956 C35 27.894 2332.357 1.891 2333.081 214.182 C36 13.828 2202.922 2.181 2203.150 199.878 C37 12.384 772.700 1.061 772.841 71.043 C41 11.548 1303.858 1.247 1303.997 118.571 C42 11.026 1125.251 1.235 1125.413 102.692 C43 14.787 466.879 1.366 467.291 45.833 C44 11.463 651.211 1.730 651.505 60.921 C45 15.468 1044.361 1.314 1044.792 97.090 C46 14.946 1675.416 1.345 1675.527 151.995 均值 17.216 1344.116 1.857 1344.518 124.003 IGSO C38 35.366 2639.648 1.975 2640.235 373.378 C40 64.105 1703.226 2.120 1706.001 253.532 均值 49.736 2171.437 2.047 2173.118 313.455 表 5 北斗导航卫星长期预报轨道倾角误差及升交点赤经误差统计(单位: mas)
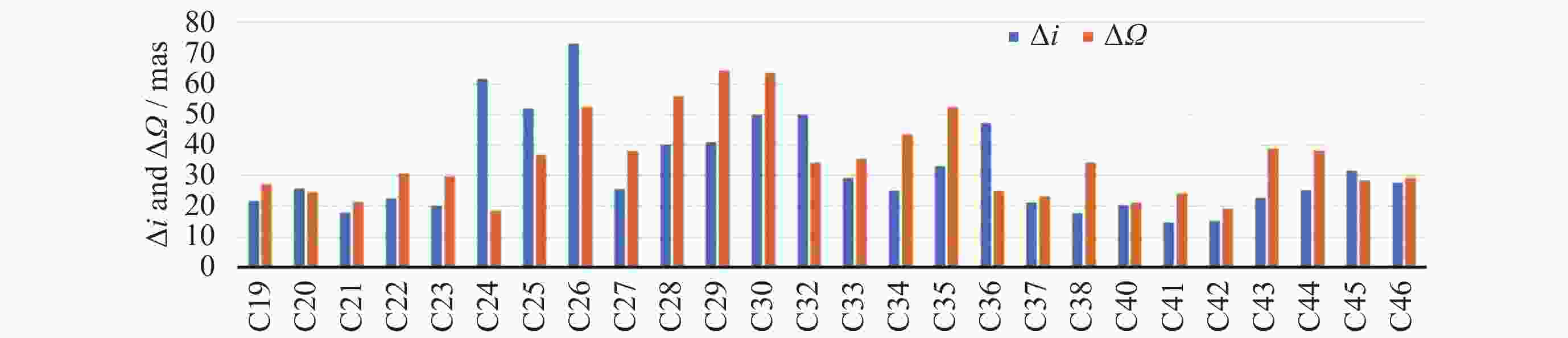
Table 5. RMS error statistics of $ \Delta i $ and $ \Delta \varOmega $ of Beidou navigation satellites’ long-term orbit prediction (Unit: mas)
卫星类型 卫星PRN 第30天 第60天 第90天 $\Delta i $ $\Delta \varOmega $ $\Delta i $ $\Delta \varOmega $ $\Delta i $ $\Delta \varOmega $ MEO C19 4.015 3.500 7.800 6.361 11.127 9.406 C20 4.180 3.816 7.816 6.648 10.997 8.918 C21 3.378 3.298 6.643 5.768 9.702 8.102 C22 4.075 4.316 7.878 7.634 11.190 11.189 C23 3.246 3.828 6.000 5.777 8.862 7.542 C24 5.768 2.485 11.657 4.070 16.933 6.731 C25 9.702 5.329 15.660 10.339 18.084 13.890 C26 15.738 8.500 24.628 17.046 28.039 24.269 C27 4.637 8.386 7.406 14.897 9.037 19.067 C28 7.701 13.155 12.823 25.217 16.765 34.095 C29 5.825 9.492 10.067 17.414 11.930 24.471 C30 8.263 12.913 14.239 24.085 16.808 32.909 C32 9.791 7.585 14.600 10.627 17.829 11.424 C33 6.811 7.707 9.123 10.453 11.404 14.507 C34 3.475 7.636 6.430 12.758 7.649 17.432 C35 4.036 8.515 5.524 16.232 5.483 22.789 C36 9.593 6.066 16.071 10.211 18.738 11.750 C37 2.484 3.785 5.240 6.559 8.096 8.847 C41 3.013 4.461 5.347 8.529 7.642 11.939 C42 2.904 3.948 5.517 7.726 7.963 11.358 C43 4.696 6.940 7.353 11.079 8.832 11.568 C44 5.183 7.778 8.706 12.147 10.628 14.210 C45 7.313 5.425 7.160 8.610 9.951 9.635 C46 7.565 5.080 7.544 7.626 10.144 9.027 均值 6.070 6.467 9.761 11.236 12.384 14.878 IGSO C38 4.164 4.401 7.227 8.640 8.125 10.240 C40 5.937 4.815 8.117 9.307 9.655 12.165 均值 5.050 4.608 7.672 8.974 8.890 11.202 -
[1] 全国北斗卫星导航标准化技术委员会. 北斗卫星导航术语: GB/T 39267—2020 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020: 11 [2] 刘林, 刘迎春. 关于星-星相对测量自主定轨中的亏秩问题[J]. 飞行器测控学报, 2000, 19(3): 13-16LIU Lin, LIU Yingchun. Deficient rank problem in autonomous orbit determination with inter-satellite link measurements[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT&C Technology, 2000, 19(3): 13-16 [3] 尚琳. 导航卫星自主定轨与时间同步算法研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2013SHANG Lin. Research on the Autonomous Orbit Determination and Time Synchronization Algorithm of Navigation Satellites[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013 [4] 杨力, 郭飞霄, 文援兰, 等. 单锚固站辅助导航星座自主定轨分析[J]. 飞行器测控学报, 2013, 32(5): 444-448 doi: 10.7642/j.issn.1674-5620.2013-05-0444-05YANG Li, GUO Feixiao, WEN Yuanlan, et al. Analysis of autonomous orbit determination for navigation constellation with one anchor station[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT&C Technology, 2013, 32(5): 444-448 doi: 10.7642/j.issn.1674-5620.2013-05-0444-05 [5] 李博. 基于星间定向观测的导航星座长期自主定轨技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010LI Bo. Research on Long-term Autonomous Orbit Determination for Navigation Constellation Based on inter-satellite Orientation Observation[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010 [6] 徐家辉, 胡敏, 王许煜, 等. 中轨道导航星座长期演化安全性分析[J]. 航天控制, 2020, 38(6): 67-73XU Jiahui, HU Min, WANG Xuyu, et al. Security analysis for long-term evolution of medium earth orbit navigation satellite constellation[J]. Aerospace Control, 2020, 38(6): 67-73 [7] 毛悦, 宋小勇, 胡小工, 等. 北斗卫星轨道预报精度分析及改进[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2017, 34(2): 124-129,134 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2017.02.003MAO Yue, SONG Xiaoyong, HU Xiaogong, et al. Orbit prediction accuracy analysis and improvement method for BeiDou satellites[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2017, 34(2): 124-129,134 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2017.02.003 [8] 张卫星, 刘万科, 龚晓颖, 等. 导航卫星自主定轨中光压模型精化方法及其影响研究[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2013, 38(6): 700-704ZHANG Weixing, LIU Wanke, GONG Xiaoying, et al. Influence of solar radiation perturbation model refinement on autonomous orbit determination of navigation satellites[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2013, 38(6): 700-704 [9] 吉长东, 张萌, 王强. 北斗卫星轨道预报方法分析[J]. 测绘科学, 2020, 45(7): 18-25,32 doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2020.07.003JI Changdong, ZHANG Meng, WANG Qiang. Research on the method of high precision orbit prediction for BDS satellite[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2020, 45(7): 18-25,32 doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2020.07.003 [10] SPRINGER T A, ROTHACHER M, BEUTLER G. Using the Extended CODE Orbit Model: First Experiences[M]//NEILAN R E. IGS 1996 Analysis Center Workshop. Pasadena, CA: IGS Central Bureau, 1996: 13-25 [11] RODRIGUEZ-SOLANO C J, HUGENTOBLER U, STEIGENBERGER P. Adjustable box-wing model for solarradiation pressure impacting GPS satellites[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2012, 49(7): 1113-1128 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2012.01.016 [12] DACH R, BOCKMANN E. International GNSS Service Technical Report 2023(IGS Annual Report)[R/OL]. (2024-06-11)[2025-01-15]. https://igs.org/news/igs-technical-report-2023 [13] SPRINGER T A, BEUTLER G, ROTHACHER M. A new solar radiation pressure model for GPS satellites[J]. GPS Solutions, 1999, 2(3): 50-62 [14] 陈秋丽, 杨慧, 陈忠贵, 等. GPS卫星光压摄动建模发展与启示[J]. 航天器工程, 2013, 22(2): 98-103CHEN Qiuli, YANG Hui, CHEN Zhonggui, et. al. Modeling and analysis of solar radiation pressure for GPS satellites[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2013, 22(2): 98-103 [15] SPRINGER T A, BEUTLER G, ROTHACHER M. Improving the orbit estimates of GPS satellites[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 1999, 73(3): 147-157 [16] 李婕. 北斗三号卫星太阳光压模型精化研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2022LI Jie. Solar Radiation Pressure Modeling for Beidou-3 Satellites[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2022 [17] BAR-SEVER Y, KUANG D D. New Empirically Derived Solar Radiation Pressure Model for Global Positioning System Satellites during Eclipse Seasons[R]. IPN Progress Report 42-159, 2004: 1-11 [18] STEIGENBERGER P, DENG Z G, GUO J, et al. Beidou-3 orbit and clock quality of the IGS Multi-GNSS pilot project[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 71(1): 355-368 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.08.058 [19] CHEN G, GUO J, GENG T, et al. Multi-GNSS orbit combination at Wuhan University: strategy and preliminary products[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2023, 97(5): 41 doi: 10.1007/s00190-023-01732-2 [20] BIZOUARD C, LAMBERT S, GATTANO C, et al. The IERS EOP 14C04 solution for Earth orientation parameters consistent with ITRF 2014[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2019, 93(5): 621-633 doi: 10.1007/s00190-018-1186-3 [21] 陈艳玲, 胡小工, 周善石, 等. 基于星间测距的导航卫星自主定轨新算法[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2015, 45(7): 079511CHEN Yanling, HU Xiaogong, ZHOU Shanshi, et al. A new autonomous orbit determination algorithm based on inter-satellite ranging measurements[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2015, 45(7): 079511 [22] GRIMES J G. Global Positioning System Standard Positioning Service Performance Standard[EB/OL]. (2008-09-01). https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/16930 -
-




 黄进 男, 2000年7月出生, 中国科学院大学硕士研究生, 研究方向为天体测量与天体力学. E-mail:
黄进 男, 2000年7月出生, 中国科学院大学硕士研究生, 研究方向为天体测量与天体力学. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: